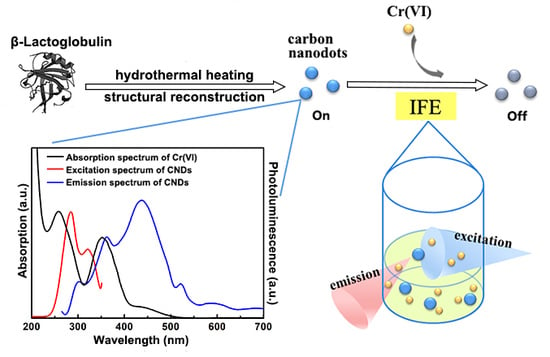
Ultraviolet Carbon Nanodots Providing a Dual-Mode Spectral Matching Platform for Synergistic Enhancement of the Fluorescent Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
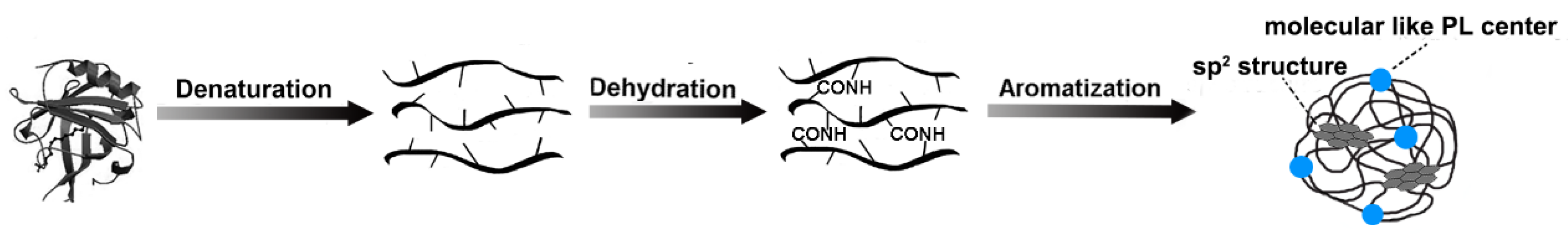
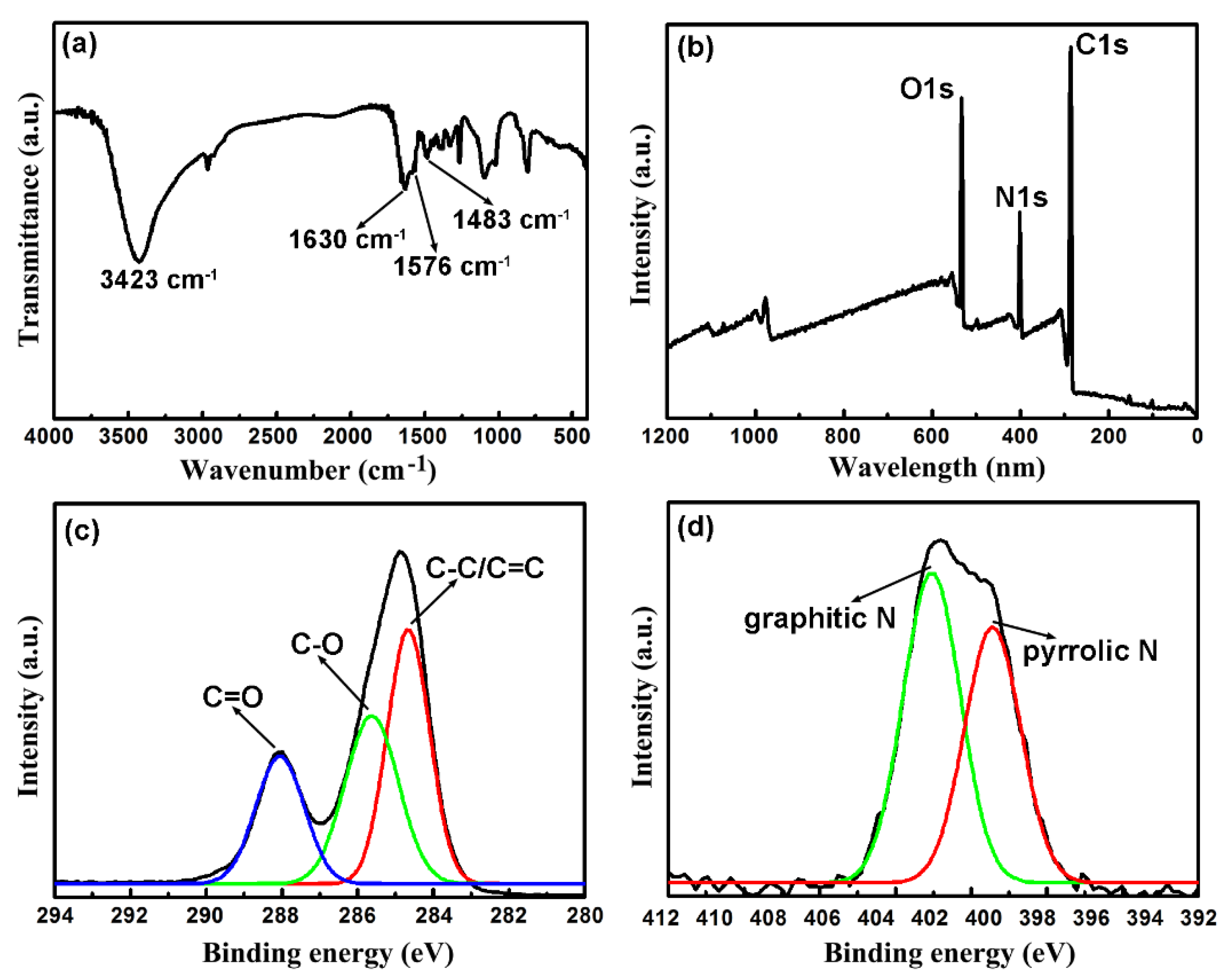
2.1. Morphology and Structure Characterization of the CNDs
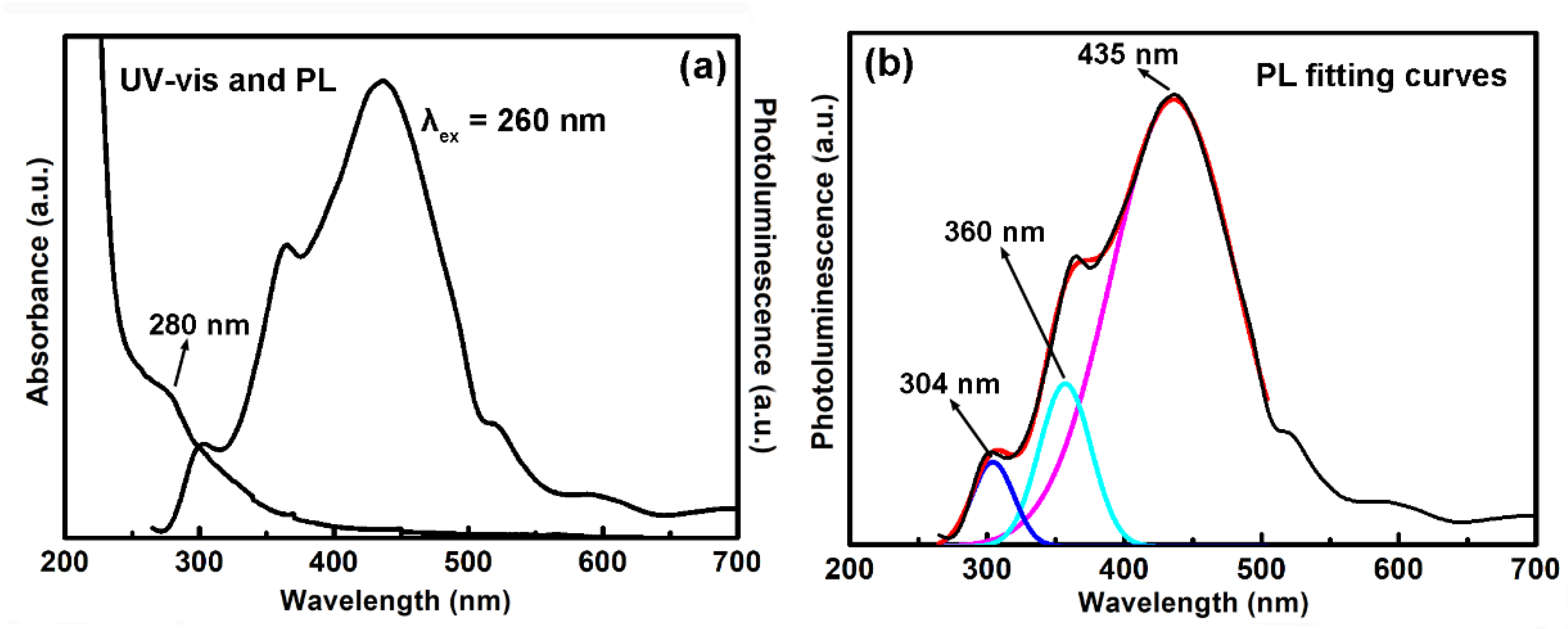
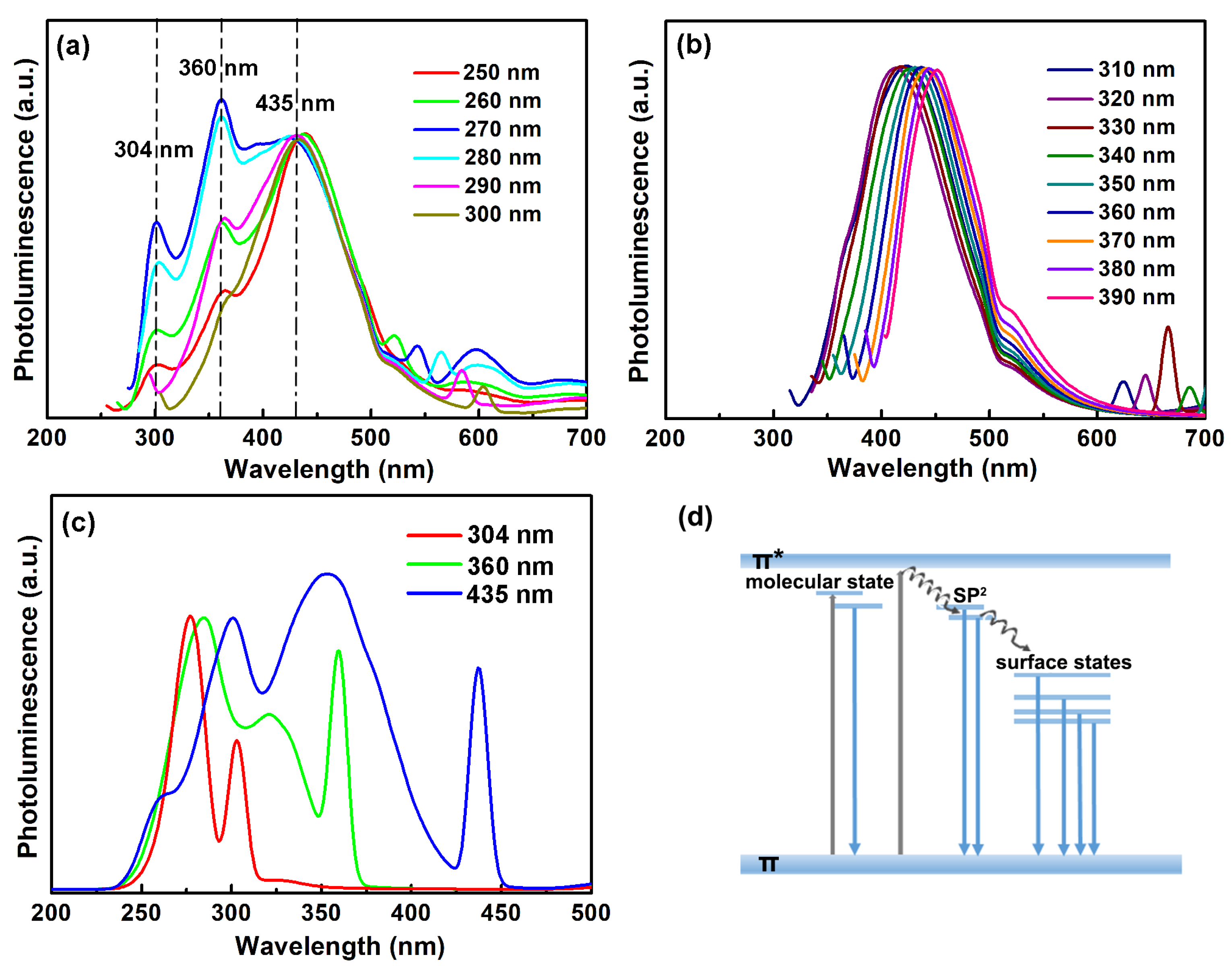
2.2. Optical Property of the CNDs
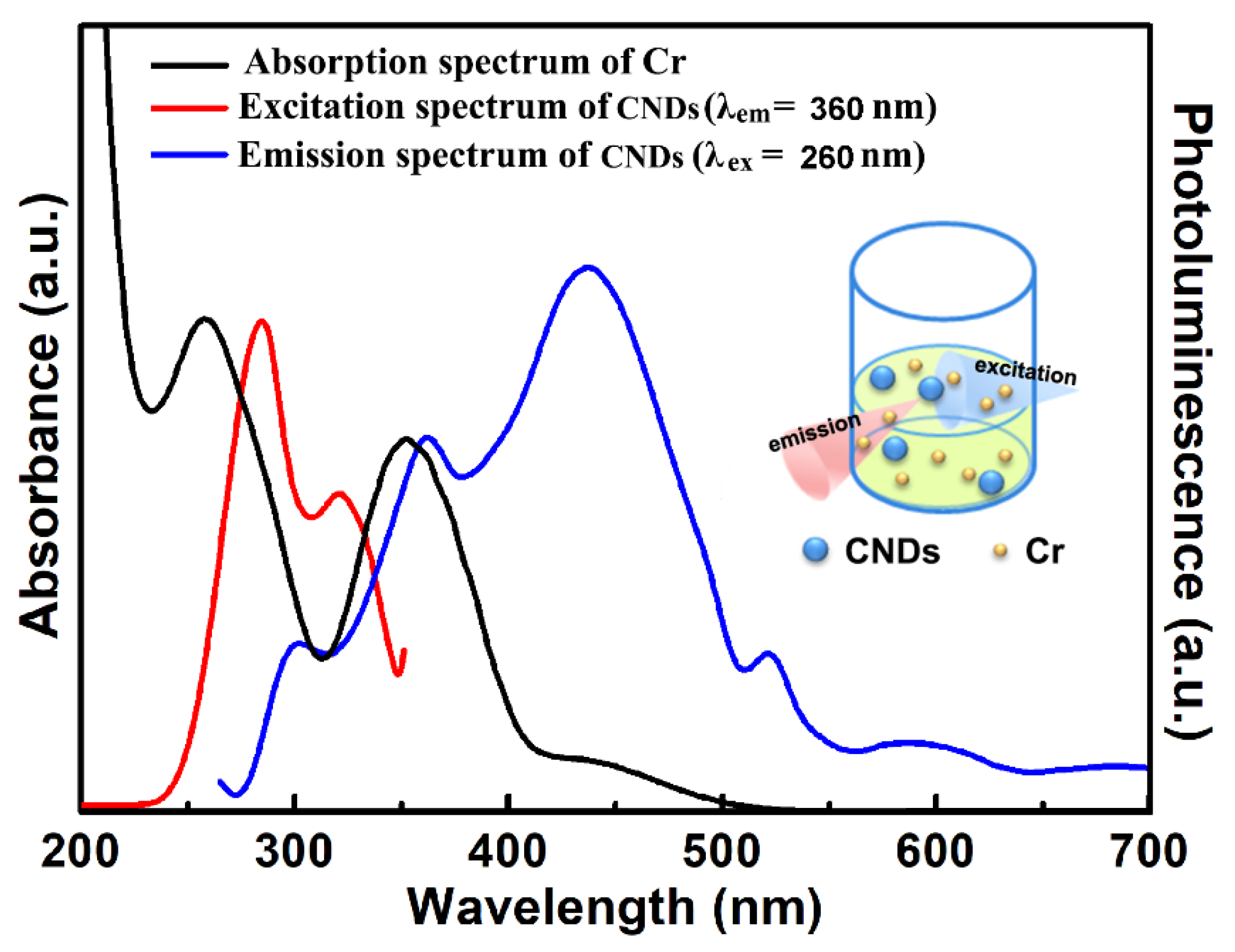
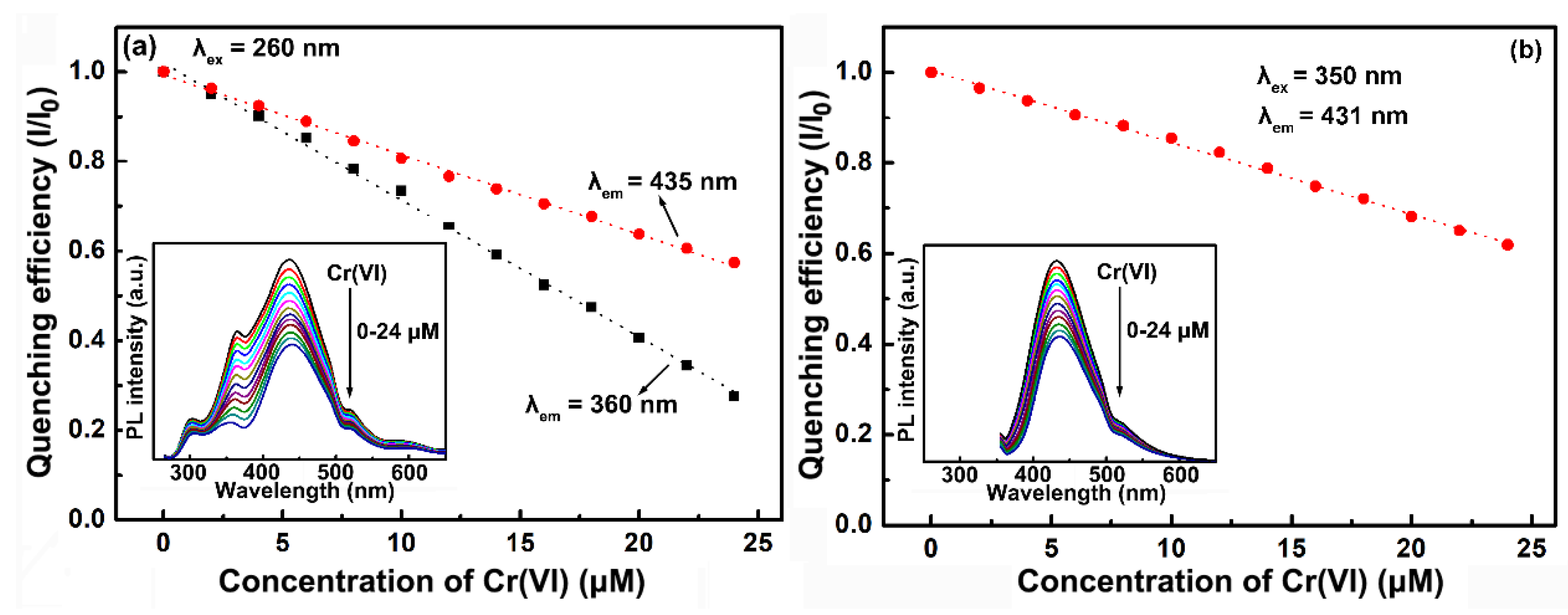
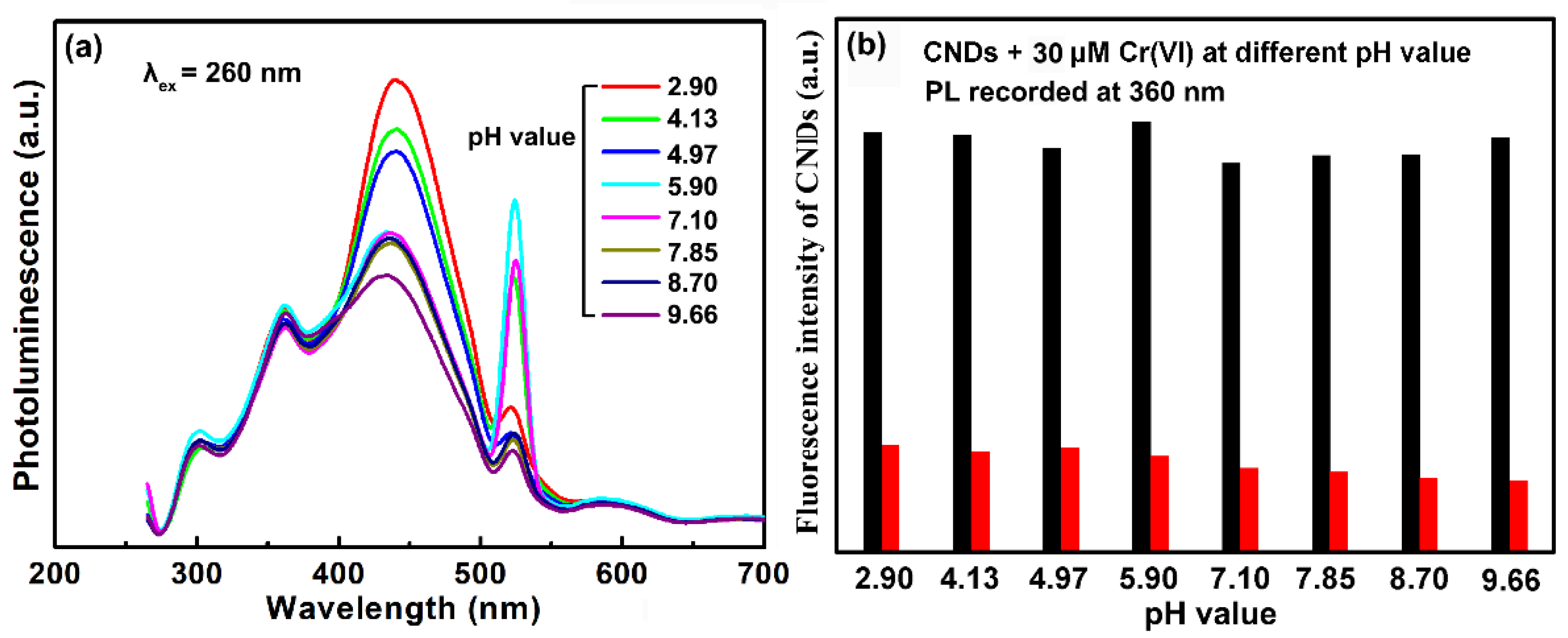
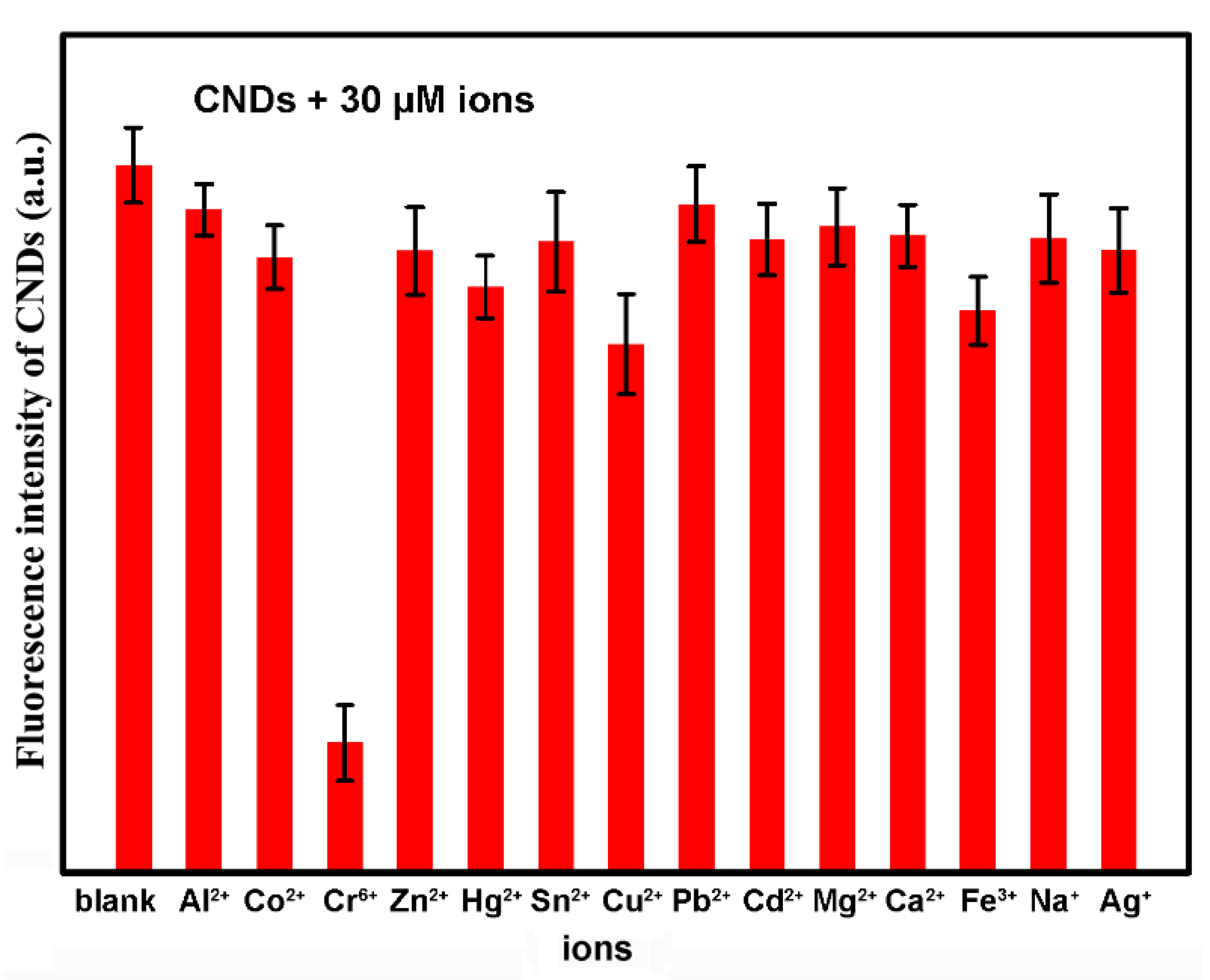
2.3. Synergistically Enhanced Fluorescent Sensing of Cr(VI)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Carbon Nanodots
3.3. Quantum Yield Calculation
3.4. Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solution
3.5. Instruments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Lee, B.-I.; Byeon, S.-H. The inner filter effect of Cr(vi) on Tb-doped layered rare earth hydroxychlorides: New fluorescent adsorbents for the simple detection of Cr(vi). Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, A.M.; Logeswari, A.; Mano, S.; Thirumarimurugan, M.; Kannadasan, T. Removal of chromium from real tannery effluent by using bioadsorbents. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 3, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Arancibia, V.; Valderrama, M.; Silva, K.; Tapia, T. Determination of chromium in urine samples by complexation–supercritical fluid extraction and liquid or gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthemidis, A.N.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Kougoulis, J.-S.; Stratis, J.A. Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of chromium(VI) by on-line preconcentration system using a PTFE packed column. Talanta 2002, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Xie, Z.; Qu, D.; Li, D.; Du, P.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. On-Off-On Fluorescent Carbon Dot Nanosensor for Recognition of Chromium(VI) and Ascorbic Acid Based on the Inner Filter Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13242–13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.M.F.; Ginjom, I.R.; Ngu-Schwemlein, M.; Ng, S.M. Synthesis of yellow fluorescent carbon dots and their application to the determination of chromium(III) with selectivity improved by pH tuning. Microchim. Acta 2017, 183, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shuang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, C. An "on-off-on" fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dualdoped carbon quantum dot. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 968, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Bi, J.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, D.; Tan, M. Facile one-step synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots as an efficient fluorescent probe for chromium(vi) detection based on the inner filter effect. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3729–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yang, E.; Yao, J.; Chu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q. Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur tri-doped carbon dots are specific and sensitive fluorescent probes for determination of chromium(VI) in water samples and in living cells. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, D.; Singh, L.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, P. Green synthesis of glowing carbon dots from Carica papaya waste pulp and their application as a label-freechemo probe for chromium detection in water. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 283, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, X.