Visual pH Sensors: From a Chemical Perspective to New Bioengineered Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
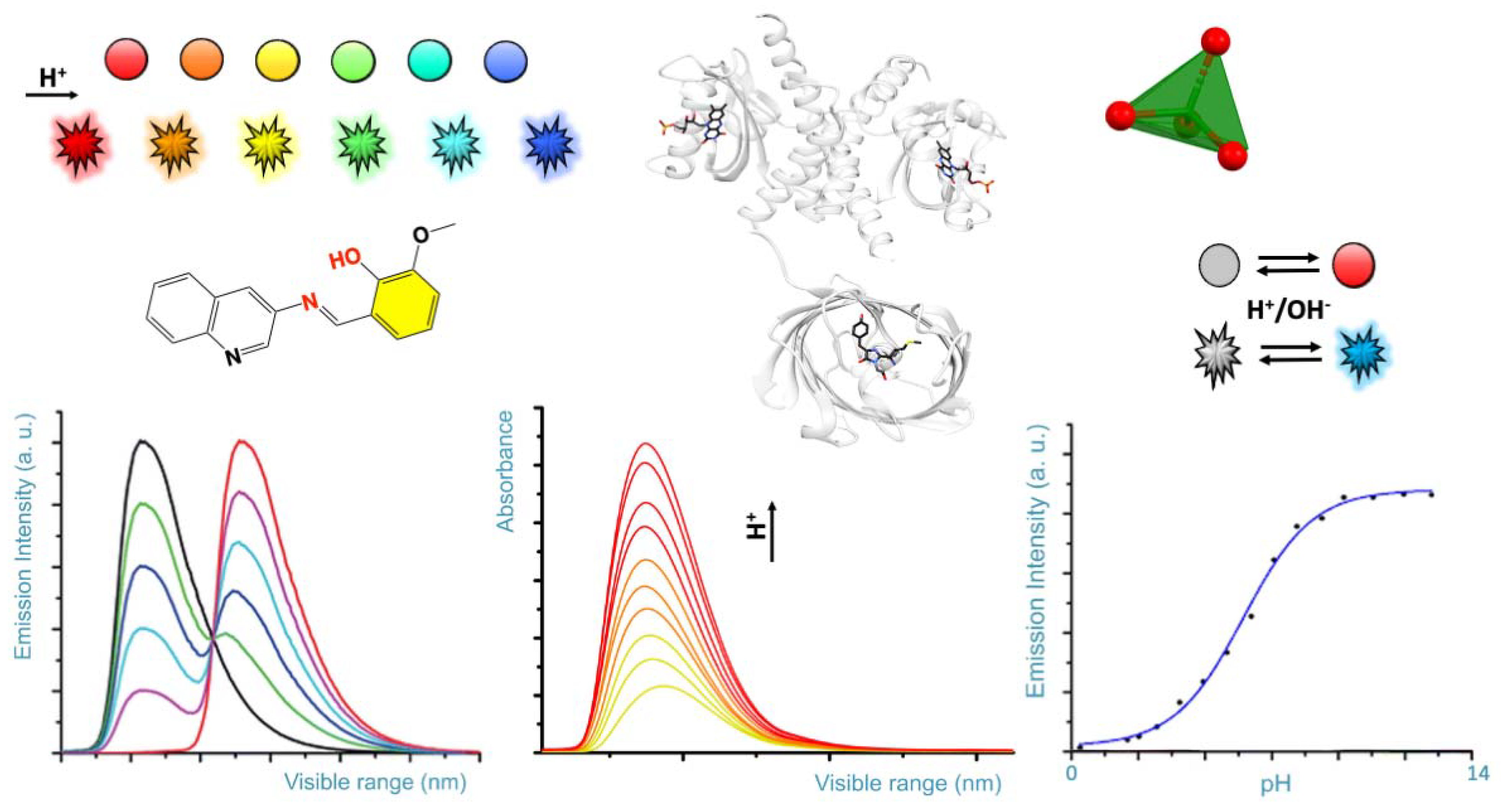
- (1)
- Molecular synthetic organic sensors;
- (2)
- Metal organic framework (MOF)-based sensors;
- (3)
- Sensors from engineered nanomaterials;
- (4)
- Bioengineered sensors.
