Modulation of Mn3+ Spin State by Guest Molecule Inclusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
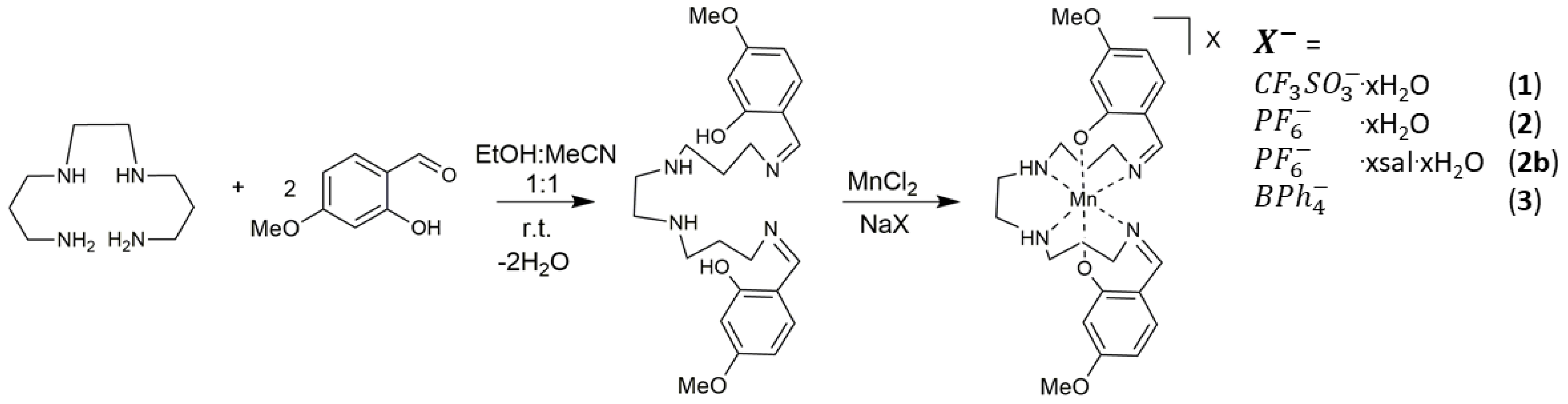
2.1. Synthetic Approach
Synthesis and Characterization of Compounds (1)–(3)
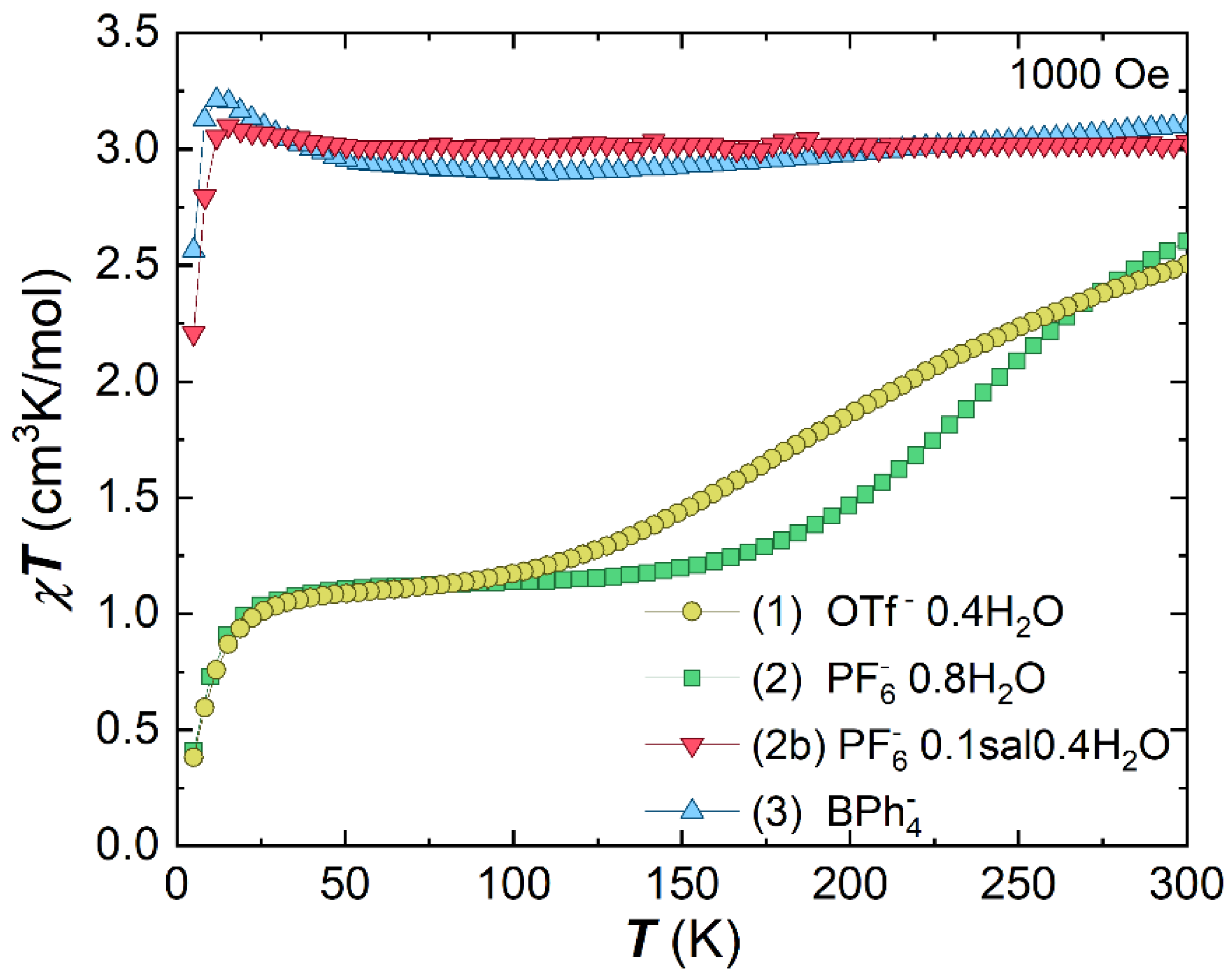
2.2. Magnetic Characterisation
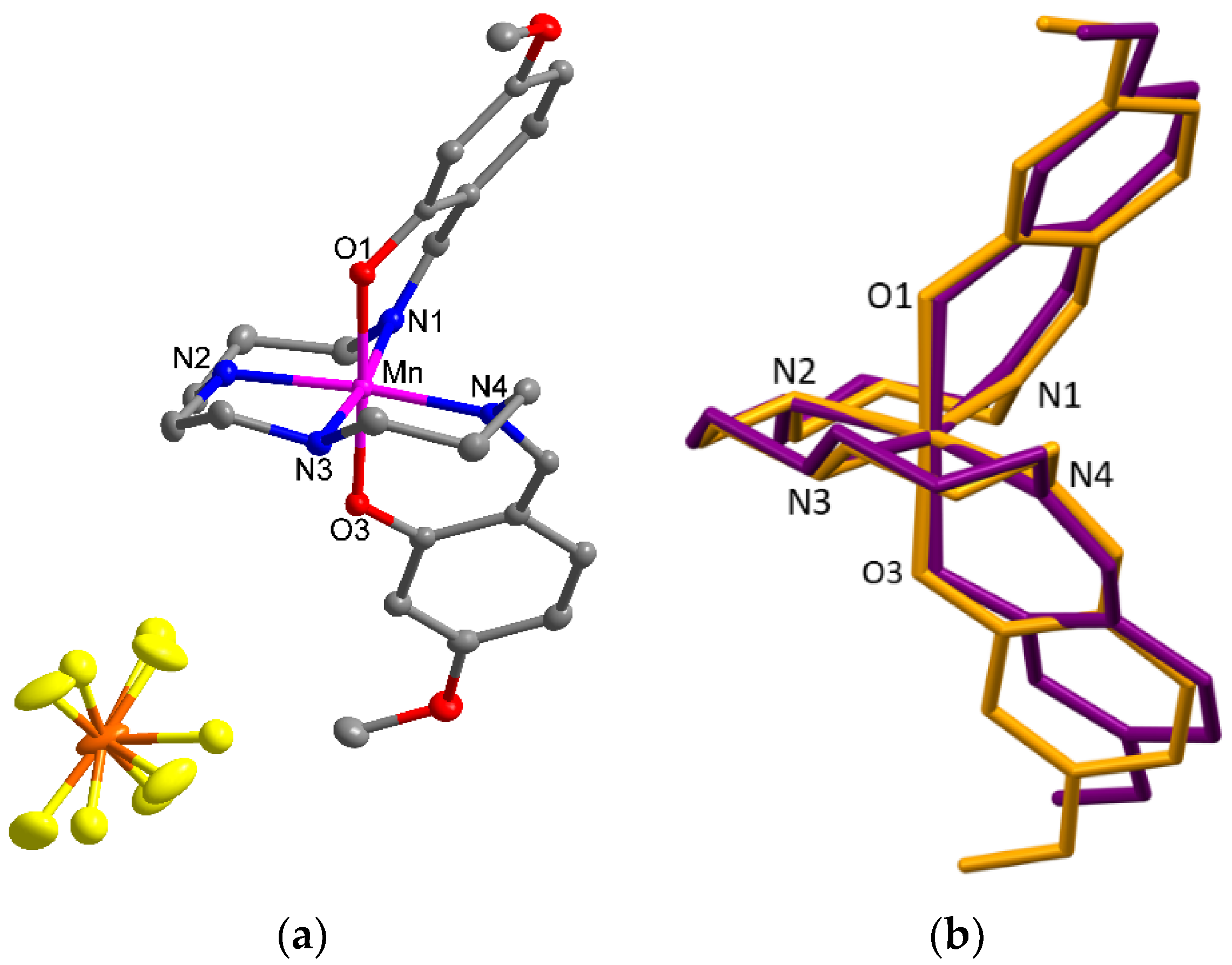
2.3. Structural Characterisation of Compounds (1)–(3)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Physical Measurements
4.2. Synthesis and Characterisation of Compounds (1)–(3)
4.3. Single-Crystal X-ray Structure Determination
4.4. Magnetic Measurements
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Compound | [MnL1]OTf·0.7H2O (1) | [MnL1]OTf·0.7H2O (1) | [MnL1]PF6·0.3H2O·0.3sal (2b) |
| Sample code | mor206 (100 K) | mor203 (293 K) | mor1106 (100 K) |
| Empirical formula | C25H33.3N4O7.7F3SMn | C25H33.5N4O7.7F3SMn | C26.6H35.3N4O5.3F6PMn |
| Formula weight | 658.06 | 658.06 | 696.58 |
| Temperature (K) | 100(2) | 293(2) | 100(2) |
| Radiation | Mo-Kα | Mo-Kα | Cu-Kα |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/c | P21/n |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.50 × 0.30 × 0.20 | 0.80 × 0.40 × 0.30 | 0.27 × 0.20 × 0.16 |
| a (Å) | 8.0779(10) | 8.2335(13) | 17.2396(6) |
| b (Å) | 20.908(3) | 21.096(3) | 9.6048(2) |
| c (Å) | 16.371(2) | 16.582(3) | 19.0249(6) |
| α (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β (°) | 97.789(2) | 98.091(3) | 105.501(3) |
| γ (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| V (Å3) | 2739.3(6) | 2851.6(8) | 3035.61(16) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| dcalc (g cm−3) | 1.586 | 1.533 | 1.524 |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.634 | 0.610 | 4.770 |
| F(000) | 1366 | 1366 | 1439 |
| Limiting indices | h = ±11, k = ±29, l = ±23 | h = ±10, k = ±26, l = ±20 | h = ±21, k = ±12, l = ±23 |
| Reflect. coll./uniq. | 29310/7944 | 24235/5593 | 34913/6368 |
| R(int) | 0.0301 | 0.0238 | 0.0621 |
| Complete to Θ (%) | 99.4 | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| Data/restr./param. | 7944/2/398 | 5593/0/389 | 6368/93/473 |
| GooF on F2 | 1.040 | 1.053 | 1.037 |
| Final R indices [I > 2σ(I)] | R1 = 0.00491, wR2 = 0.1302 | R1 = 0.0455, wR2 = 0.1215 | R1 = 0.0412, wR2 = 0.1119 |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0585, wR2 = 0.1387 | R1 = 0.0517, wR2 = 0.1277 | R1 = 0.0438, wR2 = 0.1155 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole (e·Å−3) | 1.724 and −1.337 | 0.722 and −0.432 | 0.863 and −0.554 |
| CCDC no. | 2042004 | 2042005 | 2042008 |
| Compound | [MnL1]PF6·0.5H2O (2) | [MnL1]PF6·H2O (2) | [MnL1]BPh4 (3) |
| Sample code | mor1152 (100 K) | mor141 (293 K) | mor428 |
| Empirical formula | C24H33.1N4O4.5F6P Mn | C24H34N4O5F6PMn | C48H52BN4O4Mn |
| Formula weight | 650.24 | 658.46 | 814.69 |
| Temperature (K) | 100(2) | 293(2) | 100(2) |
