Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
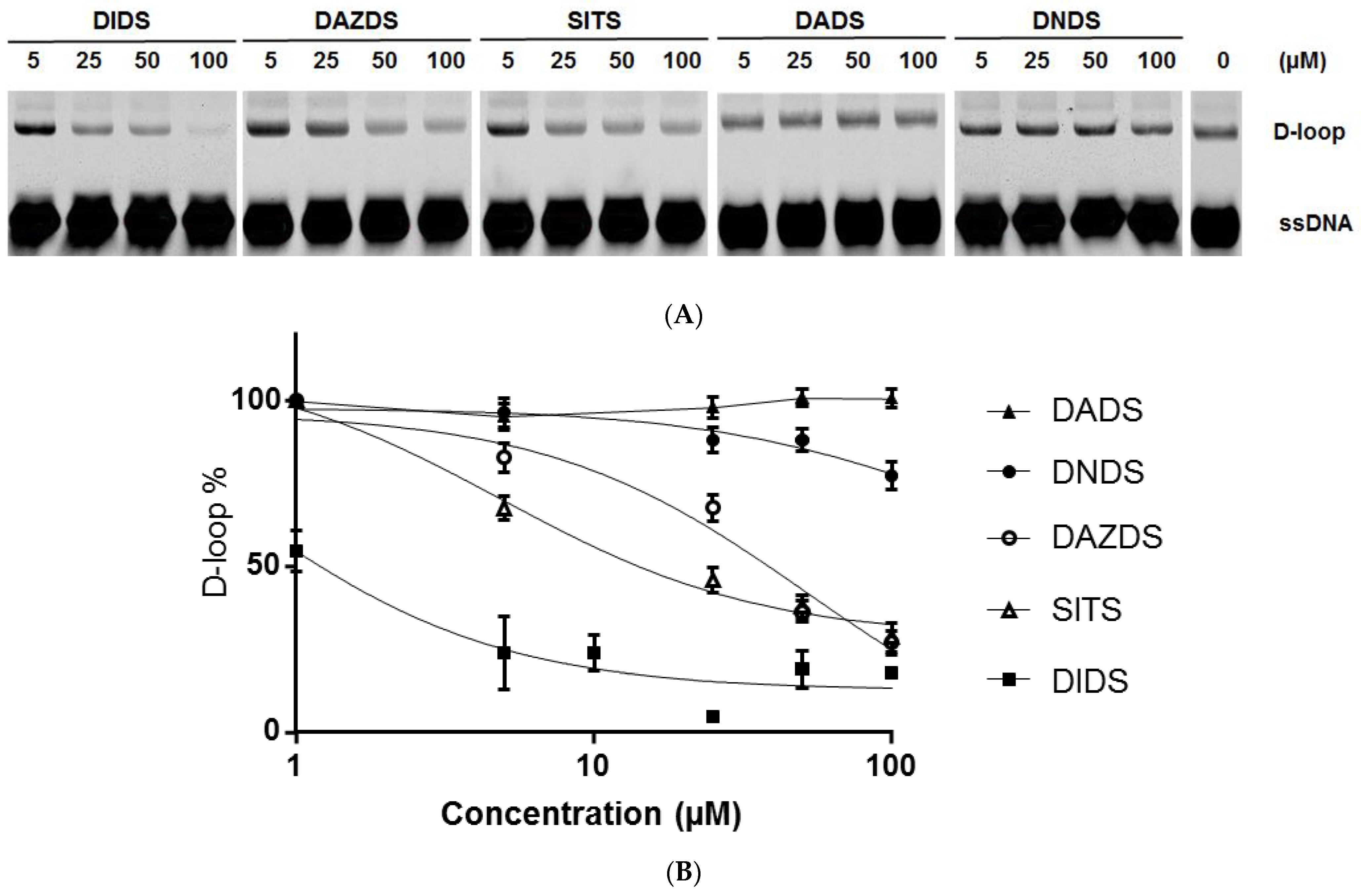
2.1. Invasion Step of RAD51 Is Impaired by DIDS Derivatives
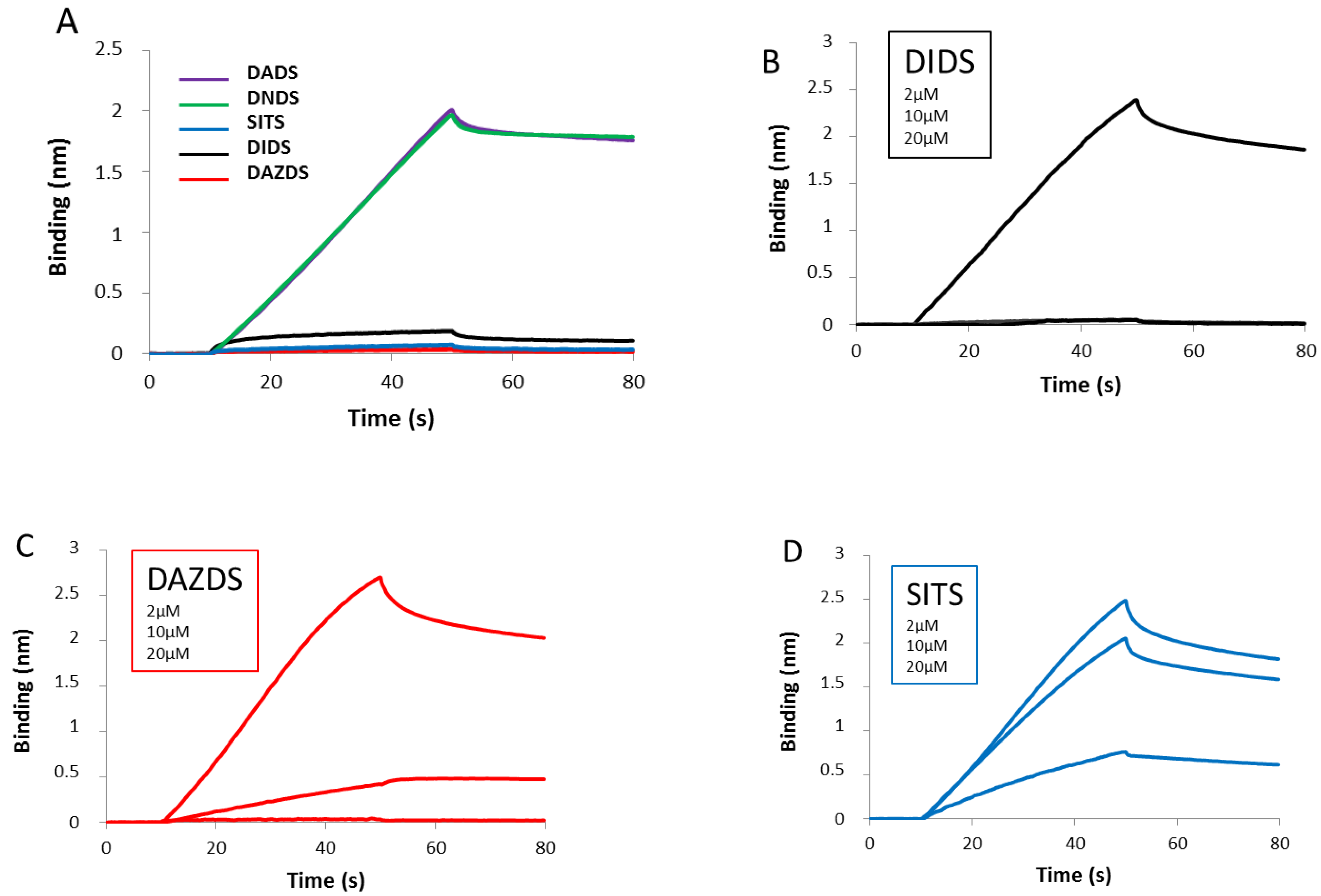
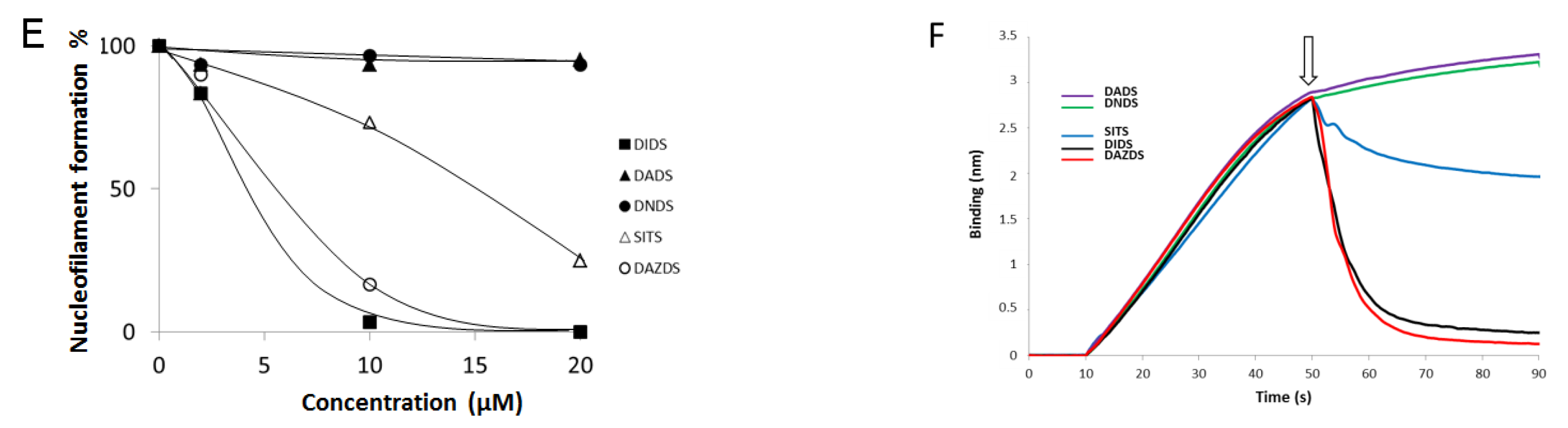
2.2. DIDS Analogs Modulate the RAD51 Nucleofilament Formation
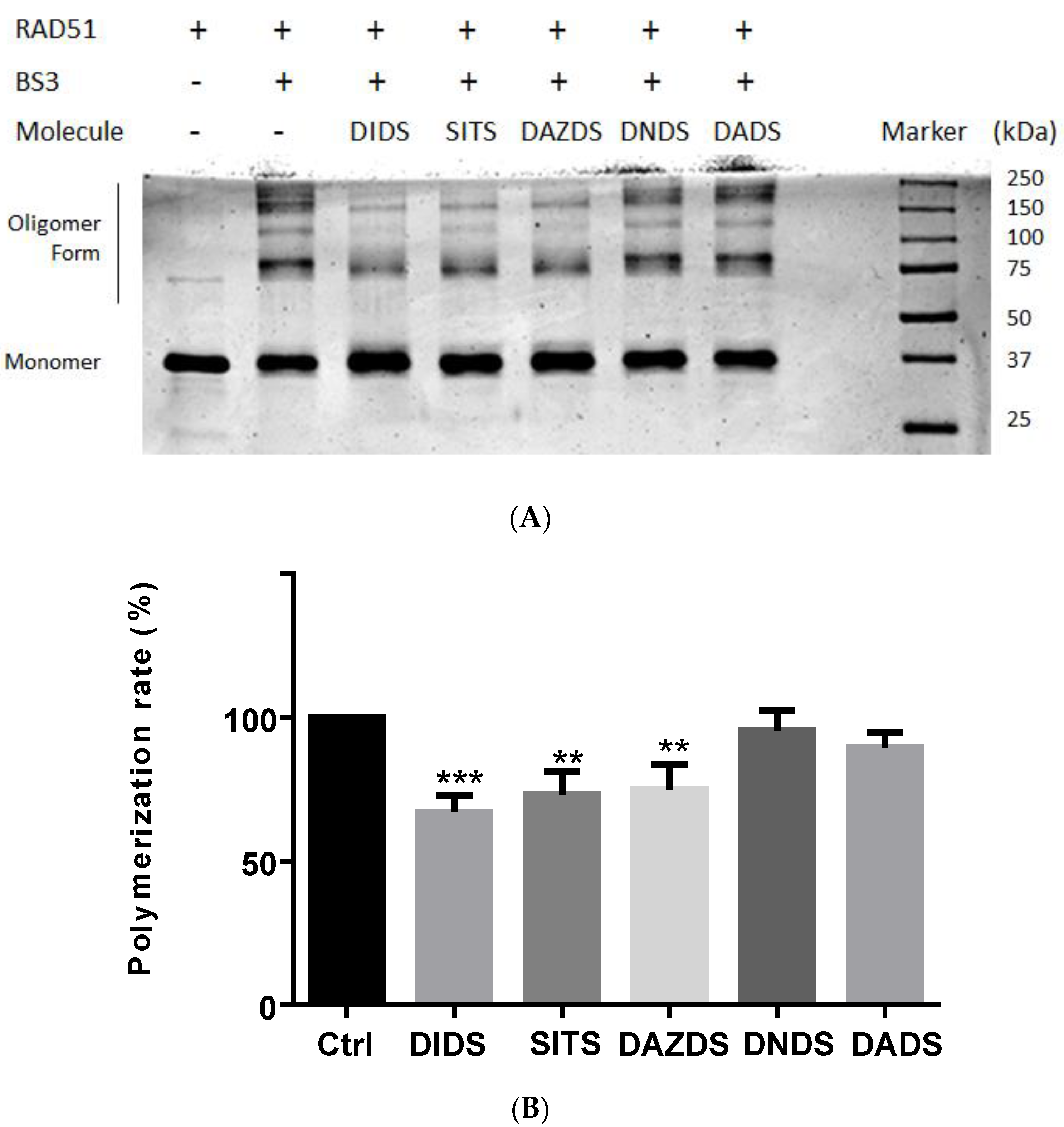
2.3. Self-Association of RAD51 Is Sensitive to Presence of DIDS Derivatives
3. Discussion
4. Material and Method
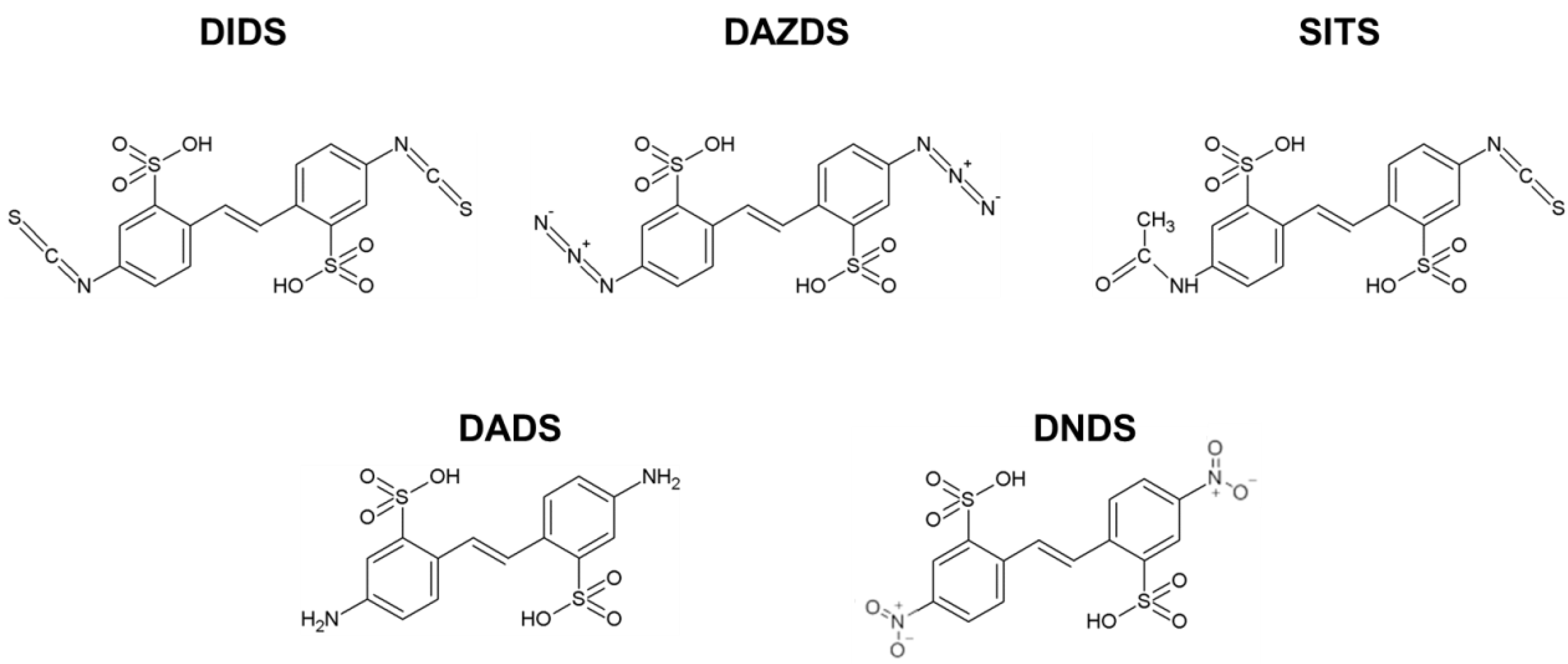
4.1. Chemical Compounds, Proteins Production and Purification
4.2. Assessment of RAD51 Self-Association by Chemical Cross Linking
4.3. Supercoiled Plasmid DNA Production
4.4. D-Loop Assay
4.5. DNA Binding Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| DIDS | 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; |
| DADS | 4,4′-diaminostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; |
| DAZDS | 4,4′-diazidostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; |
| DNDS | 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; |
| SITS | 4-acetamido-4′-isothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; |
| AZT | (azidothymidine or 1-[(2R, 4S, 5S)-4-azido-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione; |
| HR | Homologous recombination; |
| NHEJ | Non-homologous end-joining; |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline; |
| BS3 | bis-sulfosuccinimidyl suberate; |
| GAR 700 | Goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to AlexaFluor 700 nm; |
| BLItz | Bio-layer interferometry |
References
