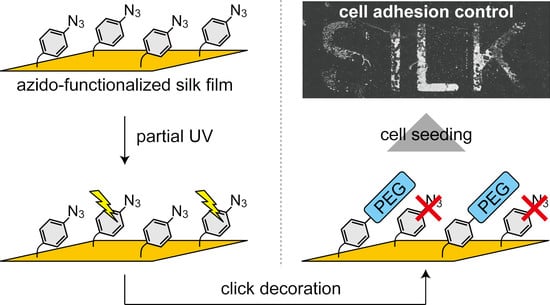
Click Decoration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin for Cell Adhesion Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
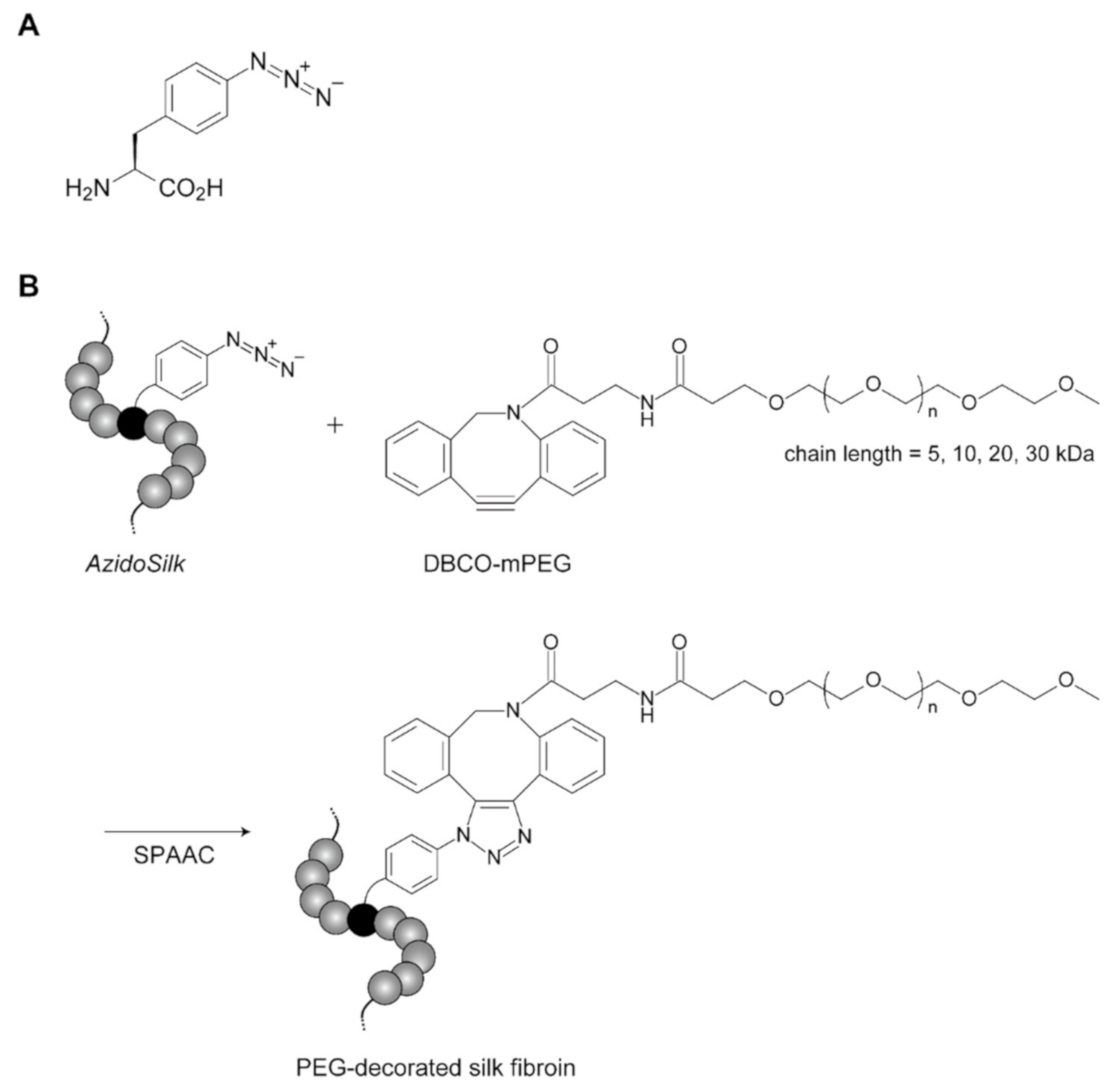
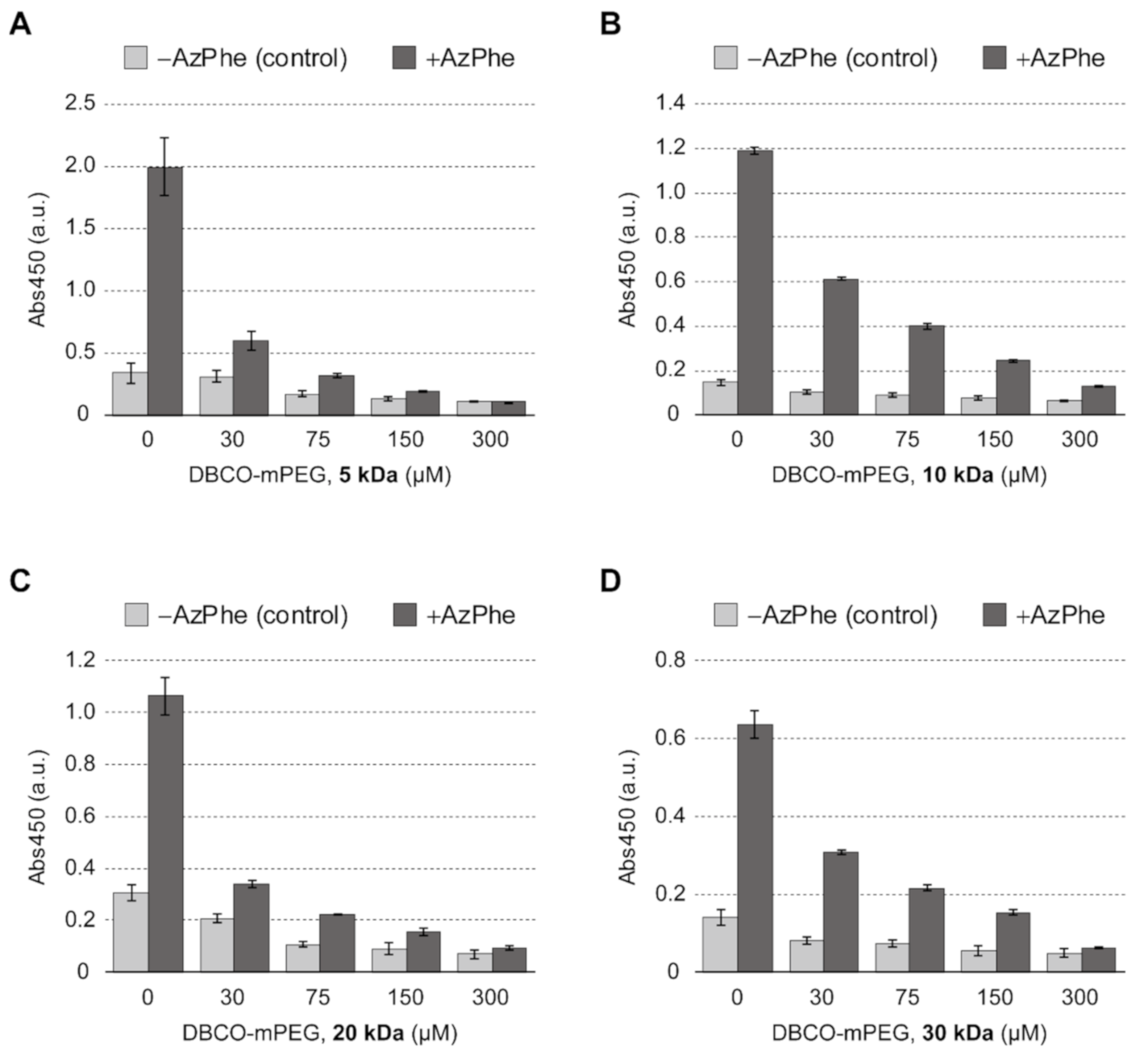
2.1. Click Decoration of Silk Fibroin with PEG
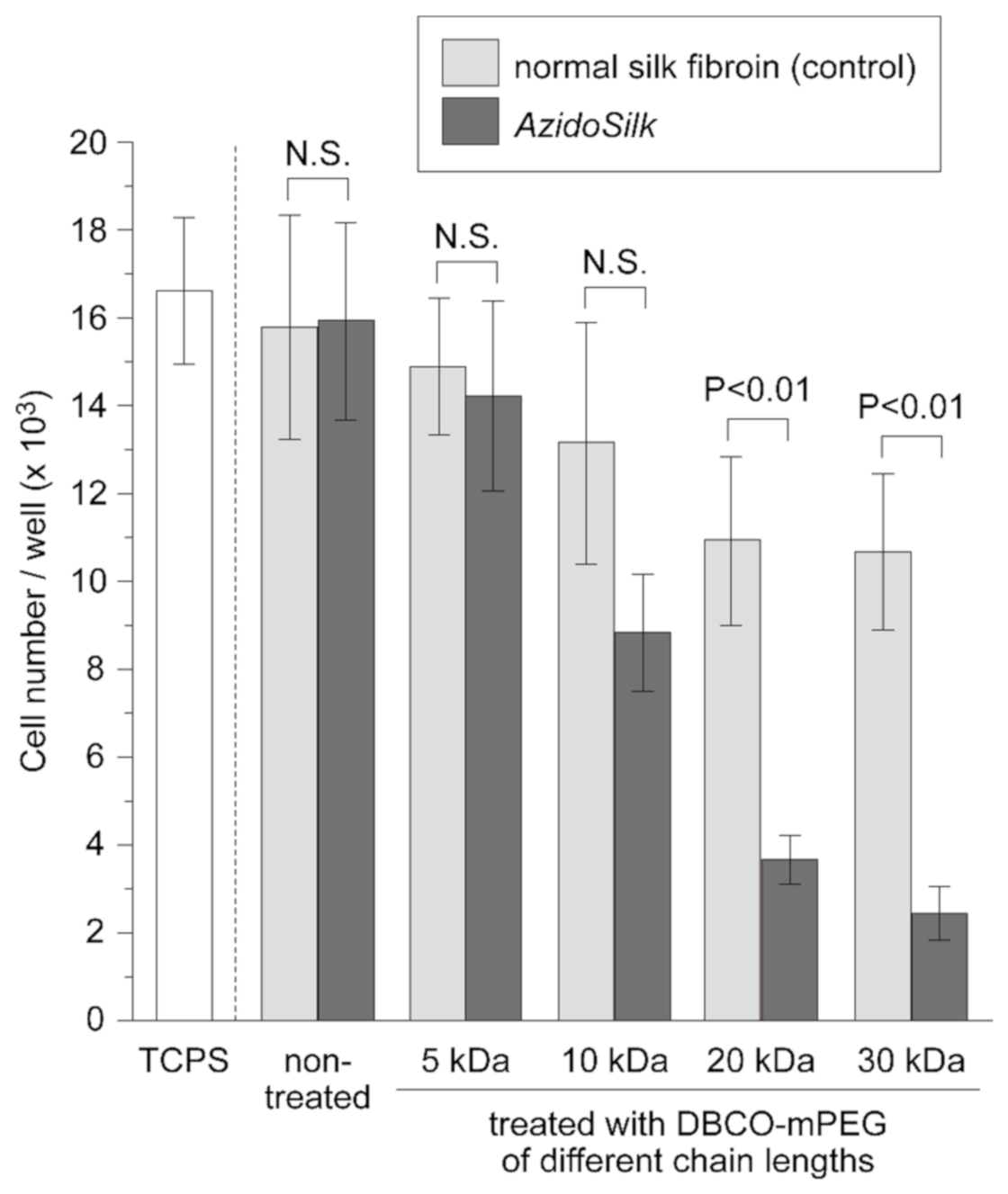
2.2. Cell Adhesion on PEG-Decorated Silk Fibroin Film
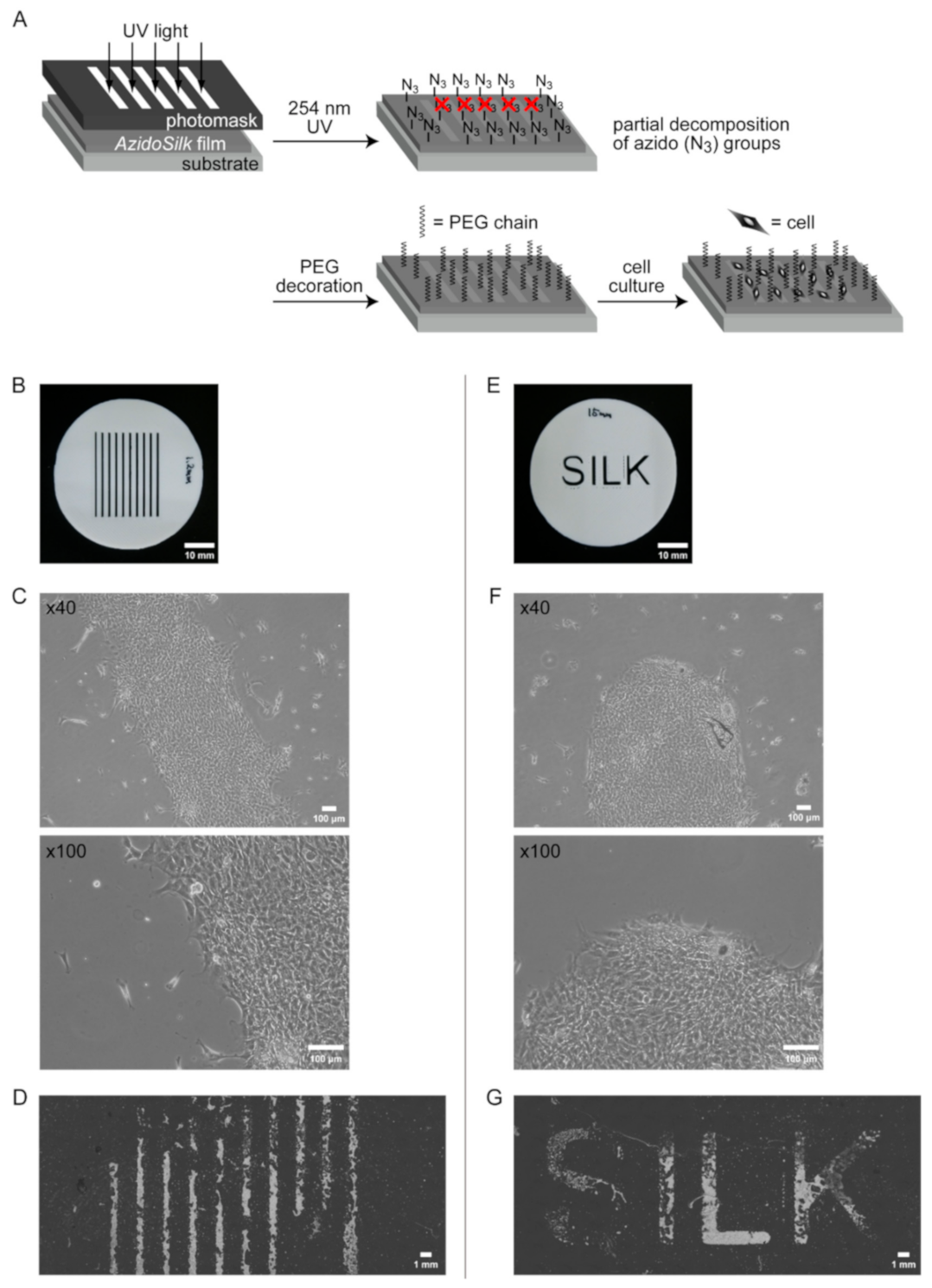
2.3. Spatial Patterning of Cells on Partially PEG-Decorated Silk Fibroin Film
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Animals
3.2. Production of AzidoSilk
3.3. Preparation of Fibroin Aqueous Solution
3.4. Preparation of Fibroin Film-Coated Cell Culture Plates and Dishes
3.5. Click Decoration Tests
3.6. Cell Adhesion Tests
3.7. Cell Patterning Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Medina, N.; Zivanovic, Y.; Esnault, C.; Yang, T.; Jacquet, M.; Janin, J.; Duguet, M.; Perasso, R.; et al. Fine organization of Bombyx mori fibroin heavy chain gene. Nucl. Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, C.; Numata, K.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Seib, F.P. The biomedical use of silk: Past, present, future. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1800465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurber, A.E.