Pyrazole Incorporated New Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis and Investigation of DPP-4 Inhibitory Effects
Abstract
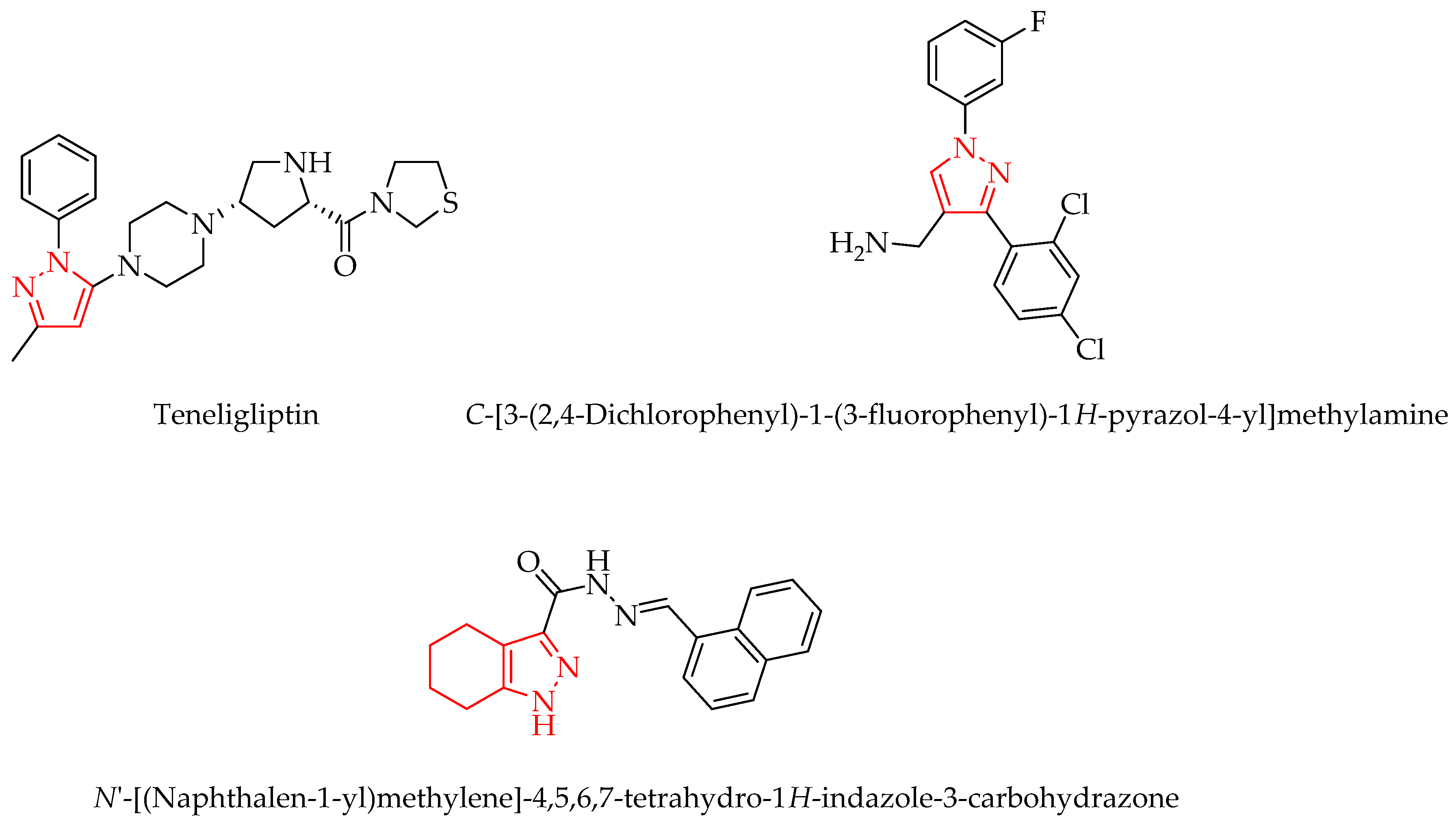
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
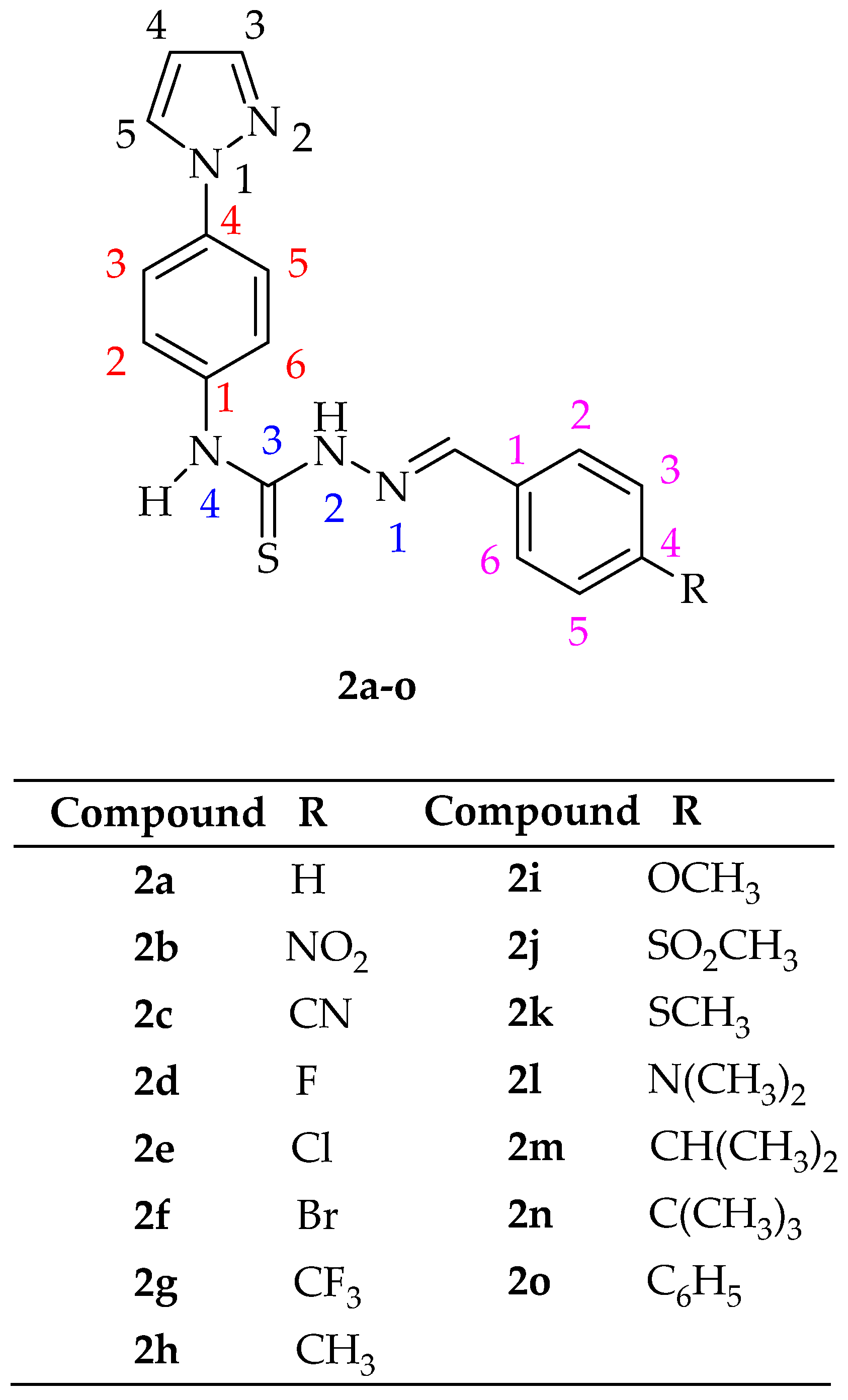
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Activity
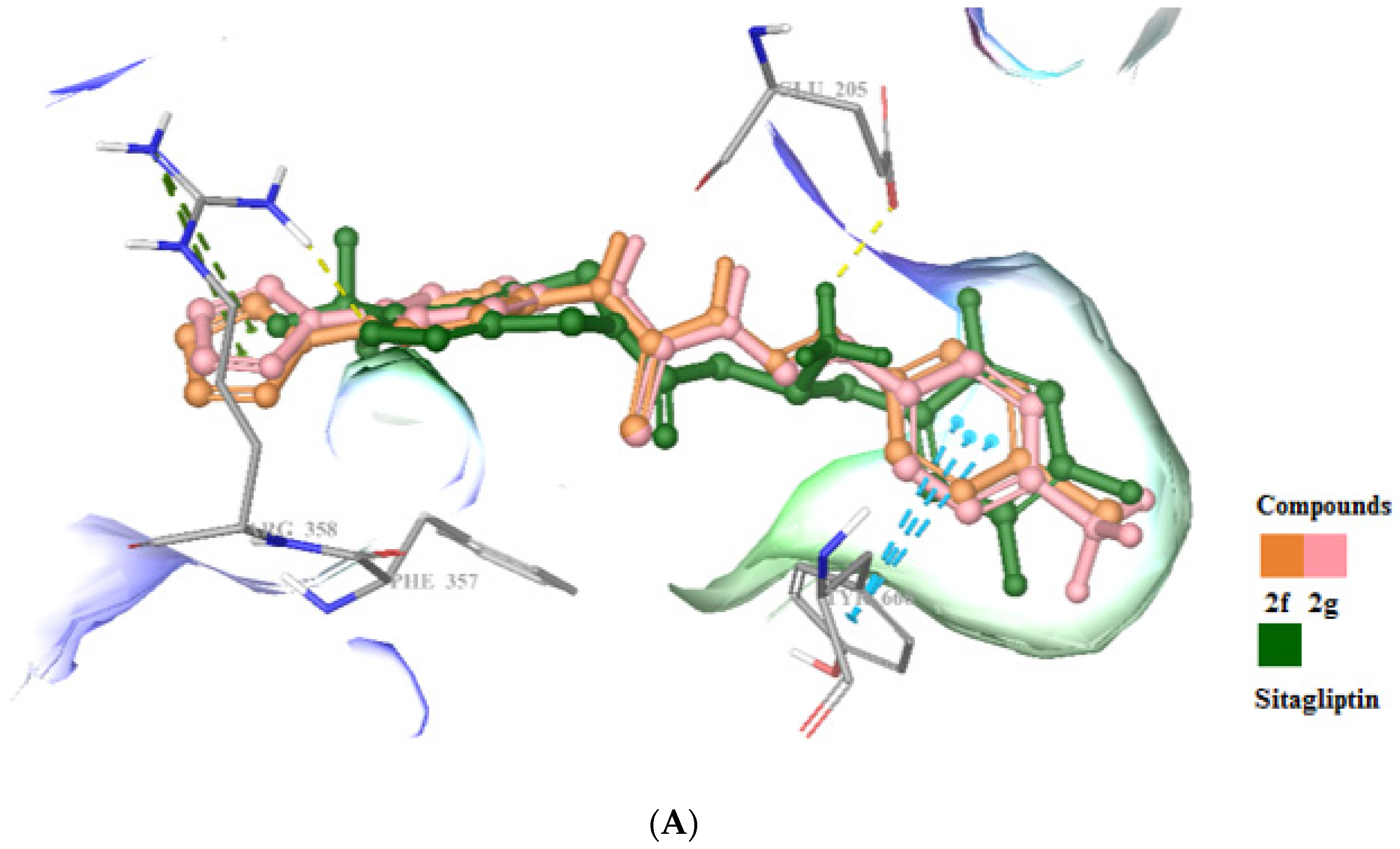
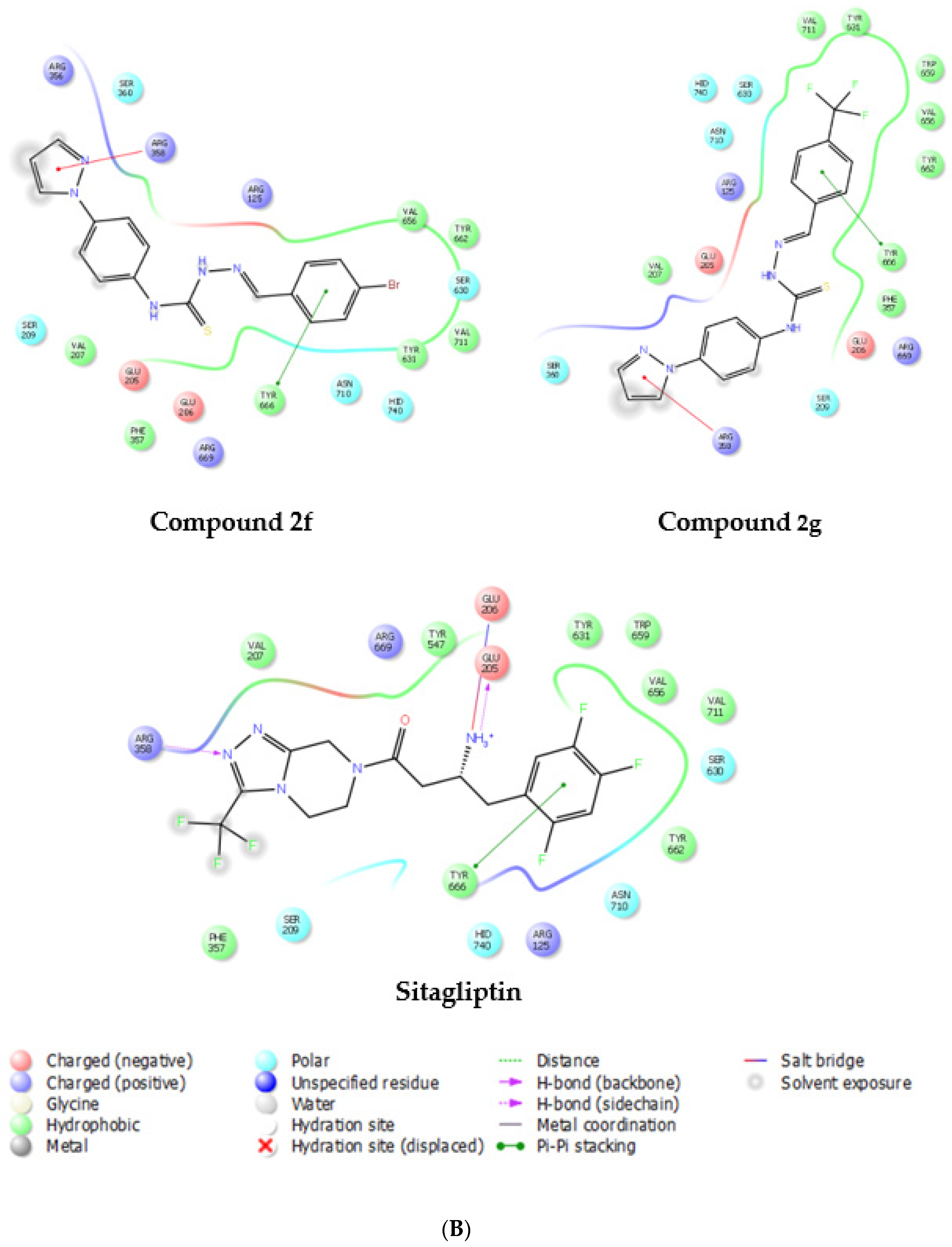
2.3. In Silico Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Compounds
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]thiosemicarbazide (1)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(arylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2a–o)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(benzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2a)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-nitrobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2b)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-cyanobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2c)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-fluorobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2d)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-chlorobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2e)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-bromobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2f)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-trifluoromethylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2g)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-methylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2h)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-methoxybenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2i)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-methylsulfonylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2j)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-methylthiobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2k)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-dimethylaminobenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2l)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-isopropylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2m)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-tert-butylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2n)
[4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1-(4-phenylbenzylidene)thiosemicarbazide (2o)
3.2. DPP-4 Inhibitor Screening Assay
3.3. Cytotoxicity
3.3.1. Cell Culture
3.3.2. MTT Assay
3.4. Statistical Analyses
3.5. Molecular Docking Studies
3.6. In Silico ADME Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantley, J.; Ashcroft, F.M. Q&A: Insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes: Why do β-cells fail? BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Kerru, N.; Singh-Pillay, A.; Awolade, P.; Singh, P. Current anti-diabetic agents and their molecular targets: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 436–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artasensi, A.; Pedretti, A.; Vistoli, G.; Fumagalli, L. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of multi-target drugs. Molecules 2010, 163, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havale, S.H.; Pal, M. Medicinal chemistry approaches to the inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Gallwitz, B. Mechanism of action of inhibitors of dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.P.; Pratley, R.E. Efficacy and safety of incretin-based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeir, A.M.; Scharpé, S.; de Meester, I. DPP4 inhibitors for diabetes—What next? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.D.; Ghate, M.D. Recent approaches to medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 574–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Bianchi, C.; del Prato, S. Use of incretin-based medications: What do current international recommendations suggest with respect to GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors? Metabolism 2020, 107, 154242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Maleki, M.; Sathyapalan, T.