Intracellular Responses Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Media in Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Devices
3. Effects of Plasma-Activated Liquids
4. Plasma’s Ability to Differentially Affect Cell Fitness
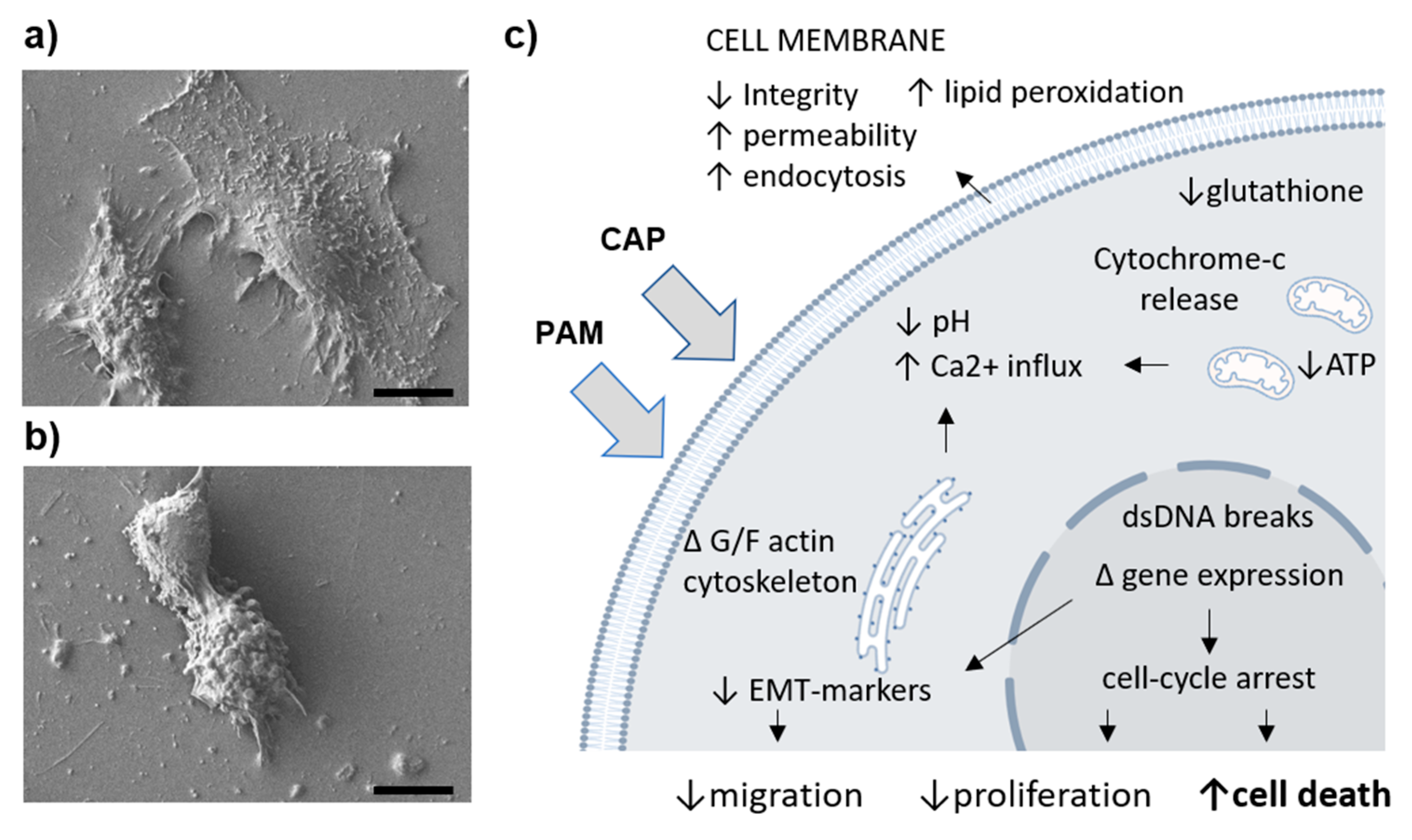
5. Intercellular Effects of Reactive Species Generated by CAP
5.1. Reactive Species Interact with Cell Membrane Enzymes
5.2. CAP Affects Membrane Integrity, Permeability, and Endocytosis
5.3. Changed Ionic Fluxes and pH Affect Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum
5.4. CAP Treatment Affects Nuclear DNA Content and Replicative/Transcriptional Activity
5.5. CAP Affects Cytoplasmic Metabolite Content
6. CAP Affects Major Cell Processes
6.1. Proliferation
6.2. Migration
6.3. Autophagy and Proteosomal Degradation
6.4. Senescence and Cell Death Involving Apoptosis, Necrosis, and Pyroptosis
6.5. Immune Response Activating Cell Death
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K.; Bogaerts, A.; Bekeschus, S. ROS from physical plasmas: Redox chemistry for biomedical therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9062098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Moon, H.; Ku, B.; Lee, K.; Hwang, C.Y.; Baek, S.J. Anticancer effects of cold atmospheric plasma in canine osteosarcoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.S.; Hsieh, J.H.; Chen, C.M.; Hou, C.W.; Wu, H.Y.; Chou, P.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Lee, J.W. Helium/argon-generated cold atmospheric plasma facilitates cutaneous wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma medicine: Applications of cold atmospheric pressure plasma in dermatology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Park, J.H.; De Backer, J.; Kim, M.; Yun, J.H.; Heo, Y.; Dewilde, S.; Shiratani, M.; Choi, E.H.; Lee, W.; et al. Structural modification of NADPH oxidase activator (Noxa 1) by oxidative stress: An experimental and computational study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gümbel, D.; Bekeschus, S.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Kramer, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold atmospheric plasma in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Walk, R.; Shashurin, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Ravi, R.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Trink, B. Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, K.; Scally, L.; Manaloto, E.; Gunes, S.; Ng, S.W.; Maher, M.; Tiwari, B.; Byrne, H.J.; Bourke, P.; et al. Cold Atmospheric plasma stimulates clathrin-dependent endocytosis to repair oxidised membrane and enhance uptake of nanomaterial in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma, a novel promising anti-cancer treatment modality. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15977–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplotnik, R.; Kregar, Z.; Biščan, M.; Vesel, A.; Cvelbar, U.; Mozetič, M.; Milološevič, S. Multiple vs. single harmonics AC-driven atmospheric plasma jet. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2014, 106, 25001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, J.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Interaction of atmospheric-pressure air microplasmas with amino acids as fundamental processes in aqueous solution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackmann, J.W.; Bruno, G.; Jablonowski, H.; Kogelheide, F.; Offerhaus, B.; Held, J.; von der Gathen, V.S.; Stapelmann, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Nitrosylation vs. oxidation—How to modulate cold physical plasmas for biological applications. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, H.; Farahmand, L.; Yaserian, K.; Jalili, N.; Majidzadeh-A, K. The antiproliferative effects of cold atmospheric plasma-activated media on different cancer cell lines, the implication of ozone as a possible underlying mechanism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6778–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Park, J.H.; Ali, A.; Choi, E.H. How does plasma activated media treatment differ from direct cold plasma treatment? Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscop, E.; Lin, A.; Van Boxem, W.; Van Loenhout, J.; De Backer, J.; Deben, C.