Novel GPR120 Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
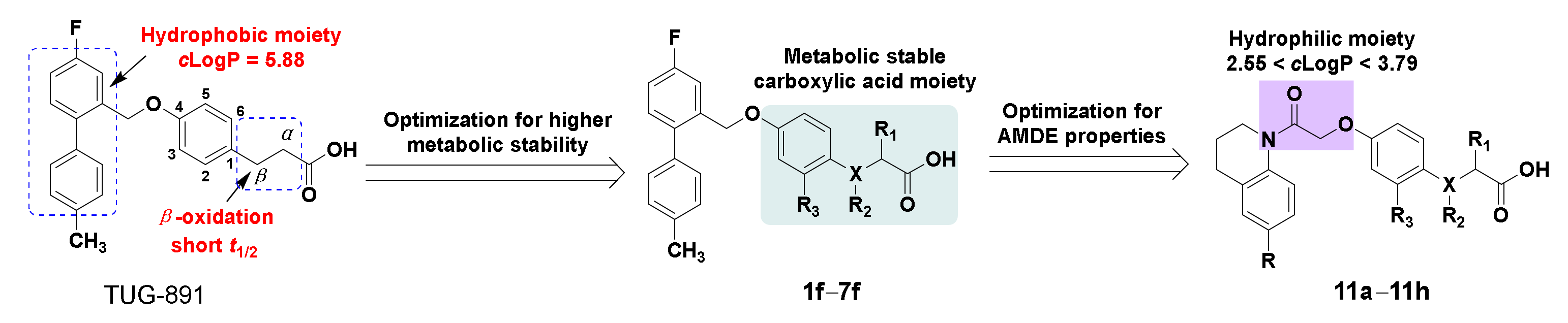
2. Results and Discussion
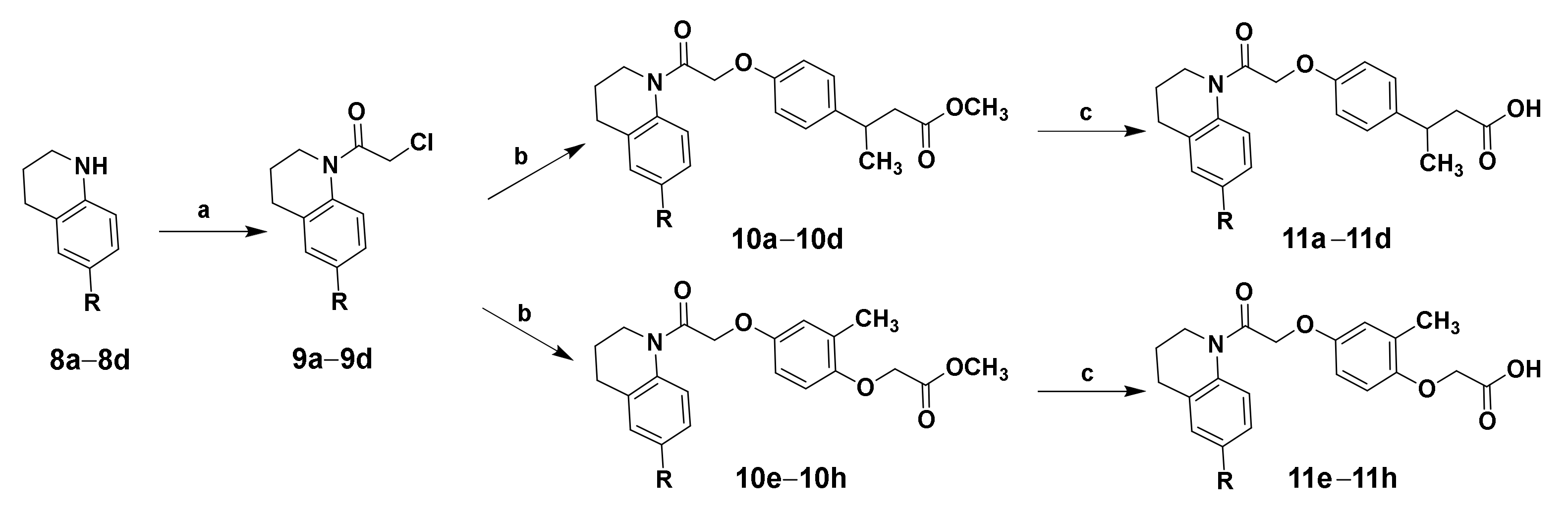
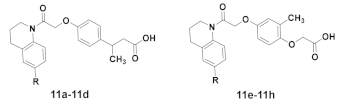
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Pharmacology
2.2.1. GPR120 Agonistic Activity and Selectivity
2.2.2. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Compounds 11b and 11g in C57BL/6 Mice
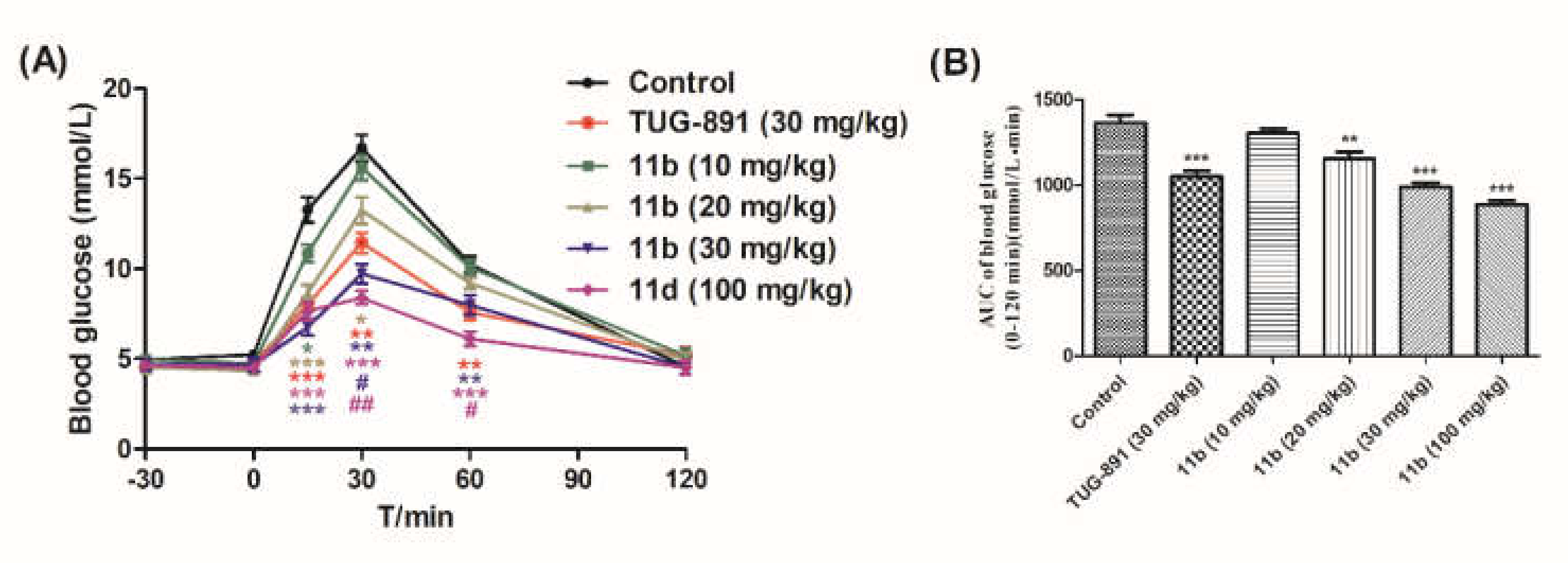
2.2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test of Compound 11b in Normal ICR Mice
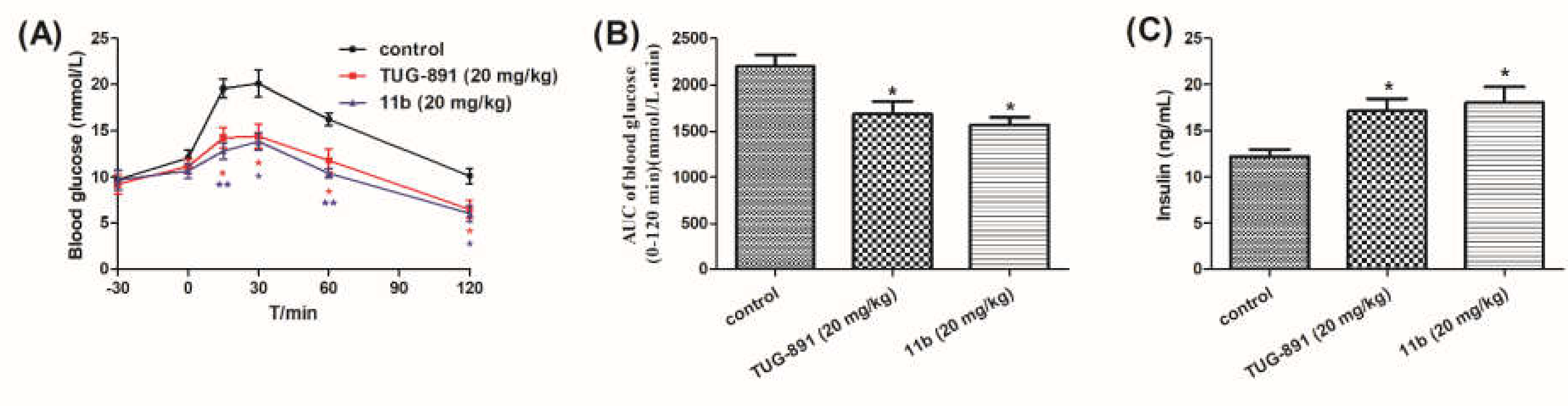
2.2.4. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effects of Compound 11b Explored in DIO Mice
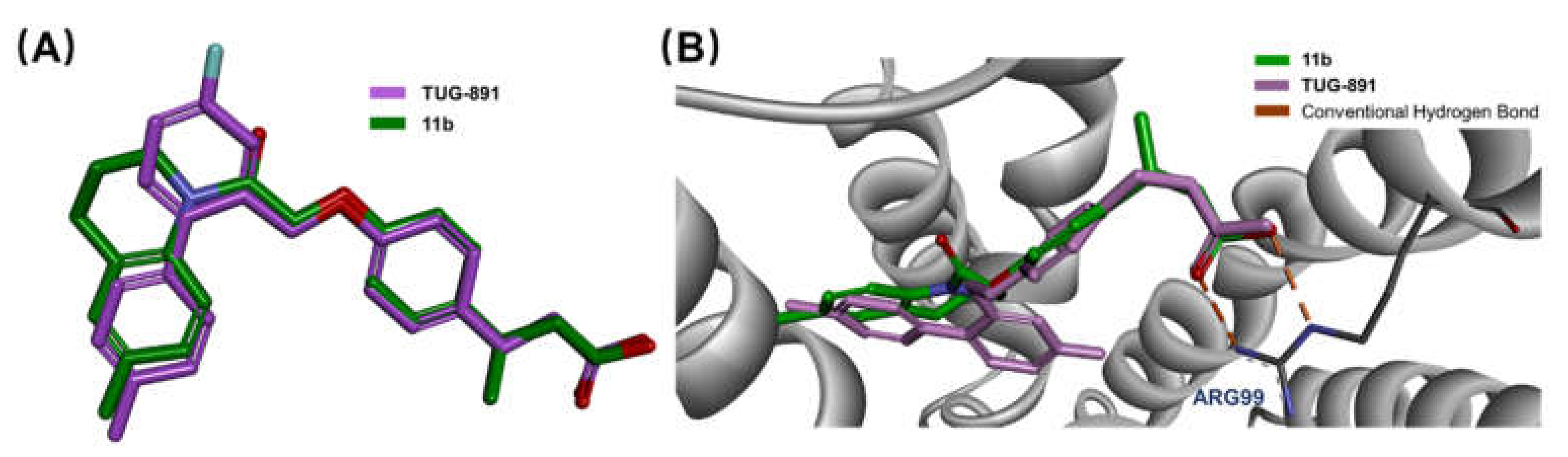
2.2.5. Molecular Modeling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. 4-Fluoro-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carbaldehyde (1b)
3.1.2. (4-Fluoro-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)methanol (1c)
3.1.3. 2-(Bromomethyl)-4-fluoro-4′-methyl-1,1′-biphenyl (1d)
3.1.4. General Synthetic Procedure for the Target Compounds 1f–7f
3.1.5. General Synthetic Procedure for Intermediates 9a–9d
3.1.6. General Synthetic Procedure for Target Compounds 11a–11h
3.2. Pharmacology
3.2.1. Ca2+ Influx Activity of Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Expressing Human GPR120
3.2.2. Animals
Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Compounds 11b and 11g in C57BL/6 Mice
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test of Compound 11b in Normal ICR Mice
Anti-Hyperglycemic Effects of Compound 11b Explored in DIO Mice
3.3. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappachan, J.M.; Fernandez, C.J.; Chacko, E.C. Diabesity and antidiabetic drugs. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 66, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurich, D.T.; McAlister, F.A.; Blackburn, D.F.; Majumdar, S.R.; Tsuyuki, R.T.; Varney, J.; Johnson, J.A. Benefits and harms of antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and heart failure: Systematic review. BMJ 2007, 335, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh, Y.; Kawamata, Y.; Harada, M. