Effects of Combined Admistration of Imatinib and Sorafenib in a Murine Model of Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Animal Study
2.1.1. Effects of ConA Injection
2.1.2. Effects of Imatinib and Sorafenib on the Expression of Alpha-SMA
2.1.3. Effects of Imatinib and Sorafenib on the Expression of Collagens
2.1.4. Effects of Imatinib and Sorafenib on the Expression of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TFGFB)1 and TGFB2 and of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
2.1.5. Effects of Imatinib and Sorafenib on the Expression of Interleukin 6 (IL-6)
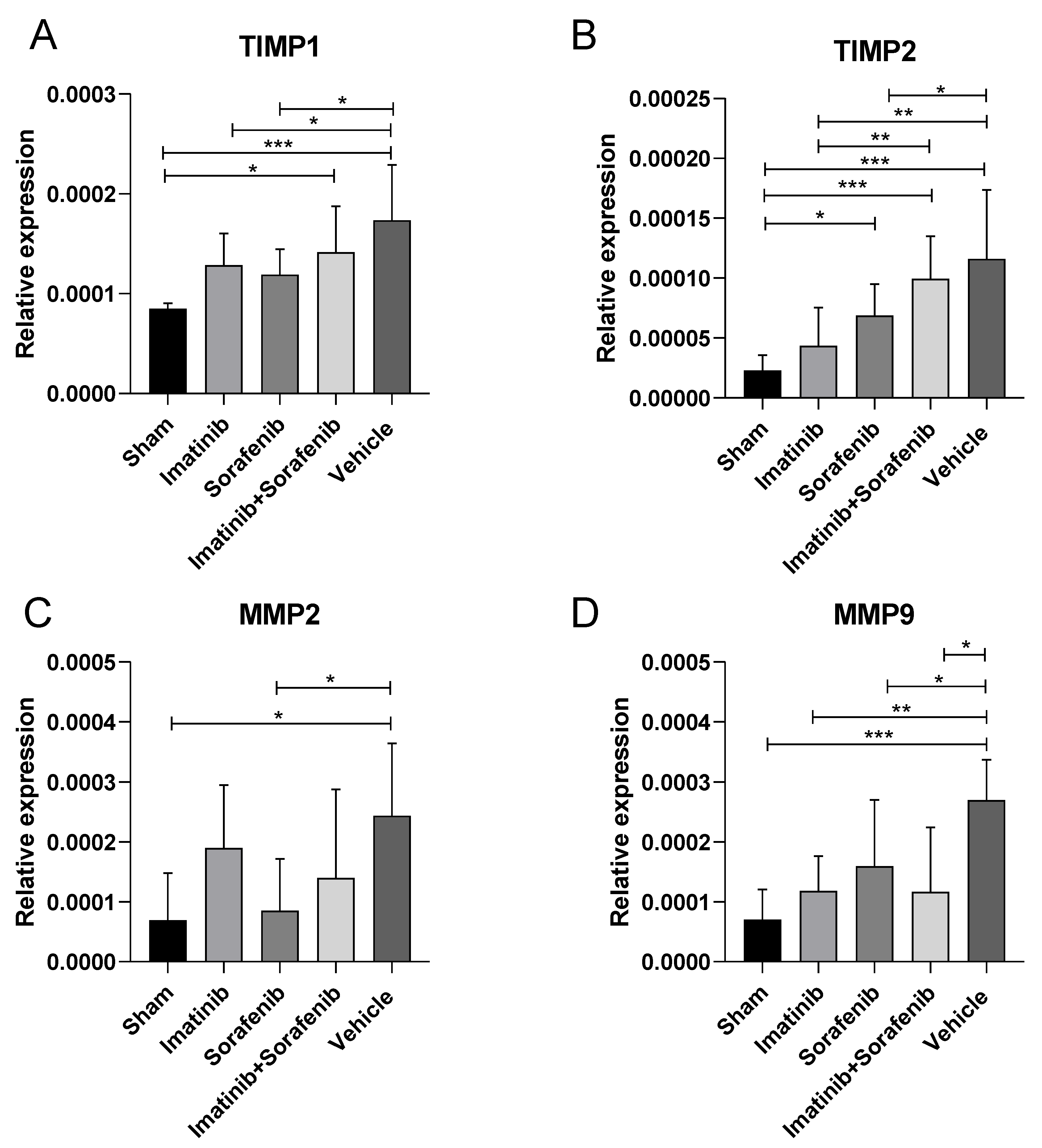
2.1.6. Effects of Imatinib and Sorafenib on the Expression of Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinases (TIMP)1, TIMP2, Matrix Metallopeptidase (MMP)2, and MMP9
2.1.7. Histopathological Analysis
2.2. In Silico Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Study
4.1.1. Induction of Liver Fibrosis and Experimental Treatments
4.1.2. Ex Vivo Analysis
4.1.3. Real-Time PCR
4.2. In Silico Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Li, X. Self-eating: Friend or foe? The emerging role of autophagy in fibrotic diseases. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7993–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Tang, S.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Su, Y.; Shen, L.; Sun, M.; Ning, B. MicroRNA-21a-5p promotes fibrosis in spinal fibroblasts after mechanical trauma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, A.; Zheng, B. To Scar or Not to Scar. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressner, A.M.; Weiskirchen, R. Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-β as major players and therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F.; Weiskirchen, R. Update on hepatic stellate cells: Pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel isolation techniques. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 6, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C.; Luedde, T.; Sauerbruch, T.; Scholten, D.; Streetz, K.; Tacke, F.; Tolba, R.; Trautwein, C.; Trebicka, J.; Weiskirchen, R. Experimental liver fibrosis research: Update on animal models, legal issues and translational aspects. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair 2013, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Yanguas, S.; Cogliati, B.; Willebrords, J.; Maes, M.; Colle, I.; van den Bossche, B.; de Oliveira, C.P.M.S.; Andraus, W.; Alves, V.A.; Leclercq, I.; et al. Experimental models of liver fibrosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1025–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwanpura, S.M.; Thomas, B.J.; Bardin, P.G. Pirfenidone: Molecular mechanisms and potential clinical applications in lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Cerbai, E.; Bartolucci, G.; Adamo, L.; Barison, A.; Lo Surdo, G.; Biagini, S.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Pirfenidone is a cardioprotective drug: Mechanisms of action and preclinical evidence. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, C.A.; Padsalgi, G.; Ahamed, R.; Paramaguru, R.; Rajesh, S.; George, T.; Mahadevan, P.; Augustine, P. Repurposing Pirfenidone for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-related Cirrhosis: A Case Series. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, P.W.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Bois, R.M.D.; Fagan, E.A.; Fishman, R.S.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Lancaster, L.; et al. Pirfenidone for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Analysis of pooled data from three multinational phase 3 trials. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, P.P.; Ishak, K.G.; Nayak, N.C.; Poulsen, H.E.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sobin, L.H. The morphology of cirrhosis. Recommendations on definition, nomenclature, and classification by a working group sponsored by the World Health Organization. J. Clin. Pathol. 