Suppressing Cdk5 Activity by Luteolin Inhibits MPP+-Induced Apoptotic of Neuroblastoma through Erk/Drp1 and Fak/Akt/GSK3β Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
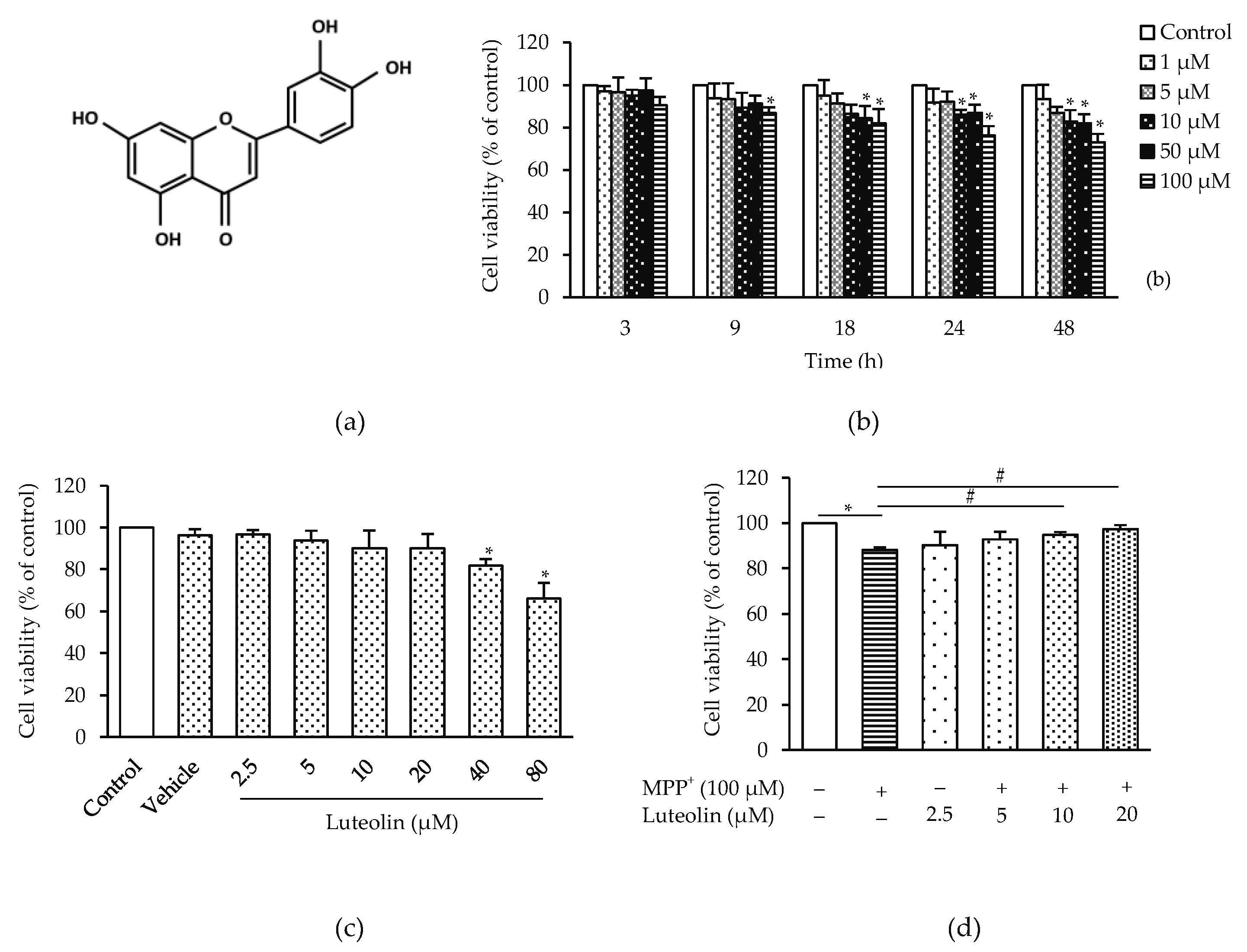
2.1. Luteolin Prevented MPP+-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
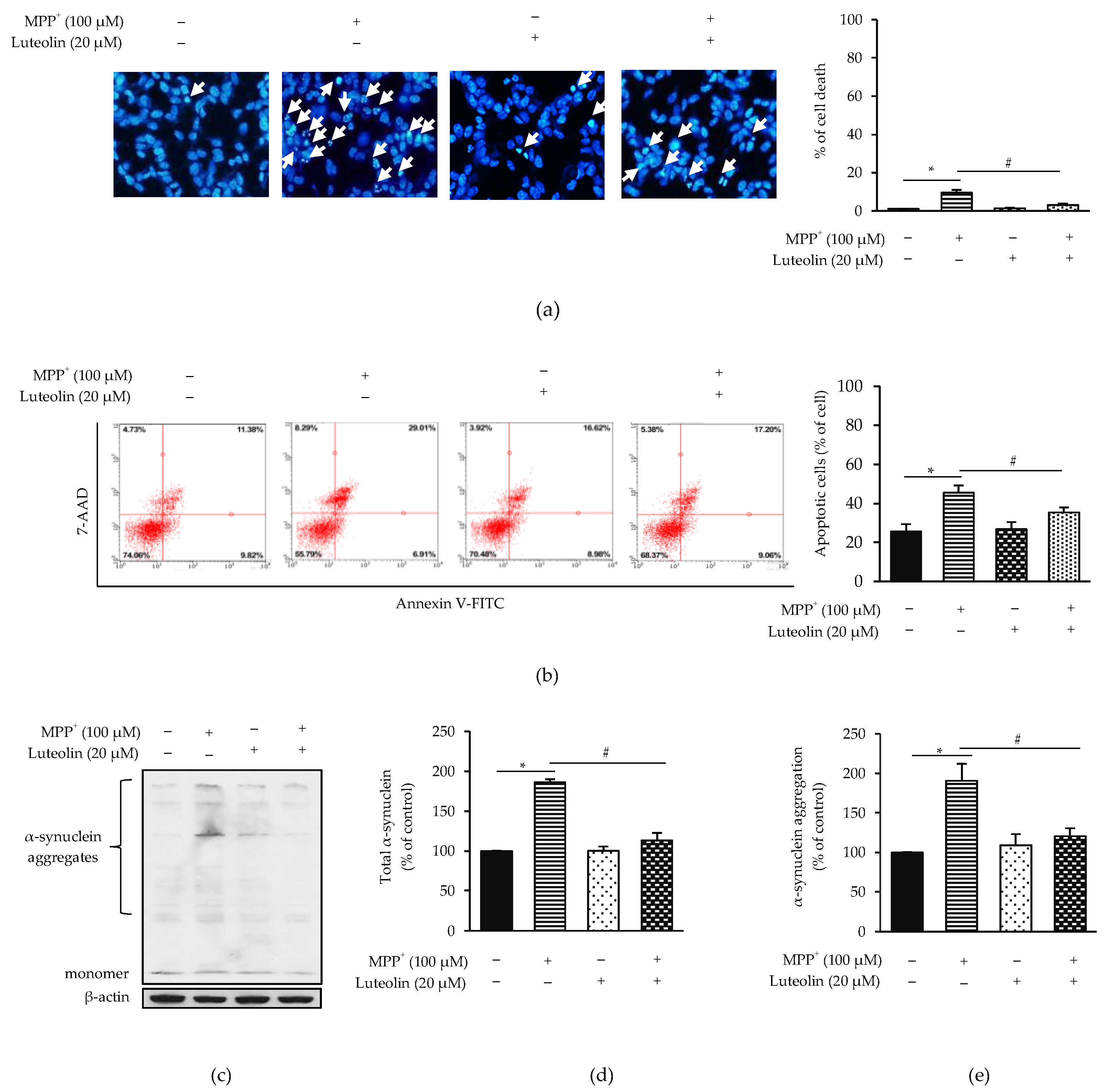
2.2. Luteolin Protected MPP+-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells
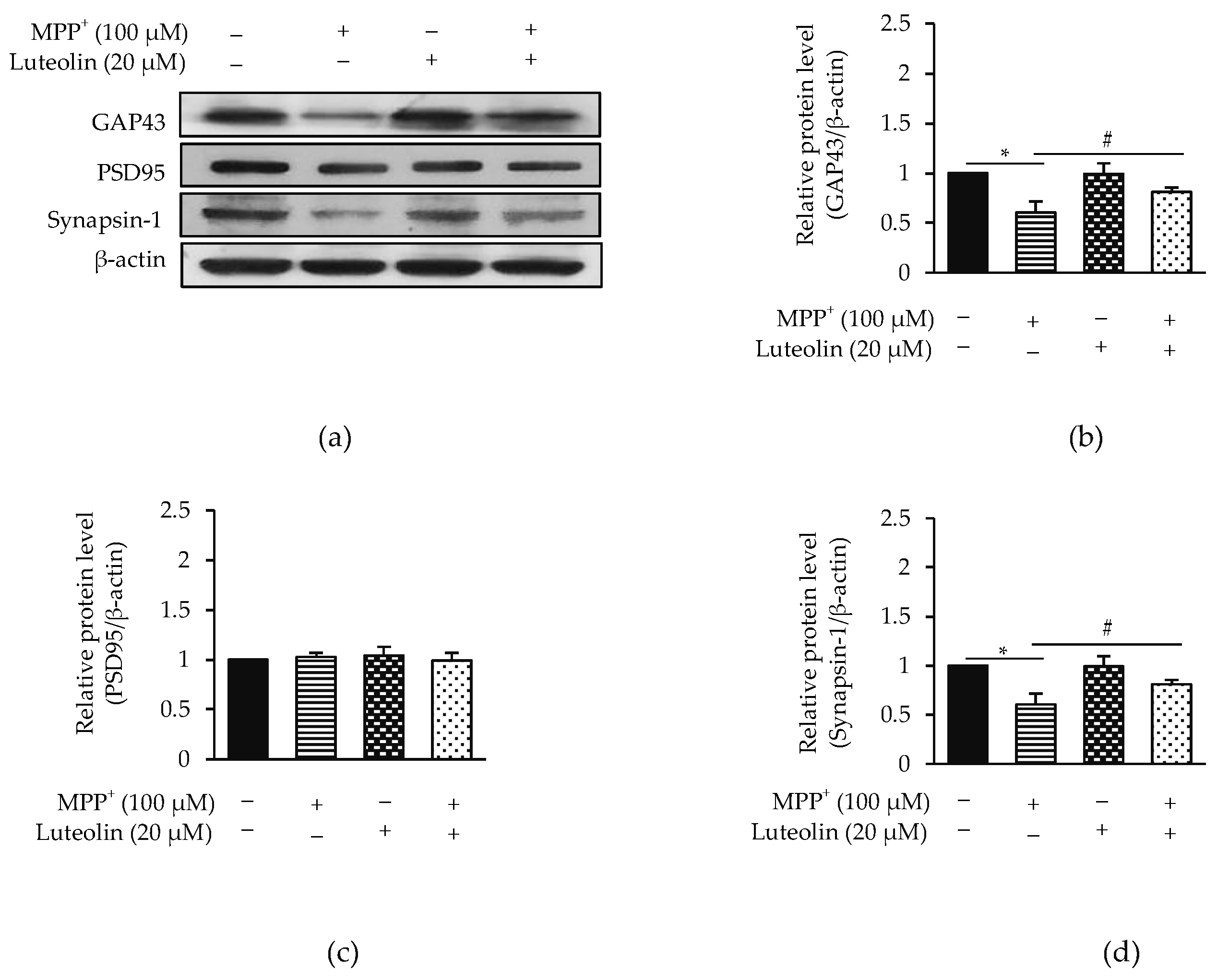
2.3. Luteolin Ameliorated MPP+-Reduced Synaptic Communication via GAP43 and Synapsin-1
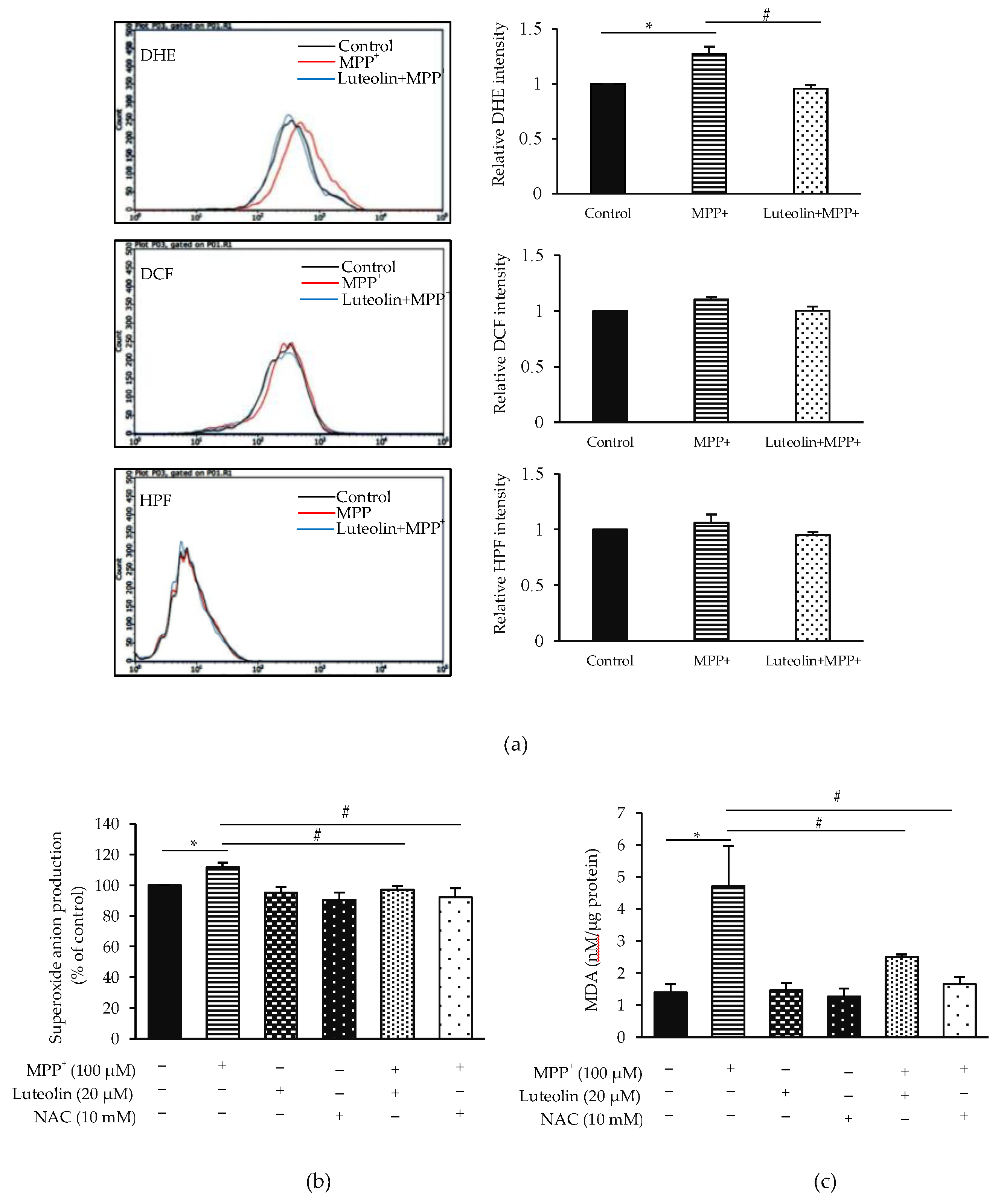
2.4. Luteolin Inhibited the Accumulation of Intracellular ROS Induced by MPP+
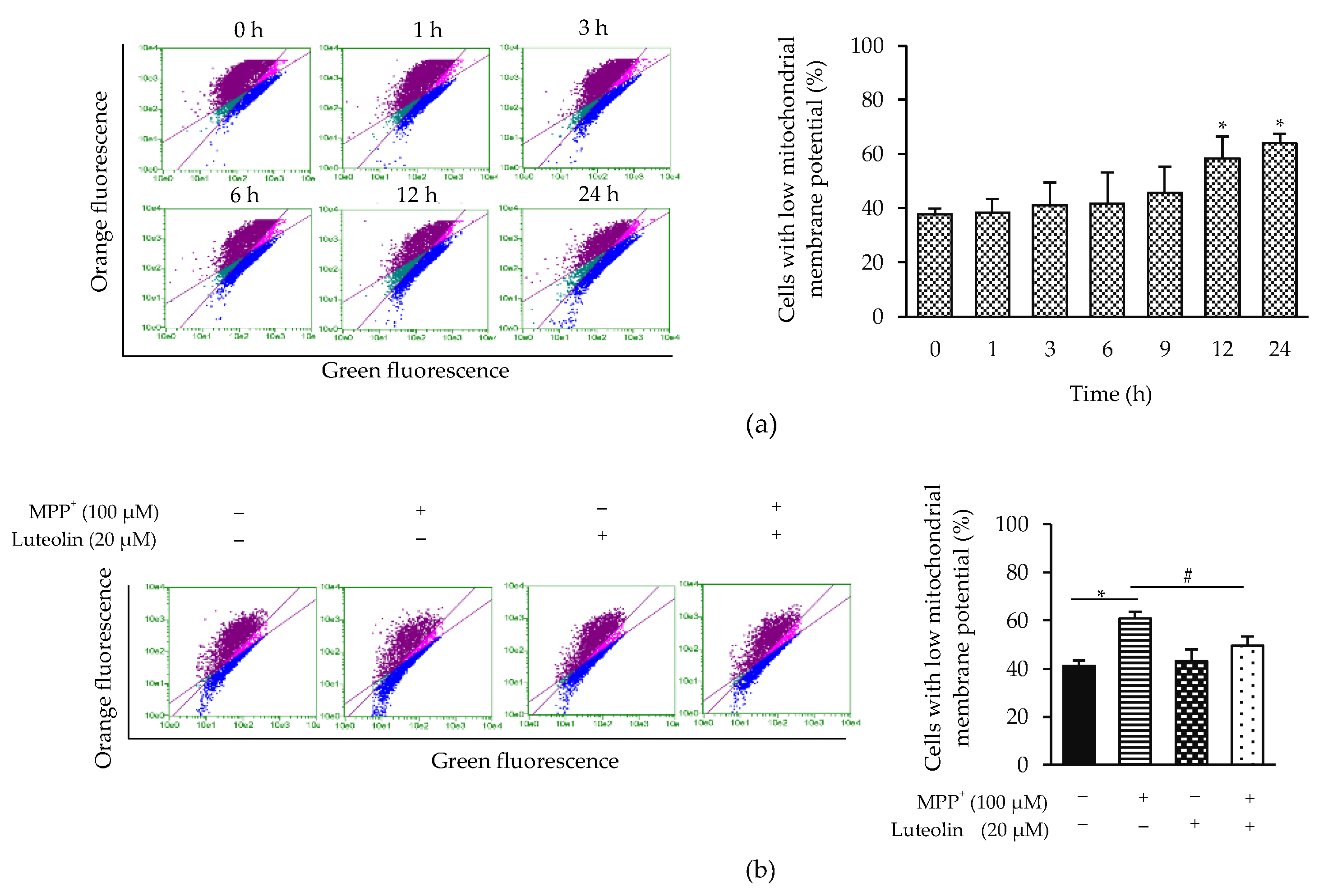
2.5. Luteolin Inhibited the Reduction of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δψm) Induced by MPP+
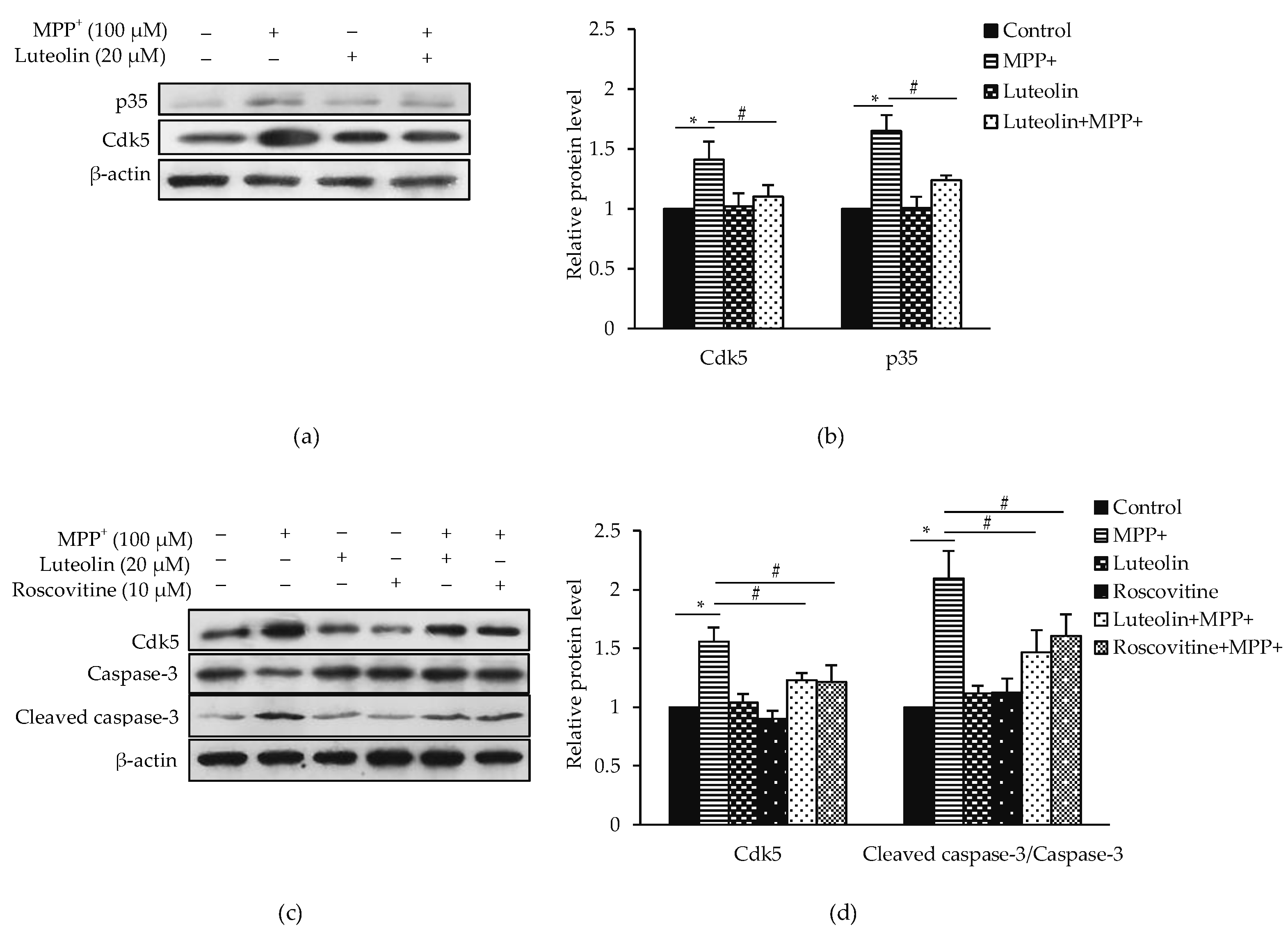
2.6. Luteolin Ameliorated MPP+-Induced Apoptosis via Cdk5
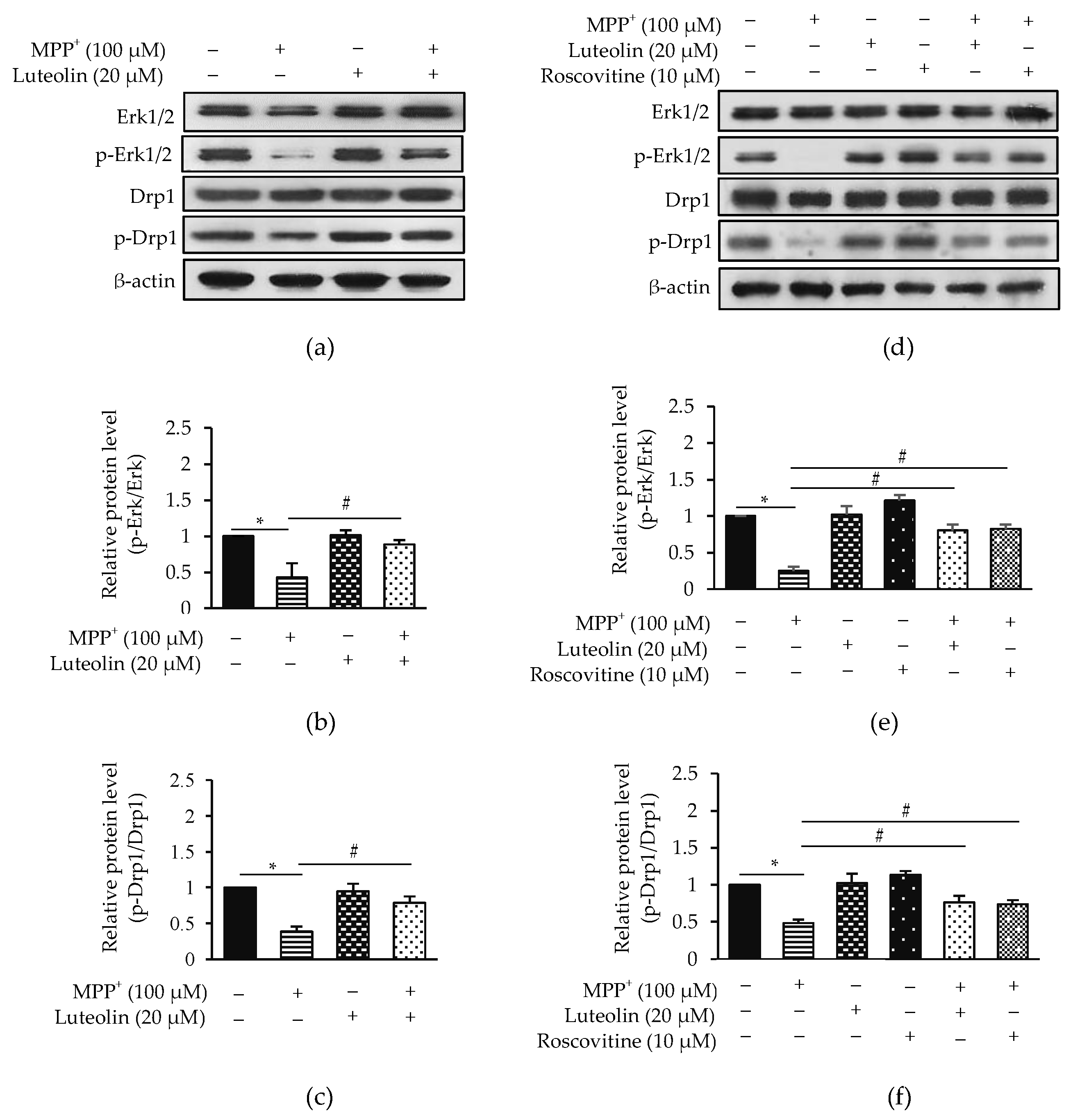
2.7. Luteolin Inhibited MPP+-Reduced Erk1/2 and Drp1 via Cdk5
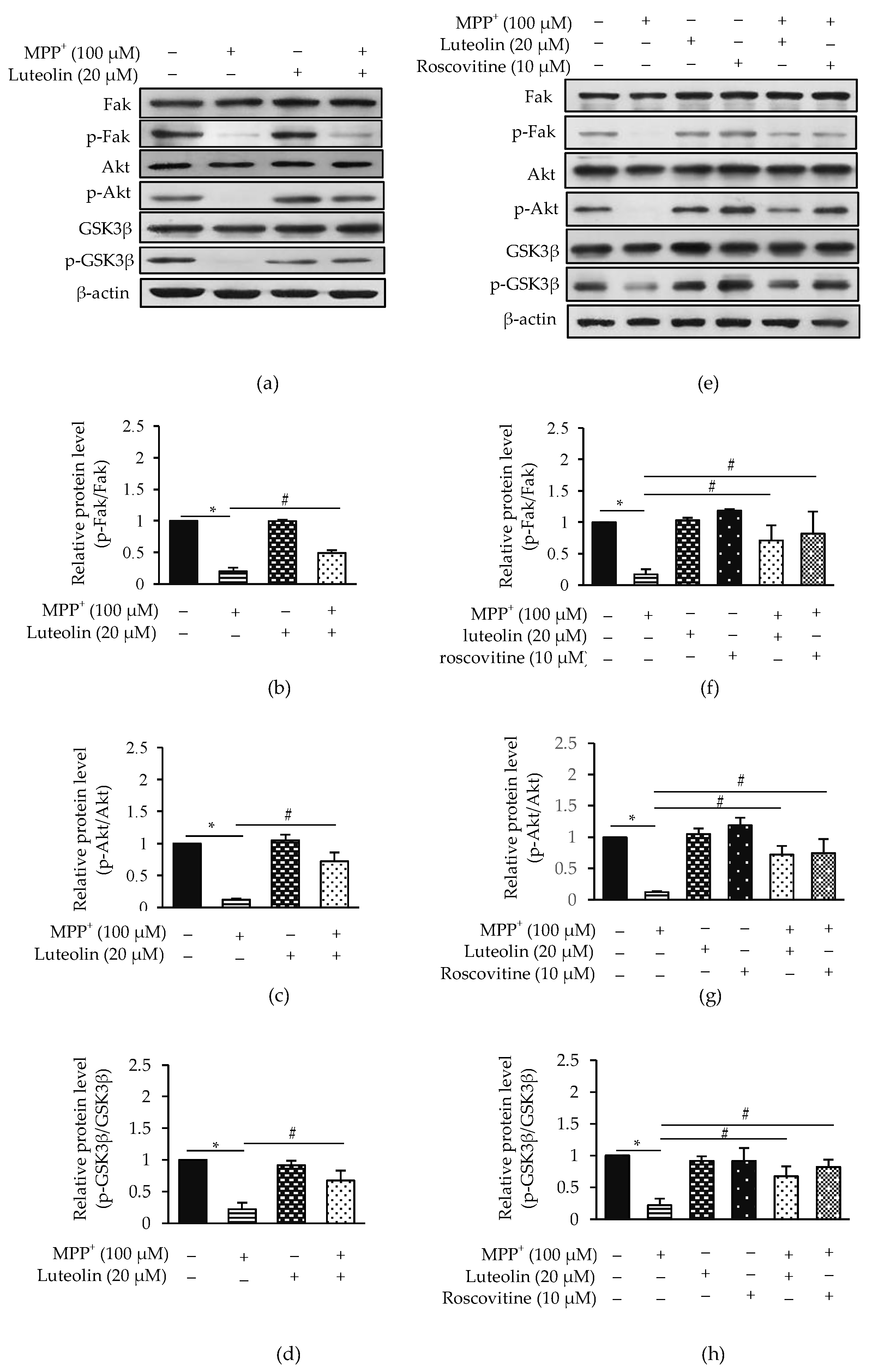
2.8. Luteolin Suppressed MPP+-Inhibited Fak/Akt/GSK3β through Cdk5
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Cell Viability Assay
5.3. Hoechst 33342 Straining
5.4. Annexin V/7-ADD Staining
5.5. Intracellular ROS Measurement
5.6. Superoxide Anion (O2−) Production Assay
5.7. Lipid Peroxidation Measurement
5.8. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δψm)
5.9. Western Blotting Analysis
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Xu, L.; Pu, J. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenetic dysfunction to potential clinical application. Parkinsons Dis. 2016, 2016, 1720621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Tanimura, A.; Graves, S.M.; Shen, W.; Surmeier, D.J. Striatal synapses, circuits and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 48, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Kalia, S.K.; Lang, A.E. Disease-modifying strategies for Parkinson’s disease. Movt. Disord. 2015, 30, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, S.; Mak, S.; Zhang, H.; Han, R.; Yuan, S.; Li, S.; Sa, F.; et al. The anti-cancer agent SU4312 unexpectedly protects against MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity via selective and direct inhibition of neuronal NOS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Chesselet, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Dar, K.B.; Anees, S.; Zargar, M.A.; Masood, A.; Sofi, M.A.; Ganie, S.A. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases: A mechanistic. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Tao, A. The neuroprotective effects of astragaloside IV against H2O2-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells are associated with synaptic plasticity. J. Chem. 2020, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.A.G.; Martins, N.M.; Sisti, F.M.; Fernandes, L.S.; Ferreira, R.S.; Queiroz, R.H.C.; Santos, A.C. The neuroprotection of cannabidiol against MPP+-induced toxicity in PC12 cells involves trkA receptors, upregulation of axonal and synapticproteins, neuritogenesis, and might be relevant to Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 30, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, S.; Mi, J.; Ueda, K.; Chan, P. Nuclear translocation of alpha-synuclein 742 increases susceptibility of MES23.5 cells to oxidative stress. Brain Res. 2013, 1500, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Rossie, S. Tale of the good and the bad Cdk5: Remodeling of the actin 724 cytoskeleton in the brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3426–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Mao, Z. Cdk5: Mediator of neuronal development, death and the response to DNA damage. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2011, 132, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangsab, J.; Prommeenate, P.; Chetsawang, B.; Chonpathompikunlert, P.; Sukketsiri, W.; Hutamekalin, P. Protective effect of valproic acid on MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells through Cdk5/p35/Erk signaling cascade. Trop. J. Pharmaceut. Res. 2019, 18, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashatus, J.A.; Nascimento, A.; Myers, L.J.; Sher, A.; Byrne, F.L.; Hoehn, K.L.; Counter, C.M.; Kashatus, D.F. Erk2 Phosphorylation of Drp1 Promotes Mitochondrial Fission and MAPK-Driven Tumor Growth. Mol. Cell. 2015, 57, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Hanna, R.A.; Gustafsson, A.B. Mitochondrial autophagy by Bnip3 involves Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and recruitment of Parkin in cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1924–H1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Kuang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, T. Drp1 regulates mitochondrial dysfunction and dysregulated metabolism in ischemic injury via Clec16a-, BAX-, and GSH- pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cao, R.; Sun, L.; Jing, W.; Zhao, J.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Huang, L.T.; Han, C.B. Effects of dynamin-related protein 1 regulated mitochondrial dynamic changes on invasion and metastasis of lung cancer cells. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4045–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.R.C.; Corredor, R.G.; Obeso, B.A.; Trakhtenberg, E.F.; Wang, Y.; Ponmattam, J.; Dvoriantchikova, G.; Ivanov, D.; Shestopalov, V.I.; Goldberg, J.L.; et al. β1 integrin-focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling modulates retinal ganglion cell (RGC) survival. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Activation of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt by IGF-1 on GAP-43 expression in DRG neurons with excitotoxicity induced by glutamate in vitro. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Chen, F.; Sima, N. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells via Src and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Guo, X.; Choksi, R. Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Src Mediates Acquired Sorafenib Resistance in A549 Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Xenografts. J. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 363, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, K.M.; Bhave, S.R.; Ferraro, D.J.; Jaboin, J.J.; Hallahan, D.E.; Thotala, D. GSK3β: A bifunctional role in cell death pathways. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 930710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuri, M.L.; Parihar, P.; Solanki, I.; Parihar, M.S. Flavonoids in modulation of cell survival signalling pathways. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Gortzi, O.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Daglia, M.; Skalicka-WoĨniak, K.; Nabavi, S.M. Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: A brief review. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Tian, X.