Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Regional Cerebral Free Fatty Acids in Rats Using the Stable Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
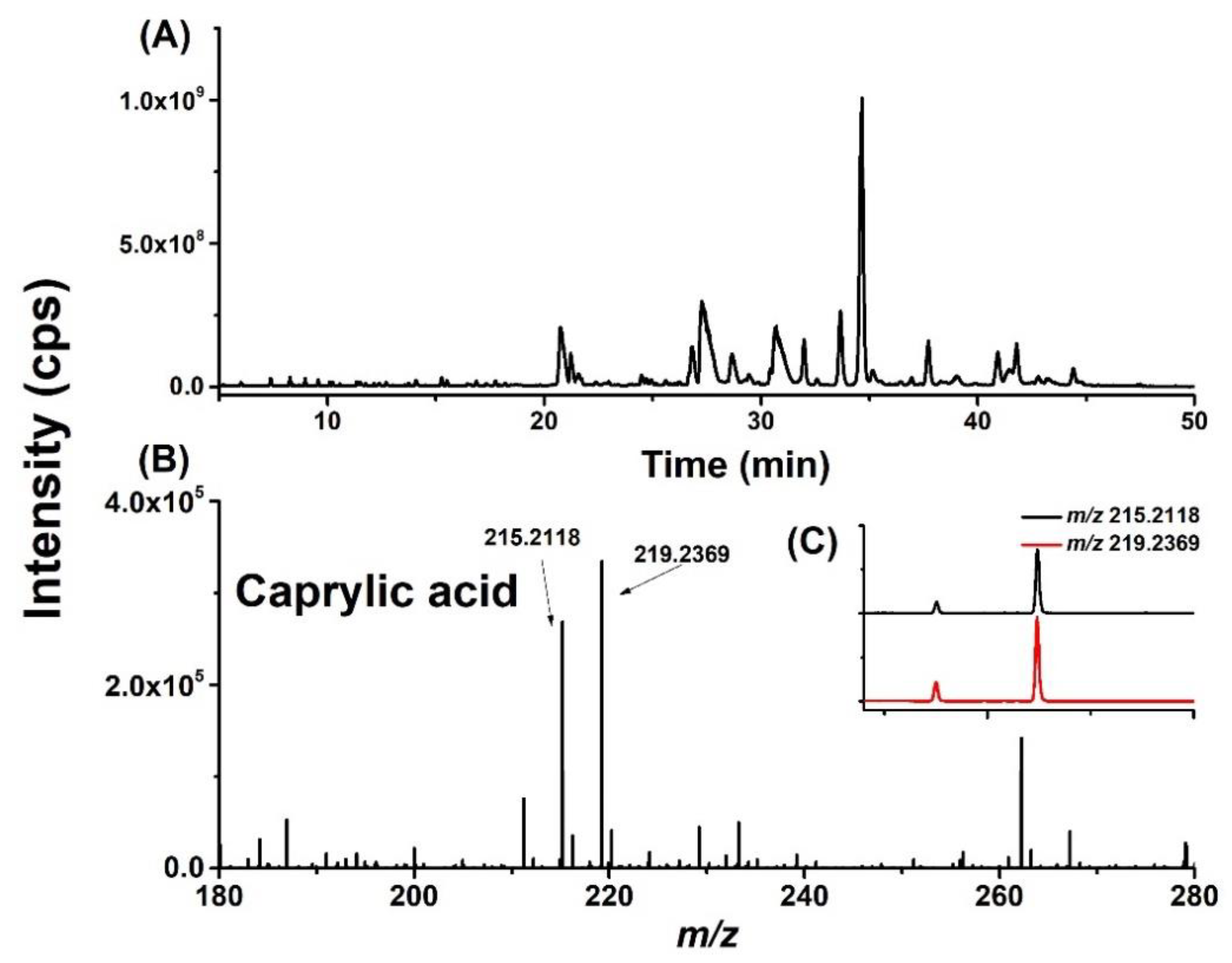
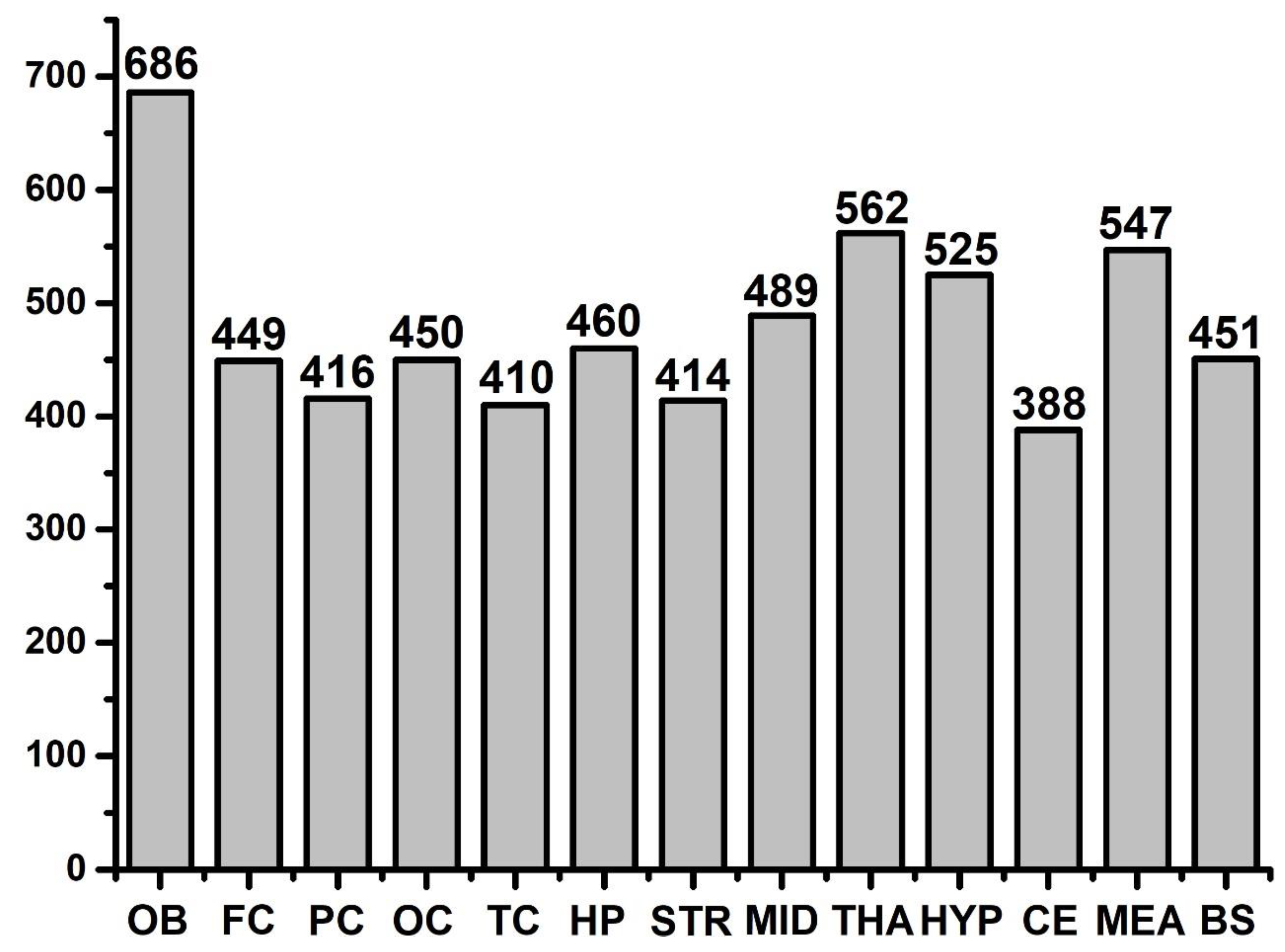
2.1. Screening and Identification of FFAs in Different Brain Regions
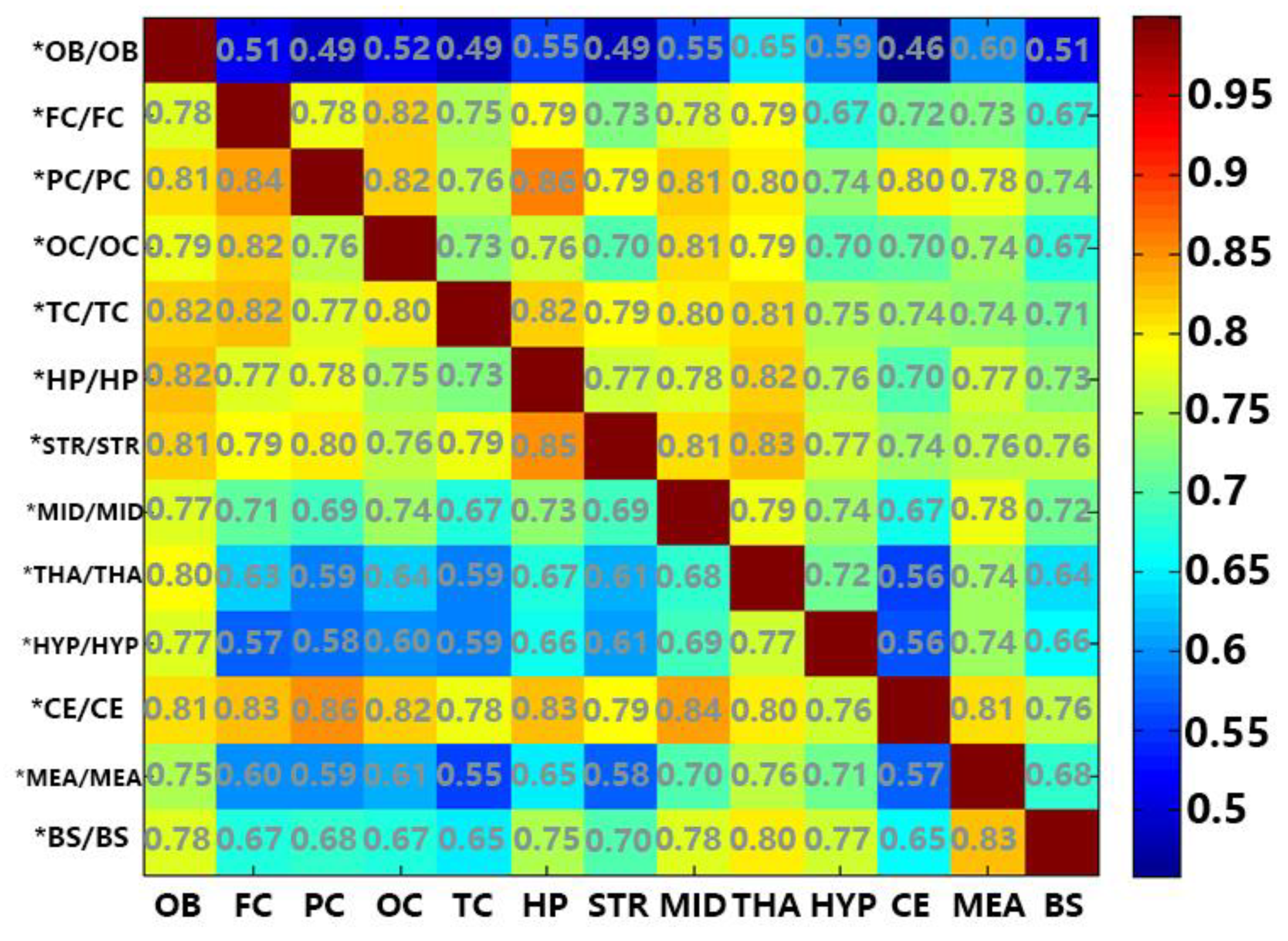
2.2. Common FFAs between Two Regions
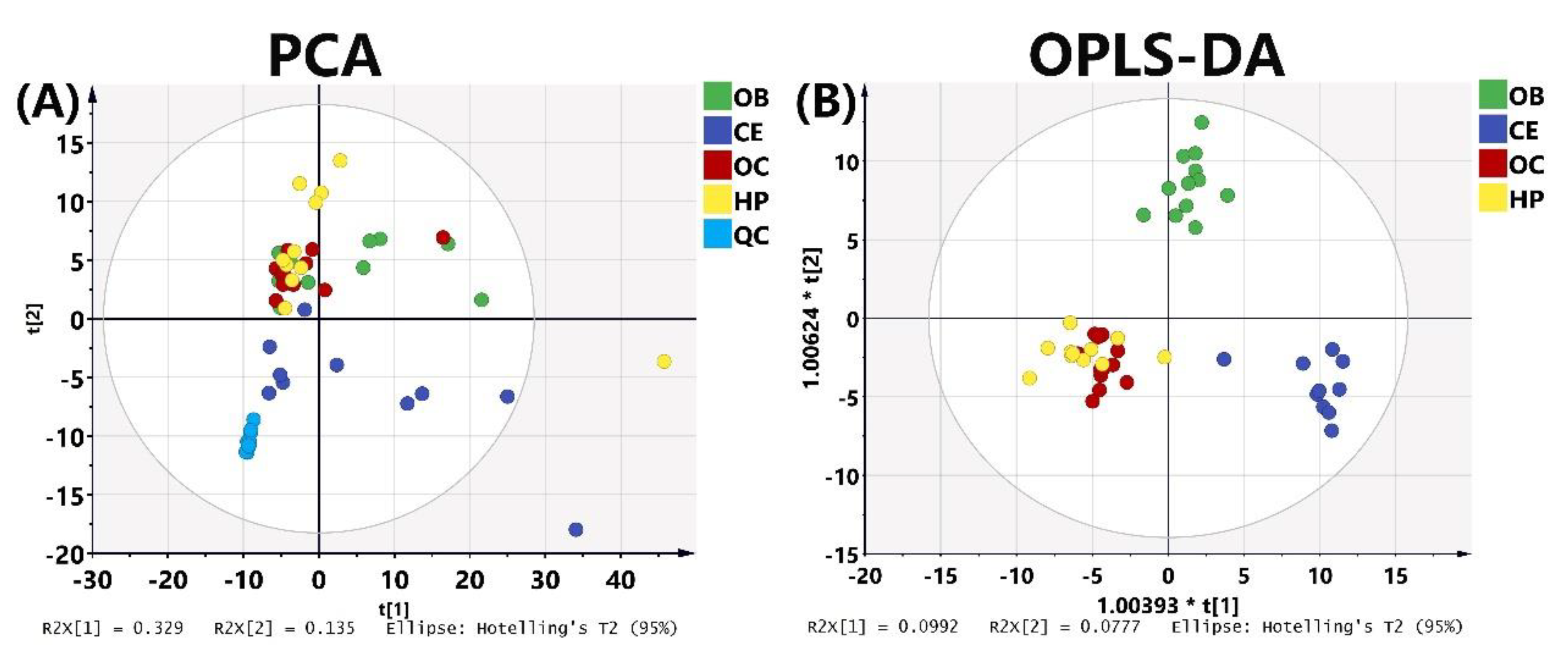
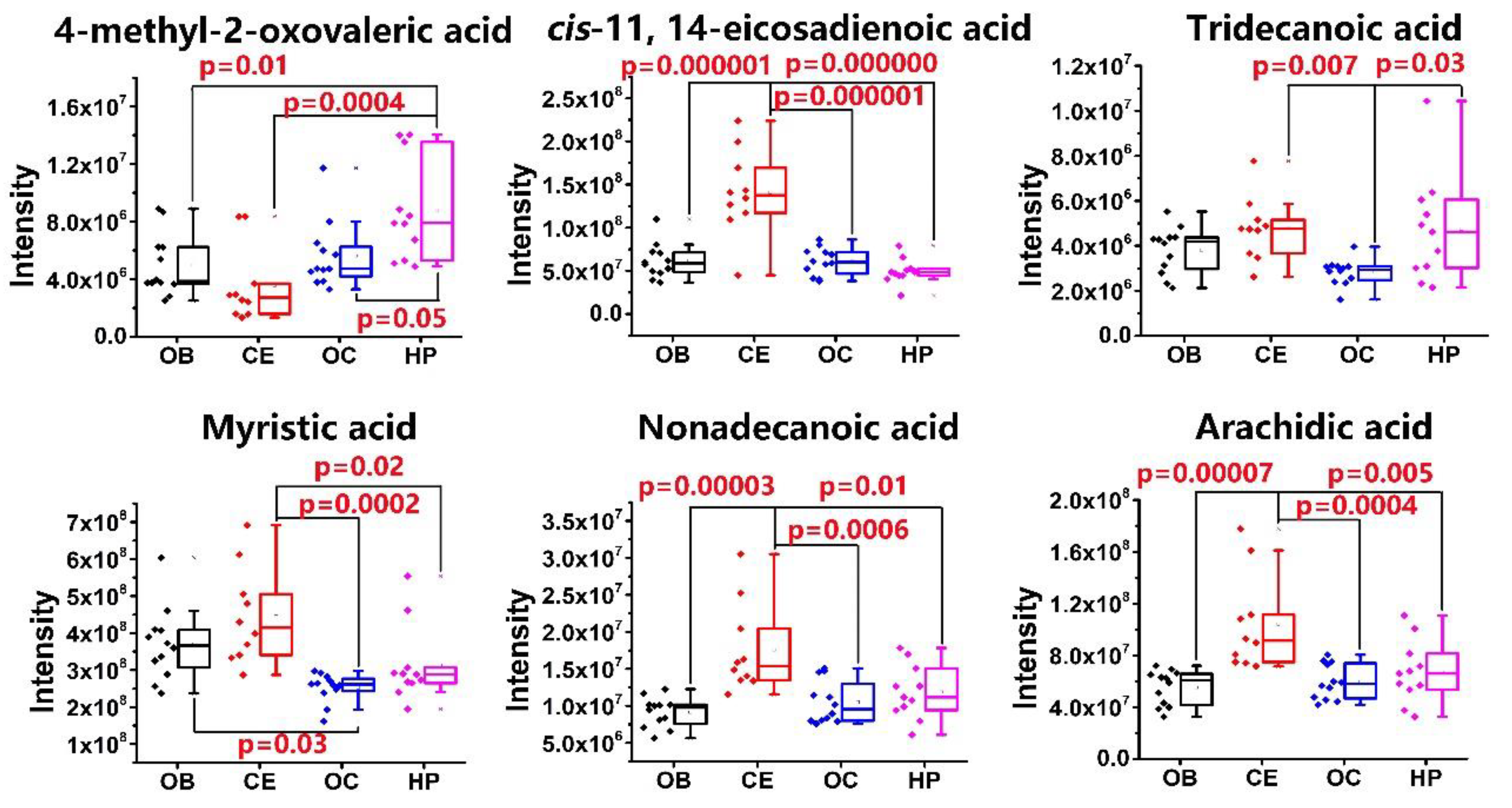
2.3. Relative Quantitation of FFAs in OB, OC, HP, and CE
3. Material and Method
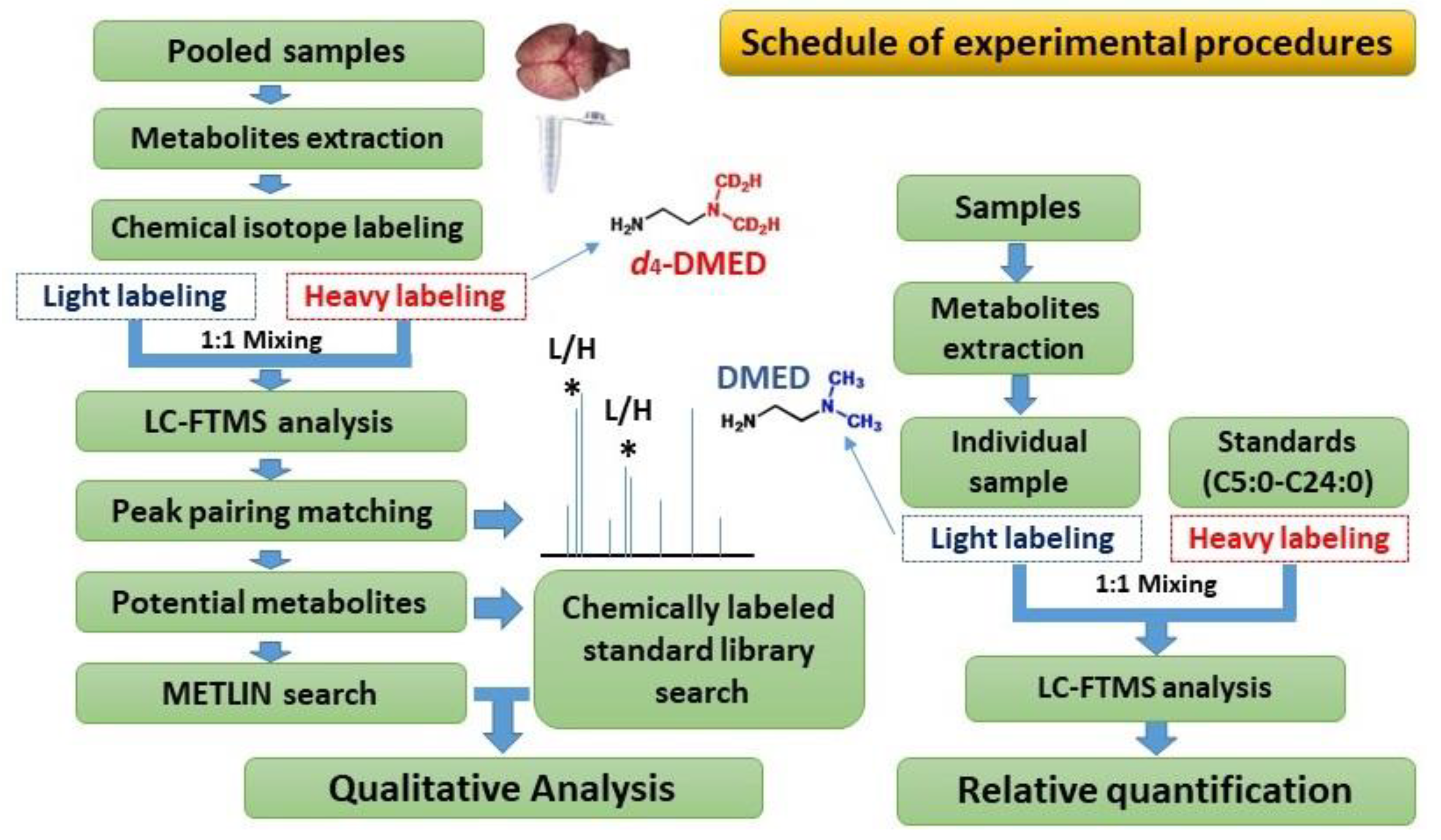
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Brain Sample Collection and Pre-Treatment
3.4. Labeling of Free Fatty Acids with DMED and d4-DMED
3.5. UPLC-MS Analysis
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burn, C.C. What is it like to be a rat? Rat sensory perception and its implications for experimental design and rat welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 112, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: Significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 2011, 70, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, P.E.; Jiang, Y.H.; Shuman, M.; Kanwisher, N. A cortical area selective for visual processing of the human body. Science 2001, 