Lichen-Derived Depsides and Depsidones Modulate the Nrf2, NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
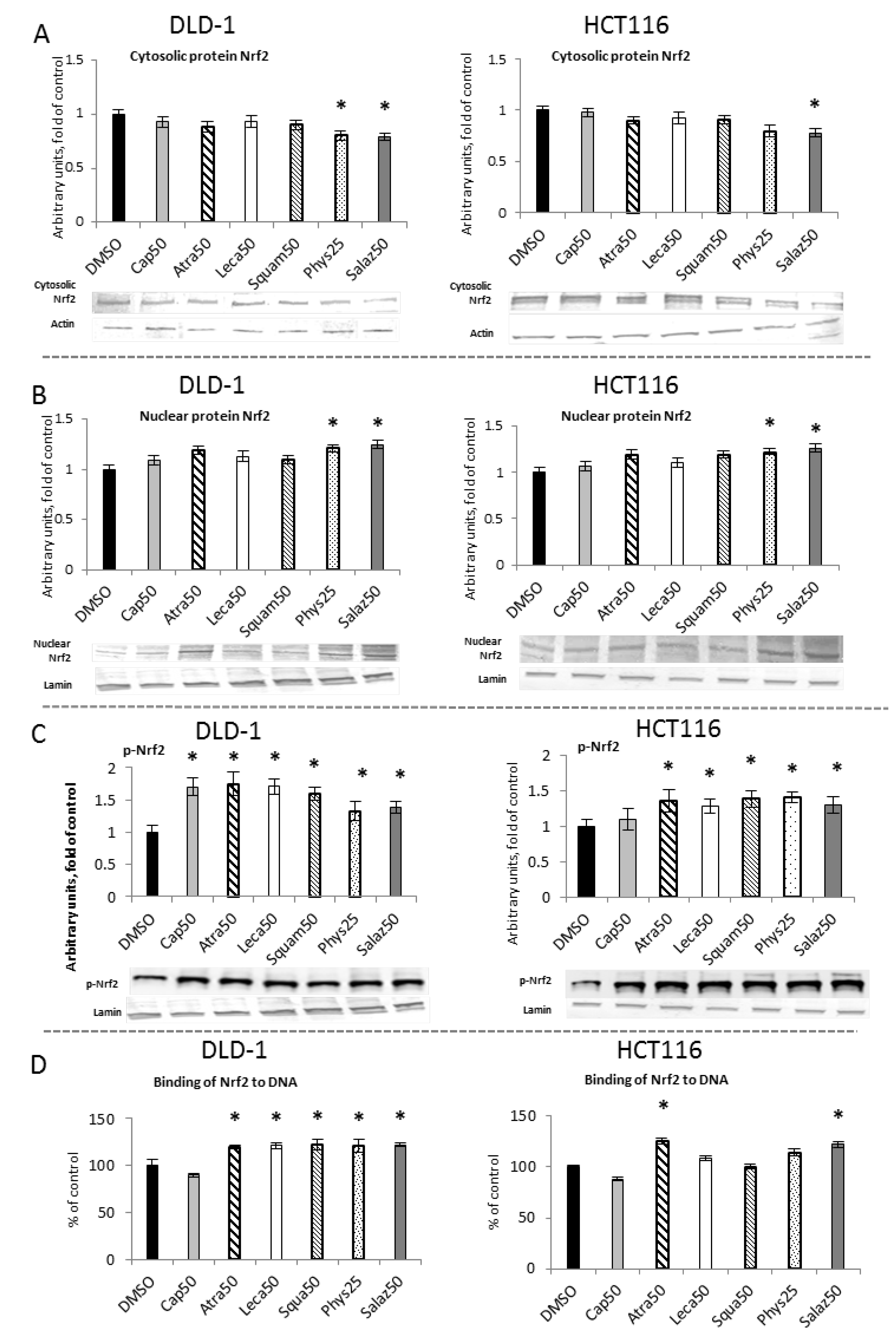
2.1. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Activation of the Nrf2
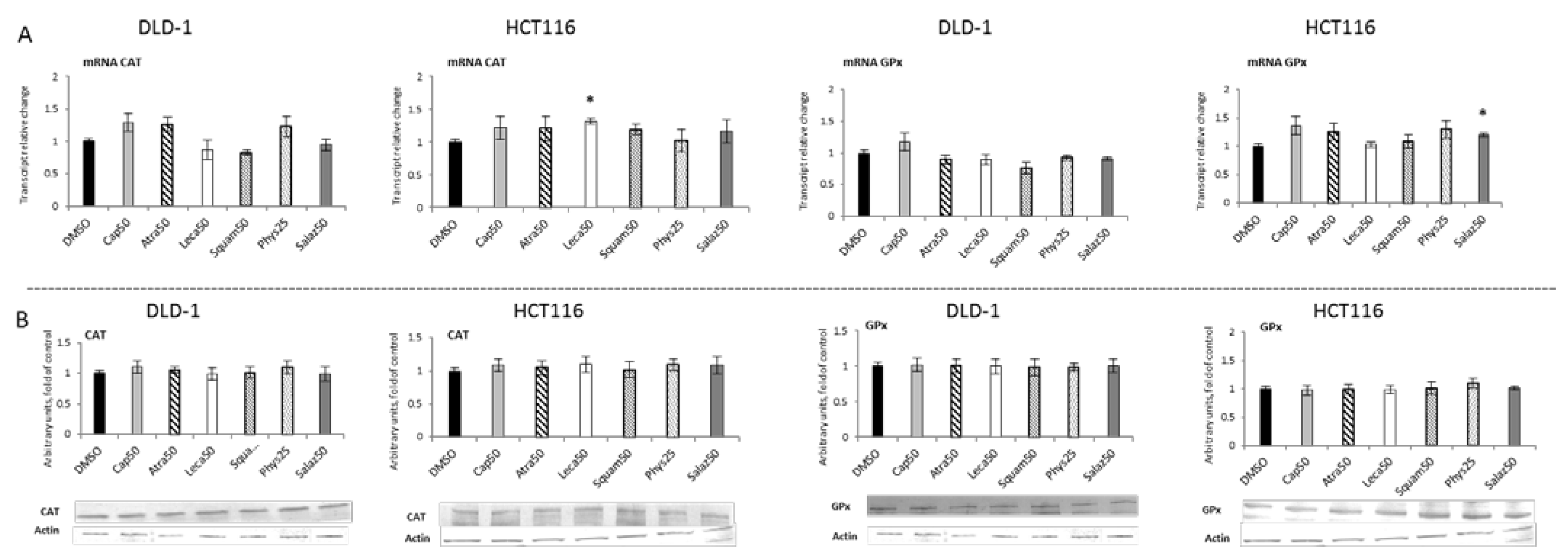
2.2. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Expression of Nrf2-Dependent Genes
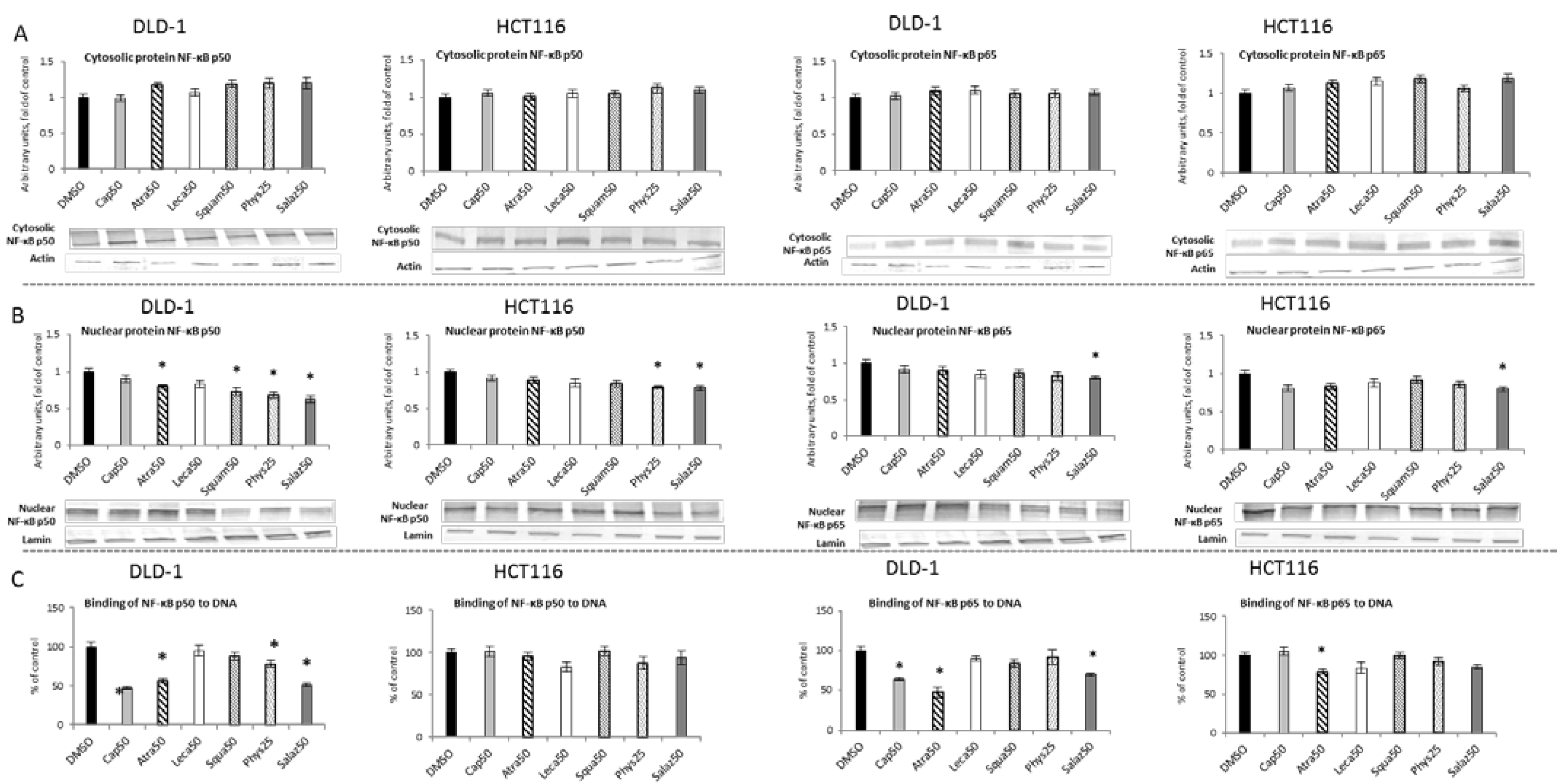
2.3. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Activation of the NF-κB
2.4. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Expression of NF-κB-Dependent Genes
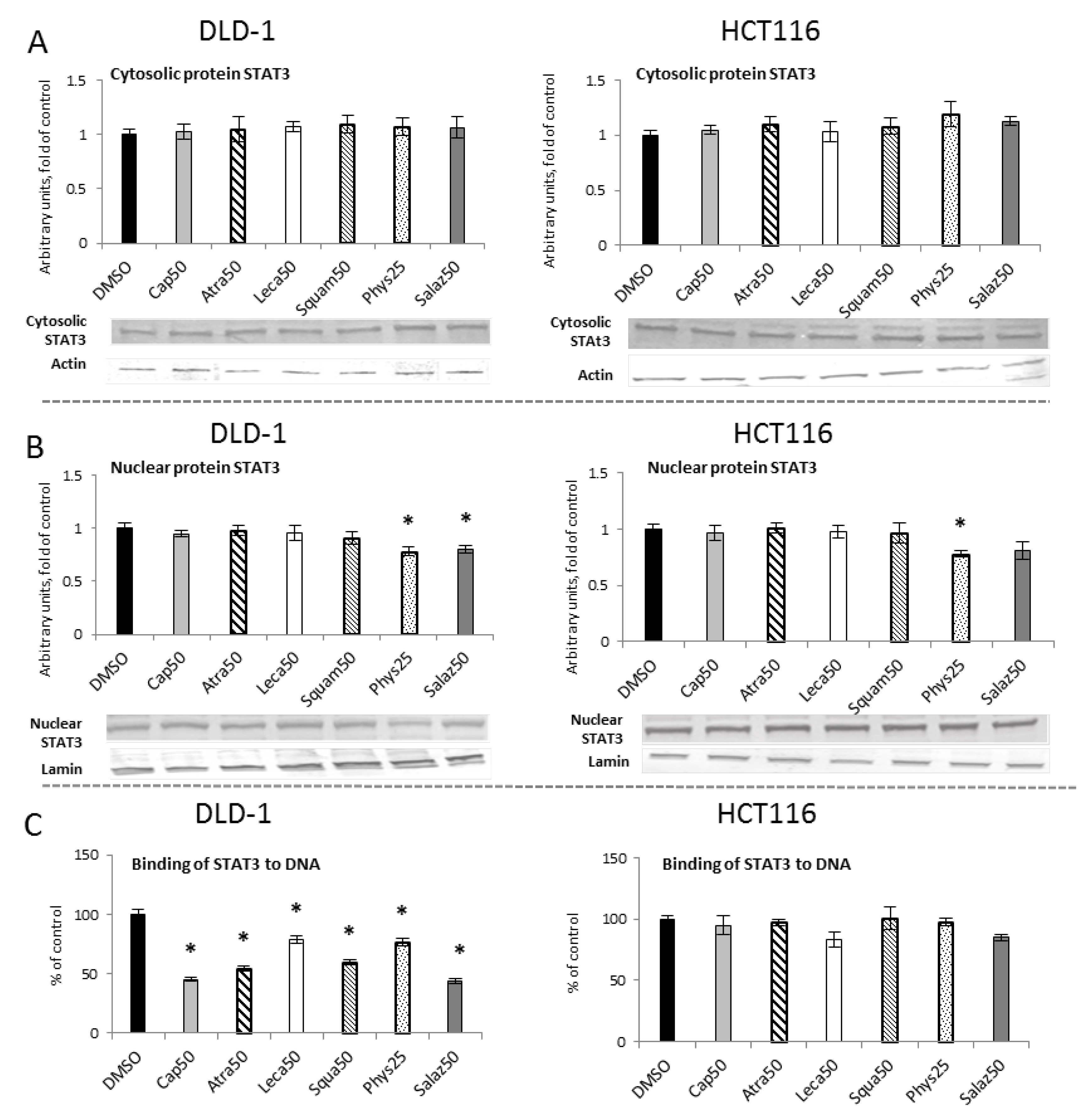
2.5. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Activation of the STAT3
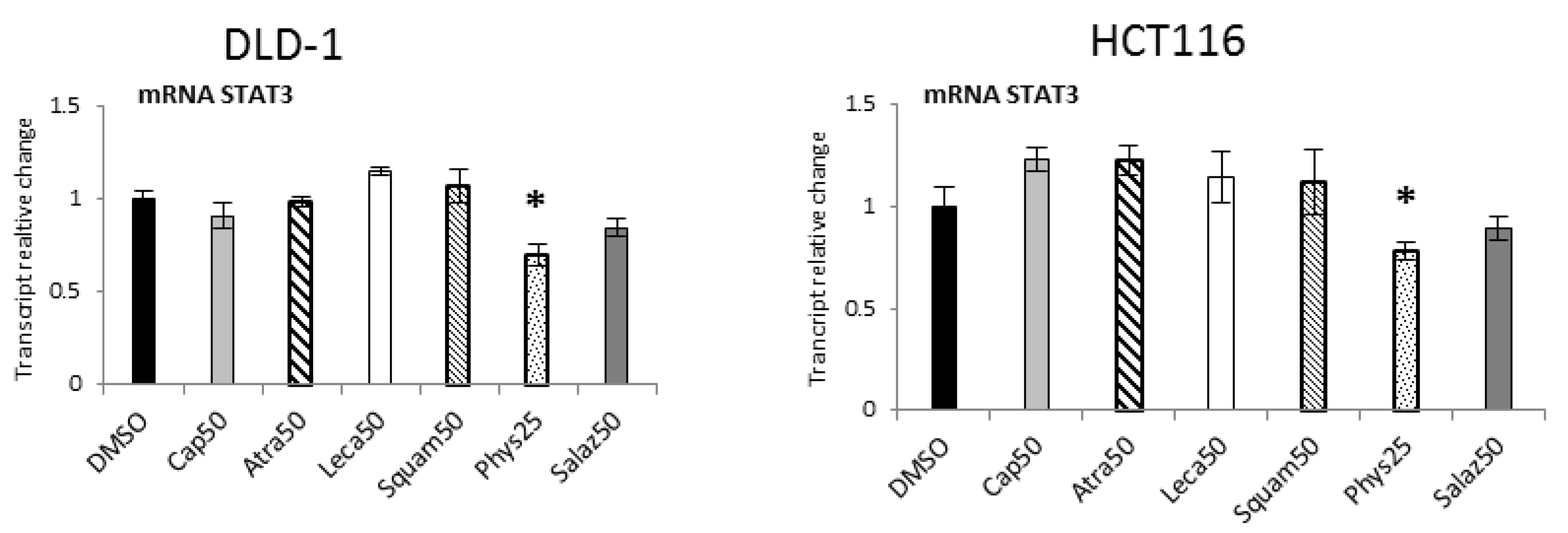
2.6. The Effect of Lichen Secondary Metabolites on the Expression of STAT3-Dependent Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
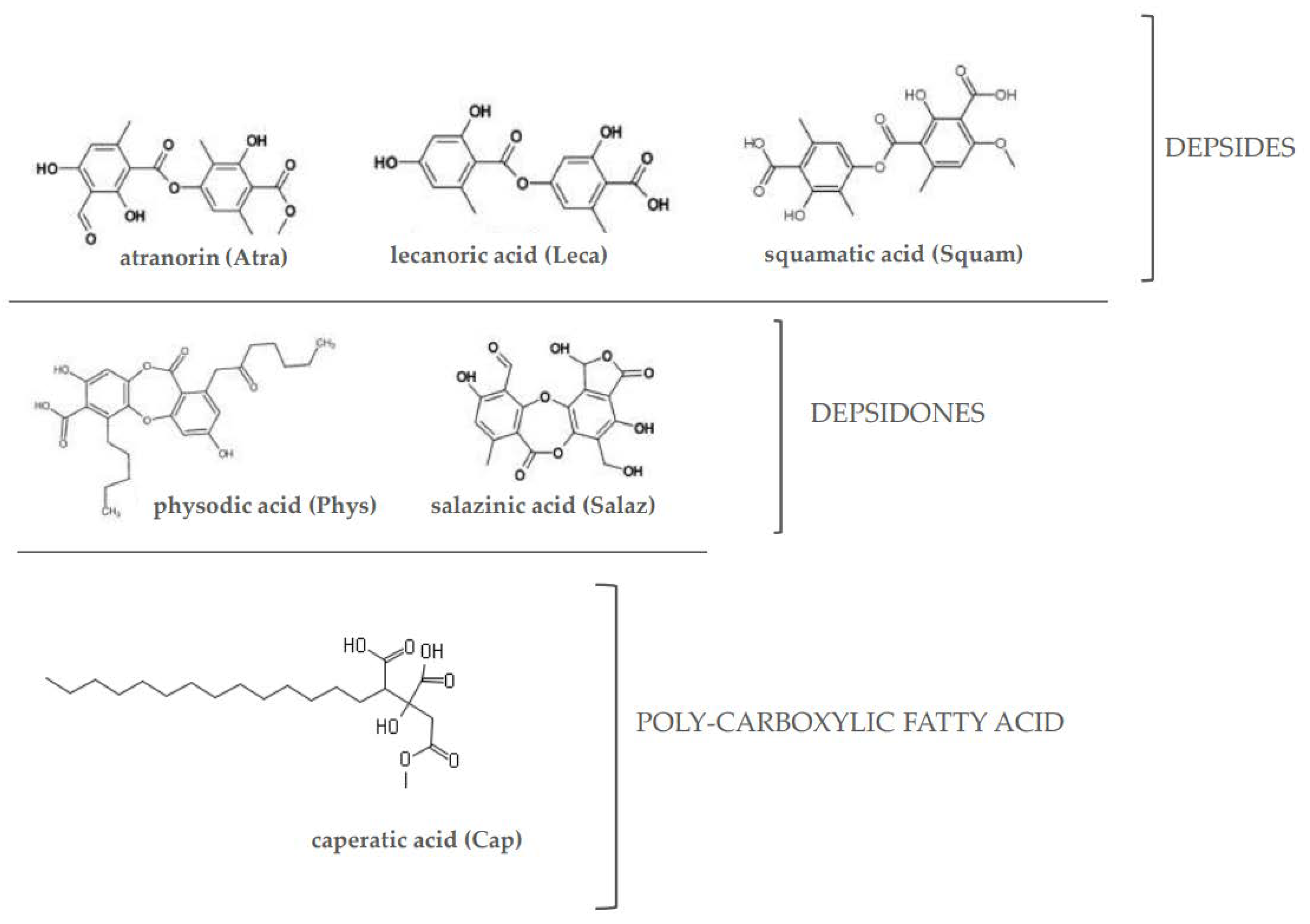
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Cell Fractionation and Preparation of RNA
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. ELISA Assay
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (R-T PCR)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Honegger, R. The Lichen Symbiosis—What Is so Spectacular about It? Lichenologist 1998, 30, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker-Wörgötter, E. Metabolic Diversity of Lichen-Forming Ascomycetous Fungi: Culturing, Polyketide and Shikimate Metabolite Production, and PKS Genes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardile, V.