Synthesis of Novel Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates and Antitumor Activity Evaluation: Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Toxicity in Non-Tumor Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates 2a–2o
2.2. Cell Growth Inhibitory Effect of Compounds 2a–2o on AGS, CaCo-2, MCF7, NCI-H460 Cell Lines and on a Non-Tumor Cell Line (Vero)
2.3. Effects of Compounds 2b, 2f, and 2g on AGS Cell Cycle Profile
2.4. Effect of Compounds 2b, 2f, and 2g on Induction of Apoptosis in AGS Cell Line
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of Methyl 7-Bromothieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (1b)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Diarylamines Using Reaction Conditions A
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Diarylamines Using Reaction Conditions B
Methyl 7-(Phenylamino)thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2a)
Methyl 7-[(2-Methoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2b)
Methyl 7-[(3-Methoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2c)
Methyl 7-[(4-Methoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2d)
Methyl 7-[(2,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2e)
Methyl 7-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2f)
Methyl 7-[(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2g)
Methyl 7-[(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2h)
Methyl 7-[(2-Fluorophenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2i)
Methyl 7-[(3-Fluorophenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2j)
Methyl 7-[(4-Fluorophenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2k)
Methyl 7-[(Pyridin-3-yl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2l)
Methyl 7-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2m)
Methyl 7-[(4-Cyanophenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2n)
Methyl 7-[(2-Nitrophenyl)amino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylate (2o)
3.2. In Vitro Antitumor Evaluation
3.2.1. Cell Growth Inhibition Assay (SRB Assay)
3.2.2. Flow Cytometric: Cell Cycle Analysis
3.2.3. Flow Cytometric: Apoptosis Detection
3.2.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hartwig, J.F. Transition Metal Catalyzed Synthesis of Arylamines and Aryl Ethers from Aryl Halides and Triflates: Scope and Mechanism. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2046–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, J.P.; Wagaw, S.; Marcoux, J.-F.; Buchwald, S.L. Rational Development of Practical Catalysts for Aromatic Carbon−Nitrogen Bond Formation. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.H.; Buchwald, S.L. Palladium-catalyzed amination of aryl halides and sulfonates. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 576, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlummer, B.; Scholz, U. Palladium-Catalyzed C-N and C-O Coupling–A Practical Guide from an Industrial Vantage Point. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1599–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, S.L.; Mauger, C.; Mignani, G.; Scholz, U. Industrial-Scale Palladium-Catalyzed Coupling of Aryl Halides and Amines –A Personal Account. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, J.-P.; Mignani, G. Selected Patented Cross-Coupling Reaction Technologies. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2651–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torborg, C.; Beller, M. Recent Applications of Palladium-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions in the Pharmaceutical, Agrochemical, and Fine Chemical Industries. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 3027–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surry, D.S.; Buchwald, S.L. Dialkylbiaryl phosphines in Pd-catalyzed amination: A user’s guide. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundgren, R.J.; Stradiotto, M. Addressing Challenges in Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions Through Ligand Design. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 9758–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Castillo, P.; Buchwald, S.L. Applications of Palladium-Catalyzed C–N Cross-Coupling Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, M.M.; Kheilkordi, Z.; Zadsirjan, V.; Haydari, M.; Malmir, M. Buchwald-Hartwig reaction: An overview. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 861, 17–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorel, R.; Grugel, C.P.; Haydl, A.M. The Buchwald–Hartwig Amination After 25 Years. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17118–17129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buskes, M.J.; Blanco, M.-J. Impact of Cross-Coupling Reactions in Drug Discovery and Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.C.; Reiter, A. Studies on the molybdenum cofactor. An unequivocal total synthesis of (.+-.)-urothione. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Altman, M.D.; Gibeau, C.R. Thienopyrazine Inhibitors of IRAK4 Activity. WO Patent 2016144849, 15 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, D.J.; Bair, K.W.; Caravella, J.A.; Ioannidis, S.; Lancia, D.R., Jr.; Li, H.; Mischke, S.; Ng, P.Y.; Richard, D.; Sciller, S.E.R.; et al. Thienopyrazine Carboxamides as Ubiquitin-Specific Proteases Inhibitors. WO Patent 2017139779, 17 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, B.J.B.; de Man, A.P.A.; Gernette, E.S.; Azevedo, R.C.R.G.; Ibrahim, H. Thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine Compounds as B-Raf Inhibitors. WO Patent 2011147764, 1 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, M.-J.R.P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Pinto, E.; Nascimento, M.S.-J. Novel 6-[(hetero)arylamino]thieno[3,2-b]pyridines: Synthesis and antitumoral activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5732–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.-J.R.P.; Peixoto, D.; Calhelha, R.C.; Soares, P.; dos Santos, T.; Lima, R.T.; Campos, J.F.; Abreu, R.M.V.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. New di(hetero)arylethers and di(hetero)arylamines in the thieno[3,2-b]pyridine series: Synthesis, growth inhibitory activity on human tumor cell lines and non-tumor cells, effects on cell cycle and on programmed cell death. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Peixoto, D.; Abreu, R.M.V.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Pinto, E.; Lima, R.T.; Alvelos, M.I.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Queiroz, M.-J.R.P. Aminodi(hetero)arylamines in the Thieno[3,2-b]pyridine Series: Synthesis, Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Evaluation of Toxicity Using Non-Tumor Cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 3834–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, G.; Quintela, J.M.; Peinador, C. Application of the aza-Wittig reaction to the synthesis of pyrazinothienotriazolopyrimidinones: A new tetracyclic ring system. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.M.; Buisson, P.; Pereira, J.M.; Pinheiro, I.M.; Fernández-Marcelo, T.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Berteina-Raboin, S.; Queiroz, M.-J.R.P. Synthesis of novel 8-(het)aryl-6H-pyrano[4′,3′:4,5]thieno[3,2-b] pyridines by 6-endo-dig cyclization of Sonogashira products and halolactonizations with Cu salts/NXS. Preliminary antitumor evaluation. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, M.M.; Huffman, M.A.; McNamara, J.M. Pd-Catalyzed N-Arylation of Heteroarylamines. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3481–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.; Da Cunha, D.C.; Barros, L.; Caires, H.R.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Eucalyptus globulus Labill. decoction extract inhibits the growth of NCI-H460 cells by increasing the p53 levels and altering the cell cycle profile. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, S.; Resende, D.; Kijjoa, A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pina, A.; Fernandez-Marcelo, T.