Aesculus hippocastanum L. Extract Does Not Induce Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Conversion but Increases Extracellular Matrix Production In Vitro Leading to Increased Wound Tensile Strength in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
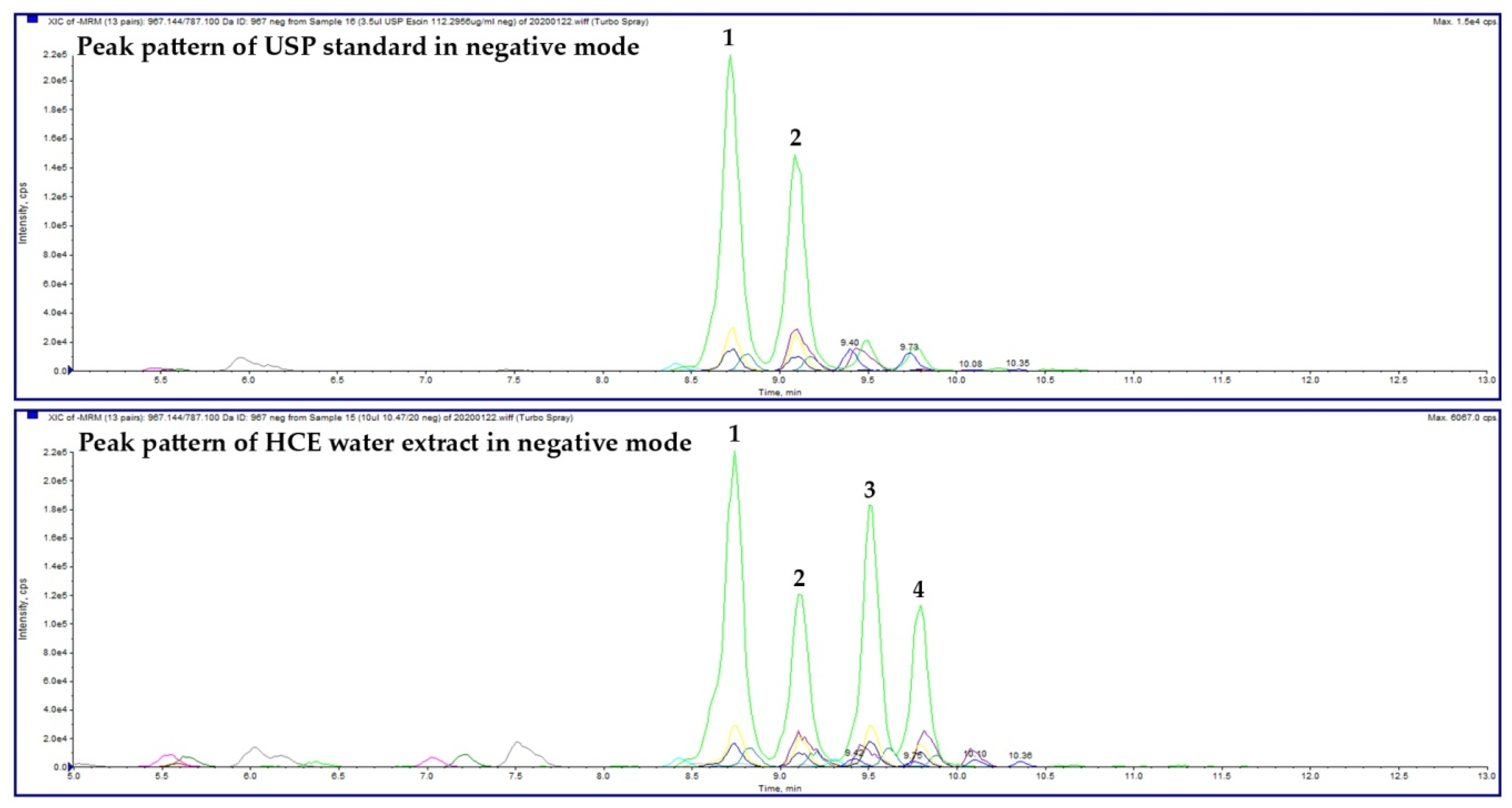
2.1. HCE Extract
2.2. In Vitro Study
2.2.1. MTT-Assay of HDFs
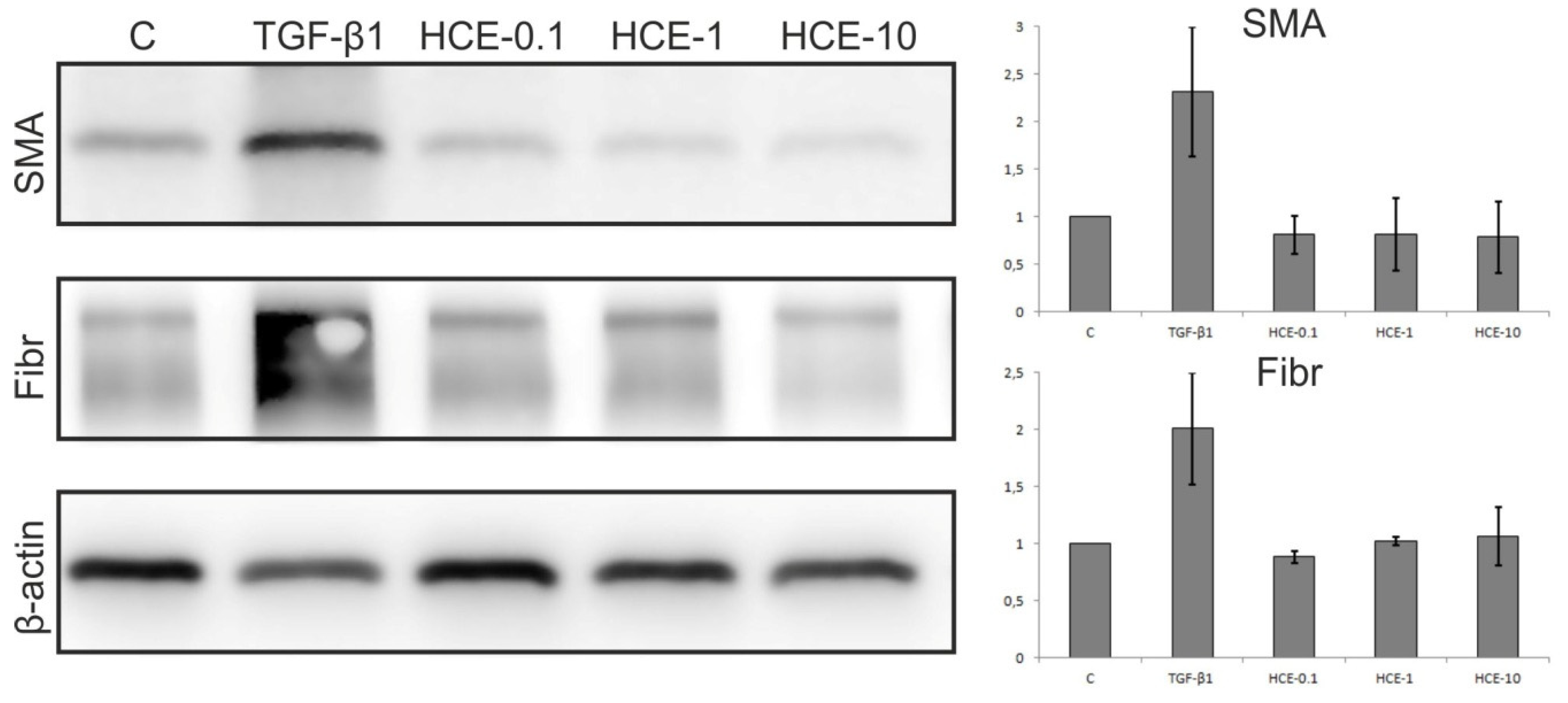
2.2.2. Western Blot Analysis of HDF
2.2.3. ICC Analysis of HDFs
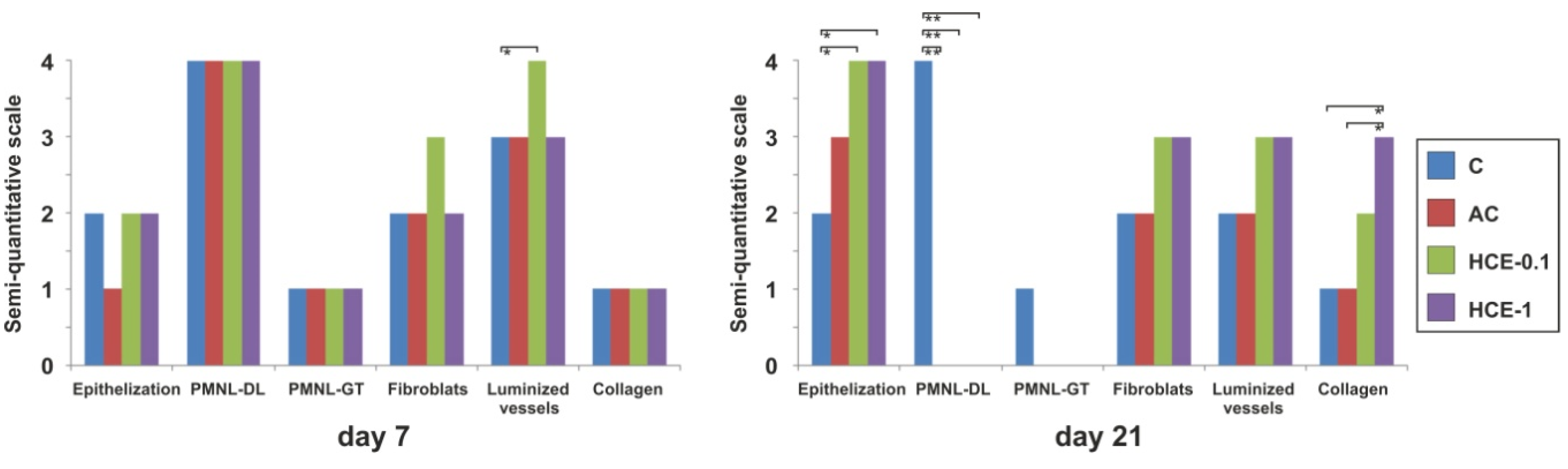
2.3. In Vivo Animal Study
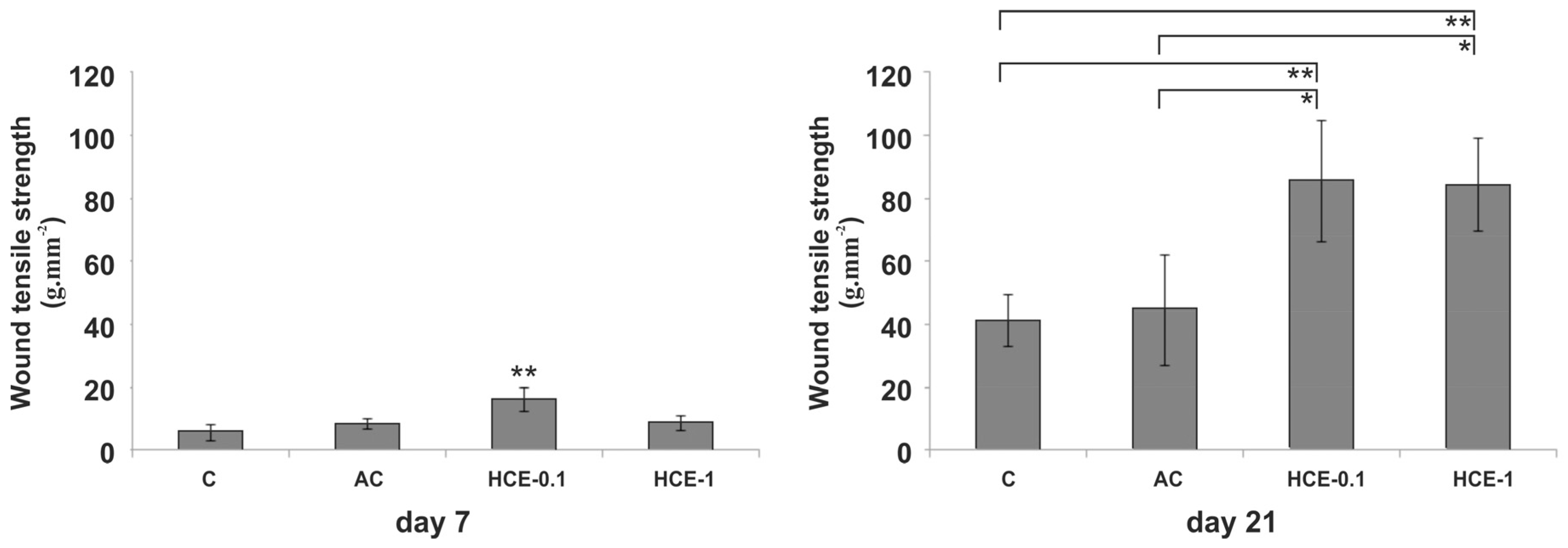
2.3.1. Wound Tensile Strength
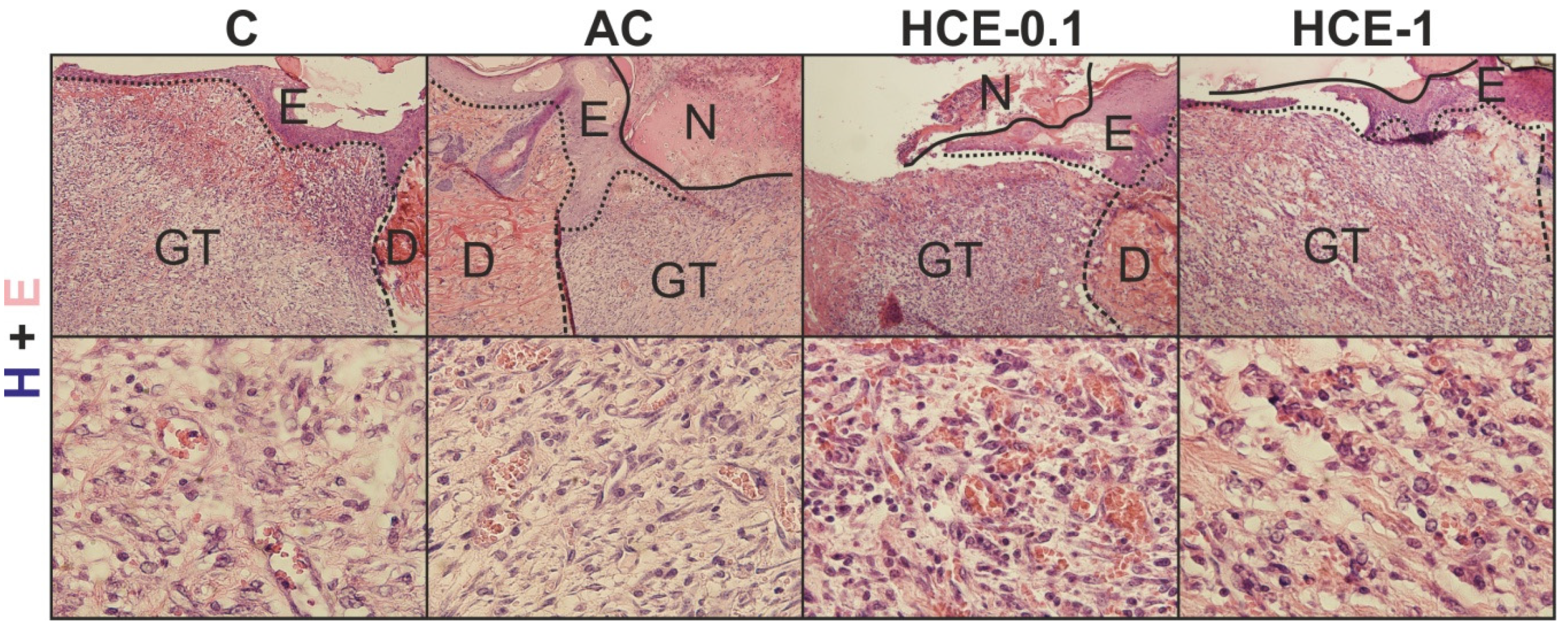
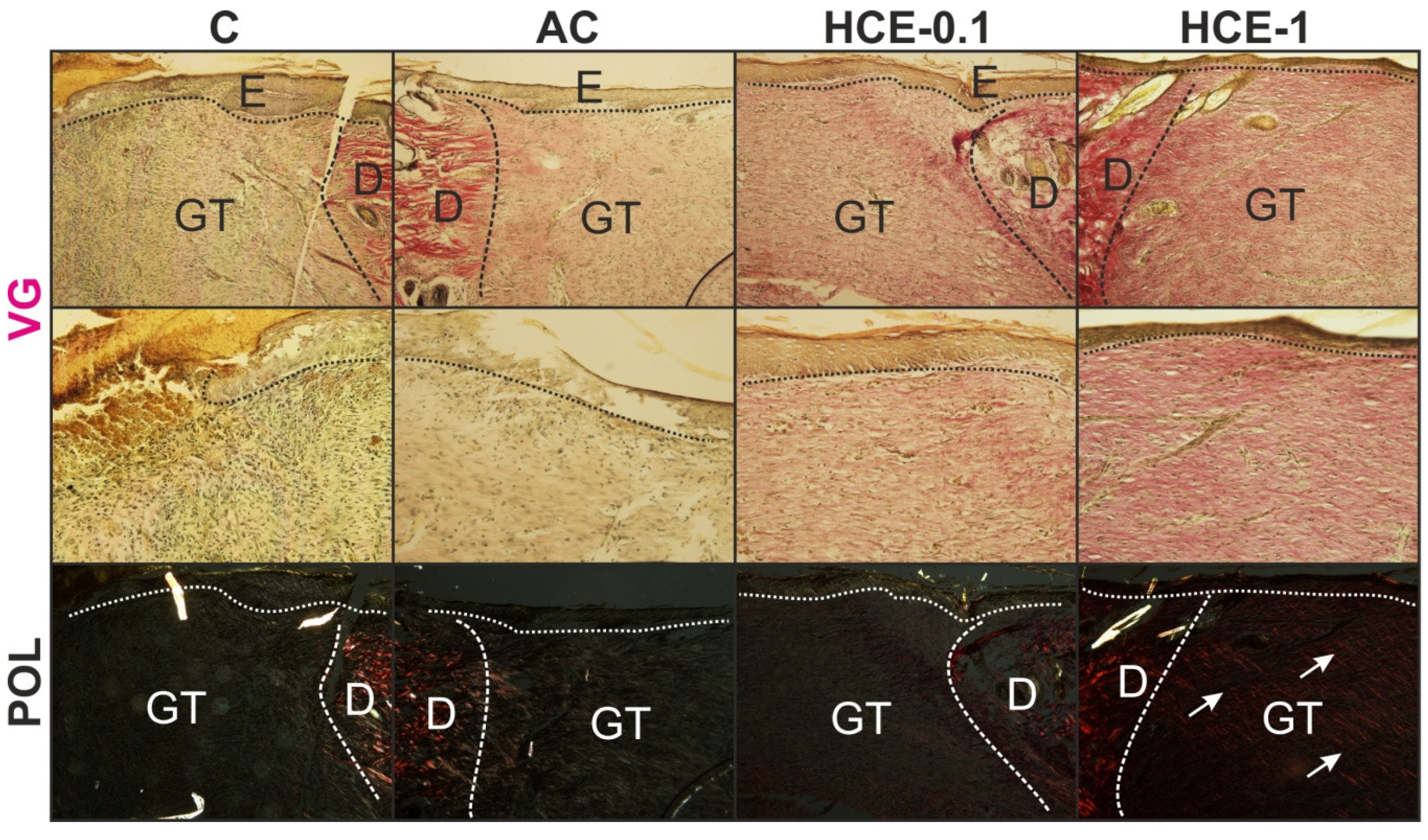
2.3.2. Histology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Preparation of the Aqueous Extract
4.2. HCE Extract Analysis
4.3. In Vitro Experiments
4.3.1. Primary Cultures of Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDFs)
4.3.2. MTT-Assay
4.3.3. Western Blot (WB) of HDFs
4.3.4. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) of HDFs
4.4. In Vivo Experiment
4.4.1. Animal Model
4.4.2. Wound Treatment
4.4.3. Wound Tensile Strength Measurement
4.4.4. Basic Histology and Semi-quantitative Scoring of Wounds
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, P.; Varinska, L.; Faber, L.; Novak, S.; Szabo, P.; Mitrengova, P.; Mirossay, A.; Mucaji, P.; Smetana, K. How Signaling Molecules Regulate Tumor Microenvironment: Parallels to Wound Repair. Molecules 2017, 22, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deonarine, K.; Panelli, M.C.; Stashower, M.E.; Jin, P.; Smith, K.; Slade, H.B.; Norwood, C.