In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
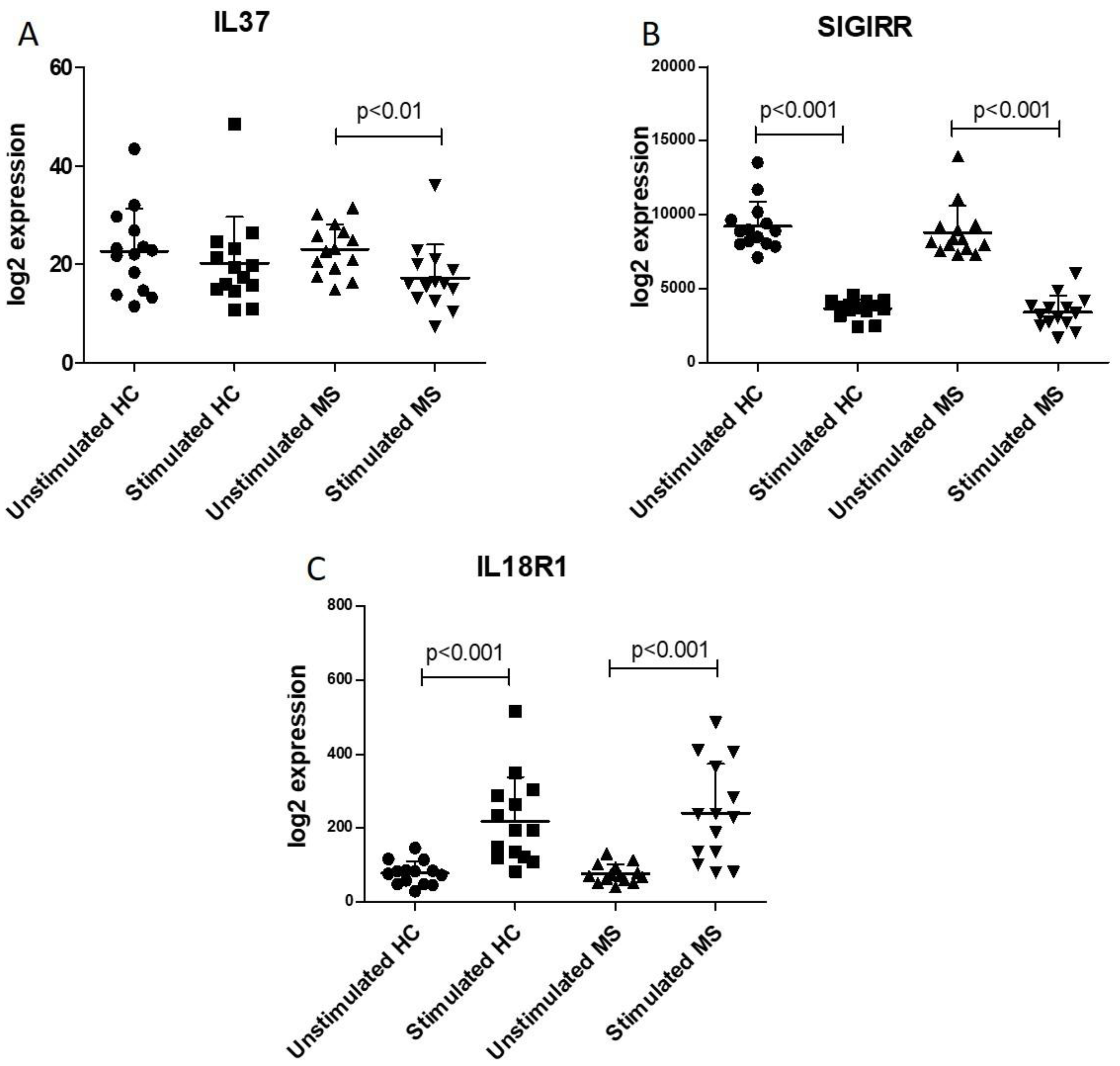
2.1. IL37 Expression in Peripheral Cluster of Differentiation (CD4)+ T Cells from MS Patients and Healthy People
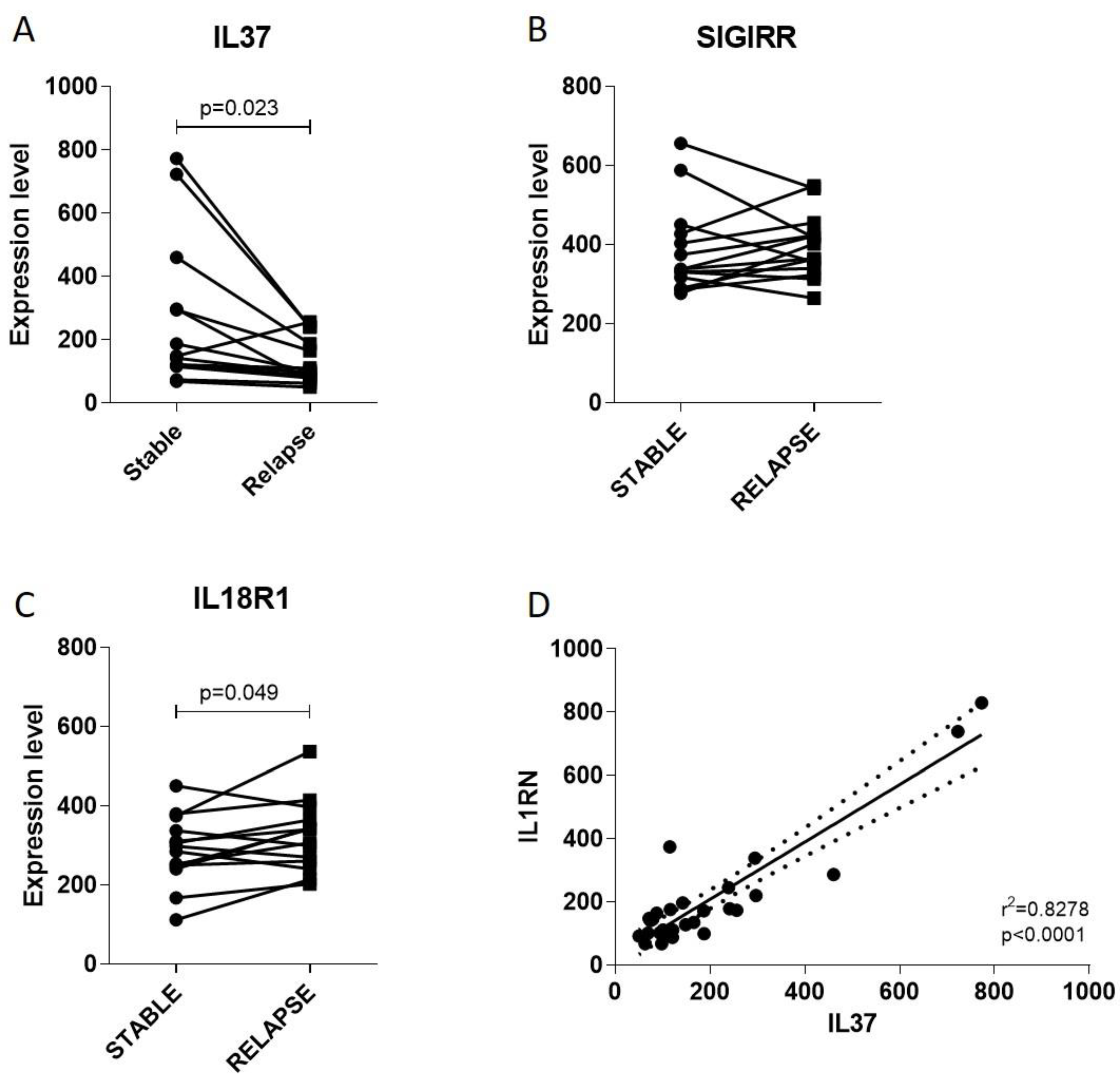
2.2. IL37 Expression during Stable and Relapsing Disease
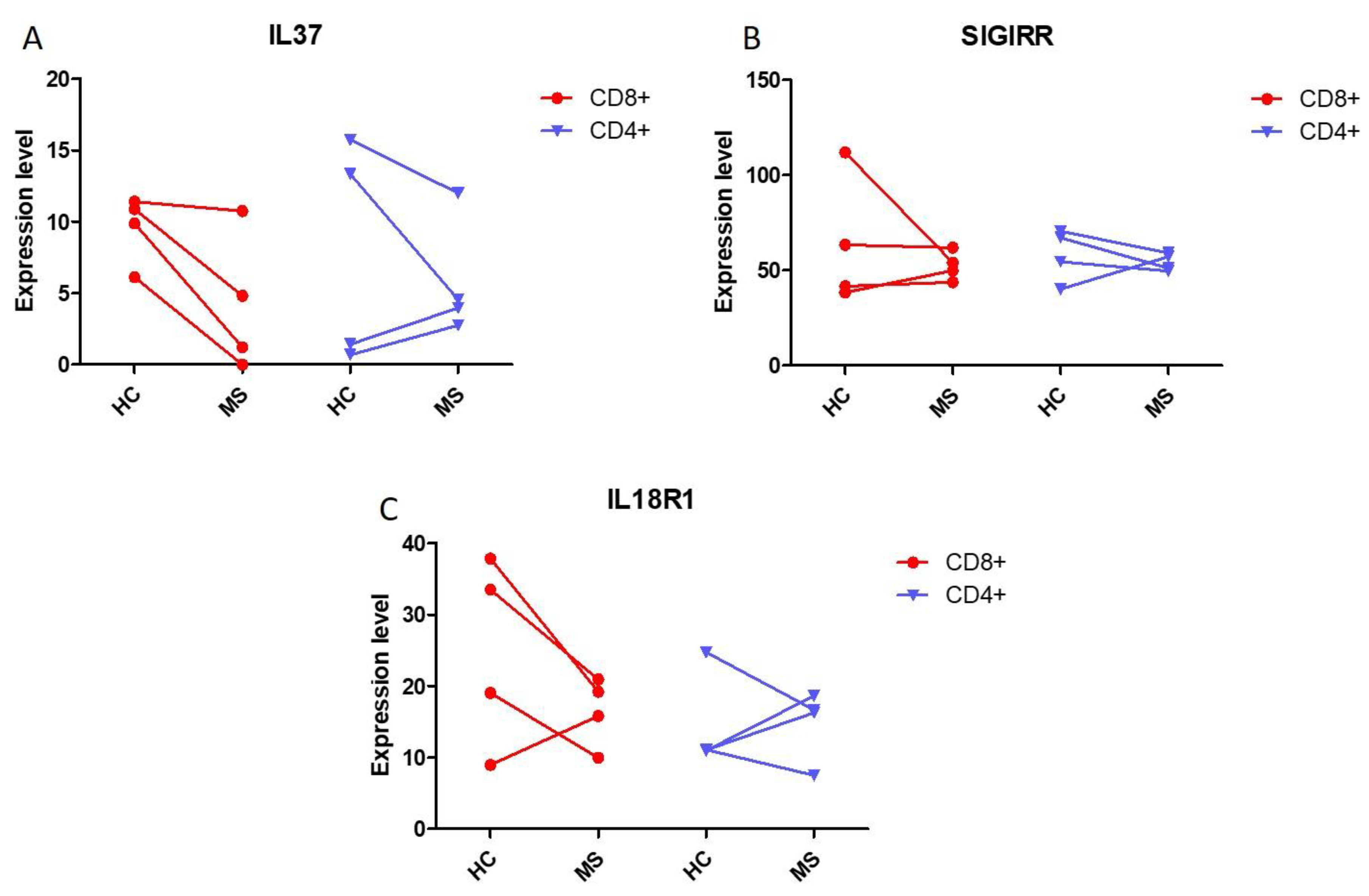
2.3. IL37 Expression in Lymphocytes from Monozygotic Twin Pairs Discordant for MS
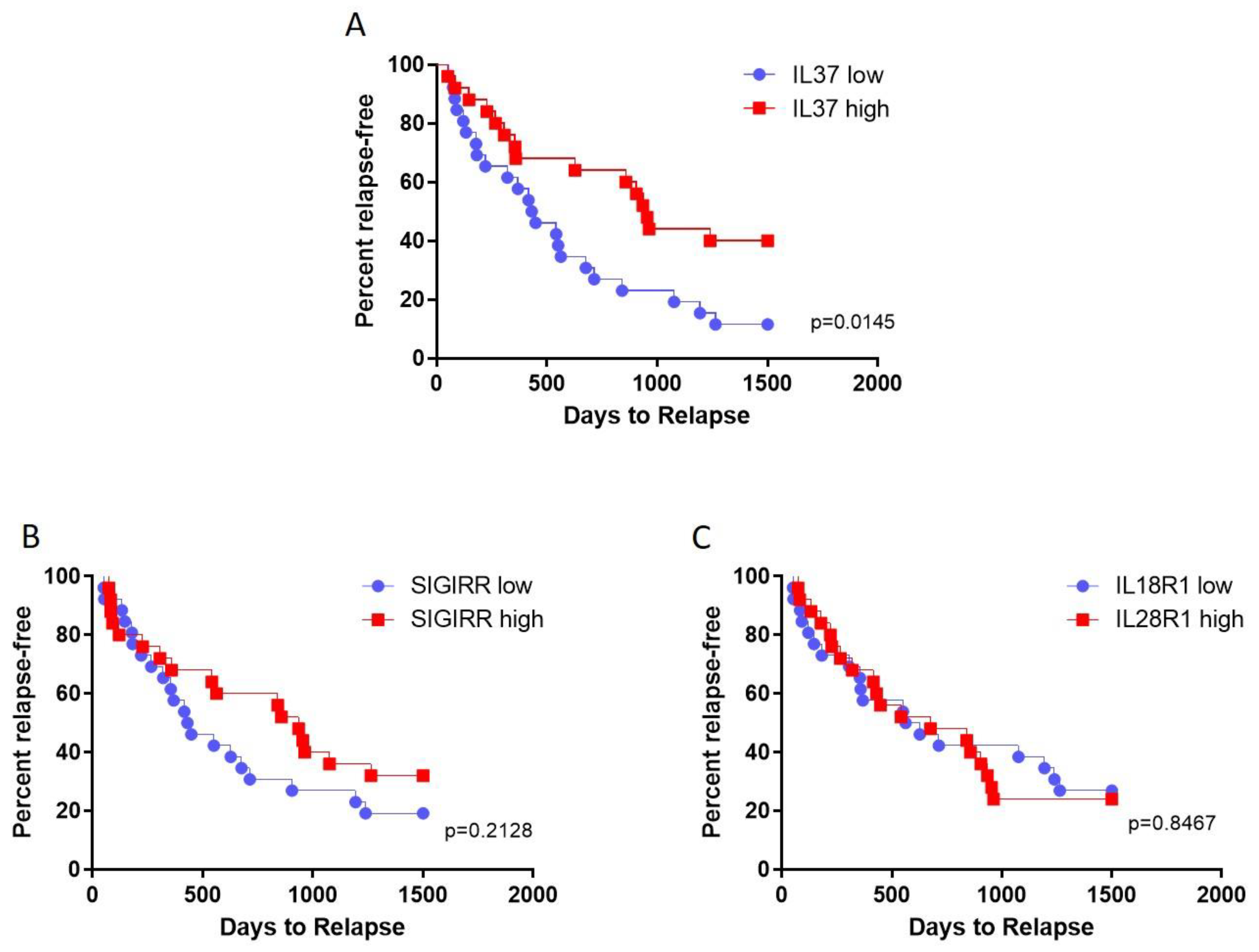
2.4. Prediction of Relapses by Transcription Levels of IL37 and Its Receptors
2.5. Analysis of IL37 in Sera from MS Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico Analysis: Microarray Selection
4.2. Patients
4.3. ELISA
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mammana, S.; Fagone, P.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.; Petralia, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The role of macrophages in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative pathways of alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis: Pathogenetic cellular effectors and potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, M.T.; Culpepper, W.J.; Nichols, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Gebrehiwot, T.T.; Hay, S.I.; Khalil, I.A.; Krohn, K.J.; Liang, X.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of multiple sclerosis 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, A.; Petralia, M.C.; Mangano, K.; Al-Abed, Y.; Bramati, P.; Nicoletti, F. Contribution of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor superfamily of cytokines in the pathogenesis of preclinical and human multiple sclerosis: In silico and in vivo evidences. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 322, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, G.; Meza-Romero, R.; Jordan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, H.; Kent, G.; Li, J.; Siu, E.; Frazer, J.; Piecychna, M.; et al. MIF and D-DT are potential disease severity modifiers in male MS subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8421–E8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Patti, F.; Cocuzza, C.; Zaccone, P.; Nicoletti, A.; Di Marco, R.; Reggio, A. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-12 in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 70, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comabella, M.; Balashov, K.; Issazadeh, S.; Smith, D.; Weiner, H.L.; Khoury, S.J. Elevated interleukin-12 in progressive multiple sclerosis correlates with disease activity and is normalized by pulse cyclophosphamide therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Di Marco, R.; Mangano, K.; Patti, F.; Reggio, E.; Nicoletti, A.; Bendtzen, K.; Reggio, A. Increased serum levels of interleukin-18 in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2001, 57, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, G.; Eruyar, E.; Mungan, S.