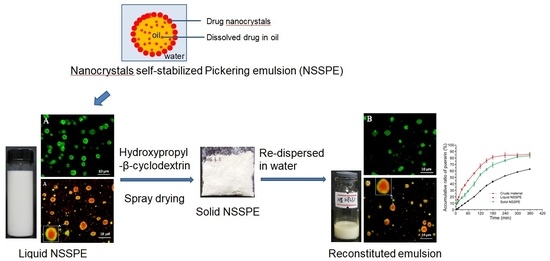
A Novel Solid Nanocrystals Self-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Prepared by Spray-Drying with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as Carriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Liquid NSSPE
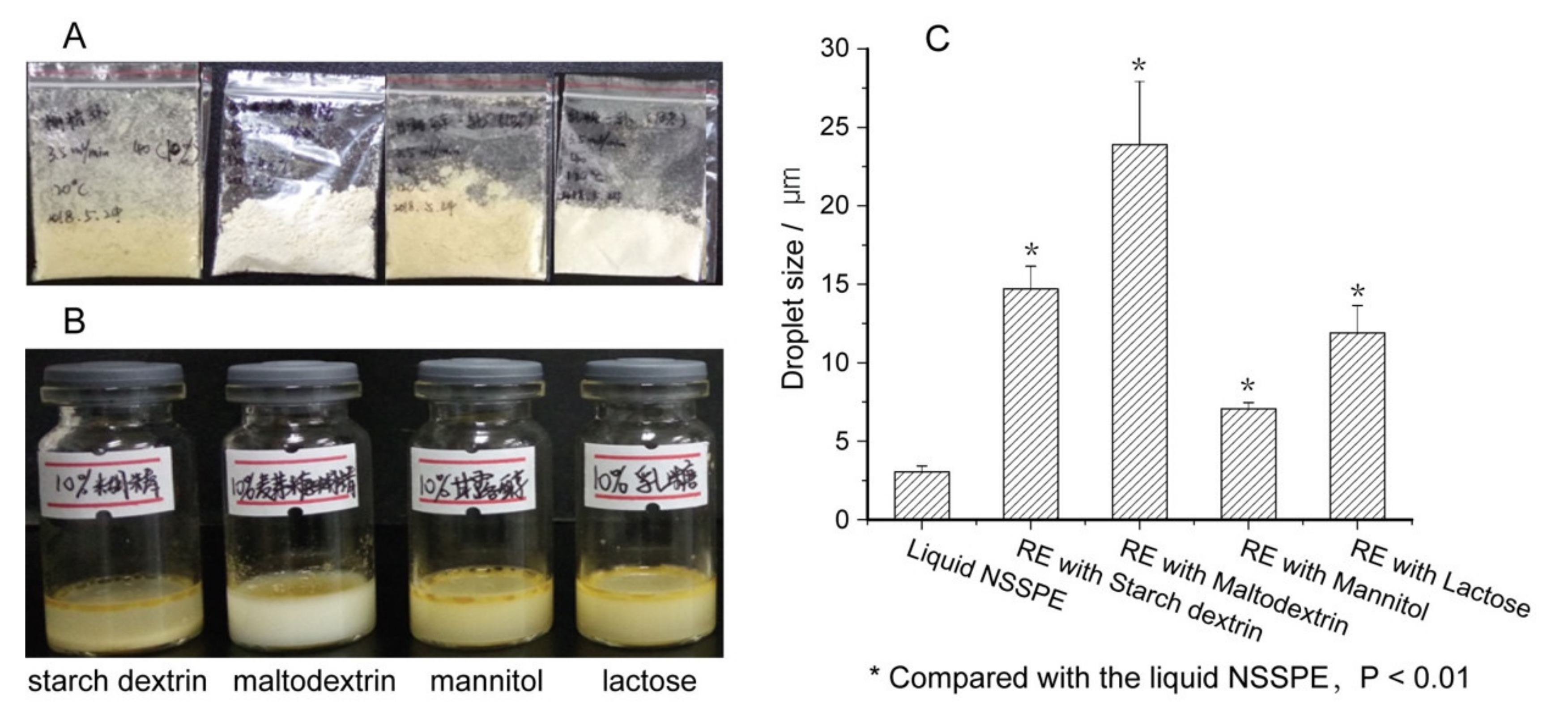
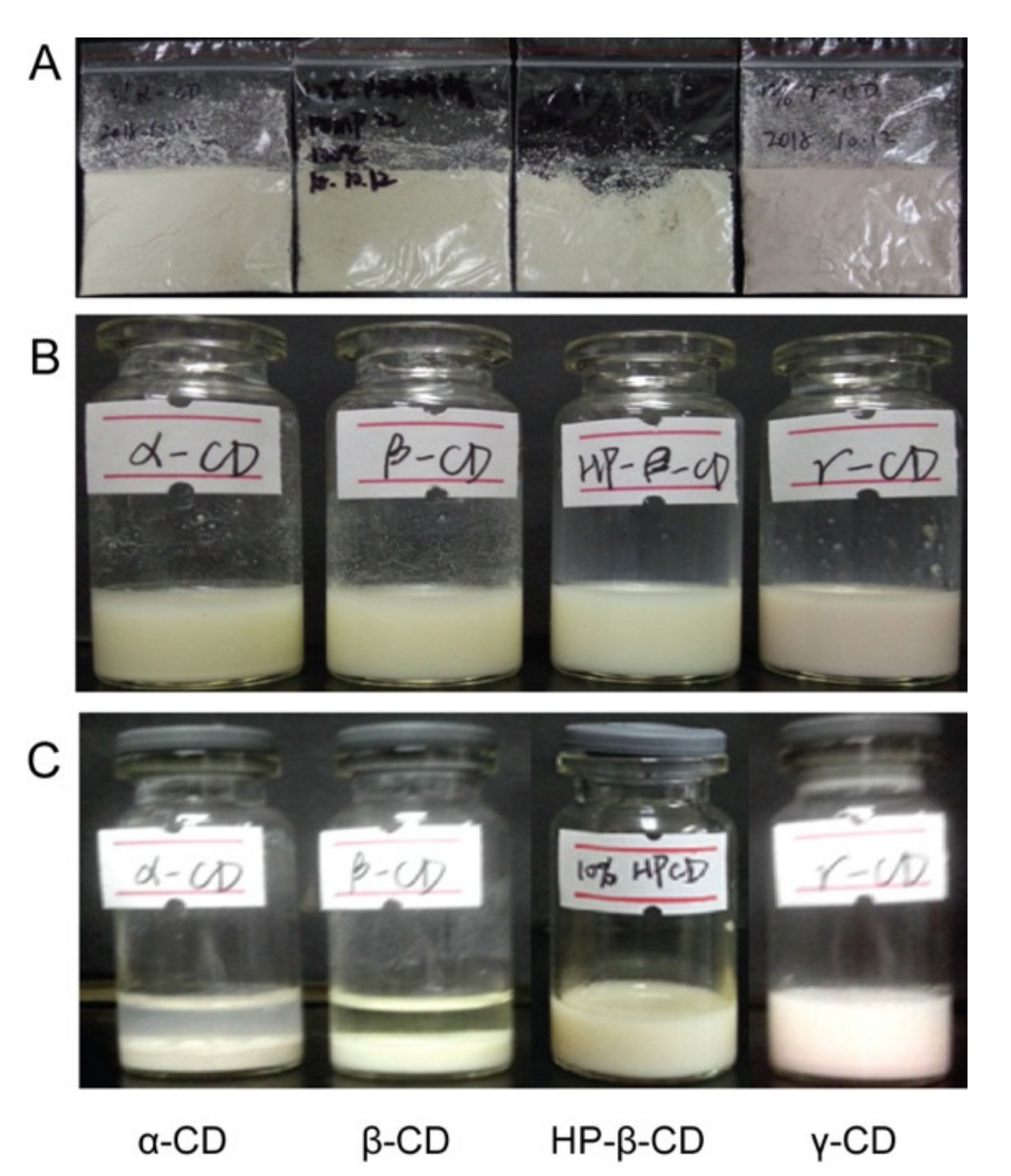
2.3. Selection of the Carrier for Solid NSSPE
2.3.1. Preparation of Solid NSSPE
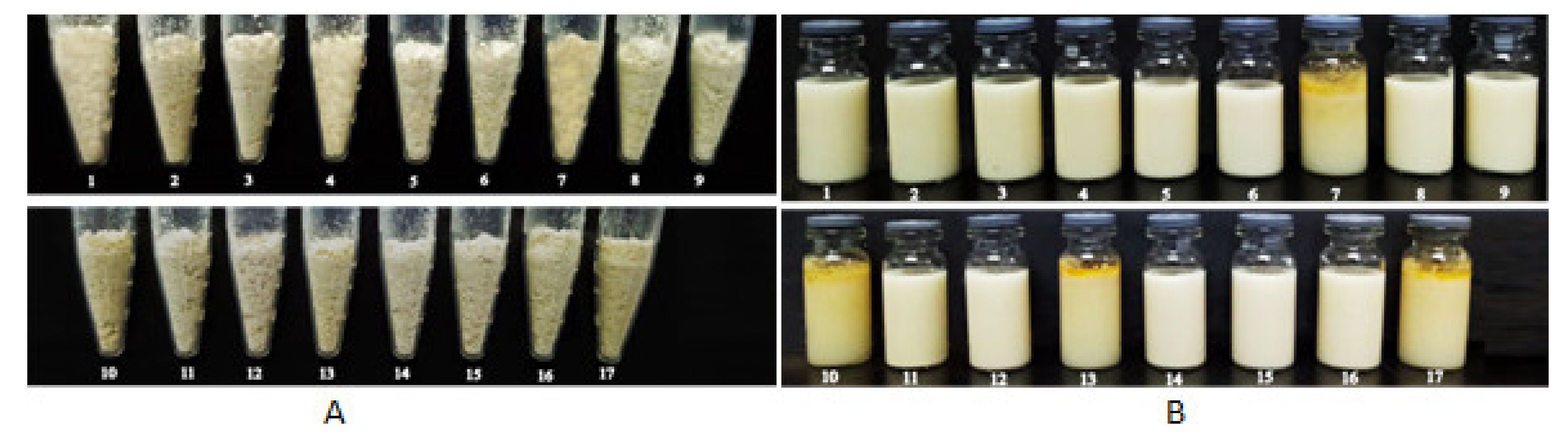
2.3.2. Reconstitution Properties of Solid NSSPE
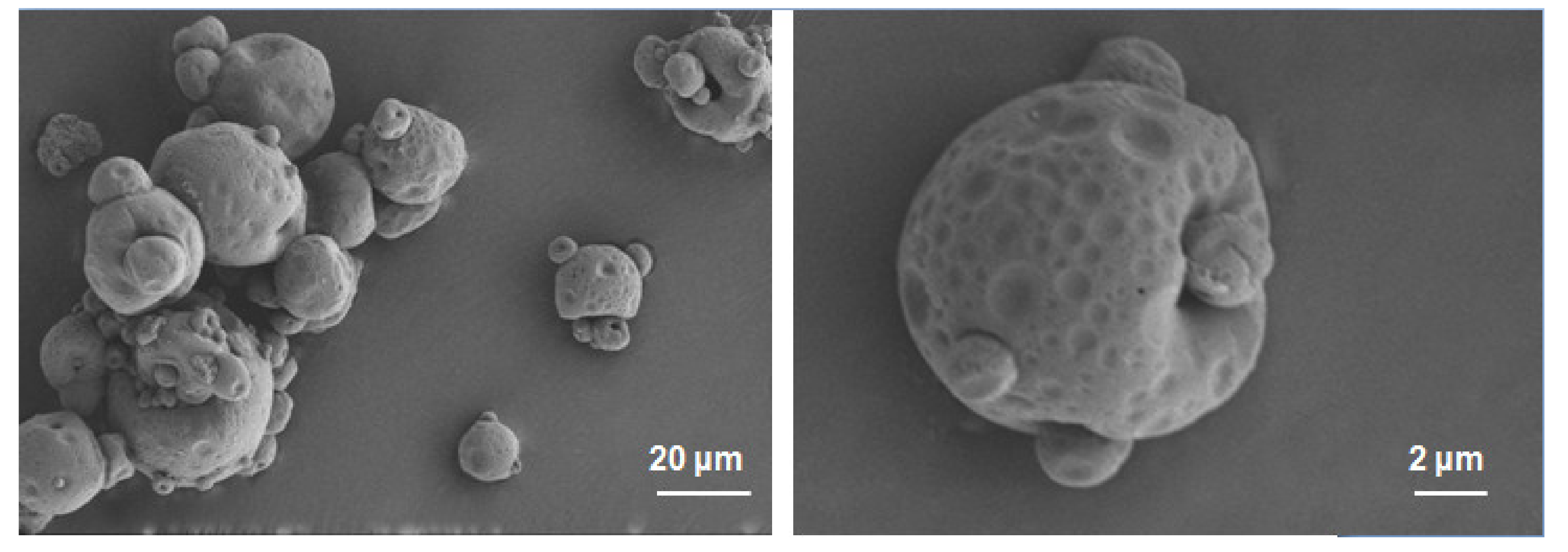
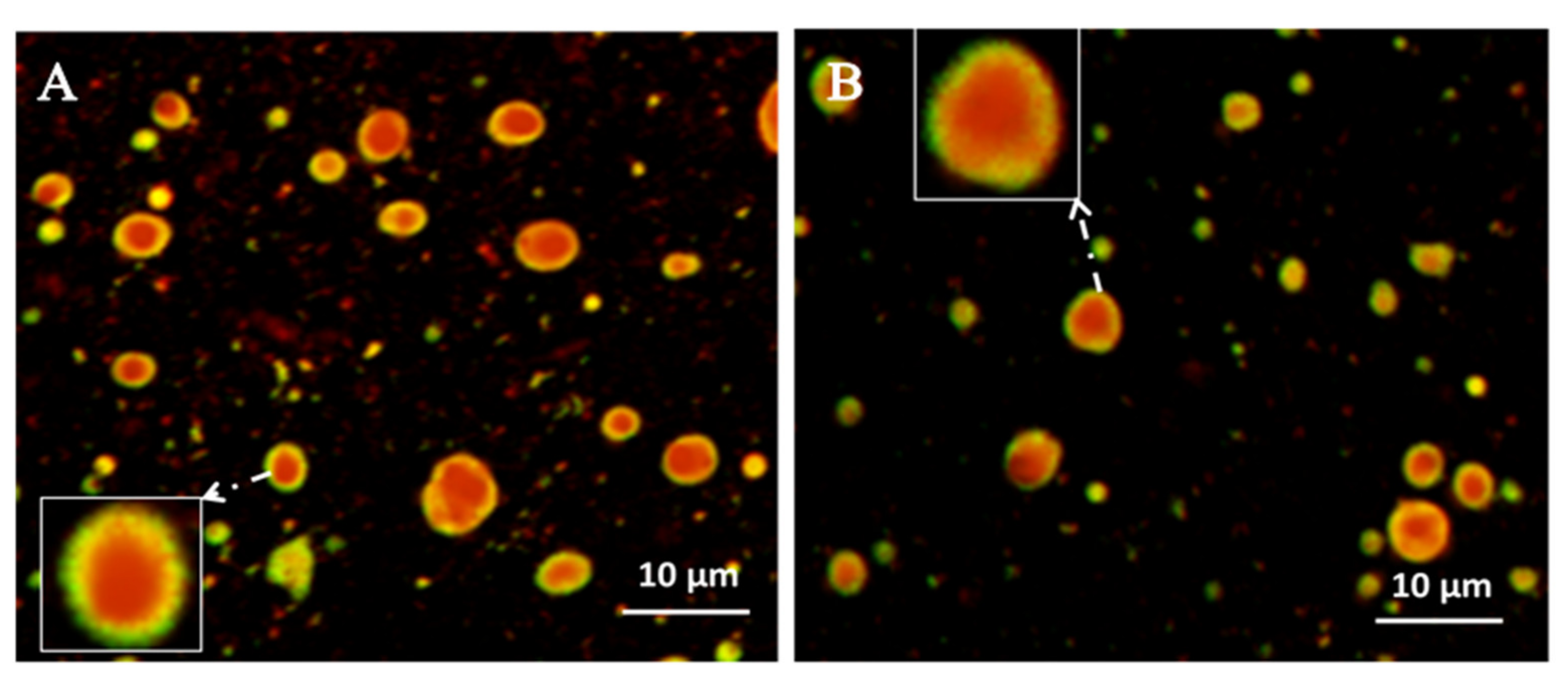
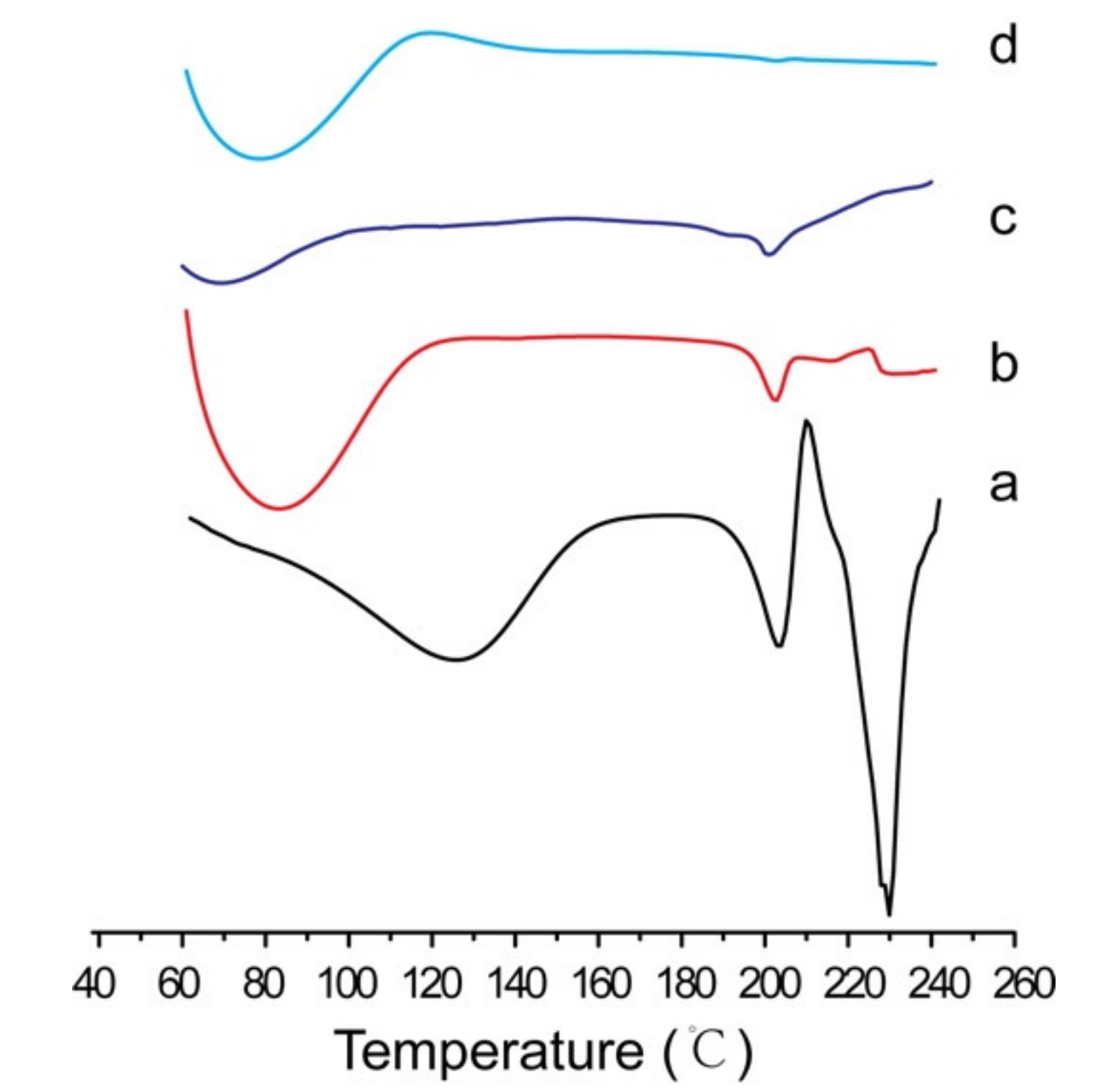
2.3.3. Microstructure Analysis of Solid NSSPE with HP-β-CD
Morphological Analysis of Solid NSSPE
Fluorescence Microscopy and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Characterization of Puerarin Nanocrystals Adsorbed at the Oil–Water Interface
2.4. Optimization of Spray Drying Process by Box–Behnken Design
2.4.1. Oil Leakage Rate of Reconstituted Emulsions
2.4.2. Drug Content in the Solid NSSPE
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution Test
2.6. Physical Stability of Solid NSSPE
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Effects of Solid Carriers on Reconstitution of Solid NSSPE
3.2. Microstructure Analysis of the Solid NSSPE with HP-β-CD
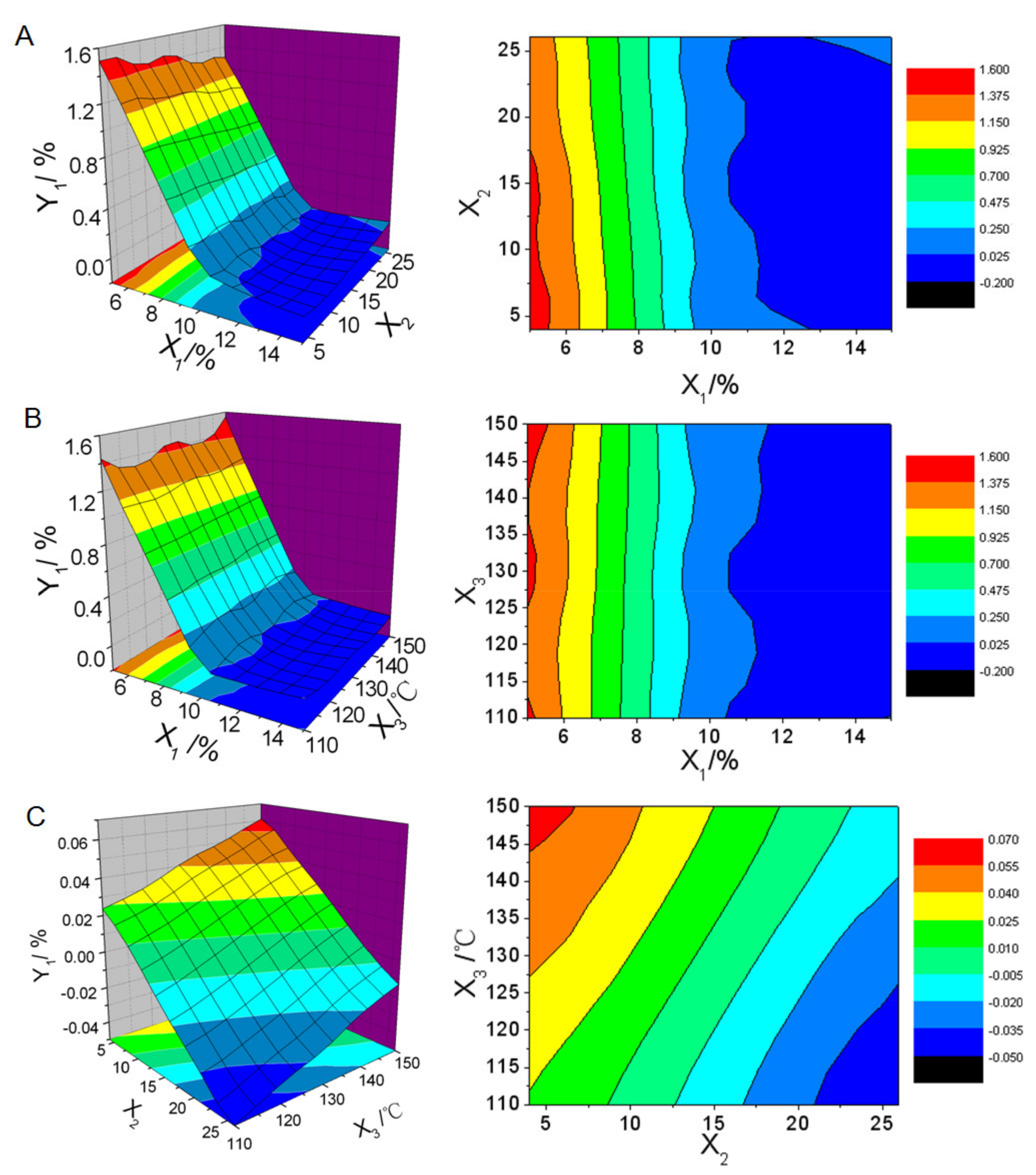
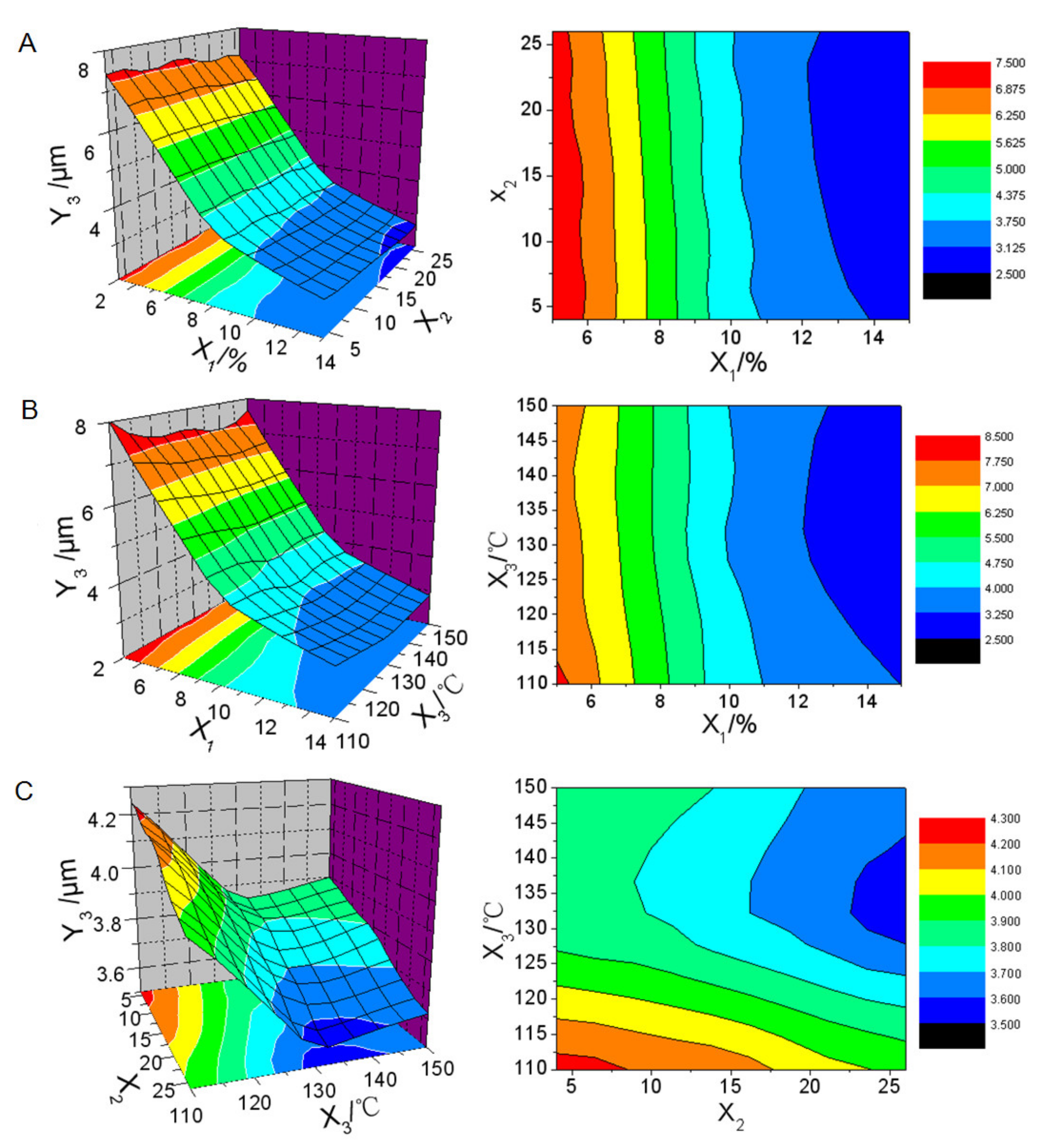
3.3. Optimization of Spray-Drying Process by Box-Behnken Design
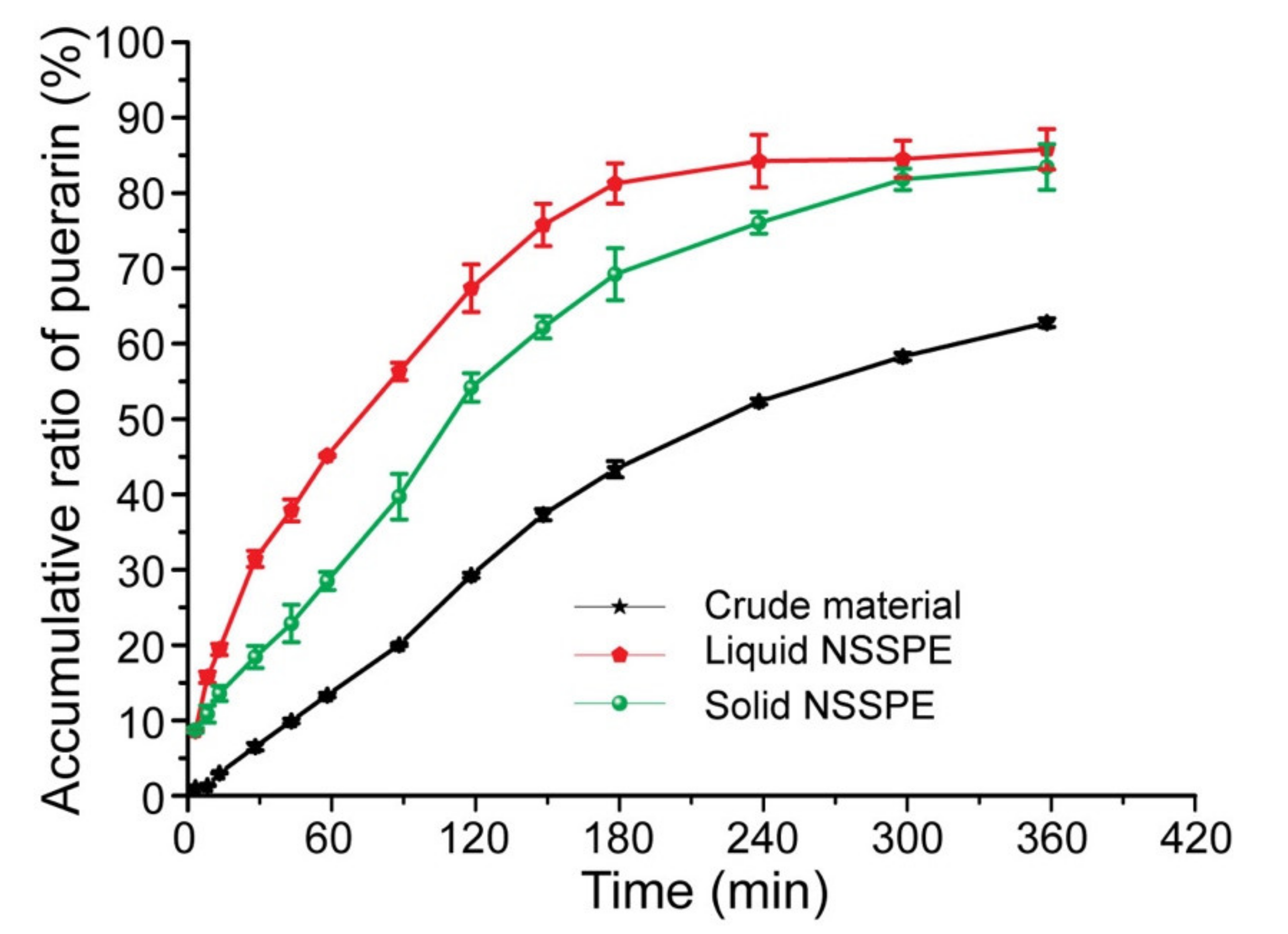