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Stroncek, D.F. Gene expression profiling of cutaneous wound healing. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Ghosh, K.; Tonnesen, M.G. Tissue engineering for cutaneous wounds. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetana Jr, K.; Szabo, P.; Gal, P.; Andre, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Kodet, O.; Dvorankova, B. Emerging role of tissue lectins as microenvironmental effectors in tumors and wounds. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Krieg, T.; Smola, H. Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, M.J.; Pincombe, J.; Foster, G. Clinical efficacy of horsechestnut seed extract in the treatment of venous ulceration. J. Wound. Care. 2006, 15, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, T.; Moriwaki, S.; Hotta, M.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y. Horse chestnut extract induces contraction force generation in fibroblasts through activation of Rho/Rho kinase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, P.C.; Marabini, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lattuada, N.; Calo, R.; Bertelli, A.; Falchi, M.; Dal Sasso, M.; Bianchi, T. Characterisation of the antioxidant effects of Aesculus hippocastanum L. bark extract on the basis of radical scavenging activity, the chemiluminescence of human neutrophil bursts and lipoperoxidation assay. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci 2012, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vaskova, J.; Fejercakova, A.; Mojzisova, G.; Vasko, L.; Patlevic, P. Antioxidant potential of Aesculus hippocastanum extract and escin against reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci 2015, 19, 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura, T.; Tsukahara, K.; Moriwaki, S.; Hotta, M.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y. A horse chestnut extract, which induces contraction forces in fibroblasts, is a potent anti-aging ingredient. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 57, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, H.; Cevik, O.; Sen, A.; Goger, F.; Sekerler, T.; Sener, A. Effect of Horse-chestnut seed extract on matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -9 during diabetic wound healing. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R. Aescin: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic profile. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, P.; Toporcer, T.; Vidinsky, B.; Mokry, M.; Novotny, M.; Kilik, R.; Smetana, K., Jr.; Gal, T.; Sabo, J. Early changes in the tensile strength and morphology of primary sutured skin wounds in rats. Folia. Biol. (Praha.) 2006, 52, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B. The role of myofibroblasts in wound healing. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2016, 64, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Xu, S.Q.; Cheng, J.; Cao, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.P.