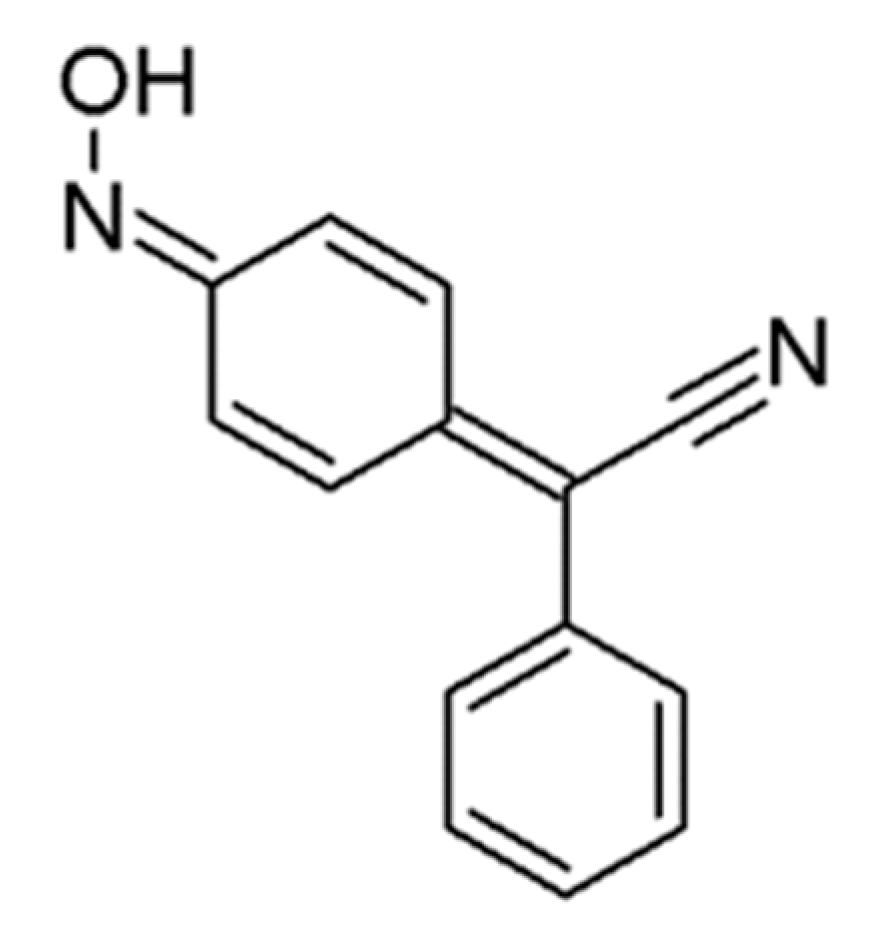
Antifungal Agent 4-AN Changes the Genome-Wide Expression Profile, Downregulates Virulence-Associated Genes and Induces Necrosis in Candida albicans Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
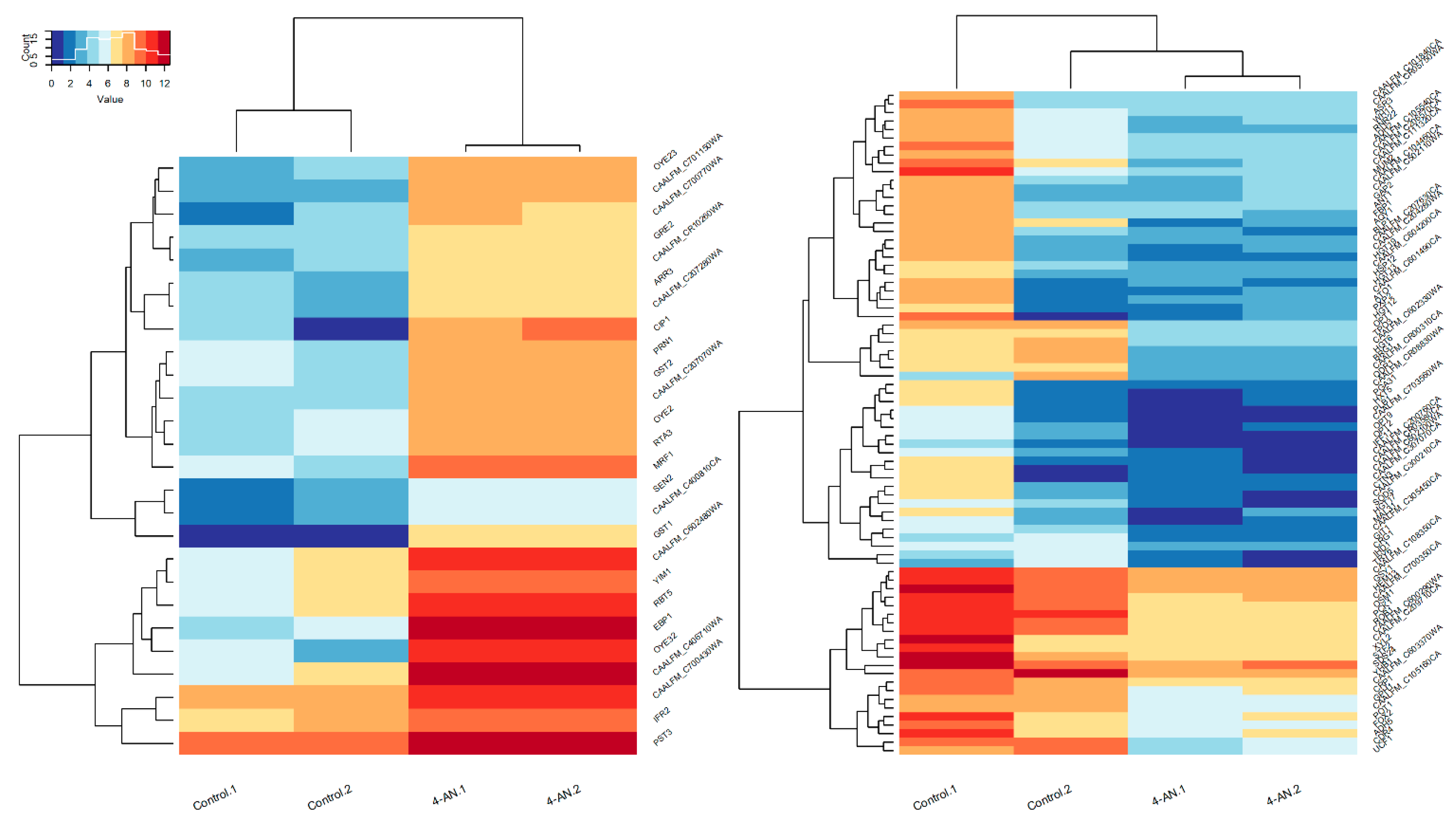
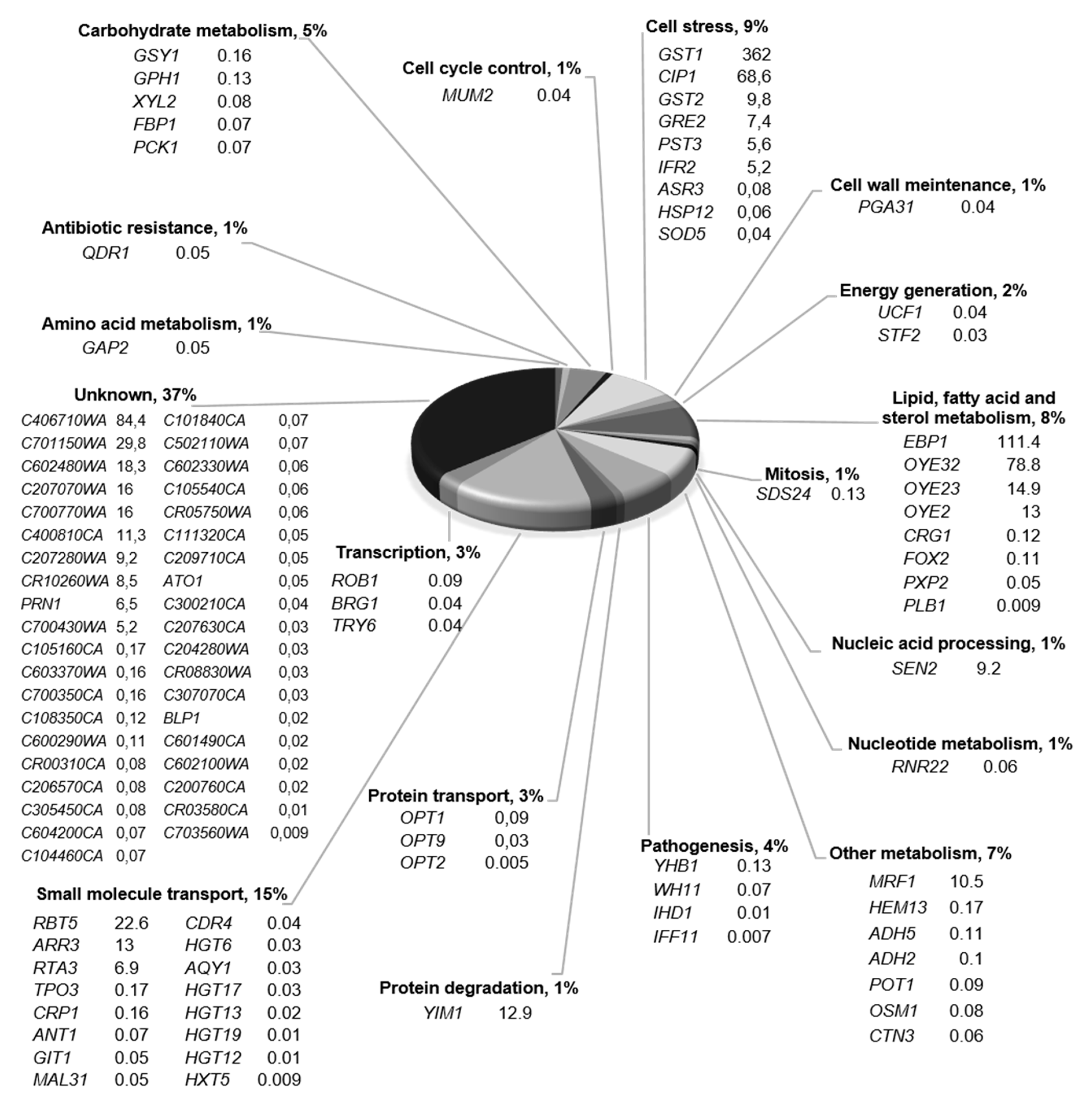
2.1. Gene-Expression Response to 4-AN Exposure
2.2. Response of Biofilm Formation—And Hyphal Growth-Associated Genes to 4-AN
2.3. Combination of 4-AN with Antifungal Drugs
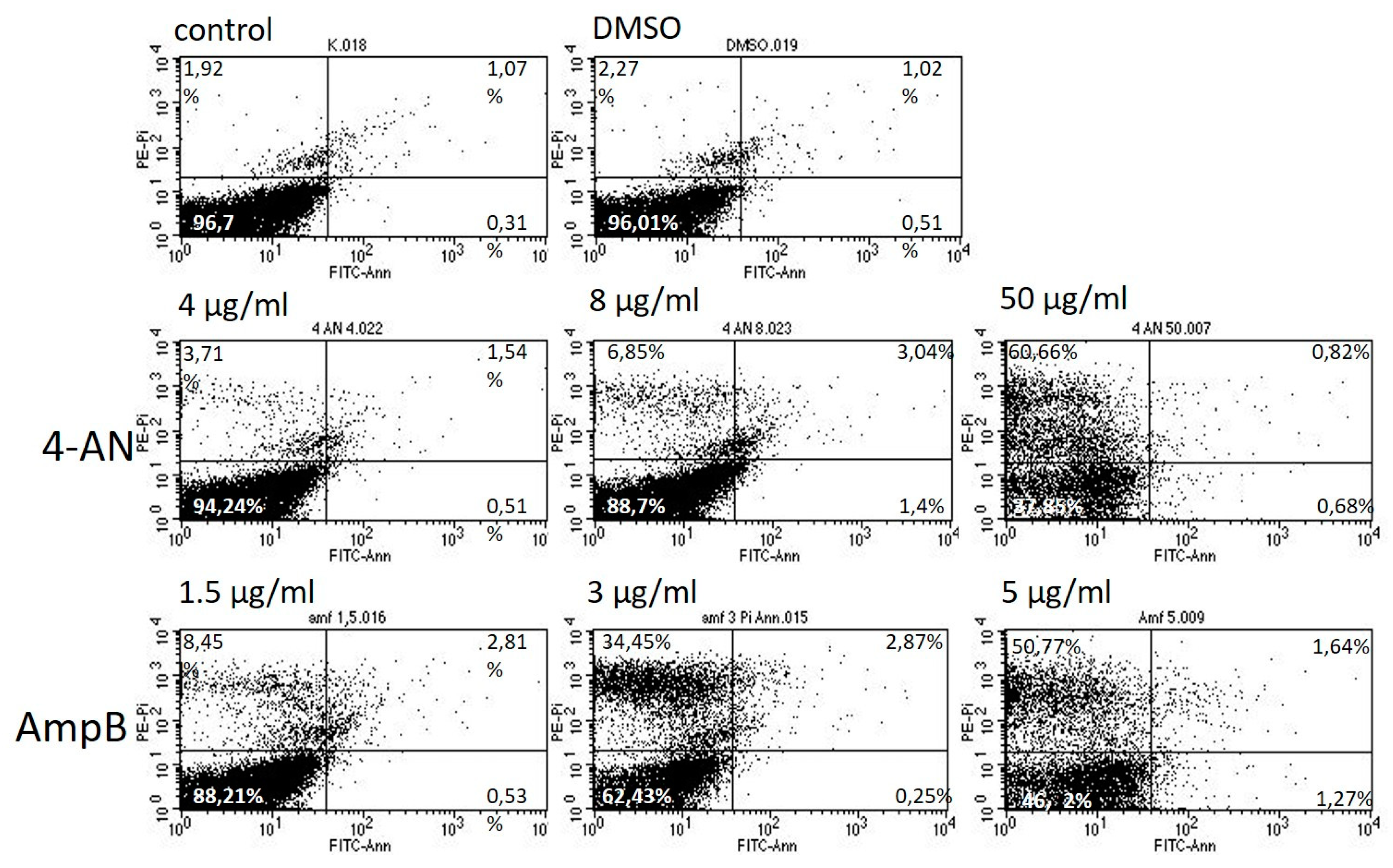
2.4. Effect of 4-AN on Cell Death in C. albicans Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. C. albicans Cultures and RNA Isolation
4.2. RNA Sequencing
4.3. Sequencing Data Analysis
4.4. Real-Time PCR
4.5. Determination of the Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index
4.6. Flow Cytometry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarty, T.P.; Pappas, P.G. Invasive Candidiasis. Infect. Dis Clin. North. Am. 2016, 30, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.A.; Butler, G. The Candida pathogenic species complex. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a019778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.; Shah, A.H.; Rawal, M.K. Antifungals: Mechanism of Action and Drug Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 892, 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira Santos, G.C.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Lopes, A.J.O.; de Sousa Cartágenes, M.D.S.; Filho, A.K.D.B.; do Nascimento, F.R.F.; Ramos, R.M.; Pires, E.R.R.B.; de Andrade, M.S.; Rocha, F.M.G.; et al. Infections and Therapeutic Strategies: Mechanisms of Action for Traditional and Alternative Agents. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritrairat, N.; Nukul, N.; Inthasame, P.; Sansuk, A.; Prasirt, J.; Leewatthanakorn, T.; Piamsawad, U.; Dejrudee, A.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Pangsomboon, K.; et al. Antifungal activity of lawsone methyl ether in comparison with chlorhexidine. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczko, M.; Kubiński, K.; Martyna, A.; Muzyczka, A.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A.; Czernik, S.; Tokarska-Rodak, M.; Chwedczuk, M.; Demchuk, O.M.; Golczyk, H.; et al. 1,4-Naphthoquinone derivatives potently suppress C. albicans growth, inhibit formation of hyphae and show no toxicity toward zebrafish embryos. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 598–609. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Thanusu, J.; Kanagarajan, V. A facile solid-state synthesis and in vitro antimicrobial activities of some 2,6-diarylpiperidin/tetrahydrothiopyran and tetrahydropyran-4-one oximes. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dufrasne, F.; Gelbcke, M.; Nève, J.; Kiss, R.; Kraus, J.-L. Quinone Methides and their Prodrugs: A Subtle Equilibrium Between Cancer Promotion, Prevention, and Cure. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 3995–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masłyk, M.; Janeczko, M.; Demchuk, O.M.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A.; Golczyk, H.; Sierosławska, A.; Rymuszka, A.; Martyna, A.; Kubiński, K. A representative of arylcyanomethylenequinone oximes effectively inhibits growth and formation of hyphae in Candida albicans and Influences the Activity of Protein Kinases in vitro. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masłyk, M.; Janeczko, M.; Martyna, A.; Czernik, S.; Tokarska-Rodak, M.; Chwedczuk, M.; Foll-Josselin, B.; Ruchaud, S.; Bach, S.; Demchuk, O.M.; et al. The Anti-C. albicans agent 4-AN inhibits multiple protein kinases. Molecules 2019, 24, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Green, C.B.; Cheng, G.; Chandra, J.; Mukherjee, P.