Delivery of Thyronamines (TAMs) to the Brain: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
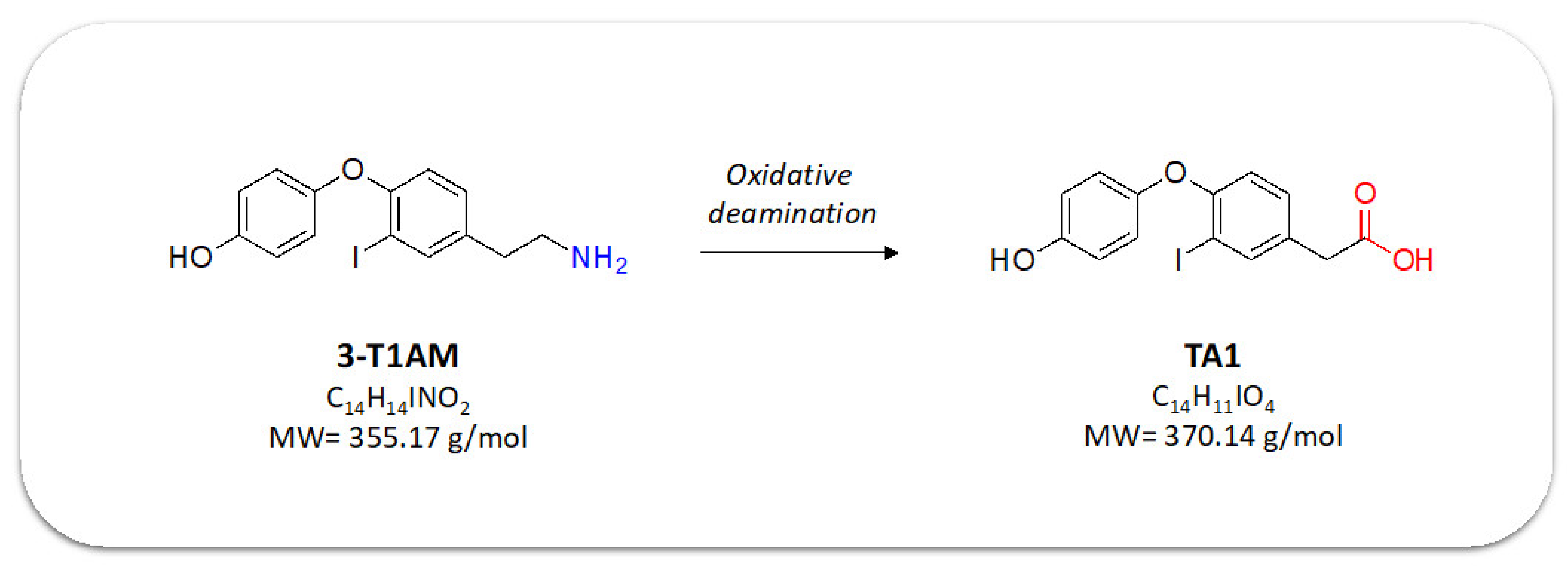
1. Introduction
2. Results
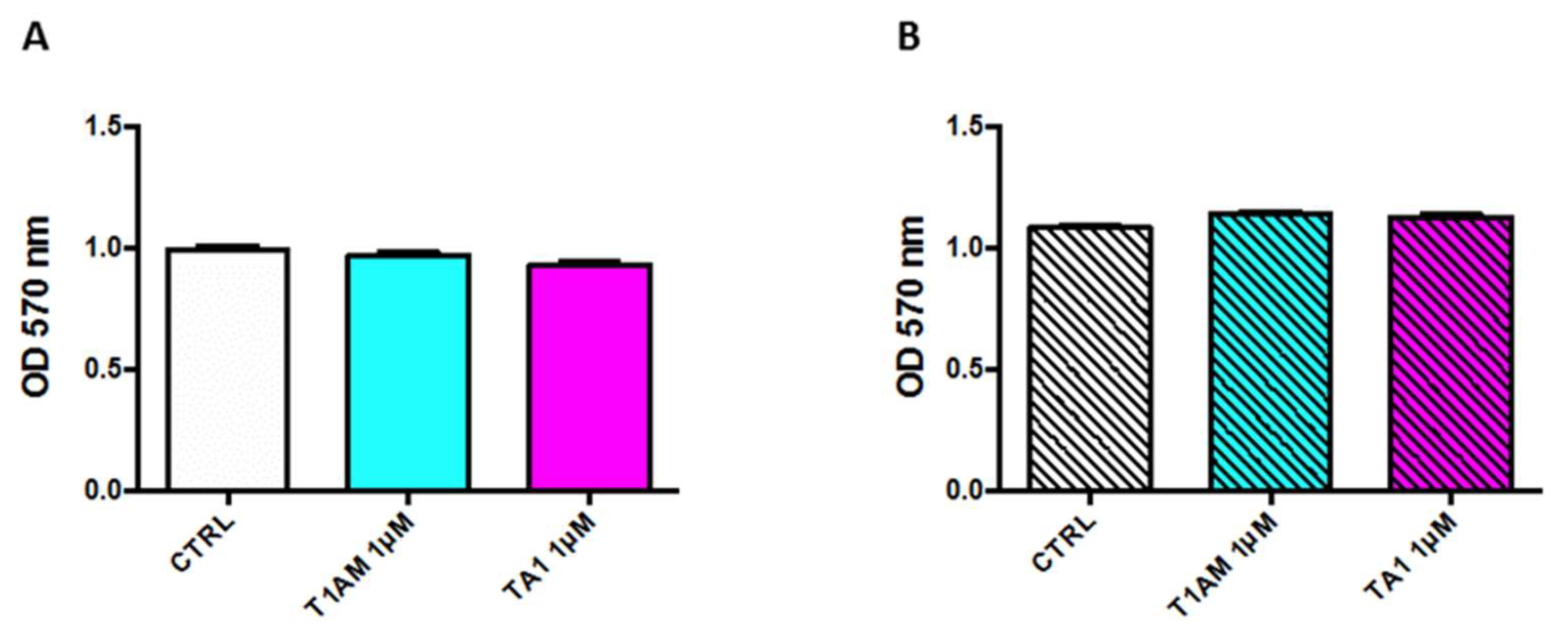
2.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
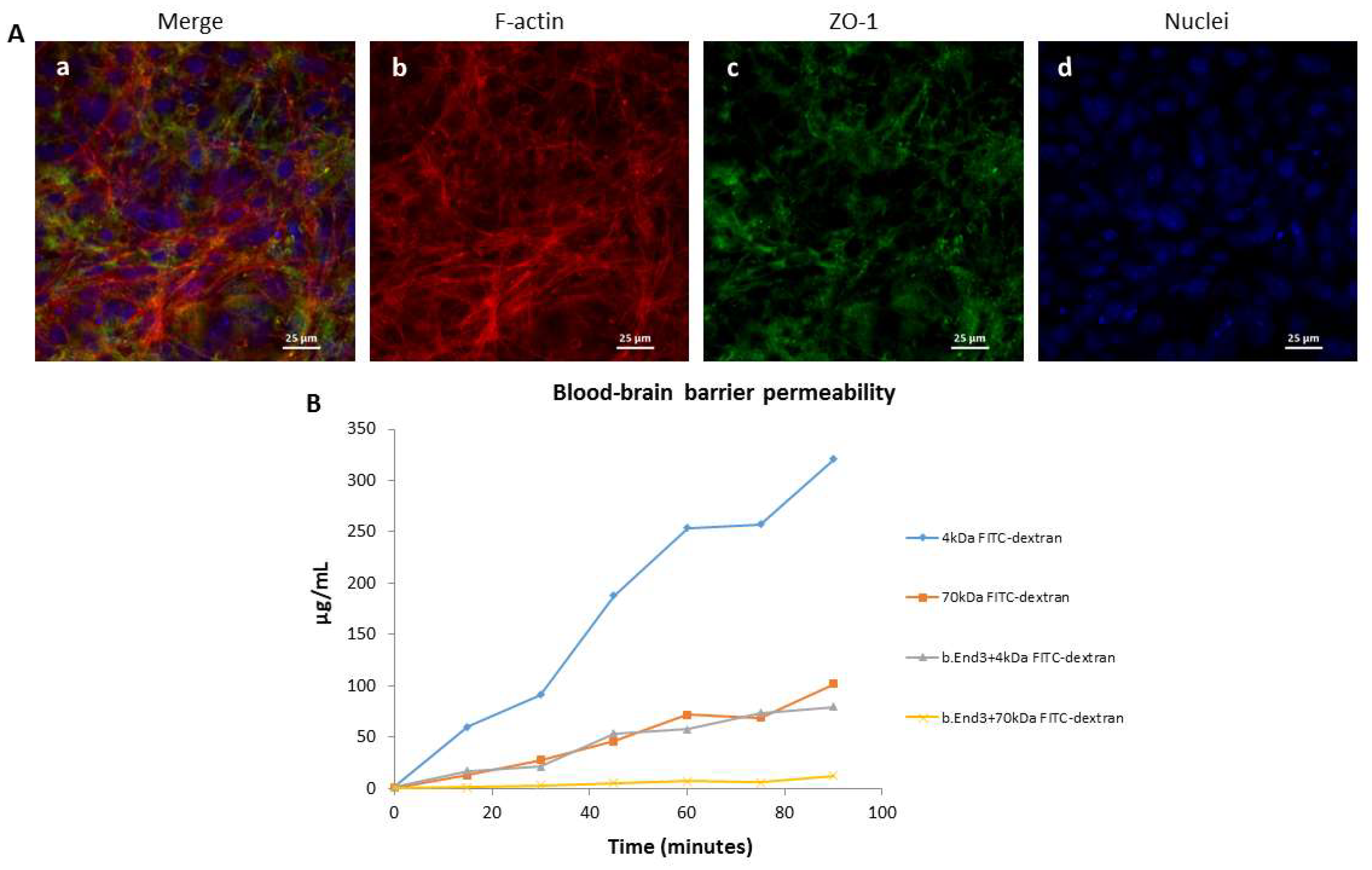
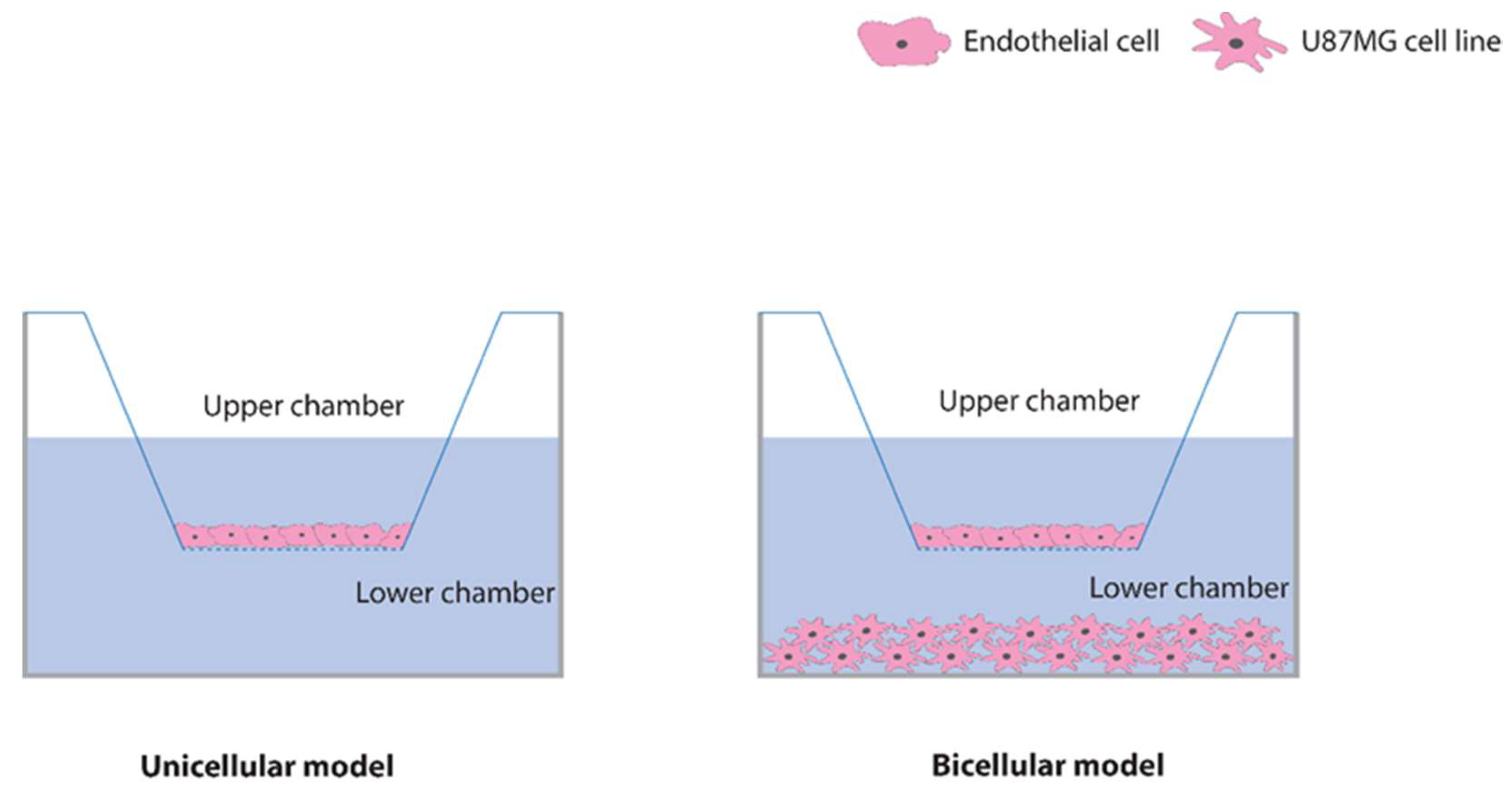
2.2. Characterization of the Blood–Brain Barrier Model
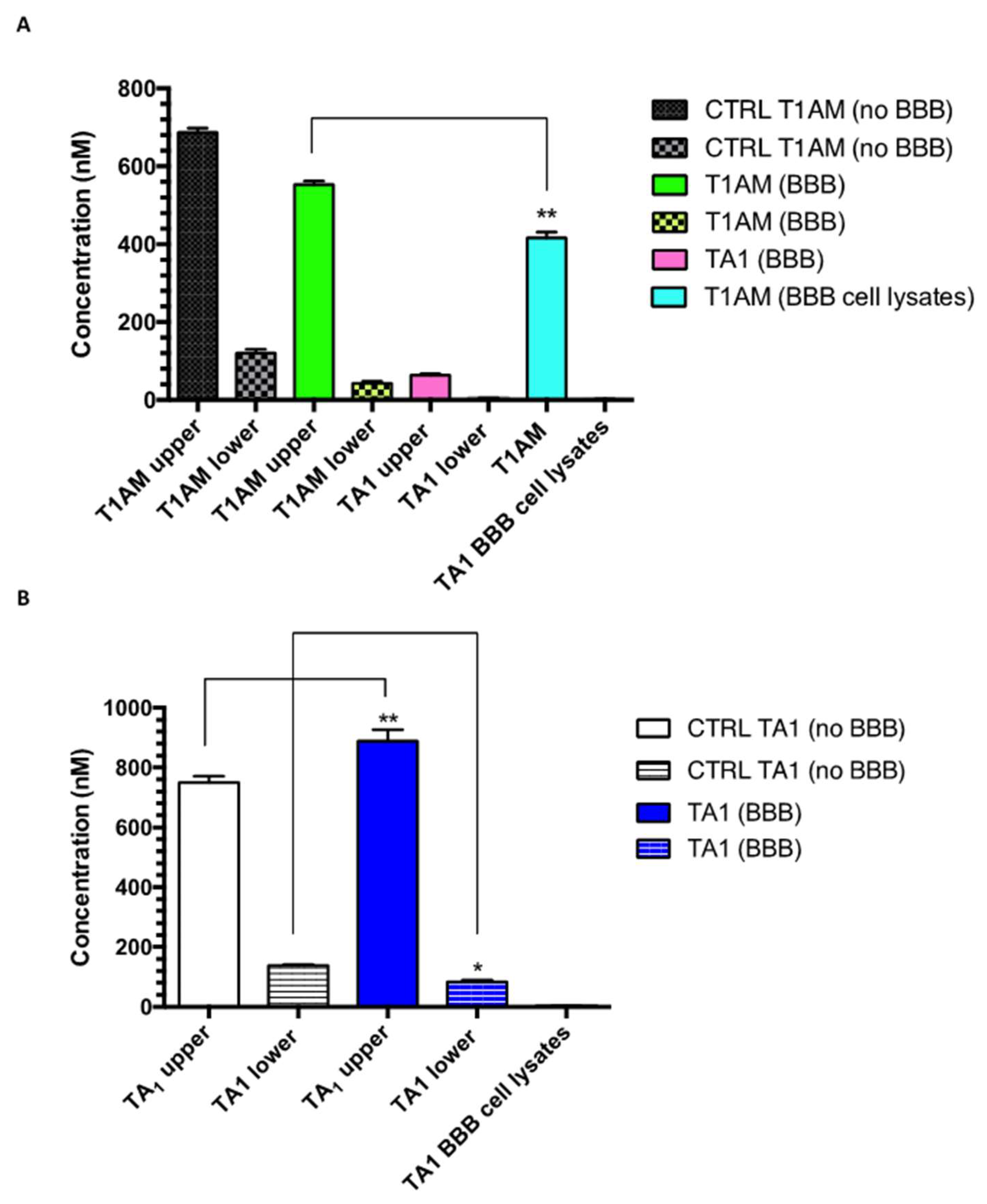
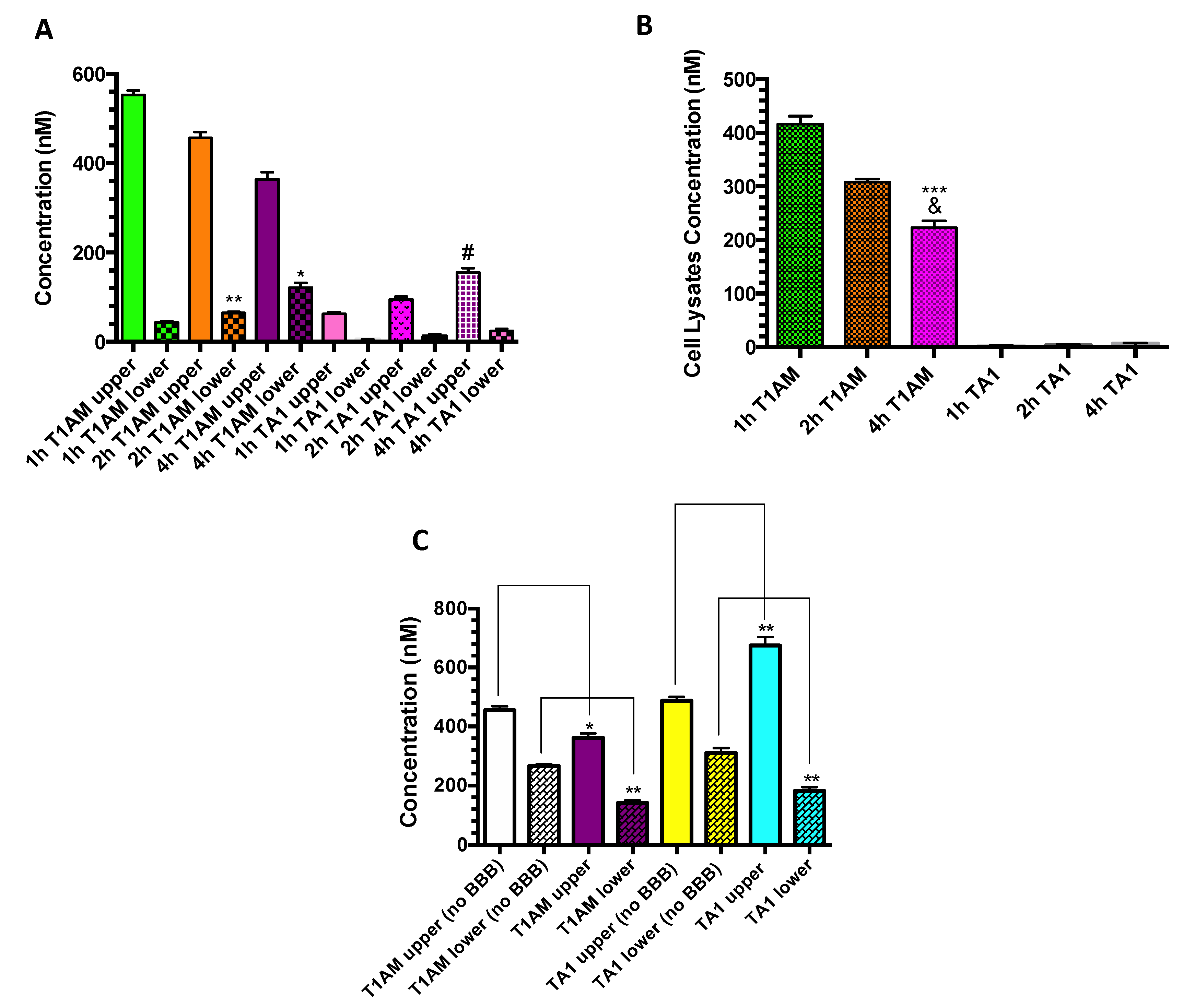
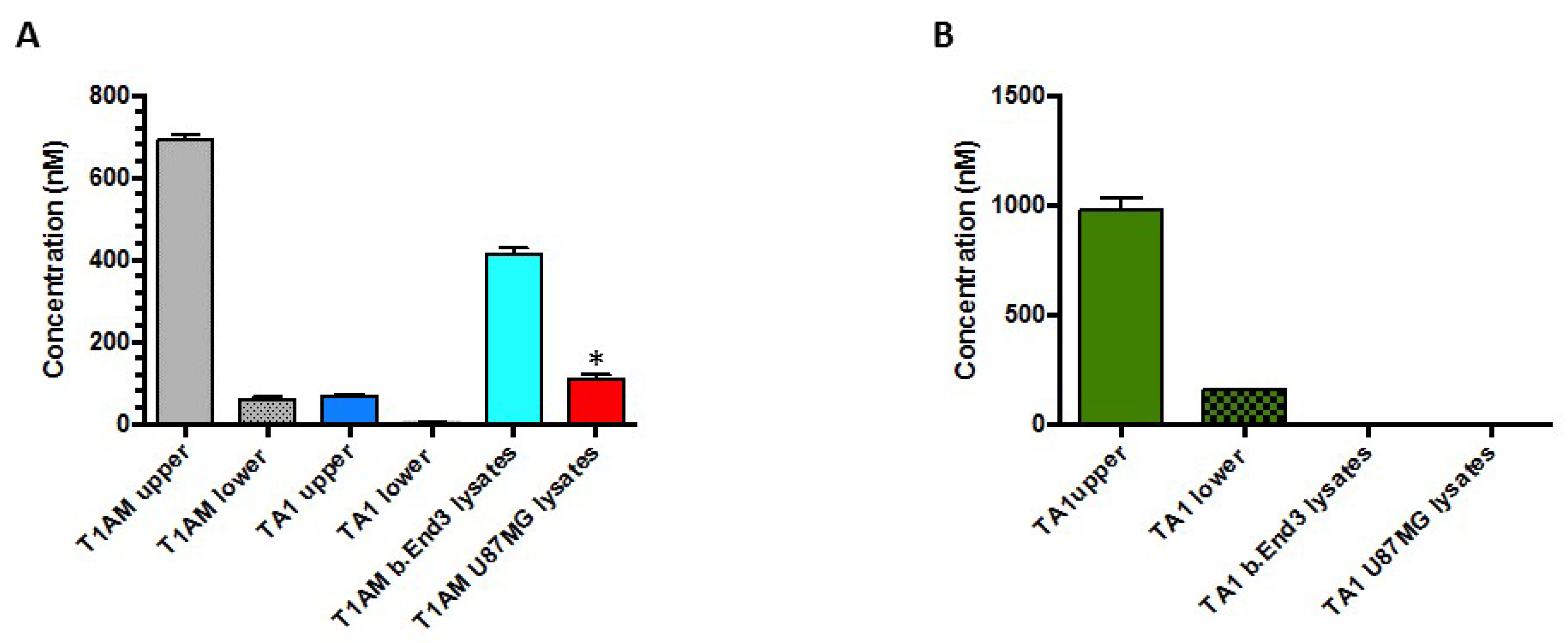
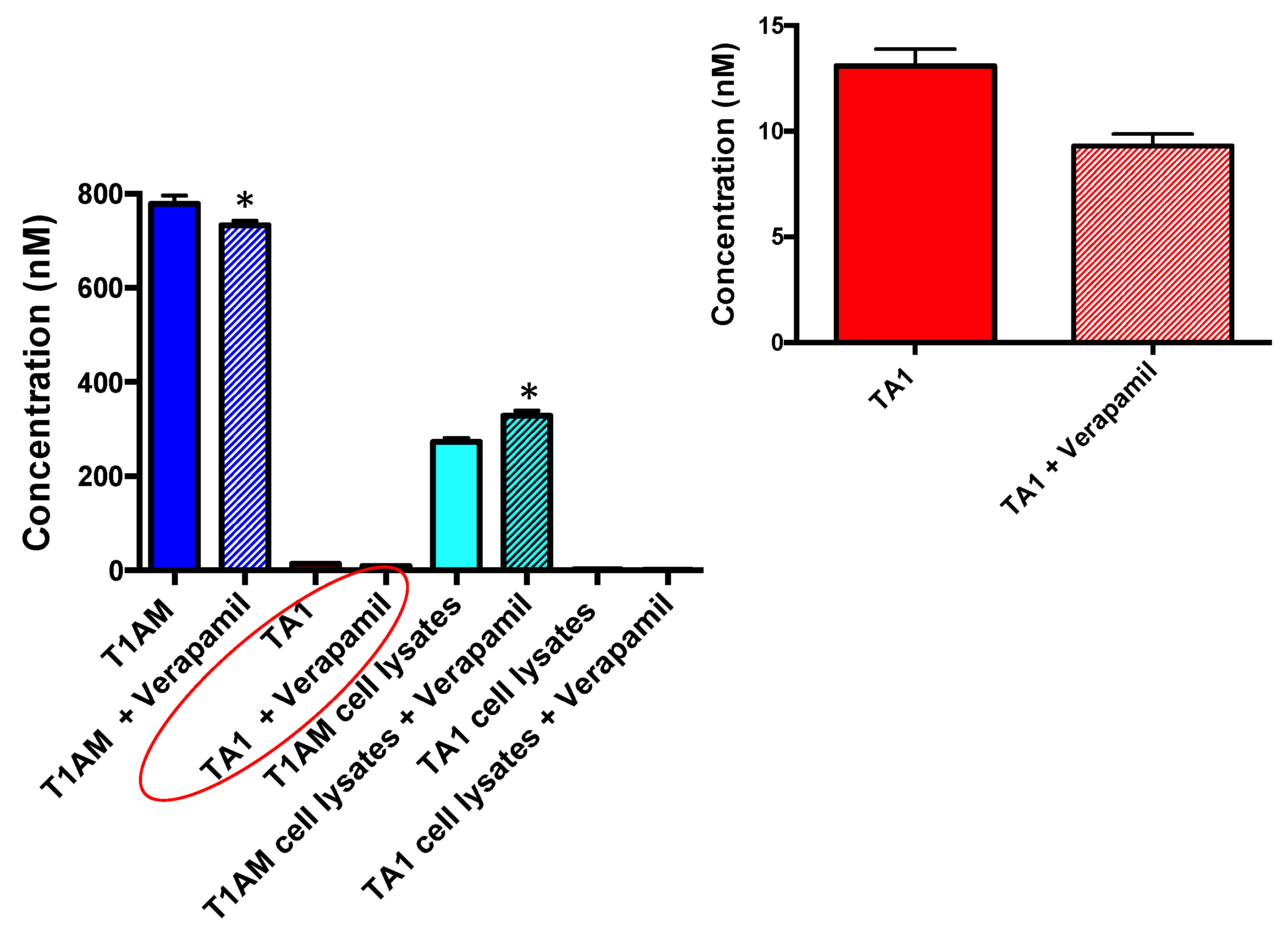
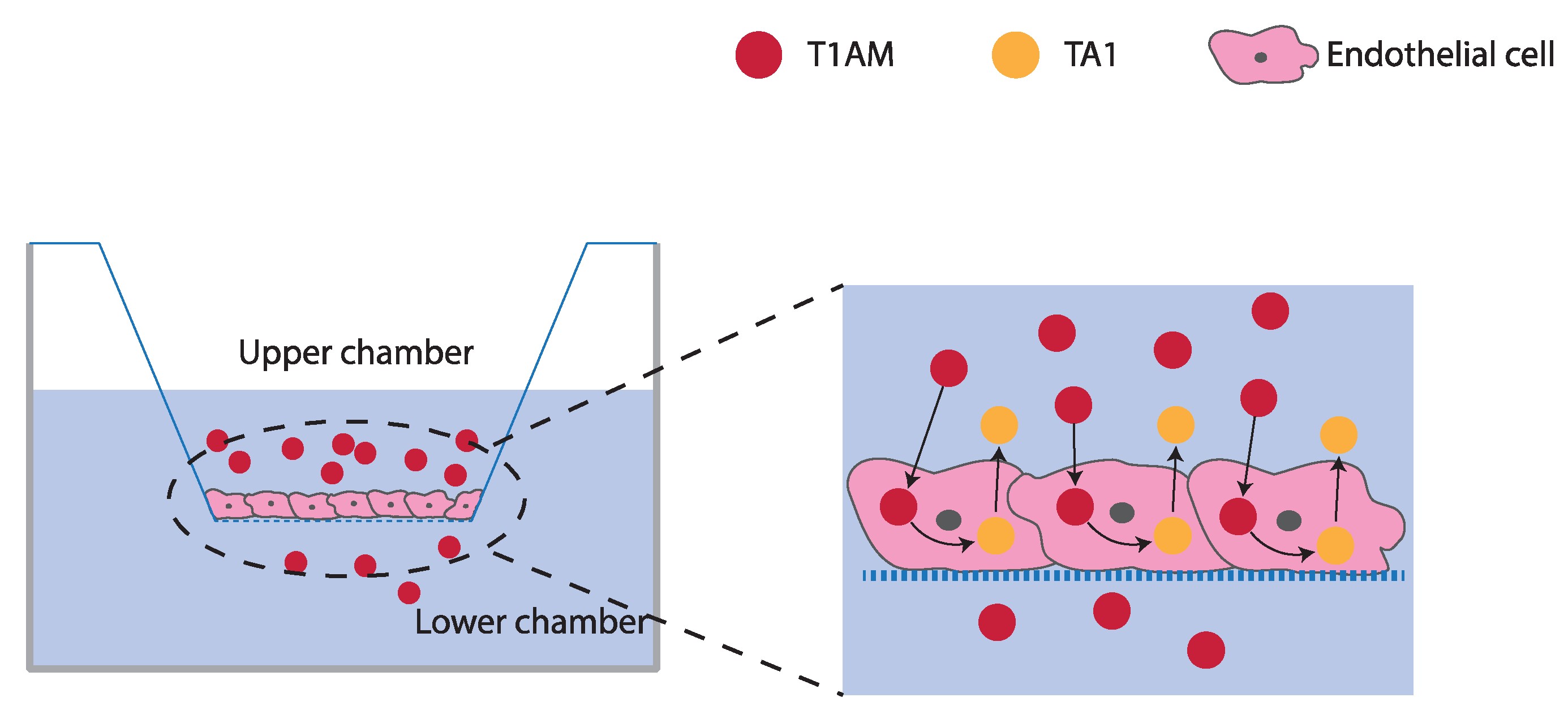
2.3. TAMs BBB Crossing
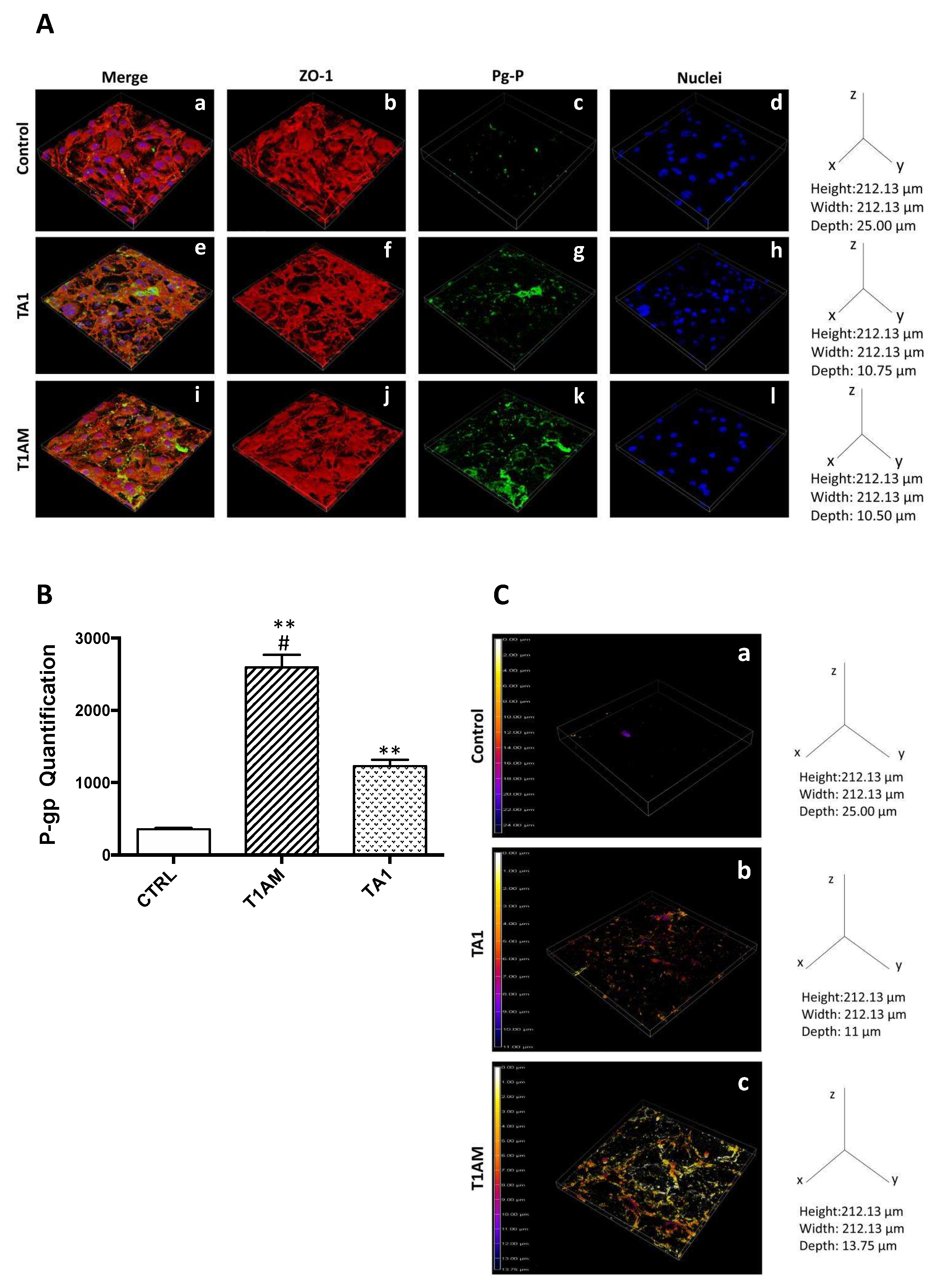
2.4. P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibition Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. In Vitro BBB Model Preparation and Characterization
4.4. T1AM and TA1 BBB Crossing Experiments
4.5. Endothelial/tumor-Glial-Derived Co-Cultures
4.6. P-gp Immunofluorescence
4.7. P-gp Inhibition Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Drugs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Piehl, S.; Hoefig, C.S.; Scanlan, T.S.; Köhrle, J. Thyronamines. Past, Present, and Future. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, T.S.; Suchland, K.L.; Hart, M.E.; Chiellini, G.; Huang, Y.; Kruzich, P.J.; Frascarelli, S.; Crossley, D.A.; Bunzow, J.R.; Ronca-Testoni, S.; et al. 3-Iodothyronamine Is an Endogenous and Rapid-Acting Derivative of Thyroid Hormone. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, V.; Melissari, E.; Iofrida, C.; Righi, M.; Di Russo, M.; Donzelli, R.; Saba, A.; Frascarelli, S.; Chiellini, G.; Zucchi, R.; et al. Modulation of Gene Expression by 3-Iodothyronamine: Genetic Evidence for a Lipolytic Pattern. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelardoni, S.; Chiellini, G.; Frascarelli, S.; Saba, A.; Zucchi, R. Uptake and Metabolic Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine in Hepatocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Venditti, P.; Napolitano, G.; Di Stefano, L.; Chiellini, G.; Zucchi, R.; Scanlan, T.S.; Di Meo, S. Effects of the Thyroid Hormone Derivatives 3-Iodothyronamine and Thyronamine on Rat Liver Oxidative Capacity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 341, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellusci, L.; Laurino, A.; Sabatini, M.; Sestito, S.; Lenzi, P.; Raimondi, L.; Rapposelli, S.; Biagioni, F.; Fornai, F.; Salvetti, A.; et al. New Insights into the Potential Roles of 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) and Newly Developed Thyronamine-Like TAAR1 Agonists in Neuroprotection. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi-Porter, F.; Reiland, H.; Sabatini, M.; Lorenzini, L.; Carnicelli, V.; Rogowski, M.; Selen Alpergin, E.; Tonelli, M.; Ghelardoni, S.; Saba, A.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming by 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM): A New Perspective to Reverse Obesity through Co-Regulation of Sirtuin 4 and 6 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, M.; Bellusci, L.; Sabatini, M.; Rapposelli, S.; Rahman, S.M.; Chiellini, G.; Assadi-Porter, F.M. Lipolytic Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) and a Novel Thyronamine-Like Analog SG-2 through the AMPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homuth, G.; Lietzow, J.; Schanze, N.; Golchert, J.; Köhrle, J. Endocrine, Metabolic and Pharmacological Effects of Thyronamines (TAM), Thyroacetic Acids (TA) and Thyroid Hormone Metabolites (THM)—Evidence from in Vitro, Cellular, Exp. Anim. and Human Studies. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutigliano, G.; Bandini, L.; Sestito, S.; Chiellini, G. 3-Iodothyronamine and Derivatives: New Allies Against Metabolic Syndrome? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorroni, A.; Rutigliano, G.; Sabatini, M.; Frascarelli, S.; Borsò, M.; Novelli, E.; Bandini, L.; Ghelardoni, S.; Saba, A.; Zucchi, R.; et al. Exogenous 3-Iodothyronamine Rescues the Entorhinal Cortex from β-Amyloid Toxicity. Thyroid 2020, 30, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biebermann, H.; Kleinau, G. 3-Iodothyronamine Induces Diverse Signaling Effects at Different Aminergic and Non-Aminergic G-Protein Coupled Receptors. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, R.; Accorroni, A.; Chiellini, G. Update on 3-Iodothyronamine and Its Neurological and Metabolic Actions. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurino, A.; Lucenteforte, E.; De Siena, G.; Raimondi, L. The Impact of Scopolamine Pretreatment on 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) Effects on Memory and Pain in Mice. Horm. Behav. 2017, 94, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.E.; De Siena, G.; Saba, A.; Marchini, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Bigagli, E.; Cinci, L.; Lodovici, M.; Chiellini, G.; Zucchi, R.; et al. 3-Iodothyronamine: A Modulator of the Hypothalamus-Pancreas-Thyroid Axes in Mice: Metabolic Effects of a Low 3-Iodothyronamine Dose. British J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, M.E.; De Siena, G.; Saba, A.; Marchini, M.; Landucci, E.; Gerace, E.; Zazzeri, M.; Musilli, C.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.; Matucci, R.