Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling of Blood for Untargeted Lipidomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
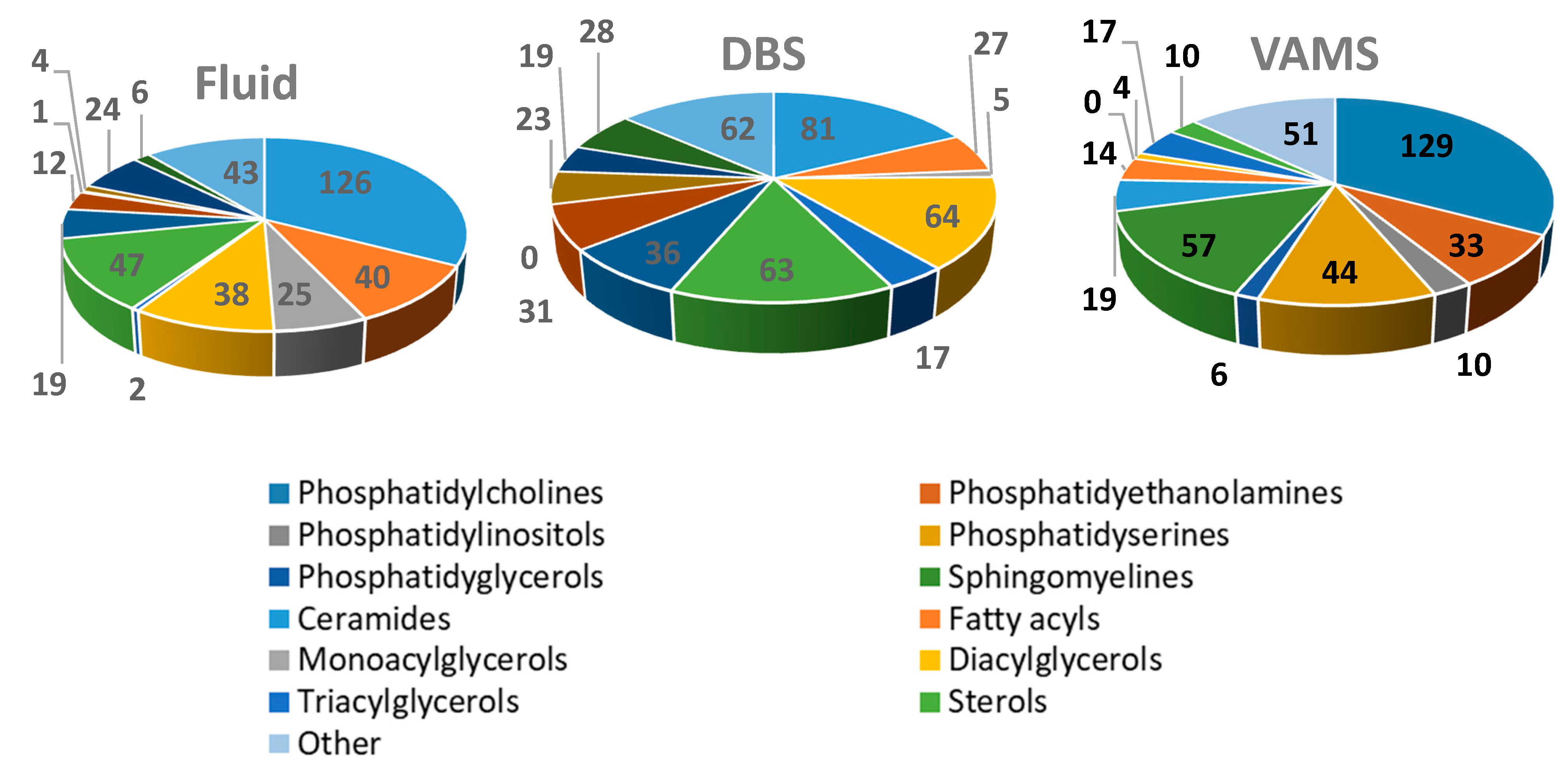
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Solvents and Instrumentation
3.2. Biological Sample Collection
3.3. Extraction of Lipids from Blood Samples
3.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.5. Data Analysis
3.6. Data Availability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wenk, M.R. The emerging field of lipidomics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afshinnia, F.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Wernisch, S.; Soni, T.; Jadoon, A.; Karnovsky, A.; Michailidis, G.; Pennathur, S. Lipidomics and Biomarker Discovery in Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herzog, K.; Pras-Raves, M.L.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Vervaart, M.A.T.; Luyf, A.C.M.; Van Kampen, A.H.C.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M. Plasma lipidomics as a diagnostic tool for peroxisomal disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 41, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.L.; Cebak, J.E. Lipidomics biomarker studies: Errors, limitations, and the future. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Y. Lipidomics: A promising cancer biomarker. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Burla, B.; Arita, M.; Arita, M.; Bendt, A.K.; Gassiot, A.C.; Dennis, E.A.; Ekroos, K.; Han, X.; Ikeda, K.; Liebisch, G.; et al. MS-based lipidomics of human blood plasma: A community-initiated position paper to develop accepted guidelines. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2001–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Zhang, J. Mass-spectrometry-based lipidomics. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 351–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zalloua, P.A.; Kadar, H.; Hariri, E.; Farraj, L.A.; Brial, F.; Hedjazi, L.; Le Lay, A.; Colleu, A.; Dubus, J.; Touboul, D.; et al. Untargeted Mass Spectrometry Lipidomics identifies correlation between serum sphingomyelins and plasma cholesterol. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 192–206. [Google Scholar]