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Avola, R.; Piovano, M.; Russo, A. Potential Anticancer Activity of Lichen Secondary Metabolite Physodic Acid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 263, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Piotrowska, H.; Kucińska, M.; Murias, M.; Bylka, W. Cytotoxic Activity of Physodic Acid and Acetone Extract from Hypogymnia Physodes against Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, M.G.D.; dos Santos, J.P.A.; Serafini, M.R.; Caregnato, F.F.; de Bittencourt Pasquali, M.A.; Rabelo, T.K.; da Rocha, R.F.; Quintans, L.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; da Silva, F.A.; et al. Redox Properties and Cytoprotective Actions of Atranorin, a Lichen Secondary Metabolite. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosanić, M.; Manojlović, N.; Janković, S.; Stanojković, T.; Ranković, B. Evernia Prunastri and Pseudoevernia Furfuraceae Lichens and Their Major Metabolites as Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Agents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.R.; Hur, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, K.W.; Park, S.C.; Seong, C.N.; Jeong, I.Y.; Byun, M.W.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Anti-Proliferative Effects of Lethariella Zahlbruckneri Extracts in Human HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hu, Y.; Winter, J.; Young, G.P. Anti-Mutagenic Lichen Extract Has Double-Edged Effect on Azoxymethane-Induced Colorectal Oncogenesis in C57BL/6J Mice. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2010, 20, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, G.; Clair, L.L. Lichens: A Promising Source of Antibiotic and Anticancer Drugs. Phytochem. Rev. 2013, 12, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszczak, J.; Kleszcz, R.; Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V. Lichen-Derived Caperatic Acid and Physodic Acid Inhibit Wnt Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 441, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manigandan, K.; Manimaran, D.; Jayaraj, R.L.; Elangovan, N.; Dhivya, V.; Kaphle, A. Taxifolin Curbs NF-ΚB-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling via up-Regulating Nrf2 Pathway in Experimental Colon Carcinogenesis. Biochimie 2015, 119, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The Complexity of NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Paluszczak, J.; Baer-Dubowska, W. The Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway: An Update on Its Regulation and Possible Role in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kong, A.N. Molecular Mechanisms of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Velasco, D.; de Sagarra, R.M.; Cuadrado, A. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Inhibits the Xenobiotic and Antioxidant Cell Response by Direct Phosphorylation and Nuclear Exclusion of the Transcription Factor Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14841–14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jope, R.S.; Yuskaitis, C.J.; Beurel, E. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3): Inflammation, Diseases, and Therapeutics. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cichocki, M.; Blumczyńska, J.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Naturally Occurring Phenolic Acids Inhibit 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate Induced NF-ΚB, INOS and COX-2 Activation in Mouse Epidermis. Toxicology 2010, 268, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Cheng, Z.M.; Li, H. Inhibition of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Expression by RNA Interference Suppresses Invasion through Inducing Anoikis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Saini, S.K.; Moukha-Chafiq, O.; Pathak, V.; Ananthan, S. Identification of Quinazoline Compounds as Novel Potent Inhibitors of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11263–11270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; Rebouissou, S.; Rossi, J.Z. NRF2/KEAP1 and Wnt/β-Catenin in the Multistep Process of Liver Carcinogenesis in Humans and Rats. Hepatology 2015, 62, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Tian, D.; Shi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Fan, F.; Fan, F. The Wnt Inhibitor LGK-974 Enhances Radiosensitivity of HepG2 Cells by Modulating Nrf2 Signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.S.; Kim, W.D.