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Jiang, W.S.; Zhou, Y.J.; Cheng, W.J. Luteolin-induced protection of H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and the associated pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7699–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, C.; Huo, K.; Wang, Q.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Luteolin Prevents H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in H9C2 Cells through Modulating Akt-P53/Mdm2 Signaling Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5125836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.B.; Miao, Z.N.; Zhang, B.; Long, W.; Zheng, F.X.; Kong, J.; Yu, B. Luteolin induces hippocampal neurogenesis in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. Neural. Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Cheng, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Luteolin ameliorates cognitive impairments by suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines and enhancing synapse associated proteins GAP-43 and SYN levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limboonreung, L.; Tuchindab, P.; Chongthammakun, S. Chrysoeriol mediates mitochondrial protection via PI3K/Akt pathway in MPP+ treated SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 714, 134545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, L.H.; Greenamyre, J.T. Oxidative damage to macromolecules in human Parkinson disease and the rotenone model. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, C.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, H. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 by FCPR16 protects SH-SY5Y cells against MPP+-induced decline of mitochondrial membrane potential and oxidative stress. Redox. Biol. 2018, 16, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.W.; Yen, J.H.; Shen, Y.T.; Wu, K.Y.; Wu, M.J. Luteolin modulates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced transcriptional changes of stress response pathways in PC12 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.V.; Choi, D.K. Atractylenolide-I protects human SH-SY5Y cells from 1-Methyl689 4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptotic cell death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.C.; Blair, H.J.; Seager, M.; Coulthard, A.; Tennant, S.; Buddles, M.; Curtis, A.; Goodship, J.A. Identification of a mutation in synapsin I, a synaptic vesicle protein, in a family with epilepsy. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chang, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Hsu, P.C.; Sun, Y.Y.; Lin, T.N.; Shie, F.S.; Kao, L.S.; et al. Astrocytic GAP43 induced by the TLR4/NF-κB/STAT3 axis attenuates astrogliosis-mediated microglial activation and neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 2027–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, J.A.; Stokholm, K.; Zareba-Paslawska, J.; Jakobsen, S.; Vang, K.; Gjedde, A.; Landau, A.M.; Romero-Ramos, M. Early synaptic dysfunction induced by α-synuclein in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.T.; Lin, W.J.; Chang, W.H.; Lo, Y.C. The novel protective effects of loganin against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurotoxicity: Enhancement of neurotrophic signaling, activation of IGF-1R/GLP-1R, and inhibition of RhoA/ROCK pathway. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Lan, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Shang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L. Luteolin protects against high fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in obesity