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Influence of cell type and culture medium on determining cancer selectivity of cold atmospheric plasma treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Milberg, J.; Zhang, L.G.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The specific vulnerabilities of cancer cells to the cold atmospheric plasma-stimulated solutions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout, J.; Flieswasser, T.; Boullosa, L.F.; De Waele, J.; Van Audenaerde, J.; Marcq, E.; Jacobs, J.; Lin, A.; Lion, E.; Dewitte, H.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma-treated PBS eliminates immunosuppressive pancreatic stellate cells and induces immunogenic cell death of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, D.; Heslin, C.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Cytotoxic and mutagenic potential of solutions exposed to cold atmospheric plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labay, C.; Roldán, M.; Tampieri, F.; Stancampiano, A.; Bocanegra, P.E.; Ginebra, M.P.; Canal, C. Enhanced generation of reactive species by cold plasma in gelatin solutions for selective cancer cell death. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 47256–47269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, G.; Liu, S. The inhibition effect of cold atmospheric plasma-activated media in cutaneous squamous carcinoma cells. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griseti, E.; Merbahi, N.; Golzio, M. Anti-cancer potential of two plasma-activated liquids: Implication of long-lived reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Cancers 2020, 12, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labay, C.; Hamouda, I.; Tampieri, F.; Ginebra, M.P.; Canal, C. Production of reactive species in alginate hydrogels for cold atmospheric plasma-based therapies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé-Martí, X.; Espona-Noguera, A.; Ginebra, M.; Canal, C. Plasma-conditioned liquids as anticancer therapies in vivo: Current state and future directions. Cancers 2021, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Stapelmann, K.; Bogaerts, A. Advances in plasma oncology toward clinical translation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, E.; Bekeschus, S. Gas plasma-oxidized liquids for cancer treatment: Pre-clinical relevance, immuno-oncology, and clinical obstacles. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaln, H.; Čerček, U.; Recek, N.; Česnik, A.B.; Mozetič, M.; Rogelj, B. Cold atmospheric plasma induces stress granule formation via an eIF2α-dependent pathway. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5293–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.K.; Adhikari, M.; Kumar, S.; Ghimire, B.; Han, I.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma generated reactive species aided inhibitory effects on human melanoma cells: An in vitro and in silico study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenová, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Cold atmospheric plasma and plasma-activated medium trigger RONS-based tumor cell apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, H.; Hashizume, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Toyokuni, S.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshikawa, N.; et al. Oxidative stress-dependent and -independent death of glioblastoma cells induced by non-thermal plasma-exposed solutions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondeti, V.S.S.K.; Phan, C.Q.; Wende, K.; Jablonowski, H.; Gangal, U.; Granick, J.L.; Hunter, R.C.; Bruggeman, P.J. Long-lived and short-lived reactive species produced by a cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet for the inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Tang, A.; Kirschner, M.; Tadvalkar, G.; Canady, J.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Adaptation of Operational Parameters of Cold Atmospheric Plasma for in Vitro Treatment of Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9269–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubitskaya, E.A.; Troitskaya, O.S.; Yelak, E.V.; Gugin, P.P.; Richter, V.A.; Schweigert, I.V.; Zakrevsky, D.E.; Koval, O.A. Cold physical plasma decreases the viability of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Acta Nat. 2019, 11, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Golpur, M.