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.M. Anti-inflammatory effect of external use of escin on cutaneous inflammation: possible involvement of glucocorticoids receptor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, M.; Vasilenko, T.; Varinska, L.; Smetana, K., Jr.; Szabo, P.; Sarissky, M.; Dvorankova, B.; Mojzis, J.; Bobrov, N.; Toporcerova, S.; et al. ER-alpha agonist induces conversion of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, while ER-beta agonist increases ECM production and wound tensile strength of healing skin wounds in ovariectomised rats. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, P.; Stausholm, M.B.; Kovac, I.; Dosedla, E.; Luczy, J.; Sabol, F.; Bjordal, J.M. Should open excisions and sutured incisions be treated differently? A review and meta-analysis of animal wound models following low-level laser therapy. Lasers. Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudayeh, Z.H.; Al Azzam, K.M.; Naddaf, A.; Karpiuk, U.V.; Kislichenko, V.S. Determination of Four Major Saponins in Skin and Endosperm of Seeds of Horse Chestnut (Aesculus Hippocastanum L.) Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Positive Confirmation by Thin Layer Chromatography. Adv. Pharm Bull. 2015, 5, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Jiang, N.; Yu, P.; Liu, F.; Chong, Y.; Fu, F. Potent anti-inflammatory agent escin does not affect the healing of tibia fracture and abdominal wound in an animal model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, D.H.J.