1978, 31, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Pesce, A.; Portale, T.R.; Puleo, S.; Nicoletti, F. Emerging therapeutic targets for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Pesce, A.; Pesce, A.; Caltabiano, R.; Giorlandino, A.; Portale, T.R.; Cavalli, E.; Lombardo, G.A.G.; et al. Identification of novel targets for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, A.; Scilletta, R.; Branca, A.; Nigro, L.; Montineri, A.; Larocca, L.; Fatuzzo, F.; Castaing, M.; Puleo, S. Does transient elastography (FibroScan®) have a role in decision making in hepatocellular carcinoma? HPB 2012, 14, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Morini, S.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Franchitto, A.; Merli, M.; Siciliano, M.; Gentili, F.; Onetti Muda, A.; Berloco, P.; Rossi, M.; et al. Alpha-SMA expression in hepatic stellate cells and quantitative analysis of hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis and in recurrent chronic hepatitis after liver transplantation. Dig. Liver Dis. 2005, 37, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. IL-6 pathway in the liver: From physiopathology to therapy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, P.; Sultan, M.; Tachlytski, I.; Safran, M.; Ben-Ari, Z. Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.B.; Hu, E.D.; Xu, L.M.; Hu, Y.B.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.L.; Li, H.; Chen, D.Z.; Chen, Y.P. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of treatments for adult autoimmune hepatitis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4838–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.L.; Yu, M.C.; Lee, J.F.; Tsai, C.N.; Chen, T.C.; Chen, M.F. Imatinib Mesylate Improves Liver Regeneration and Attenuates Liver Fibrogenesis in CCL 4-Treated Mice. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 16, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.E.; Shiha, G.E.; Ibrahim, T.M. Comparison of early treatment with low doses of nilotinib, imatinib and a clinically relevant dose of silymarin in thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chao, P.H.; Chang, C.C.; Jin, P.R.; Lin, T.T.; Lin, J.A.; Cheng, H.T.; Wang, J.; Lai, C.P.; et al. Combined delivery of sorafenib and a MEK inhibitor using CXCR4-targeted nanoparticles reduces hepatic fibrosis and prevents tumor development. Theranostics 2018, 8, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neef, M.; Ledermann, M.; Saegesser, H.; Schneider, V.; Widmer, N.; Decosterd, L.A.; Rochat, B.; Reichen, J. Oral imatinib treatment reduces early fibrogenesis but does not prevent progression in the long term. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Noguchi, R.; Ikenaka, Y.; Yoshii, J.; Yanase, K.; Namisaki, T.; Kitade, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Asada, K.; et al. Amelioration of liver fibrogenesis by dual inhibition of PDGF and TGF-β with a combination of imatinib mesylate and ACE inhibitor in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Fiel, M.I.; Albanis, E.; Chou, H.I.; Zhang, W.; Khitrov, G.; Friedman, S.L. Anti-fibrotic activity and enhanced interleukin-6 production by hepatic stellate cells in response to imatinib mesylate. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, I.M.; Oosterhuis, D.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P. The effect of antifibrotic drugs in rat precision-cut fibrotic liver slices. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mezayen, N.S.; El-Hadidy, W.F.; El-Refaie, W.M.; Shalaby, T.I.; Khattab, M.M.; El-Khatib, A.S. Hepatic stellate cell-targeted imatinib nanomedicine versus conventional imatinib: A novel strategy with potent efficacy in experimental liver fibrosis. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.R.; Ma, H.D.; Tsuneyama, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Lu, F.T.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, P.; He, X.S.; Diehl, A.M.; et al. STAT3-mediated attenuation of CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis bythe protein kinase inhibitor sorafenib. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 46, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ao, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Li, W.; Li, W. SIRT1/IGFBPrP1/TGF β1 axis involved in cucurbitacin B ameliorating concanavalin A-induced mice liver fibrosis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, M.M.; Ashour, A.A.