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Hadavi, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Niaki, H.A.; Valadan, R.; Rafiei, A. Cold atmospheric plasma is a potent tool to improve chemotherapy in melanoma in vitro and in vivo. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Holmes, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, W.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Cold atmospheric plasma for selectively ablating metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, H.; Zhao, Q.L.; Hassan, M.A.; Andocs, G.; Nojima, N.; Takeda, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Hori, M.; Kondo, T. EPR-spin trapping and flow cytometric studies of free radicals generated using cold atmospheric argon plasma and X-ray irradiation in aqueous solutions and intracellular milieu. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Cheng, X.; Canady, J.; Sherman, J.; Keidar, M. Principles of using cold atmospheric plasma stimulated media for cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubor, P.; Wang, Y.; Liskova, A.; Samec, M.; Koklesova, L.; Dankova, Z.; Dørum, A.; Kajo, K.; Dvorska, D.; Lucansky, V.; et al. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma (CAP) as a new tool for the management of vulva cancer and vulvar premalignant lesions in gynaecological oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, A.; Joh, H.M.; Chung, T.H.; Chung, J.W. Anticancer effects of plasma-activated medium produced by a microwave-excited atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4205640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. The antitumor effect of singlet oxygen. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5649–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G. Targeting protective catalase of tumor cells with cold atmospheric plasma- activated medium (PAM). Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Talbot, A.; Zhang, L.G.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The strong cell-based hydrogen peroxide generation triggered by cold atmospheric plasma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G. The synergistic effect between hydrogen peroxide and nitrite, two long-lived molecular species from cold atmospheric plasma, triggers tumor cells to induce their own cell death. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenová, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Dynamics of singlet oxygen-triggered, RONS-based apoptosis induction after treatment of tumor cells with cold atmospheric plasma or plasma-activated medium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. Intercellular singlet oxygen-mediated bystander signaling triggered by long-lived species of cold atmospheric plasma and plasma-activated medium. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, C.; Bogaerts, A. On the anti-cancer effect of cold atmospheric plasma and the possible role of catalase-dependent apoptotic pathways. Cells 2020, 9, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Kumar, N.; Hammerschmid, D.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Dewilde, S.; Bogaerts, A. Synergistic effects of melittin and plasma treatment: A promising approach for cancer therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayarangan, V.; Delalande, A.; Dozias, S.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Robert, E.; Pichon, C. New insights on molecular internalization and drug delivery following plasma jet exposures. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambiev, L.; Nitsch, A.; Jacoby, J.M.; Strakeljahn, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Mustea, A.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment of chondrosarcoma cells affects proliferation and cell membrane permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralambiev, L.; Nitsch, A.; Einenkel, R.; Muzzio, D.O.; Gelbrich, N.; Burchardt, M.; Zygmunt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B.; Gümbel, D. The Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on the membrane permeability of human osteosarcoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, K.; Manaloto, E.; Casey, A.; Cribaro, G.P.; Byrne, H.J.; Tian, F.; Barcia, C.; Conway, G.E.; Cullen, P.J.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces ATP-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles and synergistic U373MG cancer cell death. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, J.M.; Strakeljahn, S.; Nitsch, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Hinz, P.; Mustea, A.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Haralambiev, L.; Stope, M.B. An innovative therapeutic option for the treatment of skeletal sarcomas: Elimination of osteo- and ewing’s sarcoma cells using physical gas plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Sherman, J.H.; Cheng, X.; Keidar, M. Toward understanding the selective anticancer capacity of cold atmospheric plasma—A model based on aquaporins. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 040801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Qin, S.B.; Xu, X.T.; Hu, C.; Qian, D.Q.; Ye, C.; Zhou, J.Y. Killing effect and its mechanism of low-temperature plasma on different human cancer cell lines. Chin. J. Oncol. 2016, 38, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, R.; Rehman, M.U.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jawaid, P.; Mitsuhashi, Y.; Imaue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Ogawa, R.; Tomihara, K.; Saitoh, J.I.; et al. Roles of intracellular and extracellular ROS formation in apoptosis induced by cold atmospheric helium plasma and X-irradiation in the presence of sulfasalazine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Gebhardt, L.; Arndt, S.; Karrer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Acidification is an essential process of cold atmospheric plasma and promotes the anti-cancer effect on malignant melanoma cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Gebhardt, L.; Arndt, S.; Karrer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma causes a calcium influx in melanoma cells triggering CAP-induced senescence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Que, Y.; Ma, C.; Cai, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, G.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma activated Ringer’s solution inhibits the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T. Numerical modelling of the effects of cold atmospheric plasma on mitochondrial redox homeostasis and energy metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Ghimire, B.; Baboota, S.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma and silymarin nanoemulsion activate autophagy in human melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, C.; Eymann, C.; Emicke, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Wilhelm, M.; Görries, F.; Winter, J.; von Woedtke, T.; Darm, K.; Daeschlein, G.; et al. Improved wound healing of airway epithelial cells is mediated by cold atmospheric plasma: A time course-related proteome analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7071536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Unger, P.; Wacker, E.; Shimizu, T.; Heinlin, J.; Li, J.F.; Thomas, H.M.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) changes gene expression of key molecules of the wound healing machinery and improves wound healing in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Judée, F.; Vallette, M.; Decauchy, H.; Arbelaiz, A.; Aoudjehane, L.; Scatton, O.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Merabtene, F.; Augustin, J.; et al. Cold-atmospheric plasma induces tumor cell death in preclinical in vivo and in vitro models of human cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judée, F.; Fongia, C.; Ducommun, B.; Yousfi, M.; Lobjois, V.; Merbahi, N. Short and long time effects of low temperature Plasma Activated Media on 3D multicellular tumor spheroids. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, A.M.; Simms, M.S.; Mann, V.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D.; Frame, F.M. Low-temperature plasma treatment induces DNA damage leading to necrotic cell death in primary prostate epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Jarick, K.; Hasse, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Cold physical plasma modulates p53 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in keratinocytes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7017363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yu, L.; Zou, F.; Hu, H.; Liu, K.; Lin, Z. Gene expression profiling and functional analysis reveals that p53 pathway-related gene expression is highly activated in cancer cells treated by cold atmospheric plasma-activated medium. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.W.; Yun, S.H.; Park, J.E.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Genome-wide comparison of the target genes of the reactive oxygen species and non-reactive oxygen species constituents of cold atmospheric plasma in cancer cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Ahmad, N.; Meng, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhuang, J.; Sun, M. Combination of metformin and cold atmospheric plasma induces glioma cell death to associate with c-Fos. Neoplasma 2020, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Jeong, D.; Ham, J.; Kim, H.; Ji, H.W.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. ZNRD1 and its antisense long noncoding RNA ZNRD1-AS1 are oppositely regulated by cold atmospheric plasma in breast cancer cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9490567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, R.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.; Miao, J.; Ni, L.; Shi, X.; et al. Low-temperature plasma suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-203a/BIRC5 axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.; Ham, J.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. ChIP-seq analysis reveals alteration of H3K4 trimethylation occupancy in cancer-related genes by cold atmospheric plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 126, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.B.; Kim, B.; Bae, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Differential epigenetic effects of atmospheric cold plasma on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornin, J.; Mateu-Sanz, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Labay, C.; Rodríguez, R.; Canal, C. Pyruvate plays a main role in the antitumoral selectivity of cold atmospheric plasma in osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Ning, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma treatment on the metabolites of human leukemia cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Ning, N.; Xu, Y. Analysis of metabolite profiling in human endothelial cells after plasma jet treatment. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3015150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Ning, N.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Alteration of metabolite profiling by cold atmospheric plasma treatment in human myeloma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Jiang, L.; Toyokuni, S.; Nakamura, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M. Non-thermal plasma-activated lactate solution kills U251SP glioblastoma cells in an innate reductive manner with altered metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 688, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambiev, L.; Bandyophadyay, A.; Suchy, B.; Weiss, M.; Kramer, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Mustea, A.; Kaderali, L.; Stope, M.B. Determination of immediate vs. kinetic growth retardation in physically plasma-treated cells by experimental and modelling data. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 3743–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verloy, R.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment for pancreatic cancer—The importance of pancreatic stellate cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Daeschlein, G.; Kramer, A.; Sckell, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B. Peroxiredoxin expression of human osteosarcoma cells is influenced by cold atmospheric plasma treatment. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, N.; Fujita, R.; Kawano, F.; Takahashi, K.; Ohira, T.; Shibaguchi, T.; Nakata, K.; Ohira, Y. Retardation of C2C12 myoblast cell proliferation by exposure to low-temperature atmospheric plasma. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 64, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volotskova, T.; Hawley, T.S.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Targeting the cancer cell cycle by cold atmospheric plasma. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, A.; Volotskova, O.; Cheng, X.; Khalsa, S.S.; Bian, K.; Murad, F.; Keidar, M.; Sherman, J.H. Differential effects of cold atmospheric plasma in the treatment of malignant glioma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Gorbanev, Y.