Optimizing Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol from Water by Magnetic MXene Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
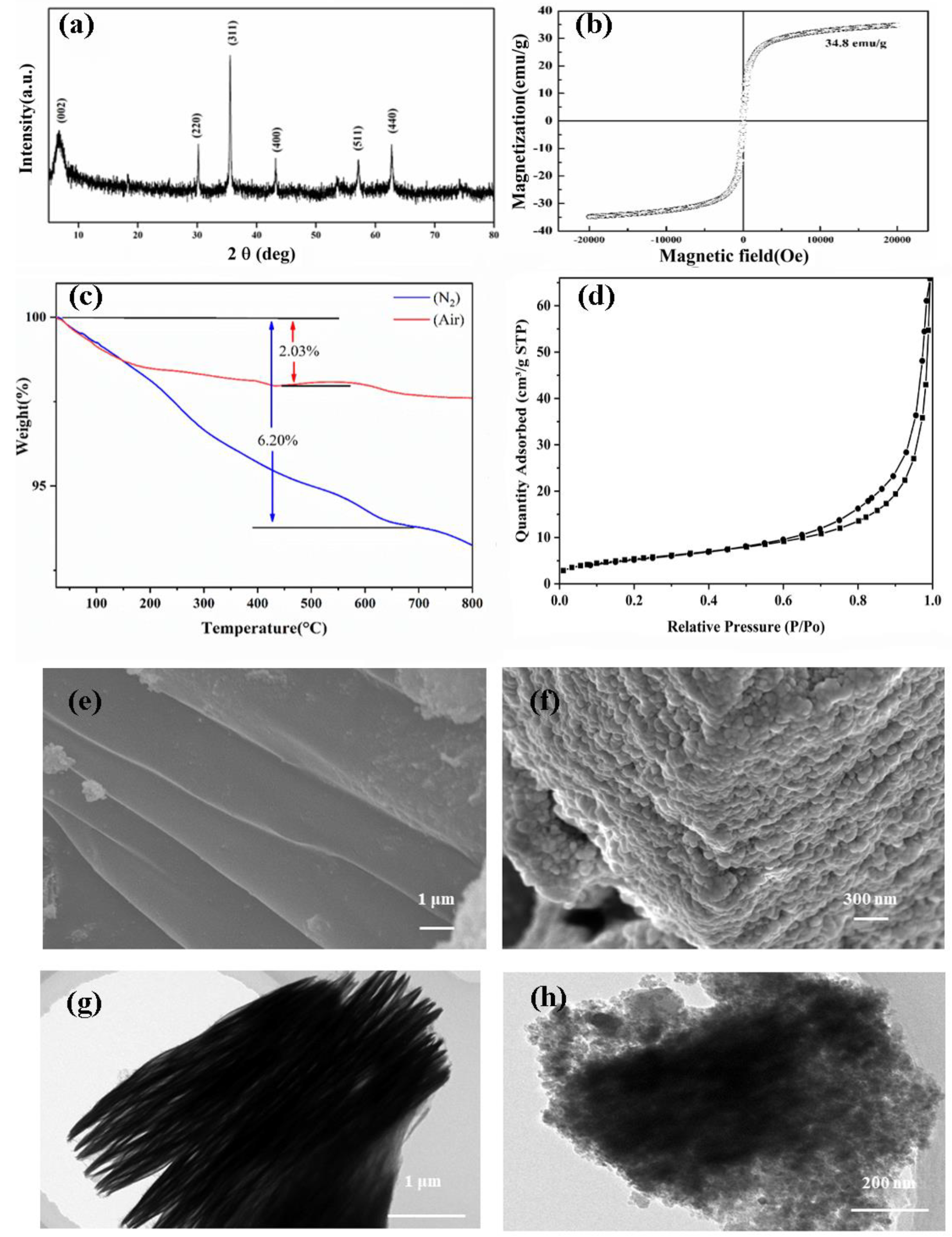
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@Ti3C2 Composite
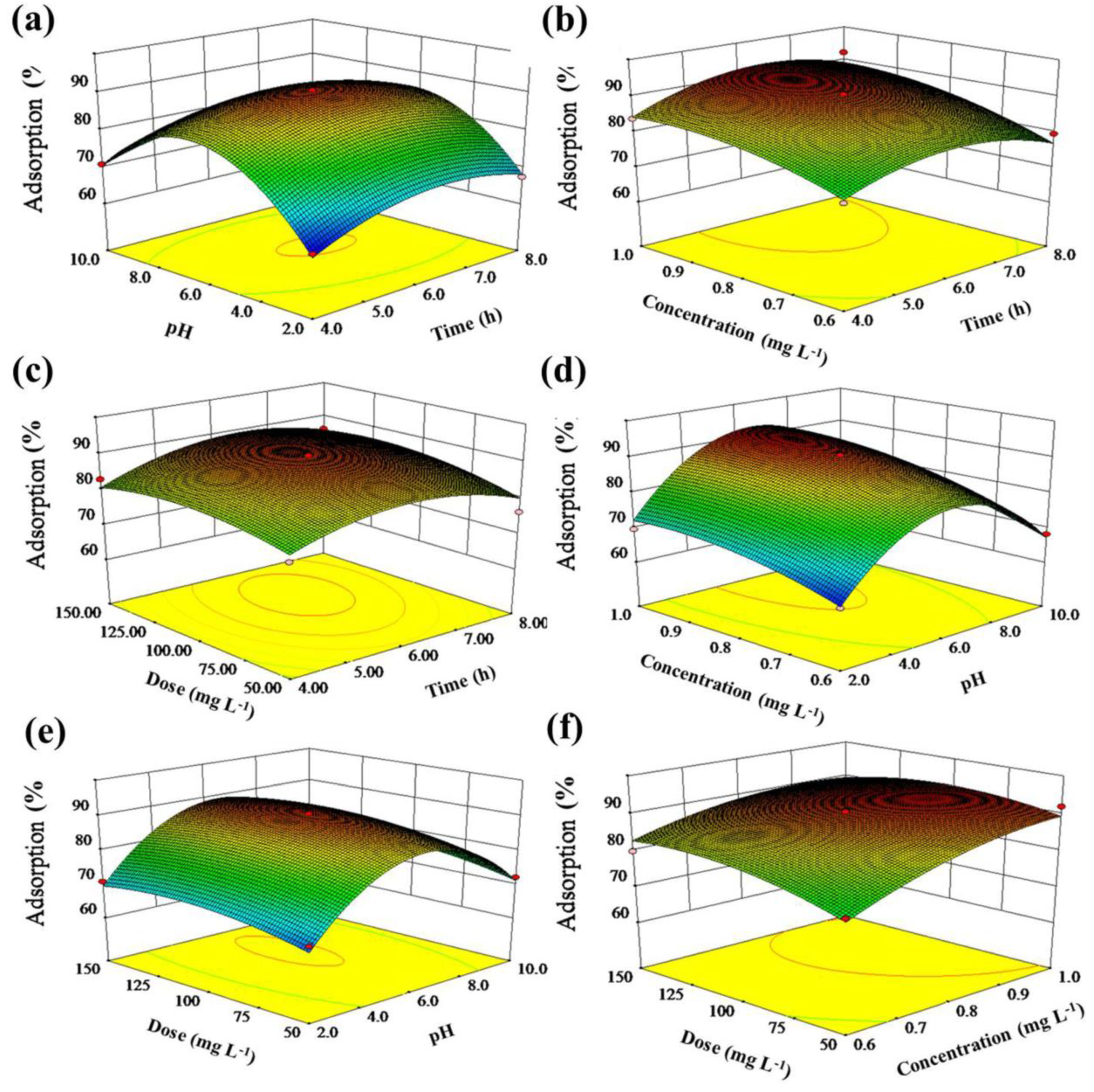
2.2. Optimum of Adsorption Condition by Response Surface Methodology
+ 0.16BD − 1.75CD − 5.01A2 − 17.15B2 − 3.39C2 − 2.28D2
2.3. Effects of Model Factors and Their Interactions on EE2 Adsorption
2.4. Three-Dimensional (3D) Response Surface and Contour Plots
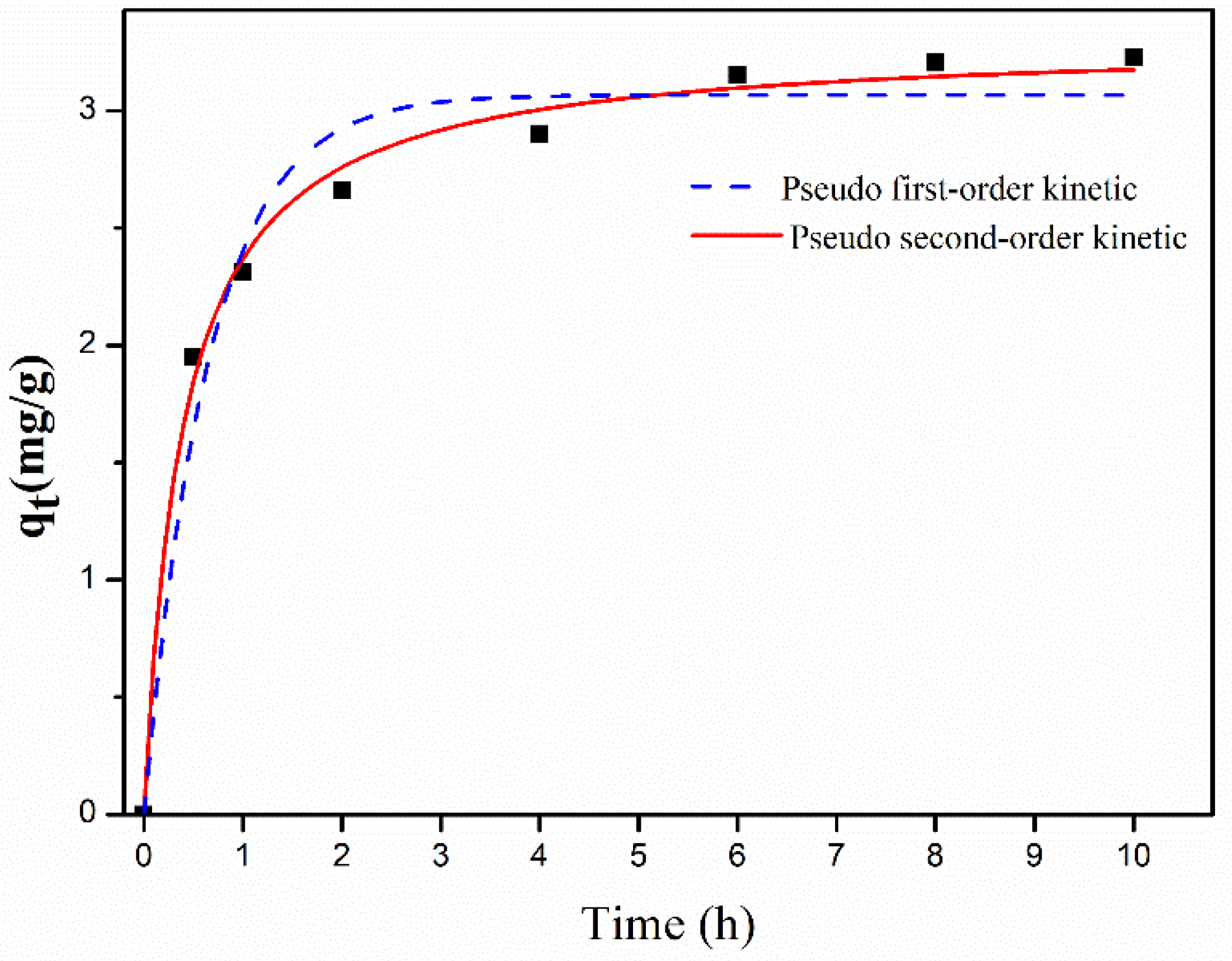
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of Fe3O4@Ti3C2
4.3. Adsorption Experiments and Analytical Method
4.4. Box–Behnken Design
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Avability
References
- Meyer, N.; Guillermina, S.C.; Mueller, J.E.; Schumacher, A.; Rodriguez, A.H.; Zenclussen, A.C. Exposure to 17α-ethinyl estradiol during early pregnancy affects fetal growth and survival in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, S.; Gorga, M.; Petrovic, M.; Gonzalez-Alonso, S.; Barcelo, D.; Valcarcel, Y. Analysis and occurrence of endocrine-disrupting compounds and estrogenic activity in the surface waters of Central Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avar, P.; Zrinyi, Z.; Maász, G.; Takátsy, A.; Lovas, S.; Tóth, L.G.; Pirger, Z. β-Estradiol and ethinyl-estradiol contamination in the rivers of the Carpathian Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 11630–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, E.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, I. A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.K.; Deem, S.L.; Holliday, D.K.; Jandegian, C.M.; Kassotis, C.D.; Nagel, S.C.; Tillitt, D.E.; Saal, F.S.; Rosenfeld, C.S. Effects of the environmental estrogenic contaminants bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on sexual development and adult behaviors in aquatic wildlife species. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 214, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Fighting, N. Effect of 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) on aggressive behavior and social hierarchy of the false clown anemonefish Amphiprion ocellaris. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.G.; Zhao, X.H.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.H.; Yang, Q.; Yu, L.Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Chen, X.Q. Aqueous adsorption and removal of organic contaminants by carbon nanotubes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankita, S.; Dhanjai, H.Z.