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Tran, T. Molecular targets and anti-cancer potential of escin. Cancer Lett. 2018, 422, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Salama, A.; Soliman, G.M.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Mostafa, E.M.; Mohammed, E.F.; Moustafa, A.; Zafar, A. Soy isoflavone-loaded alginate microspheres in thermosensitive gel base: Attempts to improve wound-healing efficacy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varinska, L.; Faber, L.; Kello, M.; Petrovova, E.; Balazova, L.; Solar, P.; Coma, M.; Urdzik, P.; Mojzis, J.; Svajdlenka, E.; et al. beta-Escin Effectively Modulates HUVECS Proliferation and Tube Formation. Molecules 2018, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strnad, H.; Lacina, L.; Kolar, M.; Cada, Z.; Vlcek, C.; Dvorankova, B.; Betka, J.; Plzak, J.; Chovanec, M.; Sachova, J.; et al. Head and neck squamous cancer stromal fibroblasts produce growth factors influencing phenotype of normal human keratinocytes. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2010, 133, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenmoehl, J.; Miller, S.N.; Hofmann, C.; Vogl, D.; Falk, W.; Scholmerich, J.; Rogler, G. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces intestinal myofibroblast differentiation and modulates their migration. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wong, M.; Mudera, V. Feedback inhibition of high TGF-beta1 concentrations on myofibroblast induction and contraction by Dupuytren’s fibroblasts. J. Hand. Surg. Br. 2006, 31, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, P.; Toporcer, T.; Vidinsky, B.; Hudak, R.; Zivcak, J.; Sabo, J. Simple interrupted percutaneous suture versus intradermal running suture for wound tensile strength measurement in rats: A technical note. Eur. Surg. Res. 2009, 43, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, I.; Durkac, J.; Holly, M.; Jakubcova, K.; Perzelova, V.; Mucaji, P.; Svajdlenka, E.; Sabol, F.; Legath, J.; Belak, J.; et al. Plantago lanceolata L. water extract induces transition of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and increases tensile strength of healing skin wounds. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
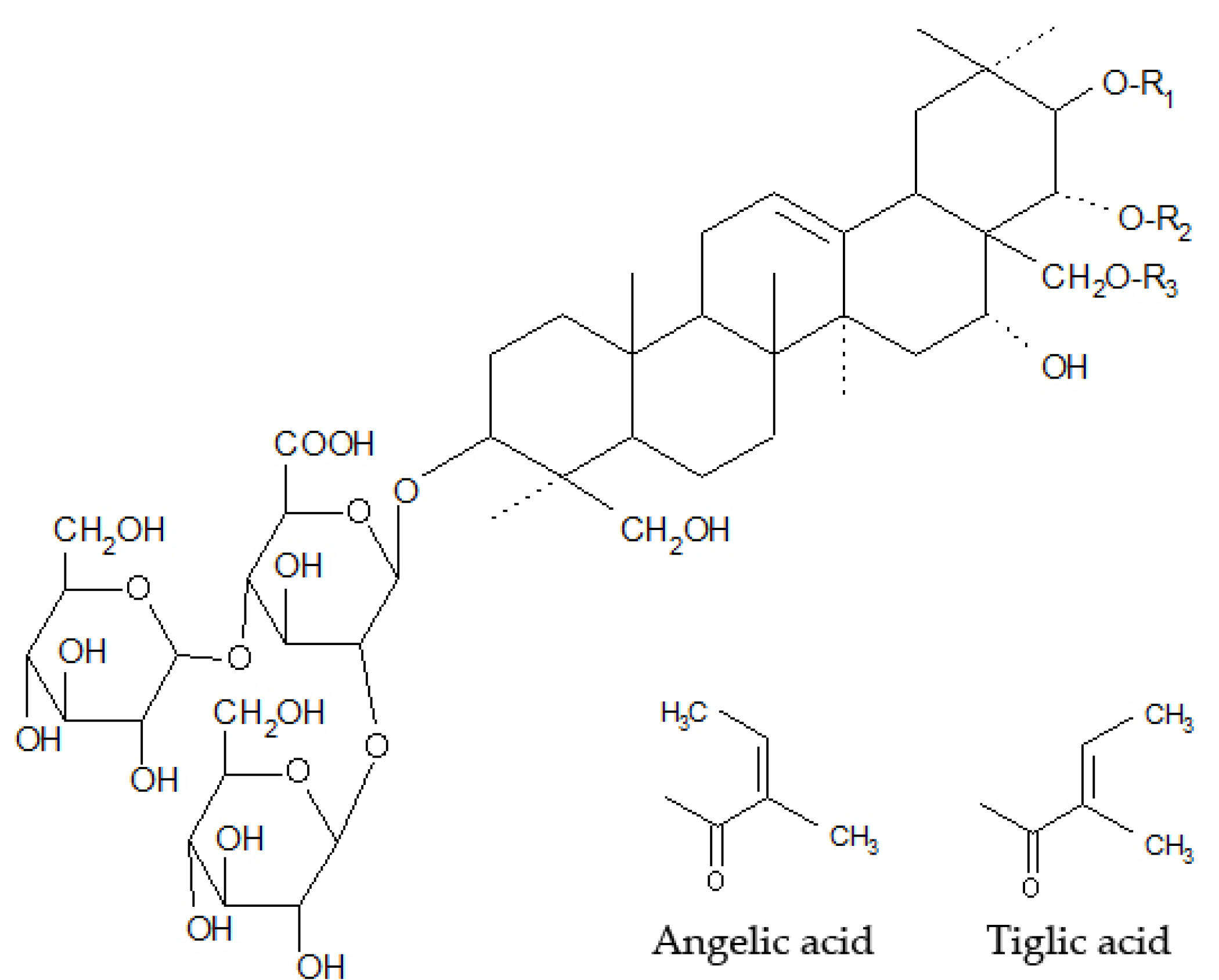

| Saponin | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escin Ia | Tiglic acid | -COCH3 | H |
| Escin Ib | Angelic acid | -COCH3 | H |
| Isoescin Ia | Tiglic acid | H | -COCH3 |
| Isoescin Ib | Angelic acid | H | -COCH3 |
| Antibodies Used for Western Blot | ||||||
| Primary Antibody | Abbreviation | Host | Isotype | Clonality | Produced by | |
| α-smooth muscle actin | SMA | rabbit | IgG | monoclonal | CST, USA | |
| Fibronectin | Fibr | rabbit | IgG | monoclonal | Abcam, UK | |
| β-actin | β-actin | rabbit | IgG | monoclonal | CST, USA | |
| Secondary Antibody | Abbreviation | Host | Isotype | Clonal | Produced by | |
| Anti-rabbit, HRP-linked | goat | IgG | CST, USA | |||