- Khanna, K.K.; Jackson, S.P. DNA double-strand breaks: Signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, P.; Goedecke, W.; Kuhfittig-Kulle, S.; Obe, G. Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair and their impact on the prevention and formation of chromosomal aberrations. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2004, 104, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.B.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response: Putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature 2000, 408, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Ünsal-Kaçmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanam, K.; Kafri, R.; Loewer, A.; Lahav, G. Quantitative live cell imaging reveals a gradual shift between DNA repair mechanisms and a maximal use of HR in mid S phase. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducy, M.; Sesma-Sanz, L.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Lashgari, A.; Gao, Y.; Brahiti, N.; Rodrigue, A.; Margaillan, G.; Caron, M.-C.; Cote, J.; et al. The Tumor Suppressor PALB2: Inside Out. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wiese, C.; Kwon, Y.; Hromas, R.; Sung, P. The BRCA Tumor Suppressor Network in Chromosome Damage Repair by Homologous Recombination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, S.J.; Satin, L.H.; Samra, H.S.; Clark, A.J. recA-like genes from three archaean species with putative protein products similar to Rad51 and Dmc1 proteins of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, Y. Crystal structure of an archaeal Rad51 homologue in complex with a metatungstate inhibitor. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6805–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesti, M.; Budzowska, M.; Baldeyron, C.; Demmers, J.; Ghirlando, R.; Kanaar, R. RAD51AP1 is a structure-specific DNA binding protein that stimulates joint molecule formation during RAD51-mediated homologous recombination. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.; Kozlov, A.G.; Lohman, T.M. Single-molecule views of protein movement on single-stranded DNA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2012, 41, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raderschall, E.; Stout, K.; Freier, S.; Suckow, V.; Schweiger, S.; Haaf, T. Elevated levels of Rad51 recombination protein in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbano, R.; Copetti, M.; Perrone, G.; Pazienza, V.; Muscarella, L.A.; Balsamo, T.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Ripoli, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Valori, V.M.; et al. High RAD51 mRNA expression characterize estrogen receptor-positive/progesteron receptor-negative breast cancer and is associated with patient’s outcome. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maacke, H.; Opitz, S.; Jost, K.; Hamdorf, W.; Henning, W.; Feller, A.C.; Lopens, A.; Diedrich, K.; Schwinger, E. Over-expression of wild-type Rad51 correlates with histological grading of invasive ductal breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Taki, T.; Hiraga, S.; Arita, N.; Morita, T. In vitro and in vivo potentiation of radiosensitivity of malignant gliomas by antisense inhibition of the RAD51 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 245, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collis, S.J.; Tighe, A.; Scott, S.; Roberts, S.A.; Hendry, J.H.; Margison, G.P. Ribozyme minigene-mediated RAD51 down-regulation increases radiosensitivity of human prostate cancer cells. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Nimura, K.; Hiraoka, K.; Tamai, K.; Kaneda, Y. Rad51 siRNA delivered by HVJ envelope vector enhances the anti-cancer effect of cisplatin. J. Gene Med. 2005, 7, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velic, D.; Couturier, A.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Rodrigue, A.; Poirier, G.G.; Fleury, F.; Masson, J.-Y. DNA Damage Signalling and Repair Inhibitors: The Long-Sought-After Achilles’ Heel of Cancer. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 3204–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Takizawa, Y.; Kainuma, T.; Inoue, J.; Mikawa, T.; Shibata, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tashiro, S.; Kurumizaka, H. DIDS, a chemical compound that inhibits RAD51-mediated homologous pairing and strand exchange. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, K.R.; Hasham, M.G.; Donghia, N.M.; Branca, J.; Chavaree, M.; Chase, B.; Breggia, A.; Hedlund, J.; Emery, I.; Cavallo, F.; et al. Attenuating homologous recombination stimulates an AID-induced antileukemic effect. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Fagarasan, S.; Yamada, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Honjo, T. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 2000, 102, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Jimenez-Sainz, J.; Jensen, R.B.; Mazin, A.V. The Post-Synaptic Function of Brca2. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Bearss, D.J.; Browne, L.W.; Calaluce, R.; Nagle, R.B.; Von Hoff, D.D. Identification of differentially expressed genes in pancreatic cancer cells using cDNA microarray. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, L.; Yu, D.S.; Lo, T.; Anand, S.; Lee, M.; Blundell, T.L.; Venkitaraman, A.R. Insights into DNA recombination from the structure of a RAD51-BRCA2 complex. Nature 2002, 420, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.T.; Lundin, C.; Spang-Thomsen, M.; Helleday, T. The role of RAD51 in etoposide (VP16) resistance in small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennstedt, P.; Fresow, R.; Simon, R.; Marx, A.; Terracciano, L.; Petersen, C.; Sauter, G.; Dikomey, E.; Borgmann, K. RAD51 overexpression is a negative prognostic marker for colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegmans, A.P.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Chee, N.; Yap, P.-Y.; Gorski, J.J.; Da Silva, L.; Bolderson, E.; Chenevix-Trench, G.; Anderson, R.; Simpson, P.; et al. Rad51 supports triple negative breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget. 2014, 5, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeyer, A.; Benhelli-Mokrani, H.; Chénais, B.; Weigel, P.; Fleury, F. Inhibiting homologous recombination by targeting RAD51 protein. BBA Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188597. [Google Scholar]
- Matulef, K.; Howery, A.E.; Tan, L.; Kobertz, W.R.; Du Bois, J.; Maduke, M. Discovery of potent CLC chloride channel inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Chemistry in living systems. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R.J. The medicinal chemistry of the azido group. Prog. Med. Chem. 1994, 31, 121–232. [Google Scholar]