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic b cells through GPR40. Nature 2003, 1600, 2001–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, A.; Tsumaya, K.; Awaji, T.; Katsuma, S.; Adachi, T.; Yamada, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Tsujimoto, G. Free fatty acids regulate gut incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through GPR120. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpukade, B.; Hudson, B.D.; Hovgaard, C.K.; Milligan, G.; Ulven, T. Discovery of a potent and selective GPR120 agonist. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4511–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, G.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, Y.; Han, J. Improving metabolic stability with deuterium: The discovery of GPU-028, a potent free fatty acid receptor 4 agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6647–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, C.; Winters, M.; Wells, M.; Wall, M.; Lanter, J.; Sui, Z.; Ma, J.; Novack, A.; Nashashibi, I.; et al. Design, synthesis and SAR of a novel series of heterocyclic phenylpropanoic acids as GPR120 agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, C.; Sui, Z.; Macielag, M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, W.; Suckow, A.; Hua, H.; Bell, A.; Haug, P.; et al. Discovery of an isothiazole-based phenylpropanoic acid GPR120 agonist as a development candidate for type 2 diabetes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoull, W.; Bailey, A.; Barton, P.; Birch, A.M.; Brown, A.J.; Butler, H.S.; Boyd, S.; Butlin, R.J.; Chappell, B.; Clarkson, P.; et al. Indazole-6-phenylcyclopropylcarboxylic acids as selective GPR120 agonists with in vivo efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3187–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.L.; Velazquez, F.; Jayne, C.; Shah, U.; Miao, S.; Ashley, E.R.; Madeira, M.; Akiyama, T.E.; Di Salvo, J.