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. In vivo bioresponses to silk proteins. Biomaterials 2015, 71, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Kimmerling, E.P.; Cairns, D.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a biomaterial to support long-term three-dimensional tissue cultures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21861–21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Egaña, A.; Scheibel, T. Silk-based materials for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2010, 55, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.; Ferreira, A.V.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. On the routines of wild-type silk fibroin processing toward silk-inspired materials: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Lajoie, M.J.; Englert, M.; Söll, D. Rewriting the genetic code. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Lercher, L.; Spicer, C.D.; Davis, B.G. Designing logical codon reassignment—Expanding the chemistry in biology. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.W. Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code of cells and animals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 379–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajoie, M.J.; Söll, D.; Church, G.M. Overcoming challenges in engineering the genetic code. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 1004–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.; Liu, J.; Deiters, A. Genetic code expansion in animals. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Engineering the genetic code in cells and animals: Biological considerations and impacts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, H.; Kojima, K. Production of Bombyx mori silk fibroin incorporated with unnatural amino acids. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, H.; Amano, Y.; Iraha, F.; Kojima, K.; Ito, T.; Sakamoto, K. Genetic code expansion of the silkworm Bombyx mori to functionalize silk fiber. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, K.; Chin, J.W. Cellular incorporation of unnatural amino acids and bioorthogonal labeling of proteins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4764–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, H.; Nakajima, K.; Kojima, K. Azide-incorporated clickable silk fibroin materials with the ability to photopattern. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikić, I.; Kang, J.H.; Girona, G.E.; Aramburu, I.V.; Lemke, E.A. Labeling proteins on live mammalian cells using click chemistry. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, S.; Watson, P.; Rizkallah, P.; Tippmann, E.; Jones, D.D. Genetically encoding phenyl azide chemistry: New uses and ideas for classical biochemistry. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, H.; Iga, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Nakajima, K. Characterization and scaled-up production of azido-functionalized silk fiber produced by transgenic silkworms with an expanded genetic code. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Hu, N.; Cairns, D.M.; Liu, H.; Timko, B.P. Photo-cross-linkable, insulating silk fibroin for bioelectronics with enhanced cell affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15482–15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurland, N.E.; Dey, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Yadavalli, V.K. Precise patterning of silk microstructures using photolithography. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Pradhan, S.; Agostinacchio, F.; Pal, R.K.; Greco, G.; Mazzolai, B.; Pugno, N.M.; Motta, A.; Yadavalli, V.K. Easy, scalable, robust, micropatterned silk fibroin cell substrates. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shmelev, K.; Sun, L.; Gil, E.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Regulation of silk material structure by temperature-controlled water vapor annealing. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamada, Y.; Ikada, Y. Fibroblast growth on polymer surfaces and biosynthesis of collagen. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Kusamori, K.; Nishikawa, M. Click chemistry as a tool for cell engineering and drug delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Scott, T.F.; Kloxin, C.J.; Bowman, C.N. Click chemistry in materials science. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2572–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teramoto, H.; Shirakawa, M.; Tamada, Y. Click Decoration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin for Cell Adhesion Control. Molecules 2020, 25, 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184106
Teramoto H, Shirakawa M, Tamada Y. Click Decoration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin for Cell Adhesion Control. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184106
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeramoto, Hidetoshi, Minori Shirakawa, and Yasushi Tamada. 2020. "Click Decoration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin for Cell Adhesion Control" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184106
APA StyleTeramoto, H., Shirakawa, M., & Tamada, Y. (2020). Click Decoration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin for Cell Adhesion Control. Molecules, 25(18), 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184106