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.M.M. Antitumor activity of quinazolinone alkaloids inspired by marine natural products. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phang, C.-P.; Karsani, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Malek, S.N.A. Flavokawain C Inhibits Cell Cycle and Promotes Apoptosis, Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Regulation of MAPKs and Akt Signaling Pathways in HCT 116 Human Colon Carcinoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esmaeelian, B.; Benkendorff, K.; Johnston, M.R.; Abbott, C.A. Purified Brominated Indole Derivatives from Dicathais orbita Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3802–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
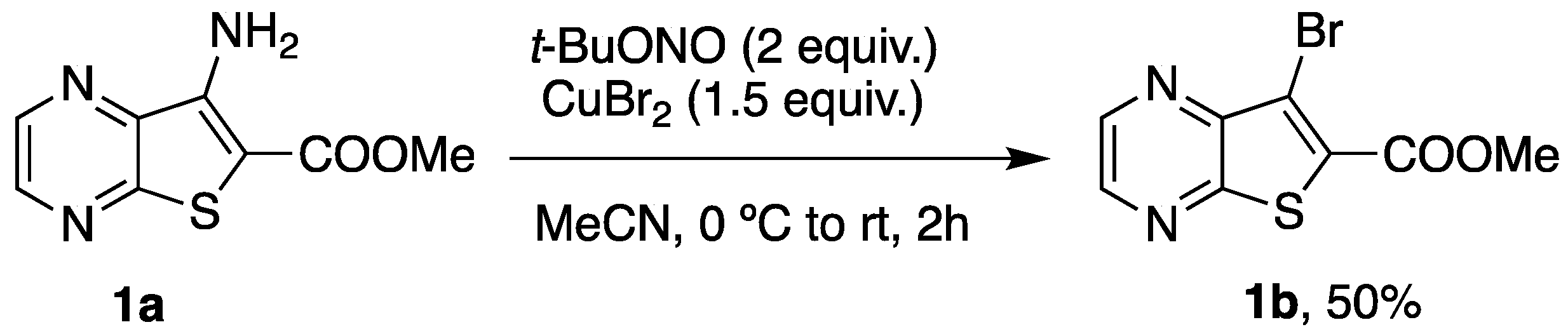




 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Precursor, Conditions | Compounds 2 | Entry | Precursor, Conditions | Compounds 2 |
| 1 | 1a, A |  | 9 | 1b, B |  |
| 2 | 1b, B |  | 10 | 1b, B |  |
| 3 | 1b, B |  | 11 | 1b, B |  |
| 4 | 1b, B |  | 12 | 1a, A |  |
| 5 | 1b, B |  | 13 | 1b, B |  |
| 6 | 1b, B |  | 14 | 1a, A |  |
| 7 | 1b, B |  | 15 | 1a, A |  |
| 8 | 1b, B |  | |||
| GI50 (µM) 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds 2 | AGS | CaCo-2 | MCF-7 | NCI-H460 | Vero |
| 2a | 95 ± 9 | 38 ± 2 | 97 ± 2 | 122 ± 9 | 120 ± 6 |
| 2b | 9.8 ± 0.2 | 36 ± 2 | 127 ± 9 | 45 ± 1 | 21.29 ± 0.03 |
| 2c | 98 ± 3 | 56 ± 1 | 160 ± 6 | 96 ± 1 | 94 ± 3 |
| 2d | 59 ± 3 | 60 ± 2 | 136 ± 3 | 52.8 ± 0.3 | 127 ± 3 |
| 2e | 34 ± 2 | 56 ± 2 | 140 ± 7 | 200 ± 3 | 138 ± 8 |
| 2f | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 8 ± 1 | 87 ± 1 | 41 ± 3 | 53 ± 3 |
| 2g | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 38 ± 4 | 182 ± 5 | 120 ± 10 | 144 ± 10 |
| 2h | 33 ± 3 | 9.2 ± 0.3 | 105.7 ± 0.5 | 77 ± 6 | 53 ± 5 |
| 2i | 48 ± 4 | 88.4 ± 0.2 | 128 ± 5 | 76 ± 1 | 117 ± 10 |
| 2j | 86 ± 6 | 142 ± 11 | 96 ± 6 | 69 ± 7 | 149 ± 4 |
| 2k | 118 ± 2 | 62 ± 4 | 160 ± 7 | 84 ± 2 | 149 ± 7 |
| 2l | 63.3 ± 0.1 | 45 ± 3 | 116 ± 5 | 122 ± 11 | 110 ± 5 |
| 2m | 88.6 ± 0.1 | 43.3 ± 0.3 | 128 ± 2 | 49 ± 2 | 140 ± 12 |
| 2n | 39 ± 3 | 10.9 ± 0.4 | 103 ± 2 | 105 ± 8 | 48 ± 4 |
| 2o | 55.0 ± 0.3 | 31.2 ± 0.2 | 103 ± 3 | 43 ± 2 | 92 ± 8 |
| Ellipticine (positive control) | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.020 ± 0.004 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, J.M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Nogueira, A.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L.; Queiroz, M.-J.R.P. Synthesis of Novel Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates and Antitumor Activity Evaluation: Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Toxicity in Non-Tumor Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164823
Rodrigues JM, Calhelha RC, Nogueira A, Ferreira ICFR, Barros L, Queiroz M-JRP. Synthesis of Novel Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates and Antitumor Activity Evaluation: Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Toxicity in Non-Tumor Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164823
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Juliana M., Ricardo C. Calhelha, António Nogueira, Isabel C. F. R. Ferreira, Lillian Barros, and Maria-João R. P. Queiroz. 2021. "Synthesis of Novel Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates and Antitumor Activity Evaluation: Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Toxicity in Non-Tumor Cells" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164823
APA StyleRodrigues, J. M., Calhelha, R. C., Nogueira, A., Ferreira, I. C. F. R., Barros, L., & Queiroz, M.-J. R. P. (2021). Synthesis of Novel Methyl 7-[(Hetero)arylamino]thieno[2,3-b]pyrazine-6-carboxylates and Antitumor Activity Evaluation: Effects in Human Tumor Cells Growth, Cell Cycle Analysis, Apoptosis and Toxicity in Non-Tumor Cells. Molecules, 26(16), 4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164823