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Reduction of human glioblastoma spheroids using cold atmospheric plasma: The combined effect of short- and long-lived reactive species. Cancers 2018, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babington, P.; Rajjoub, K.; Canady, J.; Siu, A.; Keidar, M.; Sherman, J.H. Use of cold atmospheric plasma in the treatment of cancer. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 029403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stope, M.B.; Benouahi, R.; Sander, C.; Haralambiev, L.; Nitsch, A.; Egger, E.; Mustea, A. Protherapeutic effects and inactivation of mammary carcinoma cells by a medical argon plasma device. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6205–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Kaushik, N.; Ghimire, B.; Adhikari, B.; Baboota, S.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Wahab, R.; Lee, S.J.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma and silymarin nanoemulsion synergistically inhibits human melanoma tumorigenesis via targeting HGF/c-MET downstream pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Wahab, R.; Bhartiya, P.; Linh, N.N.; Khan, F.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma and gold quantum dots exert dual cytotoxicity mediated by the cell receptor-activated apoptotic pathway in glioblastoma cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornín, J.; Villasante, A.; Solé-Martí, X.; Ginebra, M.; Canal, C. Osteosarcoma tissue-engineered model challenges oxidative stress therapy revealing promoted cancer stem cell properties. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Kirschner, M.E.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Combination therapy of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) with temozolomide in the treatment of U87MG glioblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Luo, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. The effects of cold atmospheric plasma on cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, apoptosis and drug sensitivity of multiple myeloma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Yano, K.I.; Sato, T. Nanosecond pulsed current under plasma-producing conditions induces morphological alterations and stress fiber formation in human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 681, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, C.; Banzet, S.; Lataillade, J.J.; Rousseau, A.; Frescaline, N. Cold atmospheric plasma modulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase signalling and enhances burn wound neovascularisation. J. Pathol. 2019, 249, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezest, M.; Chavatte, L.; Bourdens, M.; Quinton, D.; Camus, M.; Garrigues, L.; Descargues, P.; Arbault, S.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Casteilla, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the impact of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on human epithelial cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Liu, W.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshida, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Toyokuni, S.; Hori, M.; Kikkawa, F.; et al. Plasma-activated medium promotes autophagic cell death along with alteration of the mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.E.; He, Z.; Hutanu, A.L.; Cribaro, G.P.; Manaloto, E.; Casey, A.; Traynor, D.; Milosavljevic, V.; Howe, O.; Barcia, C.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces accumulation of lysosomes and caspase-independent cell death in U373MG glioblastoma multiforme cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Wacker, E.; Li, Y.F.; Shimizu, T.; Thomas, H.M.; Morfill, G.E.; Karrer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma, a new strategy to induce senescence in melanoma cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdens, M.; Jeanson, Y.; Taurand, M.; Juin, N.; Carrière, A.; Clément, F.; Casteilla, L.; Bulteau, A.L.; Planat-Bénard, V. Short exposure to cold atmospheric plasma induces senescence in human skin fibroblasts and adipose mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.J.; Suh, M.