| Radiation | Cu-Kα | Mo-Kα | Cu-Kα |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic | triclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/c | |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.235 × 0.136 × 0.063 | 1.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 | 0.211 × 0.161 × 0.040 |
| a (Å) | 8.00626(4) | 8.1783(9) | 12.3155(4) |
| b (Å) | 20.81514(9) | 20.882(2) | 14.1292(4) |
| c (Å) | 16.16909(8) | 16.6233(18) | 14.2513(4) |
| α (°) | 90 | 90 | 94.902(2) |
| β (°) | 97.0488(4) | 98.856(2) | 114.365(3) |
| γ (°) | 90 | 90 | 109.167(3) |
| V (Å3) | 2674.24(2) | 2805.0(5) | 2062.23(14) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| dcalc (g cm−3) | 1.615 | 1.559 | 1.312 |
| μ (mm−1) | 5.343 | 0.610 | 2.997 |
| F(000) | 1342 | 1360 | 860 |
| Limiting indices | h = ±10, k = ±26, l = ±20 | h = ±10, k = ±25, l = ±20 | h = ±15, k = ±17, l = ±17 |
| Reflections coll./uniq. | 54351/5622 | 42783/5515 | 48563/7978 |
| R(int) | 0.0331 | 0.0238 | 0.0647 |
| Complete to Θ (%) | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Data/restr./param. | 5622/0/401 | 5515/0/380 | 7978/0/533 |
| GooF on F2 | 1.064 | 1.058 | 1.066 |
| Final R indices [I > 2σ(I)] | R1 = 0.0309, wR2 = 0.0787 | R1 = 0.0568, wR2 = 0.1630 | R1 = 0.0374, wR2 = 0.1016 |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0321, wR2 = 0.0798 | R1 = 0.0621, wR2 = 0.1688 | R1 = 0.0424, wR2 = 0.1040 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole (e·Å−3) | 0.576 and −0.698 | 0.772 and −0.446 | 0.408 and −0.321 |
| CCDC no. | 2042007 | 2042006 | 2042009 |
References
- Real, J.A.; Gaspar, A.B.; Niel, V.; Muñoz, M.C. Communication between iron(II) building blocks in cooperative spin transition phenomena. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 236, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostettler, M.; Törnroos, K.W.; Chernyshov, D.; Vangdal, B.; Bürgi, H.-B. Challenges in Engineering Spin Crossover: Structures and Magnetic Properties of Six Alcohol Solvates of Iron(II) Tris(2-picolylamine) Dichloride. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4589–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, M.; Prins, F.; Bill, E.; Kooijman, H.; Gamez, P.; Roubeau, O.; Spek, A.L.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J. Counterion Effect on the Spin-Transition Properties of the Cation [Fe(btzx)3]2+ (btzx= m -Xylylenebis(tetrazole)). Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8486–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Hagiwara, H.; Torigoe, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Kojima, M.; Dahan, F.; Tuchagues, J.-P.; Re, N.; Iijima, S. A Variety of Spin-Crossover Behaviors Depending on the Counter Anion: Two-Dimensional Complexes Constructed by NH⋅⋅⋅Cl− Hydrogen Bonds, [FeIIH3LMe]Cl⋅X (X = PF6−, AsF6−, SbF6−, CF3SO3−; H3LMe = Tris[2-{[(2-methylimidazol-4-yl)methylidene]amino}ethyl]amine. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4536–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) complexes of 2,6-di(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridines—A versatile system for spin-crossover research. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2493–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Staniland, R.W.; Kruger, P.E. Spin crossover in homoleptic Fe(II) imidazolylimine complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 362, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedle, M.F.; Wilson, L.J. Variable spin iron(III) chelates with hexadentate ligands derived from triethylenetetramine and various salicylaldehydes. Synthesis, characterization, and solution state studies of a new 2T .dblarw. 6A spin equilibrium system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 4824–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. Structure: Function relationships in molecular spin-crossover complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.J.; Chadha, R.K.; Sena, K.M.; Rheingold, A.L.; Hendrickson, D.N. Dynamics and phase transitions in spin-crossover complexes: X-ray structures and basic crossover phenomena in the solvate series bis(3-ethoxysalicylideneaziridinopropylaminato)iron perchlorate.solvate. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Phonsri, W. Spin crossover in iron(III) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 313, 38–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, J.S.; Baker, W.A. Magnetic and spectral studies of some anomolous Mono-(2,2′,2″,-terpyridine) complexes of Co(II) and Ni(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1967, 1, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galet, A.; Gaspar, A.B.; Muñoz, M.C.; Real, J.A. Influence of the Counterion and the Solvent Molecules in the Spin Crossover System [Co(4-terpyridone)2]Xp·nH2O. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 4413–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palion-Gazda, J.; Świtlicka-Olszewska, A.; Machura, B.; Grancha, T.; Pardo, E.; Lloret, F.; Julve, M. High-Temperature Spin Crossover in a Mononuclear Six-Coordinate Cobalt(II) Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 10009–10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palion-Gazda, J.; Machura, B.; Kruszynski, R.; Grancha, T.; Moliner, N.; Lloret, F.; Julve, M. Spin Crossover in Double Salts Containing Six- and Four-Coordinate Cobalt(II) Ions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6281–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Koningsbruggen, P.J.; Garcia, Y.; Codjovi, E.; Lapouyade, R.; Kahn, O.; Fournès, L.; Rabardel, L. Non-classical FeII spin-crossover behaviour in polymeric iron(II) compounds of formula [Fe(NH2trz)3]X2·xH2O (NH2trz = 4-amino-1,2,4-triazole; X = derivatives of naphthalene sulfonate). J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matouzenko, G.S.; Molnar, G.; Bréfuel, N.; Perrin, M.; Bousseksou, A.; Borshch, S.A. Spin-Crossover Iron(II) Coordination Polymer with Zigzag Chain Structure. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setifi, F.; Milin, E.; Charles, C.; Thétiot, F.; Triki, S.; Gómez-García, C.J. Spin Crossover Iron(II) Coordination Polymer Chains: Syntheses, Structures, and Magnetic Characterizations of [Fe(aqin)2(μ2-M(CN)4)] (M = Ni(II), Pt(II), aqin = Quinolin-8-amine). Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Morcillo, T.; Valverde-Muñoz, F.J.; Muñoz, M.C.; Herrera, J.M.; Colacio, E.; Real, J.A. Two-step spin crossover behaviour in the chiral one-dimensional coordination polymer [Fe(HAT)(NCS)2]∞. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69782–69789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreugdenhil, W.; Van Diemen, J.H.; De Graaff, R.A.G.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Reedijk, J.; Van Der Kraan, A.M.; Kahn, O.; Zarembowitch, J. High-spin - low-spin transition in [Fe(NCS)2(4,4′-bis-1,2,4-triazole)2](H2O). X-ray crystal structure and magnetic, Mössbauer and EPR properties. Polyhedron 1990, 9, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, G.J.; Chapman, K.W.; Neville, S.M.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S.; Létard, J.-F.; Kepert, C.J. Elucidating the Mechanism of a Two-Step Spin Transition in a Nanoporous Metal-Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17552–17562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Guo, P.-H.; Liu, W.; Tucek, J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Leng, J.-D.; Chen, X.-M.; Gural’skiy, I.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A.; et al. Remarkably high-temperature spin transition exhibited by new 2D metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Trzop, E.; Valverde-Muñoz, F.J.; Piñeiro-López, L.; Muñoz, M.C.; Collet, E.; Real, J.A. Competing Phases Involving Spin-State and Ligand Structural Orderings in a Multistable Two-Dimensional Spin Crossover Coordination Polymer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusz, J.; Bronisz, R.; Zubko, M.; Bednarek, G. On the Role of Intermolecular Interactions on Structural and Spin-Crossover Properties of 2D Coordination Networks [Fe(bbtr)3]A2 (bbtr = 1,4-bis(1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)butane; A = ClO4−, BF4−). Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6807–6820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, G.N.L.; Werner, F.; Bartel, M.; Absmeier, A.; Reissner, M.; Kitchen, J.A.; Brooker, S.; Caneschi, A.; Carbonera, C.; Létard, J.-F.; et al. Anion, Solvent and Time Dependence of High-Spin-Low-Spin Interactions in a 3D Coordination Polymer. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 3948–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirera, J. Guest effect on spin-crossover frameworks. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 34, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A.; González, M.A.; Real, J.A.; Castro, M.; Muñoz, M.C.; Gaspar, A.B.; Ohtani, R.; Ohba, M.; Yoneda, K.; Hijikata, Y.; et al. A Switchable Molecular Rotator: Neutron Spectroscopy Study on a Polymeric Spin-Crossover Compound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5083–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Dong, Y.