Ö.; Ak, F.; Karahalil, B. The association of IL-18 gene promoter polymorphisms and the levels of serum IL-18 on the risk of multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 146, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Patti, F.; DiMarco, R.; Zaccone, P.; Nicoletti, A.; Meroni, P.; Reggio, A. Circulating serum levels of IL-1ra in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis are normal during remission phases but significantly increased either during exacerbations or in response to IFN-beta treatment. Cytokine 1996, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujmovic, I.; Mangano, K.; Pekmezovic, T.; Quattrocchi, C.; Mesaros, S.; Stojsavljevic, N.; Nicoletti, F.; Drulovic, J. The analysis of IL-1 beta and its naturally occurring inhibitors in multiple sclerosis: The elevation of IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 receptor type II after steroid therapy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 207, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Di Marco, R.; Patti, F.; Reggio, E.; Nicoletti, A.; Zaccone, P.; Stivala, F.; Meroni, P.L.; Reggio, A. Blood levels of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) are elevated in both relapsing remitting and chronic progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and are further augmented by treatment with interferon-beta 1b (IFN-beta1b). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 113, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, R.M.; Kaufman, M.; Balashov, K.E.; Ito, K.; Buyske, S.; Dhib-Jalbut, S. Predictive cytokine biomarkers of clinical response to glatiramer acetate therapy in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 300, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenova, A.G.; Slavov, G.S.; Manova, M.G.; Draganaova-Filipova, M.N.; Mateva, N.G.; Miteva, L.D.; Stanilova, S.A. Alterations in serum levels of IL-17 in contrast to TNF-alpha correspond to disease-modifying treatment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Song, F.; Fernandez-Escobar, A.; Luo, G.; Wang, J.-H.; Sun, Y. The properties of cytokines in multiple sclerosis: Pros and cons. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; McDonnell, P.C.; Lehr, R.; Tierney, L.; Tzimas, M.N.; Griswold, D.E.; Capper, E.A.; Tal-Singer, R.; Wells, G.I.; Doyle, M.L.; et al. Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin-1 family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10308–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, S.; Agrawal, D.K. Immunobiology of IL-37: Mechanism of action and clinical perspectives. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Quan, Y.; Yue, Y.; Heng, X.; Che, F. Interleukin-37: A crucial cytokine with multiple roles in disease and potentially clinical therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4711–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Role of interleukin-37 in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Iran. J. Immunol. 2018, 15, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold-Petry, C.A.; Lo, C.Y.; Rudloff, I.; Elgass, K.D.; Li, S.; Gantier, M.P.; Lotz-Havla, A.S.; Gersting, S.W.; Cho, S.X.; Lao, J.C.; et al. IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Rα and IL-1R8 (SIGIRR) to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, M.F.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Zepp, J.A.; Palmer, B.E.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, M.F.; Bulau, A.-M.; Rubartelli, A.; Bufler, P.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Fink, M.; Li, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Hong, J.; Mansell, A.; et al. Role of caspase-1 in nuclear translocation of IL-37, release of the cytokine, and IL-37 inhibition of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Interleukin-37 suppresses ICAM-1 expression in parallel with NF-κB down-regulation following TLR2 activation of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Neff, C.P.; Barber, K.; Hong, J.; Luo, Y.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; Fujita, M.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Extracellular forms of IL-37 inhibit innate inflammation in vitro and in vivo but require the IL-1 family decoy receptor IL-1R8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Jiang, B.; Deng, J.; Du, J.; Xiong, W.; Guan, Y.; Wen, Z.; Huang, K.; Huang, Z. IL-37 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing IL-17 and IL-17–triggering cytokine production and limiting th17 cell proliferation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5110–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Insights into IL-37, the role in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.X.; Chi, G.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ru, Y.X.; Luo, Z.L.; Yan, W.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, M.; et al. IL-37 suppresses the sustained hepatic IFN-γ/TNF-α production and T cell-dependent liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 69, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, K.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; et al. Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Huang, Z. Increased expression of IL-37 in patients with Graves’ disease and its contribution to suppression of proinflammatory cytokines production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Fan, X.; Wen, M.; Shen, Y.; Xi, X.; Men, R.; Yang, L. Comparison of concanavalin a-induced murine autoimmune hepatitis models. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Itoh, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Iimura, A.; Hayashi, S.; Takahashi, K.; Stivala, F.; Bendtzen, K.; Nicoletti, F. Proinflammatory effects of exogenously administered IL-10 in experimental autoimmune orchitis. Cytokine 2003, 22, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Zaccone, P.; Marco, R.D.; Magro, G.; Grasso, S.; Stivala, F.; Calori, G.; Mughini, L.; Meroni, P.L.; Garotta, G. Paradoxical antidiabetogenic effect of γ-interferon in DP-BB rats. Diabetes 1998, 47, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.D.; Tisch, R.; Singer, S.M.; Cao, Z.A.; Liblau, R.S.; Schreiber, R.D.; McDevitt, H.O. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. I. The early development of autoimmunity and the diabetogenic process. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi, M.; Rezaei, A.; Amani-Beni, A.; Etemadifar, M.; Kouchaki, E.; Zahedi, A. Increased serum level of IL-37 in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2015, 115, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Karami, M.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Correlation of serum levels of IL-33, IL-37, soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (vegfr2), and circulatory frequency of VEGFR2-expressing cells with multiple sclerosis severity. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 16, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Giacoppo, S.; Thangavelu, S.R.; Diomede, F.; Bramanti, P.; Conti, P.; Trubiani, O.; Mazzon, E. Anti-inflammatory effects of hypoxia-preconditioned human periodontal ligament cell secretome in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis: A key role of IL-37. Faseb J. 2017, 31, 5592–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Reale, M.; Costantini, E.; Di Nicola, M.; Porfilio, I.; de Andrés, C.; Fernández-Paredes, L.; Sánchez-Ramón, S.; Pasquali, L. Profiling of canonical and non-traditional cytokine levels in interferon-β-treated relapsing-remitting-multiple sclerosis patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemssen, T.; Medin, J.; Couto, C.A.M.; Mitchell, C.R. Multiple sclerosis in the real world: A systematic review of fingolimod as a case study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Nania, R.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulation of IL-1 receptor antagonist in a mouse model of migraine. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mangano, K.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulated expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor, its analogue D-dopachrome tautomerase, and the CD44 receptor in peripheral CD4 T cells from clinically isolated syndrome patients with rapid conversion to clinical defined multiple sclerosis. Medicina (B. Aires) 2019, 55, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Falzone, L.