Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Green Solvents in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet: Recent Applications, Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet (DLLME-SFOD)
3. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs)
4. DESs in DLLME-SFOD
4.1. DES as a Novel Disperser in DLLME-SFOD
4.2. DES as an Extracting Solvent in DLLME-SFOD
4.2.1. DES for Extracting Organic Analytes from Different Matrices
4.2.2. DES for Extracting Inorganic Analytes from Various Matrices
4.3. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents (TDESs) in DLLME-SFOD
4.4. Combination of DES-DLLME-SFOD with Other Sample Treatment Techniques
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, C. Sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1184, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M. Before the injection—Modern methods of sample preparation for separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, M.; Nikolaou, A. Analytical problems and the need for sample preparation in the determination of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in aqueous environmental matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. The role of green extraction techniques in Green Analytical Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares da Silva Burato, J.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Toffoli, A.L.; Vasconcelos Soares Maciel, E.; Mauro Lanças, F. Recent advances and trends in miniaturized sample preparation techniques. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Green analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Kecili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F.; Hussain, C.M. Green miniaturized technologies in analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Assadi, Y.; Milani Hosseini, M.-R.; Aghaee, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Berijani, S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Alhooshani, K. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based binary extraction techniques prior to chromatographic analysis: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.-I.; Fuh, M.-R.; Huang, S.-D. Beyond dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1335, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Zanjani, M.R.; Yamini, Y.; Shariati, S.; Jönsson, J.Å. A new liquid-phase microextraction method based on solidification of floating organic drop. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 585, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Avila, L.E.; Rojo-Portillo, T.; Covarrubias-Herrera, R.; Peña-Alvarez, A. Capabilities and limitations of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic drop for the extraction of organic pollutants from water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 805, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ding, Z.; Lv, L.; Song, D.; Feng, Y.-Q. A novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet method for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, M.-I.; Huang, S.-D. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method based on solidification of floating organic drop combined with gas chromatography with electron-capture or mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1211, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbodaghi, M.; Faraji, H.; Shahbaazi, H.; Shabani, M. Sustainable and green microextraction of organophosphorus flame retardants by a novel phosphonium-based deep eutectic solvent. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Dastoori, H. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent as chelating agent and extraction solvent for preconcentration of heavy metals from milk samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorizadeh, H.; Abbasi, S. Preconcentration of silver using solidification of floating organic drop and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Chem. Methodol. 2019, 3, 644–654. [Google Scholar]