293, 2470–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Wiggs, C.L.; Ungerleider, L.G.; Haxby, J.V. Neural correlates of category-specific knowledge. Nature 1996, 379, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Ogawa, S.K.; Roy, D.S.; Okuyama, T.; Morrissey, M.D.; Smith, L.M.; Redondo, R.L.; Tonegawa, S. Engrams and circuits crucial for systems consolidation of a memory. Science 2017, 356, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuelof, L.; Krakauer, J.W. Are we ready for a natural history of motor learning? Neuron 2011, 72, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.A.; Ivry, R.B. Cerebellar and prefrontal cortex contributions to adaptation, strategies, and reinforcement learning. Prog. Brain Res. 2014, 210, 217–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Resnick, S.M.; Studenski, S.A. Olfaction Is Related to Motor Function in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Laye, S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuratko, C.; Barrett, E.; Nelson, E.; Salem, N. The Relationship of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) with Learning and Behavior in Healthy Children: A Review. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2777–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, L.; Brambilla, P.; Mazzocchi, A.; Harsløf, L.; Ciappolino, V.; Agostoni, C. DHA Effects in Brain Development and Function. Nutrients 2016, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Santos, M.; Chimalapati, S.; Ray, A.; Lee, W.-R.; Rivera-Cancel, G.; Lafrance, A.; Vale, G.; Pawłowski, K.; Mitsche, M.; McDonald, J.G.; et al. Vibrio deploys Type 2 secreted lipase2 to esterify cholesterol with host fatty acids and mediate cell egress. eLife 2019, 9, e58057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetz, E.; Schroll, A.; Auer, K.; Heim, C.; Patsch, J.R.; Eller, P.; Theurl, M.; Theurl, I.; Theurl, M.; Seifert, M.; et al. The arachidonic acid metabolome serves as a conserved regulator of cholesterol metabolism. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, V.S.; Hafez, E.A.A. Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, Y.-W.; Han, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, N.; Cheng, Y. 12/15-Lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid activate PPARγ: A possible neuroprotective effect in ischemic brain. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, O. Bioactive metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid. Biochimie 2017, 136, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremmyda, L.S.; Tvrzicka, E.; Stankova, B.; Zak, A. Fatty