-J.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.-C.; Song, X.-W.; Li, Q.-W.; Zhang, C.-L.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. A New Porous Three-Dimensional Iron(II) Coordination Polymer with Solvent-Induced Reversible Spin-Crossover Behavior. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 5214–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Bauer, W.; Obel, J. An Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complex with a 70 K Wide Thermal Hysteresis Loop. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10098–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Obel, J.; Henner-Vásquez, D.; Bauer, W. Two New Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes with N4O2 Coordination Sphere and Spin Transition around Room Temperature. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 5527–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wei, R.-J.; Tao, J.; Huang, R.-B.; Zheng, L.-S.; Zheng, Z. Solvent-Induced Transformation of Single Crystals of a Spin-Crossover (SCO) Compound to Single Crystals with Two Distinct SCO Centers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Codjovi, E.; Lavastre, O.; Bravic, G.; Chasseau, D.; Kahn, O. Wide Thermal Hysteresis for the Mononuclear Spin-Crossover Compound cis-Bis(thiocyanato)bis[N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)anilino]iron(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10861–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Iijima, S. Two-Dimensional Iron(II) Spin Crossover Complex Constructed of Bifurcated NH···O− Hydrogen Bonds and π−π Interactions: [FeII(HLH,Me)2](ClO4)2·1.5MeCN (HLH,Me = Imidazol-4-yl-methylidene-8-amino-2-methylquinoline). Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 3136–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.J.; Tao, J.-Q.; Yu, Z.; Dun, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; You, X.-Z. A stacking spin-crossover iron(II) compound with a large hysteresis. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1998, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffeneder, T.M.; Thallmair, S.; Bauer, W.; Weber, B. Complete and incomplete spin transitions in 1D chain iron(II) compounds. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A.; Capel Berdiell, I.; Pask, C.M.; Kulmaczewski, R. Relationship between the Molecular Structure and Switching Temperature in a Library of Spin-Crossover Molecular Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 9811–9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunatsuki, Y.; Ikuta, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Ohta, H.; Kojima, M.; Iijima, S.; Hayami, S.; Maeda, Y.; Kaizaki, S.; Dahan, F.; et al. An Unprecedented Homochiral Mixed-Valence Spin-Crossover Compound. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.G.; Murnaghan, K.D.; Müller-Bunz, H.; McKee, V.; Harding, C.J. A Manganese(III) Complex That Exhibits Spin Crossover Triggered by Geometric Tuning. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7192–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, K.; Gildea, B.; Murray, C.; Harding, C.J.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Morgan, G.G. Lattice Effects on the Spin-Crossover Profile of a Mononuclear Manganese(III) Cation. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.J.; Trzop, E.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Dîrtu, M.M.; Garcia, Y.; Collet, E.; Morgan, G.G. Electronic vs. structural ordering in a manganese(III) spin crossover complex. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17540–17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.N.; Gildea, B.; Harris, M.M.; Lemma, T.; Naik, A.D.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Keyes, T.E.; Garcia, Y.; Morgan, G.G. Cooperative Spin Transition in a Mononuclear Manganese(III) Complex. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 12765–12769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildea, B.; Harris, M.M.; Gavin, L.C.; Murray, C.A.; Ortin, Y.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Harding, C.J.; Lan, Y.; Powell, A.K.; Morgan, G.G. Substituent Effects on Spin State in a Series of Mononuclear Manganese(III) Complexes with Hexadentate Schiff-Base Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 6022–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gildea, B.; Gavin, L.C.; Murray, C.A.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Harding, C.J.; Morgan, G.G. Supramolecular modulation of spin crossover profile in manganese(III). Supramol. Chem. 2012, 24, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.; Kelly, C.T.; Kühne, I.A.; Hill, S.; Krzystek, J.; Wix, P.; Esien, K.; Felton, S.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Morgan, G.G. Spin state solvomorphism in a series of rare S = 1 manganese(III) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 15560–15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühne, I.A.; Barker, A.; Zhang, F.; Stamenov, P.; O’Doherty, O.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Stein, M.; Rodriguez, B.J.; Morgan, G.G. Modulation of Jahn-Teller distortion and electromechanical response in a Mn3+ spin crossover complex. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 404002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, V.B.; Trzop, E.; Gavin, L.C.; Dobbelaar, E.; Chikara, S.; Ding, X.; Esien, K.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Felton, S.; Zapf, V.S.; et al. Stress-Induced Domain Wall Motion in a Ferroelastic Mn3+ Spin Crossover Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13305–13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, V.B.; O’Brien, L.; Novitchi, G.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Barra, A.-L.; Morgan, G.G. Chiral Resolution of a Mn3+ Spin Crossover Complex. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4405–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Platon Squeeze: A tool for the calculation of the disordered solvent contribution to the calculated structure factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, J. Unusual metal centres/coordination spheres in spin crossover compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 407, 213148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, M.G.B.; Harding, C.J.; McKee, V.; Morgan, G.G.; Nelson, J. Geometric control of manganese redox state. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketkaew, R.; Tantirungrotechai, Y.; Harding, P.; Chastanet, G.; Guionneau, P.; Marchivie, M.; Harding, D.J. OctaDist: A Tool for Calculating Distortion Parameters in Coordination Complexes. Available online: https://octadist.github.io (accessed on 25 August 2019).
- Clark, R.C.; Reid, J.S. The analytical calculation of absorption in multifaceted crystals. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1995, 51, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mn-X | OTf− (1) | OTf− (1) | PF6− (2) | PF6− (2) | PF6− (2b) | BPh4− (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. (K) | 100 | 293 | 100 | 293 | 100 | 100 |
| Mn-Ophen | 1.874 | 1.872 | 1.881 | 1.876 | 1.879 | 1.866 |
| 1.894 | 1.885 | 1.885 | 1.879 | 1.881 | 1.876 | |
| Mn-Nimine | 1.977 | 2.028 | 1.983 | 2.035 | 2.083 | 2.079 |
| 1.990 | 2.068 | 1.990 | 2.088 | 2.139 | 2.131 | |
| Mn-Namine | 2.056 | 2.139 | 2.054 | 2.144 | 2.216 | 2.237 |
| 2.063 | 2.161 | 2.061 | 2.179 | 2.279 | 2.268 | |
| Spin State | S = 1 | S = 1 | S = 2 | S = 2 |
| Spin State | Σ | Θ |
|---|---|---|
| S = 1 | 28°–45° | 79°–125° |
| S = 2 | 48°–80° | 135°–230° |
| OTf− (1) | OTf− (1) | PF6− (2) | PF6− (2) | PF6− (2b) | BPh4− (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. (K) | 100 | 293 | 100 | 293 | 100 | 100 |
| Σ | 30.4 | 45.3 | 30.8 | 46.3 | 72.1 | 71.1 |
| Θ | 87.1 | 140.3 | 85.9 | 145.7 | 274.5 | 256.6 |
| Spin State | S = 1 | S = 2 | S = 2 | S = 2 |
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kühne, I.A.; Esien, K.; Gavin, L.C.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Felton, S.; Morgan, G.G. Modulation of Mn3+ Spin State by Guest Molecule Inclusion. Molecules 2020, 25, 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235603
Kühne IA, Esien K, Gavin LC, Müller-Bunz H, Felton S, Morgan GG. Modulation of Mn3+ Spin State by Guest Molecule Inclusion. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235603
Chicago/Turabian StyleKühne, Irina A., Kane Esien, Laurence C. Gavin, Helge Müller-Bunz, Solveig Felton, and Grace G. Morgan. 2020. "Modulation of Mn3+ Spin State by Guest Molecule Inclusion" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235603
APA StyleKühne, I. A., Esien, K., Gavin, L. C., Müller-Bunz, H., Felton, S., & Morgan, G. G. (2020). Modulation of Mn3+ Spin State by Guest Molecule Inclusion. Molecules, 25(23), 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235603