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Abdel-Aziz, A.A.H.; Salama, S.A. Pirfenidone alleviates concanavalin A-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 116982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Quattrocchi, C.; Motterlini, R.; Di Marco, R.; Magro, G.; Penacho, N.; Romao, C.C.; Nicoletti, F. Prevention of clinical and histological signs of proteolipid protein (PLP)-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice by the water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM)-A1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 163, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Coco, M.; Perciavalle, V.; Garotta, G.; Romao, C.C.; Nicoletti, F. Therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mangano, K.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulated Expression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor, Its Analogue D-Dopachrome Tautomerase, and the CD44 Receptor in Peripheral CD4 T Cells from Clinically Isolated Syndrome Patients with Rapid Conversion to Clinical Defined Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina (Buenos Aires) 2019, 55, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothweiler, F.; Michaelis, M.; Brauer, P.; Otte, J.; Weber, K.; Fehse, B.; Doerr, H.W.; Wiese, M.; Kreuter, J.; Al-Abed, Y.; et al. Anticancer effects of the nitric oxide-modified saquinavir derivative saquinavir-NO against multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Meroni, P.; McCubrey, J.; Bendtzen, K. mTOR as a multifunctional therapeutic target in HIV infection. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coco, M.; Platania, S.; Castellano, S.; Sagone, E.; Ramaci, T.; Petralia, M.C.; Agati, M.; Massimino, S.; Di Corrado, D.; Guarnera, M.; et al. Memory, personality and blood lactate during a judo competition. Sport Sci. Health 2018, 14, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Perciavalle, V.; Basile, M.S.; Alagona, G.; Monaca, A.; Buscemi, A.; Coco, M. The rise of lactic acid, from a pharmacist’s laboratory to entry into the central nervous system. Sport Sci. Health 2018, 14, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Basile, M.S.; Lenzo, V.; Quattropani, M.C.; Bendtzen, K.; Nicoletti, F. Pathogenic contribution of the Macrophage migration inhibitory factor family to major depressive disorder and emerging tailored therapeutic approaches. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 263, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Basile, M.S.; Lenzo, V.; Quattropani, M.C.; Di Nuovo, S.; Bendtzen, K.; Nicoletti, F. The cytokine network in the pathogenesis of major depressive disorder. Close to translation? Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donia, M.; Mangano, K.; Quattrocchi, C.; Fagone, P.; Signorelli, S.; Magro, G.; Sfacteria, A.; Bendtzen, K.; Nicoletti, F. Specific and strain-independent effects of dexamethasone in the prevention and treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rodents. Scand. J. Immunol. 2010, 72, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Muthumani, K.; Mangano, K.; Magro, G.; Meroni, P.L.; Kim, J.J.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B.; Nicoletti, F. VGX-1027 modulates genes involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced Toll-like receptor 4 activation and in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 2014, 142, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, M.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, A.; Colletti, G.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in glioblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Caltabiano, R.; Russo, A.; Lupo, G.; Anfuso, C.D.; Basile, M.S.; Longo, A.; Nicoletti, F.; De Pasquale, R.; Libra, M.; et al. Identification of novel chemotherapeutic strategies for metastatic uveal melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, M.S.; Mazzon, E.; Russo, A.; Mammana, S.; Longo, A.; Bonfiglio, V.; Fallico, M.; Caltabiano, R.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Differential modulation and prognostic values of immune-escape genes in uveal melanoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, K.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Mammana, S.