- Baglai, A.; Gargano, A.F.; Jordens, J.; Mengerink, Y.; Honing, M.; van der Wal, S.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Comprehensive lipidomic analysis of human plasma using multidimensional liquid- and gas-phase separations: Two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry vs. liquid chromatography-trapped-ion-mobility-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1530, 90–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rampler, E.; Criscuolo, A.; Zeller, M.; El Abiead, Y.; Schoeny, H.; Hermann, G.; Sokol, E.; Cook, K.; Peake, D.A.; Delanghe, B.; et al. A Novel Lipidomics Workflow for Improved Human Plasma Identification and Quantification Using RPLC-MSn Methods and Isotope Dilution Strategies. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6494–6501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Meehan, M.J.; Blevitt, J.M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Milla, M.E. A highly efficient, high-throughput lipidomics platform for the quantitative detection of eicosanoids in human whole blood. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 433, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Lehmann, R.; Xu, G. Effects of pre-analytical processes on blood samples used in metabolomics studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4879–4892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Röhnike, S.; Empting, S.; Haas, D.; Mohnike, K.; Beblo, S.; Mütze, U.; Husain, R.A.; Thiery, J.; Ceglarek, U. LC-MS/MS-based quantification of cholesterol and related metabolites in dried blood for the screening of inborn errors of sterol metabolism. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5227–5233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Malkawi, A.; Albast, N.; Al Bougha, S.; Lopata, A.; Dasouki, M.; Rahman, A.M.A. A targeted metabolomics approach for clinical diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1025, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Koulman, A.; Prentice, P.; Wong, M.C.Y.; Matthews, L.; Bond, N.J.; Eiden, M.; Griffin, J.L.; Dunger, D.B. The development and validation of a fast and robust dried blood spot based lipid profiling method to study infant metabolism. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Dittakavi, S.; Jat, R.K.; Mullangi, R. Quantitative analysis of enasidenib in dried blood spots of mouse blood using an increased-sensitivity LC-MS/MS method: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Björkesten, J.; Enroth, S.; Shen, Q.; Wik, L.; Hougaard, D.M.; Cohen, A.S.; Sörensen, L.; Giedraitis, V.; Ingelsson, M.; Larsson, A.; et al. Stability of Proteins in Dried Blood Spot Biobanks. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Henao, J.J.A.; Metherel, A.H.; Smith, R.W.; Stark, K.D. Tailored Extraction Procedure Is Required to Ensure Recovery of the Main Lipid Classes in Whole Blood When Profiling the Lipidome of Dried Blood Spots. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9391–9396. [Google Scholar]
- Cozma, C.; Iurașcu, M.-I.; Eichler, S.; Hovakimyan, M.; Brandau, O.; Zielke, S.; Böttcher, T.; Giese, A.-K.; Lukas, J.; Rolfs, A. C26-Ceramide as highly sensitive biomarker for the diagnosis of Farber Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, J.E.; Casey, C.P.; Stratton, K.G.; Zink, E.M.; Kim, Y.-M.; Zheng, X.; Monroe, M.E.; Weitz, K.K.; Bloodsworth, K.J.; Orton, D.J.; et al. Comparing identified and statistically significant lipids and polar metabolites in 15-year old serum and dried blood spot samples for longitudinal studies. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; McDaniel, J.; Chen, E.Y.; Rockwell, H.E.; Drolet, J.; Vishnudas, V.K.; Tolstikov, V.; Sarangarajan, R.; Narain, N.R.; Kiebish, M.A. Dynamic and temporal assessment of human dried blood spot MS/MS(ALL) shotgun lipidomics analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denniff, P.; Spooner, N. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling: A Dried Sample Collection Technique for Quantitative Bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8489–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velghe, S.; Stove, C.P. Volumetric absorptive microsampling as an alternative tool for therapeutic drug monitoring of first-generation anti-epileptic drugs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verougstraete, N.; Lapauw, B.; Van Aken, S.; Delanghe, J.; Stove, C.; Stove, V. Volumetric absorptive microsampling at home as an alternative tool for the monitoring of HbA(1c) in diabetes patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Protti, M.; Mandrioli, R.; Mercolini, L. Tutorial: Volumetric absorptive microsampling (VAMS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1046, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, K.; Noritake, K.; Mano, Y. Application of a Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling Device to a Pharmacokinetic Study of Tacrolimus in Rats: Comparison with Wet Blood and Plasma. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 44, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, M.; Catapano, M.C.; Dekel, B.G.S.; Rudge, J.; Gerra, G.; Somaini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Mercolini, L. Determination of oxycodone and its major metabolites in haematic and urinary matrices: Comparison of traditional and miniaturised sampling approaches. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 152, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, M.; Rudge, J.; Sberna, A.E.; Gerra, G.; Mercolini, L. Dried haematic microsamples and LC-MS/MS for the analysis of natural and synthetic cannabinoids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1044, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mercolini, L.; Protti, M.; Catapano, M.C.; Rudge, J.; Sberna, A.E. LC-MS/MS and volumetric absorptive microsampling for quantitative bioanalysis of cathinone analogues in dried urine, plasma and oral fluid samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 123, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broek, I.; Fu, Q.; Kushon, S.; Kowalski, M.P.; Millis, K.; Percy, A.; Holewinski, R.J.; Venkatraman, V.; Van Eyk, J.E. Application of volumetric absorptive microsampling for robust, high-throughput mass spectrometric quantification of circulating protein biomarkers. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 4, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.G.; Nix, C.; Nys, G.; Fillet, M. Targeted metabolomics of whole blood using volumetric absorptive microsampling. Talanta 2019, 197, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volani, C.; Caprioli, G.; Calderisi, G.; Sigurdsson, B.B.; Rainer, J.; Gentilini, I.; Hicks, A.A.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Weiss, G.; Smarason, S.V.; et al. Pre-analytic evaluation of volumetric absorptive microsampling and integration in a mass spectrometry-based metabolomics workflow. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6263–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, N.S.; Haug, K.; Conesa, P.; Jayseelan, K.; Moreno, P.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Nainala, V.C.; Spicer, R.A.; Williams, M.; Philippe, R.-S.; et al. MetaboLights: An Open-Access Database Repository for Metabolomics Data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 53, 14.13.1–14.13.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.A.; Heckert, A.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Jones, C.