| Antibodies Used for Immunofluorescence | ||||||
| Primary Antibody | Abbreviation | Host | Produced by | Secondary Antibody | Produced by | Channel |
| α-smooth muscle actin | SMA | mouse monoclonal | DakoCytomation, Glostrup, Denmark | goat anti-mouse | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | TRITC-red |
| Vimentin | Vim | mouse monoclonal | DakoCytomation, Glostrup, Denmark | goat anti-mouse | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | TRITC-red |
| Fibronectin | Fibr | rabbit polyclonal | DakoCytomation, Glostrup, Denmark | swine anti-rabbit | Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA | FITC-green |
| Scale | Epithelialization | PMNL | Fibroblasts | Luminized Vessels | Collagen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | thickness of cut edges | absent | absent | absent | absent |
| 1 | migration of cells (<50%) | mild ST | mild-ST | mild-SCT | minimal-GT |
| 2 | migration of cells (≥50%) | mild DL/GT | mild-GT | mild-GT | mild-GT |
| 3 | bridging the excision | moderate DL/GT | moderate-GT | moderate-GT | moderate-GT |
| 4 | keratinization | marked DL/GT | marked-GT | marked-GT | marked-GT |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kováč, I.; Melegová, N.; Čoma, M.; Takáč, P.; Kováčová, K.; Hollý, M.; Ďurkáč, J.; Urban, L.; Gurbáľová, M.; Švajdlenka, E.; et al. Aesculus hippocastanum L. Extract Does Not Induce Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Conversion but Increases Extracellular Matrix Production In Vitro Leading to Increased Wound Tensile Strength in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081917
