DNA-Templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters Inhibit Bacterial Growth While Being Non-Toxic to Mammalian Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Template Design
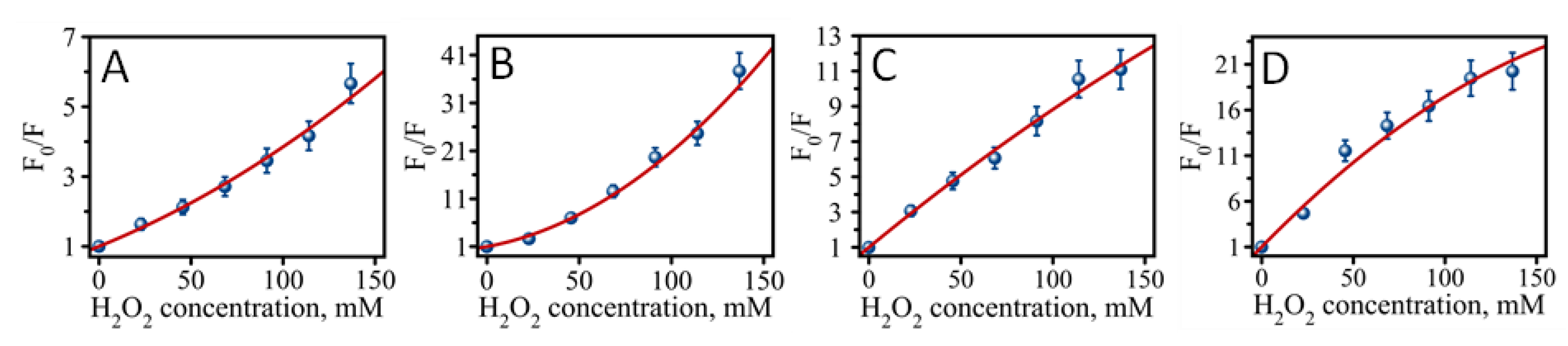
2.2. Fluorescence
2.3. Cell Culture Experiments
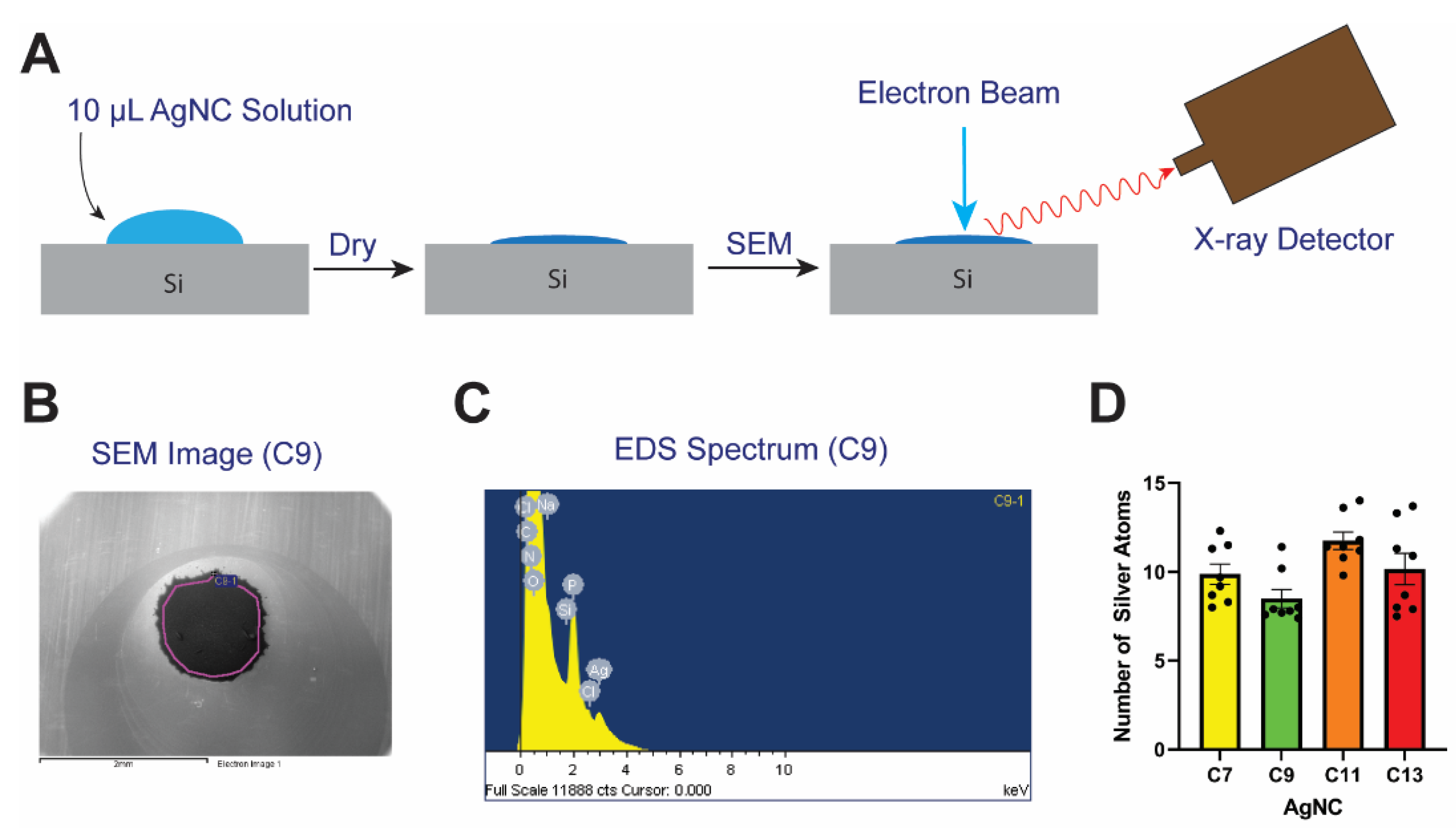
2.4. Stoichiometry Determination
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ritchie, C.M.; Johnsen, K.R.; Kiser, J.R.; Antoku, Y.; Dickson, R.M.; Petty, J.T. Ag Nanocluster Formation Using a Cytosine Oligonucleotide Template. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petty, J.T.; Zheng, J.; Hud, N.V.; Dickson, R.M. DNA-Templated Ag Nanocluster Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5207–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, M.; Shevchenko, O.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Striplin, C.D.; Afonin, K.A. DNA-Templated Synthesis of Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 1992–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, S.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Su, X.D. DNA-templated silver nanoclusters: Structural correlation and fluorescence modulation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17729–17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerretani, C.; Kanazawa, H.; Vosch, T.; Kondo, J. Crystal structure of a NIR-Emitting DNA-Stabilized Ag 16 Nanocluster. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17313–17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, D.J.E.; Demissie, A.; Kim, D.; Lewis, D.; Dickson, R.M.; Petty, J.T.; Lieberman, R.L. Atomic Structure of a Fluorescent Ag8 Cluster Templated by a Multistranded DNA Scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11465–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, P.R.; Gwinn, E.G.; Fygenson, D.K. UV Excitation of DNA Stabilized Ag Cluster Fluorescence via the DNA Bases. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 24061–24066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Gonzalez, J.I.; Zheng, J.; Dickson, R.M. Single-Molecule Optoelectronics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, E.G.; O’Neill, P.; Guerrero, A.J.; Bouwmeester, D.; Fygenson, D.K. Sequence-Dependent Fluorescence of DNA-Hosted Silver Nanoclusters. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, E.; Schultz, D.; Copp, S.; Swasey, S. DNA-Protected Silver Clusters for Nanophotonics. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 180–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, N.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Bai, J.; Ning, B.; Liang, J.; Gao, Z. An aptamer-based fluorometric zearalenone assay using a lighting-up silver nanocluster probe and catalyzed by a hairpin assembly. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonin, K.A.; Schultz, D.; Jaeger, L.; Gwinn, E.; Shapiro, B.A. Silver Nanoclusters for RNA Nanotechnology: Steps towards Visualization and Tracking of RNA Nanoparticle Assemblies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Afonin, K.A.