3.4. In Vitro Dissolution Test
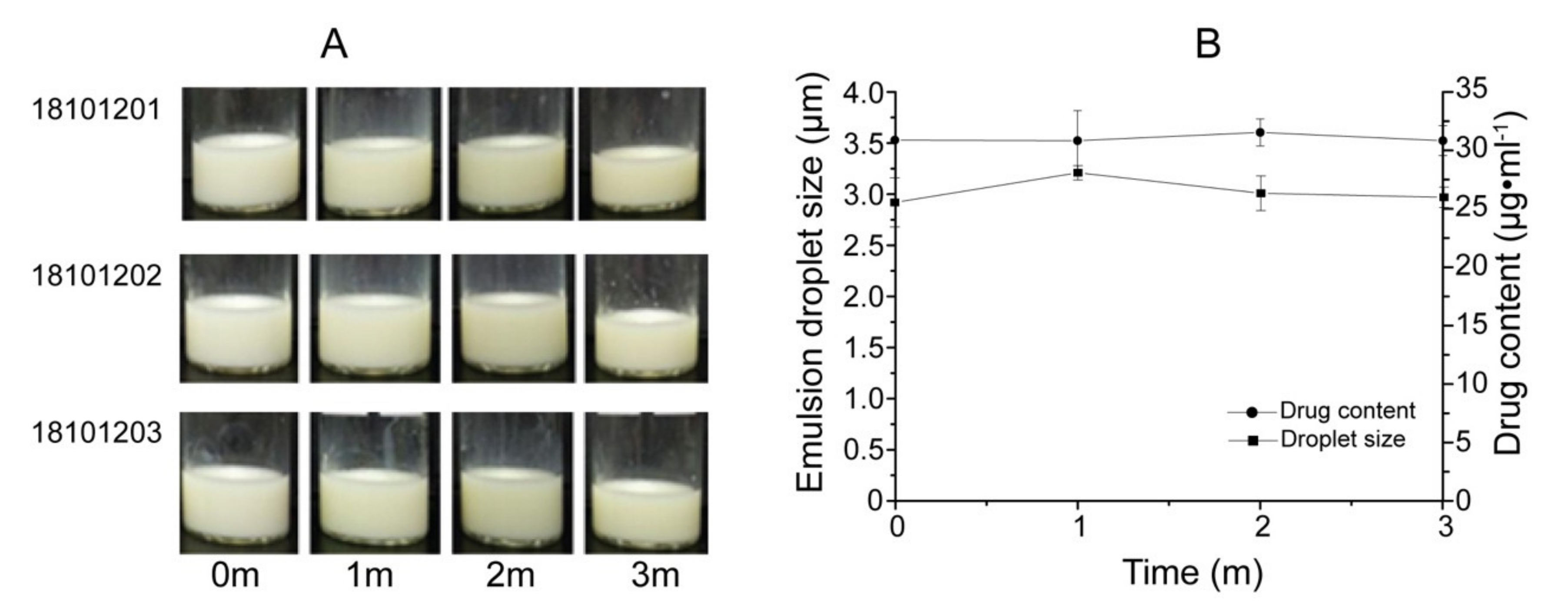
3.5. Physical Stability of Solid NSSPE
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yi, T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.F. A new drug nanocrystal self-stabilized Pickering emulsion for oral delivery of silybin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, T. Development of an oral compound Pickering emulsion composed of nanocrystals of poorly soluble ingredient and volatile oils from traditional Chinese medicine. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Q.Q.; Yi, T. Research progress of Pickering emulsion drug delivery systems. ActaPharm. Sin. 2019, 54, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Fang, Z.W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.W.; Xie, Y.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, Z.G.; Yuan, W.E. An overview of Pickering emulsions: Solid-particle materials, classification, morphology and applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adelmann, H.; Binks, B.P.; Mezzenga, R. Oil powders and gels from particle-stabilized emulsions. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. Influence of protein concentration on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions formed with aggregated milk proteins during spray drying. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitby, C.P.; Scarborough, H.; Ng, S.K.; Ngothai, Y. Spray drying particle-stabilised emulsions. In Proceedings of the Chemeca 2014: Processing Excellence, Powering Our Future, Perth, WA, Australia, 28 September–1 October 2014; p. 655. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, R.; Ito, T.; Tagami, T.; Takii, T.; Ozeki, T. Development of driedemulsion/mannitol composite microparticles through a uniquespray Nozzle for efficient delivery of hydrophilic anti-tuberculosis drug against alveolar macrophages. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goo, B.; Sim, W.Y.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, C.W.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation of spray-dried emulsionof sirolimus for enhanced oral bioavailability. B. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhao, X.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Liang, X.R.; Yang, Y.X. Fabricating multilayer emulsions by using OSA starch and chitosan suitable for spray drying: Application in the encapsulation of beta-carotene. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 93, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, Q.; Yang, C. Spray-dried curcuminnanoemulsion: A new road to improvement of oral bioavailability of curcumin. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Nuzzo, M.; Turchiuli, C.; Bergenstahl, B.; Dumoulin, E.; Millqvist-Fureby, A. The microstructure and component distribution in spray-dried emulsion particles. Food Struct. 2016, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Panahi-Azar, V.; Mohammadi, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; dela Guardia, M. Ethambutol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as dry powder inhalable formulation for tuberculosis therapy. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2019, 20, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Wan, J.L.; Xu, B.H.; Yang, X.L. A new solid self-microemulsifying formulation prepared by spray-drying to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Wan, J.L.; Xu, B.H.; Yang, X.L. Controlled poorly soluble drug release from solid self-microemulsifying formulations with high viscosity hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, C.P.; Scarborough, H.; Ngothai, Y. Drying oil-in-water Pickering emulsions to make redispersible powders. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2940–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Ye, A.; Jones, J.R.; Archer, R.; Singh, H. Behaviour of oil droplets during spray drying of milk-protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Tu, Z.C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Tian, M.; Zhang, N.H. Influence of soy lecithin concentration on the physical properties of whey protein isolate-stabilized emulsion and microcapsule formation. J. Food Eng. 2017, 207, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yin, S.W.; Wu, L.Y.; Qi, J.R.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.Q. Fabrication and characterization of Pickering emulsions and oil gels stabilized by highly charged zein/chitosan complex particles (ZCCPs). Food Chem. 2016, 213, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Tang, C.H. Soy glycinin as food-grade Pickering stabilizers: Part. III. Fabrication of gel-like emulsions and their potential as sustained-release delivery systems for β-carotene. Food Hydrocolloid. 