- Kokosa, J.M. Selecting an extraction solvent for a greener liquid phase microextraction (LPME) mode-based analytical method. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marube, L.C.; Caldas, S.S.; Soares, K.L.; Primel, E.G. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplets for simultaneous extraction of pesticides, pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Danielson, N.D. Solidification of floating organic droplet in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction as a green analytical tool. Talanta 2017, 170, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V. Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry. A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carasek, E.; Bernardi, G.; Morelli, D.; Merib, J. Sustainable green solvents for microextraction techniques: Recent developments and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1640, 461944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for green-solvent design: From hydrophilic to hydrophobic (deep) eutectic solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Fan, J. New low viscous hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of phthalate esters from food-contacted plastics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Moghadam, M.R.; Saeidi, M. Temperature-controlled liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of diazinon and fenitrothion in water and fruit juice samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitze, M.S.; Schreiter, E.R.; Patterson, E.V.; Freeman, R.G. Ionic liquids based on FeCl3 and FeCl2. Raman scattering and ab initio calculations. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; McKenzie, K.J. Application of ionic liquids to the electrodeposition of metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-based ionic liquids with metal-containing anions and cations. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deen, A.K.; Shimizu, K. Deep eutectic solvent as a novel disperser in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet (DLLME-SFOD) for preconcentration of steroids in water samples: Assessment of the method deleterious impact on the e. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Volodina, N.; Nechaeva, D.; Gagarinova, S.; Bulatov, A. Deep eutectic solvents as a new kind of dispersive solvent for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38146–38149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, S.; Qin, F.; Zhao, L. Analysis of six preservatives in beverages using hydrophilic deep eutectic solvent as disperser in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of floating organic droplet. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, K.; Ezoddin, M.; Pirooznia, N. Ultrasound-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet using deep eutectic solvent as disperser for preconcentration of Ni and Co. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Rozas, L.; Canales, R.; Lara, F.J.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Silva, M.F. A natural deep eutectic solvent as a novel dispersive solvent in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet for the determination of pesticide residues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6413–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal El-Deen, A.; Shimizu, K. Modified μ-QuEChERS coupled to diethyl carbonate-based liquid microextraction for PAHs determination in coffee, tea, and water prior to GC–MS analysis: An insight to reducing the impact of caffeine on the GC–MS measurement. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1171, 122555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-DEEN, A.K.; SHIMIZU, K. Application of D-Limonene as a bio-based solvent in low density-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of acidic drugs from aqueous samples. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Hong, K.; Li, X.; Ge, F.; Tang, Y. Freezing temperature controlled deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplets for rapid determination of benzoylureas residual in water samples with assistance of metallic salt. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56528–56536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Qiao, K.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Lu, R.