Amino Acylguanidines as Bioinspired Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction
Abstract
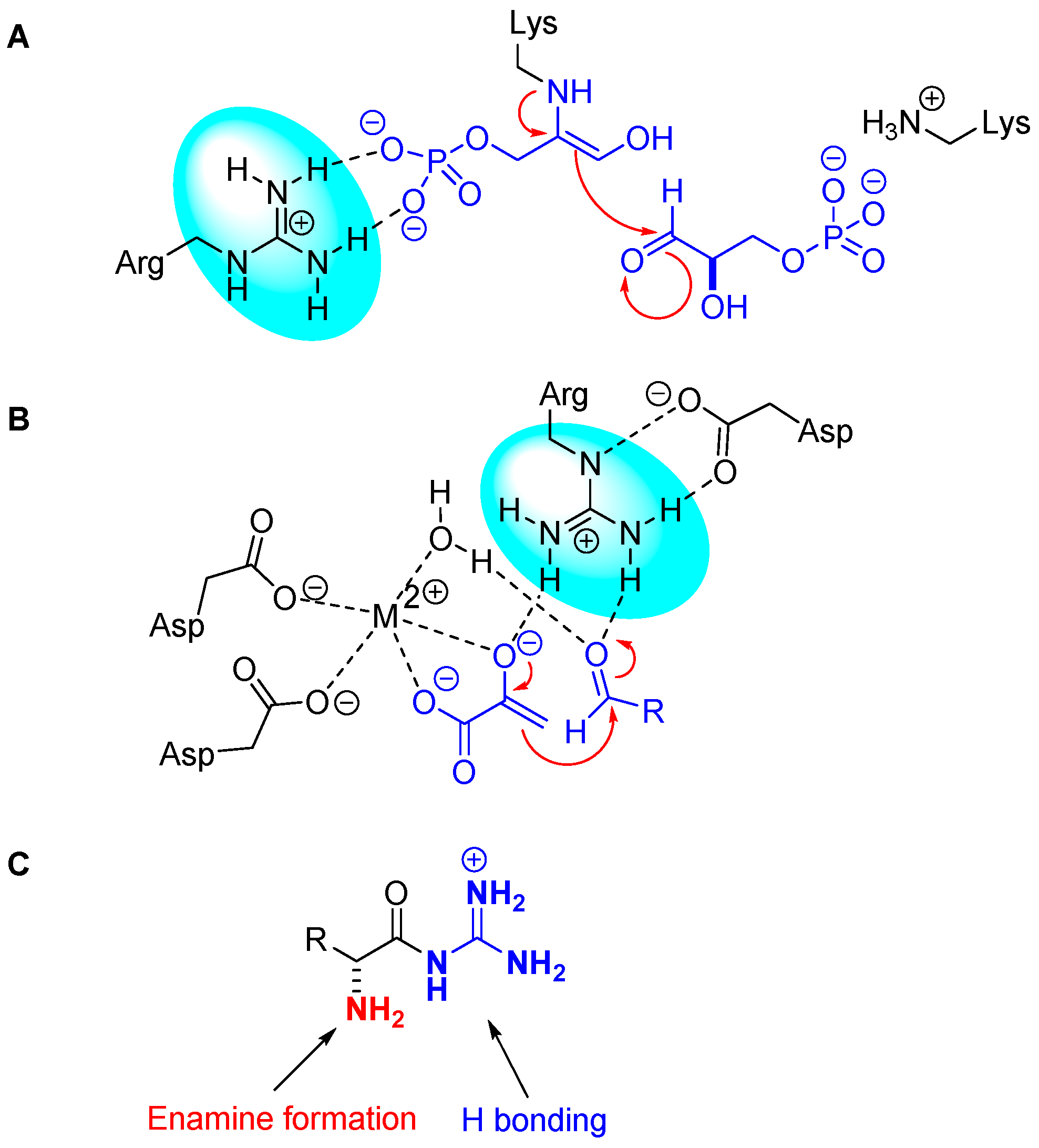
1. Introduction
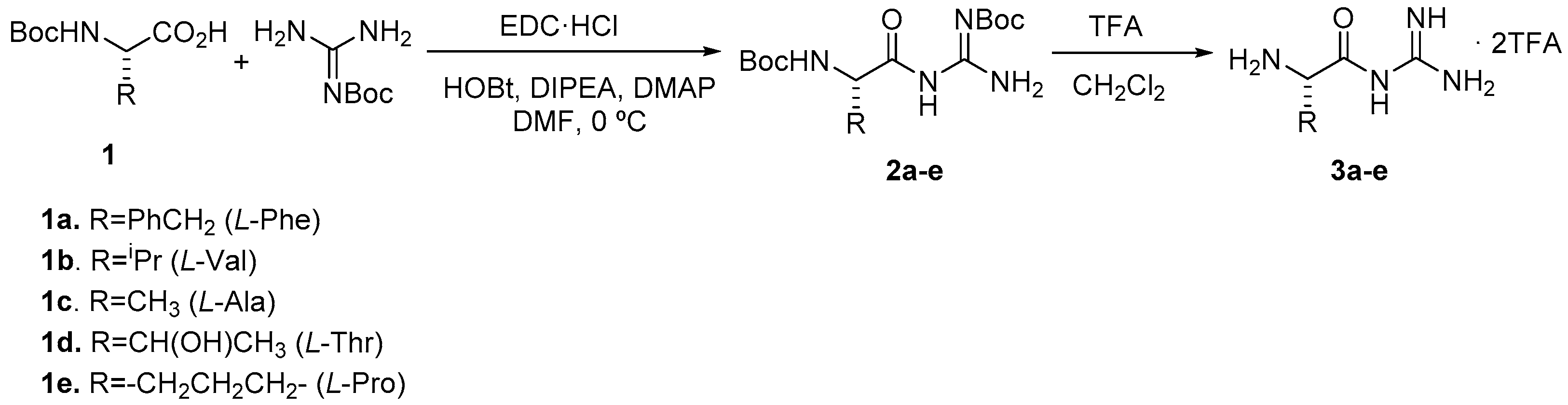
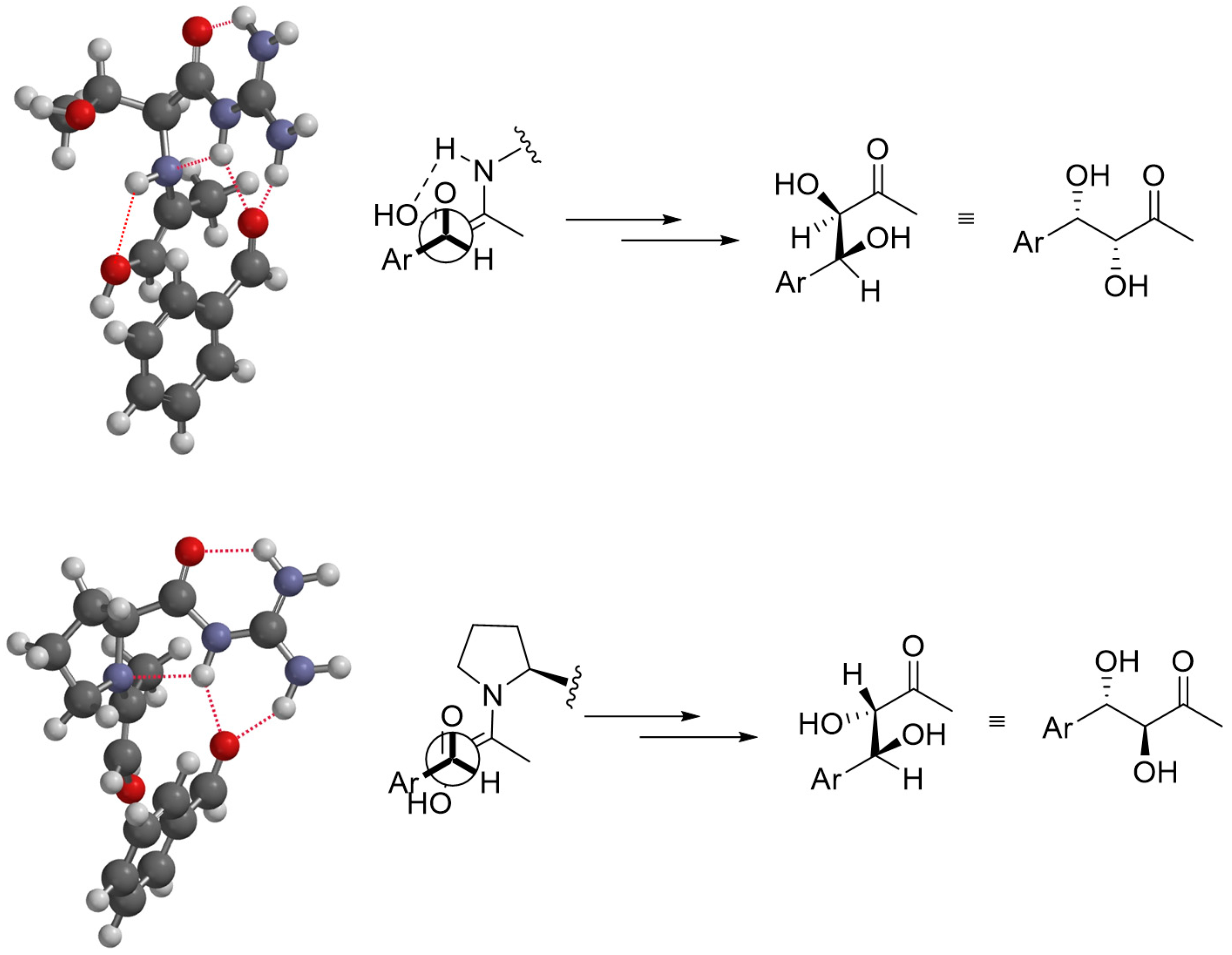
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, G.-T.; Yu, J.-S.K. Catalytic roles of histidine and arginine in pyruvate class II aldolase: A perspective from QM/MM metadynamics. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8130–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, A.; Berry, A.; Nelson, A. Directed evolution of aldolases for exploitation in synthetic organic chemistry. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 474, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coincon, M.; Wang, W.; Sygusch, J.; Seah, S.Y.K. Crystal Structure of Reaction Intermediates in Pyruvate Class II Aldolase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36208–36221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Feng, X.; Liu, X. Chiral guanidines and their derivatives in asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8525–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, P. Guanidines as Reagents and Catalysts, I. (Top. Heterocycl. Chem. 50); Selig, P., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Pont, A.; Alfonso, I.; Jimeno, C.; Solà, J. Dynamic assembly of a zinc-templated bifunctional organocatalyst in the presence of water for the asymmetric aldol reaction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17386–17389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Pont, A.; Alfonso, I.; Solà, J.; Jimeno, C. An efficient dynamic asymmetric catalytic system within a zinc-templated network. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7970–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Pont, A.; Alfonso, I.; Solà, J.; Jimeno, C. A copper-templated, bifunctional organocatalyst: A strongly cooperative dynamic system for the aldol reaction. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 6584–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivielso, A.M.; Catot, A.; Alfonso, I.; Jimeno, C. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding guides a cationic amphiphilic organocatalyst to highly stereoselective aldol reactions in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62331–62335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Sonoike, S.; Kitamura, M.; Aoki, S. Design and synthesis of chiral Zn2+ complexes mimicking natural aldolases for catalytic C-C bond forming reactions in aqueous solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2087–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimchuk, V.V.; Kucherenko, A.S.; Fakhrutdinov, A.N.; Medvedev, M.G.; Nelyubina, Y.V.; Zlotin, S.G. Towards Sustainable Amino Acid Derived Organocatalysts for Asymmetric syn-Aldol Reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 17, 2540–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimchuk, V.V.; Romanov, R.R.; Woo, G.H.T.; Dmitriev, I.A.; Kucherenko, A.S.; Zlotin, S.G. Novel L-threonine-based ionic liquid supported organocatalyst for asymmetric syn-aldol reactions: Activity and recyclability design. Arkivoc 2017, 3, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, A.H.; Ayats, C.; Pericàs, M.A. An enantioselective recyclable polystyrene-supported threonine-derived organocatalyst for aldol reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, C.; Fu, X.; Miao, Q. Cysteine-Based Organocatalysts for the Highly Efficient Direct Stoichiometric anti- and syn-Aldol Reactions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13711–13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fu, X.; Li, S. A highly efficient, large-scale, asymmetric direct aldol reaction employing simple threonine derivatives as recoverable organocatalysts in the presence of water. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fu, X.; Li, S. Simple and inexpensive threonine-based organocatalysts for the highly diastereo- and enantioselective direct large-scale syn-aldol and anti-Mannich reactions of α-hydroxyacetone. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, Z.; Ye, Z.; Qian, S.; Zhao, G. Highly efficient organocatalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reactions of hydroxyacetone and aldehydes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Luo, S.-W.; Tang, Z.; Cun, L.-F.; Mi, A.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Gong, L.