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, S.G. AMPK Facilitates Nuclear Accumulation of Nrf2 by Phosphorylating at Serine 550. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szaefer, H.; Licznerska, B.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Bartoszek, A.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Modulation of CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and CYP1B1 Expression by Cabbage Juices and Indoles in Human Breast Cell Lines. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the Regulation of Protein Abundance from Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geismann, C.; Arlt, A.; Sebens, S.; Schäfer, H. Cytoprotection “Gone Astray”: Nrf2 and Its Role in Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Chanas, S.A.; Henderson, C.J.; McLellan, L.I.; Wolf, C.R.; Cavin, C.; Hayes, J.D. The Cap ‘n’ Collar Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 P45-Related Factor 2) Controls Both Constitutive and Inducible Expression of Intestinal Detoxification and Glutathione Biosynthetic Enzymes. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Gomez, M.; Dolan, P.M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Interactive Effects of Nrf2 Genotype and Oltipraz on Benzo[a]Pyrene–DNA Adducts and Tumor Yield in Mice. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, K.L.; Lee, J.H.; Khor, T.O.; Wu, T.Y.; Li, G.X.; Chan, J.; Yang, C.S.; Kong, A.N.T. Nrf2 Knockout Enhances Intestinal Tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+ Mice Due to Attenuation of Anti-Oxidative Stress Pathway While Potentiates Inflammation. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 53, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Winiarski, B.K.; Sutton, P.A.; Jones, R.P.; Ressel, L.; Duckworth, C.A.; Pritchard, D.M.; Lin, Z.X.; Vicky, F.L.; Tweedle, E.M.; et al. The Nrf2 Inhibitor Brusatol Is a Potent Antitumour Agent in an Orthotopic Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27104–27116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaramillo, M.C.; Zhang, D.D. The Emerging Role of the Nrf2–Keap1 Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lister, A.; Nedjadi, T.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Campbell, F.; Costello, E.; Lloyd, B.; Copple, I.M.; Williams, S.; Owen, A.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; et al. Nrf2 Is Overexpressed in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Cell Proliferation and Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T. NRF2 and Cancer: The Good, the Bad and the Importance of Context. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. The Keap1–Nrf2 System in Cancers: Stress Response and Anabolic Metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhdar, H.; Loyer, P.; Rauch, C.; Corlu, A.; Guillouzo, A.; Morel, F. Involvement of Nrf2 Activation in Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil in Human Colon Cancer HT-29 Cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, A.; Schäfer, H.; Kalthoff, H. The ‘N-Factors’ in Pancreatic Cancer: Functional Relevance of NF-ΚB, NFAT and Nrf2 in Pancreatic Cancer. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Slocum, S.L.; Skoko, J.J.; Shin, S.; Kensler, T.W. When NRF2 Talks, Who’s Listening? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.-H.; Qu, J.; Shen, X. NF-ΚB/P65 Antagonizes Nrf2-ARE Pathway by Depriving CBP from Nrf2 and Facilitating Recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Healy, Z.R.; Lee, N.H.; Gao, X.; Goldring, M.B.; Talalay, P.; Kensler, T.W.; Konstantopoulos, K. Divergent Responses of Chondrocytes and Endothelial Cells to Shear Stress: Cross-Talk among COX-2, the Phase 2 Response, and Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14010–14015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusaba, T.; Nakayama, T.; Yamazumi, K.; Yakata, Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Inoue, K.; Nagayasu, T.; Sekine, I. Activation of STAT3 Is a Marker of Poor Prognosis in Human Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Gene | Primer F (5′→3′) | Primer R (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | ATTGCTACTAATCAGGCTCAG | GTTTGGCTTCTGGACTTGG |
| SOD | CGACAGAAGGAAAGTAATG | TGGATAGAGGATTAAAGTGAGG |
| GSTP | GCAAATACATCTCCCTCATC | AGGTTGTAGTCAGCGAAG |
| CAT | TGGACAAGTACAATGCTGAG | TTACACGGATGAACGCTAAG |
| GPx | CAACCAGTTTGGGCATCAG | TTCACCTCGCACTTCTCG |
| NF-κB p50 | ATCATCCACCTTCATTCTCAA | AATCCTCCACCACATCTTCC |
| NF-κB p65 | CGCCTGTCCTTTCTCATC | ACCTCAATGTCCTCTTTCTG |