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of deep eutectic solvent for the determination of benzoylureas in environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Bai, X.; Hu, S. Simultaneous determination of curcuminoids in Curcumae Longae Rhizoma and turmeric tea using liquid-phase microextraction based on solidification of floating deep eutectic solvent drop. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.M.; Shemirani, F.; Ghorbanian, S.A. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in developing microextraction methods based on solidification of floating drop: Application to the TRACE HPLC/FLD determination of PAH. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbati, M.; Mohebbi, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Simultaneous derivatization and air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of lighter than water deep eutectic solvent followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: An efficient and rapid method for trace analysis of aromatic amines in aqueous samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1032, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Hosseini, H.; Mohamadi Sorkali, H.; Fattahi, N.; Noori, N. Preconcentration and determination of amoxicillin and ceftriaxone in hospital sewage using vortex-assisted liquid-phase microextraction based on the solidification of the deep eutectic solvent followed by HPLC-UV. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. In matrix formation of deep eutectic solvent used in liquid phase extraction coupled with solidification of organic droplets dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction; application in determination of some pesticides in milk samples. Talanta 2020, 206, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Azadmard Damirchi, S.; Nemati, M. Dispersive solid phase extraction combined with solidification of floating organic drop-liquid-liquid microextraction using in situ formation of deep eutectic solvent for extraction of phytosterols from edible oil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1630, 461523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.Y.; Chislov, M.V.; Nechaeva, D.V.; Moskvin, L.N.; Bulatov, A.V. A new approach for microextraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from human urine samples based on in-situ deep eutectic mixture formation. J. Mol. Liquids 2018, 272, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J. Novel deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasounds-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with solidification of the aqueous phase for HPLC-UV determination of aromatic amines in environmental samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, A.; Javadi, A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Mirzaei, H.; Nemati, M. Development of homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating droplets of a ternary component deep eutectic solvent for the analysis of antibiotic residues in sausage samples. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4220–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Khodadadeian, F.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Development of a stir bar sorptive extraction method coupled to solidification of floating droplets dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of acidic pesticides from tomato samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, A.; Javadi, A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Mirzaei, H.; Nemati, M. Determination of three antibiotic residues in hamburger and cow liver samples using deep eutectic solvents based pretreatment method coupled with ion mobility spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, E.; Khandaghi, J.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Combination of dispersive solid phase extraction with solidification organic drop-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for extraction of organophosphorous pesticides from edible oil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Nemati, M.; Sarhangi, N.