CuFe2O4/Polyaniline (PANI) Nanocomposite for the Hazard Mercuric Ion Removal: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Properties Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Adsorbent Characterization
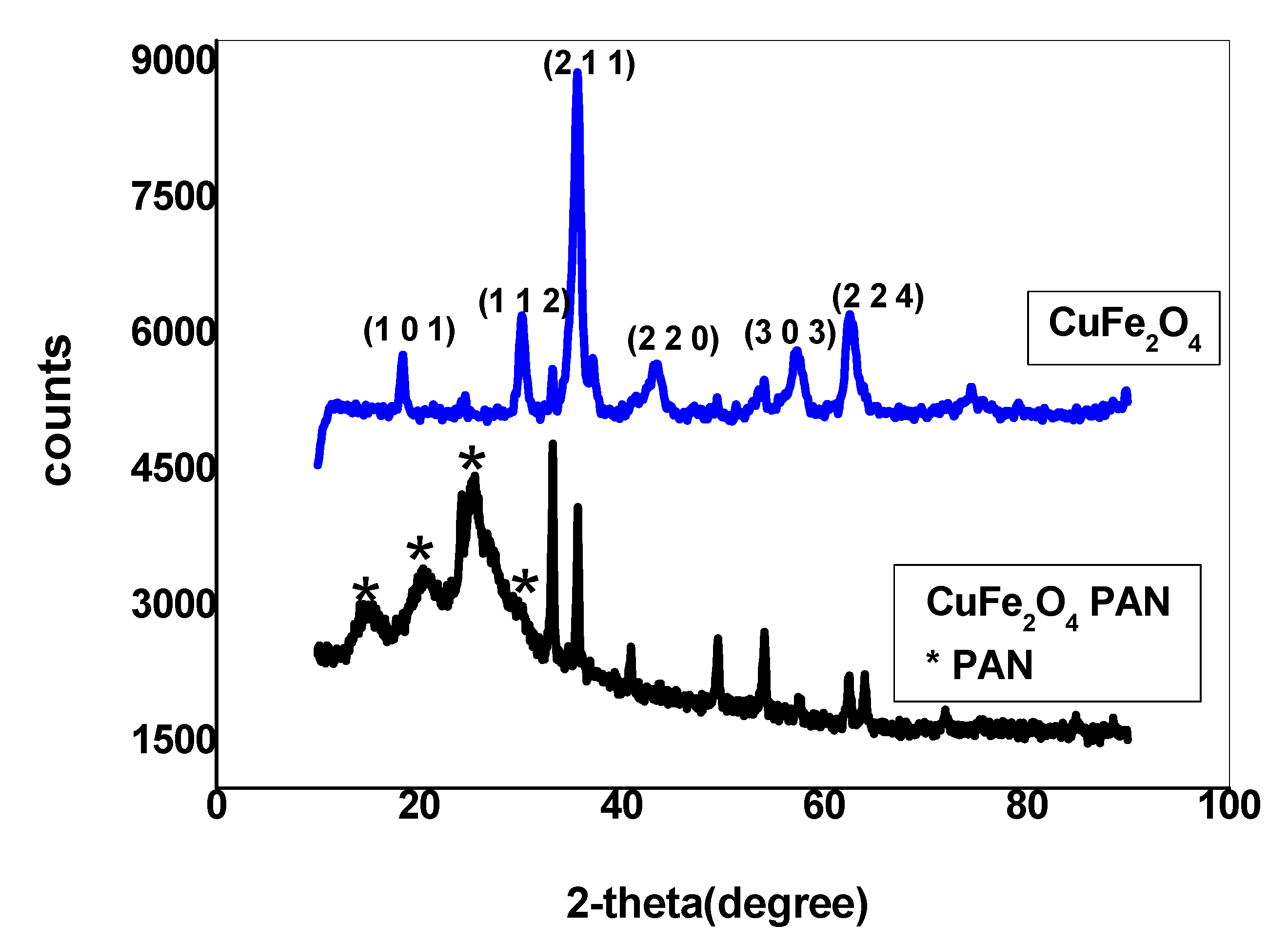
2.1.1. X-ray Diffraction Pattern
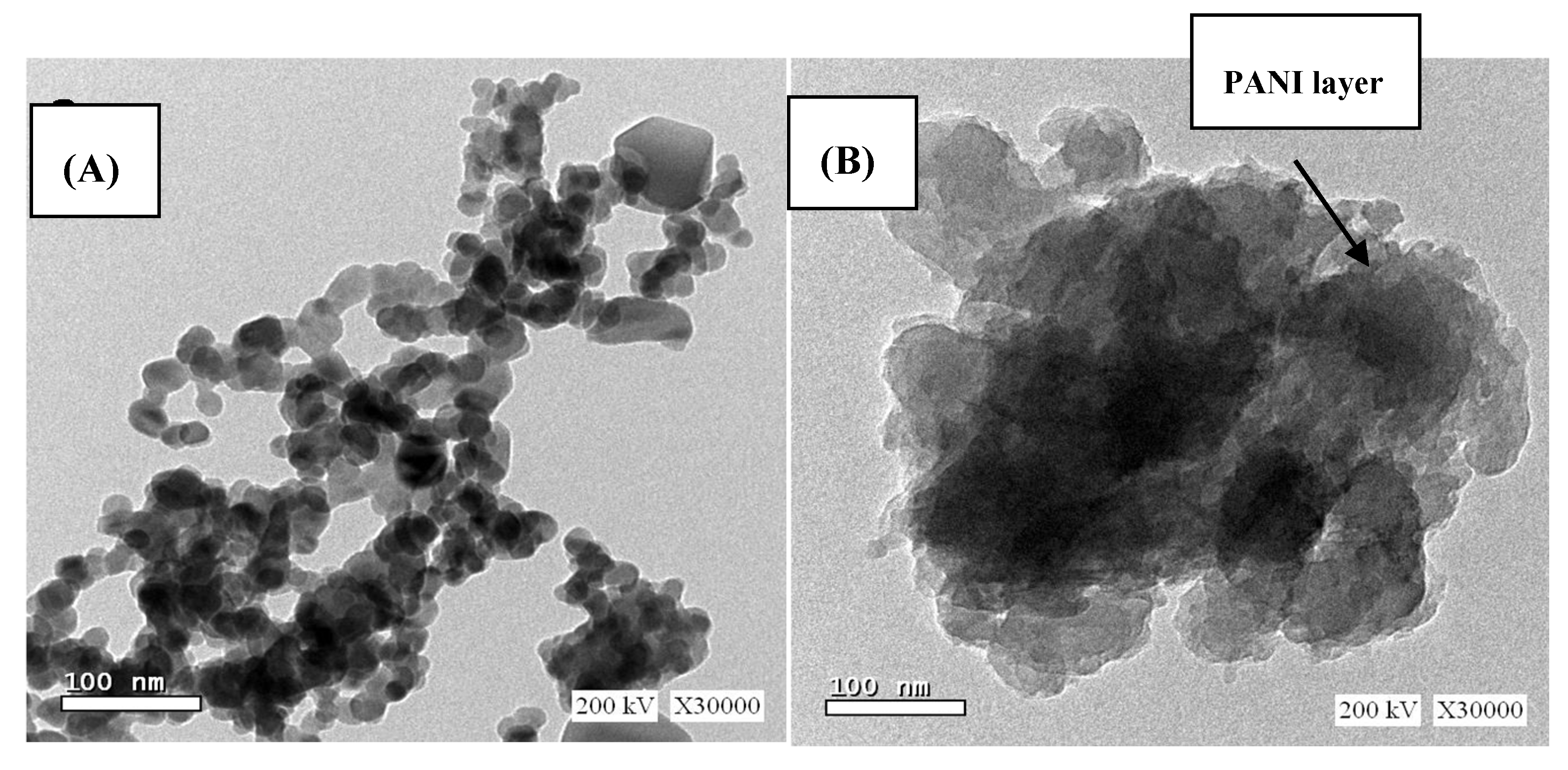
2.1.2. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
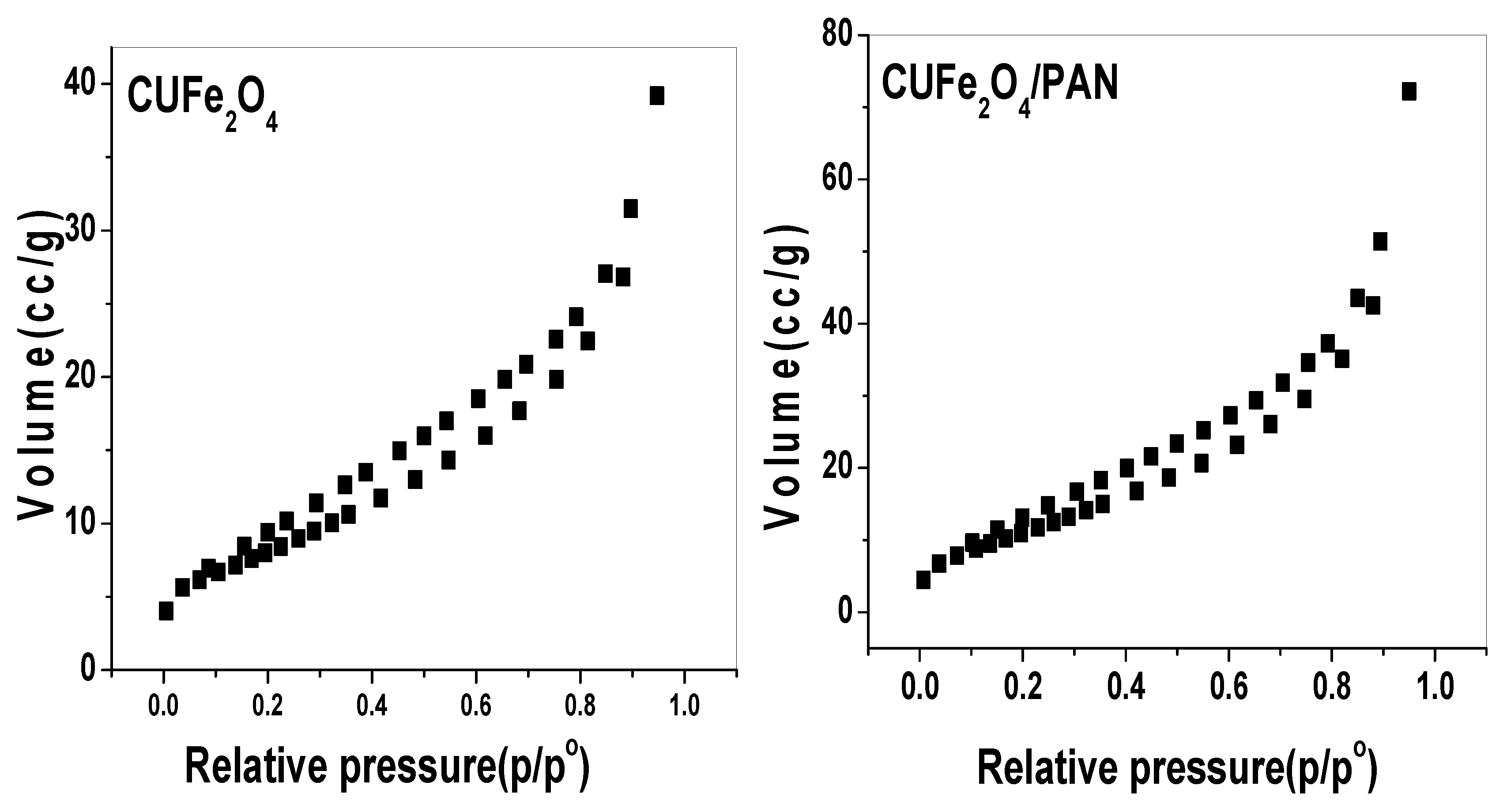