| COX-2 | CGCCTGTCCTTTCTCATC | CAGCCCGTTGGTGAAAGC |
| iNOS | AGGAGATGCTGAACTACG | GGATGGTGACTCTGACTC |
| STAT3 | GCTTCTCCTTCTGGGTCTG | AGGCTTAGTGCTCAAGATGG |
| Bcl-xl | AAGCGTAGACAAGGAGATGC | CAGCGGTTGAAGCGTTCC |
| PBGD | TCAGATAGCATACAAGAGACC | TGGAATGTTACGAGCAGTG |
| TBP | GGCACCACTCCACTGTATC | GGGATTATATTCGGCGTTTCG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papierska, K.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Paluszczak, J.; Kleszcz, R.; Skalski, M.; Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Lichen-Derived Depsides and Depsidones Modulate the Nrf2, NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164787
Papierska K, Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J, Kleszcz R, Skalski M, Studzińska-Sroka E, Baer-Dubowska W. Lichen-Derived Depsides and Depsidones Modulate the Nrf2, NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164787
Chicago/Turabian StylePapierska, Katarzyna, Violetta Krajka-Kuźniak, Jarosław Paluszczak, Robert Kleszcz, Marcin Skalski, Elżbieta Studzińska-Sroka, and Wanda Baer-Dubowska. 2021. "Lichen-Derived Depsides and Depsidones Modulate the Nrf2, NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164787
APA StylePapierska, K., Krajka-Kuźniak, V., Paluszczak, J., Kleszcz, R., Skalski, M., Studzińska-Sroka, E., & Baer-Dubowska, W. (2021). Lichen-Derived Depsides and Depsidones Modulate the Nrf2, NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Molecules, 26(16), 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164787