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Development of green sodium sulfate-induced solidification of floating organic droplets-dispersive liquid phase microextraction method: Application to extraction of four antidepressants. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Jamali, M.R.; Nezhadali, A. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) based on solidification of floating organic drop using a deep eutectic solvent for simultaneous preconcentration and determination of nickel and cobalt in food and water samples. Anal. Lett. 2021, 54, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of deep eutectic solvent droplets for analysis of pesticides in farmer urine and plasma by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1124, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Development of deep eutectic solvent based solidification of organic droplets-liquid phase microextraction; application to determination of some pesticides in farmers saliva and exhaled breath condensate samples. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L. Menthol-based deep eutectic solvent in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by solidification of floating organic droplet for the determination of three bisphenols with UPLC-MS/MS. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Jing, X. An effervescence tablet-assisted microextraction based on the solidification of deep eutectic solvents for the determination of strobilurin fungicides in water, juice, wine, and vinegar samples by HPLC. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taspinar, H.; Elik, A.; Kaya, S.; Altunay, N. Optimization of green and rapid analytical procedure for the extraction of patulin in fruit juice and dried fruit samples by air-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent-based solidified homogeneous liquid phase microextraction using experimental design and. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Zamora, C.; Jimenez-Skrzypek, G.; Gonzalez-Salamo, J.; Hernandez-Borges, J. Extraction of phthalic acid esters from soft drinks and infusions by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of the floating organic drop using a menthol-based natural deep eutectic solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1646, 462132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Z. Development and validation of vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on solidification of floating hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the determination of endocrine disrupting chemicals in sewage. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Teng, C.; Chen, Z.; Jing, X.; Zhao, W. Analysis of pyrethroids in cereals by HPLC with a deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplets. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, G. Air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of floating deep eutectic solvents for the simultaneous determination of bisphenols and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea infusions via HPLC. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Jiao, J.; Wu, H. A solidified floating organic drop-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on in situ formed fatty acid-based deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of benzophenone-UV filters from water samples. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 14082–14090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumandpassand, A.; Javadi, A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Solution decomposition of deep eutectic solvents in pH-induced solidification of floating organic droplet homogeneous liquid-liquid microextraction for the extraction of pyrethroid pesticides from milk. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Nechaeva, D.; Bulatov, A. HPLC-MS/MS determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in bovine milk based on simultaneous deep eutectic solvents formation and its solidification. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhu, G. Air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating deep eutectic solvent for the analysis of ultraviolet filters in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography with the aid of response surface methodology. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deen, A.K.; Shimizu, K. A green air assisted-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of a novel low viscous ternary deep eutectic solvent for the enrichment of endocrine disrupting compounds from water. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1629, 461498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, A.; Jiao, B. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-phase microextraction by solidifying L-menthol-decanoic acid hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for detection of five fungicides in fruit juices and tea drinks. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3870–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Nemati, M. Endocrine-disrupting compounds surveying in polyethylene packed injection solutions using microwave-accelerated air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of deep eutectic solvent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Geng, S.; Wen, T.; Qin, F.; Zhao, L. Vortex-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the solidification of a floating organic drop for the determination of benzoic acid and sorbic acid in condiments. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4805–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Hydrophobicity-switchable deep eutectic solvent-based effervescence-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with solidification of floating droplets for HPLC determination of anthraquinones in fried Cassiae semen tea infusions. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4739–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi-Jouibari, T.; Noori, N.; Fattahi, N. Assessment of toxic metal ions in tea samples using new microextraction technique based on the solidified deep eutectic solvent followed by GFAAS. Toxin Rev. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibollahi, M.H.; Karimyan, K.; Arfaeinia, H.; Mirzaei, N.; Safari, Y.; Akramipour, R.; Sharafi, H.; Fattahi, N. Extraction and determination of heavy metals in soil and vegetables irrigated with treated municipal wastewater using new mode of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidified deep eutectic solvent followed by GFAAS. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Jouibari, T.; Ahmadi Jouybari, H.; Sharafi, K.; Heydari, M.; Fattahi, N. Assessment of potentially toxic elements in vegetables and soil samples irrigated with treated sewage and human health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramipour, R.; Golpayegani, M.R.; Ghasemi, M.; Akramipour, R.; Golpayegani, M.R.; Ghasemi, M.; Noori, N.; Fattahi, N. Optimization of a methodology for speciation of arsenic, selenium and mercury in blood samples based on the deep eutectic solvent. MethodsX 2019, 6, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramipour, R.; Golpayegani, M.R.; Ghasemi, M.; Noori, N.; Fattahi, N. Development of an efficient sample preparation method for the speciation of Se(IV)/Se(VI) and total inorganic selenium in blood of children with acute leukemia. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 6951–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, B.; Feizbakhsh, A.; Konoz, E.; Faraji, H. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based on centrifugation-free dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for speciation of selenium in aqueous samples: One step closer to green analytical chemistry. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Dastoori, H.; Okhravi, T. Development of an air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction method based on a ternary solidified deep eutectic solvent in extraction and preconcentration of Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, S.; Alavi, L.; Jabbari, A. Dispersed solidified fine droplets based on sonication of a low melting point deep eutectic solvent: A novel concept for fast and efficient determination of Cr(VI) in urine samples. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 188, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, F.R.; Danielson, N.D. Solvent-terminated dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
