Determination of Eight Coccidiostats in Eggs by Liquid–Liquid Extraction–Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sample Clean-Up
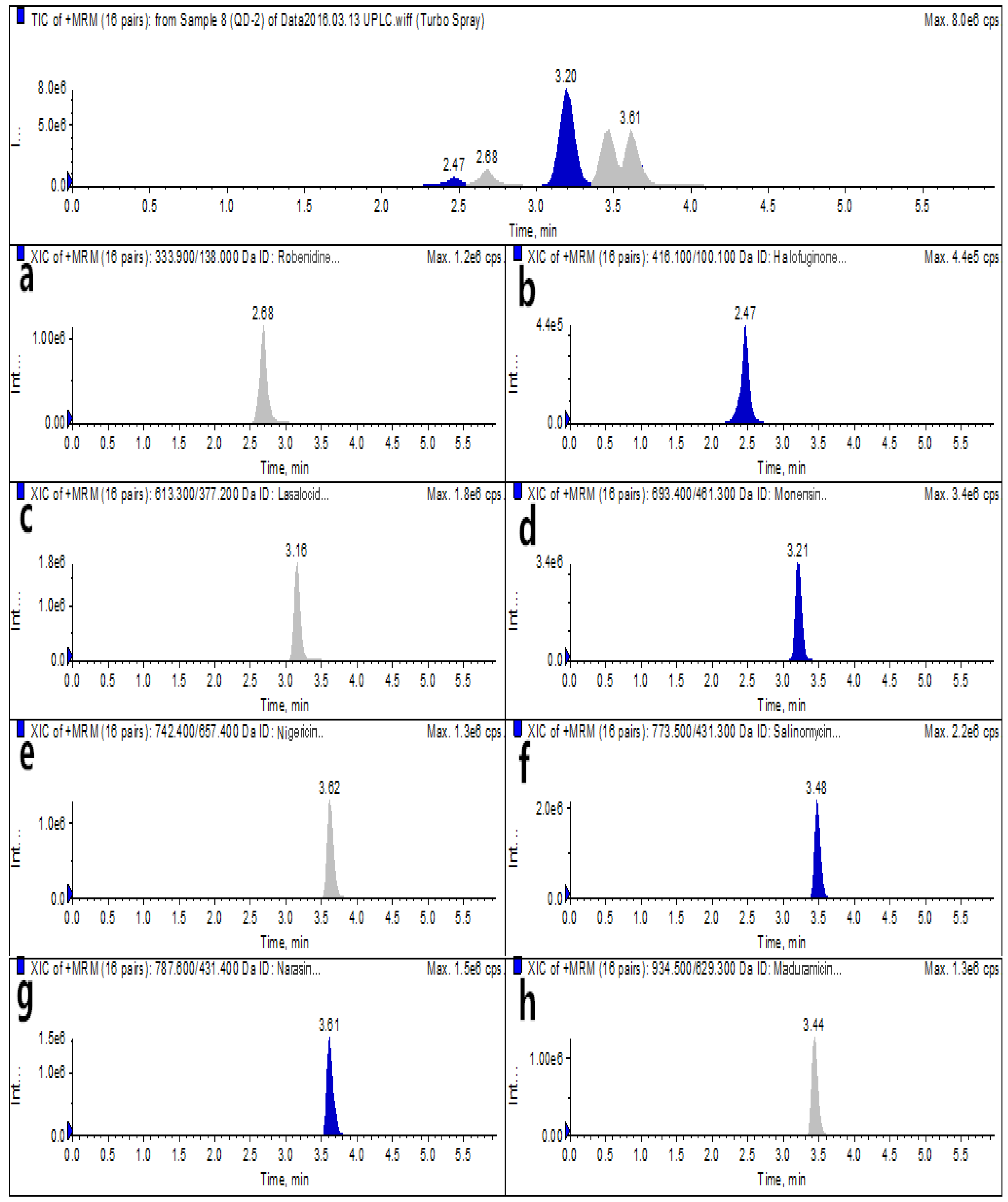
2.2. Selection of the Chromatographic Column and Mobile Phase
2.3. Optimization of Mass Spectrometric Conditions
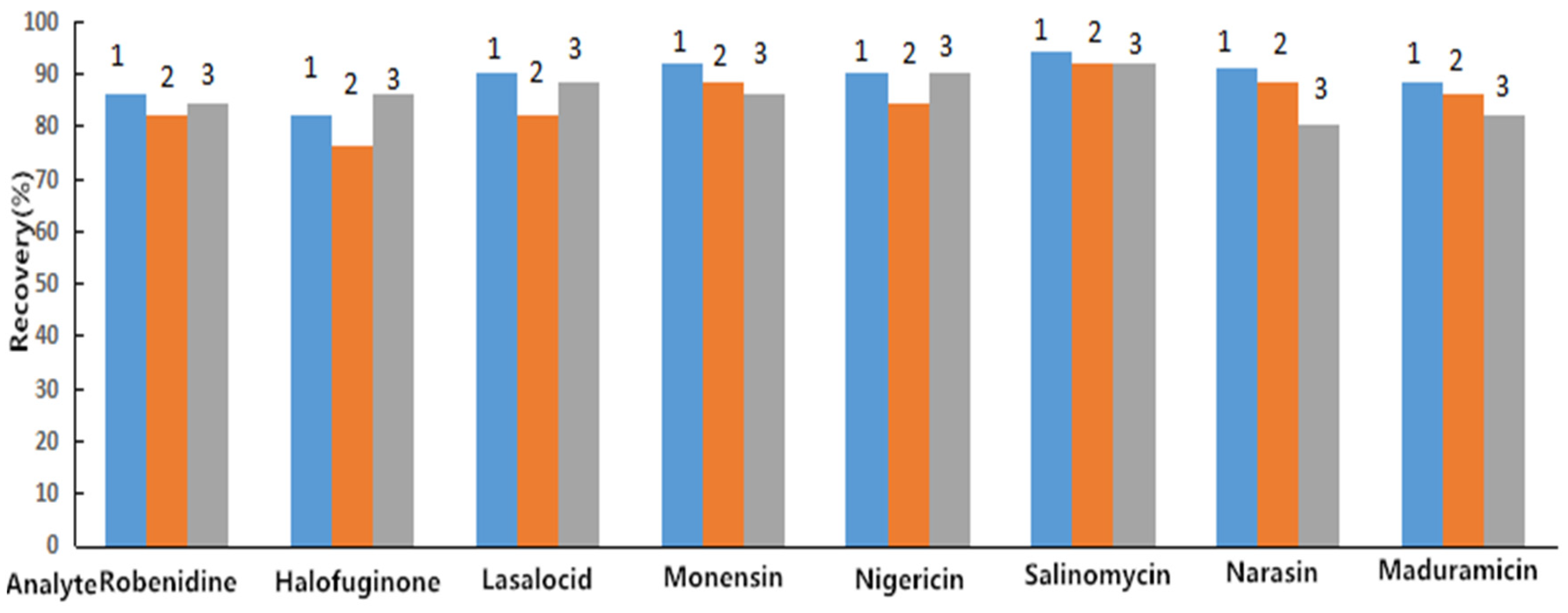
2.4. Bioanalytical Method Validation
2.5. Comparison with Other LC–MS/MS Methods
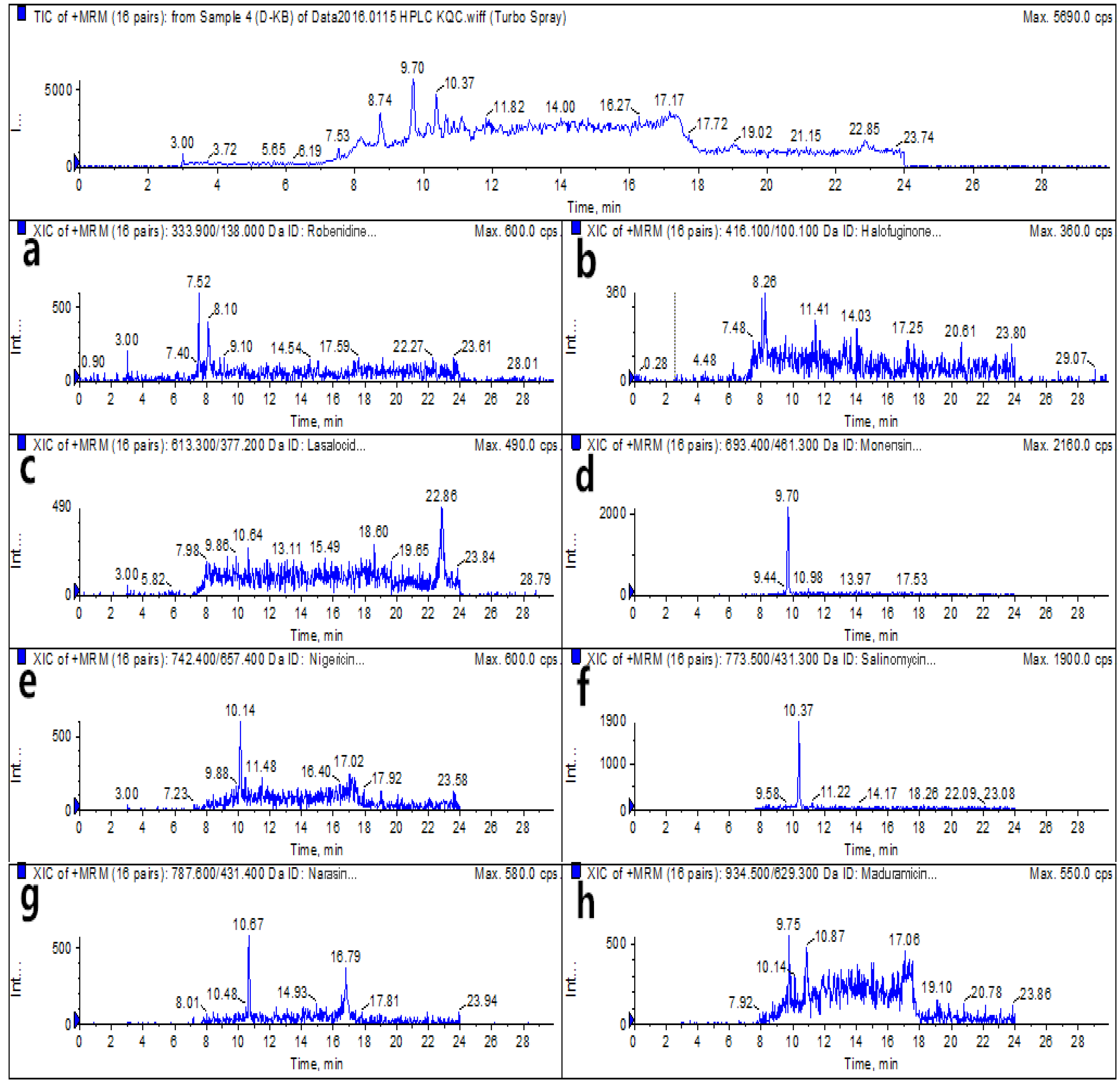
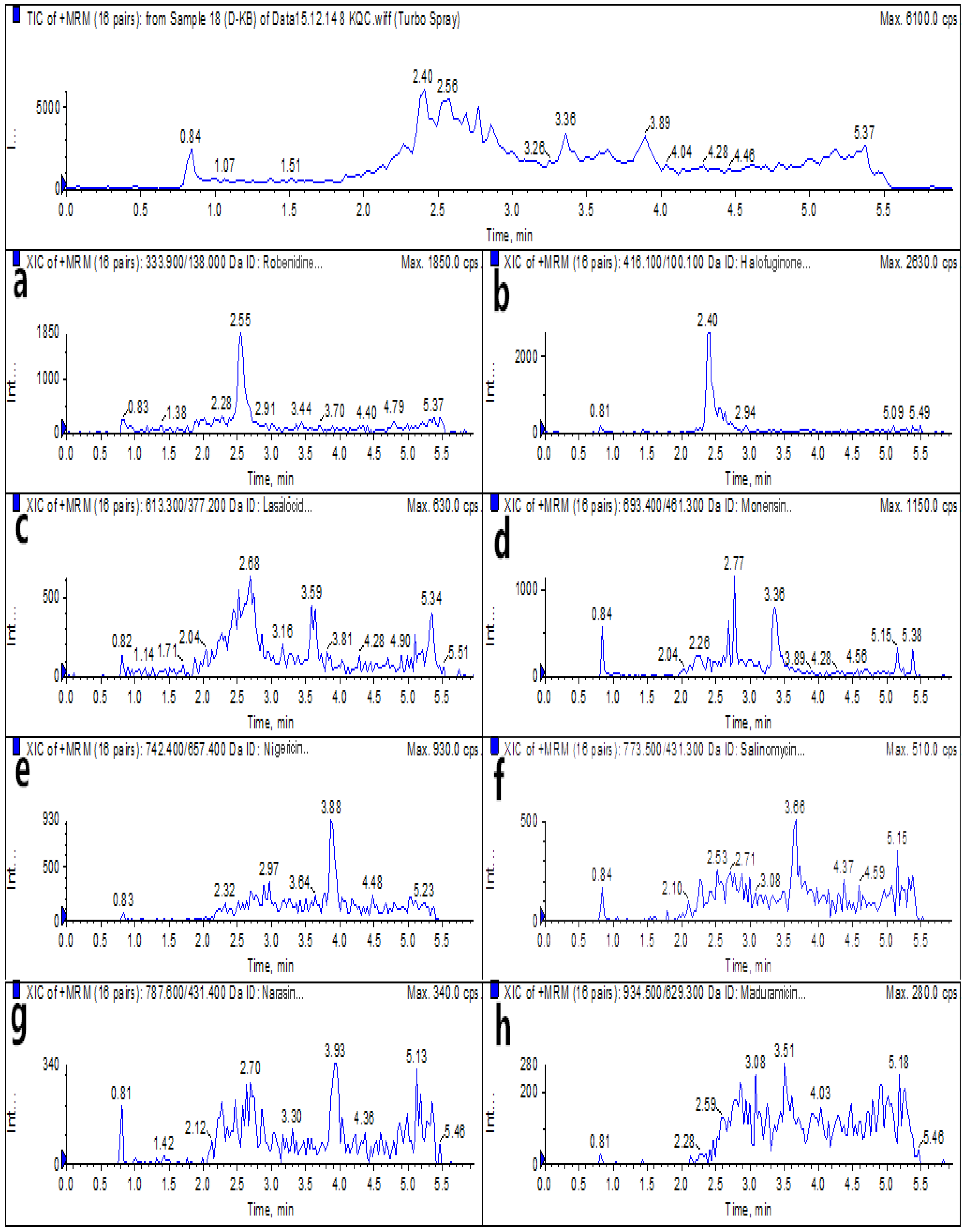
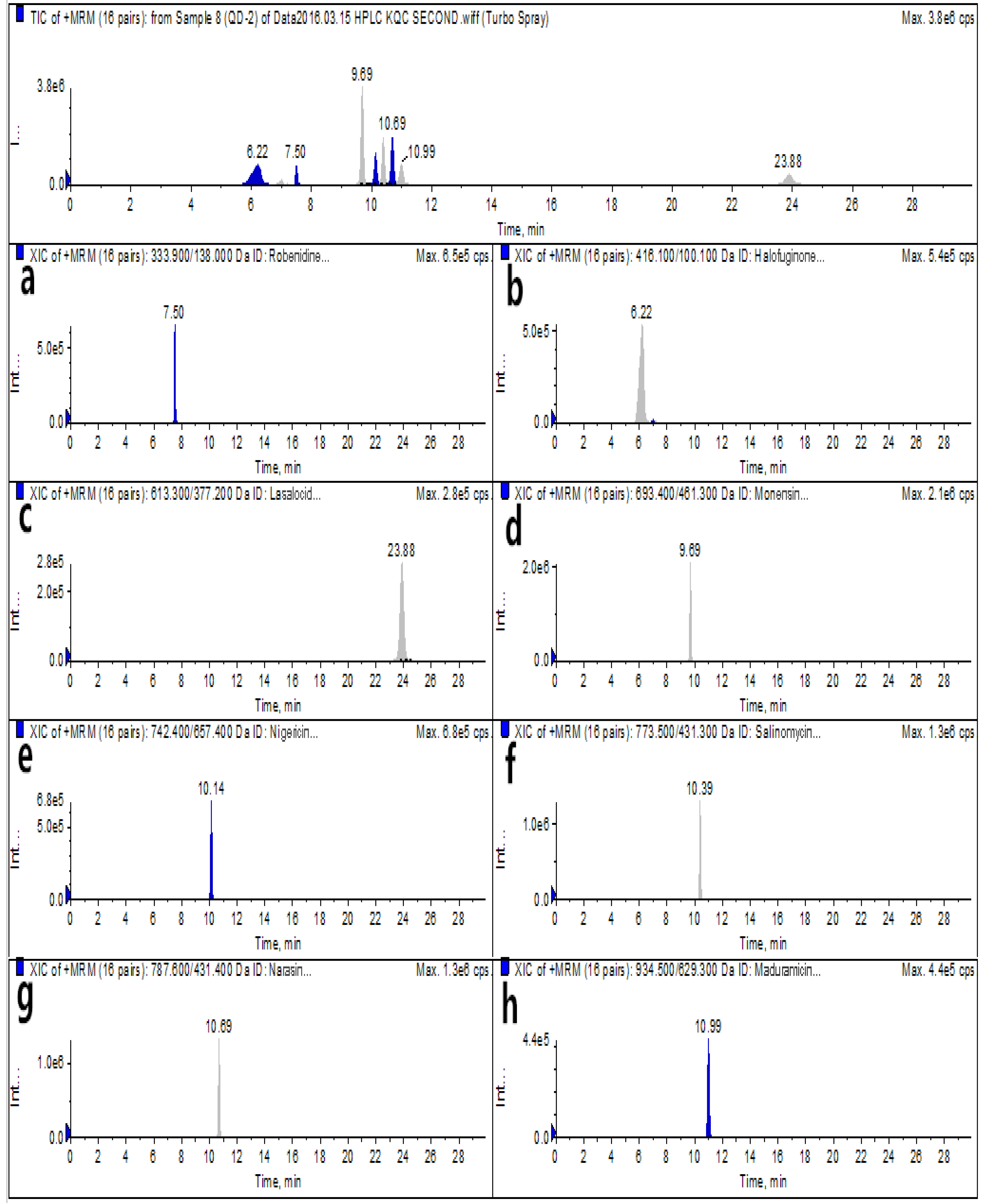
2.6. Real Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of the Standard Stock and Working Solutions
