Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Waves, Moods, and Sleep Onset Latency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
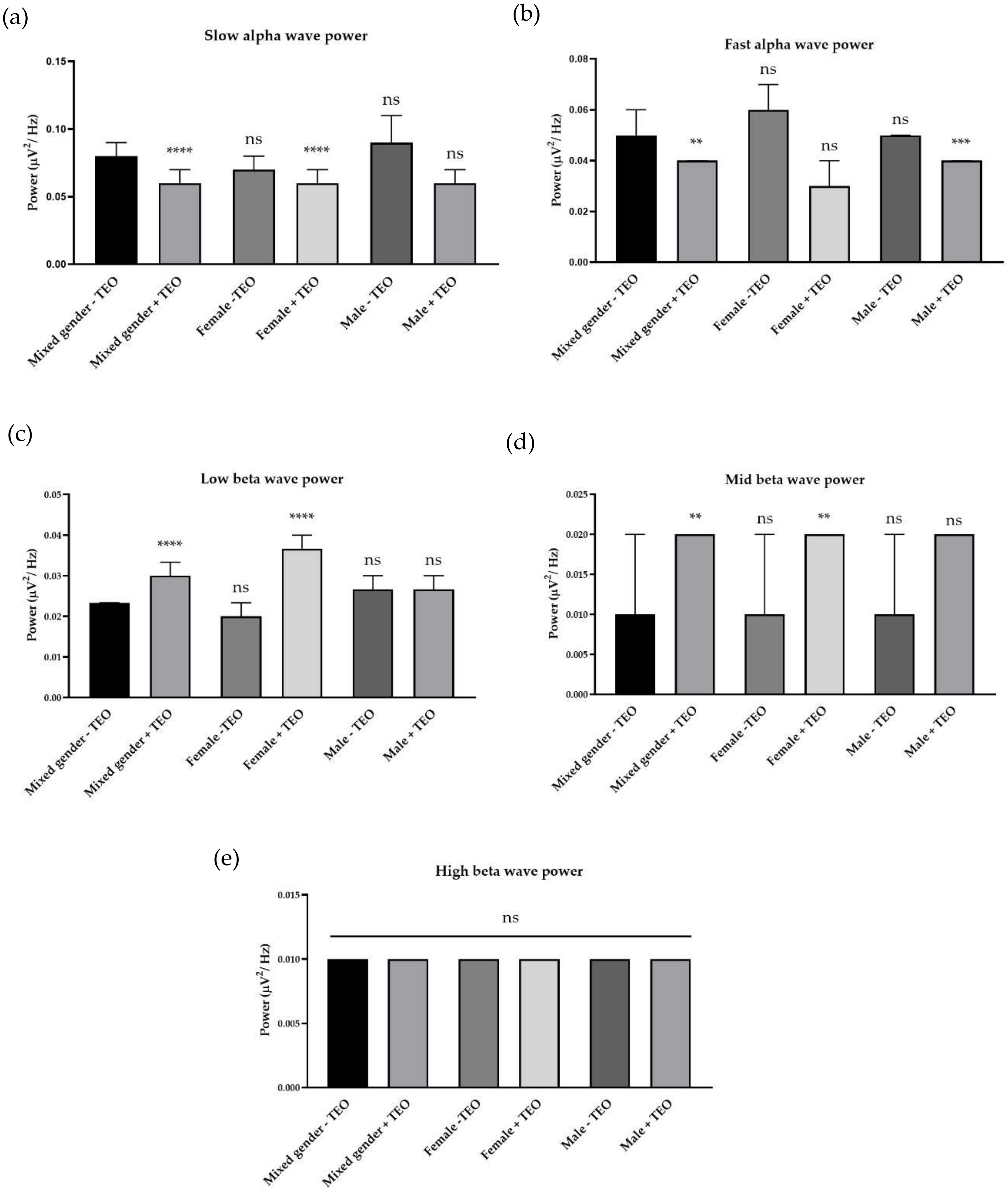
2.1. Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil Inhalation on Brain Responses
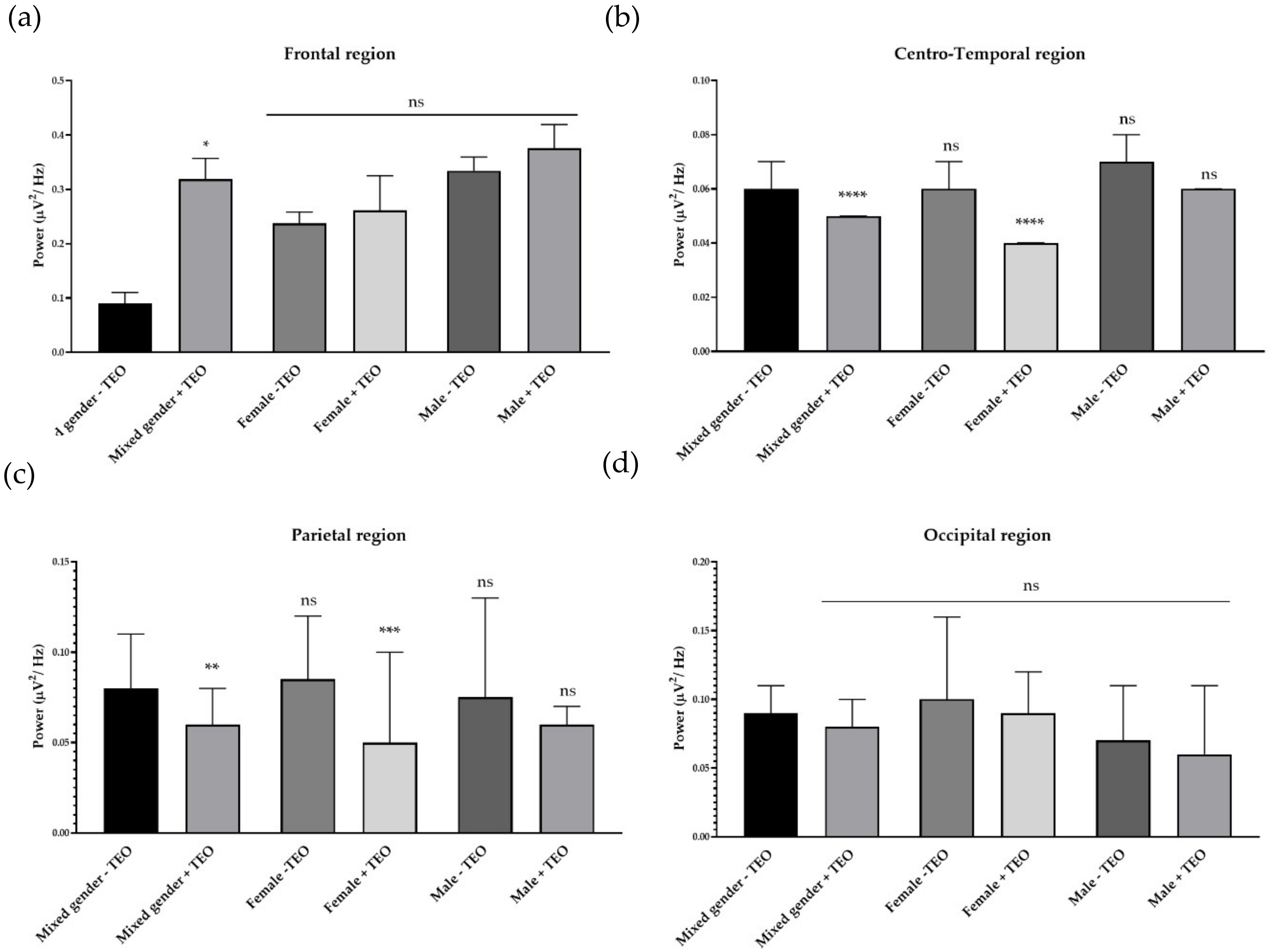
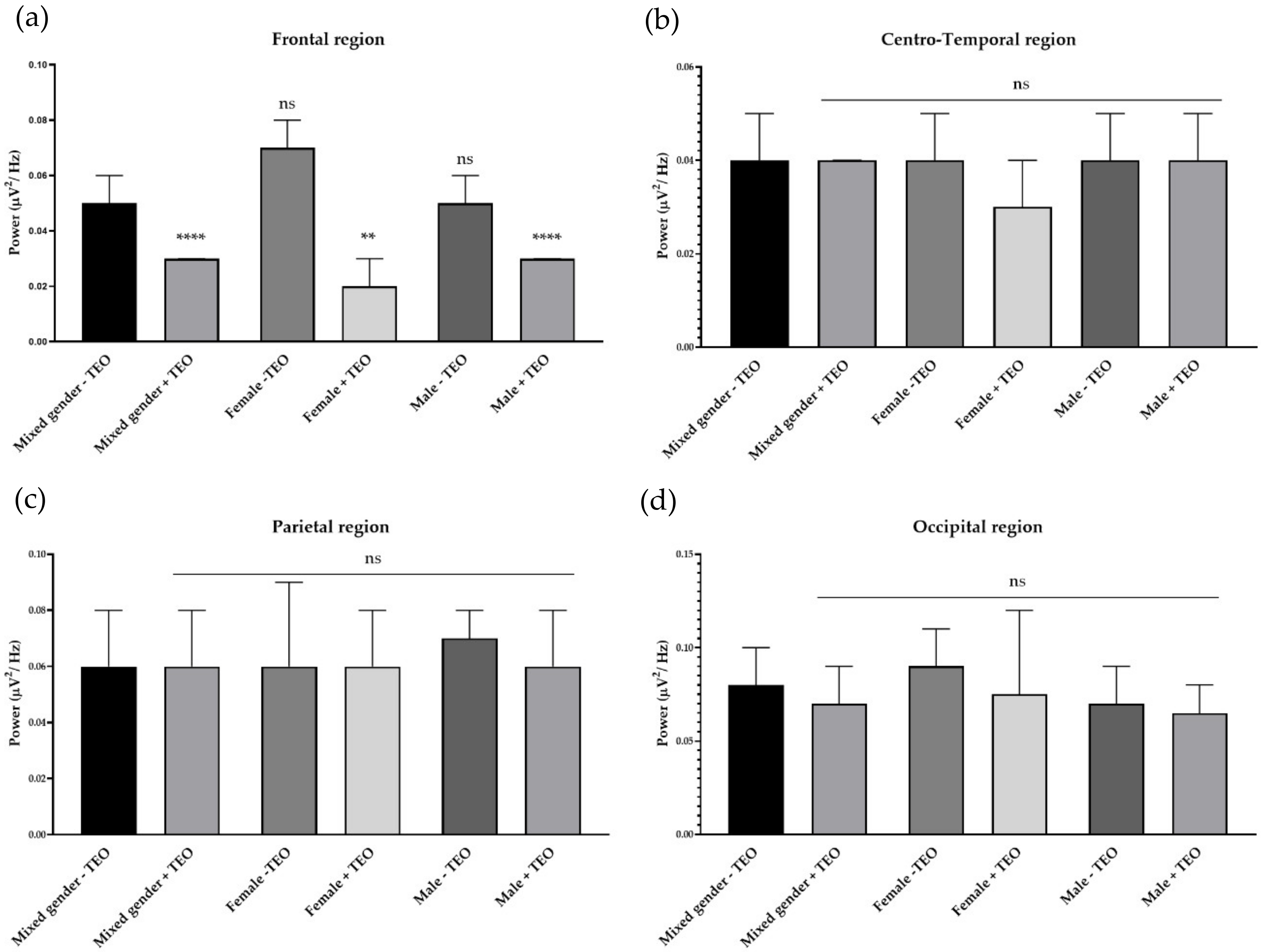
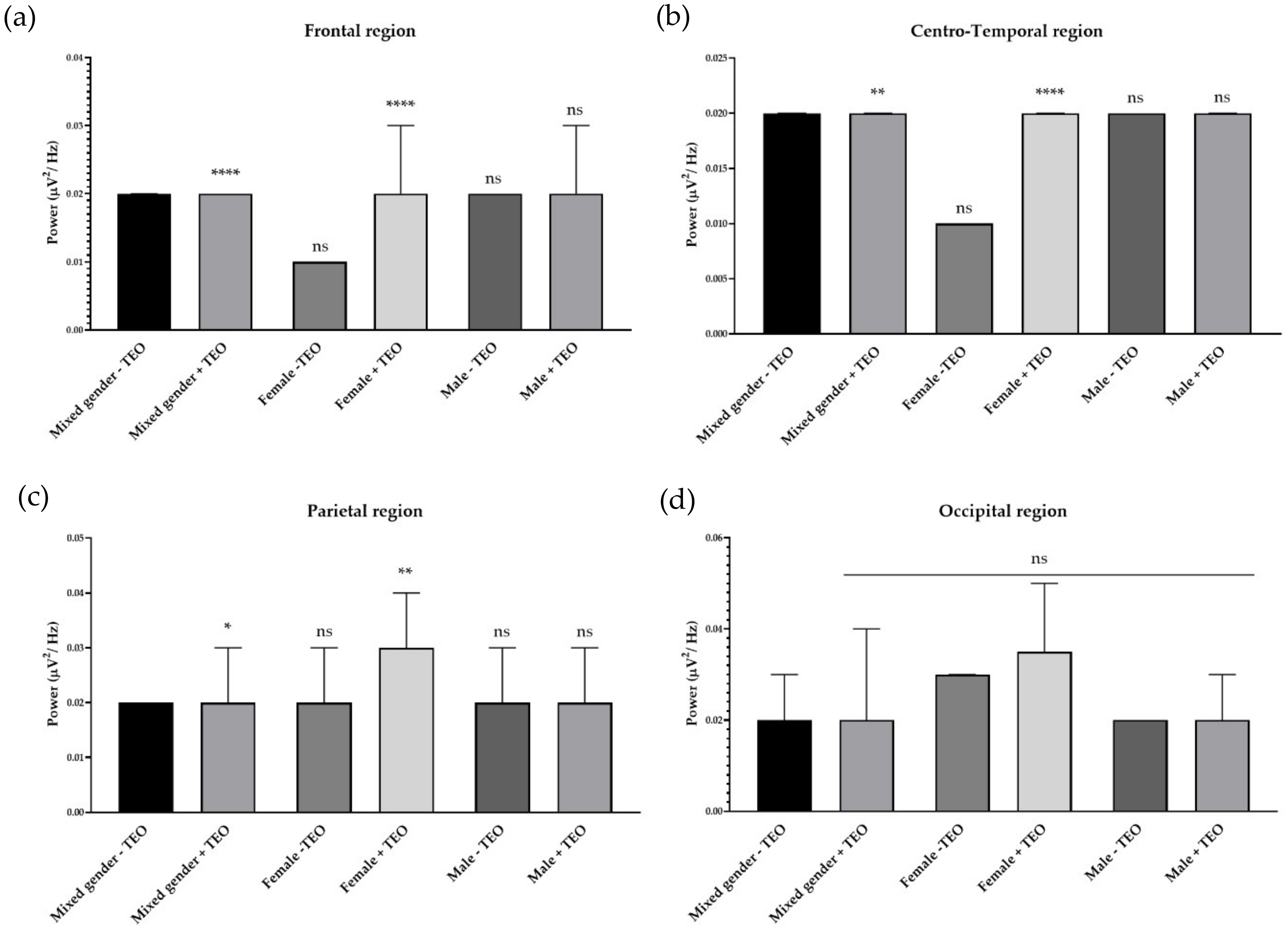
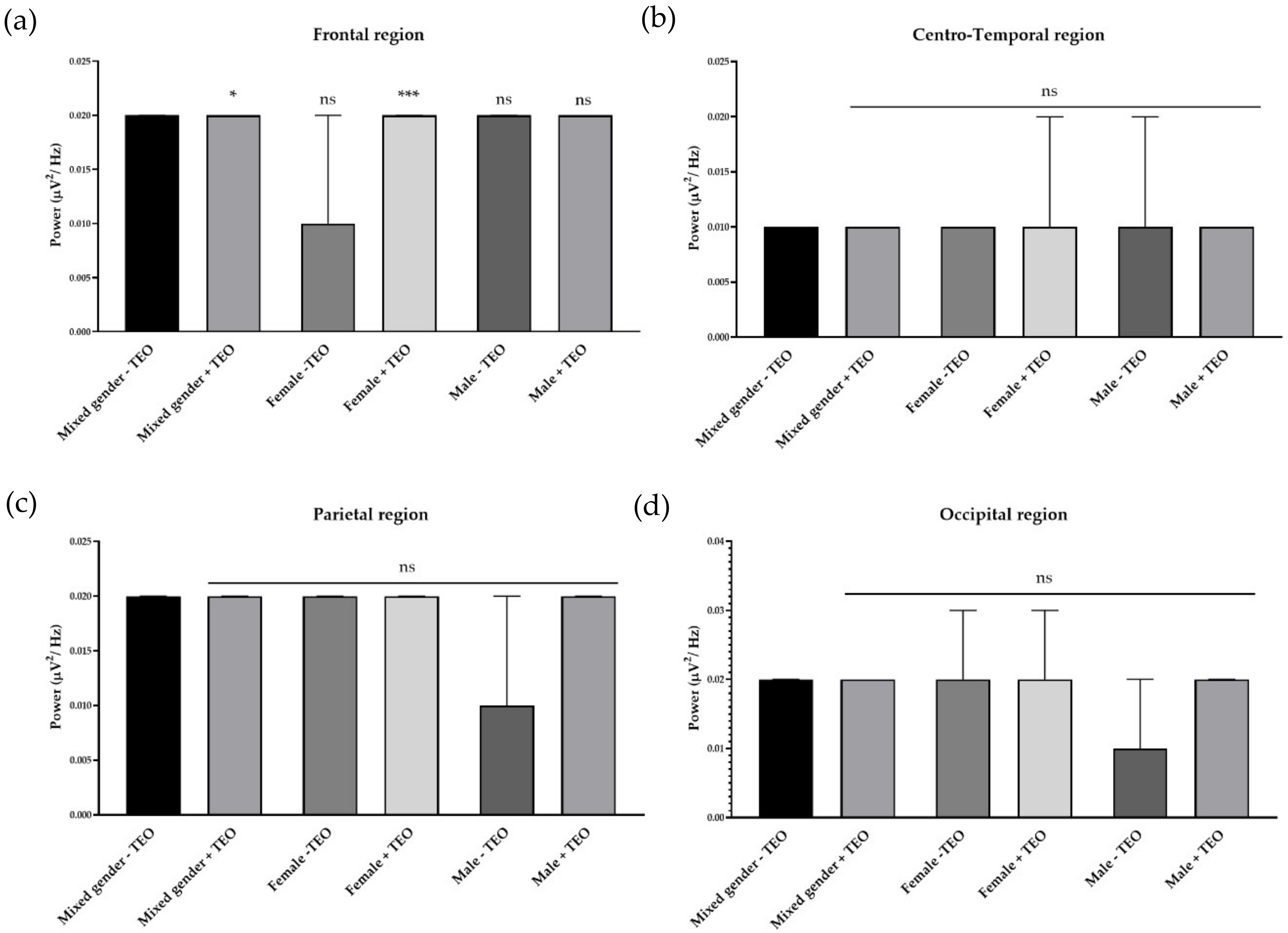
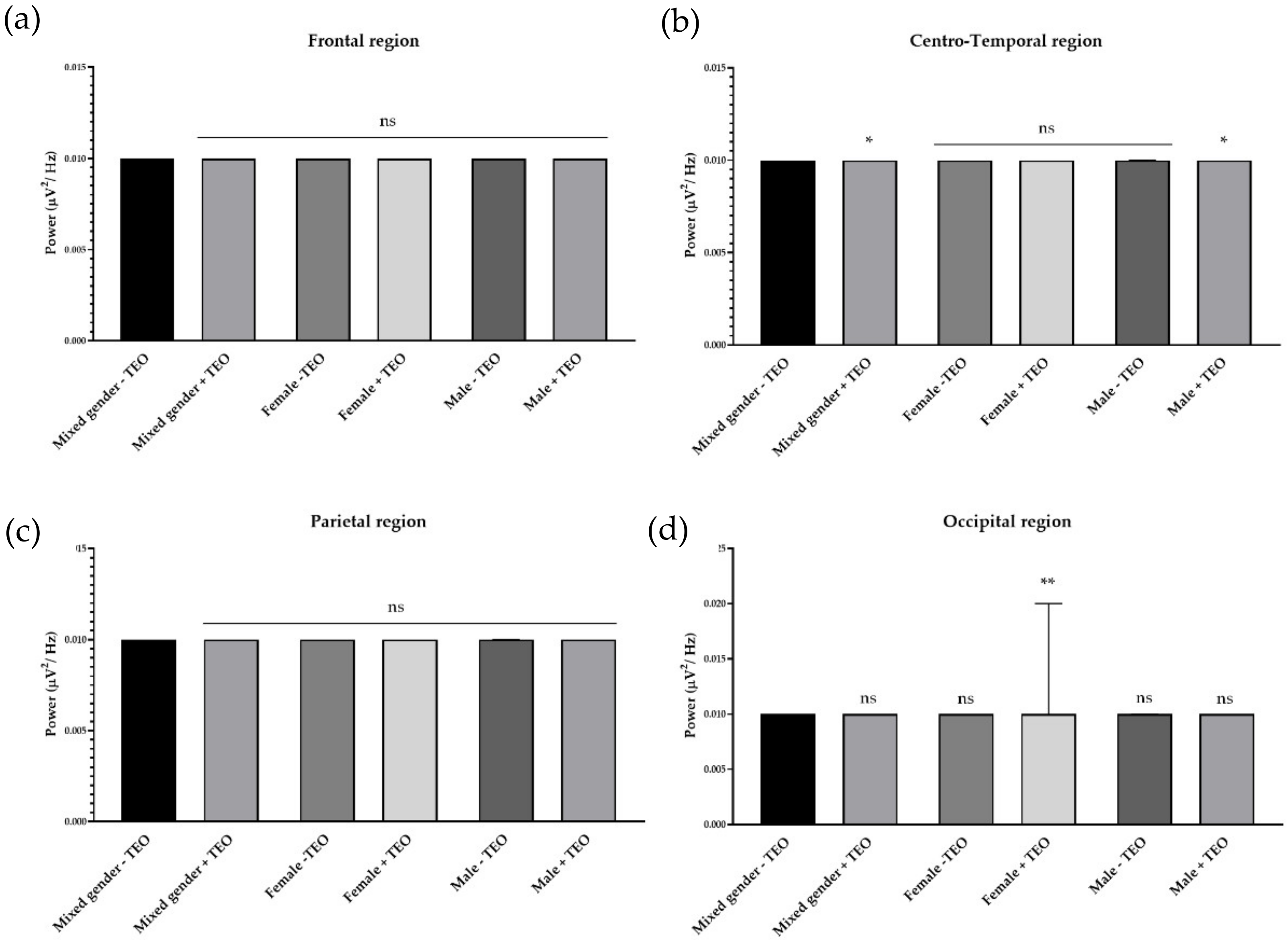
2.2. Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Regions
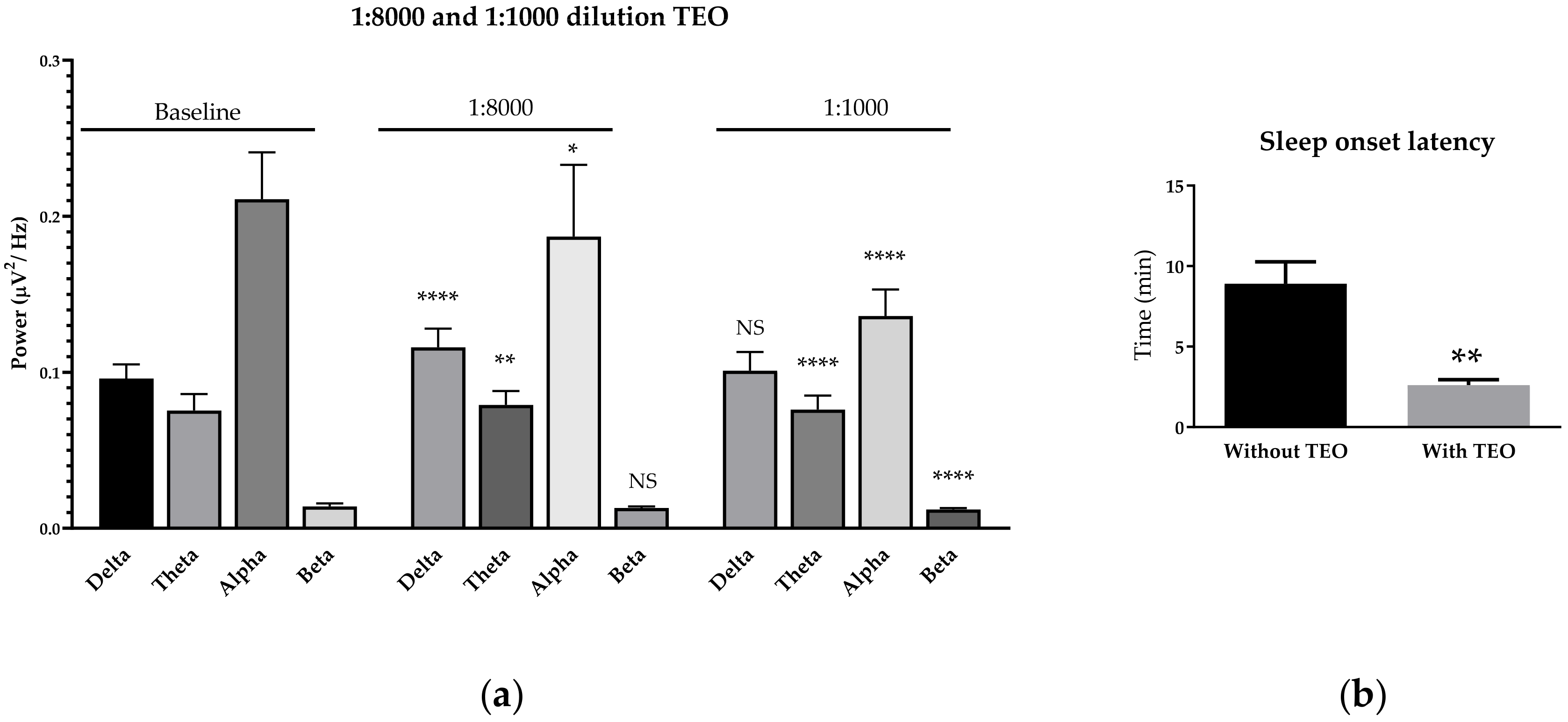
2.3. Effects of Subthreshold and Threshold Oil Dilution on Brain Wave, Sleep Onset Latency, and Emotions
3. Discussion
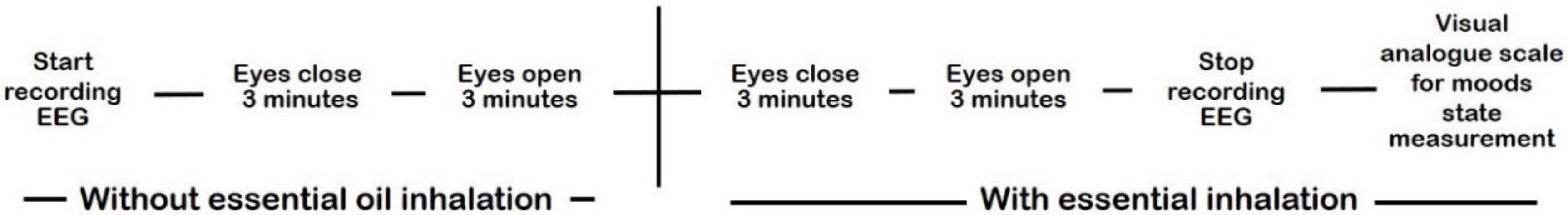
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subject
4.2. Tangerine Oil Preparation and Administration
4.3. Electroencephalography and Sleep Onset Latency
4.4. Score of Moods State Response
4.5. Data Analyses and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonti-Ankomah, S.; Yiridoe, E.K. Organic and conventional food: A literature review of the economics of consumer perceptions and preferences. Org. Agric. Cent. Can. 2006, 59, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Grandviewresearch Essential Oils Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application (Cleaning & Home, Medical, Food & Beverages, Spa & Relaxation), By Product, By Sales Channel, And Segment Forecasts, 2019–2025. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/essential-oils-market (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Alok, K.; Rakesh, T.; Sushil, K. Aromatherapy-an alternative health care through essential oils. J. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. 2000, 22, 798–804. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, B.; Ernst, E. Aromatherapy: A systematic review. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2000, 50, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunning, T. Aromatherapy: Overview, safety and quality issues. OA Altern. Med. 2013, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayorwan, W.; Siripornpanich, V.; Piriyapunyaporn, T.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Kotchabhakdi, N.; Ruangrungsi, N. The effects of lavender oil inhalation on emotional states, autonomic nervous system, and brain electrical activity. J Med Assoc Thai 2012, 95, 598–606. [Google Scholar]
- Sayorwan, W.; Ruangrungsi, N.; Piriyapunyporn, T.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Kotchabhakdi, N.; Siripornpanich, V. Effects of inhaled rosemary oil on subjective feelings and activities of the nervous system. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 81, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.A.; Chess, A. Olfactory G proteins: Simple and complex signal transduction. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, R431–R433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtiol, E.; Wilson, D.A. The olfactory thalamus: Unanswered questions about the role of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in olfaction. Front. Neural Circuits 2015, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Kim, S. Influence of fragrances on human psychophysiological activity: With special reference to human electroencephalographic response. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 724-751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Agricultural Economics, Agricultural product productivity data, Thailand. Available online: http://www.oae.go.th (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Kamal, G.; Anwar, F.; Hussain, A.; Sarri, N.; Ashraf, M. Yield and chemical composition of Citrus essential oils as affected by drying pretreatment of peels. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1275. [Google Scholar]
- Heuberger, E.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Böhm, C.; Weber, R.; Buchbauer, G. Effects of chiral fragrances on human autonomic nervous system parameters and self-evaluation. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, D.P.; Joseph, P.K.; Acharya, U.R.; Lim, C.M. EEG signal analysis: A Survey. J. Med Syst. 2010, 34, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Cho, H.; Yu, B.; Kim, S. Effect of olfactory stimulation of isomeric aroma compounds, (+)-limonene and terpinolene on human electroencephalographic activity. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 7, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, B.S.; Salinsky, M.C.; Elsas, S.M. Vigilance, alertness, or sustained attention: Physiological basis and measurement. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 1885–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S. Effect of inhalation of isomers,(+)-α-pinene and (+)-β-pinene on human electroencephalographic activity according to gender difference. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Goo, Y.-M.; Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.Y.; Sin, S.M.; Kil, Y.S.; Jeong, W.M.; Ko, K.H.; Yang, K.J. Effect of volatile organic chemicals in Chrysanthemum indicum Linné on blood pressure and electroencephalogram. Molecules 2018, 23, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Cho, H.; Yu, B.; Song, J.; Kim, S. Effect of inhalation of essential oil from Inula helenium L. root on electroencephalographic (EEG) activity of the human brain. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 8, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Nio, E.; Nashimoto, E.; Iwata, M. Effects of aroma on the autonomic nervous system and brain activity under stress conditions. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2007, 135, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I. Effects of inhalation of relaxing essential oils on electroencephalogram activity. Int. J. New Technol. Res. 2016, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Park, S.; Hong, J.W.; Jang, E.J.; Pak, C.H. Psychophysiological effects of orchid and rose fragrances on humans. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 472–487. [Google Scholar]
- Lucena, L.R.; Santos-Junior, J.G.; Tufik, S.; Hachul, H. Effect of lavender essential oil on sleep in postmenopausal women with insomnia: Double-blind randomized controlled trial. Sleep 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), A190–A191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yoshioka, M.; Yokogoshi, H. Sub-chronic effects of s-limonene on brain neurotransmitter levels and behavior of rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2009, 55, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, A.R.; Mujica-Parodi, L.R. Human gender differences in the perception of conspecific alarm chemosensory cues. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, D. Spatial localization in left and right visual fields. Can. J. Psychol. /Rev. Can. Psychol. 1969, 23, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, K.M.; Wahlsten, D. Sex differences in the human corpus callosum: Myth or reality? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J.; Schwartz, G.E.; Pugash, E.; Bromfield, E. Sex differences in patterns of EEG asymmetry. Biol. Psychol. 1976, 4, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehner, A.; Maass, H.; Croy, I.; Hummel, T. Influence of room fragrance on attention, anxiety and mood. Flavour Fragr. J. 2017, 32, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, N.