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Anti-inflammatory potentials of incretin-based therapies used in the management of diabetes. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, E.; Giampietro, O. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (CD26): Knowing the function before inhibiting the enzyme. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, N.; Vliegen, G.; de Meester, I.; Jungraithmayr, W. CD26/DPP4—A potential biomarker and target for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, L.; Xing, J.; Li, P.; Sang, H.; Hu, X.; Du, Y.; Zhao, L.; Song, R.; Gu, H. The protective role of DPP4 inhibitors in atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 875, 173037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulakayala, N.; Reddy CH, U.; Iqbal, J.; Pal, M. Synthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 4919–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, B. DPP-4 inhibitors. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Tavallaie, M.S.; Sun, R.; Wang, J.; Cai, Q.; Shen, J.; Lei, S.; Fu, L.; Jiang, F. Drug discovery approaches targeting the incretin pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Xu, Q.; Yu, X.; Pan, R.; Chen, Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and their potential immune modulatory functions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, A.P.; Sachinidis, A.; Stoica, R.A.; Nikolic, D.; Patti, A.M.; Rizvi, A.A. The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors compared to other oral glucose-lowering medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2020, 109, 154295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Kovacevic, Z.; Siafakas, A.R.; Jansson, P.J.; Stefani, C.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Sharpe, P.C.