2.1.3. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET)
2.1.4. Fourier Transforms–Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.1.5. Thermal Analysis
2.2. Adsorption Study
2.2.1. Effect of Mercury Concentration
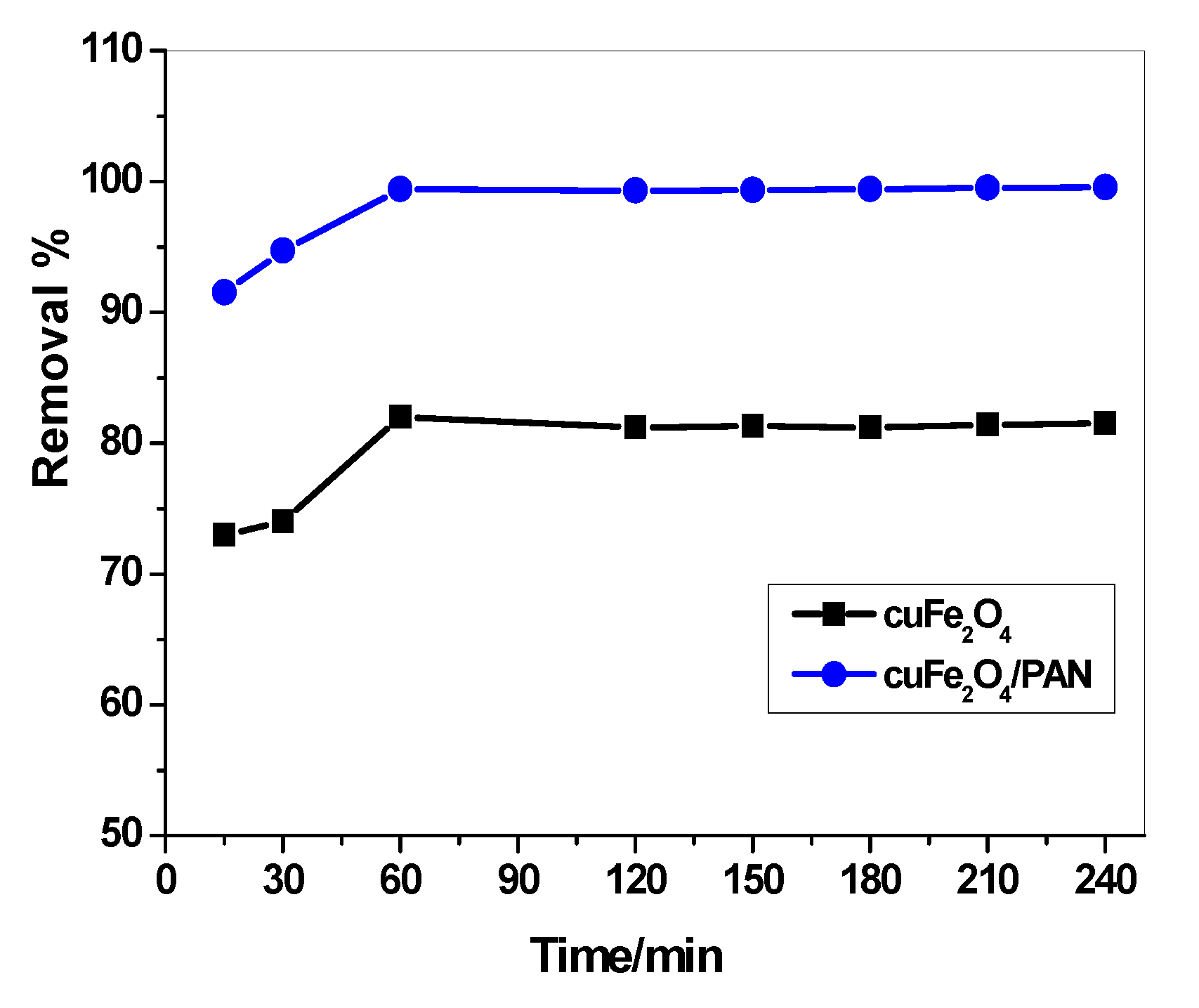
2.2.2. Effect of Contact Time
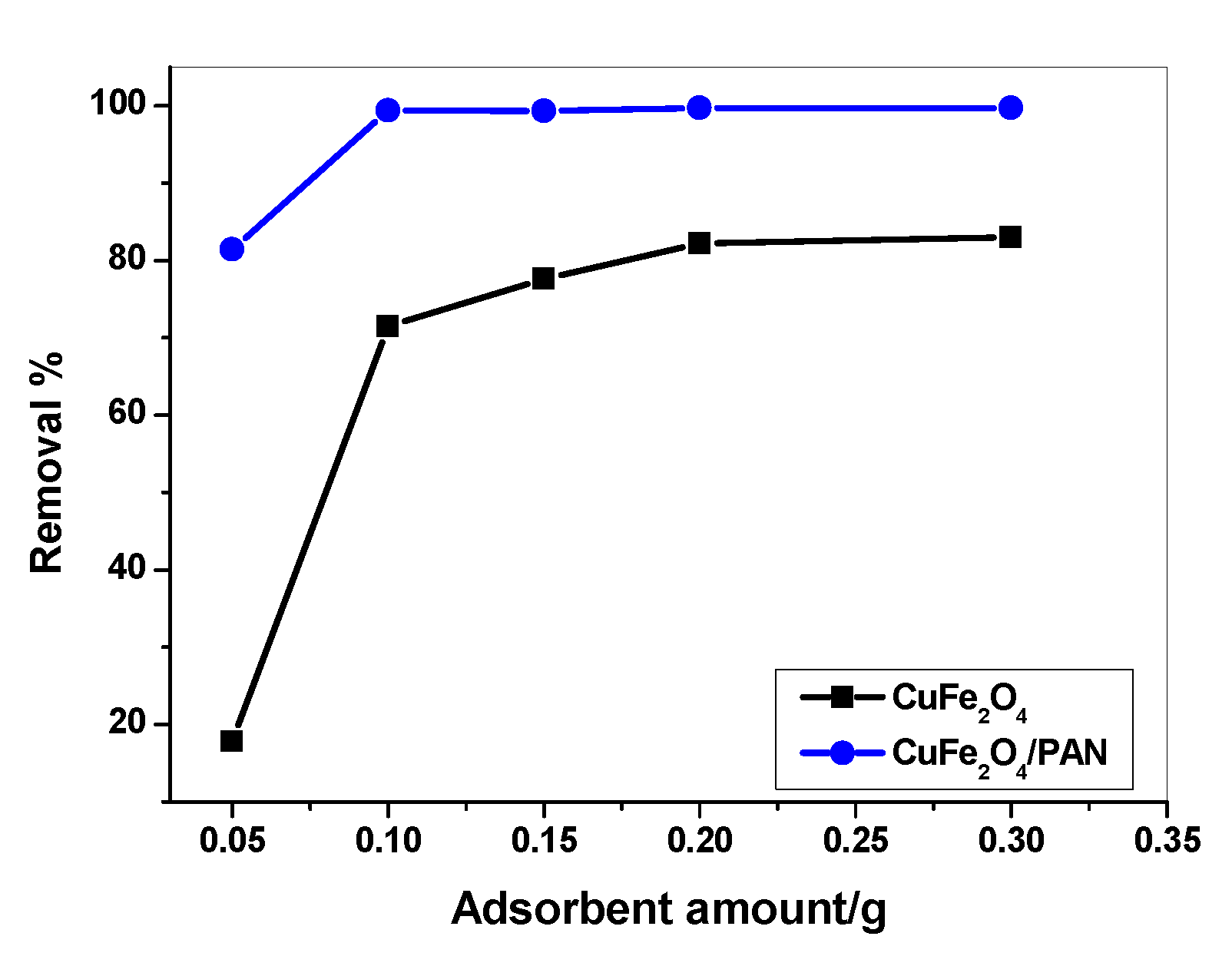
2.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Amount
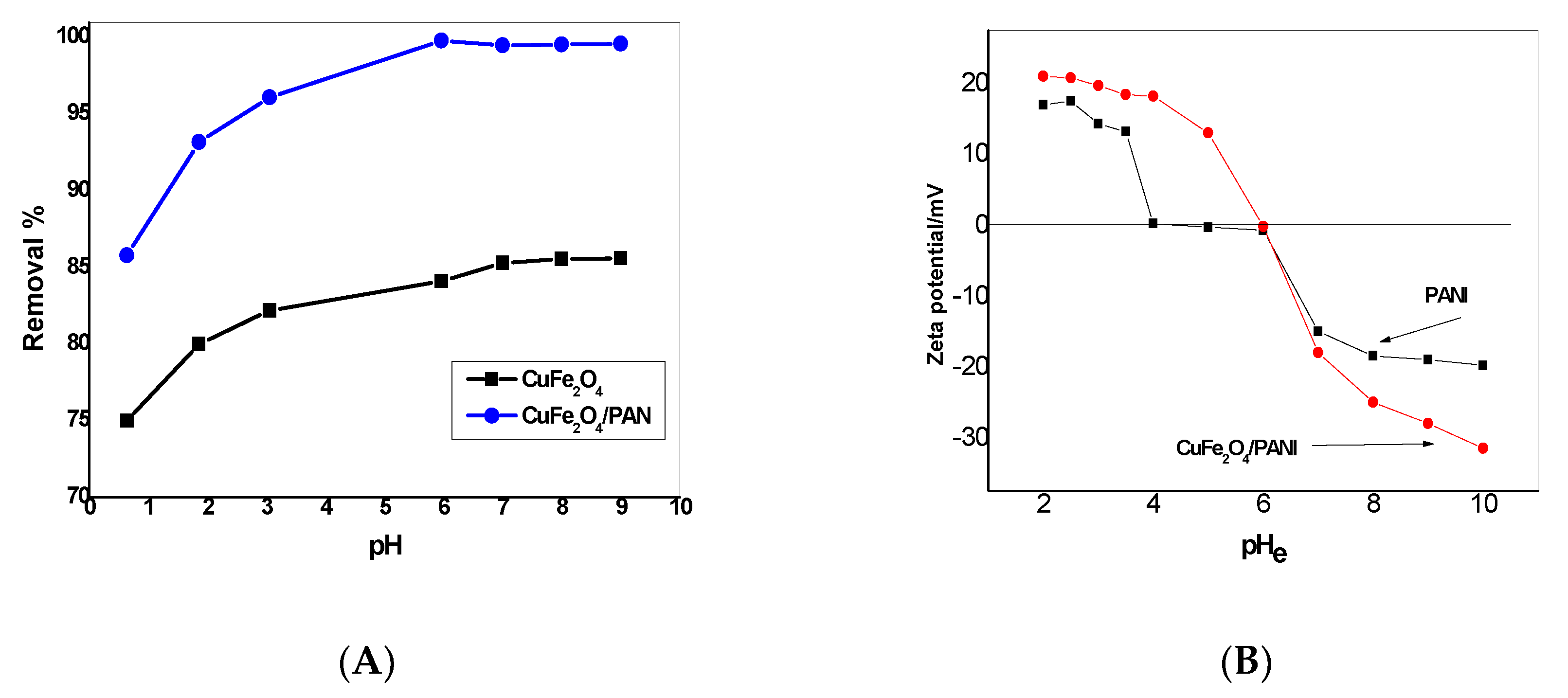
2.2.4. Effect of pH