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Discovery of chromane propionic acid analogues as selective agonists of GPR120 with in vivo activity in rodents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azevedo, C.M.; Watterson, K.R.; Wargent, E.T.; Hansen, S.V.; Hudson, B.D.; Kepczynska, M.A.; Dunlop, J.; Shimpukade, B.; Christiansen, E.; Milligan, G.; et al. Non-acidic free fatty acid receptor 4 agonists with antidiabetic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8868–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, B.D.; Shimpukade, B.; Milligan, G.; Ulven, T. The molecular basis of ligand interaction at free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20345–20358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Hopkins, M.M.; Zhang, Z.; Quisenberry, C.B.; Fix, L.C.; Galvan, B.M.; Meier, K.E. Omega-3 fatty acids and other FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate cancer cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, E.; Due-hansen, M.E.; Urban, C.; Grundmann, M.; Der, R.S.; Hudson, B.D.; Milligan, G.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Kostenis, E.; Kassack, M.U.; et al. Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1/GPR40) agonists: Mesylpropoxy appendage lowers Lipophilicity and improves ADME properties. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6624–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, N.; Sasaki, S.; Ito, M.; Kitamura, S.; Tsujihata, Y.; Ito, R.; Suzuki, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Suzuki, N.; Miyazaki, J.; et al. Identification of fused-ring alkanoic acids with improved pharmacokinetic profiles that act as g protein-coupled receptor 40/ free fatty acid receptor 1 agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, T.