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Rajeev, J. MXene: An emerging material for sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends. Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 424–435. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, G. Functional MXene materials: Progress of their applications. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2742–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z. Adsorptive environmental applications of MXene nanomaterials: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19895–19905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, B.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Li, Q.; Li, C. Modification of Bi2WO6 composites with rGO for enhanced visible light driven NO removal. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvimi, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Ebrahimi, M. Magnetic nano graphene oxide as solid phase extraction adsorbent coupled with liquid chromatography to determine pseudoephedrine in urine samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 15, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshgar, S.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Buttafava, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. Optimization of P compounds recovery from aerobic sludge by chemical modeling and response surface methodology combination. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, K.P. Response surface optimization of nitrite removal from aqueous solution by Fe3O4 stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles using a three-factor, three-level Box-Behnken design. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2015, 42, 2247–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoubarki, R.; Taoufik, M.; Ahmed, M.; Tounsadi, H.; Barka, N. Box-Behnken experimental design for the optimization of methylene blue adsorption onto Aleppo pine cones. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Dastkhoon, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Goudarzi, A.; Langroodi, S.M.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Ultrasound assisted adsorption of malachite green dye onto ZnS:Cu-NP-AC: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetic studies-response surface optimization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, H.; Capar, T.D.; Inanir, C.; Ekici, L.; Yalcin, H. Formulation of functional crackers enriched with germinated lentil extract: A Response Surface Methodology Box-Behnken Design. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, C.H.; Duan, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, J.F. TiO2 nanoparticle modified organ-like Ti3C2 MXene nanocomposite encapsulating hemoglobin for a mediator-free biosensor with excellent performances. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.F.; Li, H.P.; Yang, Y.; Lin, H.J.; Yang, Z.G. Adsorption of 17α-ethinylestradiol from aqueous solution onto a reduced graphene oxide-magnetic composite. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2017, 80, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.S.; Majumder, C.B. Corynebacterium glutamicum MTCC 2745 immobilized on granular activated carbon/MnFe2O4 composite: A novel biosorbent for removal of As(III) and As(V) ions. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 168, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.; Guardia-Puebla, Y.; Cisneros-Ortiz, M.E.; Morgan-Sagastume, J.M.; Guerra, G.; Noyola, A. Optimization of the specific methanogenic activity during the anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and rice straw, using industrial clay residues as inorganic additive. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Hajati, S.; Rezaeinejad, A.; Goudarzi, A.; Purkait, M.K. Rapid removal of Auramine-O and Methylene blue by ZnS:Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: A response surface methodology approach. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2015, 53, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Huang, X.Q.; Xu, Y.Q. Medium optimization for phenazine-1-carboxylic acid production by a gacA qscR double mutant of Pseudomonas sp. M18 using response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4089–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Sheng, G.P.; Luo, H.W.; Fang, F.; Li, W.W.; Zeng, R.J.; Tong, Z.H.; Yu, H.Q. Evaluating the influence of process parameters on soluble microbial products formation using response surface methodology coupled with grey relational analysis. Water Res. 2011, 45, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Deng, F.; Huang, S.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Ai, L.X.; She, P.Y. Optimization of magnetic field-assisted ultrasonication for the disintegration of waste activated sludge using Box-Behnken design with response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allouss, D.; Essamlali, Y.; Amadine, O.; Chakir, A.; Zahouily, M. Response surface methodology for optimization of methylene blue adsorption onto carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel beads: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and reusability studies. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37858–37869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounaas, M.; Bouguettoucha, A.; Chebli, D.; Gatica, J.M.; Vidal, H. Role of the wild carob as biosorbent and as precursor of a new high-surface-area activated carbon for the adsorption of methylene blue. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 46, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Gao, R.; Shi, L.; Liu, D.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z. Water-compatible magnetic imprinted nanoparticles served as solid-phase extraction sorbents for selective determination of trace 17β-estradiol in environmental water samples by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1396, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Gu, W.; Shi, X.; Xian, Y. Recyclable removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by reduced graphene oxide-magnetic nanoparticles: Adsorption and desorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 421, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, S.; Keppler, J.K.; Drusch, S. Mixtures of Quillaja saponin and β-lactoglobulin at the oil/water-interface: Adsorption, interfacial rheology and emulsion properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshadi, M.; Faraji, A.R.; Amiri, M.J. Modification of aluminum-silicate nanoparticles by melamine-based dendrimer l-cysteine methyl esters for adsorptive characteristic of Hg(II) ions from the synthetic and persian gulf water. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnárovits, L.; Földváry, C.M.; Takács, E. Radiation-induced grafting of cellulose for adsorption of hazardous water pollutants: A review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Gholamirad, F.; Yu, M.; Park, C.M.; Jang, A.; Jang, M.; Taheri-Qazvini, N.; Yoon, Y. Enhanced adsorption performance for selected pharmaceutical compounds by sonicated Ti3C2TX MXene. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawad, S.A.; Abdel-Aziz, H.M. Removal of ethinylestradiol by adsorption process from aqueous solutions using entrapped activated carbon in alginate biopolymer: Isotherm and statistical studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, L.A.; Obaid, A.Y.; Asiri, N.A.; Abdel Salam, M. Adsorption behavior of estrogenic compounds on carbon nanotubes from aqueous solutions: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, J.; Fang, F.; Huang, Y. Analysis of 17α-ethinylestradiol and bisphenol A adsorption on anthracite surfaces by site energy distribution. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Shi, J.; Zhao, X. Effect of corn straw biochar application to sediments on the adsorption of 17α-ethinyl estradiol and perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment-water interface. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Source | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Sum of Squares | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1099.86 | 14 | 78.56 | 62.16 | <0.0001 |
| A-Time | 7.21 | 1 | 7.21 | 3.11 | 0.0003 |
| B-pH | 65.43 | 1 | 65.43 | 30.70 | <0.0001 |
| C-Concentration | 129.69 | 1 | 129.69 | 56.00 | <0.0001 |
| D-Dose | 79.00 | 1 | 79.00 | 34.11 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 8.29 | 1 | 8.29 | 3.58 | 0.0793 |
| AC | 11.83 | 1 | 11.83 | 5.11 | 0.0603 |
| AD | 7.34 | 1 | 7.34 | 3.17 | 0.0967 |
| BC | 4.41 | 1 | 4.41 | 1.90 | 0.0493 |
| BD | 0.67 | 1 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.5985 |
| CD | 1.01 | 1 | 2.500 × 10−5 | 1.079 × 10−5 | 0.9974 |
| A2 | 16.19 | 1 | 16.19 | 6.99 | 0.0193 |
| B2 | 489.30 | 1 | 489.30 | 211.27 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 56.20 | 1 | 56.20 | 24.27 | 0.0002 |
| D2 | 88.01 | 1 | 88.01 | 38.00 | 0.0001 |
| Residual | 32.42 | 14 | 2.32 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 29.6 | 10 | 2.96 | 49.48 | 0.09 |
| Pure Error | 0.24 | 4 | 0.060 |
| Factor | Parameter | Coefficient | t Value | Standard Error | PC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | β0 | 75.45 | − | − | |
| A-Time | β1 | 0.78 | 0.245 | 2.401 | 1.86 |
| B-pH | β2 | 2.42 | 28.980 | 105.843 | 63.86 |
| C-Concentration | β3 | 3.29 | 5.494 | 24.006 | 9.48 |
| D-Dose | β4 | 2.57 | −2.751 | 0.994 | 4.86 |
| AB | β5 | −1.44 | −2.405 | 0.075 | 0.68 |
| AC | β6 | −1.72 | −2.455 | 1.497 | 0.24 |
| AD | β7 | 1.35 | 1.846 | 7.484 | 2.25 |
| BC | β8 | 1.05 | 12.754 | 0.748 | 23.06 |
| BD | β9 | 0.41 | 1.102 | 3.742 | 0.19 |
| CD | β10 | 2.500 × 10−3 | 0.839 | 74.842 | 13.01 |
| A2 | β11 | 1.58 | −2.578 | 0.118 | 0.80 |
| B2 | β12 | −8.69 | −23.612 | 0.029 | 21.06 |
| C2 | β13 | 2.94 | 1.120 | 11.754 | 3.87 |
| D2 | β14 | 3.68 | 2.960 | 293.861 | 0.05 |
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic model | Qe (mg g−1) | 3.0563 | |
| K1 (h−1) | 1.6486 | ||
| R2 | 0.9653 | ||
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic model | Qe (mg g−1) | 3.3003 | |
| K2 (g mg−1 h−1) | 0.7709 | ||
| R2 | 0.9938 |
| Isotherm Model | Equation | Parameters | T(K) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 298 | 308 | 318 | |||
