Preventive Effects of Green Tea Extract against Obesity Development in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
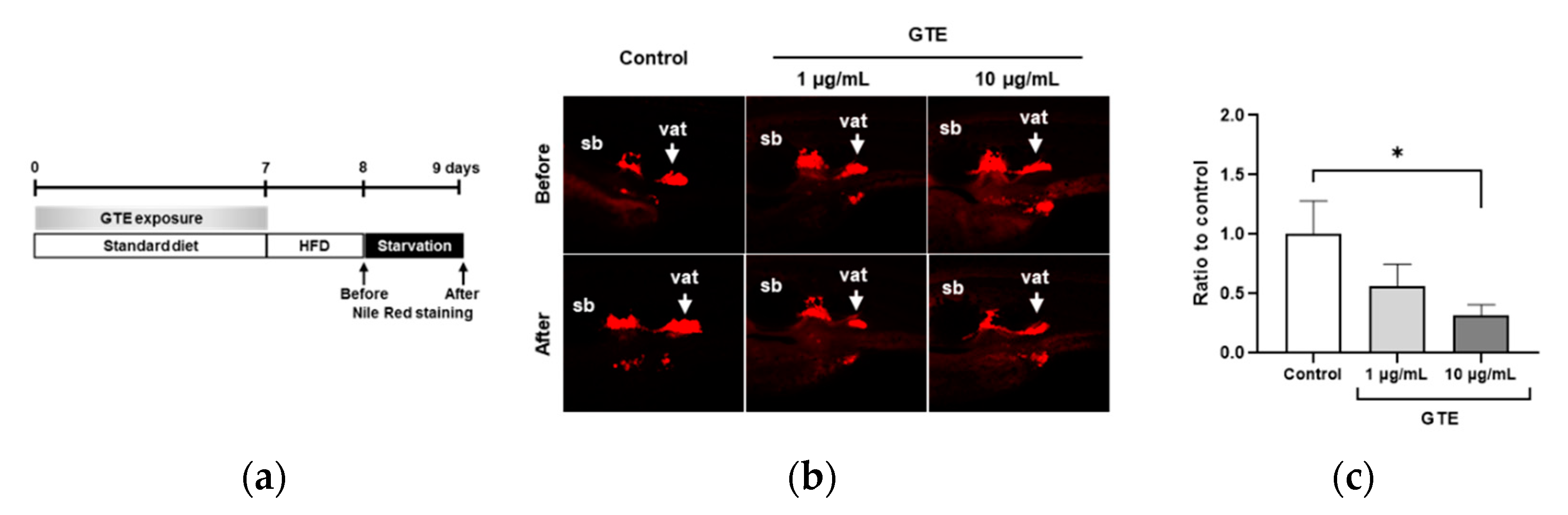
2.1. Preventive GTE Administration Decreased VAT Volume in Juvenile Zebrafish
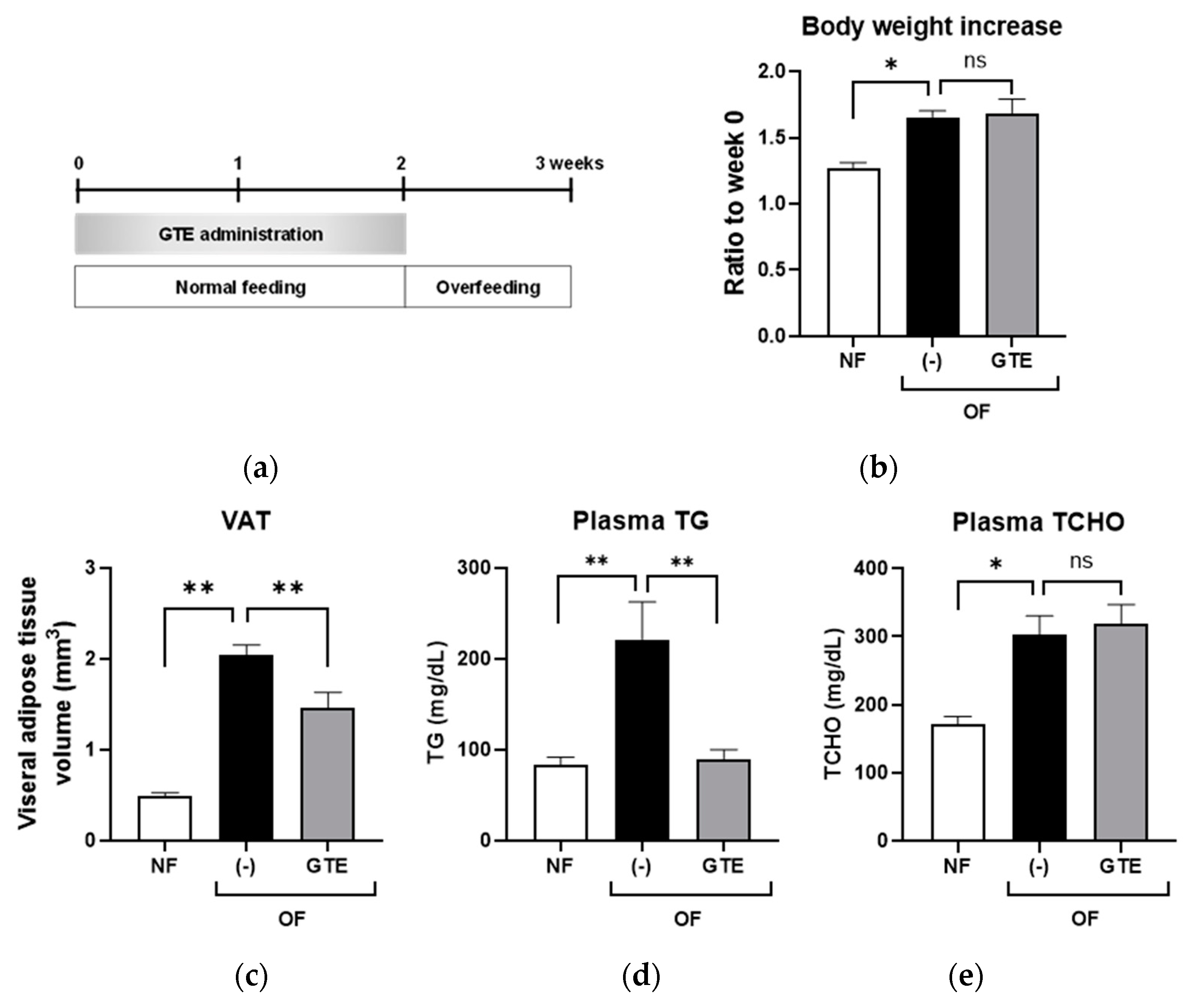
2.2. Preventive GTE Treatment Reduced VAT and Plasma TG Levels in Adult Obese Zebrafish
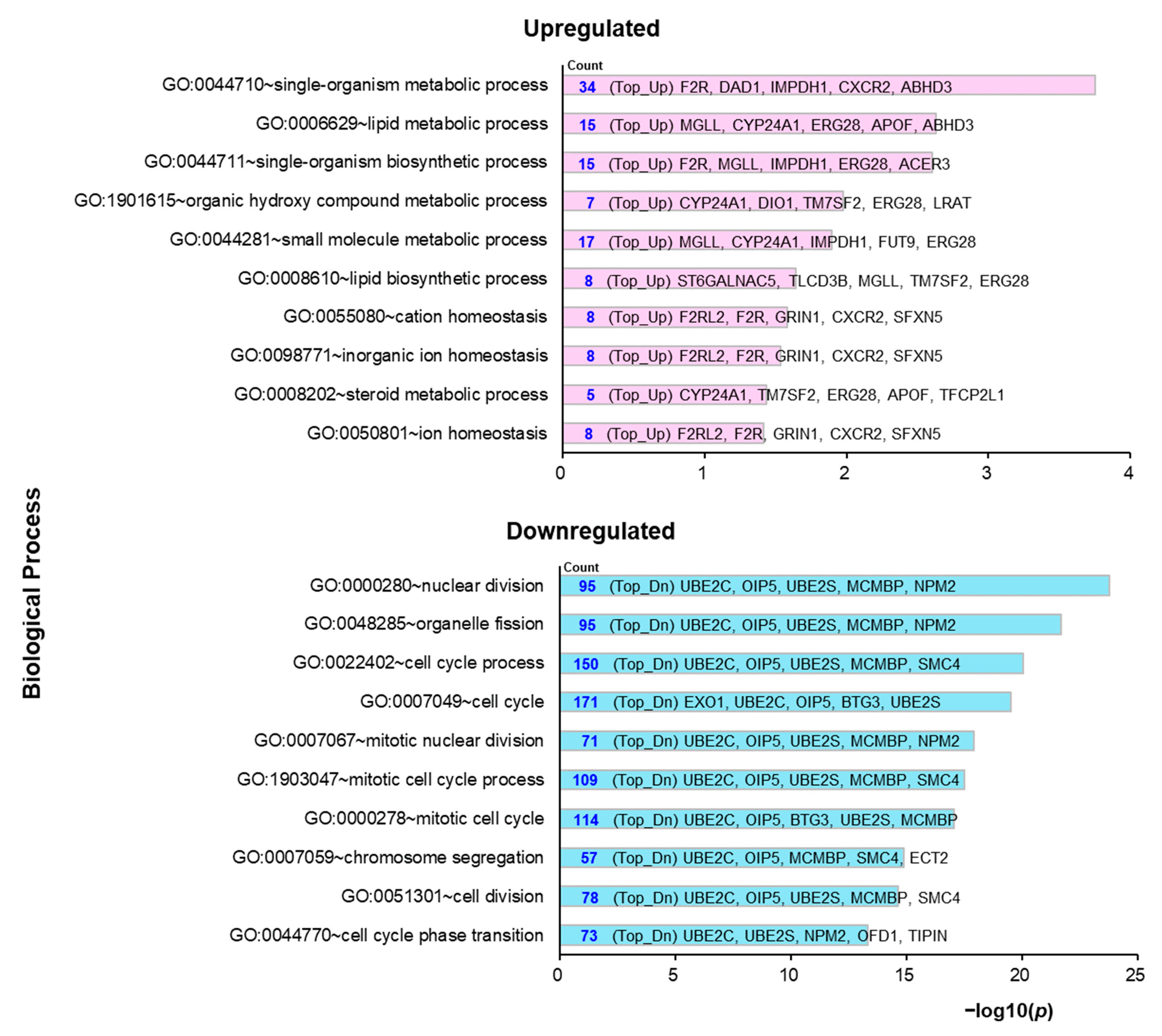
2.3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Preventive Anti-Obesity Effects of GTE
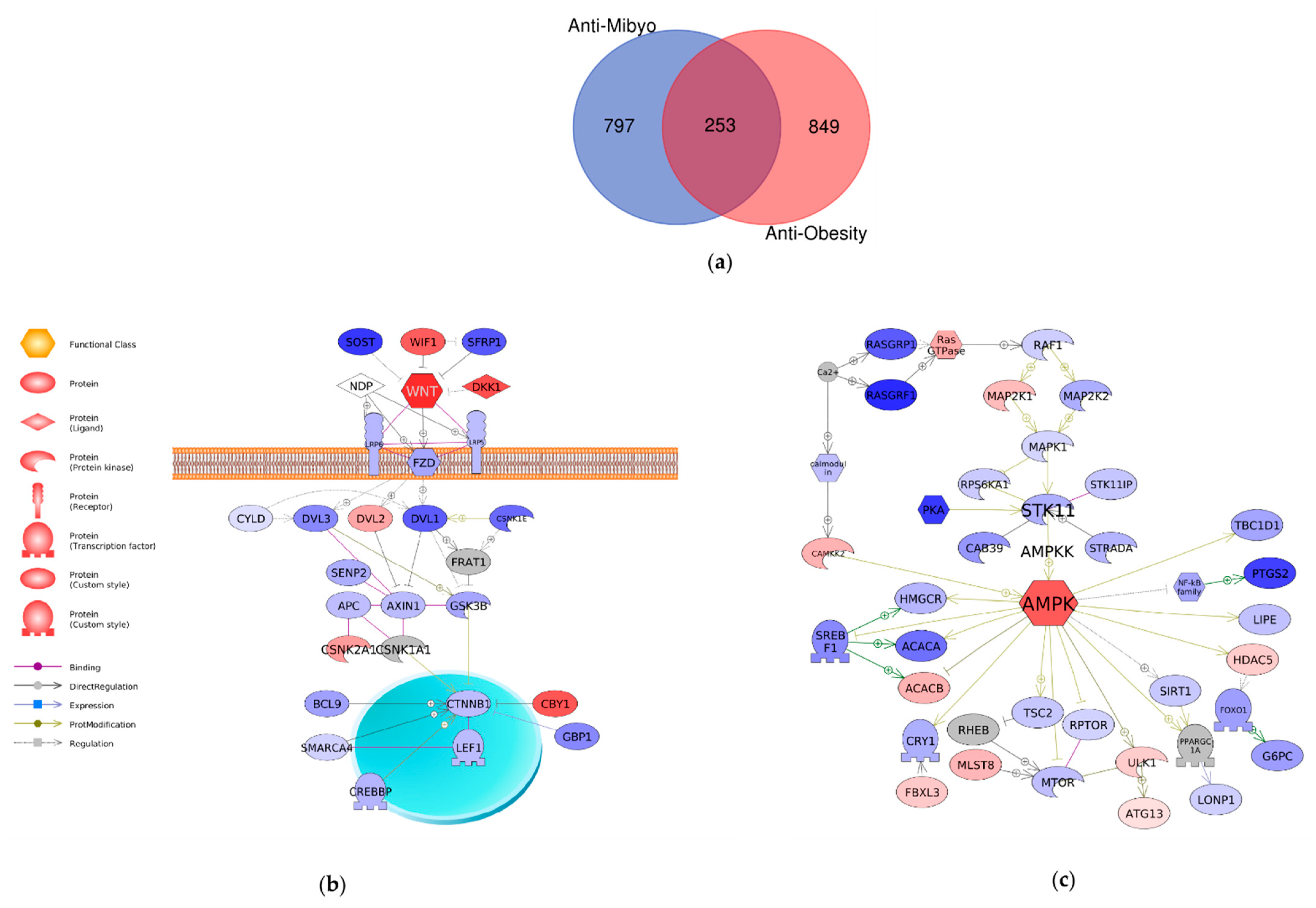
2.4. Comparison of Mechanisms Underlying Preventive Anti-Obesity Effects and Anti-Obesity Effects of GTE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Zebrafish Husbandry
4.3. Chemicals
4.4. Zebrafish Obesogenic Test (ZOT)
4.5. Preventive GTE Administration to Adult Zebrafish
4.6. Library Construction and High-Throughput Sequencing
4.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.8. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Apovian, C.M.; Mechanick, J.I. Obesity IS a disease! Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Natural Products with Anti-obesity Effects and Different Mechanisms of Action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9571–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramitsu, M.; Shimada, Y.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Inoue, T.; Katagiri, T.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Tanaka, T. Eriocitrin ameliorates diet-induced hepatic steatosis with activation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Shimada, Y.; Zang, L.; Terasawa, M.; Nishiura, K.; Matsuda, K.; Toombs, C.; Langdon, C.; Nishimura, N. Novel Anti-Obesity Properties of Palmaria mollis in Zebrafish and Mouse Models. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, N.; Reifen, R.; Kerem, Z. Weight gain reduction in mice fed Panax ginseng saponin, a pancreatic lipase inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2824–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Kim, H.-J.; Chiba, H.; Matsumoto, A. Anti-obesity effect of fish oil and fish oil-fenofibrate combination in female KK mice. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2009, 16, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyznicki, J.M.; Young, D.C.; Riggs, J.A.; Davis, R.M. Obesity: Assessment and management in primary care. Am. Fam. Physician 2001, 63, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tsumura, N.; Nakaguchi, T.; Namiki, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Terasawa, K.; Miyake, Y. Regional image analysis of the tongue color spectrum. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2011, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hahm, K.-B.; Oh, T.-Y.; Jin, J.-H.; Choue, R. Preventive Effect of the Flavonoid, Wogonin, Against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Damage in Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, N.S.; Amitani, H.; Atobe, Y.; Sameshima, Y.; Sakaki, M.; Rokot, N.; Ataka, K.; Amitani, M.; Inui, A. Herbal Medicine Ninjin’yoeito in the Treatment of Sarcopenia and Frailty. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Oku, M.; Hayashi, S.; Inujima, A.; Shibahara, N.; Chen, L.; Igarashi, Y.; Tobe, K.; Saito, S.; Kadowaki, M.; et al. Suppression of Dynamical Network Biomarker Signals at the Predisease State (Mibyou) before Metabolic Syndrome in Mice by a Traditional Japanese Medicine (Kampo Formula) Bofutsushosan. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 9129134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perva-Uzunalić, A.; Škerget, M.; Knez, Ž.; Weinreich, B.; Otto, F.; Grüner, S. Extraction of active ingredients from green tea (Camellia sinensis): Extraction efficiency of major catechins and caffeine. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, M.I.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Tencomnao, T. A Review of the Role of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Antiphotoaging, Stress Resistance, Neuroprotection, and Autophagy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, H.H.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenols and cancer chemoprevention of genitourinary cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Adhami, V.M.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Beverage in Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer: A Mini-Review. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 47, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Wang, H. Cancer Preventive Activities of Tea Catechins. Molecules 2016, 21, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeay, S.; Rodier, M.; Fillon, L.; Faure, S.; Clere, N. Epigallocatechin Gallate: A Review of Its Beneficial Properties to Prevent Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5443–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielecke, F.; Boschmann, M. The potential role of green tea catechins in the prevention of the metabolic syndrome—A review. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Pervin, M.; Goto, S.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Beneficial Effects of Tea and the Green Tea Catechin Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on Obesity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihatsu, K.; Yamabe, M.; Ebara, Y. Antiviral Mechanism of Action of Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate and Its Fatty Acid Esters. Molecules 2018, 23, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furushima, D.; Ide, K.; Yamada, H. Effect of Tea Catechins on Influenza Infection and the Common Cold with a Focus on Epidemiological/Clinical Studies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijburg, L.B.M.; Mattern, T.; Folts, J.D.; Weisgerber, U.M.; Katan, M.B. Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular diseases: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 37, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Ohishi, T.; Tanabe, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Nakamura, Y. Beneficial Effects of Green Tea Catechins on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2018, 23, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Shimada, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Kim, Y.; Chu, D.-C.; Juneja, L.R.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Nishimura, N. RNA-seq Based Transcriptome Analysis of the Anti-Obesity Effect of Green Tea Extract Using Zebrafish Obesity Models. Molecules 2019, 24, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, O.; Kajimoto, Y.; Yabune, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kotani, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nozawa, A.; Nagata, K.; Unno, T.; Sagesaka, Y.M.; et al. Tea Catechins with a Galloyl Moiety Reduce Body Weight and Fat. J. Health Sci. 2005, 51, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I. A Green Tea Extract High in Catechins Reduces Body Fat and Cardiovascular Risks in Humans. Obesity 2007, 15, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvichayapat, P.; Prapochanung, M.; Tunkamnerdthai, O.; Sripanidkulchai, B.