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Dai, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Qiang, H.; Huang, W.; Qian, H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of phenoxyacetic acid derivatives as novel free fatty acid receptor 1 agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Feng, S.; Huang, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Ge, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. A potent free fatty acid receptor 1 agonist with a glucose-dependent antihyperglycemic effect. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8975–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surwit, R.S.; Kuhn, C.M.; Cochrane, C.; McCubbin, J.A.; Feinglos, M.N. Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzell, M.S.; Ahrén, B. The high-fat diet–fed mouse: A model for studying mechanisms and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, S215–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Warne, T.; Nehmé, R.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Chaturvedi, M.; Edwards, P.C.; García-Nafría, J.; Leslie, A.G.; Shukla, A.K. Molecular basis of β-arrestin coupling to formoterol-bound β 1-adrenoceptor. Nature 2020, 583, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumm, B.E.; White, J.F.; Shah, P.; Grisshammer, R. Structural prerequisites for G-protein activation by the neurotensin receptor. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; Choi, H.-J.; Fung, J.J.; Pardon, E.; Casarosa, P.; Chae, P.S.; DeVree, B.T.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S. Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the β 2 adrenoceptor. Nature 2011, 469, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | X | clogPa | GPR120 (EC50, nM) b | GPR40 (EC50, μM) c | Selectivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUG-891 | - | - | - | - | 5.88 | 61.7 | 56.3 | 912 |
| 1f | CH3 | H | H | C | 6.45 | 146.1 | ND | ND |
| 2f | H | CH3 | H | C | 6.21 | 52.8 | 72.5 | 1373 |
| 3f | H | H | CH3 | C | 6.37 | 90.2 | ND | ND |
| 4f | H | H | F | C | 6.04 | 110.3 | ND | ND |
| 5f | H | H | H | O | 5.10 | 102.7 | ND | ND |
