Gold/Pentablock Terpolymer Hybrid Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Controlled Delivery of Tamoxifen: Effect of Nanostructure on Release Kinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Nanoparticles
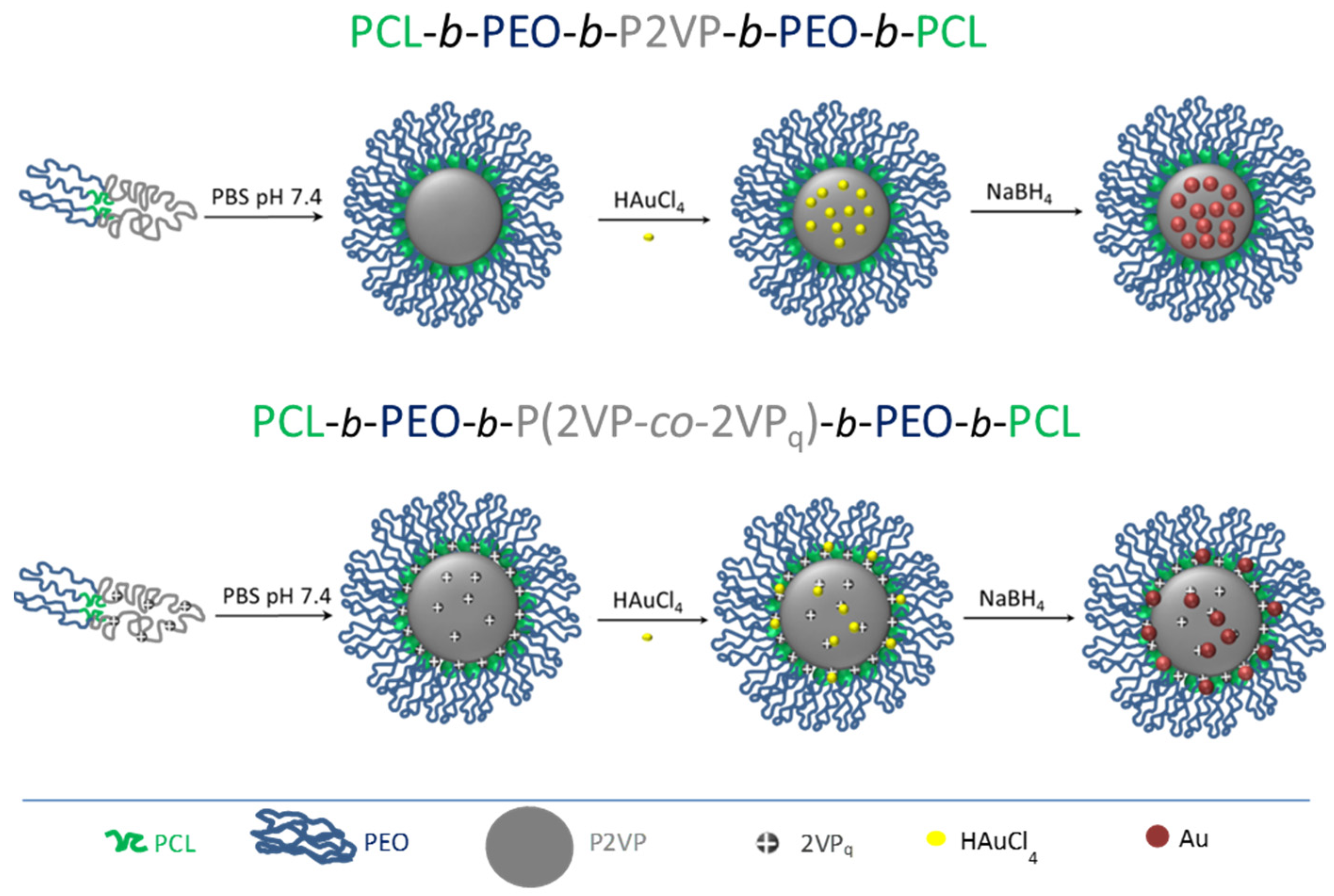
2.3. Gold-Pentablock Micellar Nanoparticles
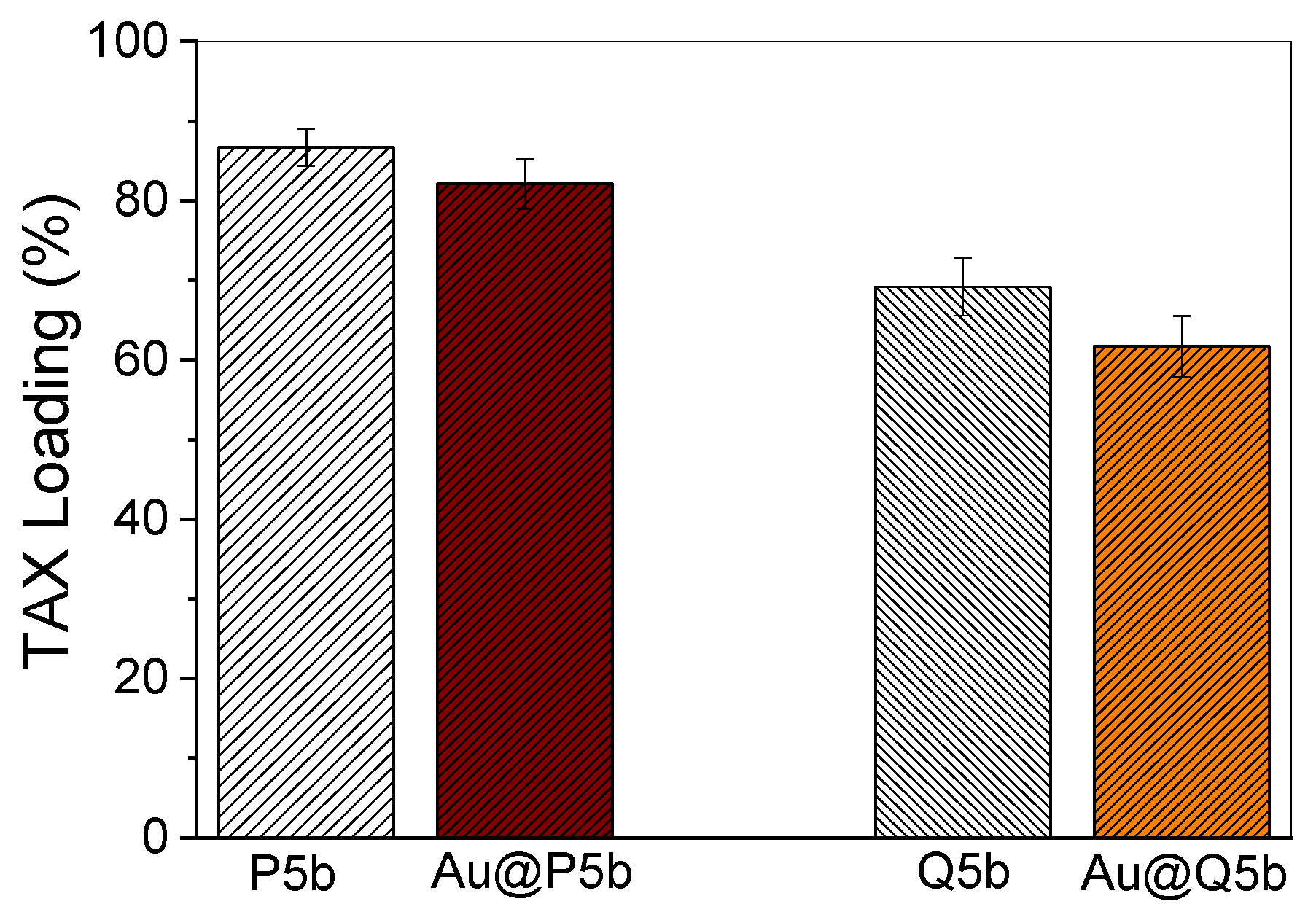
2.4. TAX Encapsulation
2.5. Drug Release
2.6. Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
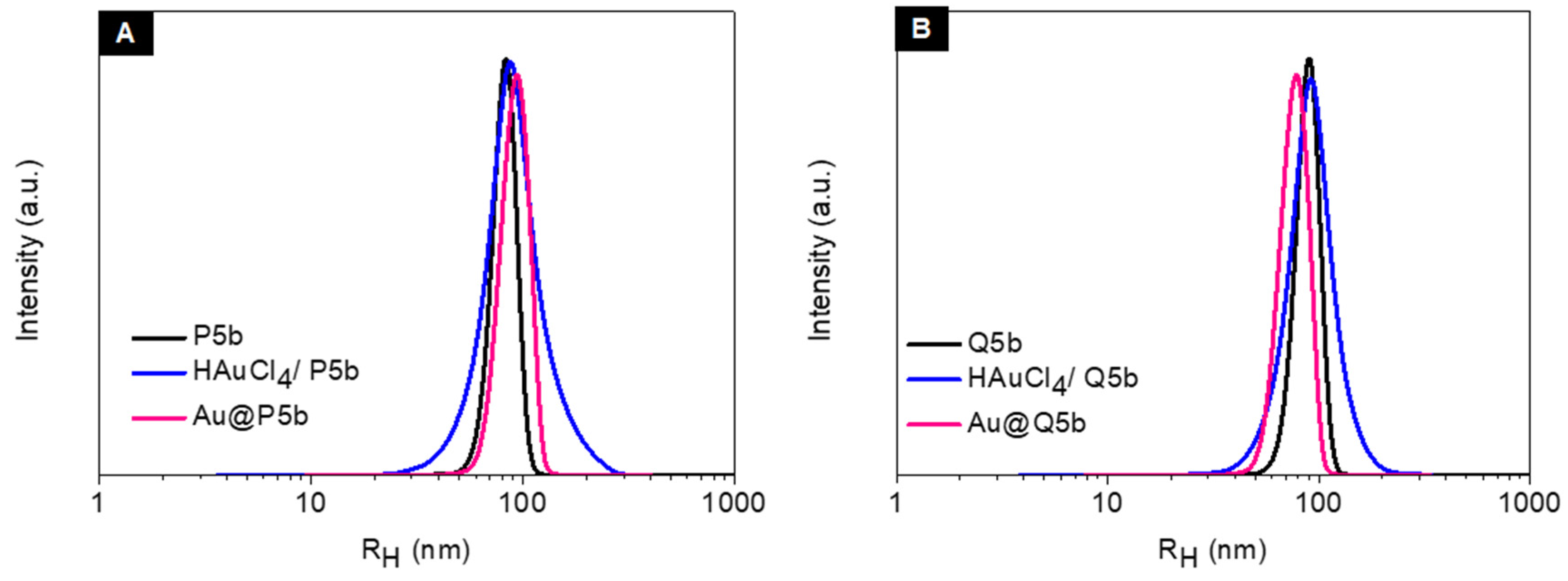
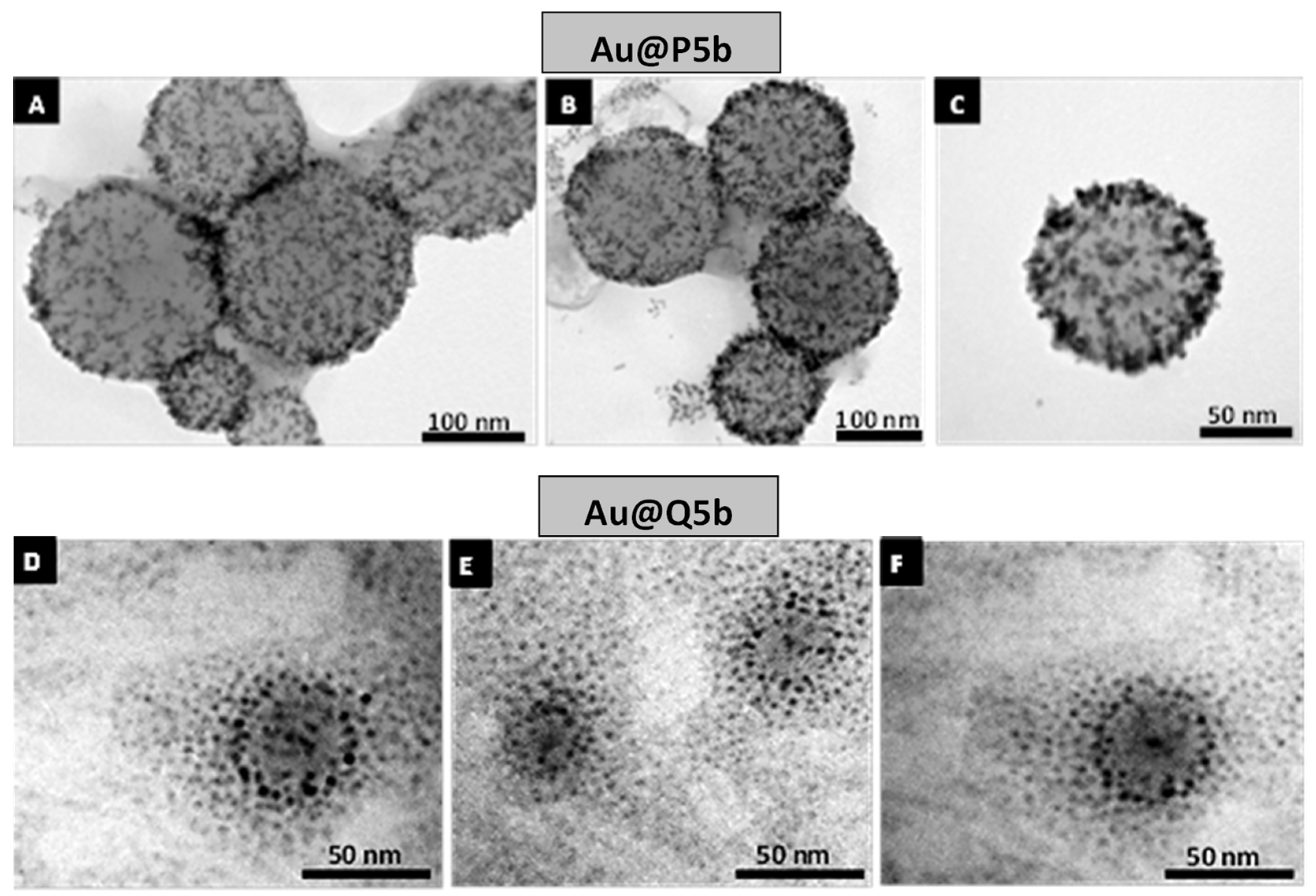
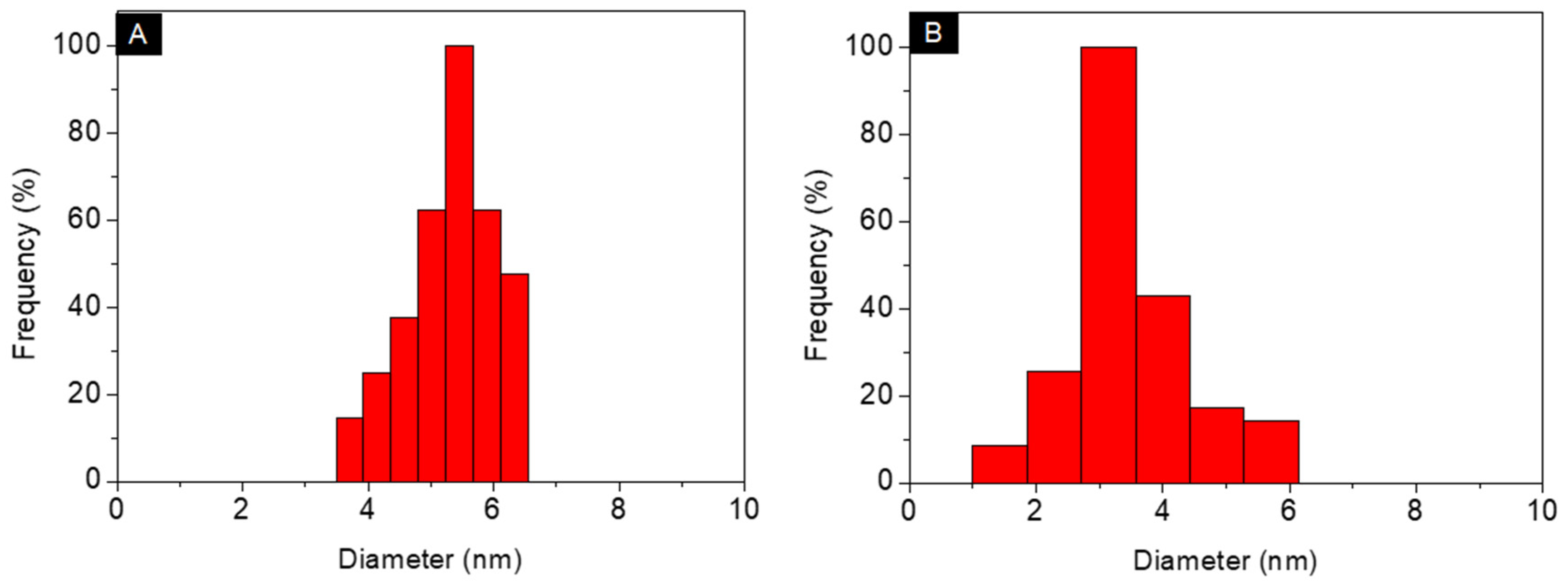
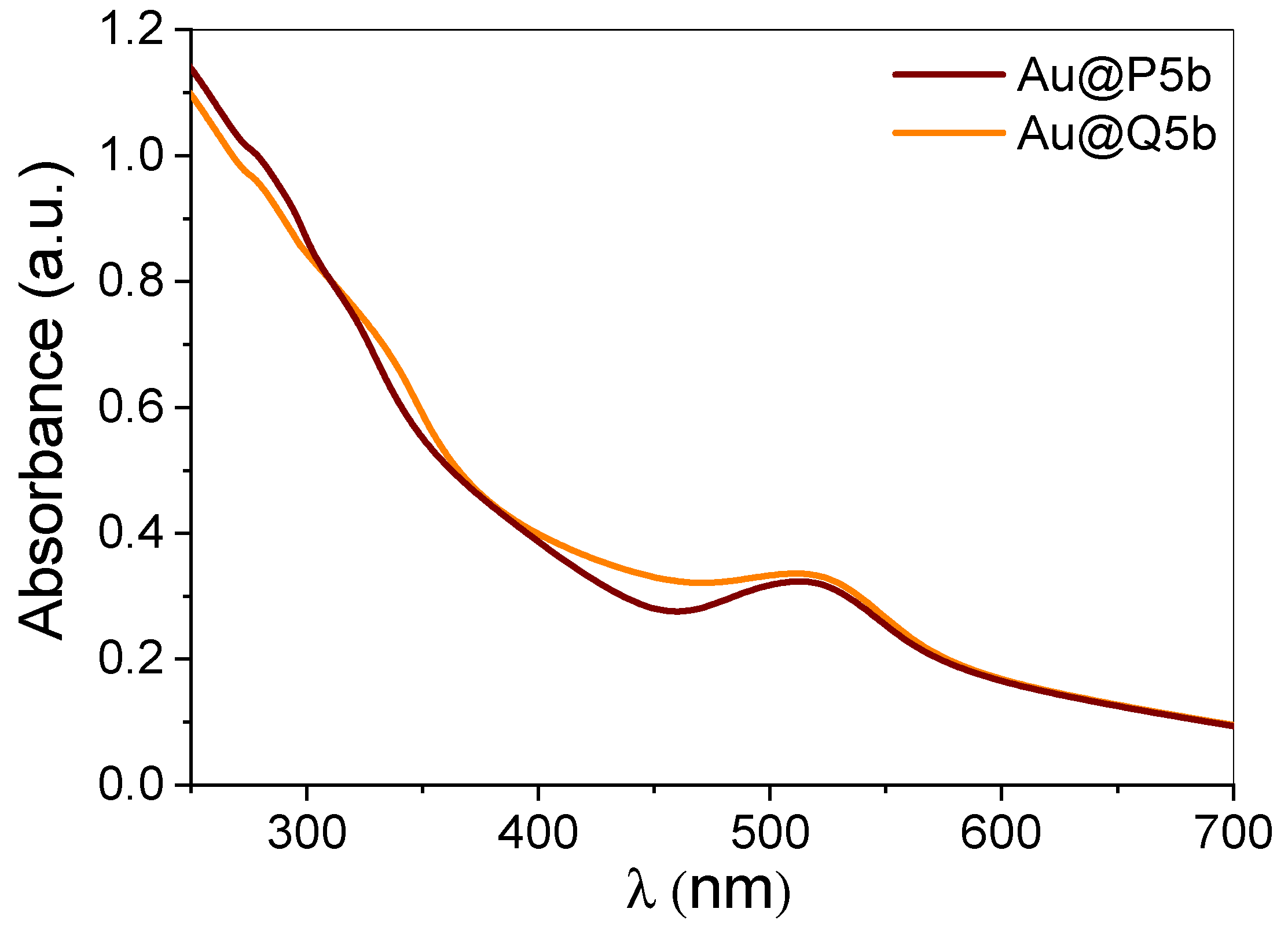
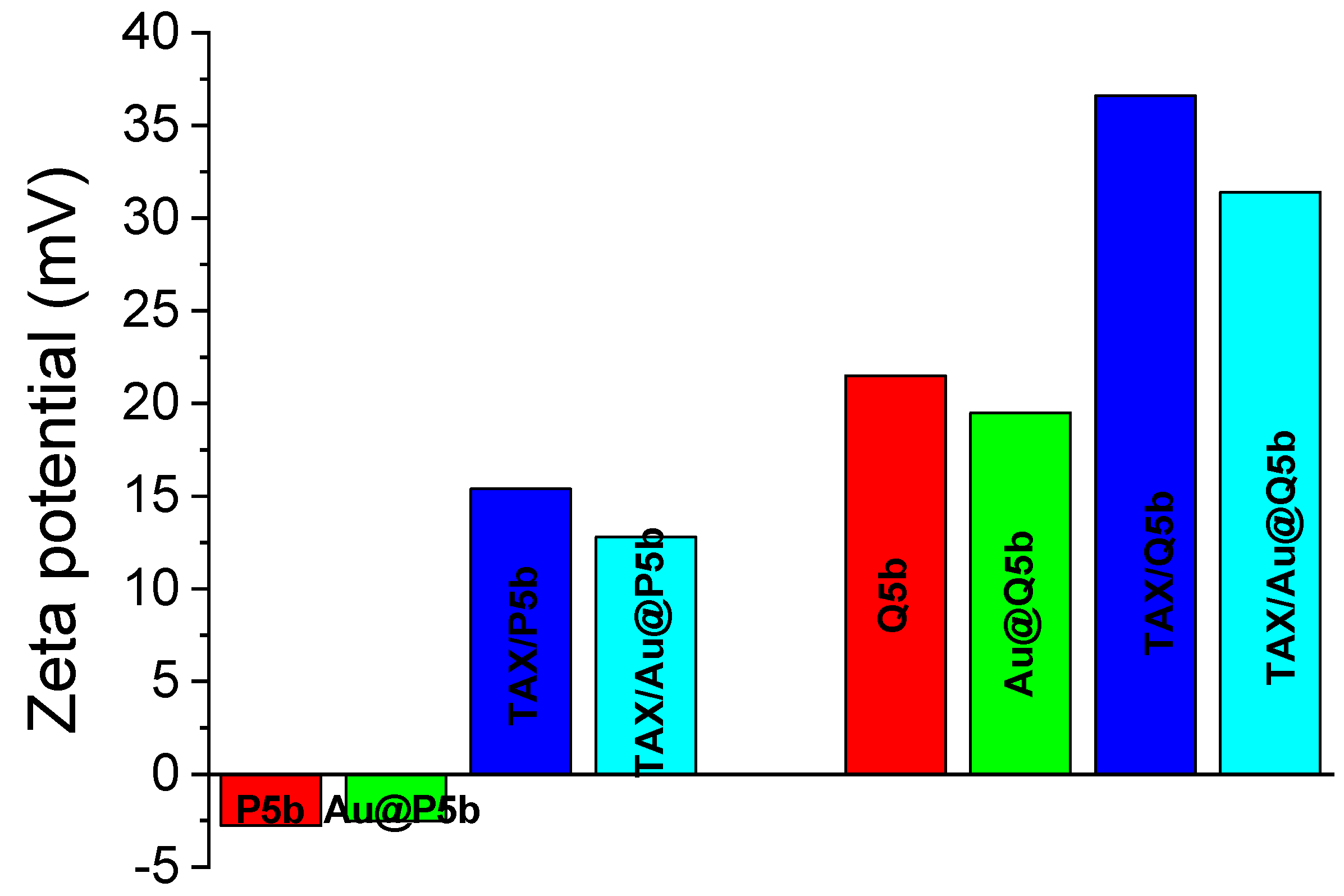
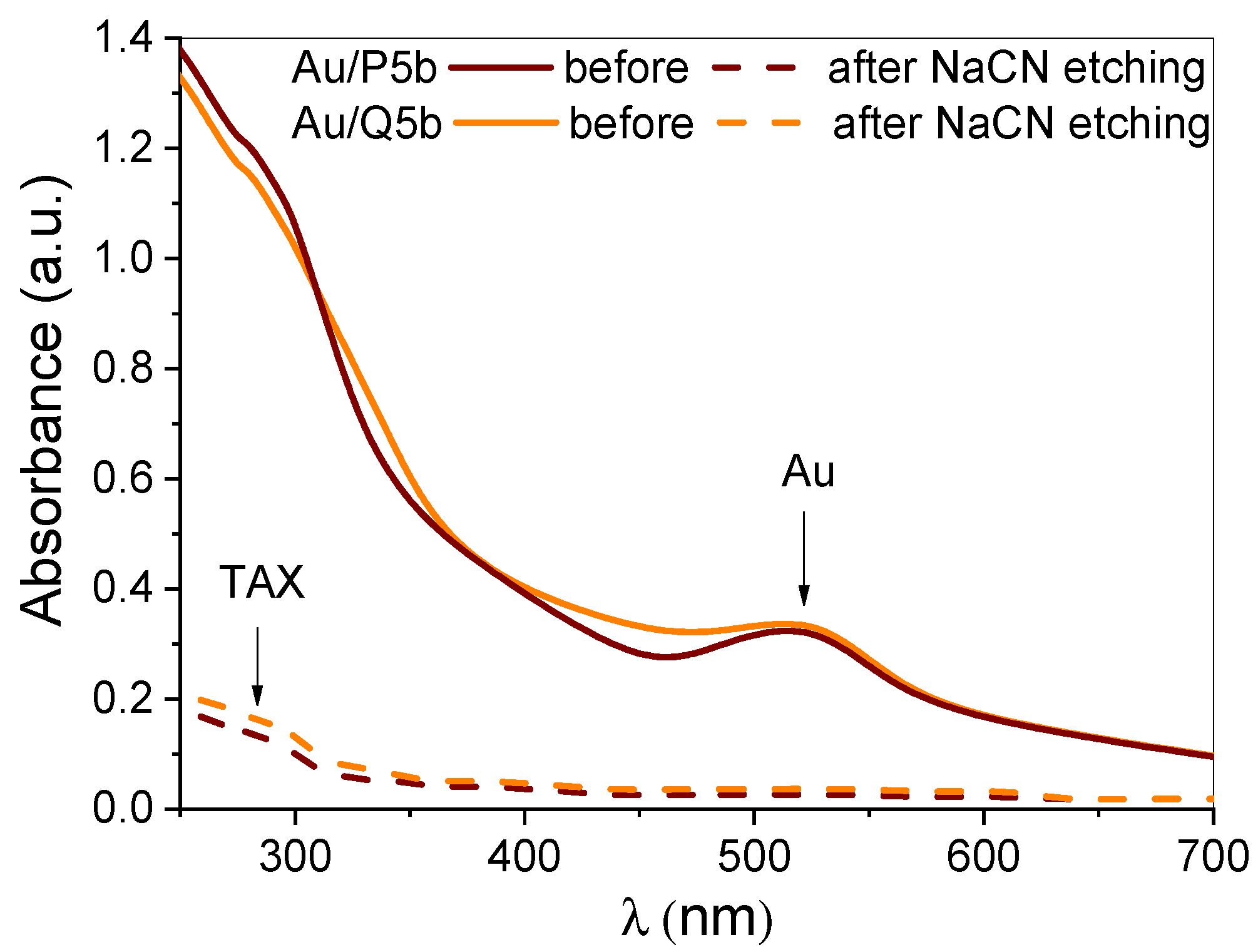
3.1. Characterization of Au@Pentablock Terpolymer Nanocomposites
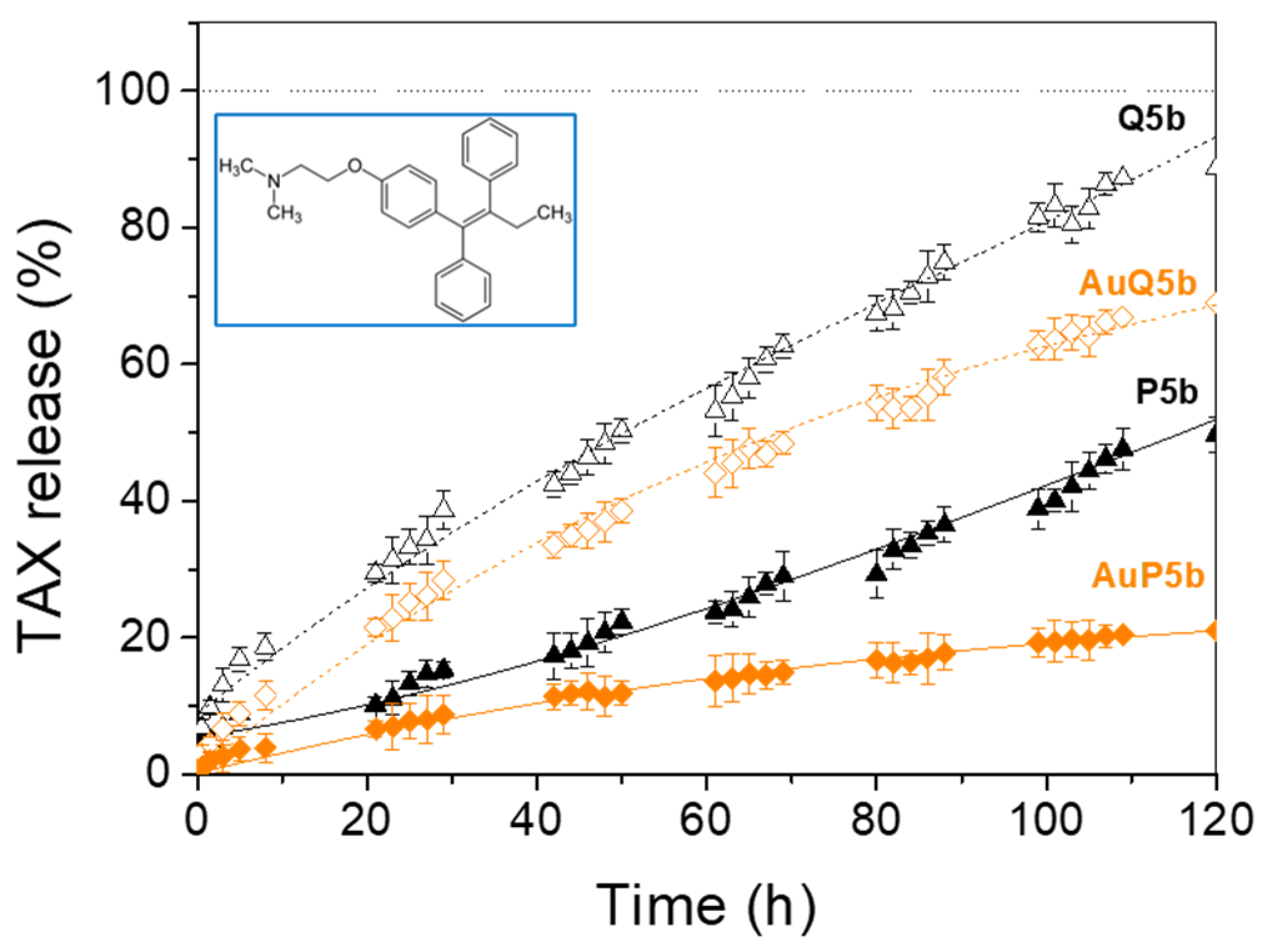
3.2. Release of TAX from Hybrid Nanoparticles at Physiological pH
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X.; Bertrand, N.; Pridgen, E.; Swami, A.; Farokhzad, O.C. Interactions of nanomaterials and biological systems: Implications to personalized nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1363–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beija, M.; Salvayre, R.; de Viguerie, N.L.; Marty, J.-D. Colloidal systems for drug delivery: From design to therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. Targeted Theranostic Nanoparticles for Brain Tumor Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klochkov, S.G.; Neganova, M.E.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Chen, K.; Somasundaram, S.G.; Kirkland, C.E.; Aliev, G. Implications of nanotechnology for the treatment of cancer: Recent advances. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.-B.; Binkhathlan, Z.; Molavi, O.; Lavasanifar, A. Amphiphilic block co-polymers: Preparation and application in nanodrug and gene delivery. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2017–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.S.; Kataoka, K. Block copolymer micelles as long-circulating drug vehicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.H.; Urban, V.S.; Littrell, K.C.; Thiyagarajan, P. Syntheses of Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers Containing a Conjugated Block and Their Self-Assembling Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 6855–6861. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, B.; Ravi, V.; Alexandridis, P. Micellization of amphiphilic block copolymers in binary and ternary solvent mixtures. J. Colloid Interface. Sci. 2013, 390, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K.; Alibolandi, M. Biocompatible polymersomes-based cancer theranostics: Towards multifunctional nanomedicine. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennemur, J.G. Poly(vinylpyridine) Segments in Block Copolymers: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Versatility. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, T.-L.; Chakroun, R.; Janoszka, N.; Chen, C.; Klein, K.; Wong, C.K.; Gröschel, A.H. pH-Controlled Hierarchical Assembly/Disassembly of Multicompartment Micelles in Water. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Eisenberg, A. Multiple Morphologies of "Crew-Cut" Aggregates of Polystyrene-b-poly(acrylic acid) Block Copolymers. Science 1995, 268, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z. Concurrent self-assembly of amphiphiles into nanoarchitectures with increasing complexity. Nano Today 2015, 10, 278–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.-T.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Papadakis, C.M.; Adelsberger, J.; Balog, S.; Busch, P.; Hadjiantoniou, N.A.; Patrickios, C.S. Stimuli-responsive Amphiphilic Polyelectrolyte Heptablock Copolymer Physical Hydrogels: An Unusual pH-response. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3523–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonar, I.; Zhou, C.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Lodge, T.P.; Siegel, R.A. ABC Triblock Terpolymers Exhibiting Both Temperature- and pH-Sensitive Micellar Aggregation and Gelation in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17785–17794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioge, S.; Fustin, C.A.; Gohy, J.F. Temperature-Responsive Aqueous Micelles From Terpyridine End-Capped Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Block-Polystyrene Diblock Copolymers. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2012, 33, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, L.M.; Kramer, E.; Berton, B.; Burger, C.; Foster, S.; Antonietti, M. Successive Use of Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Nanoreactors and Templates: Preparation of Porous Silica with Metal Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 1402–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossmer, S.; Spatz, J.P.; Moller, M.; Aberle, T.; Schmidt, J.; Burchard, W. Solution Behavior of Poly(styrene)-block-poly(2-vinylpyridine) Micelles Containing Gold Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4791–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Controlled Incorporation of Particles into the Central Portion of Vesicle Walls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10078–10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriezema, D.M.; Aragones, M.C.; Elemans, J.A.A.W.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Rowan, A.E.; Nolte, R.J.M. Self-Assembled Nanoreactors. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1445–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Thakor, A.S.; Jokerst, J.; Zavaleta, C.; Massoud, T.F.; Gambhir, S.S. Gold nanoparticles: A revival in precious metal administration to patients. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.M.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2011, 1, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.S.; Agasti, S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Bender, C.M.; Murphy, C.J. Dependence of the Gold Nanorod Aspect Ratio on the Nature of the Directing Surfactant in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9065–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Vangveravong, S.; Mach, R.H.; Xia, Y. Using SV119-Gold Nanocage Conjugates to Eradicate Cancer Stem Cells Through a Combination of Photothermal and Chemo Therapies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F.; Pasparakis, G. Hierarchically designed hybrid nanoparticles for combinational photochemotherapy against a pancreatic cancer cell line. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.I.; Paripovic, D.; Klok, H.