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Abdullah, L.; Ahonen, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Armando, A.M.; Asara, J.M.; et al. Harmonizing lipidomics: NIST interlaboratory comparison exercise for lipidomics using SRM 1950-Metabolites in Frozen Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Sud, M.; Cotter, D.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W606–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for Comprehensive Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 55, 14.10.1–14.10.91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR: An R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goracci, L.; Tortorella, S.; Tiberi, P.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Di Veroli, A.; Valeri, A.; Cruciani, G. Lipostar, a Comprehensive Platform-Neutral Cheminformatics Tool for Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barbera, G.; Antonelli, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Cruciani, G.; Goracci, L.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A.; Capriotti, A.L. Delving into the Polar Lipidome by Optimized Chromatographic Separation, High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry, and Comprehensive Identification with Lipostar: Microalgae as Case Study. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12230–12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
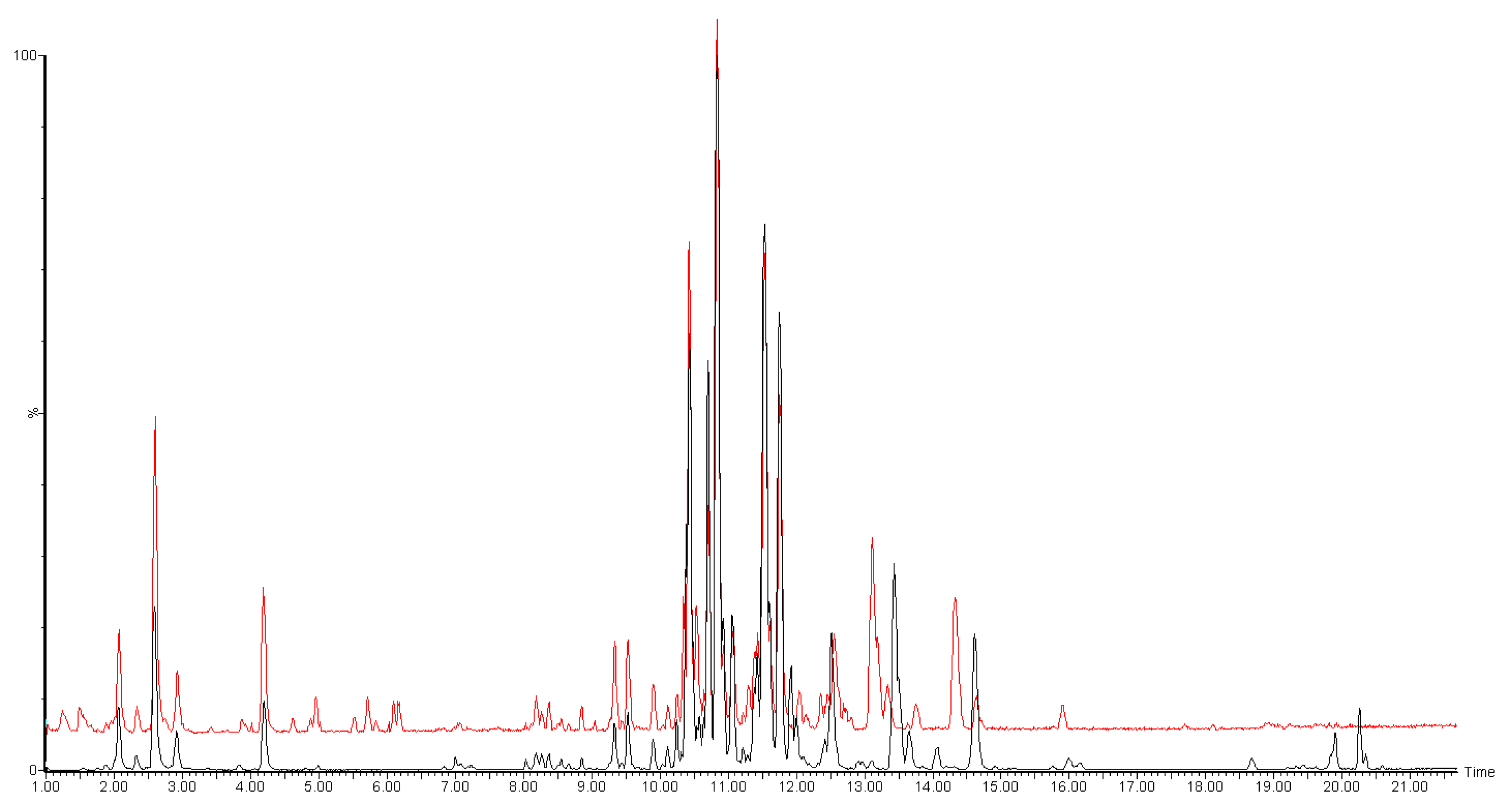
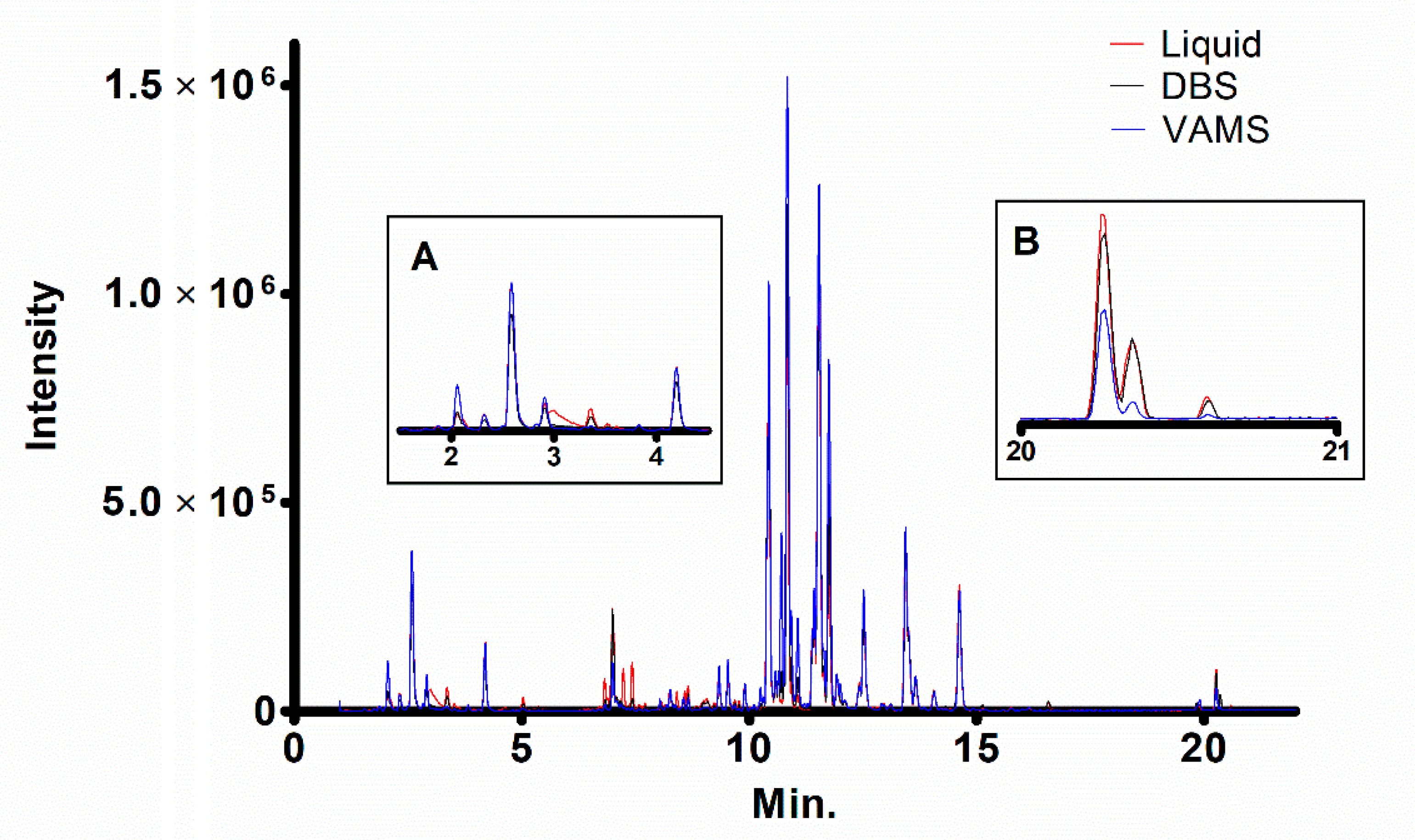

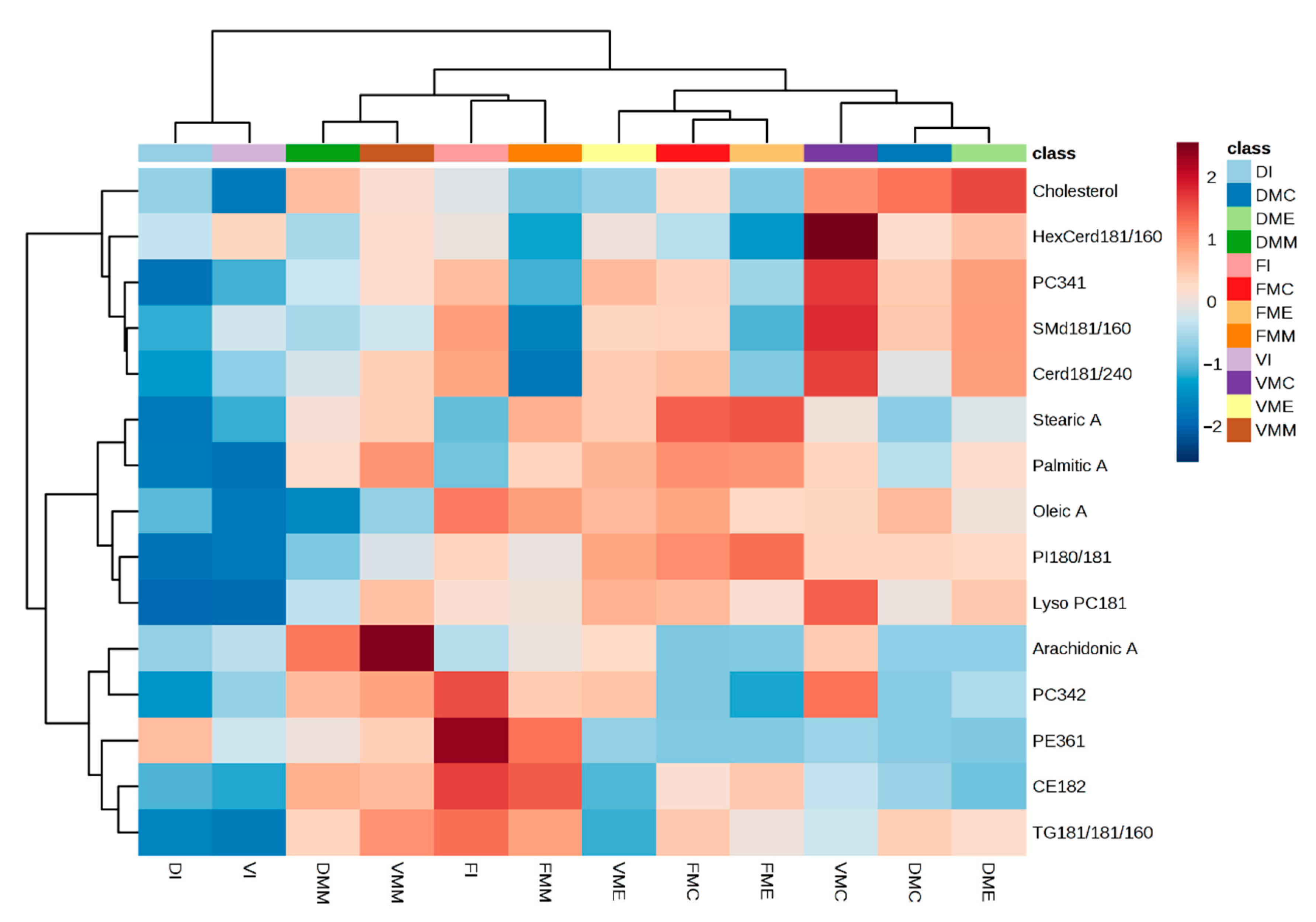
| N | Category | Lipid | Molecular Formula | LogP | m/z | Adduct | Min. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fatty Acid | Arachidonic Acid (20:4) | C20H31O2 | 6.22 | 303.23 | [M–H]− | 4.6 |
| 2 | Fatty Acid | Oleic Acid (18:1) | C18H33O2 | 6.11 | 281.24 | [M–H]− | 6.1 |
| 3 | Fatty Acid | Stearic Acid (18:0) | C18H35O2 | 6.33 | 283.20 | [M–H]− | 7.6 |
| 4 | Fatty Acid | Palmitic Acid (16:0) | C16H31O2 | 5.55 | 255.23 | [M–H]− | 5.8 |
| 5 | Phospholipid | PI (18:0/18:1) | C45H85O13P | 11.81 | 863.57 | [M–H]− | 11.2 |
