Antiviral Activities of Silymarin and Derivatives
Abstract
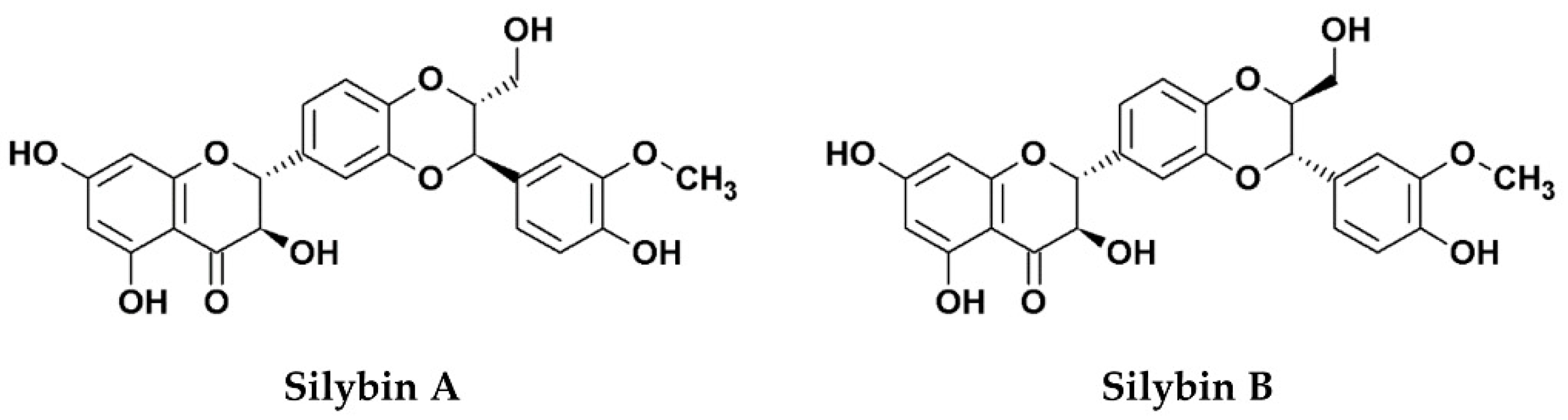
1. Silymarin, Its Components, and Derivatives
2. Antiviral Activity of Silymarin and Its Derivatives In Vitro, In Silico, and In Vivo
2.1. The Flaviviridae Family
2.1.1. Hepatitis C Virus
2.1.2. Dengue Virus
2.2. Influenza A Virus
2.3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus
2.4. The Togaviridae Family
2.5. Hepatitis B Virus
3. Antiviral Activity of Silymarin and Its Derivatives in Clinical Trials
3.1. Chronic Hepatitis C
3.2. Liver Transplantation in Hepatitis C
3.3. HIV/HCV Coinfection
4. Challenges to Clinical Application and the Need to Enhance Bioavailability
5. Prospects of Silymarin and Derivatives in Antiviral Development
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Loguercio, C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Jeon, Y. Silymarin/Silybin and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years. Molecules 2017, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N.; Kohli, K.; Ahmad, S.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Silymarin: A review of pharmacological aspects and bioavailability enhancement approaches. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2007, 39, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M. Silybin, a Major Bioactive Component of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)-Chemistry, Bioavailability, and Metabolism. Molecules 2017, 22, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strader, D.B.; Bacon, B.R.; Lindsay, K.L.; Brecque, D.R.; Morgan, T.; Wright, E.C.; Allen, J.; Khokar, M.F.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Seeff, L.B.; et al. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in patients with liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Silibinin-C-2′,3-dihydrogensuccinate, Disodium Salt for the Prevention of Recurrent Hepatitis C in Liver Transplant Recipients. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/orphan-designations/eu310828 (accessed on 23 March 2019).