2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
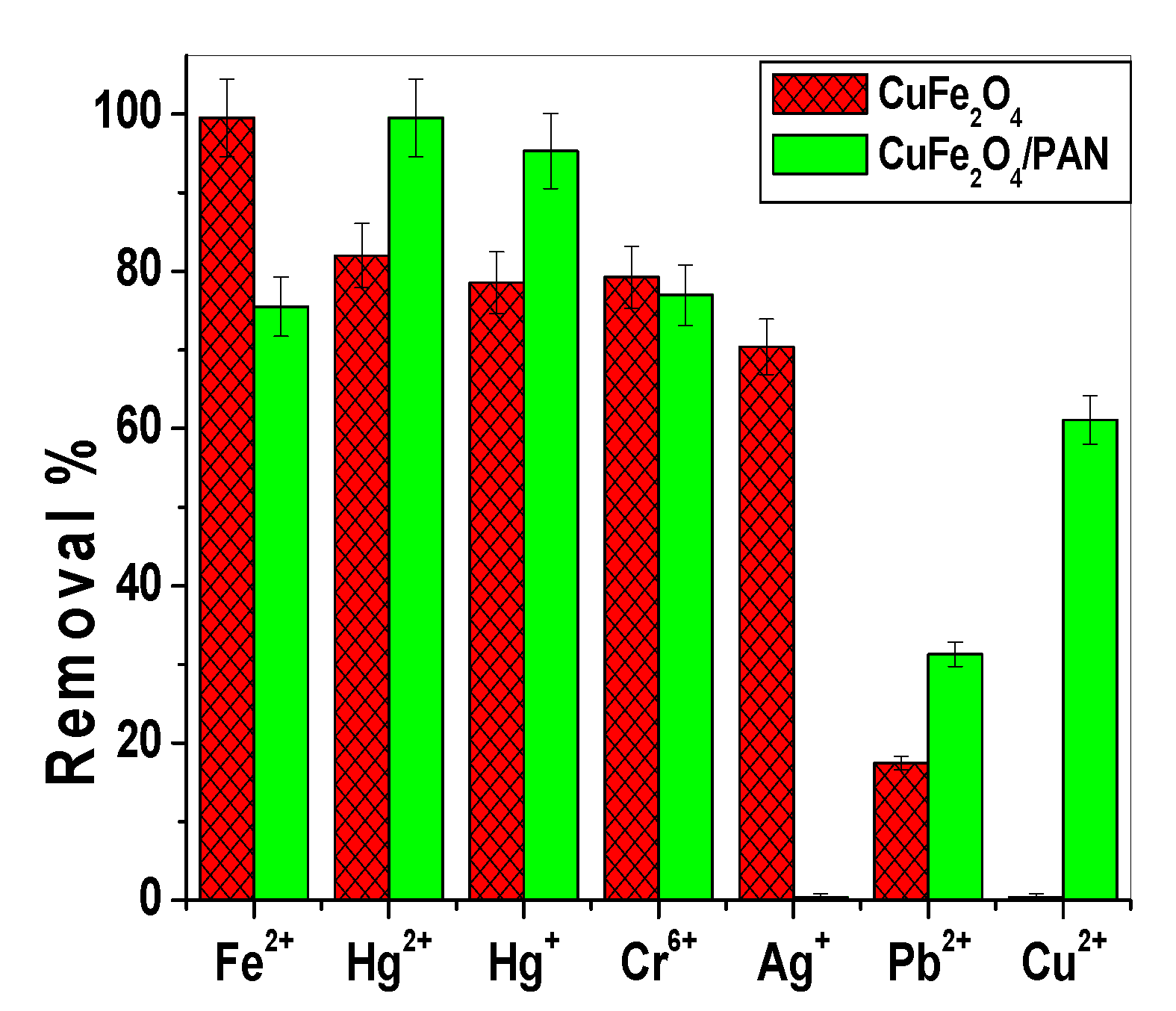
2.4. Competitive Adsorption of Different Heavy Metals
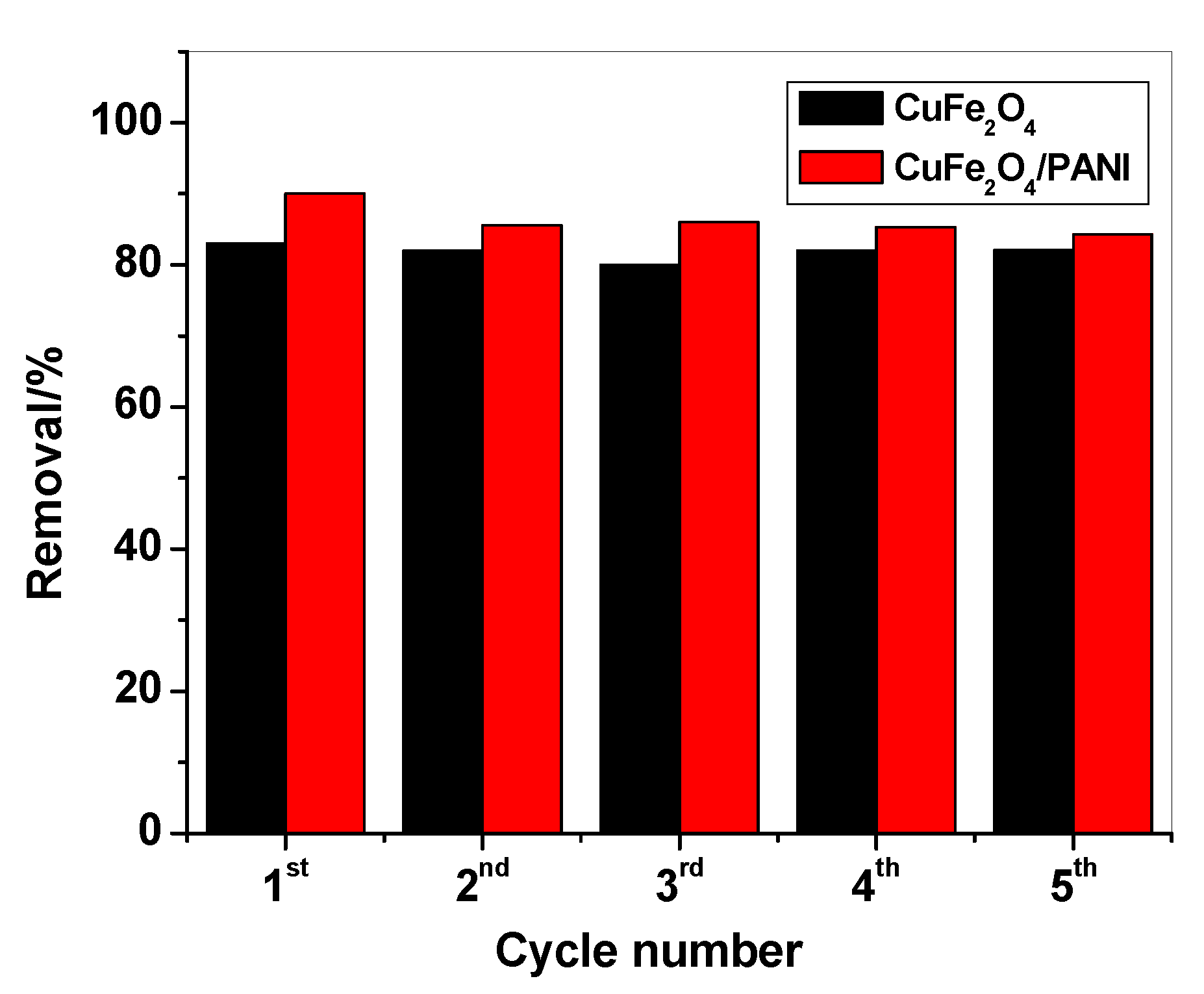
2.5. Regeneration
2.6. Comparison with Other Sorbents for Mercury Removal
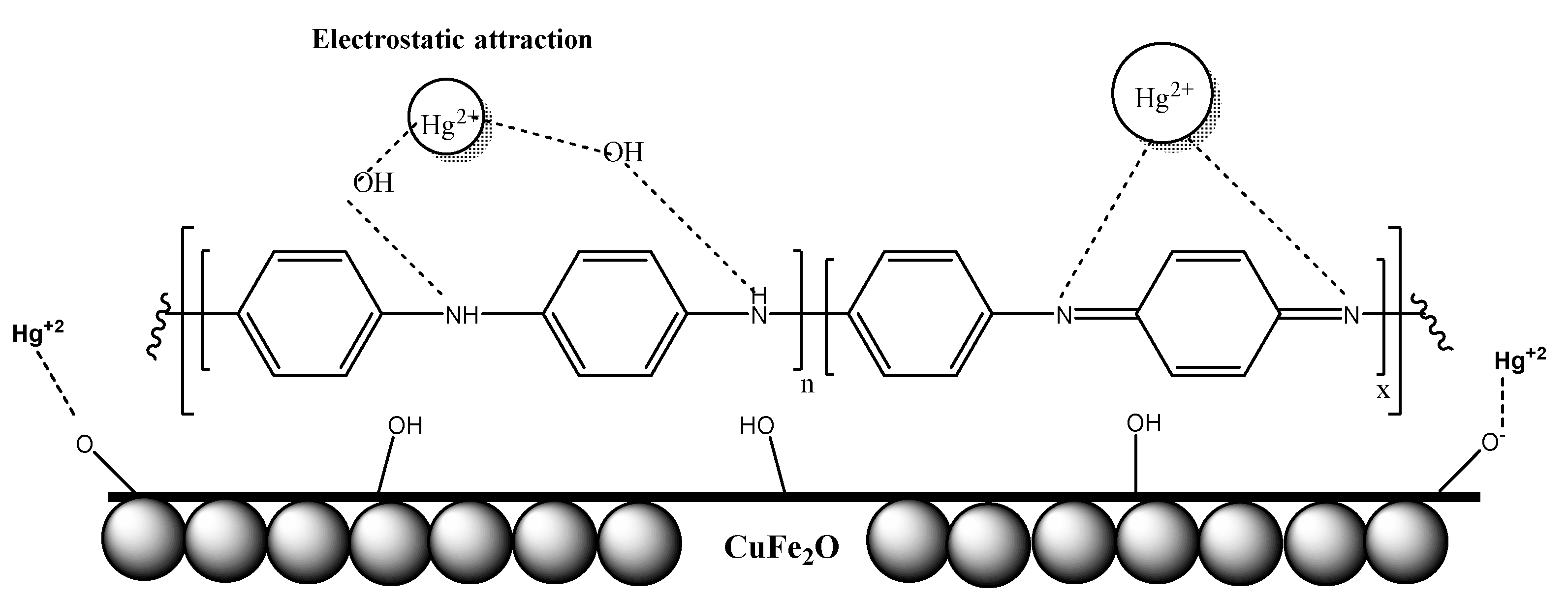
2.7. Mechanism of Adsorption
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Preparation of CuFe2O4Nano-Particles
3.4. Preparation of CuFe2O4/PANI Nano-Composite
3.5. Removal of Mercury from Waste Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Huq, A.K.O.; Yahya, R.B. The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14778–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Contamination of heavy metals in aquatic media: Transport, toxicity and technologies for remediation. In Heavy Metals in Water: Presence, Removal and Safety; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Xing, Y.; Shang, L. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basha, S.; Murthy, Z.V.P.; Jha, B. Sorption of Hg(II) onto Carica papaya: Experimental studies and design of batch sorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Sommar, J.; Wang, S. A review of studies on atmospheric mercury in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). CERCLA Priority List of Hazardous Substances; US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2001.