acids as biocompounds: Their role in human metabolism, health and disease: A review. Part 2: Fatty acid physiological roles and applications in human health and disease. Biomed. Pap. Med Fac. Palacky Univ. Olomouc. 2011, 155, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, L.C.; Clayton, C.C.; Snyderman, R. A potential second messenger role for unsaturated fatty acids: Activation of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Science 1984, 224, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M. 12-Hydroxyeicosatetrenoate (12-HETE) attenuates AMPA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity: Evidence for a G-protein-coupled HETE receptor. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Ma, K.; Gao, F.; Kim, H.-W.; Rapoport, S.I.; Rao, J.S. Disturbed Choline Plasmalogen and Phospholipid Fatty Acid Concentrations in Alzheimer’s Disease Prefrontal Cortex. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 24, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Fabelo, N.; Santpere, G.; Puig, B.; Marin, R.; Ferrer, I.; Diaz, M. Lipid Alterations in Lipid Rafts from Alzheimer’s Disease Human Brain Cortex. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, J.O.; Algamal, M.; Leary, P.; Abdullah, L.; Mouzon, B.; Evans, J.E.; Mullan, M.; Crawford, F. Converging and Differential Brain Phospholipid Dysregulation in the Pathogenesis of Repetitive Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, V.; Goodenowe, D.B. Plasmalogen deficiency and neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease: Causation or coincidence? Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 5, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Mejia, R.O.; Newman, J.W.; Toh, S.; Yu, G.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Halabisky, B.; Cisse, M.; Scearce-Levie, K.; Cheng, I.H.; Gan, L.; et al. Phospholipase A2 reduction ameliorates cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrecht, G.S.; Adesuyi, S.A.; Holt, S.; Ellis, E.F. Brain 12-Hete Formation in Different Species, Brain-Regions, and in Brain Microvessels. Neurochem. Res. 1987, 12, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.F.; Hao, Y.H.; Liu, M.Z.; Yue, J.; Ni, J.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Analysis of cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid by stable isotope probe labeling coupled with ultra high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1410, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.F.; Zhu, Q.F.; Guo, N.; Zheng, S.