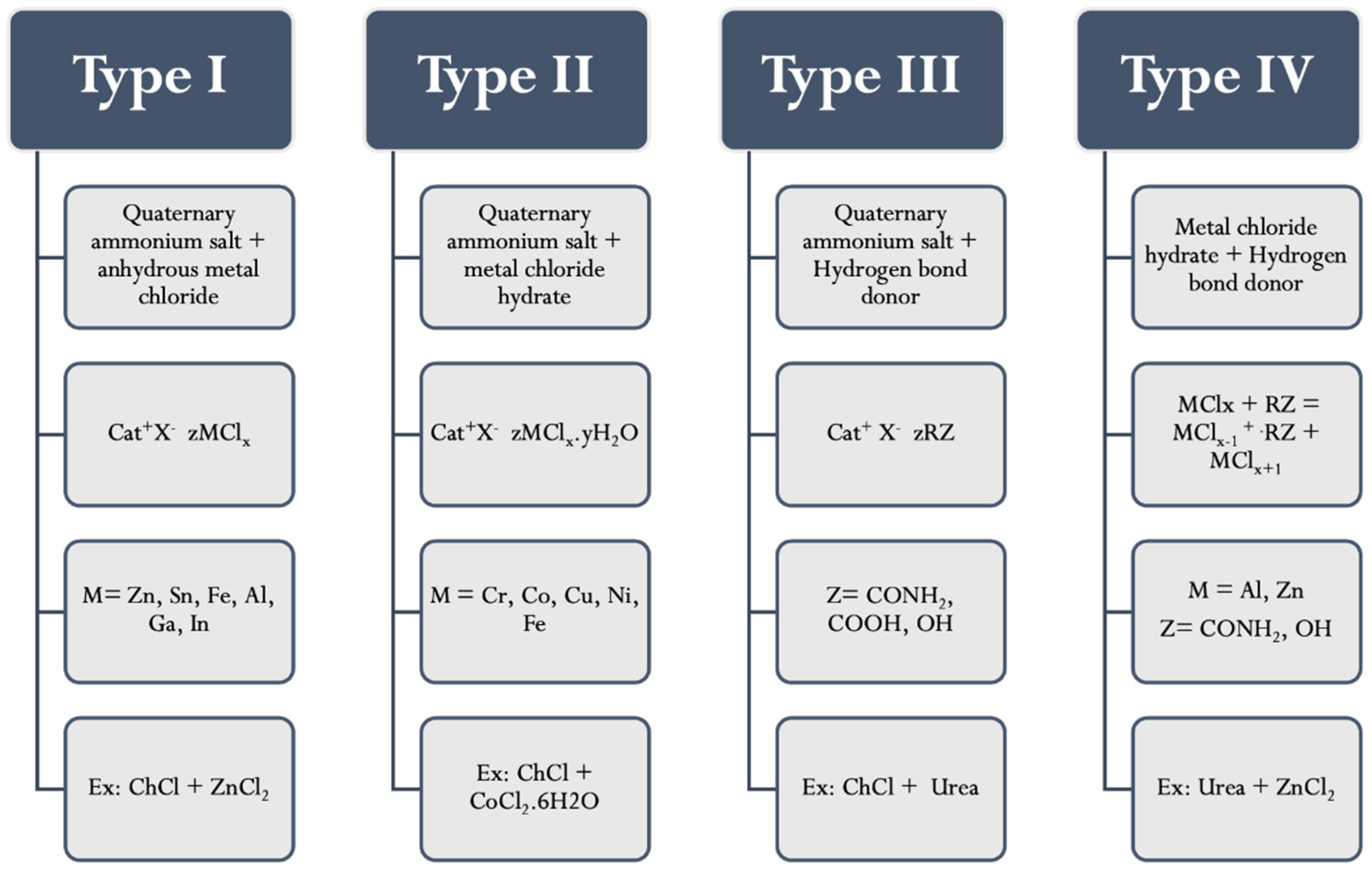
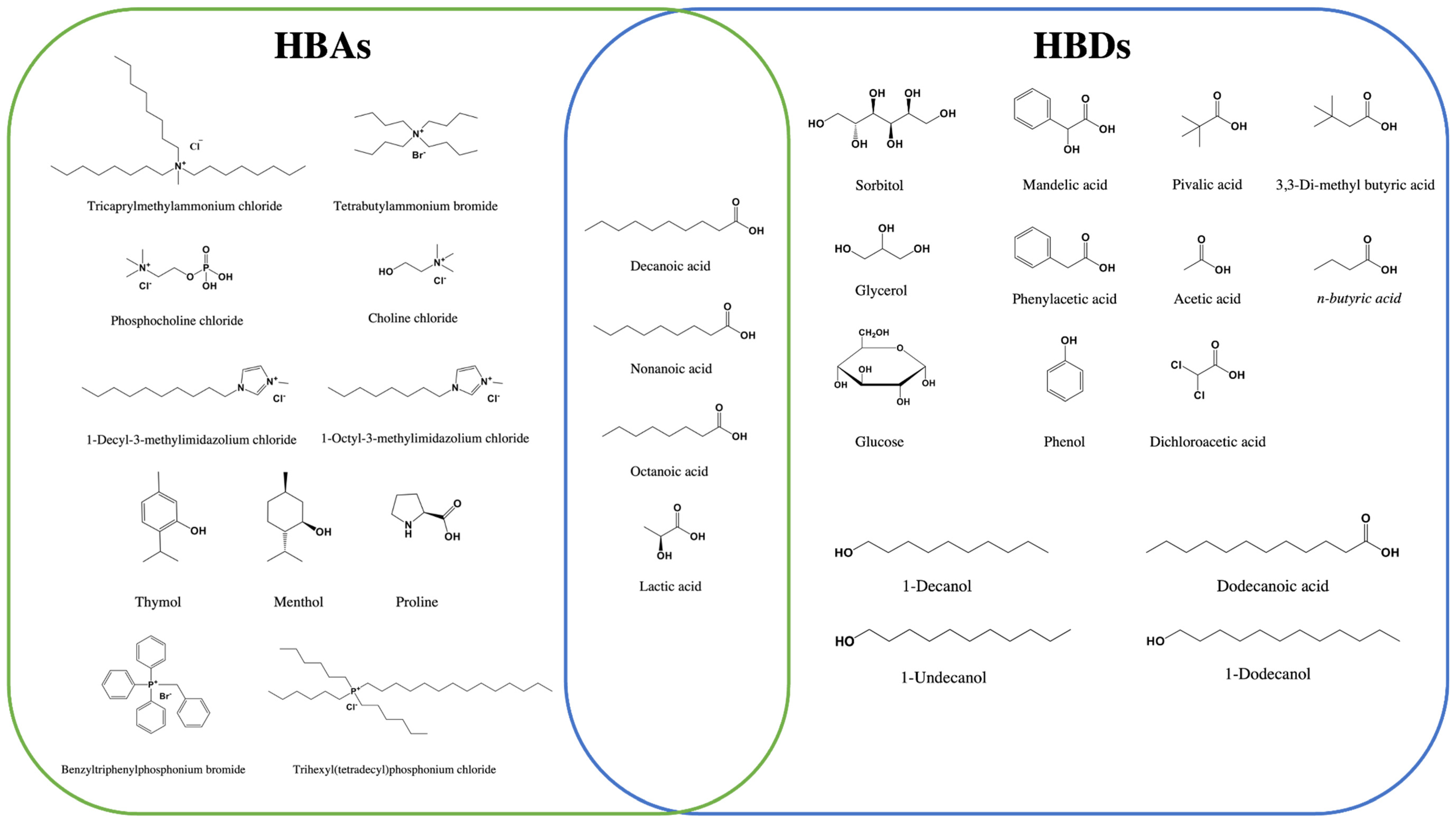
| Analysis Method | Analytes | Matrix (Amount) | Extractant (Volume) | Disperser DES (Molar Ratio) (Volume) | Assistant Techniques | EF | LOD (µg/L) | % RSD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-PDA | Steroids (Triamcinolone acetonide, dexamethasone, testosterone, prednisolone, Cortisone, 1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione, hydrocortisone acetate, Finasteride, 4-androstane-3,17-dione) | Water (5 mL) | 1-Dodecanol (50 μL) | TBABr: acetic acid (1:2), (231 μL) | - | 44–112 | 1.0–9.7 | <5 | [33] |
| HPLC-PDA | Preservatives (benzoic acid, sorbic acid, Methyl paraben, Ethyl paraben, Propyl paraben, Butyl paraben) | Beverages (4 mL) | 1-Decanol (80 µL) | TBABr: acetic acid (1:2) (200 µL) | Vortex (3 min) | 81–99 | 20–50 | <5 | [35] |
| HPLC-UV | Pesticides (fipronil, fipronil-sulfide, fipronil-sulfone, boscalid) | Water and wine (5 mL) | 1-Dodecanol (100 μL) | Lactic acid: glucose: water (5:1:3), (2 mL) | Vigorous shaking (1 min) | NA | 0.8–1.3 | <15 | [37] |
| GFAAS | Ni (II) and Co (II) | Water and food (10 mL) | 1-Dodecanol (75 μL) | TBABr: acetic acid (1:2), (250 μL) | Ultrasonication (1 min) | 100 | 0.2 and 0.4 | <3.5 | [36] |
| Analysis Method | Analytes | Matrix (Amount) | Extractant (Molar Ratio), (Volume) | Disperser (Volume) | Auxiliary Equipment | EF | LOD (µg/L) | % RSD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-VWD | Benzoylureas (triflumuron, hexaflumuron, flufenoxuron, lufenuron) | Water (8 mL) | [N8,8,8,1]Cl: 1-dodecanol (1:1), (50 μL) | FeCl3 ethanol solution (250 μL) | - | 91–97 | 0.11–0.35 | <5 | [40] |
| HPLC-VWD | Benzoylureas (triflumuron, hexaflumuron, flufenoxuron, lufenuron, diflubenzuron) | Water (8 mL) | [OMIM]Cl: 1-dodecanol (1:2), (40 μL) | Vortex (3 min) | - | 171–188 | 0.09–0.16 | <6 | [41] |
| GC-MS | Aromatic amines (aniline, p-toluidine, p-chloroaniline, p-anisidine, 4-tert–butyl aniline) | Water (10 mL) | ChCl: n-butyric acid (1:2), (65 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (4 cycles) | - | 790–940 | 0.0018–0.006 | ≤5.3 | [44] |
| HPLC-FLD | PAHs (naphthalene, fluorene, phenanthrene, anthracene, fluoranthene, pyrene) | Water (20 mL) | TBABr: decanoic acid (1:2), (80 µL) | NA | Ultrasonic bath (1 min at 35 °C) | 163–198 | 0.0007–0.0066 | <11 | [43] |
| HPLC-UV | NSAIDs (ketoprofen, diclofenac) | Human urine (8 mL) | Menthol with the studied NSAIDs | NA | Water bath (50 °C) | 27–31 | 15–44 | <5 | [48] |
| HPLC-UV | Antibiotics (amoxicillin, ceftriaxone) | Hospital Sewage (10 mL) | [DMIM]Cl: n-butanoic acid (1:2), (60 μL) | Vortex (5 min) | Water bath (55 °C) | 164–172 | 0.005–0.100 | <5.2 | [45] |
| UPLC-MS/MS | NSAIDs (diclofenac, flurbiprofen, ketoprofen, mefenamic acid) | Bovine milk (5 mL) | Menthol with the studied NSAIDs | Vortex (1 min) | Heating to 50 °C | 81–102 | 0.01–0.03 µg/kg | <7 | [67] |
| GC-MS | Pesticides (prometryn, diazinon, fenvalerate, fenamiphos–sulfone, fenpropathrin, bifenthrin, terbutryn, bromopropylate, deltamethrin, phosalone) | Urine and plasma (5 mL) | Menthol: phenylacetic acid (3:1), (41 μL) | N2 stream flow (2.0 mL/min for 2.5 min) | - | Urine (379–485) Plasma (158–194) | Urine (0.002–0.017) Plasma (0.004–0.036) | NA | [56] |
| GC-MS | Pesticides (diazinon; prometryn; terbutryn; bifenthrin; fenpropathrin; bromopropylate; fenamiphos-sulfone; phosalone; fenvalerate, deltamethrin) | Breath condensate and saliva (5 mL) | Menthol: phenylacetic acid (3:1), (41 μL) | Air stream (FR = 2.0 mL/min, for 2.0 min) | - | 79–97 | 0.002–0.059 | <7 | [57] |
| GC-MS | Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, nortriptyline, Clomipramine, imipramine) | Urine (5 mL) | Menthol: decanoic acid (1:2), (54 μL) | 30% Na2SO4 (1 mL) | NA | 122–147 | 0.013–0.025 | <11 | [54] |
| GC-MS | OPFRs (Triphenyl phosphate, tripropyl phosphate, TCP, TBP, TCEP, TCPP, TEHP) | Water (5 mL) | BTPPB: 1-undecanol (1:4), (90 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (11 times) | NA | 119–312 | 0.002–0.023 | <8.7 | [16] |