3.3. LC–MS/MS Instrumentation and Conditions
3.3.1. HPLC Method
3.3.2. UPLC Method
3.3.3. Mass Spectrometric Conditions
3.4. Sample Extraction and Purification
3.4.1. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3.4.2. Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Solid-Phase Extraction
3.4.3. Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Automated Solid-Phase Extraction
3.4.4. Sample Purification
3.5. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinard-Van Der Laan, M.H.; Monvoisin, J.L.; Pery, P.; Hamet, N.; Thomas, M. Comparison of outbred lines of chickens for resistance to experimental infection with coccidiosis (Eimeria tenella). Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Allen, P.C.; Yun, C.H.; Pollock, D.; Sadjadi, M.; Emara, M.G. Analysis of disease resistance-associated parameters in broiler chickens challenged with Eimeria maxima. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Dai, G.; Sun, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Shi, H.; Xie, K.; Wang, J. Establishing a model for evaluating chicken coccidiosis resistance based on principal component analysis. Animals 2019, 9, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatkowska, M.; Jedziniak, P.; Zmudzki, J. Residues of veterinary medicinal products and coccidiostats in eggs--causes, control and results of surveillance program in Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 15, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.H.B.; Rajab, A. Evaluation of anti-coccidial vaccines and coccidiostate drugs on growth performance in experimental coccidiosis of broiler chickens. In Proceedings of the EPC 2006-12th European Poultry Conference, Verona, Italy, 10–14 September 2006. World’s Poultry Science Association (WPSA). [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003, of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2003 on additives for use in animal nutrition. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2003, L268, 29–43.