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Thiosemicarbazones from the old to new: Iron chelators that are more than just ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5271–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexacou, K.M.; Tenchiu Deleanu, A.C.; Chrysina, E.D.; Charavgi, M.D.; Kostas, I.D.; Zographos, S.E.; Oikonomakos, N.G.; Leonidas, D.D. The binding of β-d-glucopyranosyl-thiosemicarbazone derivatives to glycogen phosphorylase: A new class of inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7911–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, N.V.; Ravenkar, V.K.; Kirasur, B.N.; Hugar, M.H. Transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones with quinoxaline hub: An emphasis on antidiabetic property. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, N.S.; Cerqueira, N.M.; Ramos, M.J.; Fernandes, P.A. Aryl- and heteroaryl-thiosemicarbazone derivatives and their metal complexes: A pharmacological template. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, K.M.R.; Desterro, M.R.D.; de Arruda, S.M.; Neto, L.N.D.A.; de Lima, M.D.C.A.; de Almeida, S.M.V.; da Silva, E.C.D.; de Aquino, T.M.; da Silva-Júnior, E.F.; Júnior, J.X.D.A.; et al. 5-Nitro-thiophene-thiosemicarbazone derivatives present antitumor activity mediated by apoptosis and DNA intercalation. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehzad, M.T.; Imran, A.; Njateng, G.S.S.; Hameed, A.; Islam, M.; Al-Rashida, M.; Uroos, M.; Asari, A.; Shafiq, Z.; Iqbal, J. Benzoxazinone-thiosemicarbazones as antidiabetic leads via aldose reductase inhibition: Synthesis, biological screening and molecular docking study. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datar, P.A.; Jadhav, S.R. Development of pyrazole compounds as antidiabetic agent: A review. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2014, 11, 686–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Cai, X.