-O.; Auvichayapat, N.; Thinkhamrop, B.; Kunhasura, S.; Wongpratoom, S.; Sinawat, S.; Hongprapas, P. Effectiveness of green tea on weight reduction in obese Thais: A randomized, controlled trial. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 93, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Ouadah, N.; Babin, P.J. Zebrafish obesogenic test: A tool for screening molecules that target adiposity. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakano, S.; Ito, S.; Oishi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Isemura, M. In Vitro and In Silico Studies of the Molecular Interactions of Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) with Proteins That Explain the Health Benefits of Green Tea. Molecules 2018, 23, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Hu, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, W.; Yuan, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.-W. Preventive Effects of Catechins on Cardiovascular Disease. Molecules 2016, 21, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Iguchi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hoshino, M.; Hara, A.; Takagaki, A.; Nanjo, F.; et al. Blood brain barrier permeability of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate, its proliferation-enhancing activity of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, and its preventive effect on age-related cognitive dysfunction in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the Regulation of Energy Balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, O.; Olefsky, J.M. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlingieri, M.T.; Pallante, P.; Guida, M.; Nappi, C.; Masciullo, V.; Scambia, G.; Ferraro, A.; Leone, V.; Sboner, A.; Barbareschi, M.; et al. UbcH10 expression may be a useful tool in the prognosis of ovarian carcinomas. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Troncone, G.; Guerriero, E.; Pallante, P.; Berlingieri, M.T.; Ferraro, A.; Del Vecchio, L.; Gorrese, M.; Mariotti, E.; Iaccarino, A.; Palmieri, E.A.; et al. UbcH10 expression in human lymphomas. Histopathology 2009, 54, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajas, L. Re-thinking cell cycle regulators: The cross-talk with metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.J.; Stephens, J.M. Emerging roles of JAK–STAT signaling pathways in adipocytes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzov, E.N.; Stanley, W.J.W.; Pappas, E.G.E.; Thomas, H.H.; Gough, D.J. The JAK/STAT pathway in obesity and diabetes. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernkovich, E.R.; Deng, J.; Bond, M.C.; Combs, T.P.; Harp, J.B. Adipose-specific disruption of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 increases body weight and adiposity. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Radaeva, S.; Pan, H.N.; Tian, Z.; Veech, R.; Gao, B. Interleukin 6 alleviates hepatic steatosis and ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice with fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2004, 40, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, S.H.; Park, O.; Zheng, M.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Kolls, J.K.; Bataller, R.; Gao, B. Interleukin-22 treatment ameliorates alcoholic liver injury in a murine model of chronic-binge ethanol feeding: Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefterova, M.I.; Lazar, M.A. New developments in adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseti, D.; Regassa, A.; Kim, W.-K. Molecular Regulation of Adipogenesis and Potential Anti-Adipogenic Bioactive Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. Effects of (+)-catechin on the differentiation and lipid metabolism of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.-L. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.-T.; Hung, P.-F.; Chen, H.-C.; Huang, R.-N.; Chang, H.-H.; Kao, Y.-H. The Apoptotic Effect of Green Tea (−)-Epigallocatechin Gallate on 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes Depends on the Cdk2 Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5695–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Morikane, D.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, N. A Novel Protocol for the Oral Administration of Test Chemicals to Adult Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2011, 8, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Zang, L.; Hirano, M.; Shimada, Y.; Wang, Z.; Umemoto, N.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Nishimura, N.; Tanaka, T. Diet-induced obesity in zebrafish shares common pathophysiological pathways with mammalian obesity. BMC Physiol. 2010, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Shimada, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, N. A Novel, Reliable Method for Repeated Blood Collection from Aquarium Fish. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Shimada, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, N. Repeated Blood Collection for Blood Tests in Adult Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e53272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.M.; Freeman, J.L. RNA Isolation from Embryonic Zebrafish and cDNA Synthesis for Gene Expression Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, e1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, J.H.; Purdom, E.; Hansen, K.D.; Dudoit, S. Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Ishida, S.; Toda, K.; Matsuda, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Shigetaka, M.; Fukuda, M.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Itai, A. New Approaches to Mechanism Analysis for Drug Discovery Using DNA Microarray Data Combined with KeyMolnet. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2005, 2, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pathway | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Transcriptional regulation by RB/E2F | 2.84 × 10−13 |
| Condensin signaling pathway | 1.37 × 10−9 |
| Calcium signaling pathway | 2.90 × 10−9 |
| Aurora kinase signaling pathway | 5.38 × 10−6 |
| Cell cycle | 6.33 × 10−6 |
| HAT signaling pathway | 1.03 × 10−5 |
| Transcriptional regulation by FOXM | 3.01 × 10−5 |
| CDK signaling pathway | 3.02 × 10−5 |
| ING signaling pathway | 9.52 × 10−5 |
| PLK signaling pathway | 1.08 × 10−4 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | 3.32 × 10−4 |
| Gene regulation by CPEB | 4.27 × 10−4 |
| Kinesin family signaling pathway | 4.94 × 10−4 |
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | 9.42 × 10−4 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | 2.36 × 10−2 |
| Function Name | GO ID | Count | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive regulation of cellular process | GO:0048522 | 69 | 6.63 × 10−16 |
| Positive regulation of biological process | GO:0048518 | 72 | 8.88 × 10−16 |
| Positive regulation of cellular metabolic process | GO:0031325 | 53 | 2.93 × 10−14 |
| Positive regulation of metabolic process | GO:0009893 | 56 | 5.93 × 10−14 |
| Cell cycle G2/M phase transition | GO:0044839 | 18 | 7.84 × 10−14 |
| G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle | GO:0000086 | 17 | 2.86 × 10−13 |
| Regulation of cellular metabolic process | GO:0031323 | 66 | 4.61 × 10−13 |