| HPLC-UV | Curcuminoids (bisdemethoxycurcumin, demethoxycurcumin, curcumin) | Curcumae Longae Rhizoma and turmeric tea (0.5 g) | TBACl: decanoic acid (1:1), (70 μL) | Magnetic stirring at 40 °C | NA | 608–848 | 0.07–0.09 | <4.2 | [42] |
| HPLC-UV | Aromatic amines (2-chloroaniline, 4-chloroaniline, 1-naphthylamine) | Water (15 mL) | [P14,6,6,6]Cl: decanol (1:2), (40 µL) | Ultrasound (60 s) | NA | 116–121 | 0.07–0.11 | <6.2 | [49] |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Bisphenols (bisphenol S, bisphenol A, bisphenol B) | Canned fruit (0.5 g) | Menthol: undecanol (1:2), (300 μL) | Acetonitrile (400 μL) | Vigorous shaking (2 min) | 4.4–4.9 | 0.0015–0.003 µg/g | <4.6 | [58] |
| GC–FID | Pesticides (carbaryl, hexythiazox, pretilachlor, iprodione, famoxadone, sethoxydim, fenazaquin) | Milk (5 mL) | ChCl: decanoic acid (1:2), (63 μL) | Vortex (1 min) | Ultrasonic bath (7 min at 50 °C) | 320–445 | 0.90–3.9 | <7 | [46] |
| HPLC-PDA | Strobilurin fungicides (Picoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, trifloxystrobin) | Water, juice, wine, vinegar (10 mL) | Thymol: octanoic acid (1:5), (120 μL) | Effervescence tablet [Na2CO3 (10 mg), citric acid (80 mg)] | NA | NA | 0.15–0.38 | NA | [59] |
| HPLC-PDA | Benzophenone and UV filters (BP, BP-1, BP-3, PS, BS) | Water (5 mL) | Decanoic acid: dodecanoic acid (2:1) (65 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (6 cycles) | NA | 41–50 | 0.045–0.54 | ≤4.2 | [68] |
| HPLC-PDA | EDCs (BPA, BP, EE, DEST, 4-NP) | Water (5 mL) | Nonanoic acid: decanoic acid: dodecanoic acid (1:1:1), (200 µL) | Aspiration/dispersion (6 cycles) | - | 38–134 | 0.96–2.3 | <7 | [69] |
| HPLC-UV | Fungicides (azoxystrobin, fludioxonil, epoxiconazole, cyprodinil, prochloraz) | Fruit juices and tea drinks (5 mL) | Menthol: decanoic acid (1:1), (70 μL) | NA | Ultrasonication (9 min) | NA | 0.75–8.45 | <14.8 | [70] |
| UV–Vis | Patulin | Fruit juice and dried fruit (2 mL) | L-proline: glycerol (3:1), (410 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (6 cycles) | NA | 150 | 3.5 | <5.6 | [60] |
| HPLC-UV | Phthalic acid esters (DPP, BPP, DBP, DCHP, DEHP, DINP, DIDP, diisopentyl phthalate, di-n-pentyl phthalate) | Teas Infusion (15 mL) and soft drinks (20 mL) | Menthol: acetic acid (1:1), (100 µL) | NA | Manual vigorous shaking (1 min) | 3–12 | NA | 1–22 | [61] |
| GC-MS | EDCs (DEP, DBP, DEHP, BPA, DEHA) | Polyethylene packed injection solutions (5 mL) | Menthol: decanoic acid (1:2), (65 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (4 cycles) | NA | 395–470 | 0.014–0.033 | <7 | [71] |
| HPLC-FLD | Endocrine disrupting compounds (estradiol, estriol, BPA, BPF) | Sewage | Octanoic acid: 1-dodecanol (1:3), (80 μL) | Vortex (1 min) | NA | 96–111 | 0.00133–0.00292 | <6.2 | [62] |
| HPLC-PDA | Pyrethroids (bifenthrin, β-cypermethrin, deltamethrin) | Corn, wheat, barley, oats Cereals (1 g) | Thymol: octanoic acid (1:4), (60 μL) | Acetonitrile (1.5 mL) | NA | NA | 2–2.7 μg/kg | <3.6 | [63] |
| HPLC-UV | Bisphenols and PAHs (BPF, BPA, BPB, naphthalene, biphenyl, fluorene, phenanthrene, anthracene) | Tea infusions (5 mL) | Menthol: dodecanoic acid (3:1), (100 μL) | Aspiration/ dispersion (9 cycles) | NA | 15–18 | 0.16–0.75 | ≤2.3 | [64] |
| HPLC-PDA | Benzoic acid and sorbic acid | Ketchup and powder bags of instant noodles (10 mL) | Menthol: p-aminophenol (1:2), (800 μL) | Vortex (2.6 min) | NA | NA | 30 and 80 | <5.6 | [72] |
| GC-FID | Pyrethroid insecticides (deltamethrin, cypermethrin, bifenthrin, cyhalothrin, permethrin) | Milk (10 mL) | Menthol: p-aminophenol (1:2), (94 μL) | Ammonia solution (300 μL) | NA | 257–299 | 1.1–2.4 | ≤6.4 | [66] |
| HPLC-UV | Anthraquinones (rhein, emodin, chrysophanol, physcion) | Fried Cassiae semen tea infusions (10 mL) | ChCl: octanoic acid (1:2), (100 μL) | CO2 (H2SO4 and Na2CO3 reaction) | NA | 94–104 | 80–110 | <3.3 | [73] |
| HPLC-UV | Benzophenone-UV filters (BP-1, BP-2, BP-3, BP-6) | Water (10 mL) | [P4,4,4,12]BF4: decanoic acid (1:9.4) | CO2 | NA | 34–42 | 0.60–1.50 | <8 | [65] |
