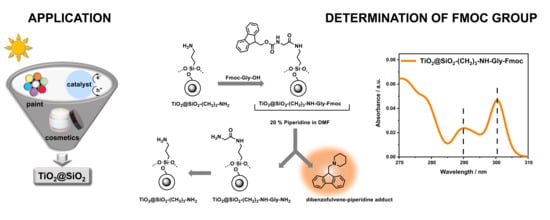
Efficient Method for the Concentration Determination of Fmoc Groups Incorporated in the Core-Shell Materials by Fmoc–Glycine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
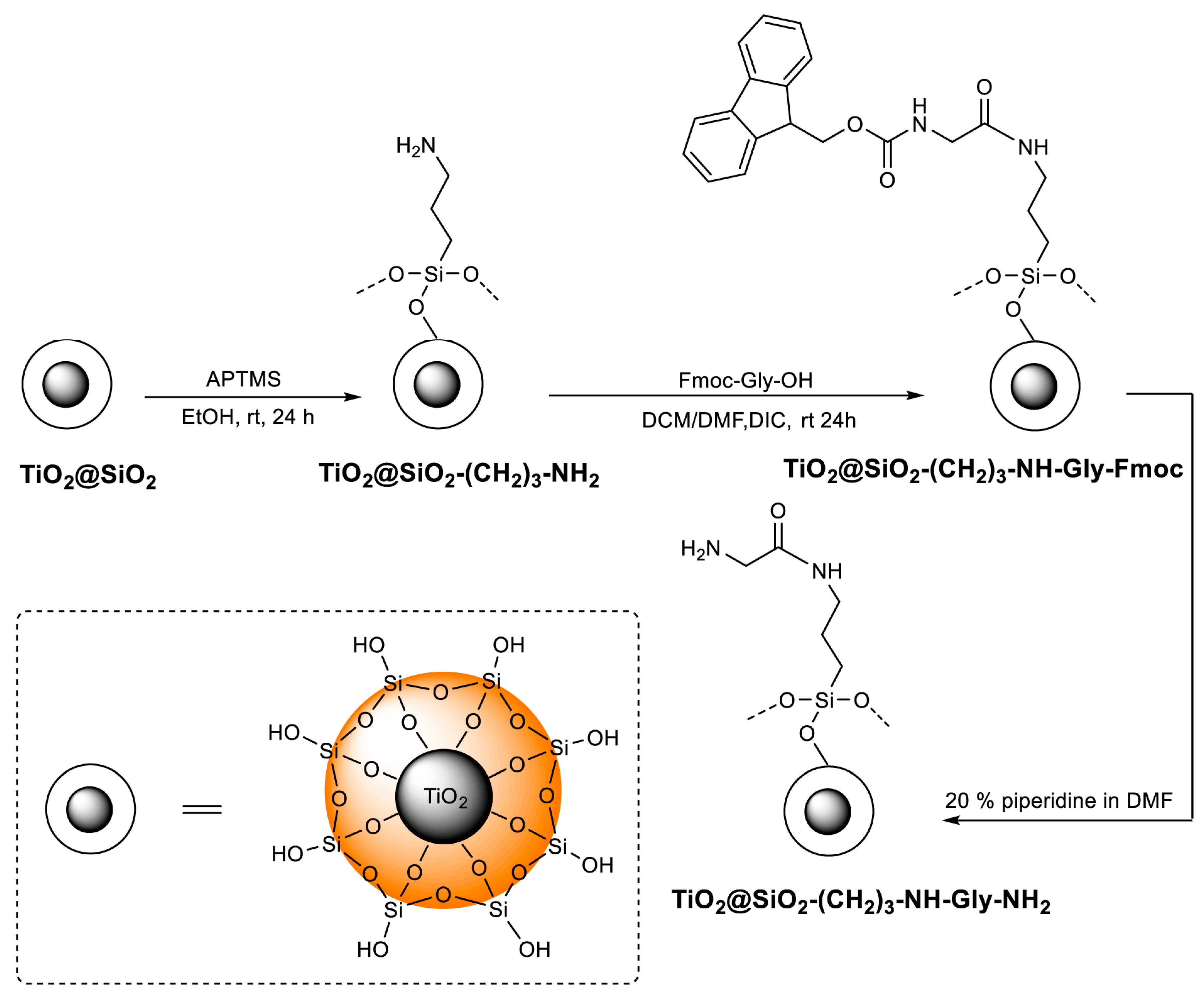
2.1. Synthesis
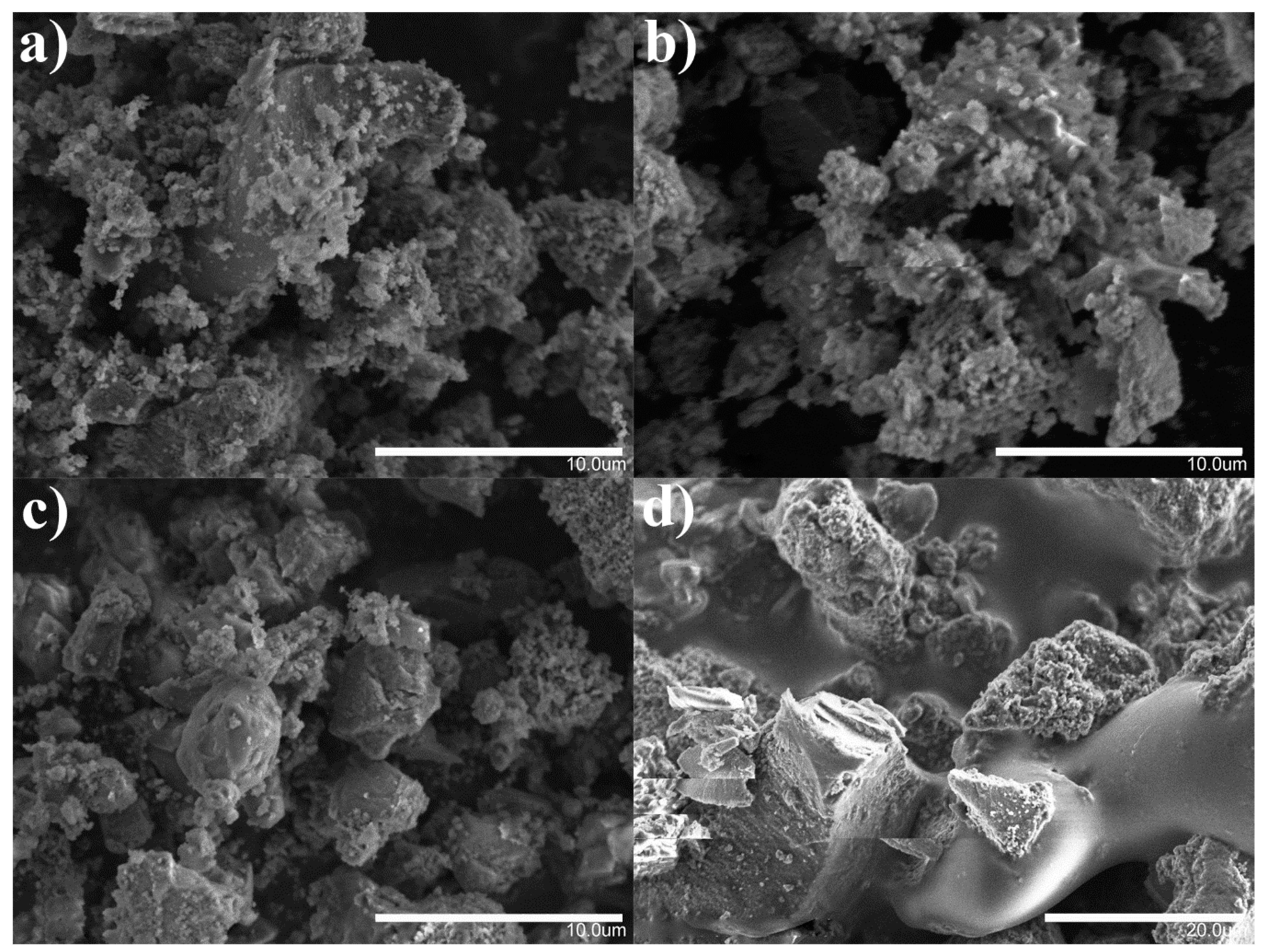
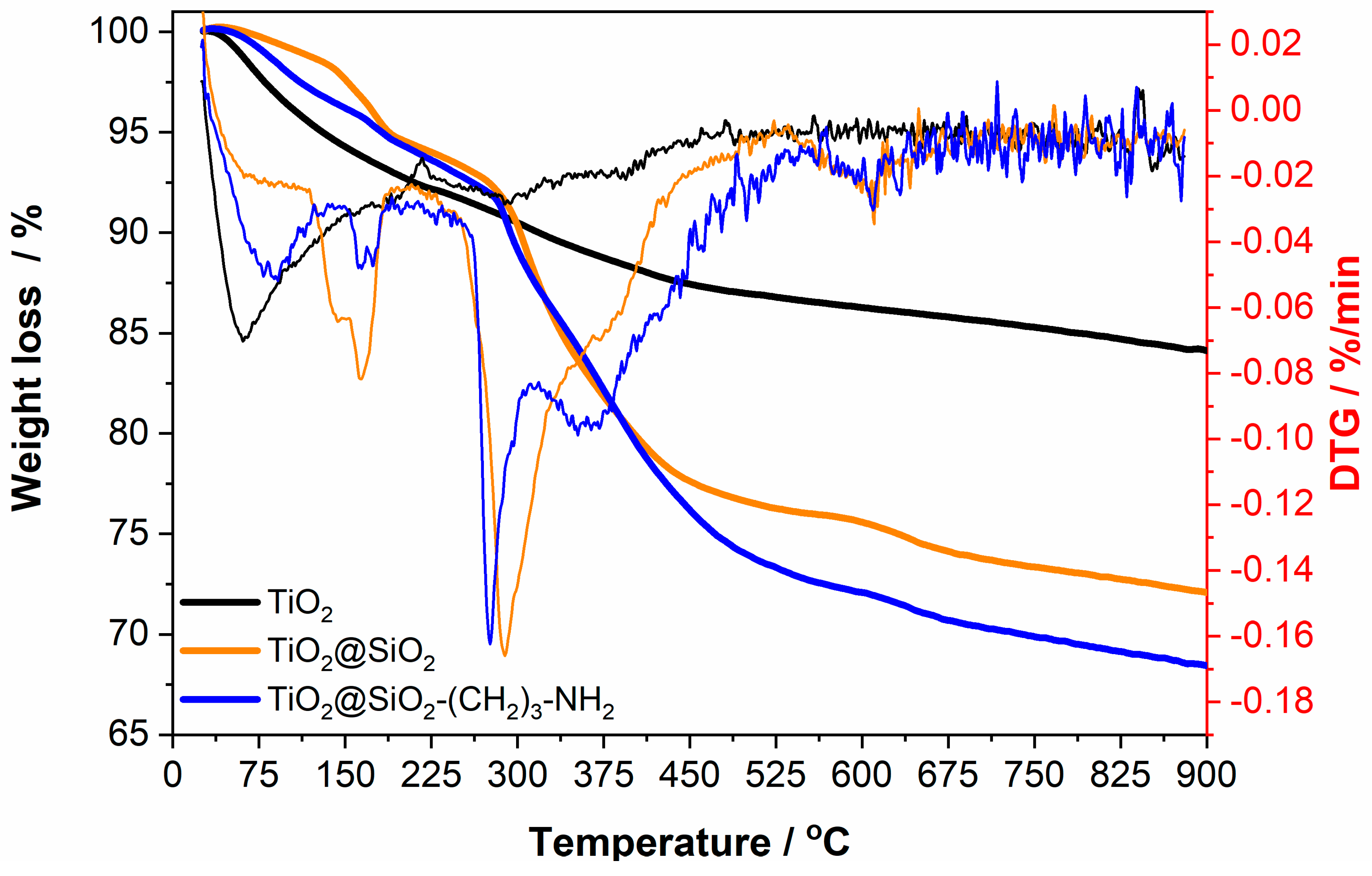
2.2. Analysis of Obtained Nanoparticles
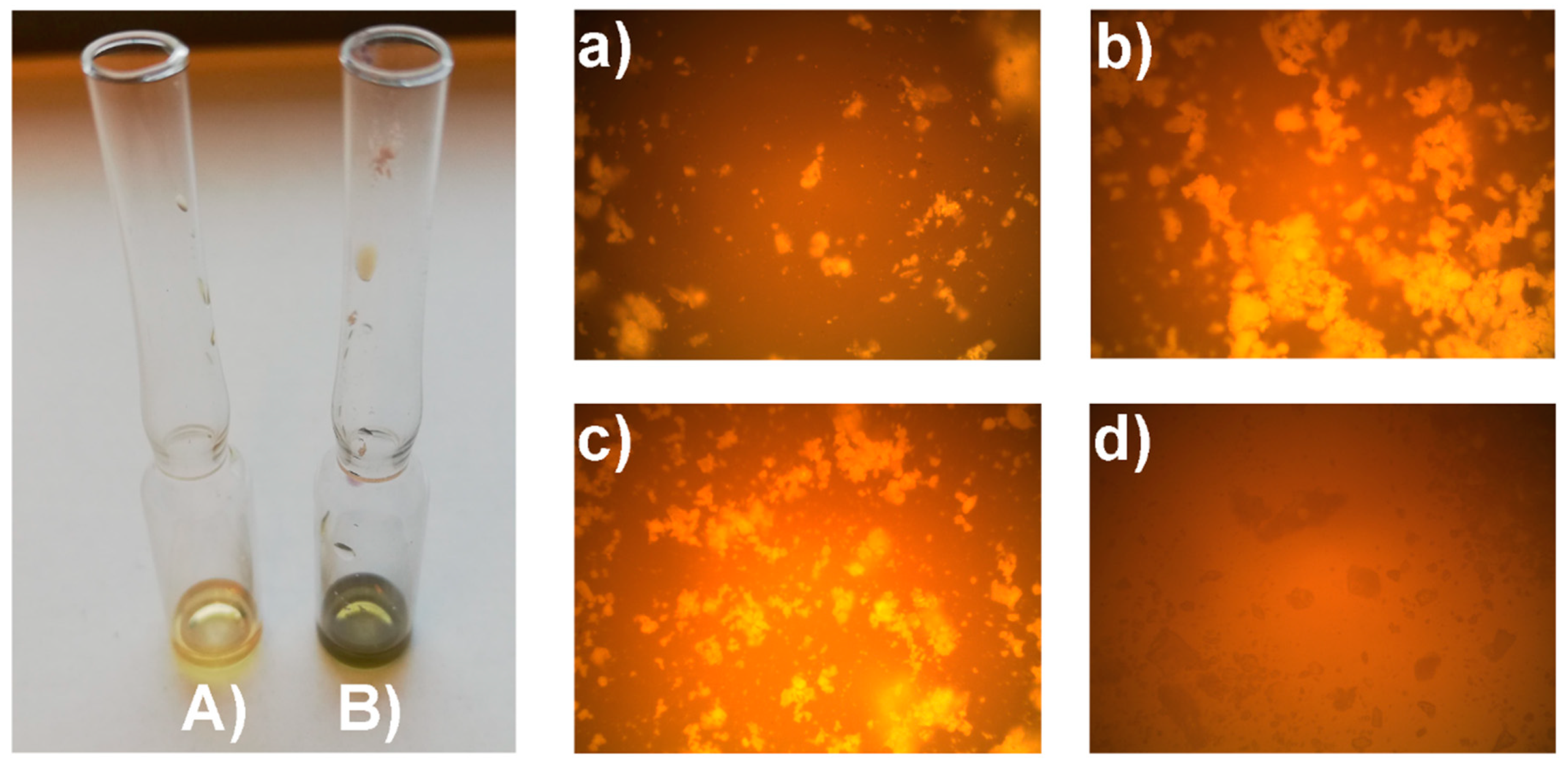
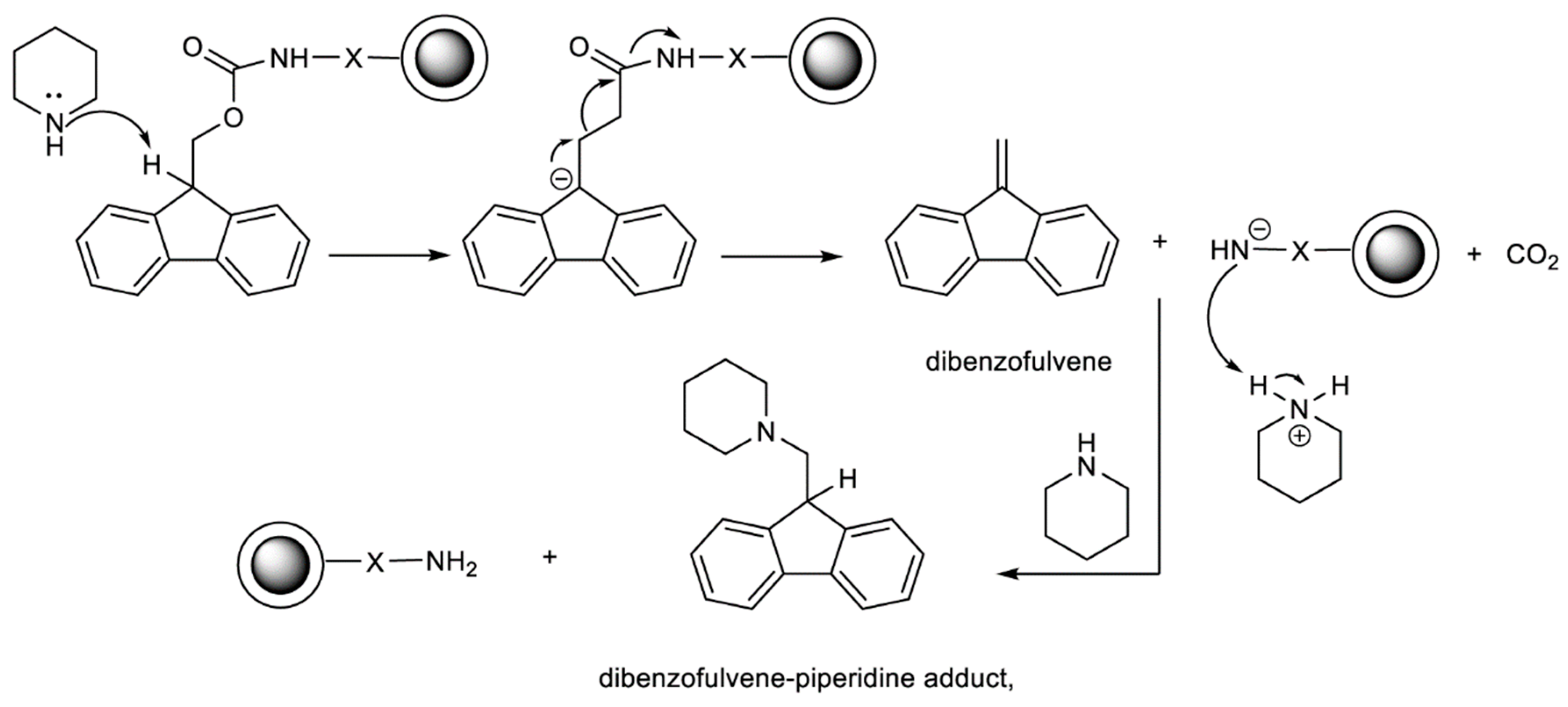
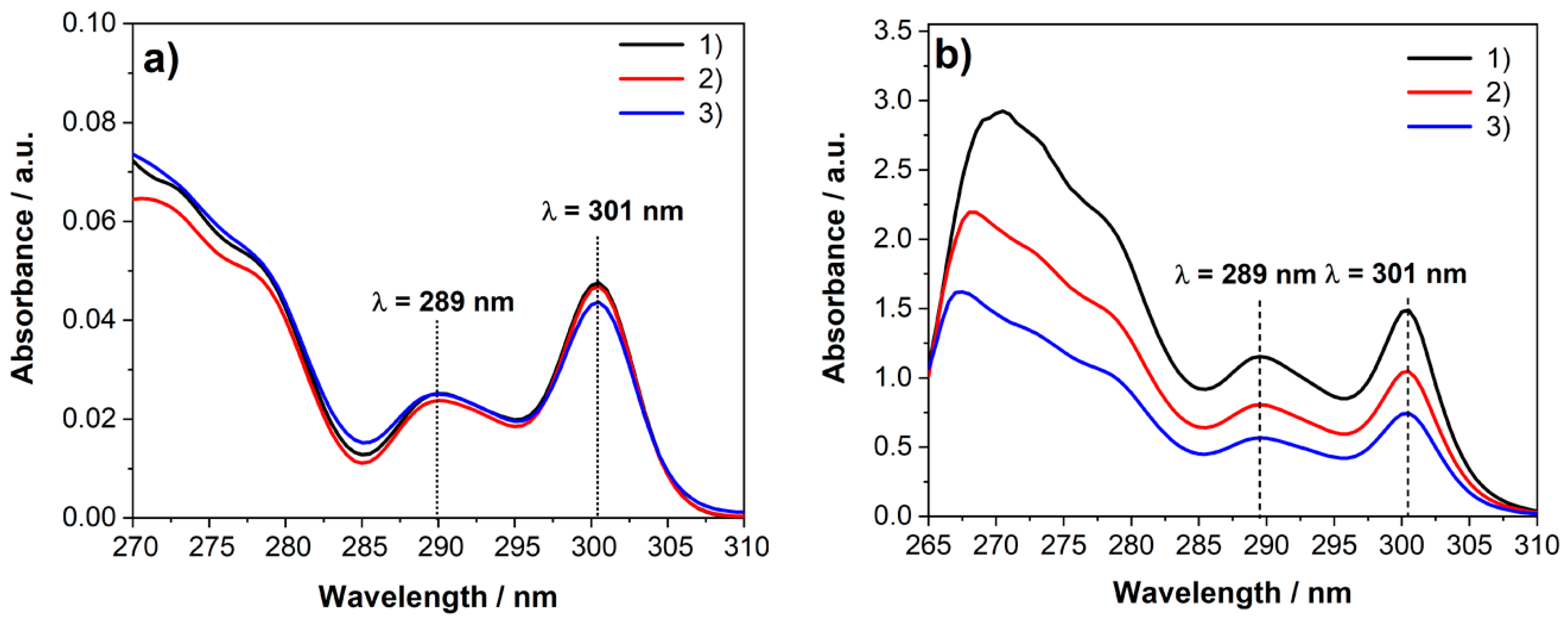
2.3. Determination of Fmoc Group Loading on TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH–Gly–Fmoc Core-Shell Nanostructure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of TiO2 Derivatives
3.2.1. Synthesis of TiO2
3.2.2. Synthesis of TiO2@SiO2
3.2.3. Synthesis of TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH2
3.2.4. Synthesis of TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH–Gly–Fmoc
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. The Procedure of Amino Group Loading on Nanoparticles
- Z—Fmoc group loading (mol/g)
- A—Absorbance value at the maximum absorption (nm)
- v—Volume of solvent (dm3)
- ε—Molar absorption coefficient (dm3×mol−1×cm−1 maximum absorption)
- m—Sample weight (mg)
- l—Length of the cell (1 cm)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewkowicz, A.; Synak, A.; Grobelna, B.; Bojarski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Karczewski, J.; Szczodrowski, K.; Behrendt, M. Thickness and structure change of titanium(IV) oxide thin films synthesized by the sol–gel spin coating method. Opt. Mater. 2014, 36, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Cui, B.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, G.; Cui, H. The Application of Nano-TiO2 Photo Semiconductors in Agriculture. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewkowicz, A.; Bojarski, P.; Synak, A.; Grobelna, B.; Akopova, I.; Gryczyński, I.; Kułak, L. Concentration-Dependent Fluorescence Properties of Rhodamine 6G in Titanium Dioxide and Silicon Dioxide Nanolayers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12304–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synak, A.; Bojarski, P.; Grobelna, B.; Kułak, L.; Szczepańska, E.; Mońka, M. Concentration—Dependent fluorescence properties of Nile Red in TiO2 based thin films. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Böttcher, H.; Rauch, K.; Dieckmann, U.; Nitsche, R.; Fritz, T. Optimized UV protecting coatings by combination of organic and inorganic UV absorbers. Thin Solid Films 2005, 1–2, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Z.-R.; Xu, Y.-J. Synthesis of One-Dimensional CdS@TiO2 Core–Shell Nanocomposites Photocatalyst for Selective Redox: The Dual Role of TiO2 Shell. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6378–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańska, E.; Bielicka-Giełdoń, A.; Niska, K.; Strankowska, J.; Żebrowska, J.; Inkielewicz-Stępniak, I.; Łubkowska, B.; Swebocki, T.; Skowron, P.; Grobelna, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in context of their cytotoxicity, antibacterial activities, skin penetration and application in skincare products. Supramol. Chem. 2020, 32, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synak, A.; Szczepańska, E.; Grobelna, B.; Gondek, J.; Mońka, M.; Gryczynski, I.; Bojarski, P. Photophysical properties and detection of Valrubicin on plasmonic platforms. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 163, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Oleszczuk, P.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exposure on Human Health—A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, H.; Pan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Modifying the surface of Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles with C18/NH2 mixed group to get an efficient sorbent for anionic organic pollutants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, T.K.H.; Trinh, M.-T.; Long, N.V.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Nguyen, T.L.T.; Thuoc, T.L.; Phan, B.T.; Mott, D.; Maenosono, S.; Tran-Van, H.; et al. Synthesis and surface functionalization of Fe3O4-SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles with 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane and 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole for bio-applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roto, R.; Yusran, Y.; Kuncaka, A. Magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiol group for chloroauric ion adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, J. Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, M.J.; Guzmán, L.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J. Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ruotolo, A.; Pong, P.W.T. Amine-Functionalized Fe2O3–SiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticles with Tunable Sizes. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpa, A.; Ryl, J.; Skowierzak, G.; Koterwa, A.; Schroeder, G.; Ossowski, T.; Niedziałkowski, P. Comparison of Cadmium Cd2+ and Lead Pb2+ Binding by Fe2O3@SiO2 -EDTA Nanoparticles—Binding Stability and Kinetic Studies. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S. Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of plasmon-enhanced core-shell upconversion luminescent photocatalytic Ag@SiO2@YF3:Ho3+@TiO2 nanocomposites. Opt. Mater. 