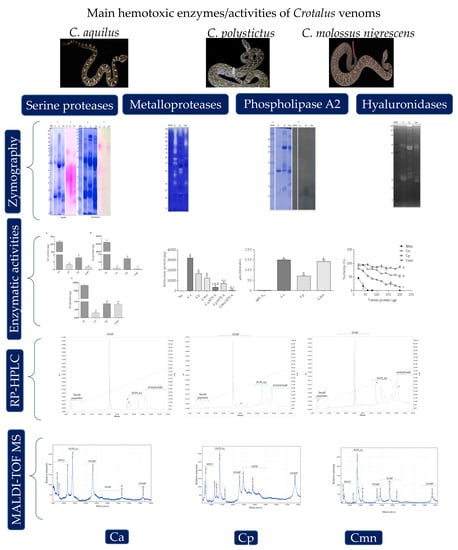
Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
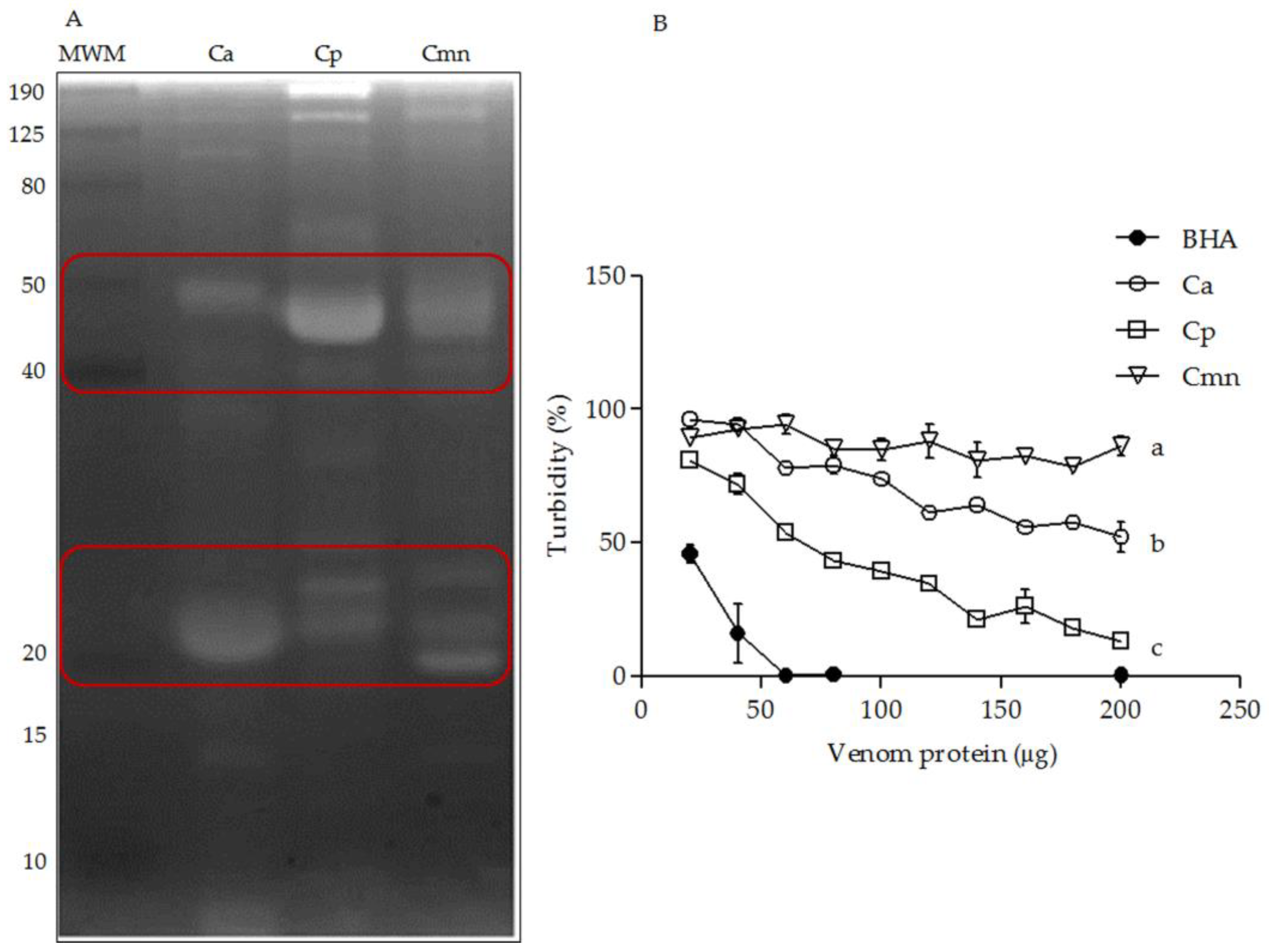
2.1. SDS-PAGE Protein Banding Pattern
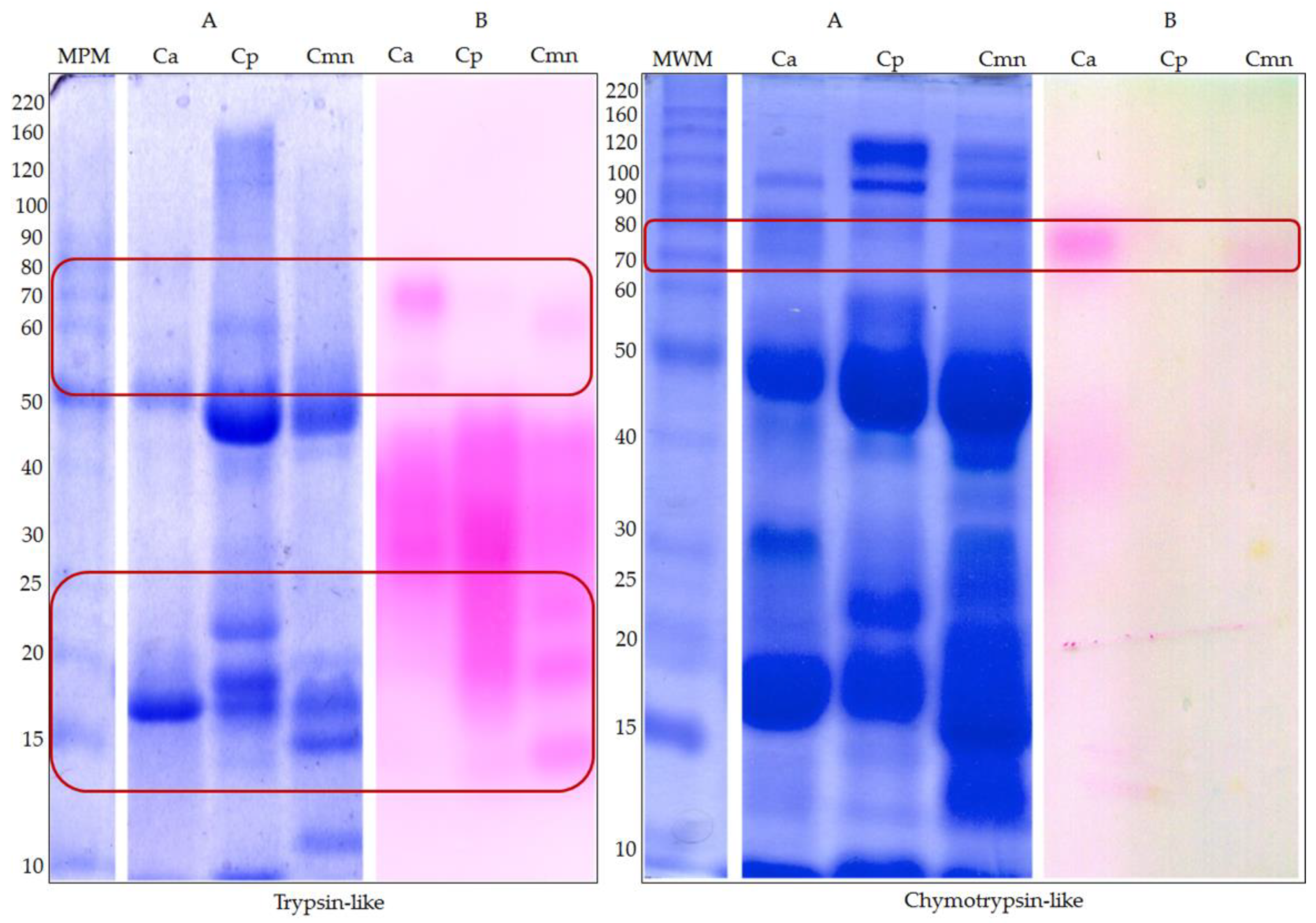
2.2. Zymography and Enzymatic Activities for Serine Proteases
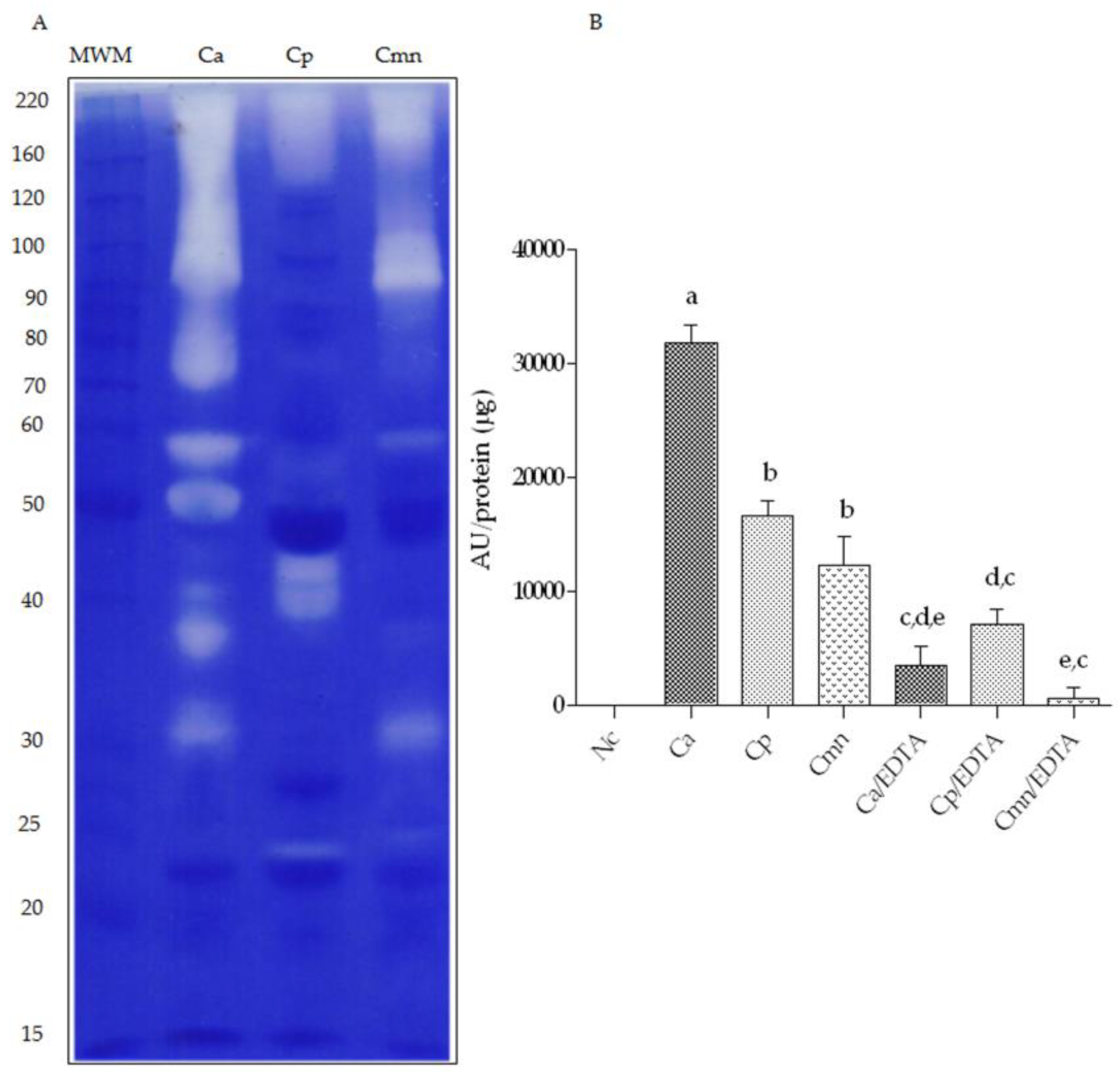
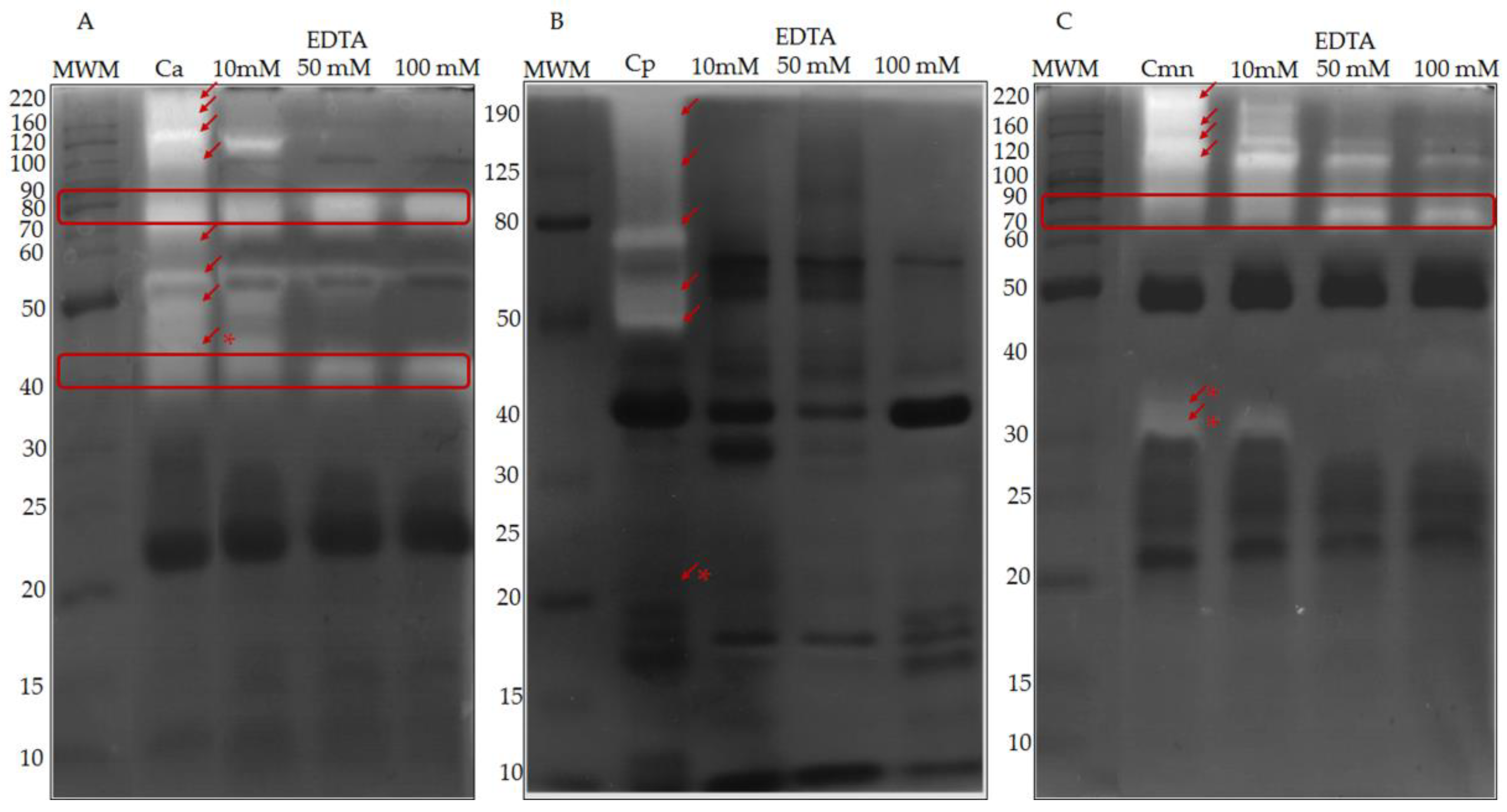
2.3. Zymography and Gelatinolytic/Caseinolytic Activities
2.4. Zymography and Enzymatic Activities of Phospholipases A2
2.5. Zymography and Enzymatic Activity of Hyaluronidases
2.6. RP-HPLC
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Venom Extraction
3.2. SDS-PAGE Protein Banding Pattern
3.3. Zymography Assays
3.3.1. Serine Proteases Zymography
3.3.2. Metalloproteases Zymography
3.3.3. PLA2 Zymography
3.3.4. Hyaluronidases Zymography
3.4. Enzyme Assays
3.4.1. Serine Protease Activities
3.4.2. Proteolytic Activity
3.4.3. Phospholipase A2 Activity
3.4.4. Hyaluronidase Activity
3.5. RP-HPLC
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; De Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; De Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-bites: Appraisal of the global situation. Bull. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G. Snakebite: When the Human Touch Becomes a Bad Touch. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.E. Snake Bite: Pit Vipers. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 21, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Progress in the Characterization of Venoms and Standardization of Antivenoms; WHO Offset Publ.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Winkel, K.; Hawdon, G.; Ashby, M.K. Venomous bites and stings. Hazard 1998, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Trape, J.F.; Pison, G.; Guyavarch, E.; Mane, Y. High mortality from snakebite in south-eastern Senegal. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, S.; Bon, C.; Wisner, A. Snake venom proteins acting on hemostasis. Biochimie 2000, 82, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Huang, C. Synergistic strategies of predominant toxins in snake venoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 287, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Perino, M.G.; Giglio, J.R.; Arantes, E.C. Isolation, enzymatic characterization and antiedematogenic activity of the first reported rattlesnake hyaluronidase