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y. Comparative anti-infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) activity of (-)-pinene: Effect on nucleocapsid (N) protein. Molecules 2011, 16, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L.; Cameron, E.L. Sex differences and reproductive hormone influences on human odor perception. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Jung, J.-W.; Jhoo, J.-W.; Kim, S. Fragrance chemicals in the essential oil of Mentha arvensis reduce levels of mental stress. J. Life Sci. 2013, 23, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Mori, T.; Suzuki, H.; Endo, S.; Kawano, K. EEG changes in odor effects after the stress of long monotonous work. J. Int. Soc. Life Inf. Sci. 2001, 19, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.-G.; Lee, B.-L.; Chung, W.-Y. Mobile healthcare for automatic driving sleep-onset detection using wavelet-based EEG and respiration signals. Sensors 2014, 14, 17915–17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosulwat, V. The nutrition and health transition in Thailand. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koomhin, P.; Sattayakhom, A.; Chandharakool, S.; Sinlapasorn, J.; Suanjan, S.; Palipoch, S.; Na-ek, P.; Punsawad, C.; Matan, N. Michelia essential oil inhalation increases fast alpha wave activity. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
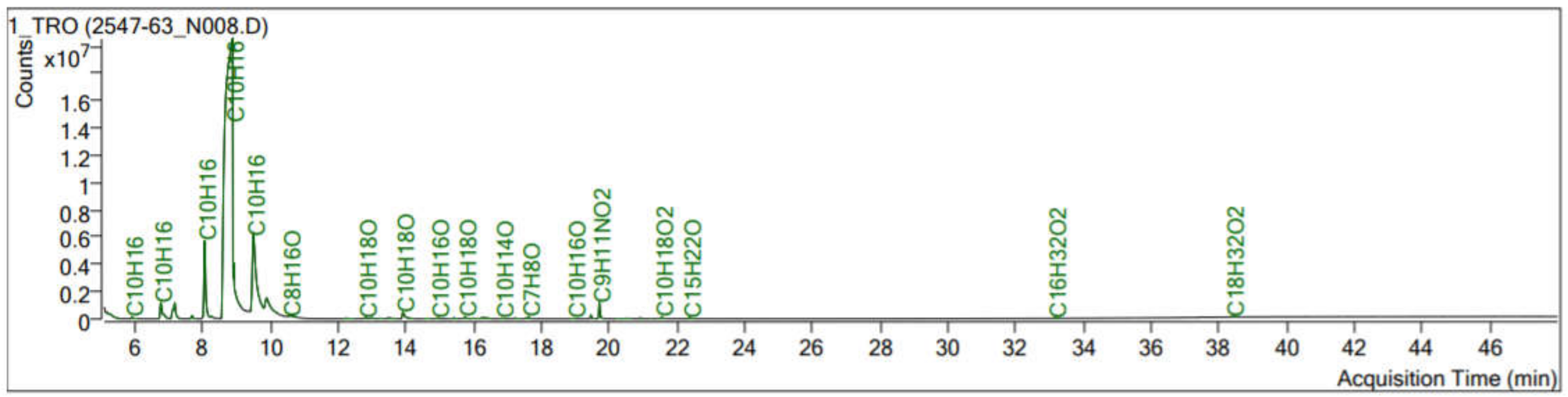
| RT Min | % (Area) | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| 5.17 | 1.05 | α-Phellandrene |
| 5.90 | 0.10 | Camphene |
| 6.76 | 1.36 | β-Pinene |
| 7.17 | 1.52 | Sabinene |
| 7.67 | 0.19 | 3-Carene |
| 8.05 | 4.87 | β-Myrcene |
| 8.24 | 0.08 | 2,4,6-Octatriene, 3,4-dimethyl- |
| 8.88 | 74.47 | d-Limonene |
| 9.49 | 10.86 | γ-Terpinene |
| 9.88 | 2.54 | o-Cymene |
| 10.55 | 0.19 | Octanal |
| 12.22 | 0.04 | Nonanal |
| 13.90 | 0.60 | Linalool |
| Total | 97.87 |
| Brainwaves | Electrodes | Without Essential Oil Inhalation (µV2) | With Essential Oil Inhalation (µV2) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow alpha wave | PZ | 1.192 | 10.869 | 0.0397 |
| Fast alpha wave | AF4 | 0.068 | 0.041 | 0.0015 |
| Low beta wave | T7 | 0.028 | 0.041 | 0.0164 |
| Emotions | Female | Male | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Good | 5.34 | 2.36 | 5.40 | 2.10 |
| Active | 4.96 | 1.01 | 4.59 | 1.79 |
| Drowsy | 4.63 | 2.75 | 3.68 | 3.22 |
| Fresh | 5.93 | 1.94 | 6.16 | 1.50 |
| Romantic | 1.54 | 1.46 | 2.49 | 1.88 |
| Gender | n | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | Sleep (Hours) | Handedness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 10 | 21.6 ± 1.43 | 50.6 ± 5.78 | 161 ± 7.3 | 19.49 ± 2.49 | 7.12 ± 1.93 | Right |
| Male | 10 | 21 ± 0.67 | 59.9 ± 9.64 | 167 ± 6.34 | 21.44 ± 3.41 | 6.2 ± 2.2 | Right |
