Synthetic Kavalactone Analogues with Increased Potency and Selective Anthelmintic Activity against Larvae of Haemonchus contortus In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Synthesis of Kavalactones and Analogues
3.2. Procurement of H. contortus
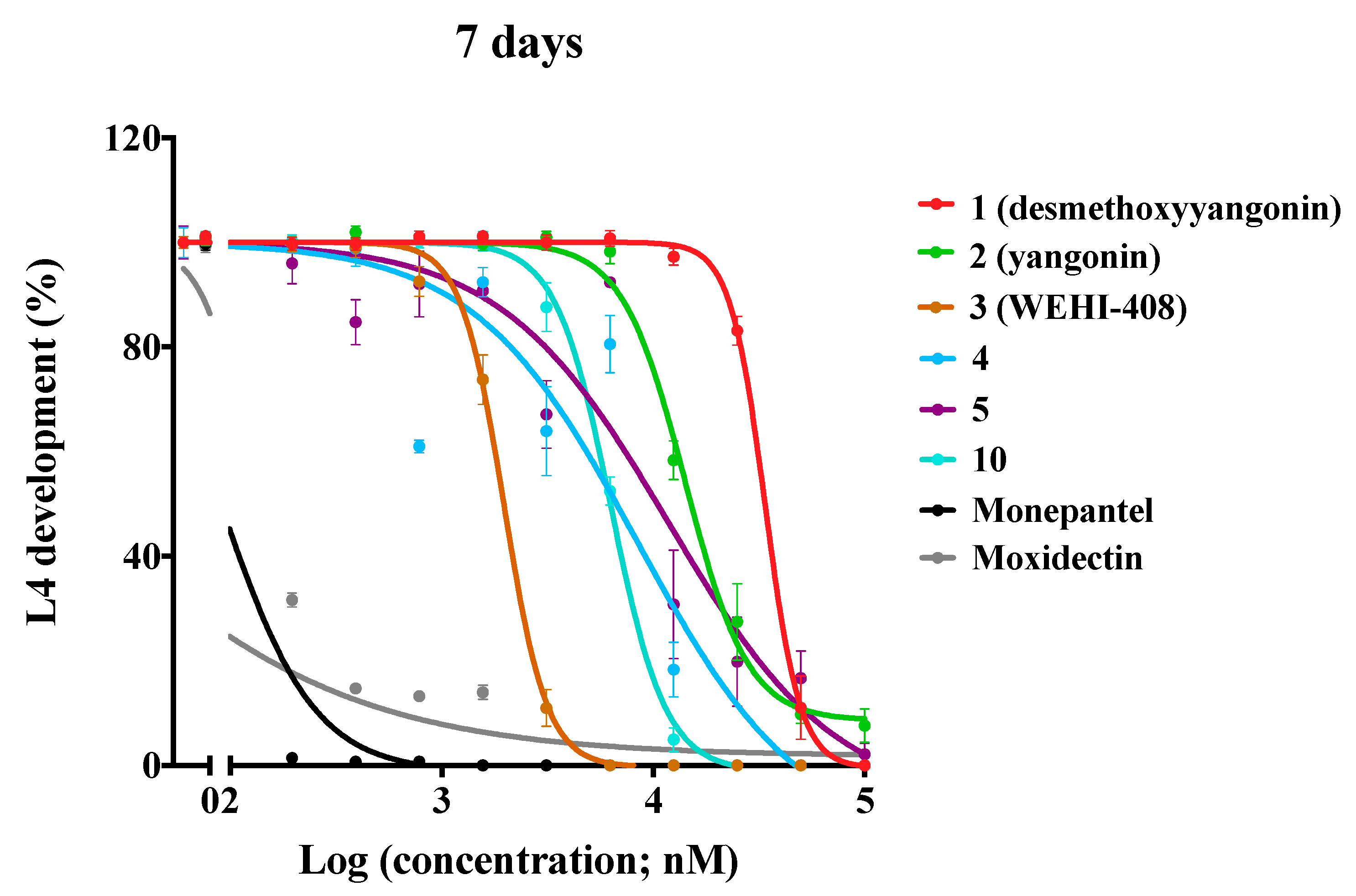
3.3. Assessment of Potency of Synthesized Compounds at Inhibiting Larval Development of H. contortus
3.4. Assessment of Cytotoxicity and Selectivity of Synthesized Compounds
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norton, S.A.; Ruze, P. Kava dermopathy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 31, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevinson, C.; Huntley, A.; Ernst, E. A systematic review of the safety of kava extract in the treatment of anxiety. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R. Kava hepatotoxicity: pathogenetic aspects and prospective considerations. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.F.D.; Diniz, M.F.F.M.; Araujo, M.S.T.; Pita, J.C.L.R.; Dantas, J.G.; Ramalho, J.A.; Xavier, A.L.; Palomaro, T.V.; Junior, B.; Nelson, L. The controvertible role of kava (Piper methysticum G. Foster) an anxiolytic herb, on toxic hepatitis. Revis. Bras. Farmacogn. 2007, 17, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebot, V.; Levesque, J. The origin and distribution of kava (Piper methysticum Forst. f., Piperaceae): A phytochemical approach. Allertonia 1989, 5, 223–281. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmaratne, H.R.W.; Nanayakkara, N.P.D.; Khan, I.A. Kavalactones from Piper methysticum, and their 13C NMR spectroscopic analyses. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.P.D.; Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Garcia-Bustos, J.S.; Addison, R.S.; Hayes, S.; Rali, T.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Chang, B.C.; et al. Selected α-pyrones from the plants Cryptocarya novoguineensis (Lauraceae) and Piper methysticum (Piperaceae) with activity against Haemonchus contortus in vitro. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israili, Z.H.; Smissman, E.E. Synthesis of kavain, dihydrokavain, and analogs. J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 4070–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, P.A.; Gouault, N.; Le Roch, M.; Eifler-Lima, V.L.; David, M. Towards synthesis of kavalactone derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6607–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollastri, M.P.; Whitty, A.; Merrill, J.C.; Tang, X.; Ashton, T.D.; Amar, S. Identification and characterization of kava-derived compounds mediating TNF-α suppression. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormann, E.C.; de Aguiar Amaral, P.; David, M.; Eifler-Lima, V.L.; Cechinel Filho, V.; de Campos Buzzi, F. Kavain analogues as potential analgesic agents. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magura, E.I.; Kopanitsa, M.V.; Gleitz, J.; Peters, T.; Krishtal, O.A. Kava extract ingredients,(+)-methysticin and (±)-kavain inhibit voltage-operated Na+-channels in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, S.S.; Hill, R.; Rommelspacher, H. Effect of kava extract and individual kavapyrones on neurotransmitter levels in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 22, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonen, G.; Haberlein, H. Influence of genuine kavapyrone enantiomers on the GABAA binding site. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebelhack, R.; Franke, L.; Schewe, H.J. Inhibition of platelet MAO-B by kava pyrone-enriched extract from Piper methysticum Forster (kava-kava). Pharmacopsychiatry 1998, 31, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.B.; Stofer, W.D.; Eichinger, M.R. Kavain inhibits murine airway smooth muscle contraction. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.S.; Dey, L.; Wang, A.; Mehendale, S.; Xie, J.T.; Aung, H.H.; Ang-Lee, M.K. Kavalactones and dihydrokavain modulate GABAergic activity in a rat gastric-brainstem preparation. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, J.; LaPorte, E.; Schweitzer, I. Kava: A comprehensive review of efficacy, safety, and psychopharmacology. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2011, 45, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligresti, A.; Villano, R.; Allara, M.; Ujvary, I.; Di Marzo, V. Kavalactones and the endocannabinoid system: The plant-derived yangonin is a novel CB1 receptor ligand. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.; Kikuchi, T.; Martinelli, A.; Tsai, I.J.; Beech, R.N.; Redman, E.; Holroyd, N.; Bartley, D.J.; Beasley, H.; Britton, C.; et al. The genome and transcriptome of Haemonchus contortus, a key model parasite for drug and vaccine discovery. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Korhonen, P.K.; Campbell, B.E.; Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Jabbar, A.; Hall, R.S.; Mondal, A.; Howe, A.C.; Pell, J.; et al. The genome and developmental transcriptome of the strongylid nematode Haemonchus contortus. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, R.B.; Schwarz, E.M.; Korhonen, P.K.; Young, N.D. Understanding Haemonchus contortus better through genomics and transcriptomics. Adv. Parasit. 2016, 93, 519–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Ang, C.; Korhonen, P.K.; Xu, R.; Nie, S.; Koehler, A.V.; Simpson, R.J.; Greening, D.W.; Reid, G.E.; et al. Somatic proteome of Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cheng, B.; Fang, S.; Zhou, H.; Gu, Q.; Xu, J. Design, syntheses and lipid accumulation inhibitory activities of novel resveratrol mimics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Nowell, C.; Joachim, A.; Ruttkowski, B.; Baell, J.; Cardno, T.; Korhonen, P.K.; Piedrafita, D.; Ansell, B.R.; et al. Low cost whole-organism screening of compounds for anthelmintic activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerville, R.I. The development of Haemonchus contortus to the fourth stage in vitro. J. Parasitol. 1996, 52, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, P.R.; Tan, C.; Jarman, K.E.; Lowes, K.N.; Curtis, J.M.; Nguyen, W.; Di Rago, A.E.; Bullen, H.E.; Prinz, B.; Duffy, S.; et al. Optimization of 2-anilino 4-amino substituted quinazolines into potent antimalarial agents with oral in vivo activity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, W.; Saha-Moeller, C.R.; Veit, M.; Welke, B. A convenient synthesis of hispidin from piperonal. Synthesis 1994, 11, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Mishima, T.; Yoshida, I.; Ide, M.; Koizumi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Morimoto, Y. Synthesis of novel 5,6-dehydrokawain analogs as osteogenic inducers and their action mechanisms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1 to 5 and 10 are available from the authors. |
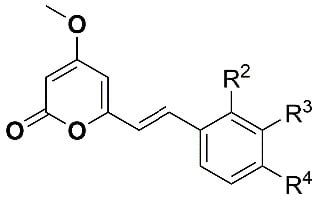
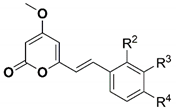 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | R2 | R3 | R4 | Inhibition of Larval Development in H. Contortus IC50 (µM) ± SEM | HepG2 EC50 (µM) |
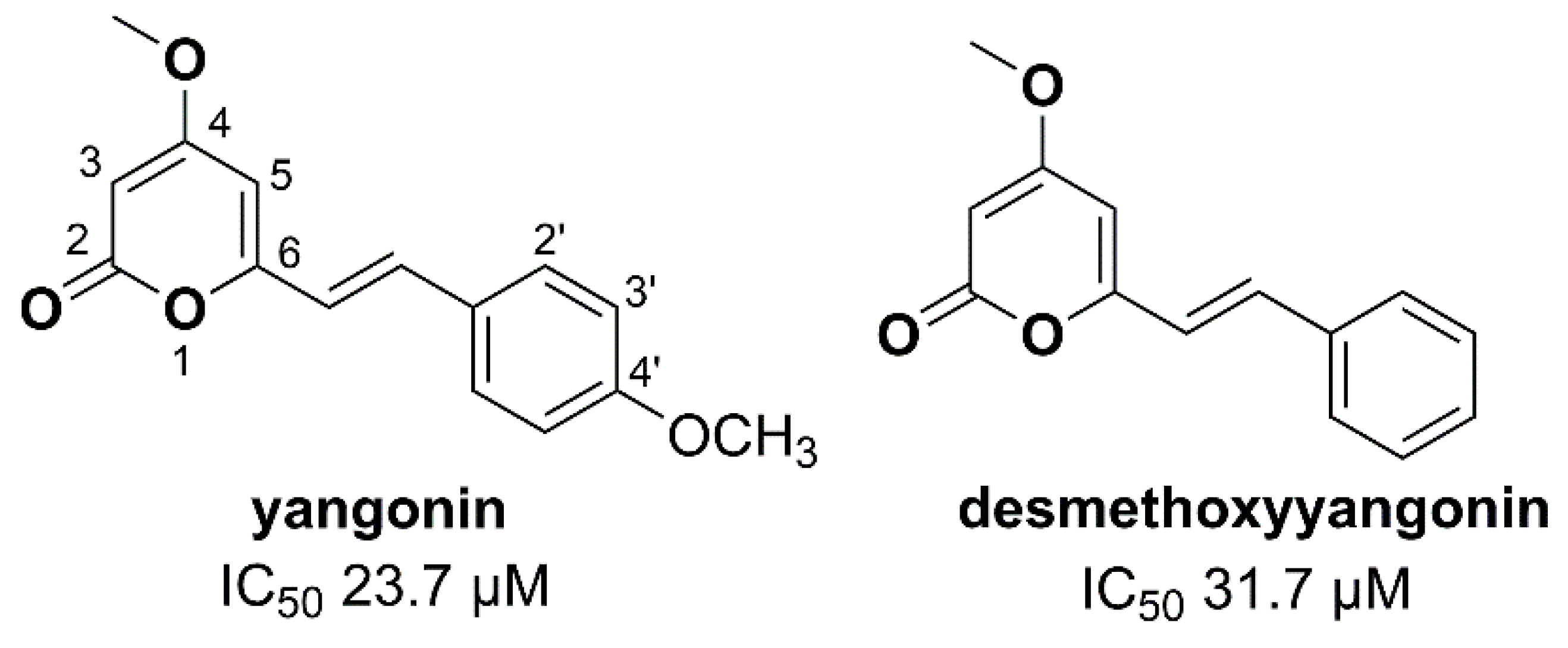
| 1 (desmethoxyyangonin) | H | H | H | 37.1 ± 3.1 | > 40 |
| 2 (yangonin) | H | H | OCH3 | 15.0 ± 3.0 | > 40 |