Kováč I, Melegová N, Čoma M, Takáč P, Kováčová K, Hollý M, Ďurkáč J, Urban L, Gurbáľová M, Švajdlenka E, et al. Aesculus hippocastanum L. Extract Does Not Induce Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Conversion but Increases Extracellular Matrix Production In Vitro Leading to Increased Wound Tensile Strength in Rats. Molecules. 2020; 25(8):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081917
Chicago/Turabian StyleKováč, Ivan, Nikola Melegová, Matúš Čoma, Peter Takáč, Katarína Kováčová, Martin Hollý, Ján Ďurkáč, Lukáš Urban, Miriam Gurbáľová, Emil Švajdlenka, and et al. 2020. "Aesculus hippocastanum L. Extract Does Not Induce Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Conversion but Increases Extracellular Matrix Production In Vitro Leading to Increased Wound Tensile Strength in Rats" Molecules 25, no. 8: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081917
APA StyleKováč, I., Melegová, N., Čoma, M., Takáč, P., Kováčová, K., Hollý, M., Ďurkáč, J., Urban, L., Gurbáľová, M., Švajdlenka, E., Mojžišová, G., Zajíček, R., Szabo, P., Mučaji, P., & Gál, P. (2020). Aesculus hippocastanum L. Extract Does Not Induce Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Conversion but Increases Extracellular Matrix Production In Vitro Leading to Increased Wound Tensile Strength in Rats. Molecules, 25(8), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081917