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Church, G.; Bathe, M. Opportunities, Barriers, and a Strategy for Overcoming Translational Challenges to Therapeutic Nucleic Acid Nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9221–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E-coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, I.; Pangule, R.C.; Kane, R.S. Antifouling Coatings: Recent Developments in the Design of Surfaces that Prevent Fouling by Proteins, Bacteria, and Marine Organisms. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 690–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javani, S.; Lorca, R.; Latorre, A.; Flors, C.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Somoza, Á. Antibacterial Activity of DNA-Stabilized Silver Nanoclusters Tuned by Oligonucleotide Sequence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10147–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yao, C.; Li, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D. Synthesis of Branched DNA Scaffolded Super-Nanoclusters with Enhanced Antibacterial Performance. Small 2018, 14, 1800185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, H.; Kwon, W.Y.; Kalimuthu, K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Ahn, J.-O.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.G.; et al. Melamine-promoted formation of bright and stable DNA–silver nanoclusters and their antimicrobial properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, B.; Sinha, S.S.; Garner, B.L.; Arany, I.; Corley, C.; Cobb, K.; Brown, E.; Ray, P.C. Influence of Aptamer-Enclosed Silver Nanocluster on the Prevention of Biofilm by Bacillus thuringiensis. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2016, 8, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigaj, M.; Johnson, M.B.; Ke, W.; McMillan, J.; Goncharova, E.A.; Chandler, M.; Afonin, K.A. Aptamers as Modular Components of Therapeutic Nucleic Acid Nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12301–12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yourston, L.E.; Lushnikov, A.Y.; Shevchenko, O.A.; Afonin, K.A.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. First Step Towards Larger DNA-Based Assemblies of Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters: Template Design and Detailed Characterization of Optical Properties. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, F.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Pei, R.; Qian, H.; Li, H.-W. DNA-Hairpin-Templated Silver Nanoclusters: A Study on Stem Sequence. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, H.; Simon, D.; Steele, E.; Hebert, A.; Oleschuk, R.D.; Stamplecoskie, K.G. The power of fluorescence excitation–emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy in the identification and characterization of complex mixtures of fluorescent silver clusters. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42080–42086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yourston, L.; Rolband, L.; Lushnikov, A.; West, C.; Afonin, K.