2016, 56, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.M.; Lee, Y. Surface modification of zein colloidal particles with sodium caseinate to stabilize oil-in-water pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocolloid. 2016, 56, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclercq, L.; Nardello-Rataj, V. Pickering emulsions based on cyclodextrins: A smart solution for antifungal azole derivatives topical delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 82, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, L.; Tessier, J.; Douyere, G.; Nardell o-Rataj, V.; Schmitzer, A.R. Phytochemical- andcyclodextrin-based Pickering emulsions: Natural potentiators of antibacterial, antifungal andantibiofilm activity. Langmuir 2020, 36, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Hashizaki, K.; Saito, Y.; Fujii, M. Application of Pickering emulsion with cyclodextrin as an emulsifier to a transdermal drug delivery vehicle. Biol. Pharm. Bulll. 2019, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Gan, L.; Gan, Y. Redispersible, dry emulsion of lovastatin protects against intestinal metabolism and improves bioavailability. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.J.; Na, Y.G.; Huh, H.W.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.K.; Cho, C.W. The Effect of Pharmaceutical Excipients for Applying to Spray-Dried Omega-3 Powder. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vestland, T.L.; Jacobsen, O.; Sande, S.A.; Myrset, A.H.; Klaveness, J. Compactible powders of omega-3 and beta-cyclodextrin. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Salmeron, R.; Chaab, I.; Carn, F.; Djabourov, M.; Bouchemal, K. Pickering emulsions with α-cyclodextrin inclusions: Structure and thermal stability. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 482, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.W.; Yen, M.W.; Wang, A.J.; Chu, I.M. Effect of oil structure on cyclodextrin-based Pickering emulsions for bupivacaine topical application. Colloid. Surface. B 2018, 161, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X. Concise Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 277–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinski, E.L.; Lavrijsen, B.W.M.; Vollenbroek, J.M.; van der Stege, H.J.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Wouters, J.T.M. Effects of spray drying on physicochemical properties of milk protein-stabilised emulsions. Colloid. Surface. B 2003, 31, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.R.H.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Turchiuli, C. Design of liquid emulsions to structure spray dried particles. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchiuli, C.; Jimenez Munguia, M.T.; Hernandez Sanchez, M.; Cortes, F.H.; Dumoulin, E.; Sanchez M, H. Use of different supports for oil encapsulation in powder by spray drying. Powder Technol. 