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, E.H.; Moon, I.S.; Song, K. Anti-tumor effects of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on vestibular schwannoma demonstrate its feasibility as an intra-operative adjuvant treatment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, M.; Anderson, H.; Gonzales, X.F. Induction of apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells by remote exposure of resistive barrier cold plasma. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, Y.; Uchiyama, H.; Zhao, Q.L.; Yunoki, T.; Andocs, G.; Nojima, N.; Takeda, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Hori, M.; Kondo, T. Effects of nitrogen on the apoptosis of and changes in gene expression in human lymphoma U937 cells exposed to argon-based cold atmospheric pressure plasma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Cai, D.; Dai, X. Cold atmospheric plasma conveys selectivity on triple negative breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Y. Inhibition of basal cell carcinoma cells by cold atmospheric plasma activated solution and differential gene expression analysis. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Liu, D.; Kong, M.G.; Dong, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis of melanoma cells via Sestrin2-mediated nitric oxide synthase signaling. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, M.; Liang, R.; Chen, H.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma as a potential tool for multiple myeloma treatment. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18002–18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, E.; Laurita, R.; Stancampiano, A.; Catanzaro, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Maffei, F.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Fimognari, C. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis and oxidative stress pathway regulation in T-lymphoblastoid leukemia cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 4271065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Gümbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Mandelkow, R.; Zimmermann, U.; Ziegler, P.; Burchardt, M.; Stope, M.B. Inhibition of cell growth of the prostate cancer cell model LNCaP by cold atmospheric plasma. Vivo 2015, 29, 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Gümbel, D.; Hanschmann, E.M.; Mandelkow, R.; Gelbrich, N.; Zimmermann, U.; Walther, R.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Sckell, A.; Kramer, A.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment induces anti-proliferative effects in prostate cancer cells by redox and apoptotic signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Weiss, M.; Napp, M.; Daeschlein, G.; Sckell, A.; Ender, S.A.; Kramer, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; et al. New treatment options for osteosarcoma—Inactivation of osteosarcoma cells by cold atmospheric plasma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5915–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Arndt, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Li, Y.; Karrer, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment inhibits growth in colorectal cancer cells. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, H.; Haruta, N.; Uchihashi, Y.; Seto, T.; Takashima, K. Strand breaks and chemical modification of intracellular DNA induced by cold atmospheric pressure plasma irradiation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralambiev, L.; Neuffer, O.; Nitsch, A.; Kross, N.C.; Bekeschus, S.; Hinz, P.; Mustea, A.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Gümbel, D.; Stope, M.B. Inhibition of angiogenesis by treatment with cold atmospheric plasma as a promising therapeutic approach in oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, K.N.; Yang, M.; Peng, S.; Ma, J.; Qin, F.; Cao, W.; Cui, S.; Nie, L.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces GSDME-dependent pyroptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeibak, R.; Mishchenko, T.A.; Shilyagina, N.Y.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Vedunova, M.V.; Krysko, D.V. Targeting immunogenic cancer cell death by photodynamic therapy: Past, present and future. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzariti, A.