Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instruments and Characterization
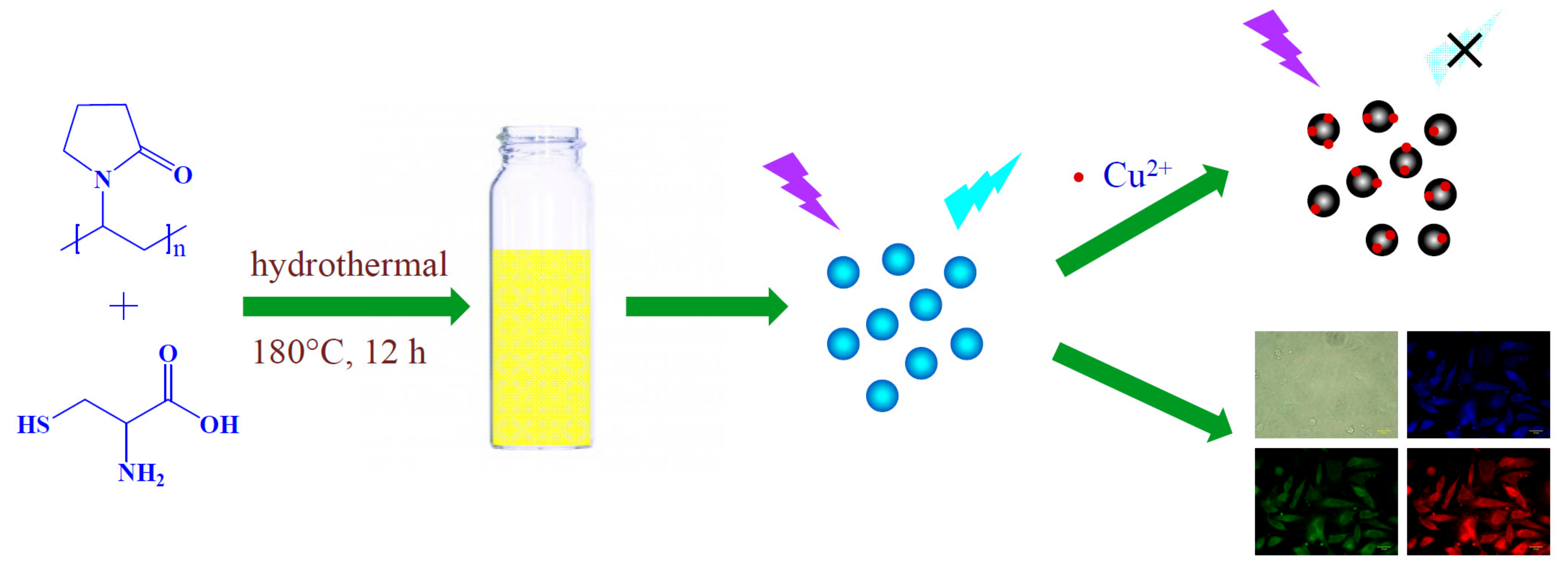
2.3. Synthesis of the CDs
2.4. Quantum Yield Calculation
2.5. Cu2+ Fluorescence Assay
2.6. Analysis of a real sample
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Cell Image Studies
3. Results
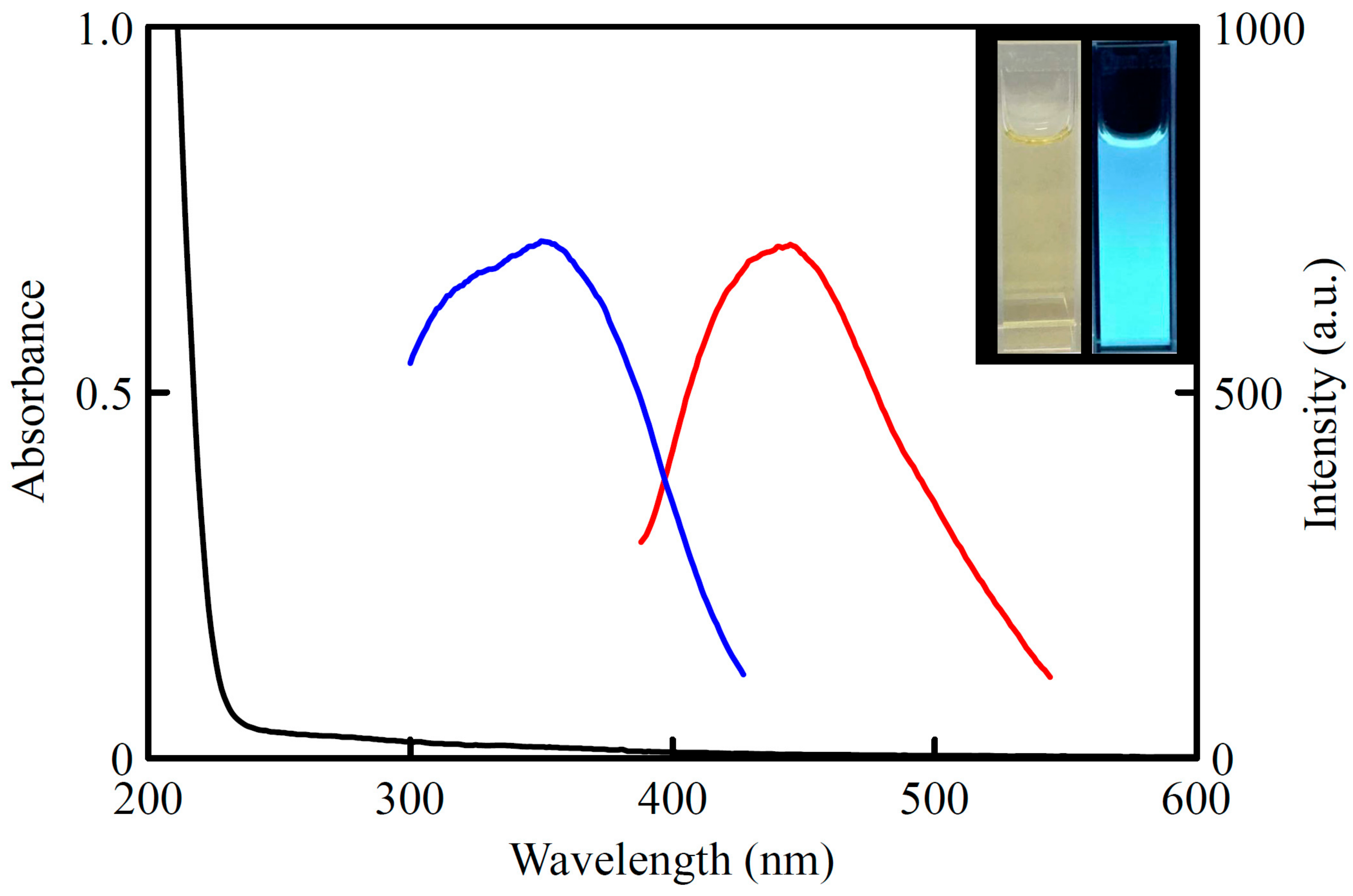
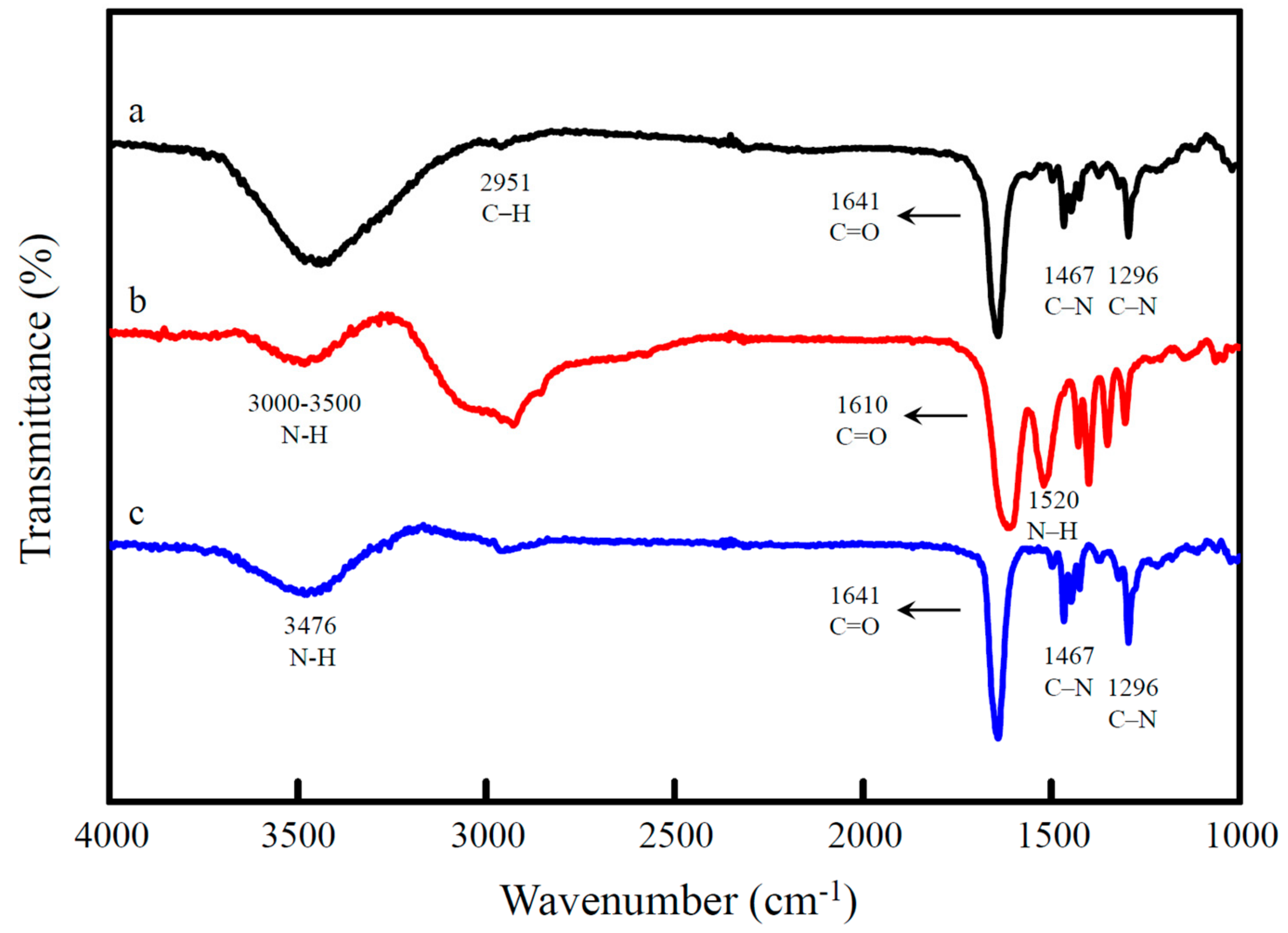
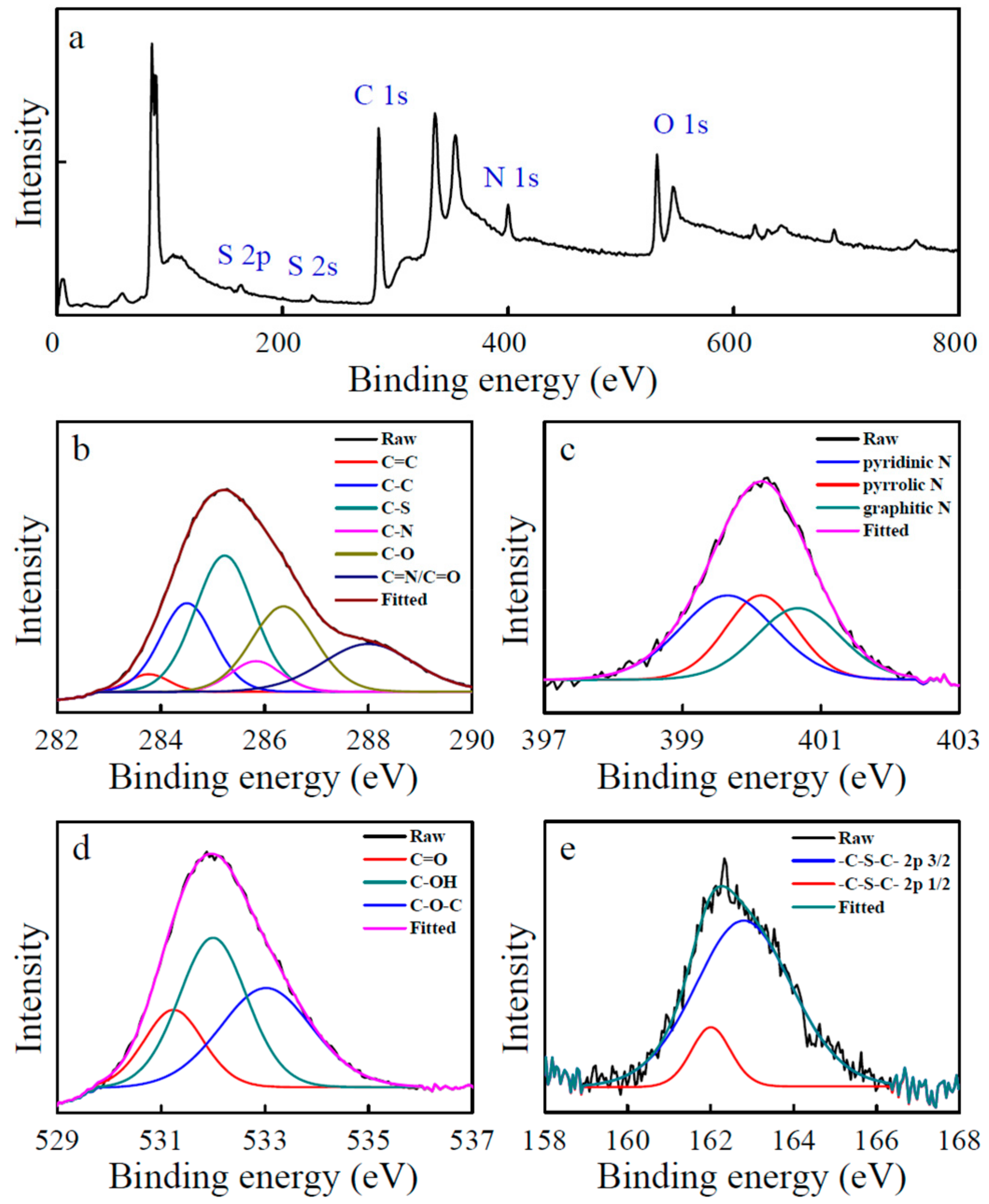
3.1. Characterization of the CDs
3.2. Fluorescence Stability of the CDs
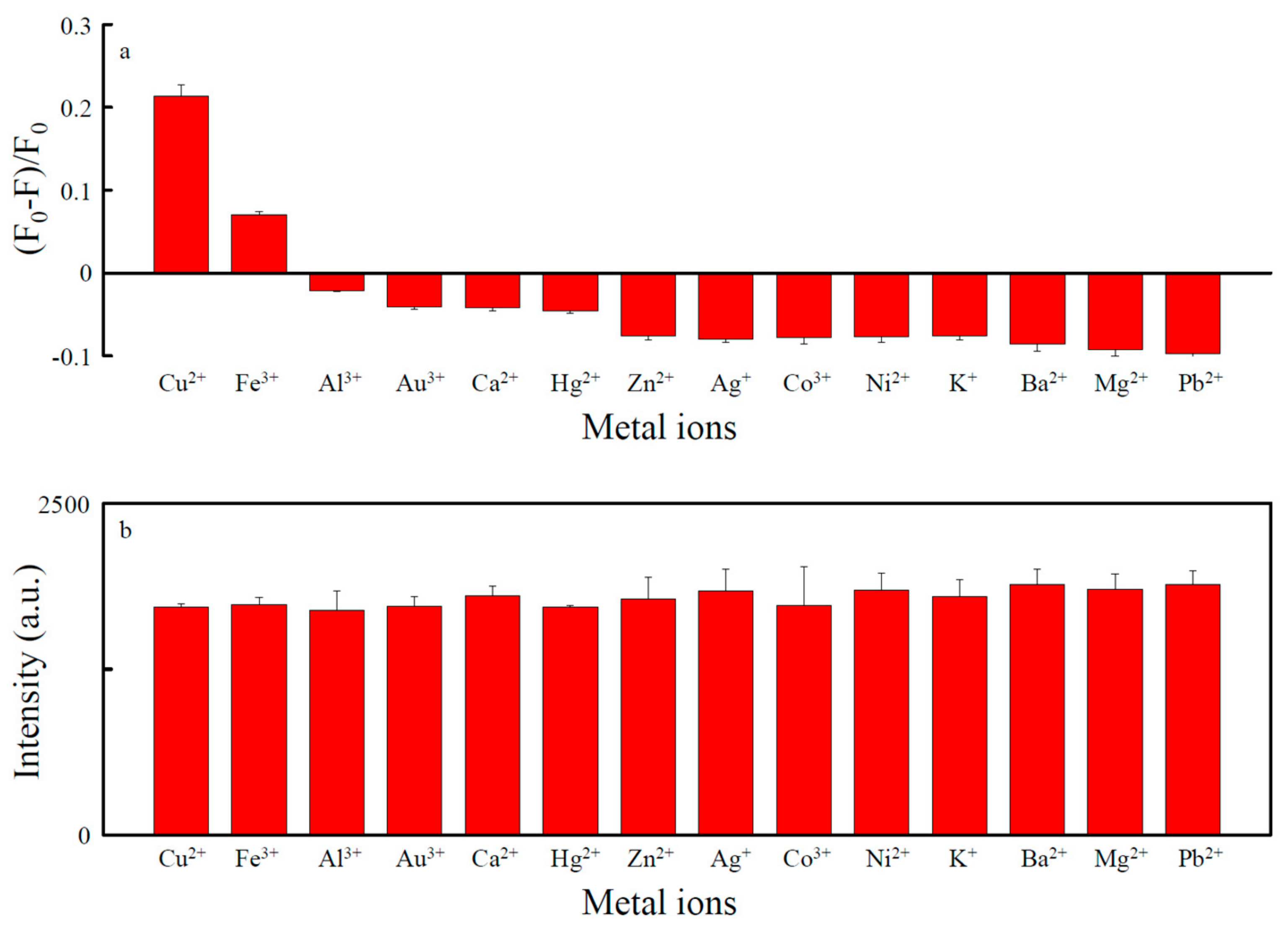
3.3. Detection of Cu2+
3.4. Detection of Cu2+ in a Water Sample
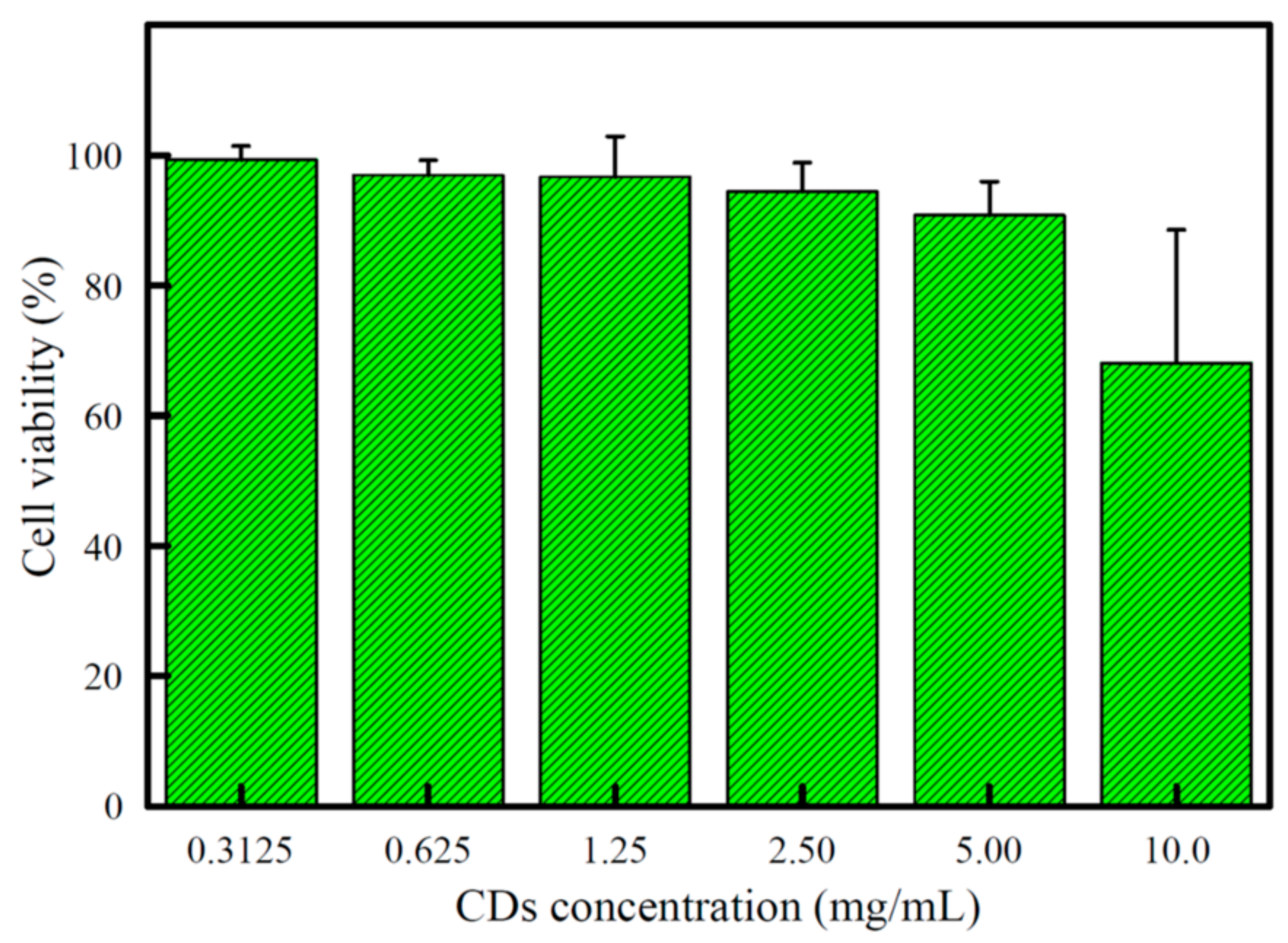
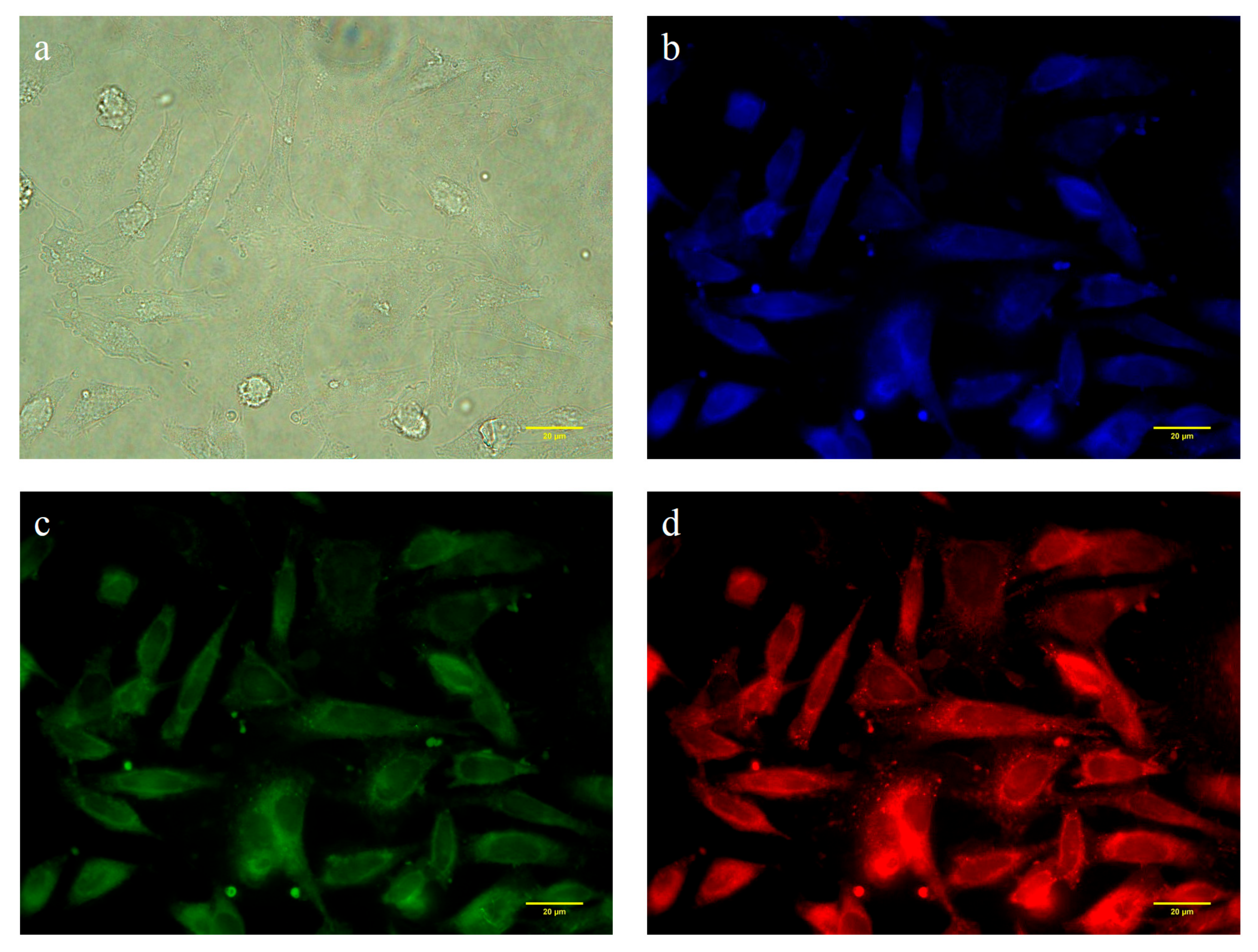
3.5. Cytotoxicity and Cell Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y. Fluorescent sensor based models for the detection of environmentally-related toxic heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gybina, A.A.; Prohaska, J.R. Intracellular copper transport in mammals. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, E.I.; Heppner, D.E.; Johnston, E.M.; Ginsbach, J.W.; Cirera, J.; Qayyum, M.; Kieber-Emmons, M.T.; Kjaergaard, C.H.; Hadt, R.G.; Tian, L. Copper active sites in biology. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3659–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaier, E.D.; Eipper, B.A.; Mains, R.E. Copper signaling in the mammalian nervous system: Synaptic effects. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, S.; Ralle, M. Opportunities in multidimensional trace metal imaging: Taking copper-associated disease research to the next level. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.; Dev, K.; Tanwar, R.S.; Selwal, K.K.; Tyagi, P.K. Copper mediated neurological disorder: Visions into amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer and Menkes disease. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 2015, 29, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadaş, C.; Kara, D. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of copper by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Sandron, S.; Townsend, A.T.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B. Determination of trace labile copper in environmental waters by magnetic nanoparticle solid phase extraction and high-performance chelation ion chromatography. Talanta 2015, 135, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liang, R.; Wang, F.; Ding, J.; Qin, W. An all-solid-state potentiometric microelectrode for detection of copper in coastal sediment pore water. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 279, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-H.; Gong, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhao, D.-Z. A turn-on fluorescent chemosensor for selective responses of copper(II) ion pairs. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5991–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, F.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, B.; Sun, H.; Du, L.; Tang, Y.; Cao, F. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescent sensor for detection of copper ions based on natural isorhamnetin from Ginkgo leaves. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 236, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, O.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Carbon dots: Bottom-up syntheses, properties, and light-harvesting applications. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, S.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Recent progress on the photocatalysis of carbon dots: Classification, mechanism and applications. Nano Today 2018, 19, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Umar, A.; Sood, S.; Mehta, S.K.; Kansal, S.K. Photoluminescent C-dots: An overview on the recent development in the synthesis, physiochemical properties and potential applications. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 748, 818–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots: Synthesis, formation mechanism, fluorescence origin and sensing applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleel, J.A.; Pramod, K. Artful and multifaceted applications of carbon dot in biomedicine. J. Control. Release 2018, 269, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Luo, Y.; Tsai, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Metal ions doped carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, physicochemical properties, and their applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Ghosh, A. Carbon dots: The next generation platform for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2019, 96, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, M.J. A review on nanostructured carbon quantum dots and their applications in biotechnology, sensors, and chemiluminescence. Talanta 2019, 196, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Yang, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z. Ratiometric fluorescent paper sensor utilizing hybrid carbon dots–quantum dots for the visual determination of copper ions. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5977–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, K.M. Highly passivated phosphorous and nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots and fluorometric assay for detection of copper ions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6331–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhamore, J.R.; Jha, S.; Park, T.J.; Kailasa, S.K. Fluorescence sensing of Cu2+ ion and imaging of fungal cell by ultra-small fluorescent carbon dots derived from Acacia concinna seeds. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 277, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Kumar, B.N.P.; Mahto, M.K.; Samanta, D.; Shaik, M.A.S.; Shaw, M.; Mandal, M.; Pathak, A. N-doped carbon dot as fluorescent probe for detection of cysteamine and multicolor cell imaging. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 286, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehvari, K.; Liu, K.Y.; Tseng, P.-J.; Gedda, G.; Girma, W.M.; Chang, J.-Y. Sonochemical-assisted green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from crab shell as targeted nanoprobes for cell imaging. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 2019, 95, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Ren, X.; Hou, Y. Hydrothermal growth of nitrogen-rich carbon dots as a precise multifunctional probe for both Fe3+ detection and cellular bio-imaging. Opt. Mater. 2019, 89, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. Dual functional N- and S-co-doped carbon dots as the sensor for temperature and Fe3+ ions. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2017, 242, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Deng, A. Fluorescent nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots from casein and their applications for sensitive detection of Hg2+ and biothiols and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2017, 964, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qin, J.; Feng, F. A novel highly fluorescent S, N, O co-doped carbon dots for biosensing and bioimaging of copper ions in live cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42246–42252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.X.-A. Fingerprint identification of copper ions with absorption and emission dual-mode responses by N,S co-doped red carbon dots. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Wei, J.; Liu, T.; Tang, F. Synthesis of ultra-stable fluorescent carbon dots from polyvinylpyrrolidone and their application in the detection of hydroxyl radicals. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Guo, H.; Jia, S. Facile and controllable synthesis of iron nanoparticles directed by montmorillonite and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-F.; Wang, J.-J.; Gan, L.; Han, X.-J.; Fan, H.-L.; Mei, L.-Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.-Q. Individual and simultaneous electrochemical detection toward heavy metal ions based on L-cysteine modified mesoporous MnFe2O4 nanocrystal clusters. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 721, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, B.; You, T. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of Hg(II) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Yan, F.; Luo, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L. Amphiphilic carbon dots for sensitive detection, intracellular imaging of Al3+. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2017, 953, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiga, M.; Cyriac, J. Understanding the photoluminescence mechanism of nitrogen-doped carbon dots by selective interaction with copper ions. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, R. Fluorescent chemosensors for Cu2+ ions: Fast, selective, and highly sensitive. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Sample | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake water | 10.0 | 10.2 | 102.0 | 6.2 |
| 50.0 | 45.7 | 91.4 | 3.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-W.; Lin, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-X.; Hu, C.-C.; Chiu, T.-C. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging. Molecules 2019, 24, 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091785
Huang S-W, Lin Y-F, Li Y-X, Hu C-C, Chiu T-C. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging. Molecules. 2019; 24(9):1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091785
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shu-Wei, Yu-Feng Lin, Yu-Xuan Li, Cho-Chun Hu, and Tai-Chia Chiu. 2019. "Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging" Molecules 24, no. 9: 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091785
APA StyleHuang, S.-W., Lin, Y.-F., Li, Y.-X., Hu, C.-C., & Chiu, T.-C. (2019). Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Selective and Sensitive Probes for Cupric Ions and Cell Imaging. Molecules, 24(9), 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091785