| 6f | H | H | CH3 | O | 5.59 | 72.7 | 58.9 | 810 |
| 7f | H | H | F | O | 5.26 | 106.2 | ND | ND |
| Compound | R | n | clogPa | GPR120 (EC50, nM) b | GPR40 (EC50, μM) c | Selectivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUG-891 | - | - | 61.7 | 56.3 | 912 | |
| 11a | H | 2 | 3.30 | 112.5 | ND | ND |
| 11b | CH3 | 2 | 3.79 | 71.2 | 82.5 | 1159 |
| 11c | CH3O | 2 | 3.18 | 99.6 | ND | ND |
| 11d | F | 2 | 3.46 | 187.4 | ND | ND |
| 11e | H | 2 | 2.68 | 254.7 | ND | ND |
| 11f | 6-F | 2 | 2.84 | 203.6 | ND | ND |
| 11g | CH3 | 2 | 3.17 | 83.4 | 86.4 | 1036 |
| 11h | CH3O | 2 | 2.55 | 145.6 | ND | ND |
| Compound | Dose (mg/kg) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (min) | AUC (ng·h/mL) | t1/2 (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUG-891 | 10 | 2160 ± 93 | 15 | 1675 ± 108 | 0.66 ± 0.23 |
| 11b | 10 | 2530 ± 115 * | 30 | 9049 ± 435 *** | 1.78 ± 0.42 ** |
| 11g | 10 | 1846 ± 102 | 30 | 6711 ± 467 *** | 1.52 ± 0.37 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, G.; Guo, Q.; Xue, Q.; Kong, R.; Wang, S.; Lei, K.; Liu, R.; Wang, X. Novel GPR120 Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2021, 26, 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226907
Ji G, Guo Q, Xue Q, Kong R, Wang S, Lei K, Liu R, Wang X. Novel GPR120 Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules. 2021; 26(22):6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226907
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Guoxia, Qinghua Guo, Qidi Xue, Ruifang Kong, Shiben Wang, Kang Lei, Renmin Liu, and Xuekun Wang. 2021. "Novel GPR120 Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes" Molecules 26, no. 22: 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226907
APA StyleJi, G., Guo, Q., Xue, Q., Kong, R., Wang, S., Lei, K., Liu, R., & Wang, X. (2021). Novel GPR120 Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Profiles for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules, 26(22), 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226907