| Gender | n | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | Handedness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 10 | 21.6 ± 0.66 | 53.1 ± 13 | 156.9 ± 3.28 | 21.56 ± 5.21 | Right |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandharakool, S.; Koomhin, P.; Sinlapasorn, J.; Suanjan, S.; Phungsai, J.; Suttipromma, N.; Songsamoe, S.; Matan, N.; Sattayakhom, A. Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Waves, Moods, and Sleep Onset Latency. Molecules 2020, 25, 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204865
Chandharakool S, Koomhin P, Sinlapasorn J, Suanjan S, Phungsai J, Suttipromma N, Songsamoe S, Matan N, Sattayakhom A. Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Waves, Moods, and Sleep Onset Latency. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204865
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandharakool, Supaya, Phanit Koomhin, Jennarong Sinlapasorn, Sarunnat Suanjan, Jantamas Phungsai, Noppharat Suttipromma, Sumethee Songsamoe, Narumol Matan, and Apsorn Sattayakhom. 2020. "Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Waves, Moods, and Sleep Onset Latency" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204865
APA StyleChandharakool, S., Koomhin, P., Sinlapasorn, J., Suanjan, S., Phungsai, J., Suttipromma, N., Songsamoe, S., Matan, N., & Sattayakhom, A. (2020). Effects of Tangerine Essential Oil on Brain Waves, Moods, and Sleep Onset Latency. Molecules, 25(20), 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204865





