Screen Printable Sol-Gel Materials for High-Throughput Borosilicate Glass Film Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Screen Printing of Functional Layers
1.2. Liquid Dopant Sources for Silicon Solar Cells
1.3. Scope of this Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Sol-Gel Derived Screen Printing Pastes
2.2. Rheological Characterization and Printing Tests
2.3. Spectroscopic Thin-Film Analysis
2.4. Evaluation of Dopant Properties
3. Results
3.1. Rheology and Suitability for Screen Printing
3.2. Thin-Film Properties after Thermal Conversion
3.3. Achievable Dopant Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pettit, R.B.; Brinker, C.J. Use of sol-gel thin films in solar energy applications. Sol. Energy Mater. 1986, 14, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, N.; Park, C.; Raja, J.; Ju, M.; Venkatesan, M.R.; Lee, H.; Yi, J. Low Surface Recombination Velocity on p-Type Cz–Si Surface by Sol–Gel Deposition of Al2O3 Films for Solar Cell Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2015, 15, 5123–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyeng, J.D.; Efinger, R.; Keding, R.J.; Doll, O.; Clement, F. Screen-Printed Borosilicate Glass Derived from Sol–Gel Materials for Back-Contact Back-Junction Solar Cells. Sol. RRL 2020, 4, 2000271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, S.; Voigt, N.; Friedrich, L.; Weber, D.; Haedrich, I.; Mittag, M.; Wirth, H.; Thaidigsmann, B.; Brucker, I.; Hofmann, M.; et al. Cost Modeling of Silicon Solar Cell Production Innovation along the PV Value Chain. In Proceedings of the 27th EU PVSEC, Frankfurt, Germany, 24–28 September 2012; pp. 1084–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Lammert, M.D.; Schwartz, R.J. The interdigitated back contact solar cell: A silicon solar cell for use in concentrated sunlight. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1977, 24, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Yoshida, W.; Irie, T.; Konishi, K.; Nakano, K.; Uto, T.; Adachi, D.; Kanematsu, M.; Uzu, H.; et al. Silicon heterojunction solar cell with interdigitated back contacts for a photoconversion efficiency over 26%. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, E.L. Recent Advancements in Low Cost Solar Cell Processing. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 6–8 May 1975; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA; pp. 315–316. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, G.; Fischer, B.; Fath, P. Formation and nature of AG thick film front contacts on crystalline silicon solar cells. In PV in Europe; From PV technology to energy solutions: Proceedings of the international conference held in Rome, Italy, 7–11 October 2002; PV Conference; PV in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Rome, Italy, 7–11 October; Bal, J.-L., Ed.; WIP-Munich: München, Germany; ETA-Florence: Florence, Italy, 2002; pp. 343–346. ISBN 3-936338-12-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.; Woodhouse, M.; Herritsch, S.; Trube, J. International Technology Roadmap for Photovoltaic (ITRPV): Results 2019, 11th ed.; Frankfurt am Main: Frankfurt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Green, M.A. Solar Cells: Operating Principles, Technology and System Applications; University of New South Wales: Kensington, CA, USA, 1998; ISBN 0 85823 580 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, A. A good recipe to make silicon solar cells. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 7–11 October 1991; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, E.; Nakamura, H.; Terenuma, Y. Interface Reactions of B2O3-Si System and Boron Diffusion into Silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1973, 1973, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, M.A.; Ohrdes, T.; Wolpensinger, B.; Bock, R.; Harder, N.