-A. Size-Dependent LCST Transitions of Polymer-Coated Gold Nanoparticles: Cooperative Aggregation and Surface Assembly. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4721–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhao, B.; Tao, P.; Yin, K.; Lei, P.; Wang, Q. Amphiphilic multiblock copolymer stabilized Au nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2008, 317, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Taton, T.A. Core/shell gold nanoparticles by self-assembly and crosslinking of micellar, block-copolymer shells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, T.G. Thermosensitive Pluronic Micelles Stabilized by Shell Cross-Linking with Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6380–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Gold Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, M.A.; Lai, J.J.; Hoffman, A.S.; Yager, P.; Stayton, P.S. “Smart” diblock copolymers as templates for magnetic-core gold-shell nanoparticle synthesis. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, X. Recent Advances in Amphiphilic Polymers as the Stabilizers of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadishad, B.; Vossoughi, M.; Alemzadeh, I. Folate-receptor-targeted delivery of doxorubicin using polyethylene glycol-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Murakami, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Che, Y. Highly efficient and controllable PEGylation of gold nanoparticles prepared by femtosecond laser ablation in water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23293–23298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.-T.; Tsitsilianis, C. Controlled Delivery of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles by pH-Sensitive Polymersomes. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.-T.; Korogiannaki, K.; Marikou, K.; Tsitsilianis, C. CBABC terpolymer-based nanostructured vesicles with tunable membrane permeability as potential hydrophilic drug nanocarriers. Polymer 2014, 55, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; He, Q.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.B. Fabrication of pH-responsive nanocomposites of gold nanoparticles/poly(4-vinylpyridine). Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntivich, R.; Choi, I.; Gupta, M.K.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Tsukruk, V.V. Gold nanoparticles grown on star-shaped block copolymer monolayers. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10730–10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, L.; Fu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X. Janus Micelle Formation Induced by Protonation/Deprotonation of Poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-Poly(ethylene oxide) Diblock Copolymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L. Formation of Gold@Polymer Core−Shell Particles and Gold Particle Clusters on a Template of Thermoresponsive and pH-Responsive Coordination Triblock Copolymer. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9393–9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, T.; Eisenberg, A. Monolayer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles by the Self-Assembly of Micellar Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-Poly(ε-caprolactone) Block Copolymer. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Qi, Y.; Bai, X.; Shi, L.; Jia, H.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, L. One-Pot Synthesis of Dendritic Gold Nanostructures in Aqueous Solutions of Quaternary Ammonium Cationic Surfactants: Effects of the Head Group and Hydrocarbon Chain Length. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4665–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, V.C. Tamoxifen (ICI46,474) as a targeted therapy to treat and prevent breast cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S269–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Butsele, K.; Morille, M.; Passirani, C.; Legras, P.; Benoit, J.P.; Varshney, S.K.; Jérôme, R.; Jérôme, C. Stealth properties of poly(ethylene oxide)-based triblock copolymer micelles: A prerequisite for a pH-triggered targeting system. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3700–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Diao, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Xue, C. Novel Polymeric Micelles of AB2 Type α-Methoxy-Poly (ethylene glycol)-b-Poly (γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) 2 Copolymers as Tamoxifen Carriers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 4805–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, T.; Colombani, O.; Chassenieux, C. Dynamic polymeric micelles versus frozen nanoparticles formed by block copolymers. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Butsele, K.; Cajot, S.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Passirani, C.; Benoit, J.-P.; Jerome, R.; Jerome, C. pH-Responsive Flower-Type Micelles Formed by a Biotinylated Poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) Triblock Copolymer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, L.M.; Sidorov, S.N.; Valetsky, P.M.; Hartmann, J.; Cölfen, H.; Antonietti, M. Induced Micellization by Interaction of Poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) with Metal Compounds. Micelle Characteristics and Metal Nanoparticle Formation. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6256–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonietti, M.; Wenz, E.; Bronstein, L.; Seregina, M. Synthesis and characterization of noble metal colloids in block copolymer micelles. Adv. Mater. 1995, 7, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.D.S.; Blanchard, G.J. Formation of Gold Nanoparticles Using Amine Reducing Agents. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5882–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, S.N.; Bronstein, L.M.; Kabachii, Y.A.; Valetsky, P.M.; Lim Soo, P.; Maysinger, D.; Eisenberg, A. Influence of Metalation on the Morphologies of Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) Block Copolymer Micelles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3543–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical Constants of the Noble Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.C.; Pietron, J.J.; Murray, R.W.; Mulvaney, P.J. Solvent Refractive Index and Core Charge Influences on the Surface Plasmon Absorbance of Alkanethiolate Monolayer-Protected Gold Clusters. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, S.; Mulvaney, P. Effect of the Solution Refractive Index on the Color of Gold Colloids. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3427–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, J.S.; Amiji, M.M. Cellular uptake and concentrations of tamoxifen upon administration in poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSci. 2003, 5, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, E.J.; Jame, A.M.; Hovich, J.H.R. Differences between the electrical charge carried by normal and homologous tumour cells. Nature 1956, 177, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Ghosh, P.; Pagliuca, C.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Menichetti, S.; Rotello, V.M. Entrapment of hydrophobic drugs in nanoparticle monolayers with efficient release into cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1360–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Merdan, T.; Schaper, A.K.; Xi, F.; Kissel, T. Core-cross-linked polymeric micelles as paclitaxel carriers. Bioconjug. Chem 2004, 15, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Ai, H.; Nasongkla, N.; Kim, S.; Gao, J. Micellar carriers based on block copolymers of poly (ε-caprolactone) and poly (ethylene glycol) for doxorubicin delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Maniscalco, L.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G. Tamoxifen-loaded polymeric micelles: Preparation, physico-chemical characterization and in vitro evaluation studies. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Jo, Y.S.; Ihm, J.E.; Kim, D.K.; Muhammed, M. Thermosensitive Nanospheres with a Gold Layer Revealed as Low-Cytotoxic Drug Vehicles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9346–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, J.S.; Amiji, M.M. Biodegradable poly (ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles for tumor-targeted delivery of tamoxifen. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 249, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G.; Du, J.; Armes, S.P.; Tang, Y.; Lewis, A.L. New folate-functionalized biocompatible block copolymer micelles as potential anti-cancer drug delivery systems. Polymer 2006, 47, 2946–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadishad, B.; Vosoughi, M.; Alamzadeh, I.; Tavakoli, A. Synthesis of folate-modified, polyethylene glycol-functionalized gold nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Simchi, A.; Imani, M.; Hafeli, U.O. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Rigid Cross-linked Polyethylene Glycol Fumarate Coating for Application in Imaging and Drug Delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8124–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.J.R.; Emamzadeh, M.; Pasparakis, G. Transiently malleable multi-healable hydrogel nanocomposites based on responsive boronic acid copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| POLYMER | Mw | PDI | PEO wt% | P2VP wt% | QP2VP | PCL wt% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | mol% | ||||||
| PCL46-PEO199-P2VP598-PEO199-PCL46 (P5b) | 90,950 | 1.14 | 19.4 | 69 | - | - | 11.6 |
| PCL46-PEO199-P(2VP-co-2VPq)598-PEO199-PCL46 (Q5b) | 108,840 | 1.14 | 16 | 45.5 | 29.9 | 19 | 8.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popescu, M.-T.; Tsitsilianis, C. Gold/Pentablock Terpolymer Hybrid Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Controlled Delivery of Tamoxifen: Effect of Nanostructure on Release Kinetics. Molecules 2022, 27, 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123764
Popescu M-T, Tsitsilianis C. Gold/Pentablock Terpolymer Hybrid Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Controlled Delivery of Tamoxifen: Effect of Nanostructure on Release Kinetics. Molecules. 2022; 27(12):3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123764
Chicago/Turabian StylePopescu, Maria-Teodora, and Constantinos Tsitsilianis. 2022. "Gold/Pentablock Terpolymer Hybrid Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Controlled Delivery of Tamoxifen: Effect of Nanostructure on Release Kinetics" Molecules 27, no. 12: 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123764
APA StylePopescu, M.-T., & Tsitsilianis, C. (2022). Gold/Pentablock Terpolymer Hybrid Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Controlled Delivery of Tamoxifen: Effect of Nanostructure on Release Kinetics. Molecules, 27(12), 3764. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123764