from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevallos, M.A.; Navarro-Duque, C.; Varela-Julia, M.; Alagon, A.C. Molecular mass determination and assay of venom hyaluronidases by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Toxicon 1992, 30, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, M.A.; Cezarette, G.N.; Jacob-Ferreira, A.L.; Frantz, F.G.; Faccioli, L.H.; Sampaio, S.V. Disseminated intravascular coagulation caused by moojenactivase, a procoagulant snake venom metalloprotease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laraba-Djebari, F.; Chérifi, F. Pathophysiological and Pharmacological Effects of Snake Venom Components: Molecular Targets. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Sanhajariya, S.; Duffull, S.B.; Isbister, G.K. Pharmacokinetics of snake venom. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Biochemistry and toxicology of toxins purified from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Toxicon 2009, 54, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Flores-Ortiz, R.J.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Eble, J.A. Direct fibrinolytic snake venom metalloproteinases affecting hemostasis: Structural, biochemical features and therapeutic potential. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, R.K.; McCleary, R.J.R.; Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Venom gland transcriptomics for identifying, cataloging, and characterizing venom proteins in snakes. Toxicon 2015, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The venomous reptiles of the western hemisphere. Comstock Books Herpetol. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McCranie, J.R. Crotalus polystictus. Soc. Study Amphib. Reptil. 1976, 180, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of Latin America. Q. Rev. Biol. 1989, 65, 516–517. [Google Scholar]
- Mackessy, S.P. The Field of Reptile Toxinology, Snakes, Lizards, and Their Venom. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, G.A.; Fletcher, P.L.; Possani, L.D. Characterization of the venom from Crotalus molossus nigrescens Gloyd (black tail rattlesnake): Isolation of two proteases. Toxicon 1990, 28, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, M.; Neri-Castro, E.; Pérez-Morales, R.; Strickland, J.; Ponce-López, R.; Parkinson, C.; Espinosa-Fematt, J.; Sáenz-Mata, J.; Flores-Martínez, E.; Alagón, A.; et al. Ontogenetic Change in the Venom of Mexican Black-Tailed Rattlesnakes (Crotalus molossus nigrescens). Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackessy, S.; Leroy, J.; Mociño-Deloya, E.; Setser, K.; Bryson, R.; Saviola, A. Venom Ontogeny in the Mexican Lance-Headed Rattlesnake (Crotalus polystictus). Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, E.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Hernánez-Dávila, A.I.; Zamudio, F.; Alagón, A. General characterization of the venoms from two species of rattlesnakes and an intergrade population (C. lepidus x aquilus) from Aguascalientes and Zacatecas, Mexico. Toxicon 2017, 138, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Dey, S.; Uddin, M.K.; Barua, R.; Hossain, M.T. Extracellular Pectinase from a Novel Bacterium Chryseobacterium indologenes Strain SD and Its Application in Fruit Juice Clarification. Enzyme Res. 2018, 2018, 3859752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, D.W. Accuracy, precision, and quality control of enzyme Assays. J. Clin. Pathol. 1970, 4, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serrano, S.M.T.; Shannon, J.D.; Wang, D.; Camargo, A.C.M.; Fox, J.W. A multifaceted analysis of viperid snake venoms by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: An approach to understanding venom proteomics. Proteomics 2005, 5, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Williams, V.; White, J. Snake venom variability: Methods of study, results and interpretation. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, L.F.M.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; et al. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: Trends in pharmacology and biochemistry. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.R.; Burin, S.M.; Menaldo, D.L.; de Castro, F.A.; Sampaio, S.V. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: An overview on their antitumor effects. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.M.T. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.M.T.; Maroun, R.C. Snake venom serine proteinases: Sequence homology vs. substrate specificity, a paradox to be solved. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.C.; Zingali, R.B.; Albuquerque, M.G.; Pujol-Luz, M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Snake venom thrombin-like enzymes: From reptilase to now. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; James, M.N.G. Molecular mechanisms for the conversion of zymogens to active proteolytic enzymes. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, O.F.; Bergmann, I.; Binder, B.R. Chromogenic substrate autography: A method for detection, characterization, and quantitative measurement of serine proteases after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 151, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baramova, E.N.; Shannon, J.D.; Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Degradation of extracellular matrix proteins by hemorrhagic metalloproteinases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 275, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Hemorrhagic metalloproteinases from snake venoms. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 62, 325–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, A.; Holm, H. Pancreatic proteinases from man, trout, rat, pig, cow, chicken, mink and fox. Enzyme activities and inhibition by soybean and lima bean proteinase inhibitors. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1983, 74, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M.T. Insights into and speculations about snake venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) synthesis, folding and disulfide bond formation and their contribution to venom complexity. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3016–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Simões-Silva, R.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; Fuly, A.L.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honório, K.M.; Da Silva, S.L.; Acosta, G.; et al. Isolation and biochemical characterization of a new thrombin-like serine protease from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.E.; Soliz, L.A.; Ramírez, M.S.; Pérez, J.C. Partial characterization of a basic protein from Crotalus molossus molossus (northern blacktail rattlesnake) venom and production of a monoclonal antibody. Toxicon 2001, 39, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Rael, E.D. Purification of M5, a fibrinolytic proteinase from Crotalus molossus molossus venom that attacks complement. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackessy, S.P. Thrombin-like enzymes in snake venoms. In Toxins and Hemostasis: From Bench to Bedside; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 519–557. [Google Scholar]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Metalloproteases affecting blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and platelet aggregation from snake venoms: Definition and nomenclature of interaction sites. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.; Kini, R.M. Protein complexes in snake venom. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.J.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, M.J. Snakebite Envenomation in Central America. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 491–507. [Google Scholar]
- Macias-Rodríguez, E.F.; Martínez-Martínez, A.; Gatica-Colima, A.; Bojórquez-Rangel, G.; Plenge-Tellechea, L.F. Análisis comparativo de la actividad hemolítica entre las subespecies Crotalus molossus y Crotalus molossus nigrescens. Rev. Bio Ciencias 2014, 2, 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Meléndez-Martínez, D.; Macías-Rodríguez, E.; Vázquez-Briones, R.; López-Vera, E.; Cruz-Pérez, M.S.; Vargas-Caraveo, A.; Gatica-Colima, A.; Plenge-Tellechea, L.F. In vitro hemotoxic, α-neurotoxic and vasculotoxic effects of the Mexican black-tailed rattlesnake (Crotalus molossus nigrescens) venom. J. Venom Res. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlan, I.; Ferlan, A.; Capel, M.S.; Russell, F.E. Isolation and characterization of two phospholipases from Crotalus molossus molossus venom. Toxicon 1983, 21, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Tu, M.C.; Tu, A.T. Purification, sequencing, and phylogenetic analyses of novel Lys-49 phospholipases A2from the venoms of rattlesnakes and other pit vipers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 394, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Manjunatha Kini, R.; Doley, R. Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Enzymes. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 173–205. ISBN 978-0-8493-9165-1. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.; Bleicher, L.; Schrago, C.G.; Silva Junior, F.P. Conservation analysis and decomposition of residue correlation networks in the phospholipase A2 superfamily (PLA2s): Insights into the structure-function relationships of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2018, 146, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S.; Nagaraju, S. Hyaluronidases, a Neglected Class of Glycosidases from Snake Venom. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Girish, K.S.; Shashidharamurthy, R.; Nagaraju, S.; Gowda, T.V.; Kemparaju, K. Isolation and characterization of hyaluronidase a “spreading factor” from Indian cobra (Naja naja) venom. Biochimie 2004, 86, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, F.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Landucci, E.C.T. Unmasking snake venom of Bothrops leucurus: Purification and pharmacological and structural characterization of new PLA2 Bleu TX-III. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 941467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Calvete, J.J. Strategies in ‘snake venomics’ aiming at an integrative view of compositional, functional, and immunological characteristics of venoms. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaldo, D.L.; Bernardes, C.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Moura, L.d.A.; Fuly, A.L.; Arantes, E.C.; Sampaio, S.V. Biochemical characterization and comparative analysis of two distinct serine proteases from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munekiyo, S.M.; Mackessy, S.P. Effects of Temperature and Storage Conditions on the Electrophoretic, Toxic and Enzymatic Stability of Venom Components. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 119, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, B.G.; Weström, B.R.; Karlsson, B.W. Enzymoblotting: A method for localizing proteinases and their zymogens using para-nitroanilide substrates after agarose gel electrophoresis and transfer to nitrocellulose. Anal. Biochem. 1986, 152, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokurov, K.S.; Oppert, B.; Elpidina, E.N. Notes & Tips An overlay technique for postelectrophoretic analysis of proteinase spectra in complex mixtures using p-nitroanilide substrates. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 337, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rice, K.; Peralta, R.; Bast, D.; De Azavedo, J.; McGavin, M.J. Description of staphylococcus serine protease (ssp) operon in Staphylococcus aureus and nonpolar inactivation of sspA-encoded serine protease. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignol, G.; Merieau, A.; Guerillon, J.; Veron, W.