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Basile, M. Retrospective follow-up analysis of the transcriptomic patterns of cytokines, cytokine receptors and chemokines at preconception and during pregnancy, in women with post-partum depression. Exp. Med. 2019, 18, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Campo, G.; Corsico, F.; Presti, M.; Bramanti, P.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Modulation of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) expression in T cell-mediated immune responses and in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.S.; Bramanti, P.; Scalabrino, G.; Lange, A.; et al. Prevention of clinical and histological signs of MOG-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by prolonged treatment with recombinant human EGF. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 332, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Di Marco, R.; Spinasanta, F.; Basile, M.; Petralia, M.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Identification of CD4+ T cell biomarkers for predicting the response of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis to natalizumab treatment. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, K.; Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Basile, M.S.; Caltabiano, R.; Pesce, A.; Puleo, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Magro, G.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1/CO axis and therapeutic intervention with the CO-releasing molecule CORM-A1, in a murine model of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4156–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Caltabiano, R.; Russo, A.; Lupo, G.; Anfuso, C.D.; Basile, M.S.; Longo, A.; Nicoletti, F.; De Pasquale, R.; Libra, M.; et al. Identification of novel chemotherapeutic strategies for metastatic uveal melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Russo, A.; Longo, A.; Avitabile, T.; Nicoletti, F.; Reibaldi, M.; Basile, M.S. Characterization of the pathophysiological role of CD47 in uveal melanoma. Molecules 2019, 24, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.S.; Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Magro, G.; Salvatorelli, L.; Li Destri, G.; La Greca, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Puleo, S.; et al. KCNMA1 Expression is downregulated in colorectal cancer via epigenetic mechanisms. Cancers 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.S.; Mazzon, E.; Russo, A.; Mammana, S.; Longo, A.; Bonfiglio, V.; Fallico, M.; Caltabiano, R.