- Vincent, U.; Ezerskis, Z.; Chedin, M.; von Holst, C. Determination of ionophore coccidiostats in feeding stuffs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Part II. Application to cross-contamination levels and non-targeted feed. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietruk, K.; Olejnik, M.; Jedziniak, P.; Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, T. Determination of fifteen coccidiostats in feed at carry-over levels using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 112, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberge, V.; Delezie, E.; Huyghebaert, G.; Delahaut, P.; Pierret, G.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S.; Daeseleire, E. Transfer of the coccidiostats monensin and lasalocid from feed at cross-contamination levels to whole egg, egg white and egg yolk. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2012, 29, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, P.P.J.; Balzer-Rutgers, P.; Te Brinke, E.M.; Bolck, Y.J.C.; Berendsen, B.J.A.; Gerçek, H.; Schat, B.; van Rhijn, J.A. Deposition and depletion of the coccidiostats toltrazuril and halofuginone in eggs. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Ham, H.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Cheong, N.-Y.; Myung, S.-W. Determination of coccidiostats (Amprolium and Decoquinate) in cattle and chicken’s muscle using high performance liquid chromatography. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olejnik, M.; Jedziniak, P.; Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, T. The determination of six ionophore coccidiostats in feed by liquid chromatography with postcolumn derivatisation and spectrofotometric/fluorescence detection. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 763402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.C.; Mortier, L.; Daeseleire, E.; Fodey, T.; Elliott, C.; Delahaut, P. Screening for the coccidiostats halofuginone and nicarbazin in egg and chicken muscle: Development of an ELISA. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, F.; El-Razeq, S.A.; Fouad, M.; Zayed, S.; Fouad, F. Simultaneous determination of five coccidiostats in veterinary powders, feed premixes, and baby food by micellar electrokinetic chromatography: Application to chicken tissues and liver. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienenmann-Ploum, M.E.; Huet, A.C.; Campbell, K.; Fodey, T.L.; Vincent, U.; Haasnoot, W.; Delahaut, P.; Elliott, C.T.; Nielen, M.W. Development of a five-plex flow cytometric immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of six coccidiostats in feed and eggs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Thomaidis, N.S. Multi-residue methodology for the determination of 16 coccidiostats in animal tissues and eggs by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, L.; Daeseleire, E.; Van Peteghem, C. Determination of the ionophoric coccidiostats narasin, monensin, lasalocid and salinomycin in eggs by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokka, M.; Peltonen, K. Simultaneous determination of four coccidiostats in eggs and broiler meat: Validation of an LC-MS/MS method. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiarelli, F.; Di Filippo, P.; Riccardi, C.; Pomata, D.; Giannetti, L.; Neri, B.; Rago, D. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis of synthetic coccidiostats in eggs. Separations 2017, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Turek, A.; Rybicki, M.J.; Gierach, A.; Korol, W.; Dzido, T.H. Solvent front position extraction procedure for preparation of biological samples with coccidiostats for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2019, 32, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nász, S.; Károlyné, E.M.; Rikker, T.; Eke, Z. Determination of coccidiostats in milk products by LC–MS and its application to a fermentation experiment. Chromatographia 2012, 75, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muharem, M.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Feng, N.; Hao, J.; Zhu, C.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Han, N. Determination of six anticoccidials in chicken using QuEChERS combined with ultra high liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2015, 33, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.U.; Spisso, B.F.; Jacob, S.C.; Monteiro, M.A.; Ferreira, R.G.; Bde, S.C.; da Nobrega, A.W. Validation of a liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric method to determine six polyether ionophores in raw, UHT, pasteurized and powdered milk. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Song, G.; Ai, L.F.; Li, J.C. Determination of six polyether antibiotic residues in foods of animal origin by solid phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1017–1018, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisso, B.F.; Ferreira, R.G.; Pereira, M.U.; Monteiro, M.A.; Cruz, T.A.; da Costa, R.P.; Lima, A.M.; da Nobrega, A.W. Simultaneous determination of polyether ionophores, macrolides and lincosamides in hen eggs by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry using a simple solvent extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 682, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, C.; Iglesias, A.; Regal, P.; Miranda, J.M.; Fente, C.; Cepeda, A. A sensitive and validated HPLC–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of seven coccidiostats in bovine whole milk. Food Control 2012, 27, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Xie, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Dai, G.; Wang, J. Development and comparison of HPLC–MS/MS and UPLC–MS/MS methods for determining eight coccidiostats in beef. J. Chromatogr., B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1087–1088, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, C.; Regal, P.; Miranda, J.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides, penicillins and coccidiostats in pork by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 50, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chico, J.; Rubies, A.; Centrich, F.; Companyo, R.; Prat, M.D.; Granados, M. Use of gel permeation chromatography for clean-up in the analysis of coccidiostats in eggs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4777–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreil-Cheneau, E.; Bessiral, M.; Roudaut, B.; Verdon, E.; Sanders, P. Validation of a multi-residue liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry confirmatory method for 10 anticoccidials in eggs according to commission decision 2002/657/EC. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8149–8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarini, R.; Fioroni, L.; Moretti, S.; Pettinacci, L.; Dusi, G. Development and validation of a multi-residue liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry confirmatory method for eleven coccidiostats in eggs. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 700, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nász, S.; Debreczeni, L.; Rikker, T.; Eke, Z. Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for determination of eleven coccidiostats in milk. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, M.; Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, T.; Jedziniak, P. Confirmatory method for determination of coccidiostats in eggs. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy. 2010, 54, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Olejnik, M.; Szprengier-Juszkiewicz, T.; Jedziniak, P. Multi-residue confirmatory method for the determination of twelve coccidiostats in chicken liver using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8141–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, C.; Iglesias, A.; Regal, P.; Miranda, J.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Development of a multi-class method for the identification and quantification of residues of antibiotics, coccidiostats and corticosteroids in milk by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 22, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.; Ribeiro, C.; Hoff, R.B.; Costa, T.D. A simple and high-throughput method for determination and confirmation of 14 coccidiostats in poultry muscle and eggs using liquid chromatography—quadrupole linear ion trap - tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-QqLIT-MS/MS): Validation according to European Union 2002/657/EC. Talanta 2017, 168, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatkowska, M.; Jedziniak, P.; Zmudzki, J. Multiresidue method for the simultaneous determination of veterinary medicinal products, feed additives and illegal dyes in eggs using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, J.L.; Boison, J.O. A multi-residue method for 17 anticoccidial drugs and ractopamine in animal tissues by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal. 2016, 8, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-N.; Peng, G.-J.; Liao, C.-D.; Kao, Y.-M.; Tseng, S.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. Multi-residue analysis using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for detection of 20 coccidiostats in poultry, livestock, and aquatic tissues. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, M.; Clarke, L.; O’Mahony, J.; Gadaj, A.; O’Kennedy, R.; Danaher, M. Determination of 20 coccidiostats in egg and avian muscle tissue using ultra high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1253, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.; Moloney, M.; O’Mahony, J.; O’Kennedy, R.; Danaher, M. Determination of 20 coccidiostats in milk, duck muscle and non-avian muscle tissue using UHPLC–MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Communities. Commission decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing council directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2002, 221, 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- US Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Center for Veterinary Medicine. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People ‘s Republic of China. Maxium Residue Level of Veterinary Drugs in Food of Animal Origin; Notice no. 235; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2002.
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Analyte | Precursor Ions (m/z) | Product Ions (m/z) | Declustering Potential (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROB | 333.9 | 138.0* 155.0 | 59.1 59.1 | 47.0 47.0 |
| HAF | 416.1 | 100.1* 138.2 | 46.2 62.2 | 25.6 25.2 |
| LAS | 613.3 | 377.2* 577.4 | 66.0 56.9 | 48.4 44.0 |
| MON | 693.4 | 461.3* 479.3 | 68.0 68.0 | 68.3 67.8 |
| NIG | 747.4 | 657.4* 675.4 | 86.0 86.9 | 37.0 32.0 |
| SAL | 773.5 | 431.3* 531.4 | 59.1 59.1 | 65.6 54.5 |
| NAR | 787.6 | 431.4* 531.4 | 84.8 87.8 | 69.9 60.3 |
| MAD | 934.5 | 629.3* 647.4 | 24.8 24.8 | 31.1 27.9 |
| Method | Analyte | Linearity | Determination Coefficient (R2) | Linearity Range (μg/kg) | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC–MS/MS | ROB | y = 34616x − 506.76 | 0.99983 | 0.82~100 | 0.23 | 0.82 |
| HAF | y = 61224x + 6543.7 | 0.99986 | 1.04~100 | 0.32 | 1.04 | |
| LAS | y = 113825.898x − 45626 | 0.99951 | 1.46~100 | 0.44 | 1.46 | |
| MON | y = 52901x + 14151 | 0.99995 | 1.21~100 | 0.37 | 1.21 | |
| NIG | y = 67809x − 22104 | 0.99966 | 1.03~100 | 0.31 | 1.03 | |
| SAL | y = 114639.404x + 26519 | 0.99974 | 1.68~100 | 0.51 | 1.68 | |
| NAR | y = 107772.7495x + 20585 | 0.99986 | 1.45~100 | 0.44 | 1.45 | |
| MAD | Y = 178339.3611x − 107324.0928 | 0.99984 | 1.73~100 | 0.52 | 1.73 | |
| UPLC–MS/MS | ROB | y = 292553.0261x + 16571 | 0.99993 | 0.81~100 | 0.24 | 0.81 |
| HAF | y = 100732.4827x − 769.94 | 0.99994 | 1.04~100 | 0.32 | 1.04 | |
| LAS | y = 538339.9425x + 32878 | 0.99994 | 1.25~100 | 0.42 | 1.25 | |
| MON | y = 463092.5586x + 30618 | 0.99993 | 1.08~100 | 0.18 | 1.08 | |
| NIG | y = 593130.8977x− 29292 | 0.99976 | 0.87~100 | 0.16 | 0.87 | |
| SAL | y = 719531.8524x − 96792 | 0.99979 | 0.85~100 | 0.19 | 0.85 | |
| NAR | y = 715834.9244x − 129389.5518 | 0.99977 | 1.02~100 | 0.28 | 1.02 | |
| MAD | y = 19688x + 2081 | 0.99976 | 0.99~100 | 0.22 | 0.99 |
| Analyte | Spiked Concentration (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) (n = 6) | RSD (%) (n = 6) | Intraday RSD (%) (n = 6) | Interday RSD (%) (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROB | 0.82 | 76.28 ± 10.31 | 13.52 | 16.32 | 14.38 |
| 50.00 | 85.42 ± 6.20 | 7.26 | 6.55 | 5.81 | |
| 100.00 a | 82.66 ± 6.89 | 8.34 | 6.47 | 6.58 | |
| 200.00 | 86.31 ± 5.39 | 6.24 | 7.23 | 8.02 | |
| HAF | 1.04 | 74.58 ± 7.82 | 10.49 | 12.18 | 13.09 |
| 50.00 | 86.44 ± 5.17 | 5.98 | 8.34 | 8.56 | |
| 100.00 a | 85.21 ± 4.53 | 5.32 | 6.17 | 5.89 | |
| 200.00 | 82.45 ± 5.47 | 6.63 | 5.84 | 4.35 | |
| LAS | 1.46 | 76.25 ± 8.59 | 11.27 | 11.68 | 14.52 |
| 300.00 | 83.61 ± 3.39 | 4.05 | 2.10 | 6.87 | |
| 600.00 a | 86.34 ± 2.28 | 2.64 | 5.58 | 7.65 | |
| 1200.00 | 85.20 ± 2.54 | 2.98 | 5.96 | 3.61 | |
| MON | 1.21 | 76.98 ± 9.03 | 11.73 | 14.25 | 13.13 |
| 750.00 | 86.77 ± 4.27 | 4.92 | 6.58 | 7.36 | |
| 1500.00 a | 94.35 ± 4.57 | 4.84 | 5.38 | 8.89 | |
| 3000.00 | 96.52 ± 4.92 | 5.10 | 5.98 | 6.74 | |
| NIG | 1.03 | 76.65 ± 8.40 | 10.96 | 12.43 | 15.09 |
| 300.00 | 81.26 ± 3.32 | 4.09 | 9.84 | 3.46 | |
| 600.00 a | 89.34 ± 4.18 | 4.68 | 5.86 | 7.82 | |
| 1200.00 | 89.98 ± 4.28 | 4.76 | 6.62 | 8.84 | |
| SAL | 1.68 | 72.81 ± 11.17 | 15.34 | 16.25 | 15.43 |
| 300.00 | 80.27 ± 4.33 | 5.39 | 5.49 | 8.46 | |
| 600.00 a | 89.80 ± 5.71 | 6.36 | 6.71 | 3.69 | |
| 1200.00 | 89.78 ± 4.75 | 5.29 | 3.56 | 8.55 | |
| NAR | 1.45 | 71.69 ± 7.79 | 10.87 | 18.72 | 18.47 |
| 300.00 | 84.57 ± 3.79 | 4.48 | 7.13 | 7.41 | |
| 600.00 a | 86.88 ± 3.27 | 3.76 | 6.98 | 6.83 | |
| 1200.00 | 86.50 ± 4.50 | 5.20 | 8.28 | 9.53 | |
| MAD | 1.73 | 79.63 ± 7.88 | 9.90 | 9.68 | 11.34 |
| 120.00 | 83.81 ± 4.79 | 5.72 | 8.34 | 7.62 | |
| 240.00 a | 86.62 ± 4.40 | 5.08 | 8.87 | 7.58 | |
| 480.00 | 84.37 ± 4.74 | 5.62 | 8.86 | 8.51 |