| Analysis Method | Analytes (Details) | Matrix (Amount) | Extractant (Molar Ratio), (Volume, μL) | Disperser | Assistant Techniques | Chelating Agent (Volume, μL) | EF | LOD (µg/L) | % RSD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETAAS | As, Se, Hg (Speciation) | Child blood (10 mL) | ChCl: Decanoic acid (1:2), (60 μL) | Vortex (5 min) | NA | DDTP (15 μL) | 98–106 | 0.015–0.10 | ≤5.8 | [77] |
| GFAAS | Se (Speciation) | Child blood (5 mL) | ChCl: Decanoic acid (1:2), (60 μL) | Vortex (4 min) | NA | DDTP (15 μL) | 112 | 0.05–5 | <3.5 | [78] |
| UV-Visible | Se (Speciation) | Water (5 mL) | BTPPB: 1-undecanol (1:4), (700 μL) | Aspiration/ dispersion (7 cycles) | NA | DAB (0.09 %) | 315 | 0.76 | ≤8.3 | [79] |
| ETAAS | Cr (VI) | Urine (10 mL) | BTPPB: phenol (128 μL) | Sonication (1 min) | NA | DPC | 34 | 0.002 | ≤4.7 | [81] |
| GFAAS | Pb, Cd, Hg | Soil and vegetables (1 g) | [DMIM]: 1-undecanol (1:2), (50.0 μL) | Vortex (4 min) | Water bath (at 55 °C) | DDTP (15 μL) | 114–172 | 0.01–0.03 μg/kg | ≤7 | [75] |
| GFAAS | Pb, Cd, Cu, As, Hg | Tea (0.5 g) | [DMIM]: n-butanoic acid (1:2), (60 μL) | Vortex (4 min) | Water bath (at 50 °C) | DDTP (20 μL) | 164–235 | 0.005–0.10 μg/kg | ≤3.5 | [74] |
| GFAAS | Ni, Co | Food and Water (50 mL) | Menthol: decanoic acid (150 μL) | NA | NA | Br-PADAP (150 μL) | 50 | 0.3–0.4 | ≤3 | [55] |
| GFAAS | Cd, Zn | Water and fruit juice (5 mL) | Menthol: Sorbitol: Mandelic acid (1:2:1), (125 μL) | Aspiration/dispersion (9 cycles) | NA | DES | 23.4–24.8 | 0.12–0.15 | ≤4.2 | [80] |
| GFAAS | Cd, Cu, Pb | Milk (5 mL) | Menthol: Sorbitol: Mandelic acid (1:2:1), (100 μL) | Methanol (1.5 mL) | NA | DES | NA | 38–0.42 | ≤4.5 | [17] |
| Analysis Method | Analytes | Sample Preatment | Matrix (Amount) | Extractant (Molar Ratio), (Volume) | Disperser (Volume) | EF | LOD (µg/L) | % RSD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMS | Antibiotic residues (oxytetracycline, penicillin G, tilmicosin) | HLLE | Sausage (20 g) | PChCl: dichloroacetic acid: dodecanoic acid (1:1:1), (70 µL) | Acetonitrile (2 mL) | 1260–1580 | 0.00152–0.00273 µg/g | <8 | [50] |
| IMS | Antibiotic residues (oxytetracycline, penicillin G, tilmicosin) | CCSHLLE | Hamburger and cow liver (10 g) | ChCl: pivalic acid (1:2), (75 μL) | Acetonitrile (1 mL) | 670–900 | 0.0017–0.0028 | ≤6.2 | [52] |
| GC/MS | Phytosterols (brassicasterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, lupeol) | d-SPE | Edible oil (5 mL) | ChCl: n-butyric acid (0.065 g: 80 µL, in situ formation) | Water bath (5 min at 75 °C) | 312–375 | 0.52–1.6 | ≤8.2 | [47] |
| GC-MS | Pesticides (Dalapon, 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, fenoxaprop, haloxyfop) | SBSE | Tomato juice (50 mL) | ChCl: n-butyric acid (1:2), (58 μL) | NA | 2530–2999 | 0.007–0.014 | ≤12 | [51] |
| GC-NPD | Organophosphorous pesticides (Etrimfos, fenthion, di-azinon, chloropyrifos) | d-SPE | Edible oil (2.5 mL) | ChCl: 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid (1:1), (15 µL) | NA | 170–192 | 0.06–0.24 | ≤9.2 | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Deen, A.K.; Shimizu, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Green Solvents in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet: Recent Applications, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237406
El-Deen AK, Shimizu K. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Green Solvents in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet: Recent Applications, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Molecules. 2021; 26(23):7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237406
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Deen, Asmaa Kamal, and Kuniyoshi Shimizu. 2021. "Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Green Solvents in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet: Recent Applications, Challenges and Future Perspectives" Molecules 26, no. 23: 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237406
APA StyleEl-Deen, A. K., & Shimizu, K. (2021). Deep Eutectic Solvents as Promising Green Solvents in Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Solidification of Floating Organic Droplet: Recent Applications, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Molecules, 26(23), 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237406