- Alter, H.J.; Seeff, L.B. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: A perspective on long-term outcome. Semin. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, L.; Palacios, G.; Martinez, J.A.; Vázquez, A.; Savji, N.; De Ory, F.; Sanchez-Seco, M.P.; Martín, D.; Lipkin, W.I.; Tenorio, A. First report of sylvatic DENV-2-associated dengue hemorrhagic fever in West Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, S.J.; Morishima, C.; Shuhart, M.C.; Wang, C.C.; Liu, Y.; Lee, D.Y. Inhibition of T-Cell Inflammatory Cytokines, Hepatocyte NF-κB Signaling, and HCV Infection by Standardized Silymarin. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, C.; Lohmann, V.; Pal, S.; Liu, Y.; Polyak, S.J.; Lee, D.Y.W.; Graf, T.N.; Oberlies, N. Identification of hepatoprotective flavonolignans from silymarin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5995–5999. [Google Scholar]
- Wagoner, J.; Negash, A.; Kane, O.J.; Martinez, L.E.; Nahmias, Y.; Bourne, N.; Owen, D.M.; Grove, J.; Brimacombe, C.; McKeating, J.A.; et al. Multiple Effects of Silymarin on the Hepatitis C Virus Lifecycle. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed–Belkacem, A.; Ahnou, N.; Barbotte, L.; Wychowski, C.; Pallier, C.; Brillet, R.; Pohl, R.; Pawlotsky, J. Silibinin and Related Compounds Are Direct Inhibitors of Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaising, J.; Lévy, P.L.; Gondeau, C.; Phelip, C.; Varbanov, M.; Teissier, E.; Ruggiero, F.; Polyak, S.J.; Oberlies, N.H.; Ivanovic, T.; et al. Silibinin inhibits hepatitis C virus entry into hepatocytes by hindering clathrin-dependent trafficking. Cell. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1866–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser-Nobis, K.; Romero-Brey, I.; Ganten, T.M.; Gouttenoire, J.; Harak, C.; Klein, R.; Schemmer, P.; Binder, M.; Schnitzler, P.; Moradpour, D.; et al. Analysis of hepatitis C virus resistance to Silibinin in vitro and in vivo points to a novel mechanism involving nonstructural protein 4B. Hepatology 2013, 57, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Egger, D.; Lohmann, V.; Bartenschlager, R.; Blum, H.E.; Bienz, K.; Moradpour, D. Identification of the Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication Complex in Huh-7 Cells Harboring Subgenomic Replicons. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5487–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, W.C.; Chung, C.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Jassey, A.; Chang, S.P.; Tai, C.J.; Tai, C.J.; Shields, J.; et al. Highly bioavailable silibinin nanoparticles inhibit HCV infection. Gut 2017, 66, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, S.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Hayes, C.N.; Akamatsu, S.; Canini, L.; Perelson, A.S.; Pohl, R.T.; Persiani, S.; Uprichard, S.L. Hepatitis C virus dynamics and cellular gene expression in uPA-SCID chimeric mice with humanized livers during intravenous silibinin monotherapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagoner, J.; Morishima, C.; Graf, T.N.; Oberlies, N.H.; Teissier, E.; Pécheur, E.-I.; Tavis, J.E.; Polyak, S.J. Differential In Vitro Effects of Intravenous versus Oral Formulations of Silibinin on the HCV Life Cycle and Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaddir, I.; Rasool, N.; Hussain, W.; Mahmood, S. Computer-aided analysis of phytochemicals as potential dengue virus inhibitors based on molecular docking, ADMET and DFT studies. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2017, 54, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Continuing challenges in influenza. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1323, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; De Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gažák, R.; Purchartová, K.; Marhol, P.; Živná, L.; Sedmera, P.; Valentova, K.; Kato, N.; Matsumura, H.; Kaihatsu, K.; Křen, V. Antioxidant and antiviral activities of silybin fatty acid conjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choi, H. Silymarin efficacy against influenza A virus replication. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.-P.; Wu, L.-Q.; Li, R.; Zhao, X.-F.; Wan, Q.-Y.; Chen, X.-X.; Li, W.-Z.; Wang, G.-F.; Li, K.-S. Identification of 23-(S)-2-Amino-3-Phenylpropanoyl-Silybin as an Antiviral Agent for Influenza A Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4433–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J. Tissue distribution of silibinin, the major active constituent of silymarin, in mice and its association with enhancement of phase II enzymes: Implications in cancer chemoprevention. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, B.; Hall, W.W. Cellular and molecular interactions in coinfection with hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2008, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.; Lovelace, E.S.; Elahi, S.; Maurice, N.J.; Wagoner, J.; Dragavon, J.; Mittler, J.E.; Kraft, Z.; Stamatatos, L.; Horton, H.; et al. Correction: Silibinin Inhibits HIV-1 Infection by Reducing Cellular Activation and Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 41832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.; Margineantu, D.H.; Sweet, I.R.; Polyak, S.J. Inhibition of HIV by Legalon-SIL is independent of its effect on cellular metabolism. Virology 2014, 449, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lani, R.; Hassandarvish, P.; Chiam, C.W.; Moghaddam, E.; Chu, J.J.H.; Rausalu, K.; Merits, A.; Higgs, S.; VanLandingham, D.; Abu Bakar, S.; et al. Antiviral activity of silymarin against chikungunya virus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camini, F.C.; Da Silva, T.F.; Caetano, C.C.D.S.; Almeida, L.T.; Ferraz, A.C.; Vitoreti, V.M.A.; Silva, B.D.M.; Silva, S.D.Q.; De Magalhães, J.C.; Magalhães, C.L.D.B. Antiviral activity of silymarin against Mayaro virus and protective effect in virus-induced oxidative stress. Antivir. Res. 2018, 158, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.; Lee, S.; Ventura, W.R.; McMenamin, J. Knowledge, Awareness, and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Among Korean American Parents. J. Immigr. Minor. Heal. 2017, 20, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umetsu, T.; Inoue, J.; Kogure, T.; Kakazu, E.; Ninomiya, M.; Iwata, T.; Takai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Sano, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Inhibitory effect of silibinin on hepatitis B virus entry. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Fu, S.-L.; Kao, C.-H.; Yang, C.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, M.-T.; Tsai, T.-F. Chemopreventive Effect of Silymarin on Liver Pathology in HBV X Protein Transgenic Mice. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tanamly, M.; Tadros, F.; Labeeb, S.; Makld, H.; Mikhail, N.; Abdel-Hamid, M.; Shehata, M.; Abu-Baki, L.; Medhat, A.; Magder, L.; et al. Randomised double-blinded trial evaluating silymarin for chronic hepatitis C in an Egyptian village: Study description and 12-month results. Dig. Liver Dis. 2004, 36, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay, E.; Zigmond, E.; Pappo, O.; Hemed, N.; Rowe, M.; Zabrecky, G.; Cohen, R.; Ilan, Y. Antioxidant therapy for chronic hepatitis C after failure of interferon: Results of phase II randomized, double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5317–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, M.W.; Navarro, V.J.; Afdhal, N.; Belle, S.H.; Wahed, A.S.; Hawke, R.L.; Doo, E.; Meyers, C.M.; Reddy, K.R.; Silymarin, N.; et al. Effect of silymarin (milk thistle) on liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C unsuccessfully treated with interferon therapy: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Motta, M.; Vacante, M.; Malaguarnera, G.; Caraci, F.; Nunnari, G.; Gagliano, C.; Greco, C.; Chisari, G.; Drago, F.; et al. Silybin-vitamin E-phospholipids complex reduces liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Bertino, G.; Chisari, G.; Motta, M.; Vecchio, M.; Vacante, M.; Caraci, F.; Greco, C.; Drago, F.; Nunnari, G.; et al. Silybin supplementation during HCV therapy with pegylated interferon-α plus ribavirin reduces depression and anxiety and increases work ability. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Festi, D.; Loguercio, C. Silybin and the liver: From basic research to clinical practice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenci, P.; Scherzer, T.M.; Kerschner, H.; Rutter, K.; Beinhardt, S.; Hofer, H.; Schöniger–Hekele, M.; Holzmann, H.; Steindl–Munda, P. Silibinin is a potent antiviral agent in patients with chronic hepatitis C not responding to pegylated interferon/ribavirin therapy. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedj, J.; Dahari, H.; Pohl, R.-T.; Ferenci, P.; Perelson, A.S. Understanding silibinin’s modes of action against HCV using viral kinetic modeling. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermer, M.; Berg, T. Rapid Suppression of Hepatitis C Viremia Induced by Intravenous Silibinin Plus Ribavirin. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, K.; Scherzer, T.-M.; Beinhardt, S.; Kerschner, H.; Stättermayer, A.F.; Hofer, H.; Popow-Kraupp, T.; Steindl-Munda, P.; Ferenci, P. Intravenous silibinin as ‘rescue treatment’ for on-treatment non-responders to pegylated interferon/ribavirin combination therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermer, M.; Schlosser, B.; Fülöp, B.; van Bömmel, F.; Brodzinski, A.; Heyne, R.; Keller, K.; Sarrazin, C.; Berg, T. High-dose silibinin rescue treatment for HCV-infected patients showing suboptimal virologic response to standard combination therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2012, 19, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahari, H.; Shteingart, S.; Gafanovich, I.; Cotler, S.J.; D’Amato, M.; Pohl, R.T.; Weiss, G.; Ashkenazi, Y.J.; Tichler, T.; Goldin, E.; et al. Sustained virological response with intravenous silibinin: Individualized IFN-free therapy via real-time modelling of HCV kinetics. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verna, E.C.; Brown, R.S., Jr. Hepatitis C Virus Infection in Liver Transplant Candidates and Recipients. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/hepatitis-c-virus-infection-in-liver-transplant-candidates-and-recipients (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Neumann, U.; Biermer, M.; Eurich, D.; Neuhaus, P.; Berg, T. Successful prevention of hepatitis C virus (HCV) liver graft reinfection by silibinin mono-therapy. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 951–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinhardt, S.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Scherzer, T.M.; Ferenci, P. Silibinin monotherapy prevents graft infection after orthotopic liver transplantation in a patient with chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurich, D.; Bahra, M.; Berg, T.; Boas-Knoop, S.; Biermer, M.; Neuhaus, R.; Neuhaus, P.; Neumann, U. Treatment of hepatitis C-virus-reinfection after liver transplant with silibinin in nonresponders to pegylated interferon-based therapy. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aghemo, A.; Bhoori, S.; De Nicola, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Colombo, M. Failure of Intravenous Silibinin Monotherapy to Prevent Hepatitis C Genotype 2A Liver Graft Reinfection. Hepat. Mon. 2012, 12, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapstein, J.; Wörns, A.M.; Galle, P.R.; Zimmermann, T. Combination therapy with silibinin, pegylated interferon and ribavirin in a patient with hepatitis C virus genotype 3 reinfection after liver transplantation: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, Z.; Crespo, G.; D’Amato, M.; Brambilla, N.; Giacovelli, G.; Rovati, L.; Costa, J.; Navasa, M.; Forns, X. Intravenous silibinin monotherapy shows significant antiviral activity in HCV-infected patients in the peri-transplantation period. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendina, M.; D’Amato, M.; Castellaneta, A.; Castellaneta, N.M.; Brambilla, N.; Giacovelli, G.; Rovati, L.; Rizzi, S.F.; Zappimbulso, M.; Bringiotti, R.S.; et al. Antiviral activity and safety profile of silibinin in HCV patients with advanced fibrosis after liver transplantation: A randomized clinical trial. Transpl. Int. 2014, 27, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, R.; Moreno, A.; Rodriguez-Gandia, M.A.; Albillos, A.; Arocena, C.; Blesa, C.; García-Hoz, F.; Graus, J.; Nuño, J.; López-Hervás, P.; et al. Safety and anti-HCV effect of prolonged intravenous silibinin in HCV genotype 1 subjects in the immediate liver transplant period. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, I.; Wu, G.Y.; Maier, G.Y.W.I. Hepatitis C and HIV co-infection: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, E.G. Update in HIV/HCV Co-Infection in the Direct Acting Antiviral Era. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payer, B.; Reiberger, T.; Rutter, K.; Beinhardt, S.; Staettermayer, A.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Ferenci, P. Successful HCV eradication and inhibition of HIV replication by intravenous silibinin in an HIV–HCV coinfected patient. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.; Rauch, A.; Durisch, N.; Eberhard, N.