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Differential modulation and prognostic values of immune-escape genes in uveal melanoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, S.; Lupo, G.; Pennisi, M.; Basile, M.; Anfuso, C.; Petralia, M.; Gattuso, G.; Vivarelli, S.; Spandidos, D.; Libra, M.; et al. The analysis of miRNA expression profiling datasets reveals inverse microRNA patterns in glioblastoma and Alzheimer’s disease. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Basile, M.S.; Lombardo, S.D.; Mangano, K.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its homologue d-dopachrome tautomerase as negative prognostic factor in neuroblastoma. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, M.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, A.; Colletti, G.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in glioblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, S.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.S.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; McCubrey, J.A.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in animal models of multiple sclerosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8263–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Presti, M.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Basile, M.S.; Libra, M.; Candido, S.; Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Prediction of PD-L1 expression in neuroblastoma via computational modeling. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, K.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Mammana, S.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F. Pathogenic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in glioblastoma and its targeting with specific inhibitors as novel tailored therapeutic approach. Oncotarget 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarević, M.; Mazzon, E.; Momčilović, M.; Basile, M.S.; Colletti, G.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Miljković, Đ. The H₂S donor GYY4137 stimulates reactive oxygen species generation in BV2 cells while suppressing the secretion of TNF and nitric oxide. Molecules 2018, 23, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Amaral, T.D.; Brosnan, C.F.; Lee, S.C. IFNs are critical regulators of IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 expression in human microglia. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, J.; Chitnis, T.; Ghezzi, A.; Pohl, D.; Brück, W.; Häring, D.A.; Karlsson, G.; Putzki, N. Relapse rate and MRI activity in young adult patients with multiple sclerosis: A post hoc analysis of phase 3 fingolimod trials. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2018, 4, 2055217318778610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürtüncü, M.; Yılmaz, V.; Akçay, H.