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Hoyer, L.L. RT-PCR detection of C. albicans ALS gene expression in the reconstituted human epithelium (RHE) model of oral candidiasis and in model biofilms. Microbiology 2004, 150, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, S.; Birse, C.; Zhou, S.; Matson, R.; Liu, H. DNA array studies demonstrate convergent regulation of virulence factors by Cph1, Cph2, and Efg1 in C. albicans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48988–48996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moyes, D.L.; Wilson, D.; Richardson, J.P.; Mogavero, S.; Tang, S.X.; Wernecke, J.; Höfs, S.; Gratacap, R.L.; Robbins, J.; Runglall, M.; et al. Candidalysin is a fungal peptide toxin critical for mucosal infection. Nature 2016, 532, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, D.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Sun, H.; Ye, L. The Activity of Fungichromin against the Formation of C. albicans Biofilm. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hube, B.; Sanglard, D.; Odds, F.C.; Hess, D.; Monod, M.; Schäfer, W.; Brown, A.J.; Gow, N.A. Disruption of each of the secreted aspartyl proteinase genes SAP1, SAP2, and SAP3 of C. albicans attenuates virulence. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3529–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eliopoulos, G.; Moellering, R. Antimicrobial combinations. In Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine, 3rd ed.; Lorian, V., Ed.; The Williams & Wilkins Co.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1991; pp. 432–492. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.D.; MacDougall, C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Perfect, J.R.; Rex, J.H. Combination antifungal therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 693–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Ren, B.; Tong, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, L. Synergistic combinations of antifungals and anti-virulence agents to fight against C. albicans. Virulence 2015, 6, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.T.; Lee, R.E.; Barker, K.S.; Wei, L.; Homayouni, R.; Rogers, P.D. Genome-wide expression profiling of the response to azole, polyene, echinocandin, and pyrimidine antifungal agents in C. albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobor, M.S.; Greenblatt, J. Regulation of transcription elongation by phosphorylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1577, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.H.; Montminy, M. Can you hear me now? Regulating transcriptional activators by phosphorylation. Sci. STKE 2005, 301, e44. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, P. Organization and regulation of gene transcription. Nature 2019, 573, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, E.; Allende, J.E. Phosphorylation of yeast TBP by protein kinase CK2 reduces its specific binding to DNA. FEBS Lett. 1999, 443, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Vona, C.; Bezdan, D.; Islam, A.B.; Salichs, E.; López-Bigas, N.; Ossowski, S.; de la Luna, S. Chromatin-wide profiling of DYRK1A reveals a role as a gene-specific RNA polymerase II CTD kinase. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chahrour, O.; Cairns, D.; Omran, Z. Small molecule kinase inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutics. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malsy, M.; Bitzinger, D.; Graf, B.; Bundscherer, A. Staurosporine induces apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells PaTu 8988t and Panc-1 via the intrinsic signaling pathway. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2019, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Gillespie, S.K.; Hersey, P. Staurosporine induces apoptosis of melanoma by both caspase-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, B.; Cheng, S.; Clancy, C.J.; Nguyen, M.H. Caspofungin kills C. albicans by causing both cellular apoptosis and necrosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, A.J.; Sudbery, I.; Ramsdale, M. Apoptosis induced by environmental stresses and amphotericin B in C. albicans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14327–14332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4-AN are available from the authors. |

| 4-AN | |
|---|---|
| Caspofungin | 1.5 |
| Amphotericin B | 0.45 |
| Ketoconazole | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martyna, A.; Masłyk, M.; Janeczko, M.; Kochanowicz, E.; Gielniewski, B.; Świercz, A.; Demchuk, O.M.; Kubiński, K. Antifungal Agent 4-AN Changes the Genome-Wide Expression Profile, Downregulates Virulence-Associated Genes and Induces Necrosis in Candida albicans Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122928
Martyna A, Masłyk M, Janeczko M, Kochanowicz E, Gielniewski B, Świercz A, Demchuk OM, Kubiński K. Antifungal Agent 4-AN Changes the Genome-Wide Expression Profile, Downregulates Virulence-Associated Genes and Induces Necrosis in Candida albicans Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(12):2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122928
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartyna, Aleksandra, Maciej Masłyk, Monika Janeczko, Elżbieta Kochanowicz, Bartłomiej Gielniewski, Aleksandra Świercz, Oleg M. Demchuk, and Konrad Kubiński. 2020. "Antifungal Agent 4-AN Changes the Genome-Wide Expression Profile, Downregulates Virulence-Associated Genes and Induces Necrosis in Candida albicans Cells" Molecules 25, no. 12: 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122928
APA StyleMartyna, A., Masłyk, M., Janeczko, M., Kochanowicz, E., Gielniewski, B., Świercz, A., Demchuk, O. M., & Kubiński, K. (2020). Antifungal Agent 4-AN Changes the Genome-Wide Expression Profile, Downregulates Virulence-Associated Genes and Induces Necrosis in Candida albicans Cells. Molecules, 25(12), 2928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122928






