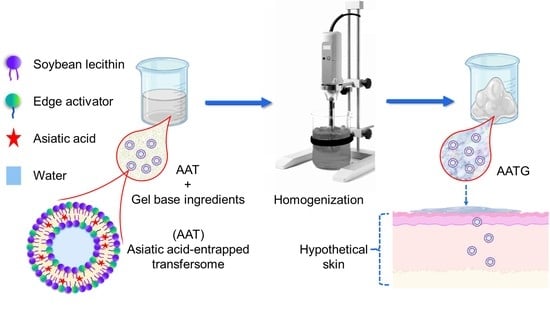
Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Study of Topical Gel Loaded with Transfersomes Containing Asiatic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of AA Transfersomal Gels (AATGs)
2.1.1. Appearance
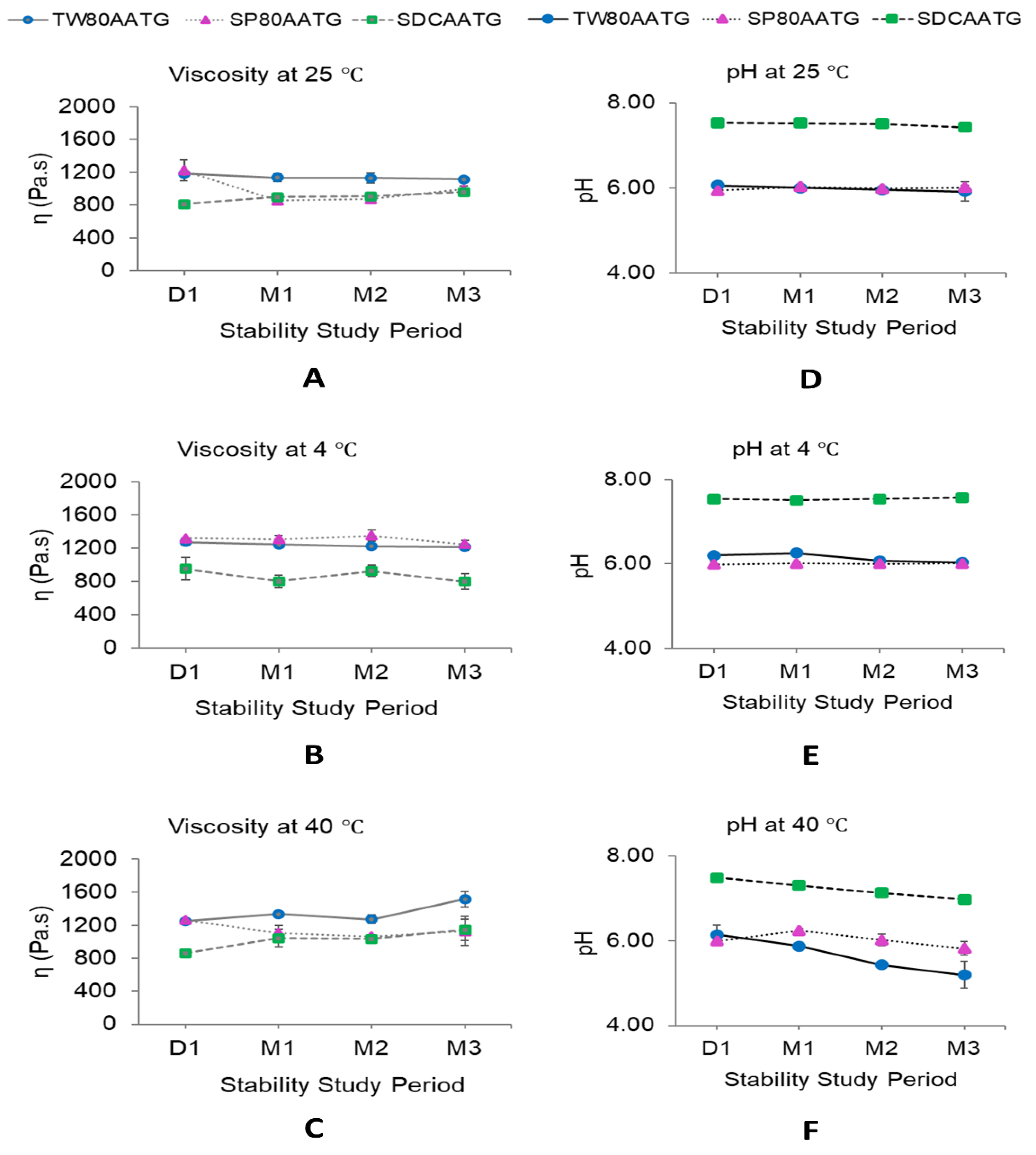
2.1.2. Viscosity
2.1.3. pH
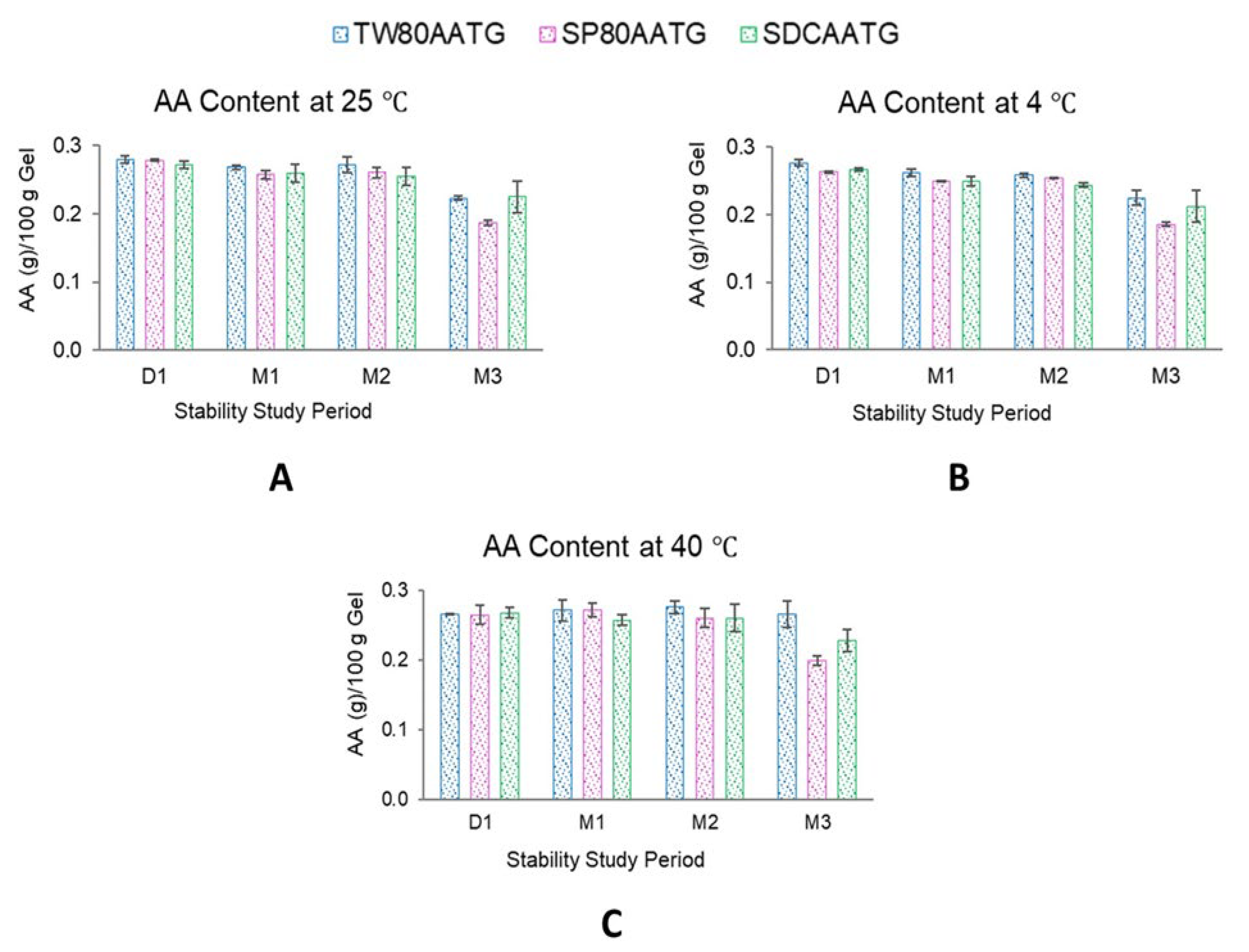
2.1.4. AA Content
2.1.5. Homogeneity
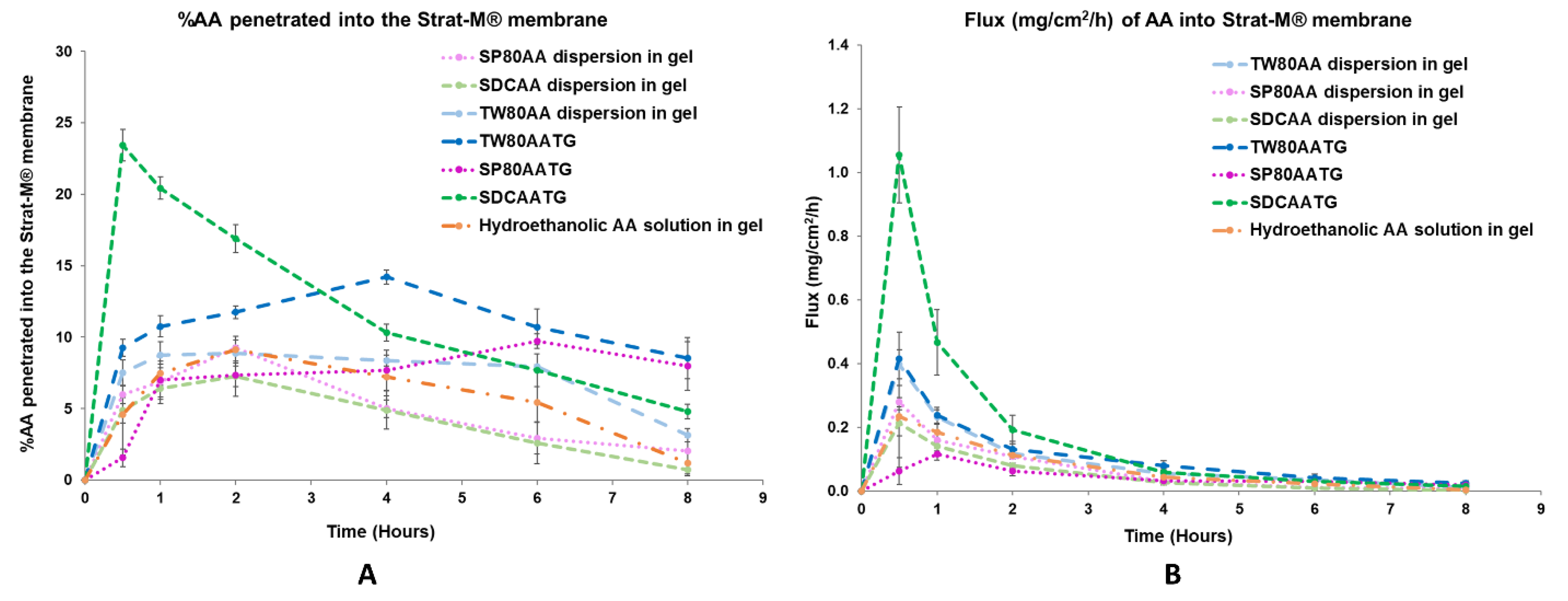
2.1.6. In Vitro Permeation
2.2. Stability of AA Transfersomal Gels
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Preparation of AA Entrapped Transfersomes (AAT)
3.2.2. Preparation of AA Transfersomal Gels (AATGs)
3.2.3. Evaluation of AA Transfersomal Gels (AATGs)
Appearance
AA Content Determination
pH Measurement
Viscosity Measurement
Homogeneity Test
In Vitro Permeation Study
3.2.4. Stability of AA Transfersomal Gels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, Z.-H. Anti-glycative effects of asiatic acid in human keratinocyte cells. BioMedicine 2014, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Sharma, A.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Ding, X. Pharmacological review on asiatic acid and its derivatives: A potential compound. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Goyal, S.N.; Suchal, K.; Sharma, C.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S.K. Pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms, and pharmaceutical development of asiatic acid: A pentacyclic triterpenoid of therapeutic promise. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylka, W.; Znajdek-Awizeń, P.; Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Brzezińska, M. Centella asiatica in cosmetology. Post. Dermatol. Alergol. 2013, 30, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Hua, X.M.; Ze, B.C.; Wang, B.; Wei, L. The anti-inflammatory effects of asiatic acid in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human corneal epithelial cells. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Fan, T.; Liu, M.; Ke, Q.; Xu, H.; Yi, Z. An aligned porous electrospun fibrous scaffold with embedded asiatic acid for accelerating diabetic wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6125–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.H.; Ahmad, W.A.N.W.; Suppian, R. The effects of individual and combination of asiatic acid and madecassoside derived from Centella asiatica (Linn.) on the viability percentage and