İ.; Türkoğlu, R.; Altunrende, B.; Çınar, S.A.; Ulusoy, C.; Gündüz, T.; İçöz, S.; Kasap, M.; et al. Impact of fingolimod on CD4+ T cell subset and cytokine profile of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 337, 577065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 1996, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, S.; Eklund, D.; Gawel, D.R.; Köpsén, M.; Zhang, H.; Nestor, C.E.; Kockum, I.; Olsson, T.; Skogh, T.; Kastbom, A.; et al. Dynamic response genes in CD4+ T cells reveal a network of interactive proteins that classifies disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2928–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, J.W.; Agarwal, S.K.; Tan, F.K. Gene expression changes in multiple sclerosis relapse suggest activation of T and Non-T cells. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annibali, V.; Ristori, G.; Angelini, D.F.; Serafini, B.; Mechelli, R.; Cannoni, S.; Romano, S.; Paolillo, A.; Abderrahim, H.; Diamantini, A.; et al. CD161highCD8+T cells bear pathogenetic potential in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2011, 134, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, M.; Tuller, T.; Rubinstein, U.; Or-Bach, R.; Achiron, A. Prediction of acute multiple sclerosis relapses by transcription levels of peripheral blood cells. BMC Med. Genom. 2009, 2, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbin, F.; Zanoni, M.; Marangi, A.; Orlandi, R.; Crestani, L.; Benedetti, M.D.; Gajofatto, A. 2017 McDonald criteria for multiple sclerosis: Earlier diagnosis with reduced specificity? Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 29, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.; Cutter, G.; Lublin, F.; Schwid, S. The MS co-operative research (MS-CORE) group: An alternate approach to fostering multicenter studies. Mult. Scler. 2004, 10, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxburgh, R.H.S.R.; Seaman, S.R.; Masterman, T.; Hensiek, A.E.; Sawcer, S.J.; Vukusic, S.; Achiti, I.; Confavreux, C.; Coustans, M.; le Page, E.; et al. Multiple sclerosis severity score: Using disability and disease duration to rate disease severity. Neurology 2005, 64, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, B.A.C.; Hollenbach, J.A.; Bove, R.; Kirkish, G.; Sacco, S.; Caverzasi, E.; Bischof, A.; Gundel, T.; Zhu, A.H.; Papinutto, N.; et al. Silent progression in disease activity–free relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors upon reasonable request. |
| Variable | IL37 in Sera | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS Phenotypes | Proportion Detected * | Proportion Not Detected * | Level (pg/mL) Median, IQR | |
| CIS | 1/10 (10.0) | 9/10 (90.0) | 616.953 | |
| RR-MS | Stable | 8/95 (8.4) | 87/95 (91.6) | 613.349, 954.357 |
| Exacerbation | 11/26 (42.3) | 15/26 (57.7) | ||
| SP-MS | 2/8 (25.0) | 6/8 (75.0) | 60.451, 77.046 | |
| PP-MS | 0/14 (0.0) | 14/14 (100.0) | ||
| Total | 22/153 (14.4) | 131/153 (85.6) | ||
| Variable | Correlations | |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient (ρ) | P | |