| 6 | Phospholipid | Lyso PC (18:1) | C26H51NO7P | 6.56 | 520.34 | [M+H]+ | 2.0 |
| 7 | Phospholipid | PC (34:2) | C42H79NO8P | 12.37 | 756.55 | [M+H]+ | 10.3 |
| 8 | Phospholipid | PC (34:1) | C42H81NO8P | 12.59 | 758.57 | [M+H]+ | 10.8 |
| 9 | Phospholipid | PE (36:1) | C41H81NO8P | 13.43 | 746.57 | [M+H]+ | 11.0 |
| 10 | Sphingolipid | SM (d18:1/16:0) | C39H80N2O6P | 11.21 | 703.57 | [M+H]+ | 10.4 |
| 11 | Sphingolipid | HexCer (d18:1/16:0) | C40H78NO8 | 9.96 | 700.57 | [M+H]+ | 10.8 |
| 12 | Sphingolipid | Cer (d18:1/24:0) | C42H84NO3 | 13.54 | 650.64 | [M+H]+ | 16.1 |
| 13 | Sterol | Cholesterol | C27H44 | 7.68 | 369.35 | [M–H2O+H]+ | 10.3 |
| 14 | Sterol | CE (18:2) | C45H77O2 | 14.04 | 666.62 | [M+NH4]+ | 19.8 |
| 15 | Triacylglycerol | TG (16:0/18:1/18:1) | C55H106NO6 | 18.4 | 876.80 | [M+NH4]+ | 20.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marasca, C.; Arana, M.E.B.; Protti, M.; Cavalli, A.; Mercolini, L.; Armirotti, A. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling of Blood for Untargeted Lipidomics. Molecules 2021, 26, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020262
Marasca C, Arana MEB, Protti M, Cavalli A, Mercolini L, Armirotti A. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling of Blood for Untargeted Lipidomics. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020262
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarasca, Camilla, Maria Encarnacion Blanco Arana, Michele Protti, Andrea Cavalli, Laura Mercolini, and Andrea Armirotti. 2021. "Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling of Blood for Untargeted Lipidomics" Molecules 26, no. 2: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020262
APA StyleMarasca, C., Arana, M. E. B., Protti, M., Cavalli, A., Mercolini, L., & Armirotti, A. (2021). Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling of Blood for Untargeted Lipidomics. Molecules, 26(2), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020262