morphological changes of mouse macrophage cell lines (J774A.1). J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somboonwong, J.; Kankaisre, M.; Tantisira, B.; Tantisira, M.H. Wound healing activities of different extracts of Centella asiatica in incision and burn wound models: An experimental animal study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bone, K.; Mills, S. Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy: Modern Herbal Medicine; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780443069925. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, R.; Vasudevan, D.T. Effect of permeation enhancers on the penetration mechanism of transfersomal gel of ketoconazole. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatha, S.A.T.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Chutoprapat, R. Transfersomes: A promising nanoencapsulation technique for transdermal drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, K.J.; Yu, C.H.; Huang, Q.L.; Du, Y.Z. Nano-drug delivery systems in wound treatment and skin regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, H.A.E.A. Transfersomes for transdermal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, P.; Ganju, E.; Upmanyu, N.; Ray, S.K.; Jain, P. Transfersomes: A novel technique for transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cevc, G.; Schätzlein, A.G.; Richardsen, H.; Vierl, U. Overcoming semipermeable barriers, such as the skin, with ultradeformable mixed lipid vesicles, transfersomes, liposomes, or mixed lipid micelles. Langmuir 2003, 19, 10753–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A.; Al-Saleh, A.A.; Al-Mohizea, A.M.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Raish, M.; Yassin, A.E.B.; Alam, M.A. Pharmacodynamic study of eprosartan mesylate-loaded transfersomes Carbopol® gel under Dermaroller® on rats with methyl prednisolone acetate-induced hypertension. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Aggarwal, G.; Singla, S.; Arora, R. Transfersomes: A novel vesicular carrier for enhanced transdermal delivery of sertraline: Development, characterization, and performance evaluation. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 1061–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sala, M.; Diab, R.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Lipid nanocarriers as skin drug delivery systems: Properties, mechanisms of skin interactions and medical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walve, J.R.; Bakliwal, S.R.; Rane, B.R. Pawar SP Transfersomes: A surrogated carrier for transdermal drug delivery system. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2011, 2, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sivannarayana, P.; Rani, A.P.; Saikishore, V.; VenuBabu, C.; SriRekha, V. Transfersomes: Ultra deformable vesicular carrier systems in transdermal drug delivery system. Res. J. Pharm. Dos. Forms Technol. 2012, 4, 243–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sachan, R.; Parashar, T.; Singh, V.; Singh, G.; Tyagi, S.; Patel, C. Drug carrier transfersomes: A novel tool for transdermal drug delivery system. Int. J. Res. Dev. Pharm. Life Sci. 2013, 2, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Opatha, S.A.T.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Chutoprapat, R. Nano-Transfersomes for Enhanced Dermal Delivery of Asiatic Acid: In Vitro Permeation, Stability and Bioactivity Evaluation. EJPB-D-22-00195 2022, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, G.; Garg, T.; Malik, B.; Chauhan, G.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Development and characterization of niosomal gel for topical delivery of benzoyl peroxide. Drug Deliv. 2013, 22, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Y. Formulation and evaluation of a topical liposomal gel containing a combination of zedoary turmeric oil and tretinoin for psoriasis activity. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 31, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Tawfeek, H.M. Transfersomal nanoparticles for enhanced transdermal delivery of clindamycin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-rodríguez, E.; Moreno, M.C.; Blanco-fernandez, B.; González, J.; Fernández-campos, F. Epidermal delivery of retinyl palmitate loaded transfersomes: Penetration and biodistribution studies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, M.M.; Hasan, O.A.; El Sisi, A.M. Preparation and optimization of lidocaine transferosomal gel containing permeation enhancers: A promising approach for enhancement of skin permeation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, N.; Jain, P.; Jain, V. Formulation development and evaluation of transferosomal GEL. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gizawy, S.A.; Nouh, A.; Saber, S.; Kira, A.Y. Deferoxamine-loaded transfersomes accelerates healing of pressure ulcers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Biskup, E. 5-Fluorouracil-loaded transfersome as theranostics in dermal tumor of hypertrophic scar tissue. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elnaggar, Y.S.R.; El-Refaie, W.M.; El-Massik, M.A.; Abdallah, O.Y. Lecithin-based nanostructured gels for skin delivery: An update on state of art and recent applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 180, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Kaur, J.; Kulkarni, R.; Chaudhari, R. In-vitro and ex-vivo evaluation of raloxifene hydrochloride delivery using nano-transfersome based formulations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, L.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Belinchón, I.; Fernández-Redondo, V.; Carretero, G.; Ruiz-Carrascosa, J.C.; Careaga, J.M.; De La Cueva, P.; Gárate, M.T.; Ribera, M. Adherence and patient satisfaction with topical treatment in psoriasis, and the use, and organoleptic properties of such treatments: A delphi study with an expert panel and members of the psoriasis group of the spanish academy of dermatology and venereolo. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013, 104, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erat, E.M.; Roso, A.; Dumaine, M.; Everine Sigurani, S. Sensory evaluation of cosmetic functional ingredients. In Nonfood Sesory Practices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 197–216. ISBN 9780128219393. [Google Scholar]
- Maggioni, D.; Cimicata, A.; Praticò, A.; Villa, R.; Bianchi, F.M.; Badiale, S.B.; Angelinetta, C. A Preliminary clinical evaluation of a topical product for reducing slight rosacea imperfections. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, N.; Agarwal, S.; Murthy, R.S.R. Latest technology advances in cosmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2012, 4, 168–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.; Sharma, A. Future prospect of nanotechnology in development of anti-ageing formulations. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Elkomy, M.H.; El Menshawe, S.F.; Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Elkarmalawy, M.H. Loratadine bioavailability via buccal transferosomal gel: Formulation, statistical optimization, in vitro/in vivo characterization, and pharmacokinetics in human volunteers. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maji, R.; Omolo, C.A.; Jaglal, Y.; Singh, S.; Devnarain, N.