-Z. Organocatalyzed highly enantioselective direct aldol reactions of aldehydes with hydroxyacetone and fluoroacetone in aqueous media: The use of water to control regioselectivity. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.-P. Highly enantioselective direct syn- and anti-Aldol reactions of dihydroxyacetones catalyzed by chiral primary amine catalysts. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Chimni, S.S. Organocatalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reaction of isatins in water: Low catalyst loading in command. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 5197–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh Chimni, S. Asymmetric syn-selective direct aldol reaction of protected hydroxyacetone catalyzed by primary amino acid derived bifunctional organocatalyst in the presence of water. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradowska, J.; Pasternak, M.; Gut, B.; Gryzlo, B.; Mlynarski, J. Direct Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Inspired by Two Types of Natural Aldolases: Water-Compatible Organocatalysts and ZnII Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popik, O.; Pasternak-Suder, M.; Lesniak, K.; Jawiczuk, M.; Gorecki, M.; Frelek, J.; Mlynarski, J. Amine-Catalyzed Direct Aldol Reactions of Hydroxy- and Dihydroxyacetone: Biomimetic Synthesis of Carbohydrates. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 5728–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Zhong, G.; List, B.; Shabat, D.; Anderson, J.; Gramatikova, S.; Lerner, R.A.; Barbas, C.F., III. Aldolase Antibodies of Remarkable Scope. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 2768–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasastry, S.S.V.; Zhang, H.; Tanaka, F.; Barbas, C.F., III. Direct Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of anti-1,2-Amino Alcohols and syn-1,2-Diols through Organocatalytic anti-Mannich and syn-Aldol Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillena, G.; Hita, M.d.C.; Nájera, C. Organocatalyzed direct aldol condensation using L-proline and BINAM-prolinamides: Regioselective, diastereoselective and enantioselective controlled synthesis of 1,2-diols. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2006, 17, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Harman, K.; Ghosh, S.; Headley, A.D. Chiral amine organocatalysts for the syn-aldol reaction involving substituted benzaldehydes and hydroxyacetone. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, P.; Plutecka, A.; Gawronski, J.; Kacprzak, K. Simple and practical direct asymmetric aldol reaction of hydroxyacetone catalyzed by 9-amino Cinchona alkaloid tartrates. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuynck, A.L.W.; Vanderleyden, J.; Sels, B.F. Direct asymmetric syn-aldol reactions of linear aliphatic ketones with primary amino acid-derived diamines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günler, Z.I.; Alfonso, I.; Jimeno, C.; Pericàs, M.A. Concentration Effect in the Asymmetric Michael Addition of Acetone to β-Nitrostyrenes Catalyzed by Primary Amine Thioureas. Synthesis 2017, 49, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Günler, Z.I.; Companyó, X.; Alfonso, I.; Burés, J.; Jimeno, C.; Pericàs, M.A. Deciphering the roles of multiple additives in organocatalyzed Michael additions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6821–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpless, K.B.; Amberg, W.; Bennani, Y.L.; Crispino, G.A.; Hartung, J.; Jeong, K.S.; Kwong, H.L.; Morikawa, K.; Wang, Z.M.; Xu, D.; et al. The osmium-catalyzed asymmetric dihydroxylation: A new ligand class and a process improvement. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 2768–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taie, Z.S.; Anetts, S.R.; Christensen, J.; Coles, S.J.; Horton, P.N.; Evans, D.M.; Jones, L.F.; de Kleijne, F.F.J.; Ledbetter, S.M.; Mehdar, Y.T.H.; et al. Proline derived guanidine catalysts forge extensive H-bonded architectures: A solution and solid state study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 22397–22416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
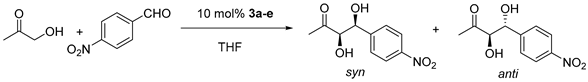
| Entry. | Catalyst | Conversion/% c | d.r. anti/syn c | ee anti/% d | ee syn/% d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3a | 53 a | 1/1.9 a | 50 a | 55 a |
| 2 | 70 b | 1/2 b | 37 b | 40 b | |
| 3 | 3b | 27 a | 1/1.4 a | 59 a | 72 a |
| 4 | 43 b | 1/2 b | 41 b | 68 b | |
| 5 | 3c | 25 a | 1/2.3 a | 43 a | 60 a |