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Dai, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, M.W.; Liu, H. Design, synthesis, structure-activity relationships, and docking studies of pyrazole-containing derivatives as a novel series of potent glucagon receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 2852–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.V.; Vegi, P.F.; Miguita, A.G.C.; dos Santos, M.S.; Boechat, N.; Bernardino, A.M.R. Recently reported biological activities of pyrazole compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5891–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Jacob, S.K. Therapeutic outlook of pyrazole analogs: A mini review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 959–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrouchi, K.; Radi, S.; Ramli, Y.; Taoufik, J.; Mabkhot, Y.N.; Al-aizari, F.A.; Ansar, M. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of pyrazole derivatives: A review. Molecules 2018, 23, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, K.R.A.; Fadaly, W.A.A.; Kamel, G.M.; Elshaier, Y.A.M.M.; El-Magd, M.A. Design, synthesis, modeling studies and biological evaluation of thiazolidine derivatives containing pyrazole core as potential anti-diabetic PPAR-γ agonists and anti-inflammatory COX-2 selective inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mothilal, S.; Kerru, N.; Singh-Pillay, A.; Gummidi, L.; Erukainure, O.L.; Islam, S. Comparative α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition studies of rhodamine-pyrazole conjugates and their simple rhodanine analogues. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brullo, C.; Rapetti, F.; Bruno, O. Pyrazolyl-ureas as interesting scaffold in medicinal chemistry. Molecules 2020, 25, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Akahoshi, F.; Sakashita, H.; Kitajima, H.; Nakamura, M.; Sonda, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ueda, N.; Sekiguchi, S.; et al. Discovery and preclinical profile of teneligliptin (3-[(2S,4S)-4-[4-(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)piperazin-1-yl]pyrrolidin-2- ylcarbonyl]thiazolidine): A highly potent, selective, long-lasting and orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5705–5719. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.; Chen, C.; Tsai, T.; Cheng, J.; Wu, S.; Chang, C.; Chien, C.; Yeh, K.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. (1,3-Diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)- methylamine analogues as inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidases. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2009, 56, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jin, F.; Lu, W.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Synthesis, structure–activity relationship, and pharmacophore modeling studies of pyrazole-3-carbohydrazone derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altıntop, M.D.; Temel, H.E.; Sever, B.; Çiftçi, G.A.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Synthesis and evaluation of new benzodioxole-based thiosemicarbazone derivatives as potential antitumor agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, A.; Altıntop, M.D.; Sever, B.; Cantürk, Z.; Kaplancıkli, Z.A. Synthesis and evaluation of tetrazole-based hydrazone derivatives bearing a pyridine moiety as antimicrobial agents. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2015, 12, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 2a–o are available from the authors. |




| Compound (100 µM) | R | DPP-4 Inhibition% |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | H | 20.67 ± 1.82 |
| 2b | NO2 | 35.54 ± 1.75 |
| 2c | CN | 28.04 ± 1.63 |
| 2d | F | 27.28 ± 2.03 |
| 2e | Cl | 38.44 ± 2.14 |
| 2f * | Br | 98.20 ± 0.89 |
| 2g * | CF3 | 62.82 ± 1.19 |
| 2h | CH3 | 53.16 ± 3.10 |
| 2i * | OCH3 | 77.18 ± 2.21 |
| 2j | SO2CH3 | 59.84 ± 1.13 |
| 2k * | SCH3 | 70.44 ± 1.03 |
| 2l | N(CH3)2 | 57.34 ± 1.04 |
| 2m | CH(CH3)2 | 47.43 ± 1.29 |
| 2n | C(CH3)3 | 28.64 ± 1.76 |
| 2o * | C6H5 | 75.72 ± 1.48 |
| Sitagliptin * | - | 90.38 ± 2.17 |
| Compound | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| 2f | 1.266 ± 0.264 |
| 2g | 4.775 ± 0.296 |
| 2i | 43.312 ± 0.372 |