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Carbon dots with red emission as a fluorescent and colorimeteric dual-readout probe for the detection of chromium(vi) and cysteine and its logic gate operation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6099–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, X. Ratiometric fluorescent detection of chromium(VI) in real samples based on dual emissive carbon dots. Talanta 2018, 185, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.-H.; Lin, J.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-F.; Yeh, Y.-C. A fluorometric paper test for chromium(VI) based on the use of N-doped carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truskewycz, A.; Beker, S.A.; Ball, A.S.; Murdoch, B.; Cole, I. Incorporation of quantum carbon dots into a PVP/ZnO hydrogel for use as an effective hexavalent chromium sensing platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1099, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kong, Y.F.; Wang, W.; Fang, H.W.; Wo, Y.; Zhou, D.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, S.Y. Direct water-phase synthesis of lead sulfide quantum dots encapsulated by beta-lactoglobulin for in vivo second near infrared window imaging with reduced toxicity. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4025–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, S. Amphiphilic Egg-Derived Carbon Dots: Rapid Plasma Fabrication, Pyrolysis Process, and Multicolor Printing Patterns. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9297–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots from hydrophilic compounds: Role of functional groups. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3984–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, Z.; Jiang, L.-P.; Zhu, J.-J. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Wavelength-Tunable Photo luminescent Carbon Nanodots and Their Potential Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, H. Amino acids as the source for producing carbon nanodots: Microwave assisted one-step synthesis, intrinsic photoluminescence property and intense chemiluminescence enhancement. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9634–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, G.; Dai, L.; Qu, L. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Oxygen-Rich Functional Groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Cui, J.H.; Zheng, M.T.; Hu, C.F.; Tan, S.Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.L. One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.; Qi, B.; Pang, D.-W. Electrochemical Tuning of Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: From Preparation to Luminescence Mechanism. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5801–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Yang, J.H.; Zeng, H.B.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, S.C.; Wu, C.; Zeng, H.; Yoshihito, O.; Zhang, Q.Q. Carbon dots with high fluorescence quantum yield: The fluorescence originates from organic fluorophores. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14374–14378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrat, F.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Schneider, J.; Lf, A.; Wyrwich, R.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Tracking the Source of Carbon Dot Photoluminescence: Aromatic Domains versus Molecular Fluorophores. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Xiong, Y.; von Seckendorff, M.; Susha, A.S.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Molecular Fluorescence in Citric Acid-Based Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Pan, P.; Chen, Z.; Meng, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Chang, C.; Tao, Y. Ultraviolet Photoluminescence of Carbon Nanospheres and its Surface Plasmon-Induced Enhancement. Small 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.G.; Cai, C.Z.; Lin, H.W. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Pang, D.-W. Photoluminescence-Tunable Carbon Nanodots: Surface-State Energy-Gap Tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.H. Hydrothermal Route for Cutting Graphene Sheets into Blue-Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, L.M.; Chen, J.; Chang, Q.H.; Shi, W.Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, L. Protein-derived carbon nanodots with an ethylenediamine-modulated structure as sensitive fluorescent probes for Cu2+ detection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16608–16615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | 2013 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2018 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection limit (μM) | 0.69 | 24.6 | 0.023 | 4.16 | 0.23 | 0.708 | 0.26 | 0.4 | 140 | 1.2 | 0.020 |
| Reference | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | This work |
| Spiked Concentration (μM) | Concentration Determined (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 19.46 | 97.30 | 4.17 |
| 50 | 52.35 | 104.70 | 2.28 |
| 100 | 96.63 | 96.63 | 1.05 |
| 150 | 145.51 | 97.00 | 1.23 |
| 200 | 206.64 | 103.32 | 1.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sai, L.; Jiao, S.; Yang, J. Ultraviolet Carbon Nanodots Providing a Dual-Mode Spectral Matching Platform for Synergistic Enhancement of the Fluorescent Sensing. Molecules 2020, 25, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112679
Sai L, Jiao S, Yang J. Ultraviolet Carbon Nanodots Providing a Dual-Mode Spectral Matching Platform for Synergistic Enhancement of the Fluorescent Sensing. Molecules. 2020; 25(11):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112679
Chicago/Turabian StyleSai, Liman, Shuping Jiao, and Jianwen Yang. 2020. "Ultraviolet Carbon Nanodots Providing a Dual-Mode Spectral Matching Platform for Synergistic Enhancement of the Fluorescent Sensing" Molecules 25, no. 11: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112679
APA StyleSai, L., Jiao, S., & Yang, J. (2020). Ultraviolet Carbon Nanodots Providing a Dual-Mode Spectral Matching Platform for Synergistic Enhancement of the Fluorescent Sensing. Molecules, 25(11), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112679