-P. Characterisation and implications of the boron rich layer resulting from open-tube liquid source BBR3 boron diffusion processes. In Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1556–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Terheiden, B. CVD Boron Containing Glasses—An Attractive Alternative Diffusion Source for High Quality Emitters and Simplified Processing—A Review. Energy Procedia 2016, 92, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keding, R.; Woehl, R.; Stüwe, D.; Fallisch, A.; Hofmann, A.; Rentsch, J.; Biro, D. Diffusion and characterization of doped patterns in silicon from prepatterned boron- and phosphorus-doped silicate glasses. In Proceedings of the 26th EU PVSEC Proceedings, Hamburg, Germany, 5–9 September 2011; pp. 1385–1389, ISBN 3-936338-27-2. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, B.; Solanki, C.S. Boron-rich layer properties formed by boron spin on dopant diffusion in n -type silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Processing 2017, 57, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perova, T.S.; Nolan-Jones, M.; McGilp, J.; Gamble, H.S. Borosilicate glass nanolayer as a spin-on dopant source: FTIR and spectroscopic ellipsometry investigations. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 6292–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaee, Z.; Reichel, C.; Feldmann, F.; Jahn, M.; Huyeng, J.D.; Keding, R.; Hermle, M.; Clement, F. Printed Dopant Sources for Locally-Doped SiOx/Poly-Si Passivating Contacts. In Proceedings of the 35th EUPVSEC, Brussels, Belgium, 24–28 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scardera, G.; Inns, D.; Wang, G.; Dugan, S.; Dee, J.; Dang, T.; Bendimerad, K.; Lemmi, F.; Antoniadis, H. All-screen-printed Dopant Paste Interdigitated Back Contact Solar Cell. Energy Procedia 2015, 77, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachiq, A.; Slaoui, A.; Georgopoulos, L.; Ventura, L.; Monna, R.; Muller, J.C. Simultaneous dopant diffusion and surface passivation in a single rapid thermal cycle. Prog. Photovolt Res. Appl. 1996, 4, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D. Simulation, Entwicklung Und Charakterisierung Von IBC-Solarzellen Mit Neuartigen Emitterschichten. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Constance, Constance, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mezger, T. Das Rheologie-Handbuch: Für Anwender von Rotations- und Oszillations-Rheometern, 4th ed.; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9783866308633. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoj, V.P.; Černyšova, I.V.; Skryševskij, V.A. Handbook of Infrared Spectroscopy of Ultrathin Films; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-471-35404-X. [Google Scholar]
- Tenney, A.S.; Wong, J. Vibrational Spectra of Vapor-Deposited Binary Borosilicate Glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 5516–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M.; Perova, T.S.; Moore, R.A.; Beitia, C.E.; McGilp, J.F.; Gamble, H.S. Spectroscopic Investigations of Borosilicate Glass and Its Application as a Dopant Source for Shallow Junctions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, D.; Luther, G.W.; Sparks, D.L. ATR-FTIR spectroscopic studies of boric acid adsorption on hydrous ferric oxide. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaşgöz, A.; Misono, T.; Abe, Y. Sol–gel preparation of borosilicates. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 243, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, M.; Moriya, Y. Glass formation of the SiO2-B2O3 system by the gel process from metal alkoxides. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, S. Viscosity and Spinnability of Gelling Solutions. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1453–1485. ISBN 978-3-319-32099-1. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, A.D.; Holmgren, J.S.; Zerda, T.W.; Jonas, J. Spectroscopic investigations of borosiloxane bond formation in the sol-gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1987, 89, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, F.; Bivour, M.; Reichel, C.; Hermle, M.; Glunz, S.W. A passivated rear contact for high-efficiency n-type Si solar cells enabling high Voc’s and FF>82%. In Proceedings of the 28th EU PVSEC and Exhibition, Paris, France, 30 September–4 October 2013; pp. 988–992. [Google Scholar]
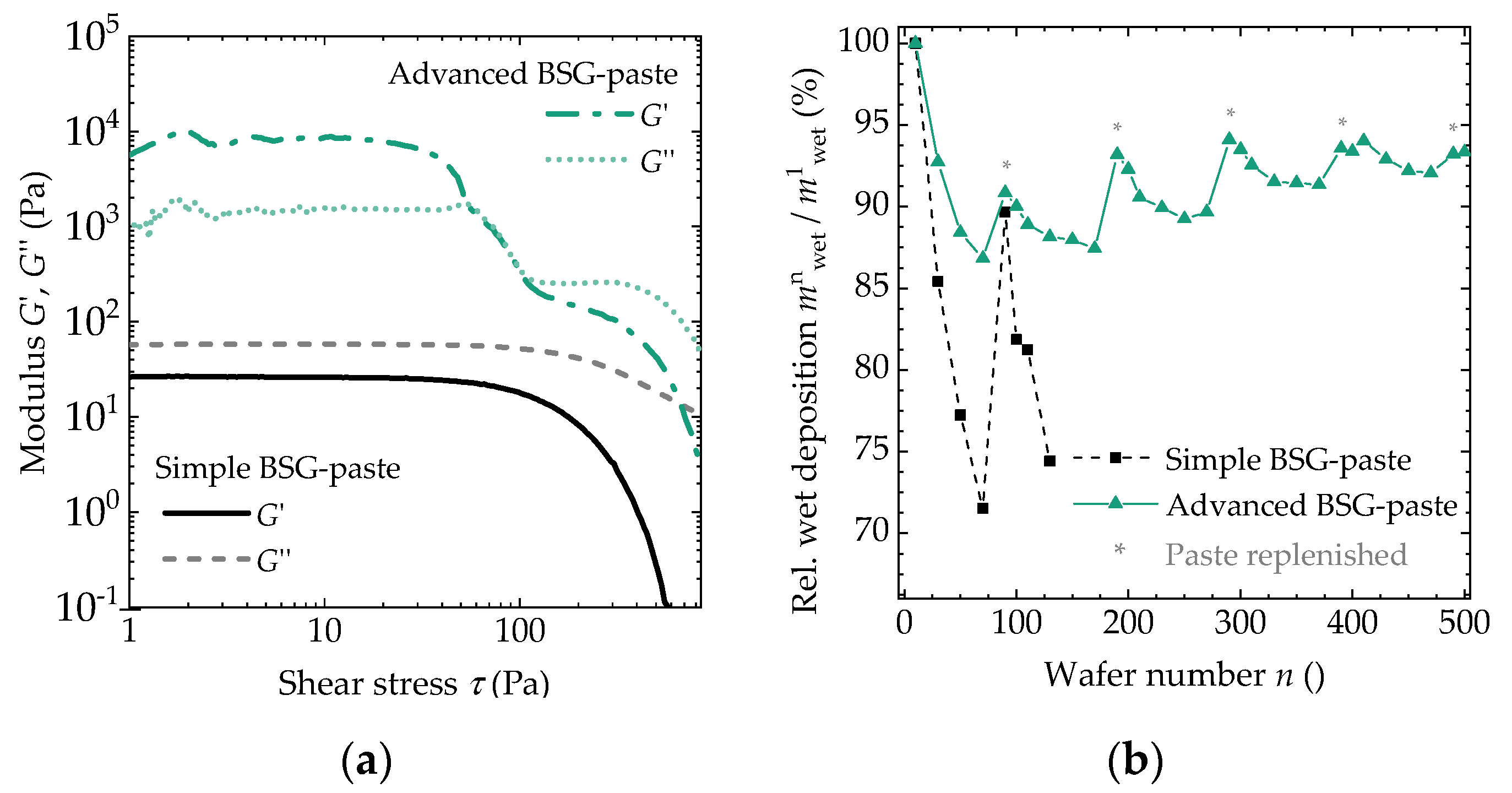
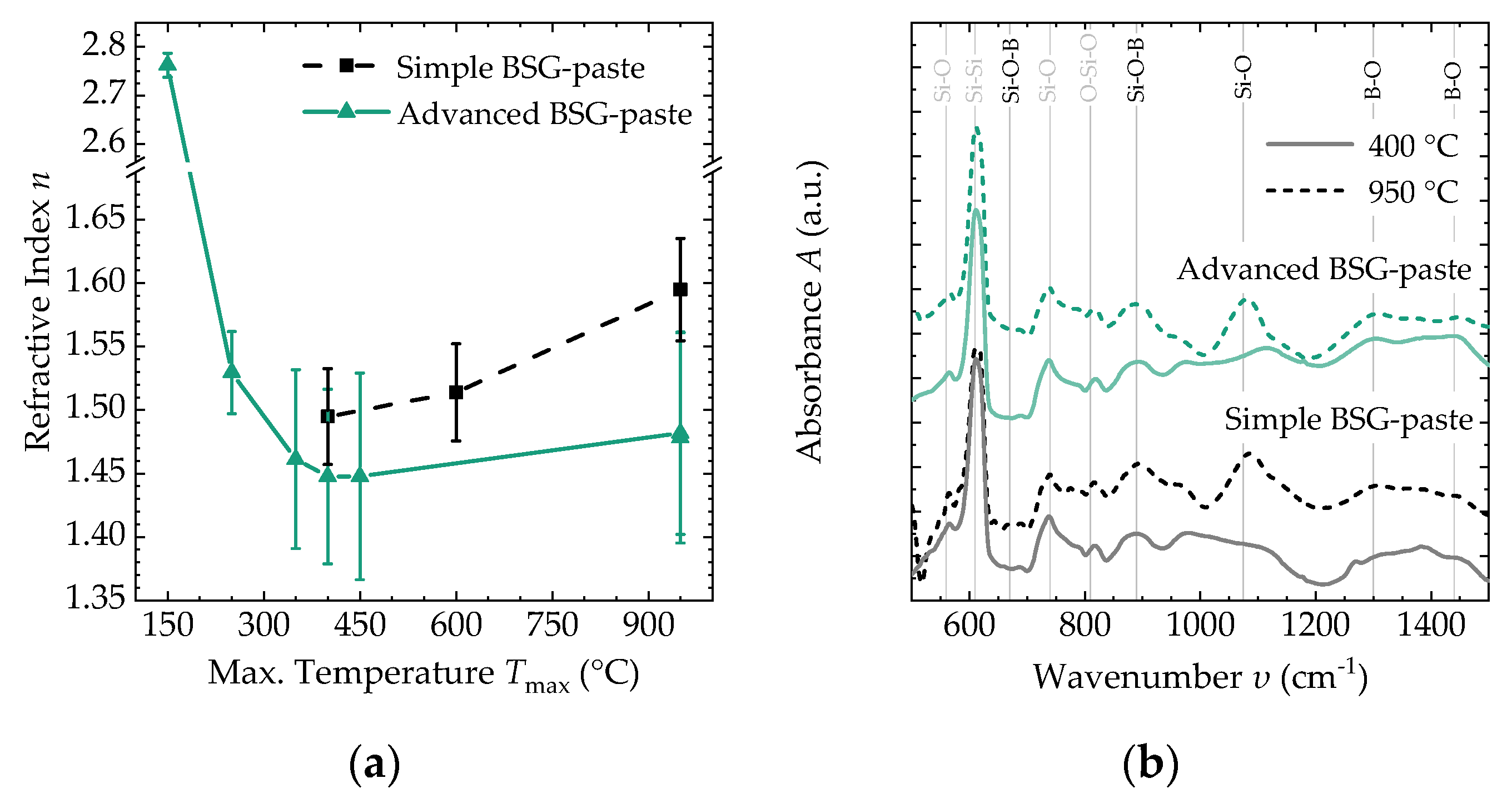
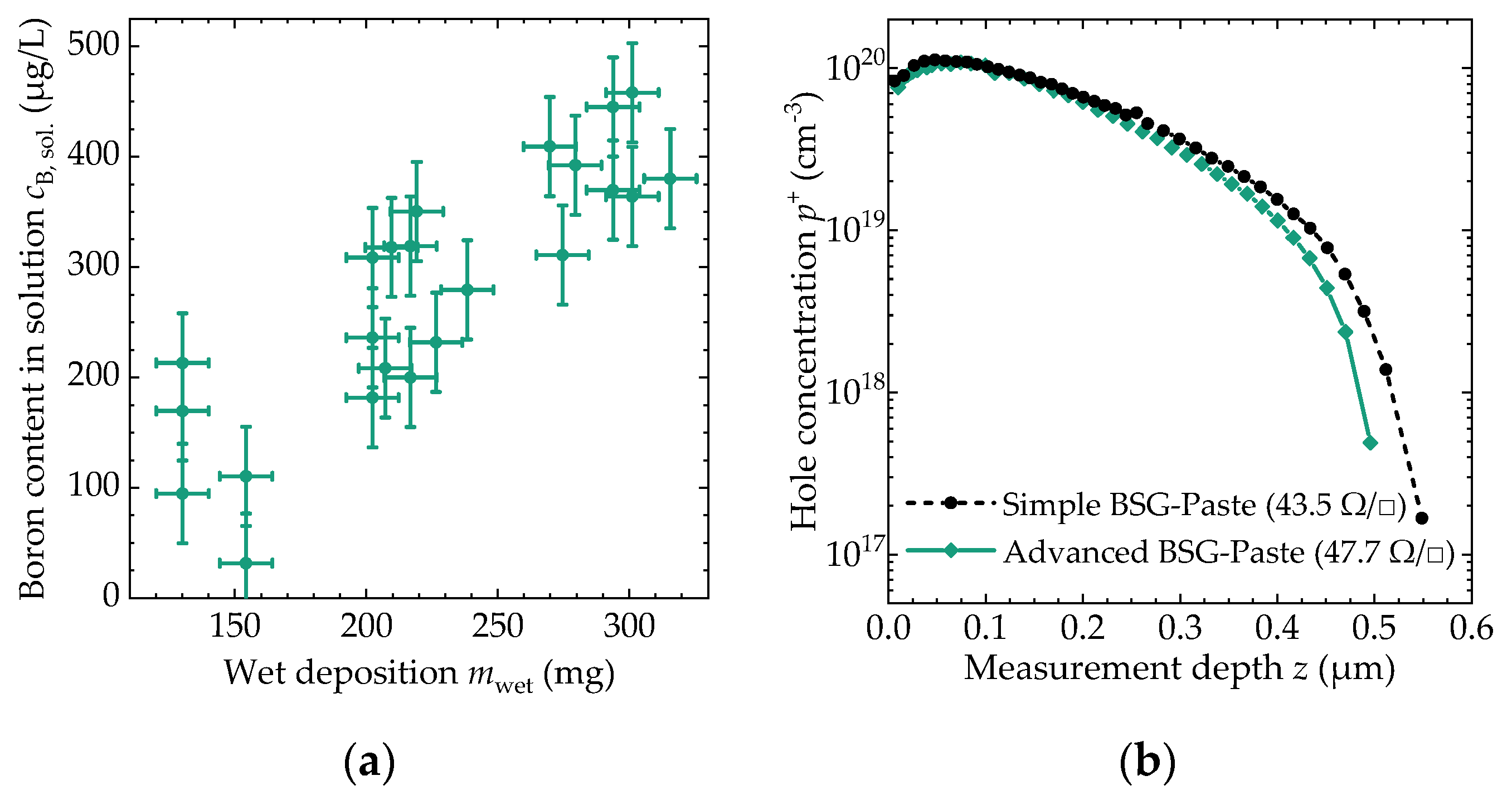
| 400 °C | 950 °C | |
|---|---|---|
| Simple BSG-paste | 1.51 ± 0.03 | 1.57 ± 0.04 |
| Advanced BSG-paste | 1.45 ± 0.07 | 1.48 ± 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huyeng, J.D.; Efinger, R.; Bruge, D.; Doll, O.; Keding, R.J.; Clement, F. Screen Printable Sol-Gel Materials for High-Throughput Borosilicate Glass Film Production. Molecules 2022, 27, 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175408
Huyeng JD, Efinger R, Bruge D, Doll O, Keding RJ, Clement F. Screen Printable Sol-Gel Materials for High-Throughput Borosilicate Glass Film Production. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175408
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuyeng, Jonas D., Raphael Efinger, David Bruge, Oliver Doll, Roman J. Keding, and Florian Clement. 2022. "Screen Printable Sol-Gel Materials for High-Throughput Borosilicate Glass Film Production" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175408
APA StyleHuyeng, J. D., Efinger, R., Bruge, D., Doll, O., Keding, R. J., & Clement, F. (2022). Screen Printable Sol-Gel Materials for High-Throughput Borosilicate Glass Film Production. Molecules, 27(17), 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175408