| 2k | 22.671 ± 0.301 |
| 2o | 18.061 ± 0.311 |
| Sitagliptin | 4.380 ± 0.319 |
| Compound | QPlogPo/w * | QPlogBB * | CIQPlogS * | QPlogKhsa * | Human Oral Absorption% * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 4.07 | −0.25 | −4.73 | 0.33 | 100.00 |
| 2b | 3.38 | −1.40 | −5.25 | 0.30 | 90.34 |
| 2c | 3.34 | −1.14 | −5.67 | 0.19 | 94.39 |
| 2d | 4.31 | −0.14 | −5.08 | 0.37 | 100.00 |
| 2e | 4.56 | −0.09 | −5.41 | 0.44 | 100.00 |
| 2f | 4.64 | −0.08 | −6.30 | 0.46 | 100.00 |
| 2g | 5.04 | 0.07 | −6.08 | 0.58 | 100.00 |
| 2h | 4.38 | −0.27 | −5.00 | 0.48 | 100.00 |
| 2i | 4.17 | −0.33 | −5.04 | 0.35 | 100.00 |
| 2j | 2.86 | −1.25 | −4.77 | −0.02 | 90.38 |
| 2k | 4.69 | −0.24 | −5.45 | 0.50 | 100.00 |
| 2l | 4.50 | −0.37 | −5.21 | 0.49 | 100.00 |
| 2m | 5.03 | −0.36 | −5.56 | 0.72 | 100.00 |
| 2n | 5.30 | −0.35 | −5.84 | 0.85 | 100.00 |
| 2o | 5.67 | −0.37 | −6.50 | 0.89 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sever, B.; Soybir, H.; Görgülü, Ş.; Cantürk, Z.; Altıntop, M.D. Pyrazole Incorporated New Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis and Investigation of DPP-4 Inhibitory Effects. Molecules 2020, 25, 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215003
Sever B, Soybir H, Görgülü Ş, Cantürk Z, Altıntop MD. Pyrazole Incorporated New Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis and Investigation of DPP-4 Inhibitory Effects. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSever, Belgin, Hasan Soybir, Şennur Görgülü, Zerrin Cantürk, and Mehlika Dilek Altıntop. 2020. "Pyrazole Incorporated New Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis and Investigation of DPP-4 Inhibitory Effects" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215003
APA StyleSever, B., Soybir, H., Görgülü, Ş., Cantürk, Z., & Altıntop, M. D. (2020). Pyrazole Incorporated New Thiosemicarbazones: Design, Synthesis and Investigation of DPP-4 Inhibitory Effects. Molecules, 25(21), 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215003