| Analyte | Spiked Concentration (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) (n = 6) | RSD (%) (n = 6) | Intraday RSD (%) (n = 6) | Interday RSD (%) (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROB | 0.81 | 81.23 ± 5.47 | 6.73 | 8.29 | 9.37 |
| 50.00 | 86.68 ± 5.12 | 5.91 | 7.29 | 11.83 | |
| 100.00 a | 86.71 ± 5.32 | 6.14 | 9.01 | 11.07 | |
| 200.00 | 86.22 ± 5.22 | 6.05 | 7.20 | 11.10 | |
| HAF | 1.04 | 72.26 ± 5.73 | 7.93 | 7.24 | 8.15 |
| 50.00 | 77.57 ± 4.20 | 5.41 | 7.34 | 8.70 | |
| 100.00 a | 80.26 ± 4.38 | 5.46 | 7.13 | 9.19 | |
| 200.00 | 79.50 ± 2.93 | 3.69 | 7.75 | 8.63 | |
| LAS | 1.25 | 75.64 ± 7.30 | 9.65 | 12.28 | 15.42 |
| 300.00 | 82.75 ± 5.25 | 6.34 | 8.40 | 9.26 | |
| 600.00 a | 83.73 ± 4.18 | 4.99 | 8.36 | 10.46 | |
| 1200.00 | 82.35 ± 5.82 | 7.07 | 8.75 | 10.79 | |
| MON | 1.08 | 80.36 ± 7.78 | 9.68 | 10.37 | 14.58 |
| 750.00 | 90.69 ± 7.00 | 7.72 | 7.96 | 8.25 | |
| 1500.00 a | 90.44 ± 7.91 | 8.75 | 9.84 | 9.86 | |
| 3000.00 | 93.55 ± 6.93 | 7.41 | 8.51 | 8.88 | |
| NIG | 0.87 | 81.39 ± 10.78 | 13.25 | 11.58 | 14.26 |
| 300.00 | 99.52 ± 7.98 | 8.02 | 8.66 | 10.19 | |
| 600.00 a | 99.14 ± 8.60 | 8.67 | 9.14 | 9.55 | |
| 1200.00 | 93.74 ± 7.33 | 7.82 | 9.77 | 9.58 | |
| SAL | 0.85 | 87.35 ± 8.16 | 9.34 | 9.48 | 11.25 |
| 300.00 | 102.74 ± 4.95 | 4.82 | 7.62 | 9.84 | |
| 600.00 a | 102.04 ± 5.60 | 5.49 | 8.06 | 9.93 | |
| 1200.00 | 96.53 ± 5.89 | 6.10 | 8.55 | 9.99 | |
| NAR | 1.02 | 74.93 ± 4.26 | 5.69 | 6.72 | 10.54 |
| 300.00 | 88.51 ± 6.69 | 7.56 | 8.79 | 10.14 | |
| 600.00 a | 88.53 ± 6.24 | 7.05 | 7.22 | 8.42 | |
| 1200.00 | 86.14 ± 7.42 | 8.61 | 8.62 | 9.15 | |
| MAD | 0.99 | 72.54 ± 7.44 | 10.26 | 9.38 | 11.76 |
| 120.00 | 84.00 ± 4.80 | 5.71 | 7.97 | 9.86 | |
| 240.00 a | 82.42 ± 4.09 | 4.96 | 9.00 | 8.45 | |
| 480.00 | 83.93 ± 6.75 | 8.04 | 9.72 | 10.07 |
| Added Levels (μg/kg) | Analyte | ROB | HAF | LAS | MON | NIG | SAL | NAR | MAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 MRL | Matrix effect (%) | 15 | 16 | −14 | −31 | −37 | −41 | −38 | −51 |
| 1 MRL | 19 | 24 | −21 | −34 | −30 | −37 | −40 | −55 | |
| 2 MRL | 22 | 18 | −29 | −33 | −41 | −38 | −34 | −52 |
| Detection Method | Sample Preparation Method | Analyte | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Detection Time (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC–MS/MS | LLE | LAS, MON, SAL, NAR | 1.0 | 1.2–1.6 | 90.3–112.7 | 5.4–13.9 | 14 | Mortier et al. [17] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | SPE | LAS, MON, SAL, NAR | 0.8–1.4 | 0.9–2.0 | 64.0–99.0 | – | 12 | Rokka and Peltonen [18] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | LLE–SPE | ROB | – | 5.0 | 62.0–76.0 | 7.1–13.7 | 11 | Buiarelli et al. [19] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | LLE | LAS, MON, SAL, NAR, MAD | 0.04–1.0 | 0.16–3.4 | - | 4.4–15.7 | 18 | Spisso et al. [25] |
| UPLC–MS/MS | GPC | LAS, MON, SAL, NAR, MAD | - | - | 55.3–77.5 | 4.2–15.6 | 11 | Chico et al. [29] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | SPE | ROB, HAF, LAS, MON, SAL, NAR, MAD | - | - | 89.0–113.0 | 3.4–16.0 | 40 | Galarini et al. [31] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | SPE | ROB, HAF, LAS, MON, NIG, SAL, NAR, MAD | 0.26–2.62 | 0.75–7.54 | 89.1–111.7 | 3.6–19.0 | 22 | Olejnik et al. [33] |
| HPLC–MS/MS | LLE–SPE | ROB, HAF, LAS, MON, NIG, SAL, NAR, MAD | 0.23–0.52 | 0.82–1.73 | 71.7–96.5 | 3.6–15.3 | 30 | this method |
| UPLC–MS/MS | LLE–SPE | ROB, HAF, LAS, MON, NIG, SAL, NAR, MAD | 0.16–0.42 | 0.81–1.25 | 72.3–102.7 | 3.7–13.3 | 6 | this method |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Xie, K.; Diao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Dai, G. Determination of Eight Coccidiostats in Eggs by Liquid–Liquid Extraction–Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040987
Wang B, Liu J, Zhao X, Xie K, Diao Z, Zhang G, Zhang T, Dai G. Determination of Eight Coccidiostats in Eggs by Liquid–Liquid Extraction–Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2020; 25(4):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040987
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Jianyu Liu, Xia Zhao, Kaizhou Xie, Zhixiang Diao, Genxi Zhang, Tao Zhang, and Guojun Dai. 2020. "Determination of Eight Coccidiostats in Eggs by Liquid–Liquid Extraction–Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 25, no. 4: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040987
APA StyleWang, B., Liu, J., Zhao, X., Xie, K., Diao, Z., Zhang, G., Zhang, T., & Dai, G. (2020). Determination of Eight Coccidiostats in Eggs by Liquid–Liquid Extraction–Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 25(4), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040987