2019, 94, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, C.; Ma, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhou, S. Gold Nanoparticles on Mesoporous SiO2-Coated Magnetic Fe3O4 Spheres: A Magnetically Separatable Catalyst with Good Thermal Stability. Molecules 2013, 18, 14258–14267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Sajedin, S.M.; Kelly, S.M.; Lee, A.F.; Kornherr, A. UV-stable paper coated with APTES-modified P25 TiO2 nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpa, A.; Ryl, J.; Schroeder, G.; Koterwa, A.; Sein Anand, J.; Ossowski, T.; Niedziałkowski, P. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cu2+ ions captured by Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanostructures of various outer amino chain length. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, H.H.; Al-Harthi, S.H.; Sellai, A.; Dutta, J. Self-organization of gold nanoparticles on silanated surfaces. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masitas, R.A.; Khachian, I.V.; Bill, B.L.; Zamborini, F.P. Effect of Surface Charge and Electrode Material on the Size-Dependent Oxidation of Surface-Attached Metal Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13075–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Hou, S.; Wang, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Shao, B.; Qiao, M. Two methods for glass surface modification and their application in protein immobilization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 60, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kwon, J.-Y. Enzyme immobilization on metal oxide semiconductors exploiting amine functionalized layer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19656–19661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Lam, E.; Hrapovic, S.; Male, K.B.; Luong, J.H.T. Immobilization of Antibodies and Enzymes on 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane-Functionalized Bioanalytical Platforms for Biosensors and Diagnostics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11083–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunda, N.S.K.; Singh, M.; Norman, L.; Kaur, K.; Mitra, S.K. Optimization and characterization of biomolecule immobilization on silicon substrates using (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) and glutaraldehyde linker. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Hwang, J.; Choi, Y.; Seo, Y.; Jeon, H.; Kang, H.C.; Woo, H.-M.; Kang, B.-J.; et al. DNA aptamer immobilized hydroxyapatite for enhancing angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 99, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cañas, M.C.; Corredor, L.M.; Quintero, H.I.; Manrique, E.; Romero Bohórquez, A.R. Morphological and Structural Properties of Amino-Functionalized Fumed Nanosilica and Its Comparison with Nanoparticles Obtained by Modified Stöber Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarter, J.A.; Youngblood, J.P. Optimization of Silica Silanization by 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11142–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, M.; Camilo, R.L.; Sampaio, L.C.; Macêdo, M.A.; Nakamura, M.; Toma, H.E. Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 279, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asenath Smith, E.; Chen, W. How To Prevent the Loss of Surface Functionality Derived from Aminosilanes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12405–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.-S.; Moon, D.-S.; Lee, J.-K. Quantitative Analysis and Efficient Surface Modification of Silica Nanoparticles. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jnm/2012/593471/ (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Kralj, S.; Drofenik, M.; Makovec, D. Controlled surface functionalization of silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles with terminal amino and carboxyl groups. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2829–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunc, F.; Balhara, V.; Brinkmann, A.; Sun, Y.; Leek, D.M.; Johnston, L.J. Quantification and Stability Determination of Surface Amine Groups on Silica Nanoparticles Using Solution NMR. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13322–13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čampelj, S.; Makovec, D.; Drofenik, M. Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with 3-aminopropyl silane. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, R.; Avdin, V.; Krivtsov, I.; Gorshkov, A.; Urzhumova, A.; Osinskaya, A.; Yuzhalkin, D. Modification with Amino Groups of Composite SiO2–TiO2 and Pure TiO2 Spheres Prepared via the Peroxo Route. Chem 2018, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torelli, M.D.; Putans, R.A.; Tan, Y.; Lohse, S.E.; Murphy, C.J.; Hamers, R.J. Quantitative Determination of Ligand Densities on Nanomaterials by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, A.; Borcherding, H.; Jaeger, C.; Hatami, S.; Würth, C.; Hoffmann, A.; Hoffmann, K.; Thiele, T.; Schedler, U.; Resch-Genger, U. Scope and Limitations of Surface Functional Group Quantification Methods: Exploratory Study with Poly(acrylic acid)-Grafted Micro- and Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8268–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D. Extension of the Stöber Method to Construct Mesoporous SiO2 and TiO2 Shells for Uniform Multifunctional Core–Shell Structures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuenyongsuwan, J.; Nithiyakorn, N.; Sabkird, P.; O’Rear, E.A.; Pongprayoon, T. Surfactant effect on phase-controlled synthesis and photocatalyst property of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, K.; Gailhanou, H.; Raison, L.; Panizza, P.; Ushiki, H.; Sellier, E.; Delville, J.P.; Delville, M.H. Smart Control of Monodisperse Stöber Silica Particles: Effect of Reactant Addition Rate on Growth Process. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, A.; Yue, B.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, H. Core–shell Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles of different silica shell thicknesses: Preparation and their effects on photoluminescence of lanthanide complexes. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 71, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Salleh, N.F.M.; Karim, A.H.; Mukti, R.R.; Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A. Role of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane in the preparation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for ibuprofen delivery: Effect on physicochemical properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 180, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorkild, C. A qualitative test for monitoring coupling completeness in solid phase peptide synthesis using chloranil. Acta Chem. Scand. B 1979, 33, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Qi, W.; He, Z.; Yang, H.; Qiao, B. Synthesis of heptapeptides and analysis of sequence by tandem ion trap mass spectrometry. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2006, 4, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupryniak, J.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Karbarz, M.; Ossowski, T.; Stojek, Z. Lysine and Arginine Oligopeptides Tagged with Anthraquinone: Electrochemical Properties. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ferreira-Neto, E.P.; Pasa, A.A.; Alcântara, C.C.J.; Acuña, J.J.S.; Bilmes, S.A.; Martínez Ricci, M.L.; Landers, R.; Fermino, T.Z.; Rodrigues-Filho, U.P. Enhanced photocatalytic properties of core@shell SiO2@TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, M.; Su, K. Higher UV-shielding ability and lower photocatalytic activity of TiO2@SiO2/APTES and its excellent performance in enhancing the photostability of poly(p-phenylene sulfide). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21758–21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, K.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. TiO2–SiO2 Janus particles with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92754–92764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, A.; Reuquen, P.; Garín, C.; Segura, R.; Vargas, P.; Zapata, P.; Orihuela, P.A. FTIR and Raman Characterization of TiO2 Nanoparticles Coated with Polyethylene Glycol as Carrier for 2-Methoxyestradiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Bai, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yen, S.; Tseng, Y. Synthesis of Neutral/Hydrosol and Its Application as Antireflective Self-Cleaning Thin Film. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Prakoso, N.I.; Sahroni, I.; Musawwa, M.M.; Sim, Y.-L.; Kooli, F.; Muraza, O. Physicochemical characteristics and photocatalytic performance of TiO2/SiO2 catalyst synthesized using biogenic silica from bamboo leaves. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wu, X. 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilanes Modified Porous Silicon as a Voltammetric Sensor for Determination of Silver Ion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-540-93809-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Milanova, M.; Warmoeskerken, M.; Dutschk, V. Surface modification of TiO2 nanoparticles with silane coupling agents. Colloid Surf. A 2012, 413, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, J.; Gonzalez, C.; de Andres, P.L.; Roman, E. Characterization of thin silicon overlayers on rutileTiO2(110)−(1×1). Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 165420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondračka, P.; Nečas, D.; Carette, M.; Elisabeth, S.; Holec, D.; Granier, A.; Goullet, A.; Zajíčková, L.; Richard-Plouet, M. Unravelling local environments in mixed TiO2–SiO2 thin films by XPS and ab initio calculations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, T.L.; Seal, S. Nature of the use of adventitious carbon as a binding energy standard. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1995, 13, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önneby, C.; Pantano, C.G. Silicon oxycarbide formation on SiC surfaces and at the SiC/SiO2 interface. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1997, 15, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Chahal, P.; Hogan, T. Selective Fabrication of SiC/Si Diodes by Excimer Laser Under Ambient Conditions. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedziałkowski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Zięba, P.; Wysocka, J.; Ryl, J.; Sobaszek, M.; Ossowski, T. Melamine-modified Boron-doped Diamond towards Enhanced Detection of Adenine, Guanine and Caffeine. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanowicz, R.; Sawczak, M.; Niedzialkowski, P.; Zieba, P.; Finke, B.; Ryl, J.; Karczewski, J.; Ossowski, T. Novel Functionalization of Boron-Doped Diamond by Microwave Pulsed-Plasma Polymerized Allylamine Film. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 8014–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calborean, A.; Martin, F.; Marconi, D.; Turcu, R.; Kacso, I.E.; Buimaga-Iarinca, L.; Graur, F.; Turcu, I. Adsorption mechanisms of L-Glutathione on Au and controlled nano-patterning through Dip Pen Nanolithography. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 57, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocka, J.; Cieślik, M.; Krakowiak, S.; Ryl, J. Carboxylic acids as efficient corrosion inhibitors of aluminium alloys in alkaline media. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 289, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinieris, N.; Leondiadis, L.; Ferderigos, N. Nα-Fmoc Removal from Resin-Bound Amino Acids by 5% Piperidine Solution. J. Comb. Chem. 2005, 7, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, R.; White, P.; Offer, J. Advances in Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis. J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, O.F.; Gomez, J.; Cárdenas, C.; Albericio, F.; Marshall, S.H.; Guzmán, F. Deprotection Reagents in Fmoc Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: Moving Away from Piperidine? Molecules 2016, 21, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergel Galeano, C.F.; Rivera Monroy, Z.J.; Rosas Pérez, J.E.; García Castañeda, J.E. Efficient Synthesis of Peptides with 4-Methylpiperidine as Fmoc Removal Reagent by Solid Phase Synthesis. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Meienhofer, J.; Waki, M.; Heimre, E.P.; Lambros, T.J.; Makofske, R.C.; Chang, C.-D. Solid Phase Synthesis Without Repetitive Acidolysis. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1979, 13, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, D.; Schreiber, J.V.; Abele, S.; Daura, X.; van Gunsteren, W.F. Structure and Conformation of β-Oligopeptide Derivatives with Simple Proteinogenic Side Chains: Circular Dichroism and Molecular Dynamics Investigations. Helv. Chim. Acta 2000, 83, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarra, R.; Montesarchio, D.; Coppola, C.; Bifulco, G.; Di Micco, S.; Izzo, I.; De Riccardis, F. Design, Synthesis, and Hybridisation of Water-Soluble, Peptoid Nucleic Acid Oligomers Tagged with Thymine. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2009, 6113–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo, D.; El-Faham, A.; Royo, M.; Albericio, F. Optimized Stepwise Synthesis of the API Liraglutide Using BAL Resin and Pseudoprolines. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8674–8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, T.; Schips, C. An efficient Mitsunobu protocol for the one-pot synthesis of S -glycosyl amino-acid building blocks and their use in combinatorial spot synthesis of glycopeptide libraries. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friligou, I.; Papadimitriou, E.; Gatos, D.; Matsoukas, J.; Tselios, T. Microwave-assisted solid-phase peptide synthesis of the 60–110 domain of human pleiotrophin on 2-chlorotrityl resin. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissler, S.; Kley, M.; Bächle, D.; Loidl, G.; Meier, T.; Samson, D. Substitution determination of Fmoc-substituted resins at different wavelengths: Substitution Determination of Fmoc-substituted Resins. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |


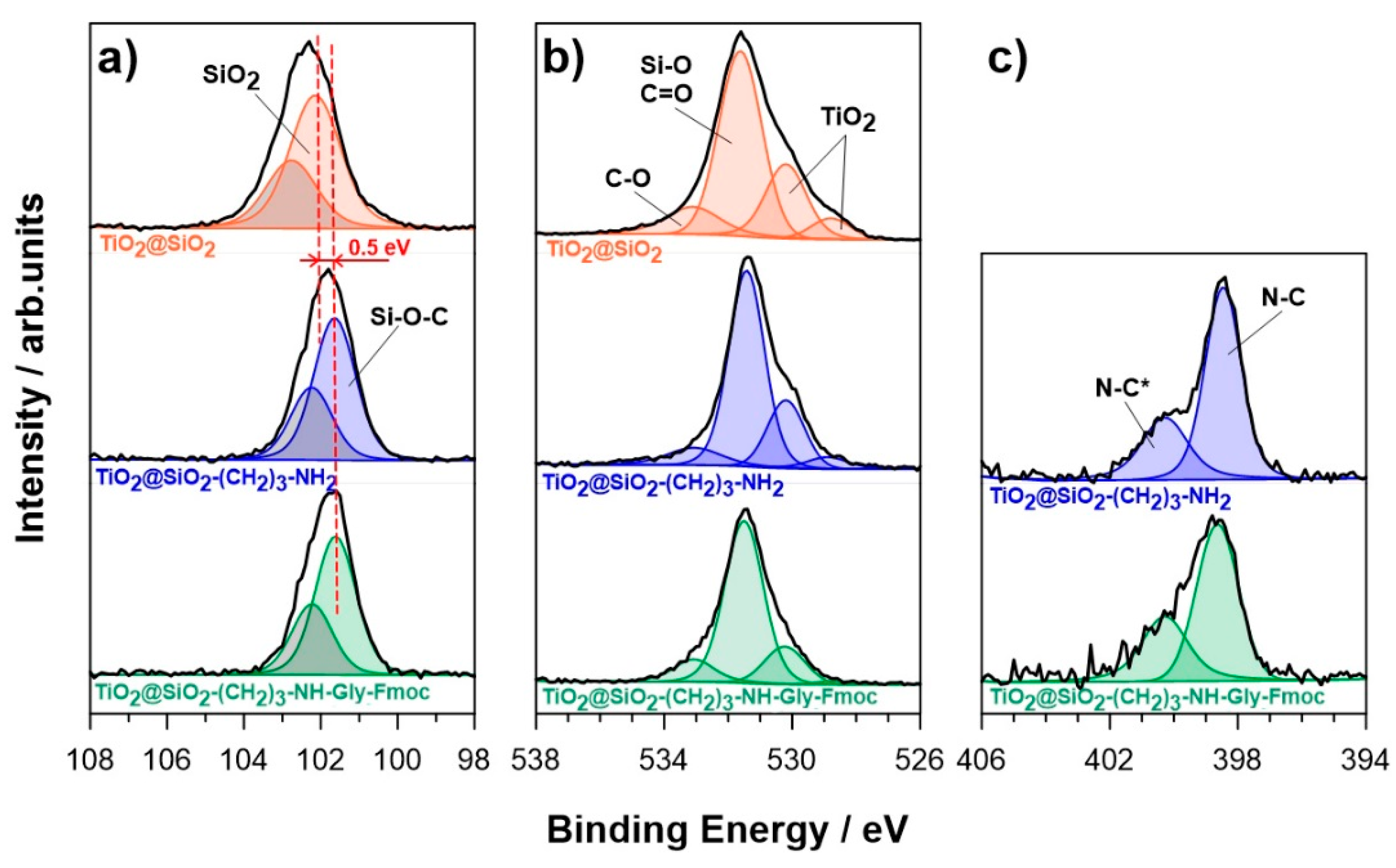
| BE/eV | TiO2@SiO2 | TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH2 | TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH–Gly–Fmoc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si2p | SiO2 | 102.1 | 27 | – | – |
| Si–O–C | 101.6 | – | 25.7 | 25.1 | |
| O1s | C–O, H2O | 533.1 | 7.2 | 5.4 | 6.4 |
| SiO2, C=O | 531.6 | 41.8 | 35.2 | 38.8 | |
| SiO2–TiO2 | 530.2 | 16.7 | 12.2 | 9.2 | |
| TiO2 | 528.8 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 1.1 | |
| N1s | N–C | 398.5 | – | 12.1 | 12.7 |
| N=C | 400.3 | – | 5.8 | 6.7 | |
| Ti2p | TiO2 | 459.2 | 2.8 | 0.9 | – |
| Sample | TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH–Gly–Fmoc | Fmoc–Gly–OH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m (mg) | A@289 nm | A@301 nm | m (mg) | A@289 nm | A@301 nm | |
| (1) | 2.06 | 0.025 | 0.048 | 0.25 | 1.15 | 1.49 |
| (2) | 2.06 | 0.024 | 0.047 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 1.03 |
| (3) | 2.08 | 0.025 | 0.044 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.74 |
| TiO2@SiO2–(CH2)3–NH–Gly–Fmoc | Fmoc–Gly–OH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε (dm3 × mol−1 × cm−1) | Z@289 nm (µmol/g) | Z@ 301 nm (µmol/g) | Z@289 nm (mmol/g) | Z@ 301 nm (mmol/g) |
| 5800 | 6.3; 6.0; 6.2 | – | 2.38; 2.46; 2.68 | – |
| 7800 | – | 9.0;8.8;8.1 | – | 2.29; 2.33; 2.58 |
| 6089 | 6.0; 5.7; 5.9 | – | 2.27; 2.35; 2.55 | – |
| 8021 | – | 8.7; 8.5; 7.9 | – | 2.23; 2.27; 2.52 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczepańska, E.; Grobelna, B.; Ryl, J.; Kulpa, A.; Ossowski, T.; Niedziałkowski, P. Efficient Method for the Concentration Determination of Fmoc Groups Incorporated in the Core-Shell Materials by Fmoc–Glycine. Molecules 2020, 25, 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173983
Szczepańska E, Grobelna B, Ryl J, Kulpa A, Ossowski T, Niedziałkowski P. Efficient Method for the Concentration Determination of Fmoc Groups Incorporated in the Core-Shell Materials by Fmoc–Glycine. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173983
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczepańska, Elżbieta, Beata Grobelna, Jacek Ryl, Amanda Kulpa, Tadeusz Ossowski, and Paweł Niedziałkowski. 2020. "Efficient Method for the Concentration Determination of Fmoc Groups Incorporated in the Core-Shell Materials by Fmoc–Glycine" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173983
APA StyleSzczepańska, E., Grobelna, B., Ryl, J., Kulpa, A., Ossowski, T., & Niedziałkowski, P. (2020). Efficient Method for the Concentration Determination of Fmoc Groups Incorporated in the Core-Shell Materials by Fmoc–Glycine. Molecules, 25(17), 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173983