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Ledergerber, B.; Metzner, K.J.; Böni, J.; Weber, R.; Fehr, J. Efficacy of lead-in silibinin and subsequent triple therapy in difficult-to-treat HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients. HIV Med. 2014, 15, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.L.; Rauch, A.; Aouri, M.; Durisch, N.; Eberhard, N.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Ledergerber, B.; Müllhaupt, B.; Metzner, K.J.; Decosterd, L.; et al. A Lead-In with Silibinin Prior to Triple-Therapy Translates into Favorable Treatment Outcomes in Difficult-To-Treat HIV/Hepatitis C Coinfected Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.S.; Kim, T.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Chi, S.-C. Formulation and biopharmaceutical evaluation of silymarin using SMEDDS. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2007, 30, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-W.; Lin, L.-C.; Hung, S.-C.; Chi, C.-W.; Tsai, T.-H. Analysis of silibinin in rat plasma and bile for hepatobiliary excretion and oral bioavailability application. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-W.; Lin, L.-C.; Tsai, T.-H. Drug–drug interactions of silymarin on the perspective of pharmacokinetics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 121, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, R.; Mascher, H.; Birkmayer, J. Study on dose-linearity of the pharmacokinetics of silibinin diastereomers using a new stereospecific assay. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 1992, 30, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, P.; Head, K. A review of the bioavailability and clinical efficacy of milk thistle phytosome: A silybin-phosphatidylcholine complex (Siliphos). Altern. Med. A J. Clin. Ther. 2005, 10, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Voinovich, D.; Perissutti, B.; Grassi, M.; Passerini, N.; Bigotto, A. Solid State Mechanochemical Activation of Silybum marianum Dry Extract with Betacyclodextrins: Characterization and Bioavailability of the Coground Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4119–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosina, P.; Kren, V.; Gebhardt, R.; Grambal, F.; Ulrichova, J.; Walterova, D. Antioxidant properties of silybin glycosides. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16 (Suppl. 1), S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, L.; Silva, M.; Manso, C. Scavenging of reactive oxygen species by silibinin dihemisuccinate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, H.; Agarwal, R.; Patil, C.; Katare, O.P. Preparation and pharmacological evaluation of silibinin liposomes. Arzneimittelforschung 2003, 53, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Rai, A.; Reddy, N.D.; Raj, P.V.; Jain, P.; Deshpande, P.; Mathew, G.; Kutty, N.G.; Udupa, N.; Rao, C.M. Silymarin liposomes improves oral bioavailability of silybin besides targeting hepatocytes, and immune cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.-Q.; Hu, J.-H. Improvement of the Dissolution Rate of Silymarin by Means of Solid Dispersions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2004, 52, 972–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.-F.; Jia, W.; Li, S.-S.; Xu, Z.-H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.-R.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Xie, G.-X. A new silymarin preparation based on solid dispersion technique. Adv. Ther. 2005, 22, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Development of Silymarin Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Que, L. Enhanced bioavailability of silymarin by self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, R.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J.; Ahuja, A.; Ahmad, S. Stability studies of silymarin nanoemulsion containing Tween 80 as a surfactant. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Duan, C.; Jia, L.; Feng, F.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q. In vitroandin vivoevaluation of silybin nanosuspensions for oral and intravenous delivery. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 155104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-C.; Ng, L.-T.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, L.-T.; Yen, F.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Huang, L.-T. Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Silymarin Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, S.J.; Ferenci, P.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Hepatoprotective and antiviral functions of silymarin components in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Virus | Substrate(s) | Method(s) | Suggested Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis C virus (HCV) | Silymarin extract (MK-001) | Western blot and RT-PCR | Potentiation of the JAK-STAT antiviral signaling pathway | [8] |