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A. Tuning properties of silver nanoclusters with RNA nanoring assemblies. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16189–16200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yourston, L.E.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. Micro RNA Sensing with Green Emitting Silver Nanoclusters. Molecules 2020, 25, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, J.T.; Sergev, O.O.; Kantor, A.G.; Rankine, I.J.; Ganguly, M.; David, F.D.; Wheeler, S.K.; Wheeler, J.F. Ten-Atom Silver Cluster Signaling and Tempering DNA Hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5302–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloupka, K.; Malam, Y.; Seifalian, A.M. Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.P.; Patil, S.M.; Mullani, S.B.; Delekar, S.D. Silver nanoparticles as an effective disinfectant: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerretani, C.; Vosch, T. Switchable Dual-Emissive DNA-Stabilized Silver Nanoclusters. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7895–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Rørvig-Lund, A.; Chaabane, S.B.; Thulstrup, P.W.; Kjaergaard, H.G.; Fron, E.; Hofkens, J.; Yang, S.W.; Vosch, T. Design Aspects of Bright Red Emissive Silver Nanoclusters/DNA Probes for MicroRNA Detection. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8803–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkin, N.; Wang, F.; Sharon, E.; Albada, H.B.; Willner, I. Multiplexed Analysis of Genes Using Nucleic Acid-Stabilized Silver-Nanocluster Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11666–11673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Jiang, X.; Welch, C.; Croley, T.R.; Wong, T.-Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, S.; Chong, Y.; Li, R.; Ge, C.; et al. Bactericidal Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Lactobacilli and the Underlying Mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8443–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdolino, V.; Cammi, R.; Munk, B.H.; Schlegel, H.B. Calculation of pKa Values of Nucleobases and the Guanine Oxidation Products Guanidinohydantoin and Spiroiminodihydantoin using Density Functional Theory and a Polarizable Continuum Model. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16860–16873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambucci, M.; Cerretani, C.; Latterini, L.; Vosch, T. The effect of pH and ionic strength on the fluorescence properties of a red emissive DNA-stabilized silver nanocluster. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2019, 8, 014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, S.M.; Schultz, D.; Swasey, S.; Pavlovich, J.; Debord, M.; Chiu, A.; Olsson, K.; Gwinn, E. Magic Numbers in DNA-Stabilized Fluorescent Silver Clusters Lead to Magic Colors. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerawardene, K.L.D.M.; Häkkinen, H.; Aikens, C.M. Connections Between Theory and Experiment for Gold and Silver Nanoclusters. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2018, 69, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Setyawati, M.I.; Tan, A.S.; Ong, C.N.