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.J.; He, K.; Hu, T.; et al. Comprehensive Profiling of Fecal Metabolome of Mice by Integrated Chemical Isotope Labeling-Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.X.; Wang, X.N.; Jiang, R.Q.; Zhao, A.H.; Yan, J.Y.; Zheng, X.J.; Huang, F.J.; Liu, X.Z.; Panee, J.; Rajani, C.; et al. Dysregulated bile acid signaling contributes to the neurological impairment in murine models of acute and chronic liver failure. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Zhao, A.; Wang, X.; Xie, G.; Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; et al. The Brain Metabolome of Male Rats across the Lifespan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Ueta, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Sakurai, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Nakazato, M. Orexins, orexigenic hypothalamic peptides, interact with autonomic, neuroendocrine and neuroregulatory systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, J.K.; Elias, C.F.; Saper, C.B. From lesions to leptin: Hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 1999, 22, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.P.; Dube, M.G.; Pu, S.Y.; Xu, B.; Horvath, T.L.; Kalra, P.S. Interacting appetite-regulating pathways in the hypothalamic regulation of body weight. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 68–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Huang, W.C.; Li, C.W.; Chuang, L.T. Eicosadienoic acid differentially modulates production of pro-inflammatory modulators in murine macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 358, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaruddin, M.L.; Pan, X.; McGuinness, B.; Passmore, P.; Kehoe, P.G.; Holscher, C.; Graham, S.E.; Green, B.D. Evidence That Parietal Lobe Fatty Acids May Be More Profoundly Affected in Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Pathology Than in Severe AD Pathology. Metabolites 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkoff, M.; Daikhin, Y.; Nissim, A.; Horyn, O.; Luhovyy, B.; Lazarow, A.; Nissim, I. Brain amino acid requirements and toxicity: The example of leucine. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1531S–1538S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuolikainen, A.; Jonsson, P.; Ahnlund, M.; Antti, H.; Marklund, S.L.; Moritz, T.; Forsgren, L.; Andersen, P.M.; Trupp, M. Multi-platform mass spectrometry analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolomes of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, S.E.; Basselin, M.; Chang, L.; Heidenreich, K.A.; Rapoport, S.I.; Murphy, R.C. Formation of eicosanoids, E2/D2 isoprostanes, and docosanoids following decapitation-induced ischemia, measured in high-energy-microwaved rat brain. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Kamal, G.M.; Feng, Y.; Manyande, A.; Wang, J.; Xu, F. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Regional Cerebral Free Fatty Acids in Rats Using the Stable Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215163
Hu T, Zhu Q, Hu Y, Kamal GM, Feng Y, Manyande A, Wang J, Xu F. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Regional Cerebral Free Fatty Acids in Rats Using the Stable Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215163
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ting, Quanfei Zhu, Yuning Hu, Ghulam Mustafa Kamal, Yuqi Feng, Anne Manyande, Jie Wang, and Fuqiang Xu. 2020. "Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Regional Cerebral Free Fatty Acids in Rats Using the Stable Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215163
APA StyleHu, T., Zhu, Q., Hu, Y., Kamal, G. M., Feng, Y., Manyande, A., Wang, J., & Xu, F. (2020). Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Regional Cerebral Free Fatty Acids in Rats Using the Stable Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method. Molecules, 25(21), 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215163