2. Mechanisms of Fluorescence and Colorimetric pH Sensing
3. Synthetic Visual pH Sensors
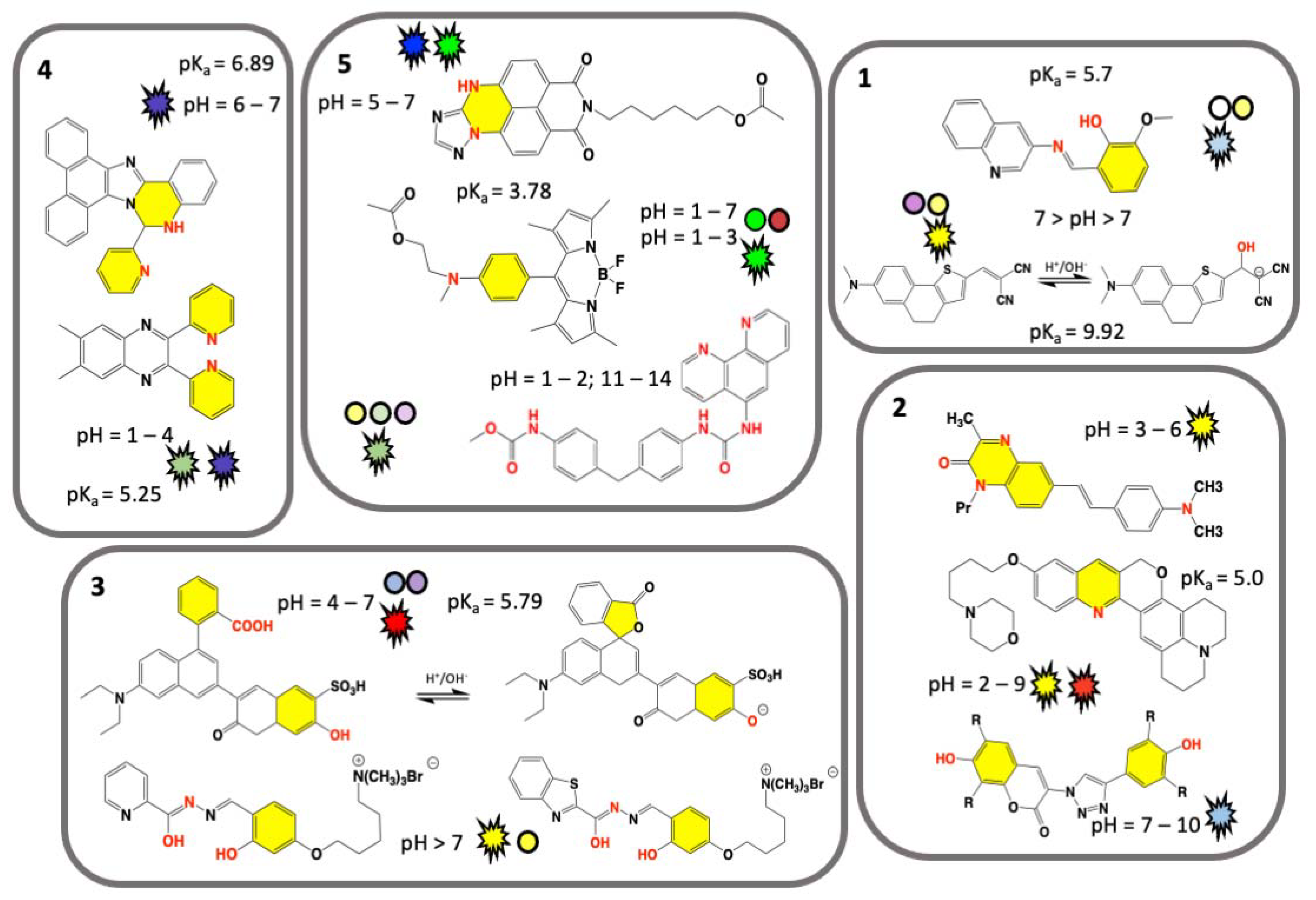
3.1. Molecular Organic Visual pH Sensors
3.2. Polymeric Organic Visual pH Sensors
3.3. Nucleic Acids Visual pH Sensors
4. Nano-Sized Visual pH Sensors
4.1. MOF and COF Based pH VSs
4.2. pH VSs from Highly Engineered Nanomaterials
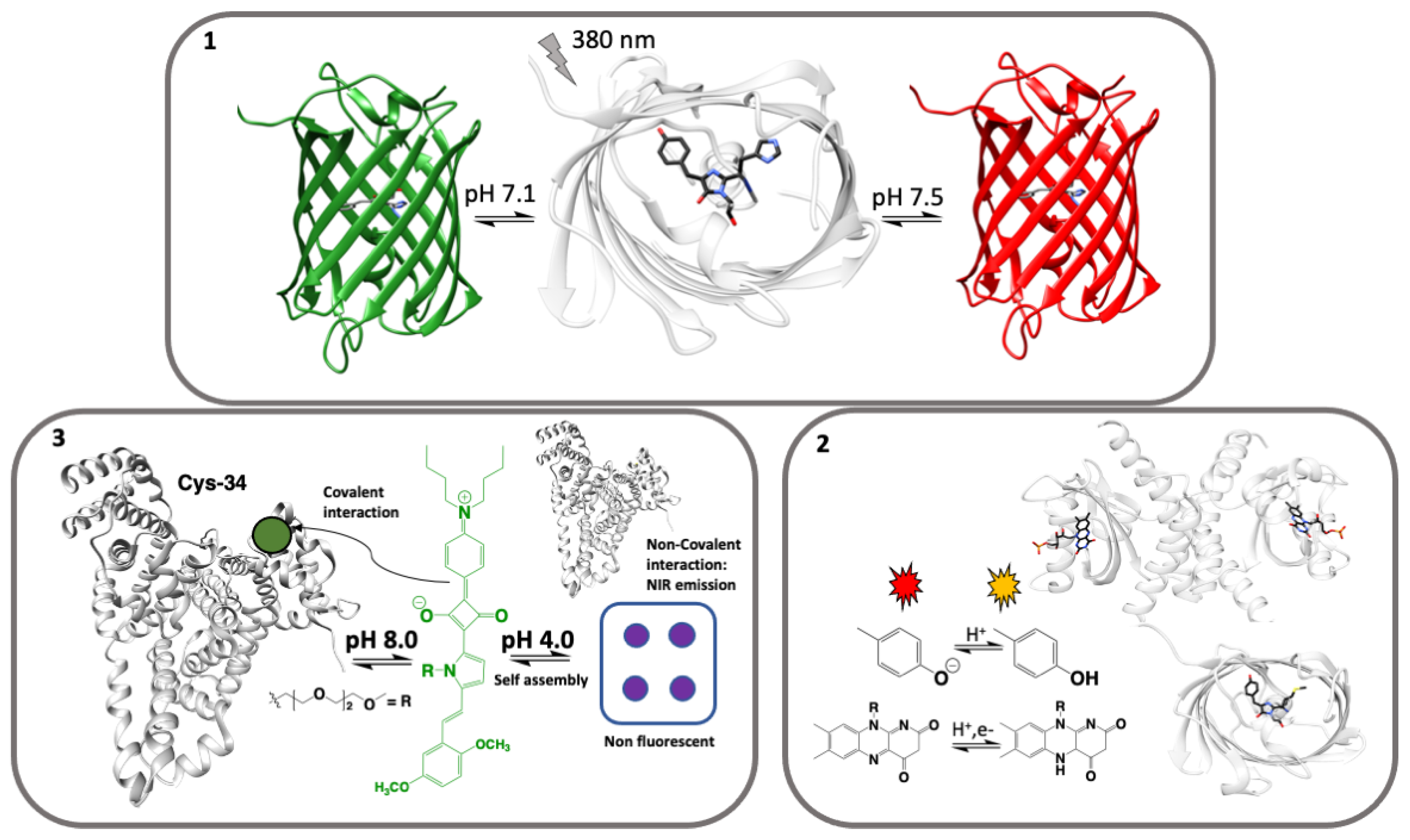
5. Bioengineered Visual pH Sensors
5.1. Genetically Encoded Visual pH Sensors
5.2. Bioengineered Materials Visual pH Sensors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wencel, D.; Abel, T.; McDonagh, C. Optical chemical pH sensors. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical Sensors: Industrial Environmental and Diagnostic Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; ISBN 978-3-642-07421-9. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, G.; Magnano, G.; Benesperi, I.; Saccone, D.; Priola, E.; Gianotti, V.; Milanesio, M.; Conterosito, E.; Barolo, C.; Viscardi, G. One pot synthesis of low cost emitters with large Stokes’ shift. Dye Pigment. 2017, 137, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Rouxel, D.; Ponnamma, D. Spectroscopy of Polymer Nanocomposites; Elsevier: Amsterdan, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780323401838. [Google Scholar]
- Pushina, M.; Farshbaf, S.; Shcherbakova, E.G.; Anzenbacher, P. A dual chromophore sensor for the detection of amines, diols, hydroxy acids, and amino alcohols. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 4495–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B.; Shikler, R.; Nabha, S.; Caruso, U. A symmetrical azo-based fluorophore and the derived salen multipurpose framework for emissive layers. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 104, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäferling, M. The art of fluorescence imaging with chemical sensors. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3532–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasch, T. The Eye and Visual Optical Instruments. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1998, 75, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal, P. The eye as an optical instrument. In Optics in Our Time; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319319032. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X. Flexible mechanochromic photonic crystals: Routes to visual sensors and their mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 3182–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Nitrogen and sulfur Co-doped carbon dots as selective and visual sensors for monitoring cobalt ions. Opt. Mater. 2021, 112, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, M.; Somasundaram, A.; Grimm, J.B.; Gruber, T.D.; Choquet, D.; Taraska, J.W.; Lavis, L.D.; Perrais, D. Semisynthetic fluorescent pH sensors for imaging exocytosis and endocytosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Leung, C.W.T.; Li, M.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Zhao, E.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Yu, Y.; et al. Full-range intracellular pH sensing by an aggregation-induced emission-active two-channel ratiometric fluorogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4926–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinto, S.O. Fluorescent, colourimetric, and ratiometric probes based on diverse fluorophore motifs for mercuric(II) ion (Hg2+) sensing: Highlights from 2011 to 2019. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3195–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panunzi, B.; Diana, R.; Concilio, S.; Sessa, L.; Tuzi, A.; Piotto, S.; Caruso, U. Fluorescence pH-dependent sensing of Zn(II)by a tripodal ligand. A comparative X-ray and DFT study. J. Lumin. 2019, 212, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4185–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, M.M.; Engle, J.M.; Fairley, K.C.; Robitshek, T.E.; Haley, M.M.; Johnson, D.W. “off-on” aggregation-based fluorescent sensor for the detection of chloride in water. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 4266–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Lyu, Q.; Zhu, J. Bioinspired structural color nanocomposites with healable capability. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 6413–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W. Visual sensors of an inverse opal hydrogel for the colorimetric detection of glucose. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3576–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Zhong, L.; Song, Q.H. A ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for selective and visual detection of phosgene in solutions and in the gas phase. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1530–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Borisov, S.M. Optical Sensing and Imaging of pH Values: Spectroscopies, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12357–12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Ghorai, P.; Brandão, P.; Pal, K.; Karmakar, P.; Saha, A. An aminoquinoline based biocompatible fluorescent and colourimetric pH sensor designed for cancer cell discrimination. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 19818–19826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 0387312781. [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi, T.; Ohta, N. Sensing of intracellular environments by fluorescence lifetime imaging of exogenous fluorophores. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Purkayastha, P.; Chattopadhyay, N. Photoprocesses of excited molecules in confined liquid environments: An overview. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2007, 8, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.P.; Moody, T.S.; Wright, G.D. Fluorescent PET (Photoinduced Electron Transfer) sensors as potent analytical tools. Analyst 2009, 134, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasmal, D.K.; Pulido, L.E.; Kasal, S.; Huang, J. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer in molecular biology. Nanoscale 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Kinetic investigation into pH-dependent color of anthocyanin and its sensing performance. Dye Pigment. 2019, 170, 107643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.; Chen, M.H.; Chiang, P.Y. Stability and quality of anthocyanin in purple sweet potato extracts. Foods 2019, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Gao, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X. Recent Advances in Developing Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks for Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensing. Front. Chem. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, A.; Ghasemi, F.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Shahrajabian, M.; Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Jafarinejad, S.; Farahmand Nejad, M.A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobes for visual detection: Design principles and recent advances—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1079, 30–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamry, K.A.; Georgiev, N.I.; El-Daly, S.A.; Taib, L.A.; Bojinov, V.B. A highly selective ratiometric fluorescent pH probe based on a PAMAM wavelength-shifting bichromophoric system. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 135, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Chen, J.; Du, J.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, X.; et al. Ratiometric optical sensor for high-resolution imaging of pH with low cross-talk. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9922–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchmans, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Gupta, S.; Poinern, G.E.J.; Issa, T.B.; Singh, P. Glassy carbon electrode modified with hybrid films containing inorganic molybdate anions trapped in organic matrices of chitosan and ionic liquid for the amperometric sensing of phosphate at neutral pH. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouka, Z.; Senapati, S.; Chang, H.C. Microfluidic systems with ion-selective membranes. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Hua Liu, S.; Yin, J. Fluorescent probes for pH and alkali metal ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierotti, M.R.; Gobetto, R. Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials. Supramol. Chem. Mol. Nanomater. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Kitazumi, Y.; Shirai, O.; Kano, K. Development perspective of bioelectrocatalysis-based biosensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concilio, S.; Ferrentino, I.; Sessa, L.; Massa, A.; Iannelli, P.; Diana, R.; Panunzi, B.; Rella, A.; Piotto, S. A novel fluorescent solvatochromic probe for lipid bilayers. Supramol. Chem. 2017, 29, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Wang, X.; Sheng, K.; Yang, L.; Han, W.; Xiao, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S. A novel colorimetric and fluorescence turn-on pH sensor with a notably large Stokes shift for its application. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14510–14516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, T.P.; Burganov, T.I.; Katsyuba, S.A.; Kalinin, A.A.; Islamova, L.N.; Fazleeva, G.M.; Ahmadeev, B.S.; Mustafina, A.R.; Monari, A.; Assfeld, X.; et al. Halochromic luminescent quinoxalinones as a basis for pH-sensing in organic and aqueous solutions. Dye Pigment. 2021, 186, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Foley, J.W. Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Lysosomal pH Measurement and Imaging in Living Cells Using Single-Wavelength Excitation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7038–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Noji, Y.; Shiraishi, T.; Ishigami-Yuasa, M.; Kagechika, H. Development of an ‘OFF-ON-OFF’ fluorescent pH sensor suitable for the study of intracellular pH. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 4925–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, A. Water-soluble organic probe for pH sensing and imaging. Talanta 2019, 205, 120095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, R.; Caruso, U.; Tuzi, A.; Panunzi, B. A highly water-soluble fluorescent and colorimetric pH probe. Crystals 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B.; Tuzi, A.; Piotto, S.; Concilio, S.; Caruso, U. An amphiphilic pyridinoyl-hydrazone probe for colorimetric and fluorescence pH sensing. Molecules 2019, 24, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, P.; Maity, S.; Shyamal, M.; Das, D.; Sahoo, G.P.; Misra, A. Proton triggered emission and selective sensing of picric acid by the fluorescent aggregates of 6,7-dimethyl-2,3-bis-(2-pyridyl)-quinoxaline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 7055–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, B.; Kan, W.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Song, B.; Wang, W.; Deng, Q. A phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole-based optical sensor for dual-responsive turn-on detection of acidic pH and Cu2+ in chicken blood and living cells. Dye Pigment. 2020, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Agarwal, S.; Pan, T.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Kong, X.; Day, K.; Chen, M.; Meldrum, D.; et al. Multifunctional PHPMA-Derived Polymer for Ratiometric pH Sensing, Fluorescence Imaging, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, U.; Lee, H. Il BODIPY-derived multi-channel polymeric chemosensor with pH-tunable sensitivity: Selective colorimetric and fluorimetric detection of Hg2+ and HSO4- in aqueous media. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 4882–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, U.; Chaudhury, S.S.; Sharma, R.; Ruidas, B.; Patra, S.G.; Mukhopadhyay, C.D.; Lee, H.-I. A fluorimetric water-soluble polymeric pH chemosensor for extremely acidic conditions: Live-cell and bacterial imaging application. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2020, 320, 128379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. Cellulose-Based Sensor Containing Phenanthroline for the Highly Selective and Rapid Detection of Fe2+ Ions with Naked Eye and Fluorescent Dual Modes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, H.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Yang, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. Visual and Precise Detection of pH Values under Extreme Acidic and Strong Basic Environments by Cellulose-Based Superior Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Caruso, U.; Di Costanzo, L.; Bakayoko, G.; Panunzi, B. A novel DR/NIR T-shaped aiegen: Synthesis and x-ray crystal structure study. Crystals 2020, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ravi, P.; Tam, K.C. pH-Responsive polymers: Synthesis, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.U.; Qin, Y.; Nambiar, S.; Yeow, J.T.W.; Howlader, M.M.R.; Hu, N.X.; Deen, M.J. Polymers and organic materials-based pH sensors for healthcare applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 96, 174–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.T.; Nguyen, A.; Dereje, N.; Huang, J.; Moore, G.C.; Murzynowski, P.J.; Dagdeviren, C. Recent Progress in Electrochemical pH-Sensing Materials and Configurations for Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5248–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capel-Cuevas, S.; Cuéllar, M.P.; de Orbe-Payá, I.; Pegalajar, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Full-range optical pH sensor array based on neural networks. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arppe, R.; Näreoja, T.; Nylund, S.; Mattsson, L.; Koho, S.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Soukka, T.; Schäferling, M. Photon upconversion sensitized nanoprobes for sensing and imaging of pH. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6837–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Luo, Z.D.; Pan, Y.; Kumar Singh, A.; Trivedi, M.; Kumar, A. Recent developments in luminescent coordination polymers: Designing strategies, sensing application and theoretical evidences. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 406, 213145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. PH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fuller, E.; Klug, S.; Lee, F.; Su, F.; Zhang, L.; Chao, S.H.; Meldrum, D.R. A fluorescent colorimetric pH sensor and the influences of matrices on sensing performances. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembska, A.; Kierzek, E.; Juskowiak, B. Studying the influence of stem composition in pH-sensitive molecular beacons onto their sensing properties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 990, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Discover of Graphene: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.B.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, G.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Criado, A.; Vázquez, E.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Promises, facts and challenges for graphene in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4400–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, Y.; Huang, K.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Functional magnetic graphene composites for biosensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chang, Y.N.; Yin, W.; Liu, X.; Xiao, D.; Xing, G.; Zhao, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible and flexible graphene oxide/upconversion nanoparticle hybrid film for optical pH sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y. Developing fluorescent copper nanoclusters: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, T.; Gooding, J.J.; Liu, J. Review of carbon and graphene quantum dots for sensing. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, J. A review of carbon dots in biological applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, T.; Mao, C. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6473–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulay, M.R.; Chauhan, A.; Patel, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Halder, A.; Vaish, R. Candle soot: Journey from a pollutant to a functional material. Carbon N. Y. 2019, 144, 684–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Park, J.; Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, W.; Ruoff, R.S.; Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Sun, X.; Dai, H.; et al. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Mater. Today 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Liang, S.; Tan, Y.; Sheng, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.X.A. Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Hassan, Z.; Bräse, S.; Tsotsalas, M. Polymerization in MOF-Confined Nanospaces: Tailored Architectures, Functions, and Applications. Langmuir 2020, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B.; Concilio, S.; Marrafino, F.; Shikler, R.; Caruso, T.; Caruso, U. The effect of bulky substituents on two π-conjugated mesogenic fluorophores. Their organic polymers and zinc-bridged luminescent networks. Polymers 2019, 11, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Pan, G.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Dong, B.; Song, H. Ratiometric photoluminescence sensing based on Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots as an intracellular pH sensor. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, N.D.; Wang, H.; Fuentes-Fernandez, E.M.A.; Teat, S.J.; Chen, F.; Hall, G.; Chabal, Y.J.; Li, J. Highly Efficient Luminescent Metal-Organic Framework for the Simultaneous Detection and Removal of Heavy Metals from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30294–30303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Barati, A.; Nematifar, Z. Fluorescent pH nanosensors: Design strategies and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2019, 39, 76–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge structural database. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Liu, W.S.; Li, G.; Bu, R.; Li, P.; Gao, E.Q. A pH-Sensing Fluorescent Metal-Organic Framework: PH-Triggered Fluorescence Transition and Detection of Mycotoxin. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 15421–15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Shan, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Dual-Emitting Fluorescent Metal-Organic Framework Nanocomposites as a Broad-Range pH Sensor for Fluorescence Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7056–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.L.; Xie, L.H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, M.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.R. Flexible metal-organic frameworks for the wavelength-based luminescence sensing of aqueous pH. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10628–10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateklum, R.; Gauthier-Manuel, B.; Pieralli, C.; Mankhetkorn, S.; Wacogne, B. Improving the sensitivity of amino-silanized sensors using self-structured silane layers: Application to fluorescence pH measurement. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, K.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. A luminescent ratiometric pH sensor based on a nanoscale and biocompatible Eu/Tb-mixed MOF. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 7549–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, J.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. Single wavelength excited multi-channel nanoMOF sensor for simultaneous and ratiometric imaging of intracellular pH and O2. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3904–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, L.; Ma, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Silver, M.A.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Gui, D.; Diwu, J.; et al. Covalent Organic Framework Functionalized with 8-Hydroxyquinoline as a Dual-Mode Fluorescent and Colorimetric pH Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15364–15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fei, Y.; Ma, J.; Qu, S.; Mi, L. Carbon dots for intracellular pH sensing with fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, E.S.; Himmelstoß, S.F.; Wiesholler, L.M.; Hirsch, T.; Hall, E.A.H. Upconversion nanoparticles for sensing pH. Analyst 2019, 144, 5547–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopikrishna, P.; Meher, N.; Iyer, P.K. Functional 1,8-Naphthalimide AIE/AIEEgens: Recent Advances and Prospects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12081–12111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, A.; Yu, Y.; Chang, X.; Hei, X. Sensing Organic Amines and Quantitative Monitoring of Intracellular pH Change Using a Fluorescent Self-Assembly System. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripongpreda, T.; Somchob, B.; Rodthongkum, N.; Hoven, V.P. Bacterial cellulose-based re-swellable hydrogel: Facile preparation and its potential application as colorimetric sensor of sweat pH and glucose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Barber, D.L.; Jacobson, M.P. Intracellular pH sensors: Design principles and functional significance. Physiology 2007, 22, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S.; Llopis, J.; Deveraux, Q.L.; Tsien, R.Y.; Reed, J.C. Changes in intramitochondrial and cytosolic pH: Early events that modulate caspase activation during apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinning, A.; Hübner, C.A. Minireview: PH and synaptic transmission. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, D.G.; Budd, S.L. Mitochondria and neuronal survival. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, R.A.; Nordberg, J.; Skowronski, E.; Babior, B.M. Apoptosis induced in Jurkat cells by several agents is preceded by intracellular acidification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommer, W.B.; Davidson, M.W.; Campbell, R.E. Genetically encoded biosensors based on engineered fluorescent proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.I.; Pakhomov, A.A.; Deyev, I.E.; Petrenko, A.G. Genetically encoded fluorescent indicators for live cell pH imaging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2924–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swietach, P.; Vaughan-Jones, R.D.; Harris, A.L.; Hulikova, A. The chemistry, physiology and pathology of pH in cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czowski, B.J.; Romero-Moreno, R.; Trull, K.J.; White, K.A. Cancer and pH dynamics: Transcriptional regulation, proteostasis, and the need for new molecular tools. Cancers 2020, 12, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, R.Y. The green fluorescent protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 509–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormö, M.; Cubitt, A.B.; Kallio, K.; Gross, L.A.; Tsien, R.Y.; Remington, S.J. Crystal structure of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Science 1996, 273, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barondeau, D.P.; Kassmann, C.J.; Tainer, J.A.; Getzoff, E.D. Understanding GFP chromophore biosynthesis: Controlling backbone cyclization and modifying post-translational chemistry. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruller, R.; Silva-Rocha, R.; Silva, A.; Cruz Schneider, M.P.; Ward, R.J. A practical teaching course in directed protein evolution using the green fluorescent protein as a model. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2011, 39, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Fisher, H.E.; Temirov, J.; Kiss, C.; Phipps, M.E.; Pavlik, P.; Werner, J.H.; Bradbury, A.R.M. The creation of a novel fluorescent protein by guided consensus engineering. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2007, 20, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barondeau, D.P.; Kassmann, C.J.; Tainer, J.A.; Getzoff, E.D. Structural chemistry of a green fluorescent protein Zn biosensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3522–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliye, N.; Fabbretti, A.; Lupidi, G.; Tsekoa, T.; Spurio, R. Engineering color variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) for thermostability, pH-sensitivity, and improved folding kinetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutol, J.N.; Kam, H.C.; Dodani, S.C. Identification of mNeonGreen as a pH-Dependent, Turn-On Fluorescent Protein Sensor for Chloride. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesenböck, G.; De Angelis, D.A.; Rothman, J.E. Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature 1998, 394, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Burgess, K. Fluorescent indicators for intracellular pH. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Wang, Z.; Yue, X.; Ma, Y.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. PH-sensitive fluorescent dyes: Are they really ph-sensitive in cells? Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotthard, G.; Von Stetten, D.; Clavel, D.; Noirclerc-Savoye, M.; Royant, A. Chromophore Isomer Stabilization Is Critical to the Efficient Fluorescence of Cyan Fluorescent Proteins. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 6418–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerboom, J.; Calderón, N.C.; Tian, L.; Wabnig, S.; Prigge, M.; Tolö, J.; Gordus, A.; Orger, M.B.; Severi, K.E.; Macklin, J.J.; et al. Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, H.; Shannon, M.; Nagai, T. Fluorescent proteins for investigating biological events in acidic environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myšková, J.; Rybakova, O.; Brynda, J.; Khoroshyy, P.; Bondar, A.; Lazar, J. Directionality of light absorption and emission in representative fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32395–32401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbachev, D.A.; Sarkisyan, K.S.; Mishin, A.S.; Lukyanov, K.A. Green fluorescent protein with tryptophan-based chromophore stable at low pH. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2017, 43, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinkevich, P.; Sinha, D.; Iermak, I.; Guzanova, A.; Weiserova, M.; Ludwig, J.; Mesters, J.R.; Ettrich, R.H. Crystal structure of a novel domain of the motor subunit of the Type i restriction enzyme EcoR124 involved in complex assembly and DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15043–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, V.; Nienhaus, K.; Bourgeois, D.; Nienhaus, G.U. Structural basis of enhanced photoconversion yield in green fluorescent protein-like protein Dendra2. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 4905–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletnev, S.; Shcherbo, D.; Chudakov, D.M.; Pletneva, N.; Merzlyak, E.M.; Wlodawer, A.; Dauter, Z.; Pletnev, V. A crystallographic study of bright far-red fluorescent protein mKate reveals pH-induced cis-trans isomerization of the chromophore. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 28980–28987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedhart, J.; Von Stetten, D.; Noirclerc-Savoye, M.; Lelimousin, M.; Joosen, L.; Hink, M.A.; Van Weeren, L.; Gadella, T.W.J.; Royant, A. Structure-guided evolution of cyan fluorescent proteins towards a quantum yield of 93%. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meulenaere, E.; Nguyen Bich, N.; De Wergifosse, M.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Vanderleyden, J.; Champagne, B.; Clays, K. Improving the second-order nonlinear optical response of fluorescent proteins: The symmetry argument. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4061–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatkevich, K.D.; Malashkevich, V.N.; Almo, S.C.; Verkhusha, V.V. Engineering ESPT pathways based on structural analysis of LSSmKate red fluorescent proteins with large stokes shift. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10762–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakhomov, A.A.; Martynov, V.I.; Orsa, A.N.; Bondarenko, A.A.; Chertkova, R.V.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Petrenko, A.G.; Deyev, I.E. Fluorescent protein Dendra2 as a ratiometric genetically encoded pH-sensor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, M.; Song, Y.; Bai, L.; Miao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Song, C.P. Dynamic imaging of cellular pH and redox homeostasis with a genetically encoded dual-functional biosensor, pHaROS, in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15768–15780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, K.S.; Bilwes, A.M.; Crane, B.R. Light-induced subunit dissociation by a light-oxygen-voltage domain photoreceptor from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, B.; Wang, Q.; Lee, F.; Byrnes, L.J.; Chudakov, D.M.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Sondermann, H.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Circular permutation of red fluorescent proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujacz, A. Structures of bovine, equine and leporine serum albumin. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees, P.; Sudheesh, K.V.; Jayamurthy, P.; Chandrika, A.R.; Omkumar, R.V.; Ajayaghosh, A. A protein-dye hybrid system as a narrow range tunable intracellular pH sensor. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6808–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees, P.; Sreejith, S.; Ajayaghosh, A. Self-assembled near-infrared dye nanoparticles as a selective protein sensor by activation of a dormant fluorophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13233–13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labas, Y.A.; Gurskaya, N.G.; Yanushevich, Y.G.; Fradkov, A.F.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Matz, M.V. Diversity and evolution of the green fluorescent protein family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4256–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isom, D.G.; Castañed, C.A.; Cannon, B.R.; García-Moreno, B.E. Large shifts in pKa values of lysine residues buried inside a protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5260–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahms, M.; Klingauf, J. Novel pH-sensitive lipid based exo-endocytosis tracers reveal fast intermixing of synaptic vesicle pools. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, G.J.; Goedhart, J.; Van Munster, E.B.; Gadella, T.W.J. Cyan and yellow super fluorescent proteins with improved brightness, protein folding, and FRET förster radius. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6570–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgstaller, S.; Bischof, H.; Gensch, T.; Stryeck, S.; Gottschalk, B.; Ramadani-Muja, J.; Eroglu, E.; Rost, R.; Balfanz, S.; Baumann, A.; et al. PH-Lemon, a Fluorescent Protein-Based pH Reporter for Acidic Compartments. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, M.; Claywell, B.; Haynes, E.P.; Scales, U.; Henning, C.K.; Tantama, M. Imaging pH Dynamics Simultaneously in Two Cellular Compartments Using a Ratiometric pH-Sensitive Mutant of mCherry. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 9476–9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Huang, X.; He, W.; Xue, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, L.; Xu, P. pHmScarlet is a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein to monitor exocytosis docking and fusion steps. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; De Angelis, D.; Rothman, J.E.; Ryan, T.A. The use of pHluorins for optical measurements of presynaptic activity. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbasova, T.; Nosrati, M.; Vasileiou, C.; Wang, W.; Lee, K.S.S.; Yapici, I.; Geiger, J.H.; Borhan, B. Rational design of a colorimetric ph sensor from a soluble retinoic acid chaperone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16111–16119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, D.F.; Rotello, V.M. Nanoparticle-GFP “chemical nose” sensor for cancer cell identification. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 991, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolati, T.; Bolivar, J.M.; Petrasek, Z.; Berenguer, J.; Hidalgo, A.; Guisán, J.M.; Nidetzky, B. Biobased, Internally pH-Sensitive Materials: Immobilized Yellow Fluorescent Protein as an Optical Sensor for Spatiotemporal Mapping of pH Inside Porous Matrices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6858–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

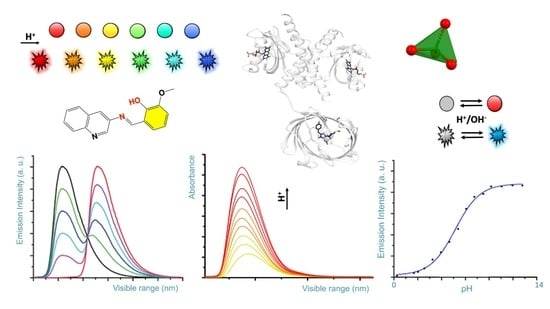
| Green Fluorescent Protein Name | PDB Entry Code and Chromophore Cif Code Identifier | Amino Acids Undergoing Post-Transitional Modification and Resulting in a Specific Chromophore |
|---|---|---|
| Ratiometric pHluorin | 5j3n: GYS [123] | GYS: SER, TYR, GLY |
| Dendra2 | 2vzx: CR8 [124] | CR8: HIS, TYR, GLY |
| mKate (variant) | 3bxa: NRQ [125] | NRQ: MET, TYR, GLY |
| Cyan FP SCFP3A (K206A) | 2ydz: CRF [126] | CRF: THR, TRP, GLY |
| Cyan FP SCFP3A | 5ox9, 5ox8: B2H [117] | B2H: THR, TRP, GLY |
| SHardonnay | 3v3d: CR2 [127] | CR2: GLY, TYR, GLY |
| mEos4b | 6yls: 5SQ [120] | 5SQ: HIS, TYR, GLY |
| mCherryEA | 3nt3, 3nt9: NRQ [128] | NRQ: MET, TYR, GLY |
| mRuby | 3u0l, 3u0m: NRQ [118] | NRQ: MET, TYR, GLY |
| mTurquoise2 (K206A) | 3ztf: SWG [126] | SWG: SER, TRP, GLY |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Costanzo, L.; Panunzi, B. Visual pH Sensors: From a Chemical Perspective to New Bioengineered Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102952
Di Costanzo L, Panunzi B. Visual pH Sensors: From a Chemical Perspective to New Bioengineered Materials. Molecules. 2021; 26(10):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102952
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Costanzo, Luigi, and Barbara Panunzi. 2021. "Visual pH Sensors: From a Chemical Perspective to New Bioengineered Materials" Molecules 26, no. 10: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102952
APA StyleDi Costanzo, L., & Panunzi, B. (2021). Visual pH Sensors: From a Chemical Perspective to New Bioengineered Materials. Molecules, 26(10), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102952