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Highly luminescent silver nanoclusters with tunable emissions: Cyclic reduction–decomposition synthesis and antimicrobial properties. NPG Asia Mater. 2013, 5, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabed, M.A.; Dandu, N.; Tretiak, S.; Kilina, S. Passivating Nucleobases Bring Charge Transfer Character to Optically Active Transitions in Small Silver Nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 8931–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Cerretani, C.; Vosch, T. Disentangling optically activated delayed fluorescence and upconversion fluorescence in DNA stabilized silver nanoclusters. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5326–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewster, J.D. A simple micro-growth assay for enumerating bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 53, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.R.; Velazquez, L.R.; Dunn, D.G.; Gwinn, E.G.; Fygenson, D.K. Hairpins with Poly-C Loops Stabilize Four Types of Fluorescent Agn:DNA. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4229–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

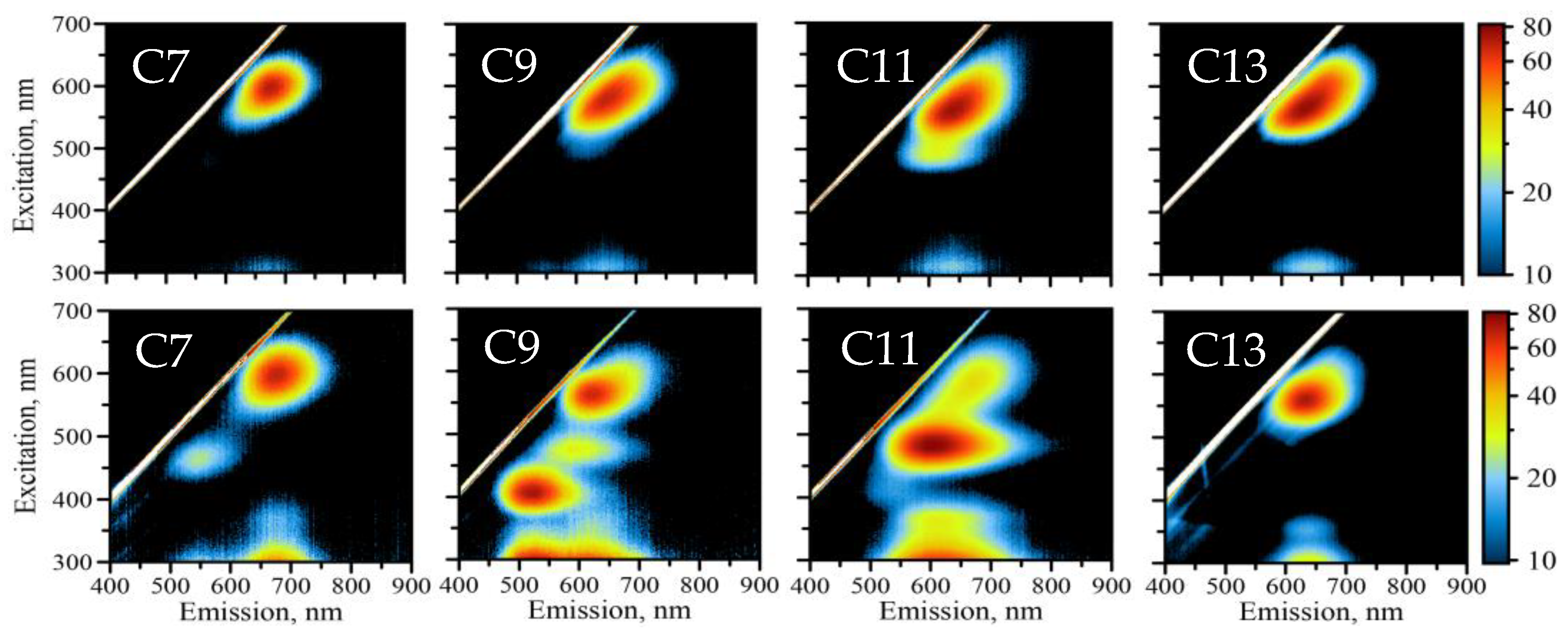

| Wavelength, nm | C7 | C9 | C11 | C13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXCMAX | 600 | 580 | 562 | 562 |
| FLUMAX | 685 | 661 | 647 | 645 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rolband, L.; Yourston, L.; Chandler, M.; Beasock, D.; Danai, L.; Kozlov, S.; Marshall, N.; Shevchenko, O.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V.; Afonin, K.A. DNA-Templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters Inhibit Bacterial Growth While Being Non-Toxic to Mammalian Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 4045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134045
Rolband L, Yourston L, Chandler M, Beasock D, Danai L, Kozlov S, Marshall N, Shevchenko O, Krasnoslobodtsev AV, Afonin KA. DNA-Templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters Inhibit Bacterial Growth While Being Non-Toxic to Mammalian Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):4045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134045
Chicago/Turabian StyleRolband, Lewis, Liam Yourston, Morgan Chandler, Damian Beasock, Leyla Danai, Seraphim Kozlov, Nolan Marshall, Oleg Shevchenko, Alexey V. Krasnoslobodtsev, and Kirill A. Afonin. 2021. "DNA-Templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters Inhibit Bacterial Growth While Being Non-Toxic to Mammalian Cells" Molecules 26, no. 13: 4045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134045
APA StyleRolband, L., Yourston, L., Chandler, M., Beasock, D., Danai, L., Kozlov, S., Marshall, N., Shevchenko, O., Krasnoslobodtsev, A. V., & Afonin, K. A. (2021). DNA-Templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters Inhibit Bacterial Growth While Being Non-Toxic to Mammalian Cells. Molecules, 26(13), 4045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134045