| 6 | 44 b | 1/2.3 b | 45 b | 48 b | |
| 7 | 3d | 17 a | 1/2.5 a | 52 a | 82 a |
| 8 | 33 b | 1/3.8 b | 51 b | 81 b | |
| 9 | 3e | 31 a | 2.5/1 a | 62 a | 35 a |
| 10 | 46 b | 2.7/1 b | 69 b | 41 b |
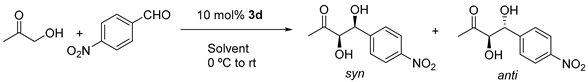
| Entry | Solvent | Conversion/% c | d.r. anti/syn c | ee syn/% d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | THF | 33 | 1/3.8 | 81 |
| 2 | DMF | 19 | 1/5.0 | 92 |
| 3 | CH2Cl2 a | 3 | 1/1.4 | 57 |
| 4 | CH3CN | 41 | 1/2.3 | 80 |
| 5 | AcOEt b | 46 | 1/2.0 | 67 |
| 6 | iPrOH b | 59 | 1/2.0 | 79 |
| 7 | EtOH | 23 | 1/2.8 | 89 |
| 8 | water | N. R. | - | - |
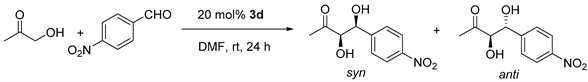
| Entry | Conc./M a | Conv./% c | dr anti/syn c | ee syn/% d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.18 | 75 | 1/4.4 | 91 |
| 2 | 0.31 | 75 | 1/4.1 | 90 |
| 3 | 0.46 | 81 | 1/3.7 | 88 |
| 4 | 1.43 b | 71 | 1/1.6 | 57 |
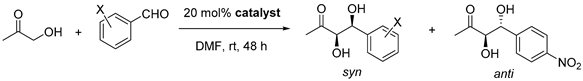
| Entry | Catalyst | Aldehyde | Conversion/% d | d.r. anti/syn d | ee Major/% e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3d |  | 94 | 1/4.5 | 91 |
| 2 | 26 a | 1/4.4 a | 93 a | ||
| 3 | 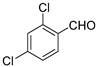 | 99 | 1/12 | 94 | |
| 4 |  | 64 | 1/4.2 | 97 | |
| 5 b | 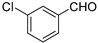 | 58 b | 1/4.5 b | 89 b | |
| 6 c | 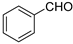 | 18 c | 1/3 c | 86 c | |
| 7 | 3e | 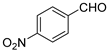 | 95 | 3.7/1 | 77 |
| 8 | L-Pro | 76 f | 3.1/1 | 92 | |
| 9 | L-Thr | 11 | 1/3.7 | 69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jimeno, C. Amino Acylguanidines as Bioinspired Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction. Molecules 2021, 26, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040826
Jimeno C. Amino Acylguanidines as Bioinspired Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040826
Chicago/Turabian StyleJimeno, Ciril. 2021. "Amino Acylguanidines as Bioinspired Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction" Molecules 26, no. 4: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040826
APA StyleJimeno, C. (2021). Amino Acylguanidines as Bioinspired Catalysts for the Asymmetric Aldol Reaction. Molecules, 26(4), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040826