- Nomme, J.; Takizawa, Y.; Martinez, S.F.; Renodon-Cornière, A.; Fleury, F.; Weigel, P.; Yamamoto, K.-I.; Kurumizaka, H.; Takahashi, M. Inhibition of filament formation of human Rad51 protein by a small peptide derived from the BRC-motif of the BRCA2 protein. Genes Cells 2008, 13, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Fioretti, F.M.; Fucci, L.; Ausió, J.; Piscopo, M. High efficiency method to obtain supercoiled DNA with a commercial plasmid purification kit. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Molecules | DADS | DNDS | DIDS | DAZDS | SITS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | >100 | >100 | 0.9 | 41.3 | 29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velic, D.; Demeyer, A.; Peterlini, T.; Benhelli-Mokrani, H.; Mathé-Allainmat, M.; Masson, J.-Y.; Fleury, F. Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185460
Velic D, Demeyer A, Peterlini T, Benhelli-Mokrani H, Mathé-Allainmat M, Masson J-Y, Fleury F. Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity. Molecules. 2021; 26(18):5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185460
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelic, Denis, Alexandre Demeyer, Thibaut Peterlini, Houda Benhelli-Mokrani, Monique Mathé-Allainmat, Jean-Yves Masson, and Fabrice Fleury. 2021. "Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity" Molecules 26, no. 18: 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185460
APA StyleVelic, D., Demeyer, A., Peterlini, T., Benhelli-Mokrani, H., Mathé-Allainmat, M., Masson, J.-Y., & Fleury, F. (2021). Molecular Determinant of DIDS Analogs Targeting RAD51 Activity. Molecules, 26(18), 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185460