| Silymarin and its-derived pure compounds | NS5B polymerase assay, luciferase reporter assay | Inhibition of HCV infection and the HCV-induced oxidative stress, as well as, the NS5B RdRp activity, NF-κB-dependent transcription, and T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated proliferation | [9] | |
| Silymarin | NS5B polymerase assay, luciferase reporter assay, qPCR, and western blot | Inhibition of NS5B polymerase activity and blocking viral entry and transmission | [10] | |
| Silybin A, silybin B, and Legalon® SIL | RdRp Enzyme Assay, qPCR and luciferase reporter activity | Inhibition of the NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | [11] | |
| Silibinin and Legalon® SIL | HCV entry assay | Silibinin impeded HCV endosomal trafficking and blocked CME | [12] | |
| Silibinin | RT-PCR and luciferase reporter assay | Inhibition of HCV NS4B and hence the membranous web morphogenesis | [13] | |
| Silibinin nanoparticles | HCV entry assays and pharmacokinetic studies | Inhibition of HCV cell-to-cell spread and attenuation of HCV infection of PHHs | [15] | |
| Dengue virus (DENV) | Silymarin | Docking to NS4B | All three silymarin derivatives docked with high binding affinity (≥−8 kal/mol) to DENV NS4B | [18] |
| Influenza A virus (IAV) | Silymarin | CPE reduction method | Inhibition of late viral RNA synthesis | [22] |
| Silybin and amino acid derivatives (S0-S5) | CPE reduction method and plaque assay | S0 and S3 inhibited IAV replication and disrupted the formation of the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16L complex | [23] | |
| Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) | Legalon® SIL | HIV replication in TZM-bl cells, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and CEM | Attenuating cellular functions involved in T-cell activation, proliferation, and HIV infection | [26] |
| Silibinin and Legalon® SIL | HIV infection of PBMCs and CEM cells with respect to cell growth, ATP content, and metabolism | Perturbation of T-cell metabolism in vitro; Legalon® SIL additionally blocked HIV infection of T-cells | [27] | |
| Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) | Silymarin | CPE inhibition assay, RT-PCR and Western blot | Inhibition of CHIKV replication and proteinsynthesis | [28] |
| Mayaro virus (MAYV) | Silymarin | CPE inhibition, viral replication and plaque reduction assays in HepG2 cells | Inhibition of replication and ROS induction | [29] |
| Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) | Silibinin | HBV entry assay | Blockade of clathrin-mediated endocytosis | [31] |
| Virus | Substrate(s) | Analysis/Model | Route of Administration | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCV | Legalon® SIL | HCV infection of uPA-SCID-chimeric mice with humanized livers | Intravenous | Legalon® SIL blocked HCV production and increased anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative gene expressions without affecting serum albumin levels | [16] |
| IAV | Silybin derivatives (S0 and S3) | IAV infection of BALB/c mice | Oral | S0 and S3 increased the survival rate of mice (40% and 60% respectively), and S3 decreased virus titers in the lungs (100-fold) | [23] |
| HBV | Silymarin | HBV X protein (HBx) transgenic mice | Oral | Silymarin had no effect on HBx expression and late stage carcinogenesis, but recovered fatty acid change and liver pathology in the early stages of liver damage | [32] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-H.; Jassey, A.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Lin, L.-T. Antiviral Activities of Silymarin and Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081552
Liu C-H, Jassey A, Hsu H-Y, Lin L-T. Antiviral Activities of Silymarin and Derivatives. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ching-Hsuan, Alagie Jassey, Hsin-Ya Hsu, and Liang-Tzung Lin. 2019. "Antiviral Activities of Silymarin and Derivatives" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081552
APA StyleLiu, C.-H., Jassey, A., Hsu, H.-Y., & Lin, L.-T. (2019). Antiviral Activities of Silymarin and Derivatives. Molecules, 24(8), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081552