| 3 (WEHI-408) | H | H | OCF3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | > 40 |
| 4 | H | H | OCHF2 | 8.9 ± 0.3 | > 40 |
| 5 | H | H | OPh | 5.2 ± 2.2 | > 40 |
| 6 | H | H | Cl | 12.4 ± 3.5 | > 40 |
| 7 | H | H | Me | 12.6 ± 2.1 | > 40 |
| 8 | H | H | CF3 | 10.3 ± 1.2 | > 40 |
| 9 | H | H | N(CH3)2 | > 50 | > 40 |
| 10 | H | H | N-morpholine | 6.4 ± 0.2 | > 40 |
| 11 | H | H | N-piperazine | > 100 | >40 |
| 12 | H | H | CO2Me | > 100 | > 40 |
| 13 | H | H | CN | > 100 | > 40 |
| 14 | OCH3 | H | H | > 100 | >40 |
| 15 | H | OCH3 | H | 61.9 ± 7.3 | > 40 |
| 16 | H | -OCH2O- | > 100 | > 40 | |
| 17 | H | CN | H | > 100 | > 40 |
| 18 | H | CO2Me | H | > 100 | > 40 |
| 19 | H | [N] | OCH3 | > 100 | > 40 |
| Monepantel | 0.07 ± 0.01 | nd | |||
| Moxidectin | 0.02 ± 0.00 | nd | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herath, H.M.P.D.; Taki, A.C.; Nguyen, N.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Hofmann, A.; Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Chang, B.C.H.; Jabbar, A.; Sleebs, B.E.; et al. Synthetic Kavalactone Analogues with Increased Potency and Selective Anthelmintic Activity against Larvae of Haemonchus contortus In Vitro. Molecules 2020, 25, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25082004
Herath HMPD, Taki AC, Nguyen N, Garcia-Bustos J, Hofmann A, Wang T, Ma G, Chang BCH, Jabbar A, Sleebs BE, et al. Synthetic Kavalactone Analogues with Increased Potency and Selective Anthelmintic Activity against Larvae of Haemonchus contortus In Vitro. Molecules. 2020; 25(8):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25082004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerath, H.M.P. Dilrukshi, Aya C. Taki, Nghi Nguyen, José Garcia-Bustos, Andreas Hofmann, Tao Wang, Guangxu Ma, Bill C.H. Chang, Abdul Jabbar, Brad E. Sleebs, and et al. 2020. "Synthetic Kavalactone Analogues with Increased Potency and Selective Anthelmintic Activity against Larvae of Haemonchus contortus In Vitro" Molecules 25, no. 8: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25082004
APA StyleHerath, H. M. P. D., Taki, A. C., Nguyen, N., Garcia-Bustos, J., Hofmann, A., Wang, T., Ma, G., Chang, B. C. H., Jabbar, A., Sleebs, B. E., & Gasser, R. B. (2020). Synthetic Kavalactone Analogues with Increased Potency and Selective Anthelmintic Activity against Larvae of Haemonchus contortus In Vitro. Molecules, 25(8), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25082004