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Orange, N. Involvement of a phospholipase C in the hemolytic activity of a clinical strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntenhöner, M.W.; Pogrel, M.A.; Stern, R. A substrate-gel assay for hyaluronidase activity. Matrix 1992, 12, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlanger, B.F.; Kokowsky, N.; Cohen, W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 95, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Rucavado, A.; Warrell, D.A.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the lesser antillean pit vipers bothrops caribbaeus and Bothrops lanceolatus: Correlation with toxicological activities and immunoreactivity of a heterologous antivenom. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4396–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Bonfim, V.L.; Novello, J.C.; Navarro Oviedo, R.; Yarlequé Chocas, A.; Marangoni, S. Isolation and characterization of a serine protease, Ba III-4, from Peruvian Bothrops atrox venom. Protein J. 2007, 26, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ferrante, N. Turbidimetric measurement of acid mucopolysaccharides and hyaluronidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 220, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Snake venoms samples are available from the authors. |




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roldán-Padrón, O.; Castro-Guillén, J.L.; García-Arredondo, J.A.; Cruz-Pérez, M.S.; Díaz-Peña, L.F.; Saldaña, C.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico. Molecules 2019, 24, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081489
Roldán-Padrón O, Castro-Guillén JL, García-Arredondo JA, Cruz-Pérez MS, Díaz-Peña LF, Saldaña C, Blanco-Labra A, García-Gasca T. Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081489
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoldán-Padrón, Octavio, José Luis Castro-Guillén, José Alejandro García-Arredondo, Martha Sandra Cruz-Pérez, Luis Fernando Díaz-Peña, Carlos Saldaña, Alejandro Blanco-Labra, and Teresa García-Gasca. 2019. "Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081489
APA StyleRoldán-Padrón, O., Castro-Guillén, J. L., García-Arredondo, J. A., Cruz-Pérez, M. S., Díaz-Peña, L. F., Saldaña, C., Blanco-Labra, A., & García-Gasca, T. (2019). Snake Venom Hemotoxic Enzymes: Biochemical Comparison between Crotalus Species from Central Mexico. Molecules, 24(8), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081489