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F. Pathogenic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in glioblastoma and its targeting with specific inhibitors as novel tailored therapeutic approach. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17951–17970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoletano, C.; Bellati, F.; Ruscito, I.; Pernice, M.; Zizzari, I.G.; Caponnetto, S.; Tomao, F.; Frigerio, L.; Liberati, M.; Rughetti, A.; et al. Immunological and clinical impact of cancer stem cells in vulvar cancer: Role of cd133/cd24/abcg2-expressing cells. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5109–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponnetto, S.; Draghi, A.; Borch, T.H.; Nuti, M.; Cortesi, E.; Svane, I.M.; Donia, M. Cancer immunotherapy in patients with brain metastases. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.S.; Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Magro, G.; Salvatorelli, L.; Li Destri, G.; La Greca, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Puleo, S.; et al. KCNMA1 Expression is Downregulated in Colorectal Cancer via Epigenetic Mechanisms. Cancers 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, M.; Tibullo, D.; Vecchio, M.; Nunnari, G.; Saccone, S.; Di Raimondo, F.; Malaguarnera, L. Determination of chitinases family during osteoclastogenesis. Bone 2014, 61, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, I.; Tibullo, D.; Di Rosa, M.; Giallongo, C.; Palumbo, G.A.; Raciti, G.; Campisi, A.; Vanella, A.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. A cytoprotective role for the heme oxygenase-1/CO pathway during neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, A.B.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Koplev, S.; He, E.; Torre, D.; Wang, Z.; Dohlman, A.B.; Silverstein, M.C.; Lachmann, A.; et al. The Library of Integrated Network-Based Cellular Signatures NIH Program: System-Level Cataloging of Human Cells Response to Perturbations. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, C.; Longo, A.; Lazzara, F.; Cambria, D.; Distefano, G.; Palumbo, M.; Cantarella, A.; Malaguarnera, L.; Di Rosa, M. CHI3L1 and CHI3L2 overexpression in motor cortex and spinal cord of sALS patients. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Lin, H.M.; Sibille, E.; Tseng, G.C. Meta-analysis methods for combining multiple expression profiles: Comparisons, statistical characterization and an application guideline. BMC Bioinformatics 2013, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors upon reasonable request. |





| Group | N° Animals | Treatment | Dose | Route | Regime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | Sham | ------- | ------ | ------- |
| B | 15 | Vehicle | 100 μL | p.o.* | 5 days/week |
| C | 15 | Imatinib | 50 mg/kg | p.o.* | 5 days/week |
| D | 15 | Sorafenib | 30 mg/kg | p.o.* | 5 days/week |
| E | 15 | Imatinib + Sorafenib | 50 mg/kg + 30 mg/kg | p.o.* | 5 days/week |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pesce, A.; Ciurleo, R.; Bramanti, A.; Armeli Iapichino, E.C.; Petralia, M.C.; Magro, G.G.; Fagone, P.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Effects of Combined Admistration of Imatinib and Sorafenib in a Murine Model of Liver Fibrosis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184310
Pesce A, Ciurleo R, Bramanti A, Armeli Iapichino EC, Petralia MC, Magro GG, Fagone P, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F, Mangano K. Effects of Combined Admistration of Imatinib and Sorafenib in a Murine Model of Liver Fibrosis. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184310
Chicago/Turabian StylePesce, Antonio, Rosella Ciurleo, Alessia Bramanti, Eliana Concetta Armeli Iapichino, Maria Cristina Petralia, Gaetano Giuseppe Magro, Paolo Fagone, Placido Bramanti, Ferdinando Nicoletti, and Katia Mangano. 2020. "Effects of Combined Admistration of Imatinib and Sorafenib in a Murine Model of Liver Fibrosis" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184310
APA StylePesce, A., Ciurleo, R., Bramanti, A., Armeli Iapichino, E. C., Petralia, M. C., Magro, G. G., Fagone, P., Bramanti, P., Nicoletti, F., & Mangano, K. (2020). Effects of Combined Admistration of Imatinib and Sorafenib in a Murine Model of Liver Fibrosis. Molecules, 25(18), 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184310