| Gender | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Age | −0.609 | 0.047 |
| EDSS | −0.222 | 0.597 |
| Disease duration | −0.429 | 0.188 |
| MSSS | −0.733 | 0.039 |
| Treatment history | 0.107 | 0.755 |
| Variable | IL37 in Sera | |
|---|---|---|
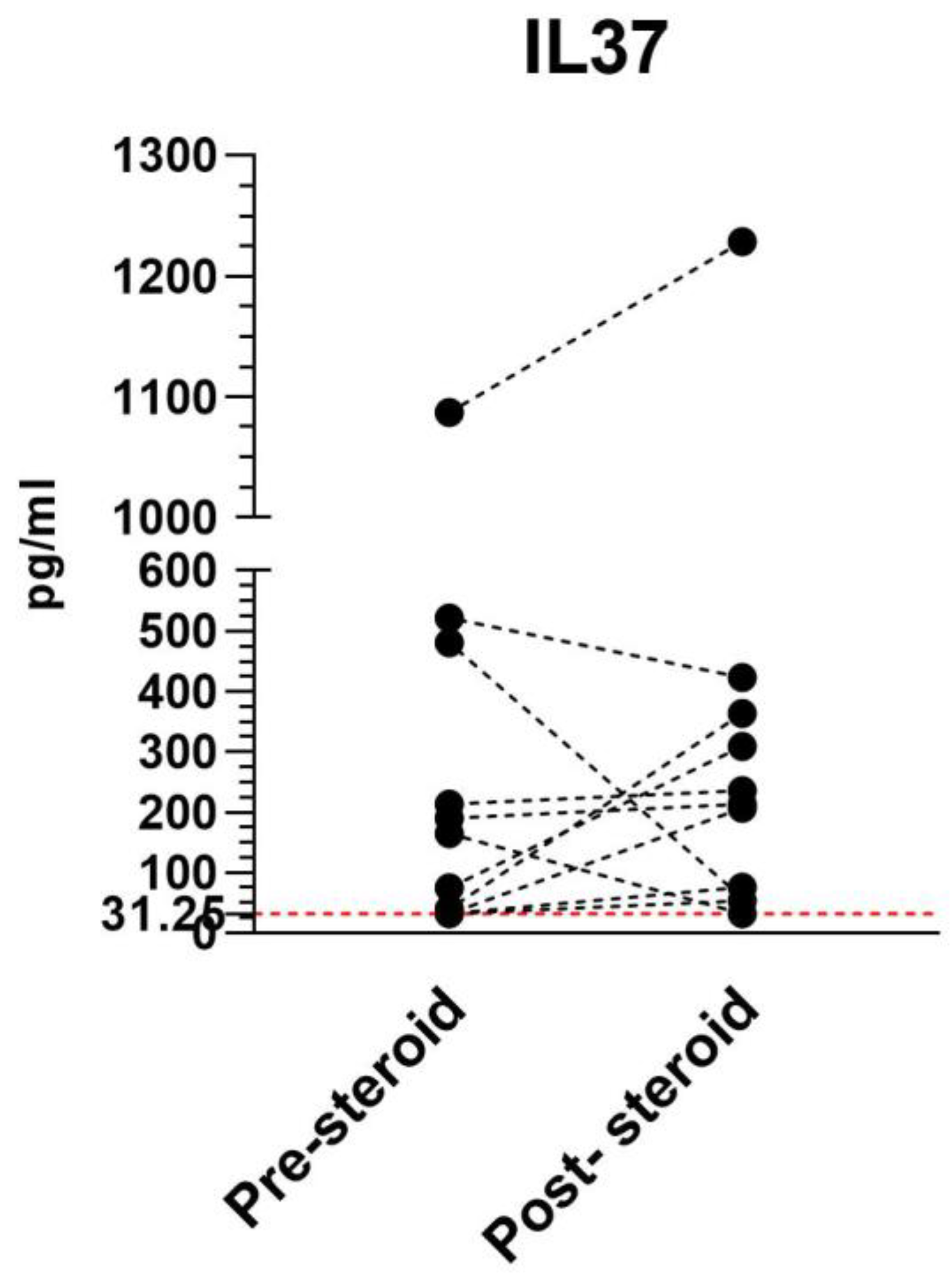
| Proportion Detected * | Level (pg/mL) Median, IQR | |
| Before steroids | 9/26 (34.6) | 119.331, 418.069 |
| After steroids | 11/26 (42.3) | 220.793, 389.109 |
| GSE78244 | GSE19224 | GSE16461 | GSE15245 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of MS patients | 14 | 14 | 4 twins | 51 |
| Number of healthy controls | 14 | - | 4 co-twins | - |
| Gender | All females | 9 females 5 males | 6 females 2 males | 35 females 16 males |
| Age of MS patients (years) | 39.9 ± 13 | - | 39.2 ± 4.5 | 38.5 ± 1.4 |
| Age of healthy controls (years) | 40.4 ± 8.9 | - | 39.2 ± 4.5 | - |
| MS phenotypes | RR-MS | RR-MS stable/relapse | 3 RR-MS1 SP | - |
| EDSS score | - | - | - | 2.4 ± 0.2 |
| Treatment history | None | 6 interferon 2 untreated 4 glatiramer acetate 2 untreated (relapse)/glatiramer (stable) | None | None |
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| Number | 129 |
| Gender * | |
| Male | 40 (31.0) |
| Female | 89 (69.0) |
| Age (years) | |
| Mean ± SD | 41.1 ± 10.1 |
| MS phenotypes * | |
| CIS | 10 (7.8) |
| RR-MS | 96 (74.3) |
| SP-MS | 9 (7.0) |
| PP-MS | 14 (10.9) |
| Disease duration (years) | |
| Mean ± SD | 11.1 ± 7.5 |
| EDSS score | |
| Median (range) | 2.5 (0.0–8.5) |
| MSSS | |
| Mean ± SD | 3.7 ± 2.3 |
| Treatment history | |
| No treatment | 48 (37.2) |
| Platform therapy | 59 (45.7) |
| High potency | 22 (17.1) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mammana, S.; Pennisi, M.; Fagone, P.; Kalfin, R.; Martinovic, V.; Ivanovic, J.; Andabaka, M.; et al. In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod. Molecules 2020, 25, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010020
Cavalli E, Mazzon E, Basile MS, Mammana S, Pennisi M, Fagone P, Kalfin R, Martinovic V, Ivanovic J, Andabaka M, et al. In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalli, Eugenio, Emanuela Mazzon, Maria Sofia Basile, Santa Mammana, Manuela Pennisi, Paolo Fagone, Reni Kalfin, Vanja Martinovic, Jovana Ivanovic, Marko Andabaka, and et al. 2020. "In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod" Molecules 25, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010020
APA StyleCavalli, E., Mazzon, E., Basile, M. S., Mammana, S., Pennisi, M., Fagone, P., Kalfin, R., Martinovic, V., Ivanovic, J., Andabaka, M., Mesaros, S., Pekmezovic, T., Drulovic, J., Nicoletti, F., & Petralia, M. C. (2020). In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod. Molecules, 25(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010020