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. A Transferosome-loaded bigel for enhanced transdermal delivery and antibacterial activity of vancomycin hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Yielding characterization of waxy gels by energy dissipation. Rheol. Acta 2018, 57, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enscore, D.J.; Shaw, J.E. The role of synthetic and biological membranes in the transdermal delivery of drugs. In Synthetic Membranes; Chenoweth, M.B., Ed.; Sixteenth MMI Press Symposium Series; Harwood Academic Publisher: Midland, MI, USA, 1984; Volume 5, pp. 88–99. ISBN 3-7186-0327-6. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, D.R. The role of membrane pressure in reverse osmosis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1972, 16, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, W.; Sagita, E.; Iskandarsyah, I. Effect of hydrophilicity surfactants toward characterization and in vitro transfersomes penetration in gels using franz diffusion test. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 9, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Tiwari, G.; Singh, R. Allopurinol loaded transferosomes for the alleviation of symptomatic after-effects of gout: An account of pharmaceutical implications. Curr. Drug Ther. 2020, 15, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, P.K.; Clark, B.A.; Juluri, A.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Renukuntla, J. Evaluation of formulation parameters on permeation of ibuprofen from topical formulations using Strat-M® membrane. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milanowski, B.; Wosicka-Frąckowiak, H.; Główka, E.; Sosnowska, M.; Woźny, S.; Stachowiak, F.; Suchenek, A.; Wilkowski, D. Optimization and evaluation of the in vitro permeation parameters of topical products with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs through Strat-M® membrane. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Needham, R.; Yousaf, S.; Houacine, C.; Islam, Y.; Bnyan, R.; Sadozai, S.K.; Elrayess, M.A.; Elhissi, A. Impact of phospholipids, surfactants and cholesterol selection on the performance of transfersomes vesicles using medical nebulizers for pulmonary drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Council of Experts and Expert Committees (Ed.) The United State Pharmacopoeia (USP) 36, National Formulary (NF) 31; United State Pharmacopoeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Surini, S.; Leonyza, A.; Suh, C.W. Formulation and in vitro penetration study of recombinant human epidermal growth factor-loaded transfersomal emulgel. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangare, S.; Bhatane, D.; Mali, R.; Shitole, M. Development of a novel freeze-dried mulberry leaf extract-based transfersome gel. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.M.; Salem, H.F.; Abdelmohsen, H.F.; Attia, S.K. Preparation and clinical evaluation of nano-transferosomes for treatment of erectile dysfunction. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batool, S.; Zahid, F.; Ud-Din, F.; Naz, S.S.; Dar, M.J.; Khan, M.W.; Zeb, A.; Khan, G.M. Macrophage targeting with the novel carbopol-based miltefosine-loaded transfersomal gel for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis: In vitro and in vivo analyses. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.; Shen, S.; He, B.; Mo, R. Enhanced transdermal drug delivery by transfersome-embedded oligopeptide hydrogel for topical chemotherapy of melanoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9693–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwa, K.K.; Mazumder, B.; Rudrapal, M.; Verma, V.K. Potential of capsaicin-loaded transfersomes in arthritic rats. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibis, M.; Zeeb, B.; Weiss, J. Formation, characterization, and stability of encapsulated hibiscus extract in multilayered liposomes. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.S.; Li, Y.S.; Kuo, Y.C.; Tsai, S.J.J.; Lin, C.C. Preparation and evaluation of novel transfersomes combined with the natural antioxidant resveratrol. Molecules 2019, 24, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qushawy, M.; Nasr, A.; Abd-Alhaseeb, M.; Swidan, S. Design, optimization and characterization of a transfersomal gel using miconazole nitrate for the treatment of candida skin infections. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, I.; Suthar, N.; Kaur, J.; Bansal, Y.; Bansal, G. Accelerated stability studies on dried extracts of Centella asiatica through chemical, HPLC, HPTLC, and biological activity analyses. J. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 21, NP127–NP137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, S.; Dubey, A.; Ravi, G.S.; Kumar, H.; Saha, S. RP-Hplc method development and validation of asiatic acid isolated from the plant Centella asiatica. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, G.A. Validation of high-performance liquid chromatography methods for pharmaceutical analysis: Understanding the differences and similarities between validation requirements of the US food and drug administration, the US pharmacopeia and the international conference on harmonization. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 987, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batheja, P.; Sheihet, L.; Kohn, J.; Singer, A.J.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Topical drug delivery by a polymeric nanosphere gel: Formulation optimization and in vitro and in vivo skin distribution studies. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, N.; Krajisnik, D.; Milic, J.; Fahr, A.; Maibach, H. Development of hydrophilic gels containing coenzyme Q 10 -loaded liposomes: Characterization, stability and rheology measurements. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Verma, D.; Mirza, M.A.; Das, A.K.; Dudeja, M.; Anwer, M.K.; Sultana, Y.; Talegaonkar, S.; Iqbal, Z. Development and optimization of ketoconazole loaded nano-transfersomal gel for vaginal delivery using box-behnken design: In vitro, ex vivo characterization and antimicrobial evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.; Goodyear, B.; Ameen, D.; Joshi, V.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Strat-M® synthetic membrane: Permeability comparison to human cadaver skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, F.J.; Asano, N.; See, G.L.; Itakura, S.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K. Usefulness of artificial membrane, Strat-M®, in the assessment of drug permeation from complex vehicles in finite dose conditions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunita, R.; Nishijima, T.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K.; Sakaguchi, H. A mathematical approach using Strat-M®; to predict the percutaneous absorption of chemicals under finite dose conditions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderch, L.; Collini, I.; Carrer, V.; Barba, C.; Alonso, C. Assessment of finite and infinite dose in vitro experiments in transdermal drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzer, D.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A.; Hahn, T.; Schaefer, U.F.; Neumann, D. Finite and infinite dosing: Difficulties in measurements, evaluations and predictions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, Ç.; Ozkan, Y.; Savaşer, A.; Baykara, T. In vitro and ex vivo permeation studies of chlorpheniramine maleate gels prepared by carbomer derivatives. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Banerjee, S.; Sinha, B.; Mukherjee, B. Improved skin penetration using in situ nanoparticulate diclofenac diethylamine in hydrogel systems: In vitro and in vivo studies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Chutoprapat, R.; Abe, M.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Transdermal absorption enhancement of rice bran bioactive compounds entrapped in niosomes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, S.; Singla, D.; Sakhuja, N. Stability testing of pharmaceutical products. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
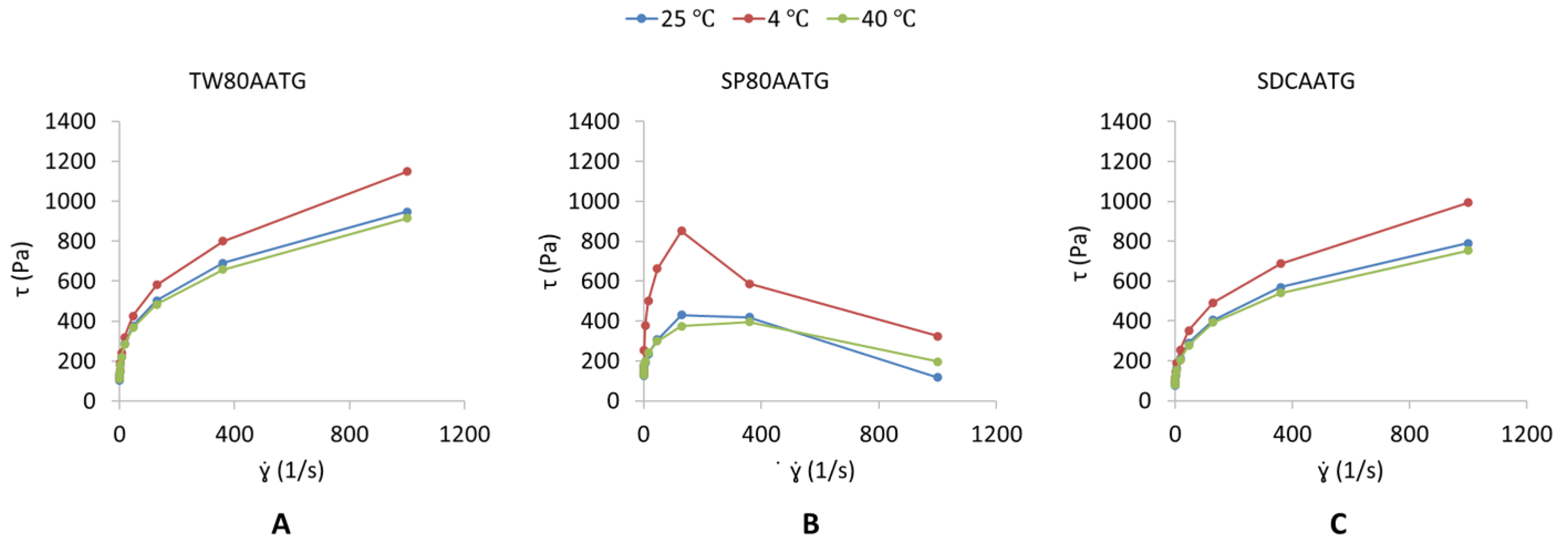
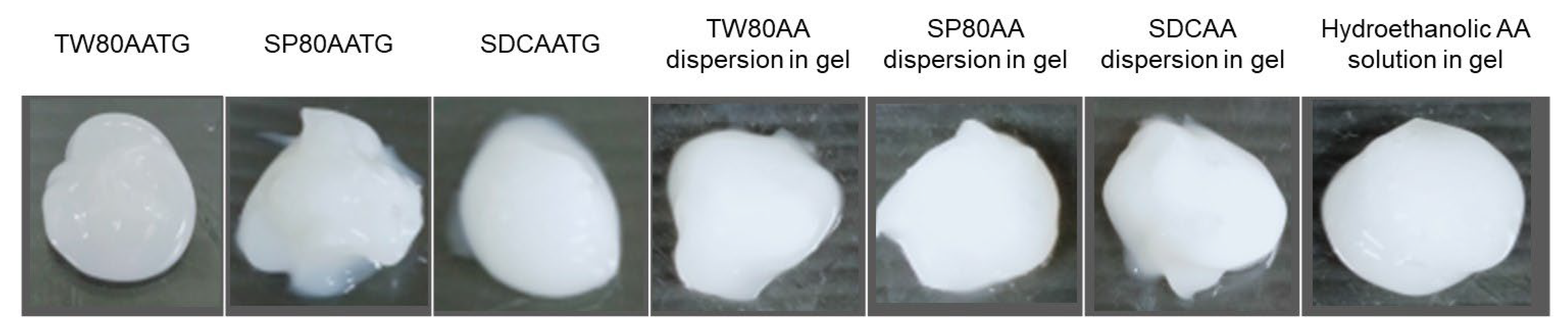

| AATG | AA Content (AA g/100 g gel) | AA Content (%) | Dynamic Viscosity (Pa.s.) | pH | Homogeneity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW80AATG | 0.280 ± 0.005 | 97.85 | 1184.62 ± 6.45 | 6.06 ± 0.09 | Good (+++) |
| SP80AATG | 0.279 ± 0.001 | 97.69 | 1222.76 ± 131.99 | 5.94 ± 0.03 | Good (+++) |
| SDCAATG | 0.272 ± 0.006 | 95.26 | 812.21 ± 20.22 | 7.53 ± 0.03 | Good (+++) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Opatha, S.A.T.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Boonpisutiinant, K.; Chutoprapat, R. Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Study of Topical Gel Loaded with Transfersomes Containing Asiatic Acid. Molecules 2022, 27, 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154865
Opatha SAT, Titapiwatanakun V, Boonpisutiinant K, Chutoprapat R. Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Study of Topical Gel Loaded with Transfersomes Containing Asiatic Acid. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154865
Chicago/Turabian StyleOpatha, Shakthi Apsara Thejani, Varin Titapiwatanakun, Korawinwich Boonpisutiinant, and Romchat Chutoprapat. 2022. "Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Study of Topical Gel Loaded with Transfersomes Containing Asiatic Acid" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154865
APA StyleOpatha, S. A. T., Titapiwatanakun, V., Boonpisutiinant, K., & Chutoprapat, R. (2022). Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Study of Topical Gel Loaded with Transfersomes Containing Asiatic Acid. Molecules, 27(15), 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154865