mice. Behav Brain Res. 2014, 1, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Int. Stroke 2009, 4, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, Y.J. Astaxanthin protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Jain, P.D.; Sancheti, J.S.; Ghumatkar, P.J.; Tambe, R.; Sathaye, S. Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of Apigenin and Luteolin in MPTP induced parkinsonism in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, M.; Amin, N.D.; Sihag, R.K.; Grant, P.; Ahn, N.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Pant, H.C. Phosphorylation of MEK1 by cdk5/p35 down-regulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.; Cassady, S.J.; VanLaar, V.S.V.; Berman, S.B. Integrating multiple aspects of mitochondrial dynamics in neurons: Age-related differences and dynamic changes in a chronic rotenone model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sanada, K.; Samuels, B.A.; Shih, H.; Tsai, L.H. Serine 732 phosphorylation of FAK by Cdk5 is important for microtubule organization, nuclear movement, and neuronal migration. Cell 2003, 114, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.T.; Chen, X.L.; Lim, Y.; Hanson, D.A.; Vo, T.T.; Howerton, K.; Larocque, N.; Fisher, S.J.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Ilic, D. Nuclear FAK promotes cell proliferation and survival through FERM-enhanced p53 degradation. Mol. Cell 2008, 18, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jope, R.S.; Roh, M.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) in psychiatric diseases and therapeutic interventions. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Bai, R.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H. Artesunate may inhibit liver fibrosis via the FAK/Akt/β-catenin pathway in LX-2 cells. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Wei, X.; Jin, Y.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, K.; et al. Luteolin attenuates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by regulating ERK/Lrp-5/GSK-3β signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 4472–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reudhabibadh, R.; Binlateh, T.; Chonpathompikunlert, P.; Nonpanya, N.; Prommeenate, P.; Chanvorachote, P.; Hutamekalin, P. Suppressing Cdk5 Activity by Luteolin Inhibits MPP+-Induced Apoptotic of Neuroblastoma through Erk/Drp1 and Fak/Akt/GSK3β Pathways. Molecules 2021, 26, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051307
Reudhabibadh R, Binlateh T, Chonpathompikunlert P, Nonpanya N, Prommeenate P, Chanvorachote P, Hutamekalin P. Suppressing Cdk5 Activity by Luteolin Inhibits MPP+-Induced Apoptotic of Neuroblastoma through Erk/Drp1 and Fak/Akt/GSK3β Pathways. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051307
Chicago/Turabian StyleReudhabibadh, Ratchaneekorn, Thunwa Binlateh, Pennapa Chonpathompikunlert, Nongyao Nonpanya, Peerada Prommeenate, Pithi Chanvorachote, and Pilaiwanwadee Hutamekalin. 2021. "Suppressing Cdk5 Activity by Luteolin Inhibits MPP+-Induced Apoptotic of Neuroblastoma through Erk/Drp1 and Fak/Akt/GSK3β Pathways" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051307
APA StyleReudhabibadh, R., Binlateh, T., Chonpathompikunlert, P., Nonpanya, N., Prommeenate, P., Chanvorachote, P., & Hutamekalin, P. (2021). Suppressing Cdk5 Activity by Luteolin Inhibits MPP+-Induced Apoptotic of Neuroblastoma through Erk/Drp1 and Fak/Akt/GSK3β Pathways. Molecules, 26(5), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051307