- Caner, N.; Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Adsorption characteristics of mercury(II) ions from aqueous solution onto chitosan-coated diatomite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on Hg(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by silica-multiwall carbon nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16721–16731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A.; Shamsuddeen, A.A. Response surface methodology optimization of adsorptive desulfurization on nickel/activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A. Effects of bimetallic Ce/Fe nanoparticles on the desulfurization of thiophenes using activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.; Budinova, T.; Yardim, F.; Petrov, N.; Razvigorova, M.; Minkova, V. Removal of mercury ion from aqueous solution by activated carbons obtained from biomass and coals. Fuel Proce. Technol. 2002, 77–78, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessboussea, H.; Rhlalou, T.; Verchère, J.F.; Lebrun, L. Mercury removal from wastewater using a poly(vinylalcohol)/poly(vinylimidazole) complexing membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 164, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarle, S.; Ratto, M.; Rovatti, M. Mercury Removal from Water by Ion Exchange Resins Adsorption. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2971–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmen, A.; Vergel, D.; Fradinho, J.; Reis, M.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Mercury removal from water streams through the ion exchange membrane bioreactor concept. J. Hazar. Mat. 2014, 264, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Q.; Meng, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, C. Alkynyl carbon materials as novel and efficient sorbents for the adsorption of mercury(II) from wastewater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, P.; To, M.; Hui, C.; Lin, C.S.K.; McKay, G. Aqueous Mercury Adsorption by Activated Carbons. Water Res. 2015, 15, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denizli, A.; Kesenci, K.; Arica, Y.; Piskin, E. Dithiocarbamate-incorporated monosize polystyrene microspheres for selective removal of mercury ions. Reactive Funct. Poly. 2000, 44, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Elserw, M.I.A. Development of microwave-assisted functionalized nanosilicas for instantaneous removal of heavy metals. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavifar, M.; Bahramifar, N.; Younesi, H.; Rastakhiz, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, J.; Eftekhari, E. Removal of mercury(II) and cadmium(II) ions from synthetic wastewater by a newly synthesized amino and thiolated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.S.; Dwivedi, V.; Dasgupta, K.; Ali, S.M.; Shenoy, K.T. Novel Amidoamine Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for removal of Mercury(II) Ions from Wastewater: Combined Experimental and Density Functional Theoretical. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viltužnik, B.; Lobnik, A.; Košak, A. The removal of Hg(II) ions from aqueous solutions by using thiol-functionalized cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 74, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, E.; Campillo, G.E.; Morales, G.; Hincapié, C.; Osorio, J.; Arnache, O.; Uribe, J.I.; Jaramillo, F. Mercury removal in wastewater by iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 687, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, H.; Huang, M. Strong Adsorbability of Mercury Ions on Aniline/Sulfoanisidine Copolymer Nanosorbents. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4573–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Chen, P.; Huang, C.; Chang, H. Gold Nanoparticle−Aluminum Oxide Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Mercury Species from Natural Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2724−2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baoa, S.; Lia, K.; Ninga, P.; Peng, J.; Jina, X.; Tang, L. Highly effective removal of mercury and lead ions from wastewater by mercaptoamine-functionalised silica-coated magnetic nano-adsorbents: Behaviours and mechanisms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, R.E.; Elsabee, M.Z. Polyaniline Nanotubes: Mercury and Competative Heavy Metals Uptake. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 5, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Parham, H.; Zargar, B.; Shiralipour, R. Hazardous Materials, Fast and efficient removal of mercury from water samples using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. J. Hazard Mat. 2012, 205–206, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaeigohar, S. The Nanosized Dye Adsorbents for Water Treatment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Botcha, N.K.; Zarie, E.S.; Elbahri, M. Ups and downs of water photodecolorization by nanocomposite polymer nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. An amphiphilic, graphitic buckypaper capturing enzyme biomolecules from water. Water 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Photocatalyticozonation of dyes using copper ferrite nanoparticle prepared by co-precipitation method. Desalination 2011, 279, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Gu, N. Magnetic nanoparticles separation based on nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 2007, 312, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngomsik, A.F.; Bee, A.; Draye, M.; Cote, G.; Cabuil, V. Magnetic nano- and microparticles for metal removal and environmental applications: A review. Comptes Rendus Chimie. 2005, 8, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lu, M.; Huang, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L. Decoration of defective MoS2 nanosheets with Fe3O4nano particles as superior magnetic adsorbent for highly selective and efficient mercury ions (Hg2+) removal. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 737, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, S.; Guyo, U.; Zinyama, N.P.; Chigondo, F.; Nyamunda, B.C.; Muchanyereyi, N. Response surface methodology for optimization of Cd (II) adsorption from wastewaters by fabricated tartaric acid-maize tassel magnetic hybrid sorbent. Bioint. Res. in Appl. Chem. 2019, 9, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, M.K.; Abdul Quadir, M.G.; Bhaduri, R.; Kaushik, S.; Goswami, P. Composite polymer coated magnetic nanoparticles based anode enhances dye degradation and power production in microbial fuel cells. Biosens.Bioelectr. 2018, 119, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Casamachin, D.A.; De la Rosa, J.R.; Lucio–Ortiz, C.J.; Sandoval-Rangel, L.; García, C.D. Partial oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid using O2 and a photocatalyst of a composite of ZnO/PPy under visible-light: Electrochemical characterization and kinetic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wainaina, J.; Na, J.S. Synthesis of amphiphilic silica/polymer composite nanoparticles as water-dispersible nano-absorbent for hydrophobic pollutants. J. Indust. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.X.; Zhou, W.X. Studies on magnetic properties of film of polyaniline. Acta Phys. Sin. 1992, 41, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.H.; Chao, C.M.; Liu, C.H.; Chang, T.C. Characterization and corrosion resistance of organically modified silicate–NiZn ferrite/polyaniline hybrid coatings on aluminum alloys. Corrosion Sci. 2007, 49, 3001–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouget, J.P.; Jozefowicz, M.E.; Epstein, A.J.; Tang, X.; Macdiarmid, A.G. X-ray structure of polyaniline. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Guo, K. Diffraction of Crystal and Pseudo Crystal; Beijing Universities Public House: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. (IOSR-JAC) 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, M.; Raja, M.M.; Asokan, K.; Kanjilal, D.; Rajasekaran, T.R.; Padiyan, D.P. Effect of thermal spike energy created in CuFe2O4 by 150 MeV Ni11+ swift heavy ion irradiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Section B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2011, 269, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |

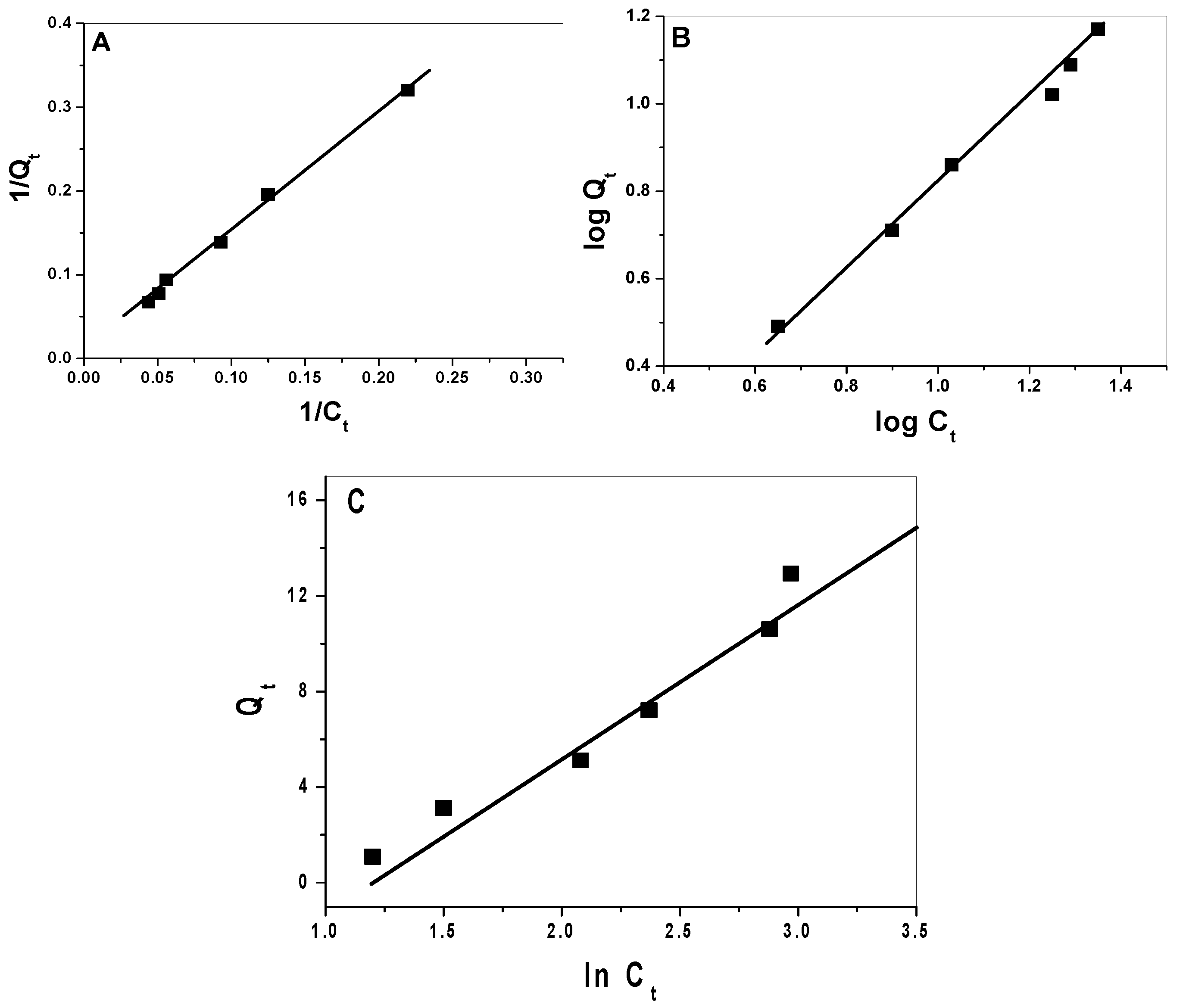
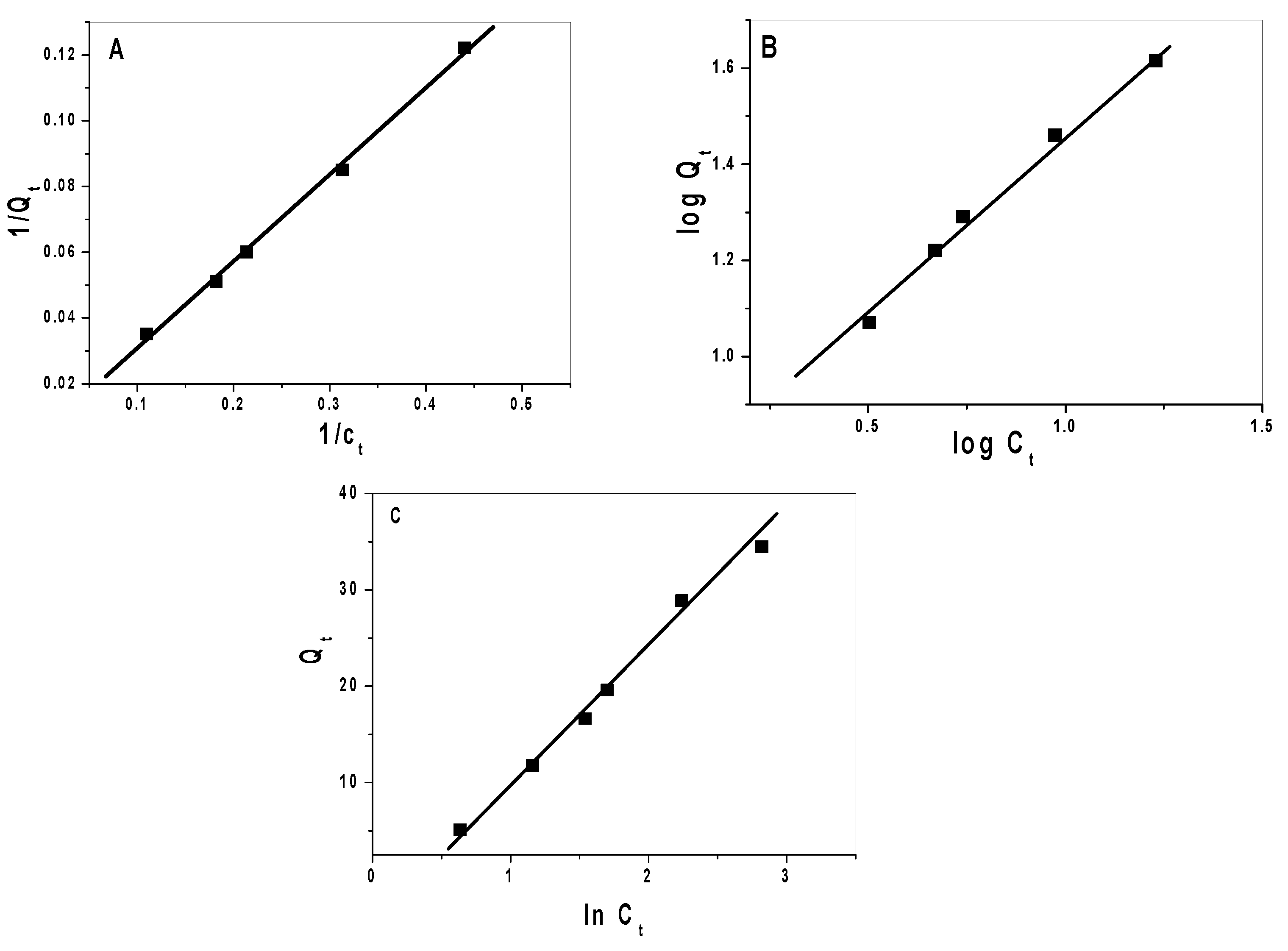
| Sample | Surface Area(m2/g) | Average Pore Volume(cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuFe2O4/PANI | 30.8 | 0.06 | 17.8 |
| CuFe2O4 NP | 44.7 | 0.11 | 9.9 |
| Adsorbent | Pseudo-First Order | Second Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1(min−1) | qe1(mg/g) | R2 | k2(g/(mg. min)) | qe2(mg/g) | qeexp | R2 | |
| CuFe2O4 | 0.0056 | 1.571 | 0.942 | 5.3 × 10−3 | 5.8922 | 7.1086 | 0.991 |
| CuFe2O4/PANI | 0.0732 | 2.2134 | 0.953 | 0.1121 | 8.3356 | 8.4123 | 0.998 |
| Model | Parameters | CuFe2O4 | CuFe2O4/PANI | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Xm | 12.5 | 157.1 | mg/g |
| B | 0.561 | 0.153 | L/mg | |
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.999 | ||
| Freundlich | N | 1.06 | 1.34 | mg/g |
| Kf | 2.75 | 5.24 | mg/g | |
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.995 | ||
| Temkin | KT | 0.34 | 0.744 | L/mg |
| bT | 0.371 | 0.162 | K J/mol | |
| R2 | 0.980 | 0.997 |
| Adsorbent Type | Maximum Adsorption Capacity mg/g | Contact Time | Removal % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinylalcohol)/poly(vinylimidazole) complexing membrane | 120 | 125 min | 99.4 | [12] |
| Dithiocarbamate-incorporated mono size polystyrene | 33.2 | 30 min | NR | [17] |
| Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole | 0.59 | 4 min | 98.6 | [18] |
| Thiolated multi-walled carbon nanotubes | 204.64 | 40 min | 98 | [19] |
| Amidoamine functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-AA) | 101.35 | 180 min | 80 | [20] |
| Mercaptopropyl-coated cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) magnetic nanoparticles | NR | 30 min | 97 | [21] |
| Poly(aniline-co-5-sulfo-2-anisidine) nanoparticles | 2063 | 48 h | 99.8 | [23] |
| Gold Nanoparticle−Aluminum Oxide | 676 | 30 min | >97 | [24] |
| Mercaptoamine-functionalised silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (MAF-SCMNPs) | 355 | 120 min | NR | [25] |
| Polyaniline Nanotubes | 0.8239 | 60 min | 90 | [26] |
| Iron oxide nanoparticles | NR | 24 h | 87 | [27] |
| CuFe2O4 CuFe2O4/PAN | 12.5 157.1 | 120 min 60 min | 82 99.5 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, S.S.M.; H. Kamel, A.; A. Hassan, A.; Amr, A.E.-G.E.; Abd El-Naby, H.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Sayed, A.Y.A. CuFe2O4/Polyaniline (PANI) Nanocomposite for the Hazard Mercuric Ion Removal: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Properties Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122721
Hassan SSM, H. Kamel A, A. Hassan A, Amr AE-GE, Abd El-Naby H, Al-Omar MA, Sayed AYA. CuFe2O4/Polyaniline (PANI) Nanocomposite for the Hazard Mercuric Ion Removal: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Properties Study. Molecules. 2020; 25(12):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122721
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Saad S. M., Ayman H. Kamel, Amr A. Hassan, Abd El-Galil E. Amr, Heba Abd El-Naby, Mohamed A. Al-Omar, and Ahmed Y. A. Sayed. 2020. "CuFe2O4/Polyaniline (PANI) Nanocomposite for the Hazard Mercuric Ion Removal: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Properties Study" Molecules 25, no. 12: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122721
APA StyleHassan, S. S. M., H. Kamel, A., A. Hassan, A., Amr, A. E.-G. E., Abd El-Naby, H., Al-Omar, M. A., & Sayed, A. Y. A. (2020). CuFe2O4/Polyaniline (PANI) Nanocomposite for the Hazard Mercuric Ion Removal: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Properties Study. Molecules, 25(12), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122721