2014, 255, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Emulsion Droplet Size/μm | Particle Size of Adsorbed Nanocrystals/nm | Adsorption Rate of Nanocrystals/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| the liquid NSSPE | 3.05 ± 0.38 | 264.4 ± 9.8 | 29.3 ± 0.5 |
| Reconstituted emulsion from the solid NSSPE | 2.81 ± 0.14 | 280.9 ± 10.9 | 26.8 ± 1.7 |
| Number | Amount of Solid Carrier (X1) | Feed Pump Parameter (X2) | Inlet Air Temperature (X3)/°C | Oil Leakage Rate (Y1)/% | Droplet Size of Reconstituted Emulsion (Y2)/μm | Drug Content in Solid NSSPE (Y3)/mgg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0(10%) | 0 (15) | 0(130) | 0 | 4.08 | 38.95 |
| 2 | 0(10%) | 0(15) | 0(130) | 0 | 3.65 | 38.68 |
| 3 | 0(10%) | 0(15) | 0(130) | 0 | 3.57 | 38.65 |
| 4 | 0(10%) | 0(15) | 0(130) | 0 | 4.00 | 38.79 |
| 5 | 0(10%) | 0(15) | 0(130) | 0 | 4.49 | 38.86 |
| 6 | 0(10%) | 1(25) | −1(110) | 0 | 4.04 | 38.56 |
| 7 | −1(5%) | 0(15) | 1(150) | 1.52 | 8.04 | 53.05 |
| 8 | 0(10%) | 1(25) | 1(150) | 0 | 3.55 | 37.78 |
| 9 | 0(10%) | −1(5) | 1(150) | 0 | 3.61 | 39.08 |
| 10 | −1(5%) | 1(25) | 0(130) | 1.39 | 7.16 | 60.07 |
| 11 | 1(15%) | 0(15) | −1(110) | 0 | 3.00 | 29.56 |
| 12 | 1(15%) | 1(25) | 0(130) | 0 | 2.62 | 29.90 |
| 13 | −1(5%) | −1(5) | 0(130) | 1.69 | 7.31 | 57.53 |
| 14 | 1(15%) | 0(15) | 1(150) | 0 | 2.78 | 31.59 |
| 15 | 1(15%) | −1(5) | 0(130) | 0 | 3.10 | 30.53 |
| 16 | 0(10%) | −1(5) | −1(110) | 0 | 4.28 | 37.87 |
| 17 | −1(5%) | 0(15) | −1(110) | 1.36 | 8.18 | 56.48 |
| Response | Oil Separation Rate (Y1)/% | Droplet Size (Y2)/μm | Drug Content in the Solid NSSPE (Y3)/mg·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive value | −01779 | 2.85 | 34.91 |
| Measured value | 0 | 2.81 ± 0.14 | 31.26 ± 0.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yi, T. A Novel Solid Nanocrystals Self-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Prepared by Spray-Drying with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as Carriers. Molecules 2021, 26, 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061809
Zhang J, Wang Y, Wang J, Yi T. A Novel Solid Nanocrystals Self-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Prepared by Spray-Drying with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as Carriers. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061809
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jifen, Yanhua Wang, Jirui Wang, and Tao Yi. 2021. "A Novel Solid Nanocrystals Self-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Prepared by Spray-Drying with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as Carriers" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061809
APA StyleZhang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, J., & Yi, T. (2021). A Novel Solid Nanocrystals Self-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Prepared by Spray-Drying with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as Carriers. Molecules, 26(6), 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061809