| Langmuir | Qe (mg g−1) | 6.38 | 6.25 | 6.24 | 5.76 | |
| Kl (L mg−1) | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.82 | ||
| R2 | 0.9940 | 0.9968 | 0.9959 | 0.9971 | ||
| Freundlich | Kf (g mg−1 h−1) | 2.56 | 2.25 | 2.67 | 2.39 | |
| 1/n | 0.662 | 0.689 | 0.641 | 0.645 | ||
| R2 | 0.9693 | 0.9772 | 0.9691 | 0.9729 | ||
| Temperature (K) | InK | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | ΔS° (kJ mol−1k−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 0.5704 | −13.65 | 3.837 | 0.01799 |
| 298 | 0.5931 | −14.69 | ||
| 308 | 0.6846 | −17.53 | ||
| 318 | 0.7080 | −18.72 |
| Adsorbent | pH | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entrapped activated carbon in alginate biopolymer | 3 | 0.53 | [35] |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes | 6 | 0.47 | [36] |
| 4K anthracite | 7 | 1.28 | [37] |
| Biochar | 7 | 2.24 | [38] |
| Fe3O4@Ti3C2 | 6.4 | 3.83 | Present work |
| Variable | Unit | Notation | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Time | h | A | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| pH | B | 4 | 7 | 10 | |
| Concentration | mg L−1 | C | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| Dose | mg L−1 | D | 50 | 100 | 150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Huang, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Xiao, L.; Luo, Z. Optimizing Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol from Water by Magnetic MXene Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113150
Xu M, Huang C, Lu J, Wu Z, Zhu X, Li H, Xiao L, Luo Z. Optimizing Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol from Water by Magnetic MXene Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Studies. Molecules. 2021; 26(11):3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113150
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Mengwei, Chao Huang, Jing Lu, Zihan Wu, Xianxin Zhu, Hui Li, Langtao Xiao, and Zhoufei Luo. 2021. "Optimizing Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol from Water by Magnetic MXene Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Studies" Molecules 26, no. 11: 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113150
APA StyleXu, M., Huang, C., Lu, J., Wu, Z., Zhu, X., Li, H., Xiao, L., & Luo, Z. (2021). Optimizing Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol from Water by Magnetic MXene Using Response Surface Methodology and Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Studies. Molecules, 26(11), 3150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113150