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) in Mice Include Facilitation of Memory Acquisition and Retention and Reduction of Pain Threshold: T1AM, a Hyperalgic and Memory-Enhancing Amine. British J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musilli, C.; De Siena, G.; Manni, M.E.; Logli, A.; Landucci, E.; Zucchi, R.; Saba, A.; Donzelli, R.; Passani, M.B.; Provensi, G.; et al. Histamine Mediates Behavioural and Metabolic Effects of 3-Iodothyroacetic Acid, an Endogenous End Product of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism: A Novel Link between Thyroid and Histamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurino, A.; Landucci, E.; Raimondi, L. Central Effects of 3-Iodothyronamine Reveal a Novel Role for Mitochondrial Monoamine Oxidases. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, G.; Frascarelli, S.; Ghelardoni, S.; Carnicelli, V.; Tobias, S.C.; DeBarber, A.; Brogioni, S.; Ronca-Testoni, S.; Cerbai, E.; Grandy, D.K.; et al. Cardiac Effects of 3 − iodothyronamine: A New Aminergic System Modulating Cardiac Function. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, A.; Chiellini, G.; Frascarelli, S.; Marchini, M.; Ghelardoni, S.; Raffaelli, A.; Tonacchera, M.; Vitti, P.; Scanlan, T.S.; Zucchi, R. Tissue Distribution and Cardiac Metabolism of 3-Iodothyronamine. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, G.; Erba, P.; Carnicelli, V.; Manfredi, C.; Frascarelli, S.; Ghelardoni, S.; Mariani, G.; Zucchi, R. Distribution of Exogenous [125I]-3-Iodothyronamine in Mouse in Vivo: Relationship with Trace Amine-Associated Receptors. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 213, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and Function of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The Blood-Brain Barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obert, E.; Strauss, R.; Brandon, C.; Grek, C.; Ghatnekar, G.; Gourdie, R.; Rohrer, B. Targeting the Tight Junction Protein, Zonula Occludens-1, with the Connexin43 Mimetic Peptide, ACT1, Reduces VEGF-Dependent RPE Pathophysiology. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 2017, 95, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Potschka, H. Blood-Brain Barrier Active Efflux Transporters: ATP-Binding Cassette Gene Family. Neurotherapeutics 2005, 2, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosain, F.G.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tomar, L.K.; Kumar, P.; Tyagi, C.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. Bypassing P-Glycoprotein Drug Efflux Mechanisms: Possible Applications in Pharmacoresistant Schizophrenia Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, L.M.; Markova, S.M.; Chinn, L.W.; Gow, J.M.; Kroetz, D.L.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Very Important Pharmacogene Summary. Pharm. Genom. 2011, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzopoulou, A.; Skoczyńska, E.; Van den Berg, J.H.J.; Brand, W.; Legay, S.; Klein, S.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Murk, A.J. P-Gp Efflux Pump Inhibition Potential of Common Environmental Contaminants Determined in Vitro: P-Gp Efflux Pump Inhibition by Environmental Contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, D.J. Delivery of Therapeutic Agents to the Central Nervous System: The Problems and the Possibilities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 104, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Helm, M.W.; van der Meer, A.D.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; van den Berg, A.; Segerink, L.I. Microfluidic Organ-on-Chip Technology for Blood-Brain Barrier Research. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1142493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillone, A.; Battaglini, M.; Moscato, S.; Mattii, L.; de Julián Fernández, C.; Scarpellini, A.; Giorgi, M.; Sinibaldi, E.; Ciofani, G. Nutlin-Loaded Magnetic Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Targeted Glioblastoma Treatment. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 727–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, A.S.; Jameson, B.J.; Jesaitis, L.A.; Anderson, J.M. The Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 Establishes a Link between the Transmembrane Protein Occludin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29745–29753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keaney, J.; Campbell, M. The Dynamic Blood-Brain Barrier. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, R.; Kim, H. Characterization of a Microfluidic in Vitro Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier (ΜBBB). Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papademetriou, I.; Vedula, E.; Charest, J.; Porter, T. Effect of Flow on Targeting and Penetration of Angiopep-Decorated Nanoparticles in a Microfluidic Model Blood-Brain Barrier. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcella, A.; Biagioni, F.; Antonietta Oliva, M.; Bucci, D.; Frati, A.; Esposito, V.; Cantore, G.; Giangaspero, F.; Fornai, F. Rapamycin Inhibits the Growth of Glioblastoma. Brain Res. 2013, 1495, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryskalin, L.; Limanaqi, F.; Biagioni, F.; Frati, A.; Esposito, V.; Calierno, M.T.; Lenzi, P.; Fornai, F. The Emerging Role of M-TOR up-Regulation in Brain Astrocytoma. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, M.; Tominaga, Y.; Nagao, K.; Kimura, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Kioka, N.; Ueda, K. ATPase Activity of Nucleotide Binding Domains of Human MDR3 in the Context of MDR1. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouan, E.; Le Vée, M.; Mayati, A.; Denizot, C.; Parmentier, Y.; Fardel, O. Evaluation of P-Glycoprotein Inhibitory Potential Using a Rhodamine 123 Accumulation Assay. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehl, S.; Heberer, T.; Balizs, G.; Scanlan, T.S.; Smits, R.; Koksch, B.; Köhrle, J. Thyronamines Are Isozyme-Specific Substrates of Deiodinases. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefig, C.S.; Zucchi, R.; Köhrle, J. Thyronamines and Derivatives: Physiological Relevance, Pharmacological Actions, and Future Research Directions. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellusci, L.; Runfola, M.; Carnicelli, V.; Sestito, S.; Fulceri, F.; Santucci, F.; Lenzi, P.; Fornai, F.; Rapposelli, S.; Origlia, N.; et al. Endogenous 3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) and Synthetic Thyronamine-Like Analog SG-2 Act as Novel Pleiotropic Neuroprotective Agents through the Modulation of SIRT6. Molecules 2020, 25, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, R.; Chen, L.; Götz, J. The Blood-Brain Barrier: Physiology and Strategies for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 165–166, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.C.; Morris, A.P.; O’Neil, R.G. Tight Junction Protein Expression and Barrier Properties of Immortalized Mouse Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells. Brain Res. 2007, 1130, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Dohgu, S.; Takata, F.; Nishioku, T.; Nakashima, A.; Futagami, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Kataoka, Y. Paracellular Barrier and Tight Junction Protein Expression in the Immortalized Brain Endothelial Cell Lines bEND.3, bEND.5 and Mouse Brain Endothelial Cell 4. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, W. In Vitro Models of the Blood-Brain Barrier. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sestito, S.; Daniele, S.; Pietrobono, D.; Citi, V.; Bellusci, L.; Chiellini, G.; Calderone, V.; Martini, C.; Rapposelli, S. Memantine Prodrug as a New Agent for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidi, Y.; Campbell, L.; Barar, J.; Connell, D.; Akhtar, S.; Gumbleton, M. Evaluation of the Immortalised Mouse Brain Capillary Endothelial Cell Line, b.End3, as an in Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model for Drug Uptake and Transport Studies. Brain. Res. 2003, 990, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
di Leo, N.; Moscato, S.; Borso', M.; Sestito, S.; Polini, B.; Bandini, L.; Grillone, A.; Battaglini, M.; Saba, A.; Mattii, L.; et al. Delivery of Thyronamines (TAMs) to the Brain: A Preliminary Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061616
di Leo N, Moscato S, Borso' M, Sestito S, Polini B, Bandini L, Grillone A, Battaglini M, Saba A, Mattii L, et al. Delivery of Thyronamines (TAMs) to the Brain: A Preliminary Study. Molecules. 2021; 26(6):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061616
Chicago/Turabian Styledi Leo, Nicoletta, Stefania Moscato, Marco Borso', Simona Sestito, Beatrice Polini, Lavinia Bandini, Agostina Grillone, Matteo Battaglini, Alessandro Saba, Letizia Mattii, and et al. 2021. "Delivery of Thyronamines (TAMs) to the Brain: A Preliminary Study" Molecules 26, no. 6: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061616
APA Styledi Leo, N., Moscato, S., Borso', M., Sestito, S., Polini, B., Bandini, L., Grillone, A., Battaglini, M., Saba, A., Mattii, L., Ciofani, G., & Chiellini, G. (2021). Delivery of Thyronamines (TAMs) to the Brain: A Preliminary Study. Molecules, 26(6), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061616