| Response to endogenous stimulus | GO:0009719 | 34 | 8.64 × 10−13 |
| Positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process | GO:0010604 | 52 | 9.72 × 10−13 |
| Positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process | GO:0051173 | 49 | 1.62 × 10−12 |
| Pathway | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Transcriptional regulation by STAT | 3.68 × 10−16 |
| Transcriptional regulation by CEBP | 7.61 × 10−12 |
| PAK signaling pathway | 8.24 × 10−12 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 2.03 × 10−11 |
| PIN1 signaling pathway | 2.51 × 10−11 |
| JNK signaling pathway | 8.28 × 10−11 |
| Nucleophosmin signaling pathway | 1.52 × 10−10 |
| Transcriptional regulation by POU domain factor | 1.16 × 10−9 |
| Sirtuin signaling pathway | 1.53 × 10−9 |
| PARP signaling pathway | 7.57 × 10−9 |
| GH signaling pathway | 8.46 × 10−9 |
| Transcriptional regulation by SMAD | 1.16 × 10−8 |
| Transcriptional regulation by high-mobility group protein | 1.40 × 10−8 |
| Bcl-2 family signaling pathway | 1.76 × 10−8 |
| Arrestin signaling pathway | 1.90 × 10−8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, L.; Shimada, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Katsuzaki, H.; Kim, Y.; Chu, D.-C.; Juneja, L.R.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Nishimura, N. Preventive Effects of Green Tea Extract against Obesity Development in Zebrafish. Molecules 2021, 26, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092627
Zang L, Shimada Y, Nakayama H, Katsuzaki H, Kim Y, Chu D-C, Juneja LR, Kuroyanagi J, Nishimura N. Preventive Effects of Green Tea Extract against Obesity Development in Zebrafish. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092627
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Liqing, Yasuhito Shimada, Hiroko Nakayama, Hirotaka Katsuzaki, Youngil Kim, Djong-Chi Chu, Lekh Raj Juneja, Junya Kuroyanagi, and Norihiro Nishimura. 2021. "Preventive Effects of Green Tea Extract against Obesity Development in Zebrafish" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092627
APA StyleZang, L., Shimada, Y., Nakayama, H., Katsuzaki, H., Kim, Y., Chu, D.-C., Juneja, L. R., Kuroyanagi, J., & Nishimura, N. (2021). Preventive Effects of Green Tea Extract against Obesity Development in Zebrafish. Molecules, 26(9), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092627