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Di Fonte, R.; Porcelli, L.; Gristina, R.; Favia, P.; Fracassi, F.; Trizio, I.; Silvestris, N.; Guida, G.; et al. Plasma-activated medium triggers cell death and the presentation of immune activating danger signals in melanoma and pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troitskaya, O.; Golubitskaya, E.; Biryukov, M.; Varlamov, M.; Gugin, P.; Milakhina, E.; Richter, V.; Schweigert, I.; Zakrevsky, D.; Koval, O. Non-thermal plasma application in tumor-bearing mice induces increase of serum HMGB1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Ku, B.; Lee, K.; Jung, Y.J.; Baek, S.J. Cold atmospheric plasma induces HMGB1 expression in cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Landthaler, M.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Unger, P.; Wacker, E.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.F.; Morfill, G.E.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Karrer, S. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on β-defensins, inflammatory cytokines, and apoptosis-related molecules in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Med. Type | Cell Type | Process Affected | Deregulated Genes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP-media | CAL-78, SW1353, A549, H1299, U-2 OS, 3T3 fibroblasts, HaCaT keratinocytes, glioblastoma cells, Pancreatic cancer cells, C2C12 myoblasts | ↓ proliferation | ↑ PRX1, PRX2 | [29,48,71,79,81,82] |
| CAP-Ringer’s solution | MG-63 osteosarcoma cells | ↓ proliferation | [57] | |
| CAP-media | MDA-MB-231, BrCa, DN-17, DSN osteosarcoma cells, MCF-7 | ↓ migration | - | [2,34,87] |
| CAP-media | Melanoma cells | ↓ migration | ↓ E-cadherin, YKL40, N-cadherin, SNAI1 | [88] |
| CAP-Ringer’s solution | MG-63 osteosarcoma cells (3D) | ↑ migration ↑ adhesion | ↑ MMP2, MMP9 ↑ FN1, PTK2 | [90] |
| CAP-media + Tmz | Glioma cells | ↓ migration | ↑ αvβ3, αvβ5 | [91] |
| CAP-media | Myeloma cells | ↓ migration | ↑ MMP2, MMP9 | [92] |
| CAP-media | Melanoma cells, glioblastoma cells (3D), MG-63 osteosarcoma cells (3D) | ↓ stemness ↑ stemness | ↓ CD133, ABCB5 ↑ BGLAP, ALPL, BMP2, RUNX2 | [88,89,90] |
| CAP-media | Human epithelial cells, primary prostate cancer cells, melanoma cells | ↑ autophagy | - | [33,64,95] |
| CAP-media | Endometrial cancer cells | ↑ autophagy | ↓ mTOR, PI3K | [96] |
| CAP-media + silymarin | G-361 cells | ↑ autophagy | ↓ HRAS, MEK ↑ BECN1, AMBRA1, MAP1LC3A, SQSTM | [59] |
| CAP-media | Melanoma cells, dermal fibroblast, adipose-derived stromal cells | ↑ senescence | ↑ H3K9, p21 ↑ p53, p16 | [98,99] |
| CAP-media | HEI-193, mSC4 VS, THP-1, U37 | ↑ necrosis ↑ apoptosis | - | [64,100,101,102] |
| CAP | T-lymphoblastoid leukemia cells, LNCaP prostate cancer cells | ↑ apoptosis | ↑ p53, Bax ↓ Bcl2, XRCC1 | [53,107,108,109] |
| CAP-media | BrCa cells, TE354T basal cell carcinoma, A875 melanoma cells, G361 melanoma cells, U-2 OS | ↑ apoptosis | ↑ MAPK, JNK, NFkB ↑ Sestrin2, p38, MAPK, Fas ↑ Ask1, cJUN, STAT3 | [27,74,89,103,104,105] |
| CAP-media | Myeloma cells, osteosarcoma cells, HT29, SW480 colon cancer cells | ↑ apoptosis | ↑ p53, Fas ↑ p21, OGG1, GADD45 | [29,62,106,107,110,111,112] |
| CAP-media | Prostate cancer LNCaP, choloangiocarcinoma cells, HDMEC, G-361 | ↑ apoptosis | ↑ PARP ↑ Casp3, Casp7 | [62,88,108,109,113] |
| CAP-media | MX-7, vestibular schwannoma cancer cells | ↑ ICD ↑ apoptosis | ↑ CALR ↑ HMGB1, HSP70 | [118,119] |
| CAP-PBS | Prostate cancer cells Kertinocytes | ↑ ICD ↑ apoptosis | ↑ TNF-α, IFN-γ, ↓ TGF-β ↑ IL-8, TGF-β1, TGF-β2 | [17,120] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motaln, H.; Recek, N.; Rogelj, B. Intracellular Responses Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Media in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051336
Motaln H, Recek N, Rogelj B. Intracellular Responses Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Media in Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051336
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotaln, Helena, Nina Recek, and Boris Rogelj. 2021. "Intracellular Responses Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Media in Cancer Cells" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051336
APA StyleMotaln, H., Recek, N., & Rogelj, B. (2021). Intracellular Responses Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Media in Cancer Cells. Molecules, 26(5), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051336







