Preparation of Silicophosphate Alternating Hybrid Copolymers via Nonaqueous Acid-Base Reactions of Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(chlorosilane)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
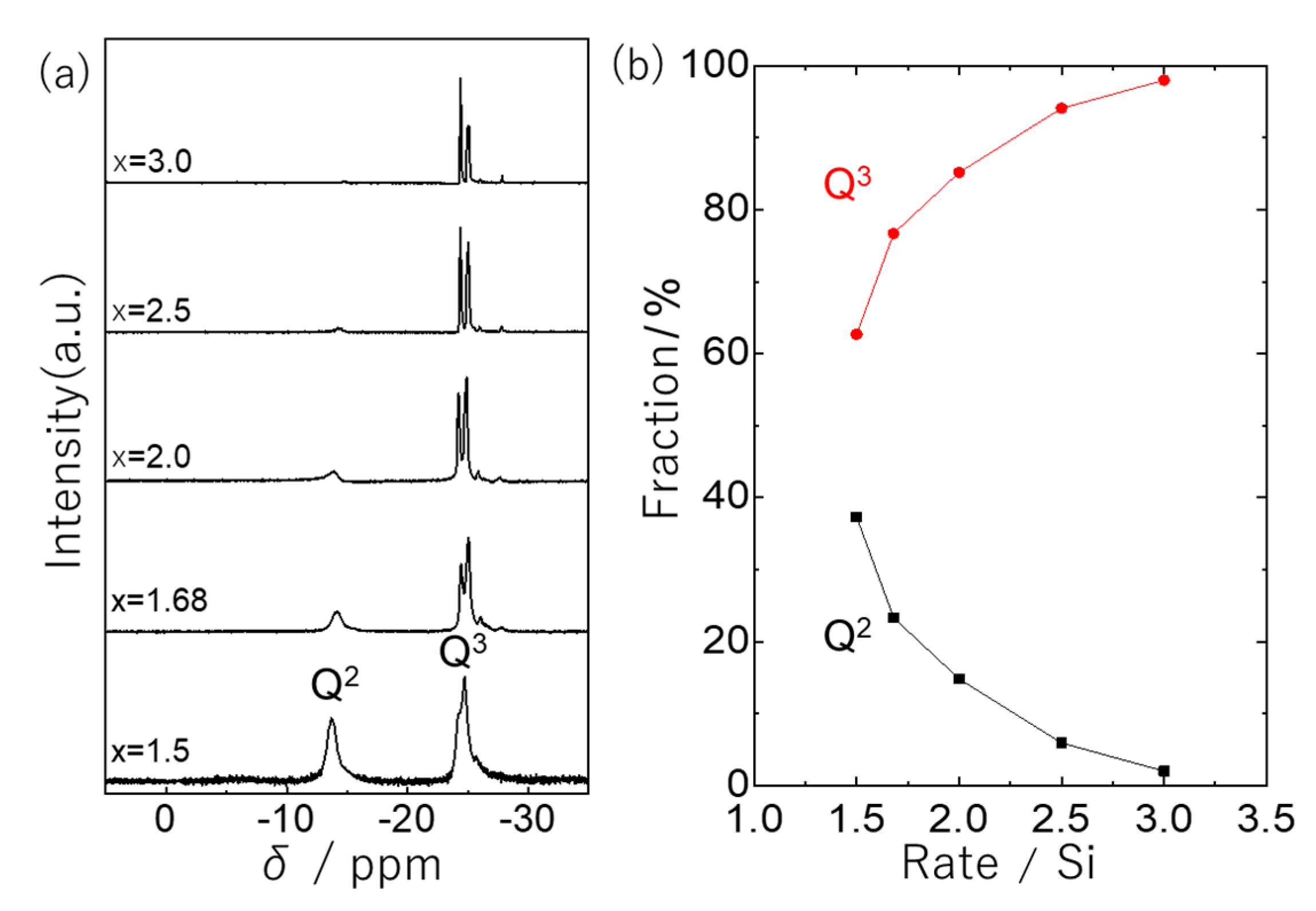
2.1. Reactivity between Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(Chlorosilane) and the Preparation of Silicophosphate Oligomers
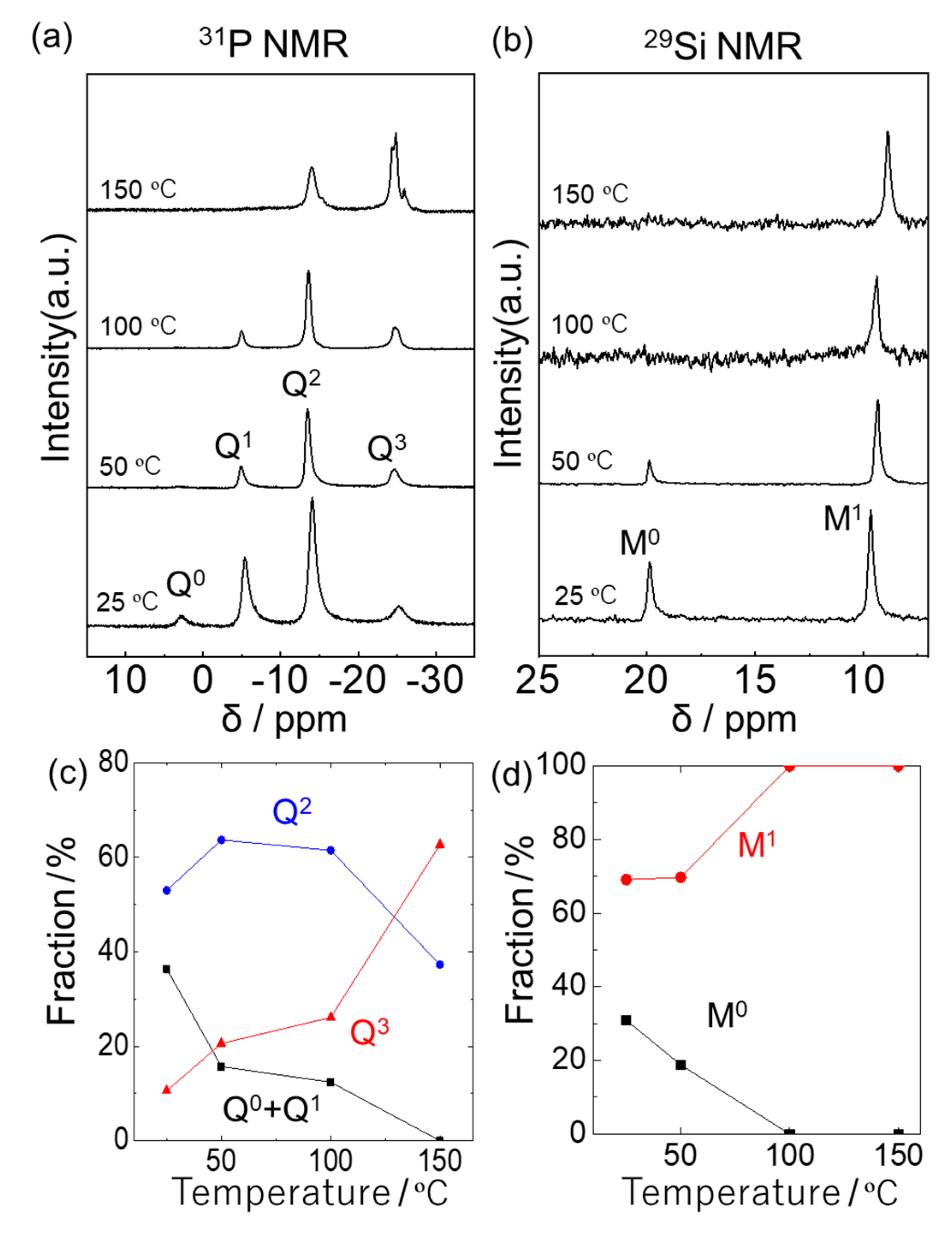
2.2. Silicophosphate Hybrid Network Formation from Phosphoric Acid and (C2H4)(Me2SiCl)2
2.3. Silicophosphate Hybrid Network Formation from Phosphoric Acid and (C6H4)(Me2SiCl)2
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schubert, U.; Huesing, N.; Lorenz, A. Hybrid Inorganic-Organic Materials by Sol-Gel Processing of Organofunctional Metal Alkoxides. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.A.; Shea, K.J. Bridged Polysilsesquioxanes. Highly Porous Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Materials. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wilkes, G.L. Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Network Materials by the Sol−Gel Approach. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottner, G. Hybrid Sol−Gel-Derived Polymers: Applications of Multifunctional Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutin, R.H.; Guerrero, G.; Vioux, A. Hybrid materials from organophosphorus coupling molecules. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buestrich, R.; Kahlenberg, F.; Popall, M.; Dannberg, P.; Müller-Fiedler, R.; Rösch, O. ORMOCER® s for optical interconnection technology. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2001, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zha, C.; Luther-Davies, B. Preparation and optical properties of titania-doped hybrid polymer via anhydrous sol–gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioux, A. Nonhydrolytic sol-gel routes to oxides. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, H.; Takahashi, M.; Uchino, T.; Yoko, T. Preparation and structure of organic–inorganic hybrid precursors for new type low-melting glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2002, 306, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, H.; Takahashi, M.; Uchino, T.; Yoko, T. Structure of organic–inorganic hybrid low-melting glasses from 29Si NMR and ab initio molecular orbital calculations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2002, 311, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, H.; Takahashi, M.; Uchino, T.; Yoko, T. Preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid precursors O = P(OSiMe3)x (OH)3−x for low-melting glasses. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 111, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mizuno, M.; Takahashi, M.; Tokuda, Y.; Yoko, T. Substituent effect on the formation of organically-modified silicate-phosphate alternating copolymer through nonaqueous acid–base reaction. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 44, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Niida, H.; Tokuda, Y.; Yoko, T. Organic-inorganic hybrid phosphite low-melting glasses for photonic applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 326, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M.; Takahashi, M.; Uchino, T.; Yoko, T. Organic-inorganic hybrid material of phenyl-modified polysilicophosphate prepared through nonaqueous acid–base reaction. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M.; Takahashi, M.; Yoko, T. Structure and water durability of tin(II) organosilicophosphate glasses prepared by nonaqueous acid–base reactions. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchida, H.; Takahashi, M.; Tokuda, Y.; Yoko, T. Rewritable holographic structures formed in organic-inorganic hybrid materials by photothermal processing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 19, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Guan, S.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasak, O. An ordered mesoporous organosilica hybrid material with a crystal-like wall structure. Nature 2002, 416, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.; Maas, R.G.M.; Reuter, A.; Kilgenstein, F.; Asfaha, Y.; Hänisch, C. Synthesis of heteroatomic bridged paracyclophanes. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Fang, M. A Zr metal–organic framework based on tetrakis (4-carboxyphenyl) silane and factors affecting the hydrothermal stability of Zr-MOFs. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Ko, N.; Go, Y.-B.; Aratani, N.; Choi, S.B.; Choi, E.; Yazaydin, A.Ö.; Snurr, R.Q.; O’Keeffe, M.; Kim, J.; et al. Ultrahigh porosity in metal–organic frameworks. Science 2010, 329, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.C.; Craig, G.A.; Larpent, P.; Guillerm, V.; Urayama, K.; Maspoch, D.; Furukawa, S. A Coordinative Solubilizer Method to Fabricate Soft Porous Materials from Insoluble Metal-Organic Polyhedra. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaugeois, Y.; De Jaeger, R.; Levalois-Mitjaville, J.; Mazzah, A.; Wörle, M.; Grützmacher, H. Synthesis and Structure of New Eight-Membered Si-O-λ5σ4-P Heterocycles. New J. Chem. 1998, 22, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugavel, R.; Prabusankar, G.; Walawalkar, M.G. Organic Soluble Silicophosphonate [RSi(OH){OP(O)(H)(OH)}]2O (R = (2,6-i-Pr2C6H3)NSiMe3): The First Silicophosphonate Containing Free Si−OH and P−OH Groups. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jähnigen, S.; Brendler, E.; Böhme, U.; Kroke, E. Synthesis of Silicophosphates Containing SiO6-Octahedra under Ambient Conditions—Reactions of Anhydrous H3PO4 with Alkoxysilanes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähnigen, S.; Böhme, U.; Kroke, E. Silicophosphates containing SiO6 octahedra—Anhydrous synthesis under ambient conditions. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styskalik, A.; Babiak, M.; Machac, P.; Relichova, B.; Pinkas, J. New adamantane-like silicophosphate cage and its reactivity towards tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styskalik, A.; Skoda, D.; Moravec, Z.; Babiak, M.; Barnes, C.E.; Pinkas, J. Control of Micro/mesoporosity in Non-Hydrolytic Hybrid Silicophosphate Xerogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Montgomery, J.A.; Stratmann, R.E., Jr.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 98, Revision A.11; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okada, K.; Takano, M.; Tokudome, Y.; Tokuda, Y.; Takahashi, M. Preparation of Silicophosphate Alternating Hybrid Copolymers via Nonaqueous Acid-Base Reactions of Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(chlorosilane). Molecules 2020, 25, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010127
Okada K, Takano M, Tokudome Y, Tokuda Y, Takahashi M. Preparation of Silicophosphate Alternating Hybrid Copolymers via Nonaqueous Acid-Base Reactions of Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(chlorosilane). Molecules. 2020; 25(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkada, Kenji, Masanari Takano, Yasuaki Tokudome, Yomei Tokuda, and Masahide Takahashi. 2020. "Preparation of Silicophosphate Alternating Hybrid Copolymers via Nonaqueous Acid-Base Reactions of Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(chlorosilane)" Molecules 25, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010127
APA StyleOkada, K., Takano, M., Tokudome, Y., Tokuda, Y., & Takahashi, M. (2020). Preparation of Silicophosphate Alternating Hybrid Copolymers via Nonaqueous Acid-Base Reactions of Phosphoric Acid and Organo-Bridged Bis(chlorosilane). Molecules, 25(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010127





