Regulation of Noise-Induced Loss of Serotonin Transporters with Resveratrol in a Rat Model Using 4-[18F]-ADAM/Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
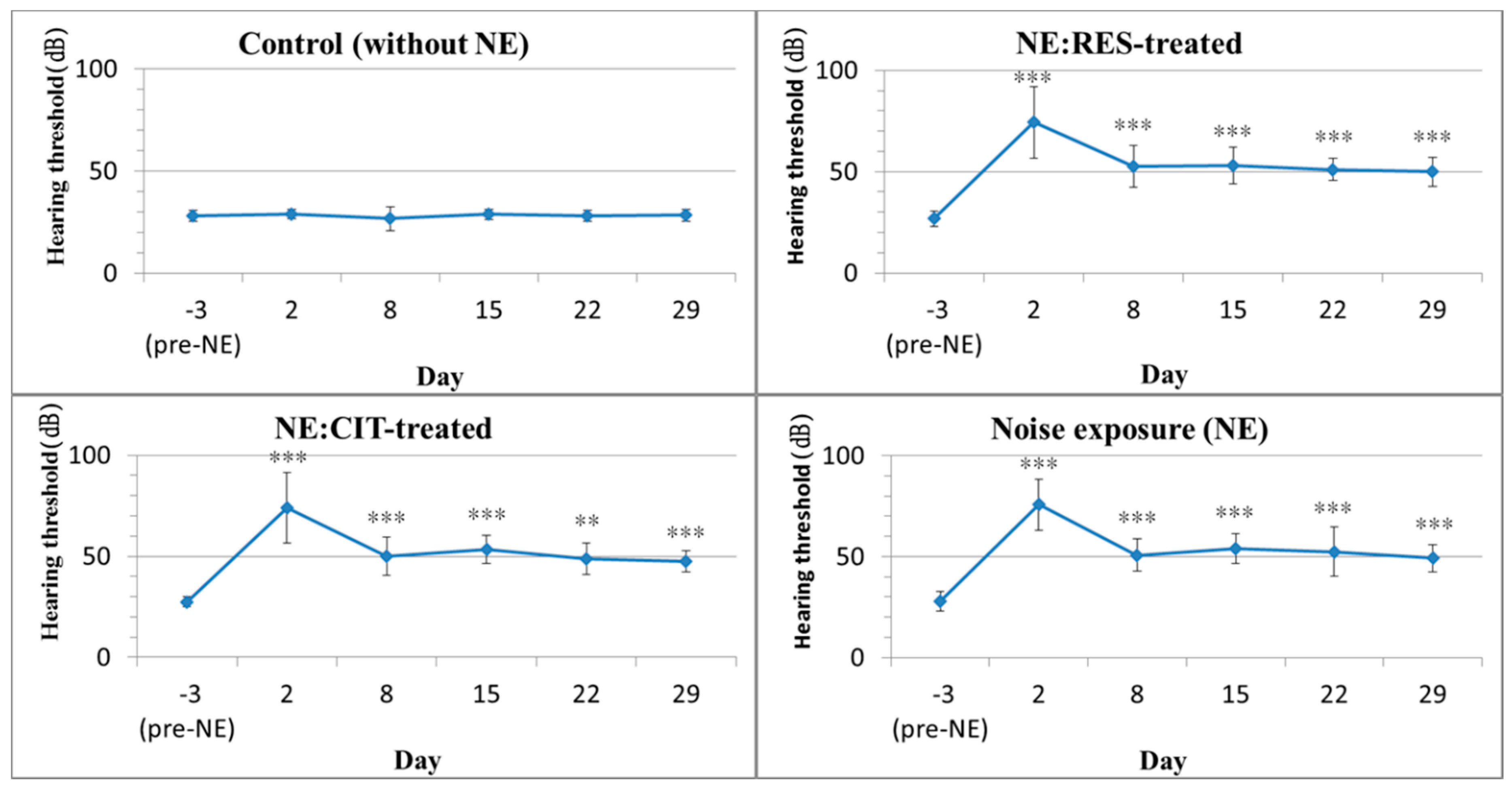
2.1. High Intensity Noise Induced Permanent Hearing Loss
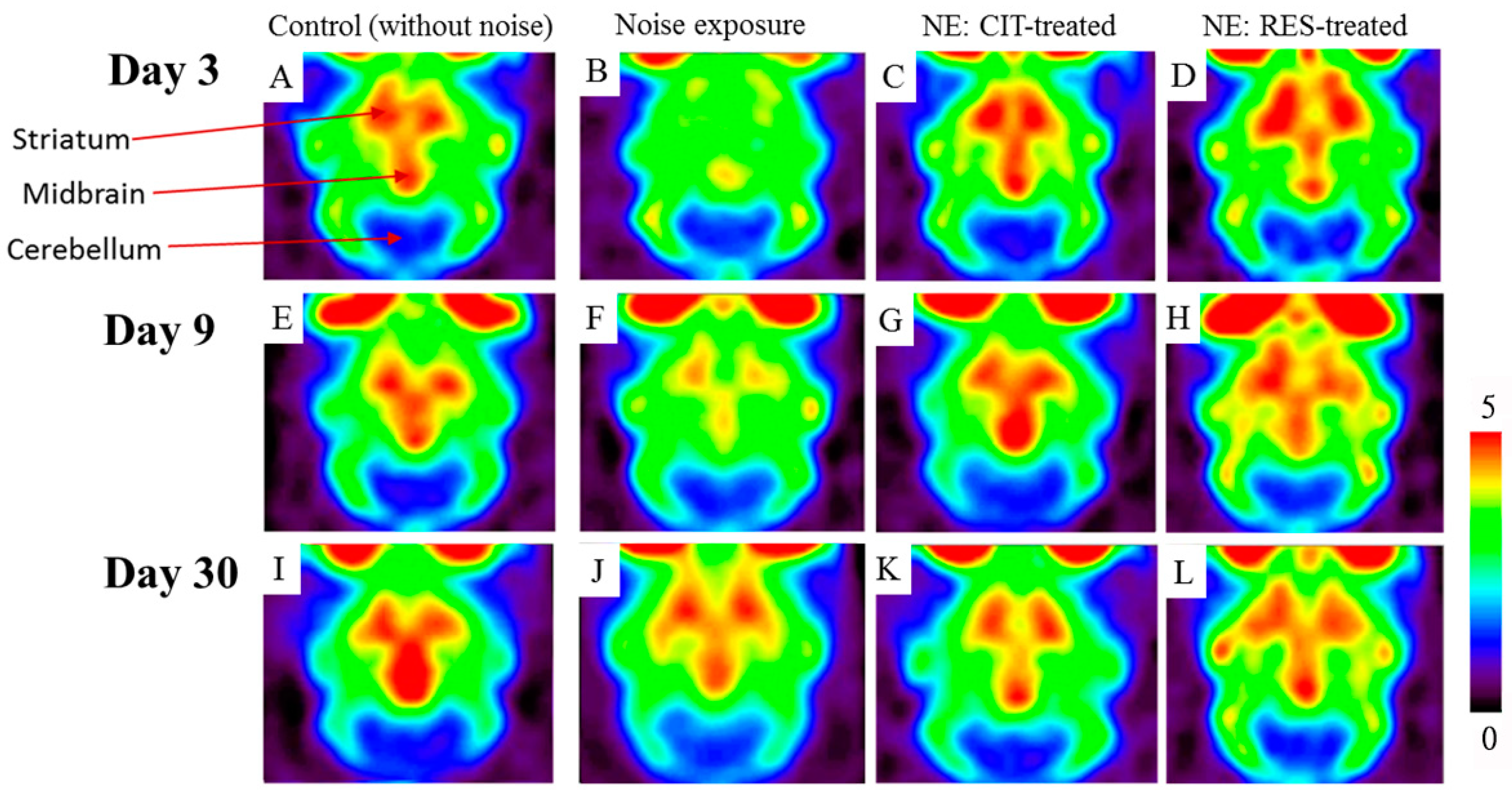
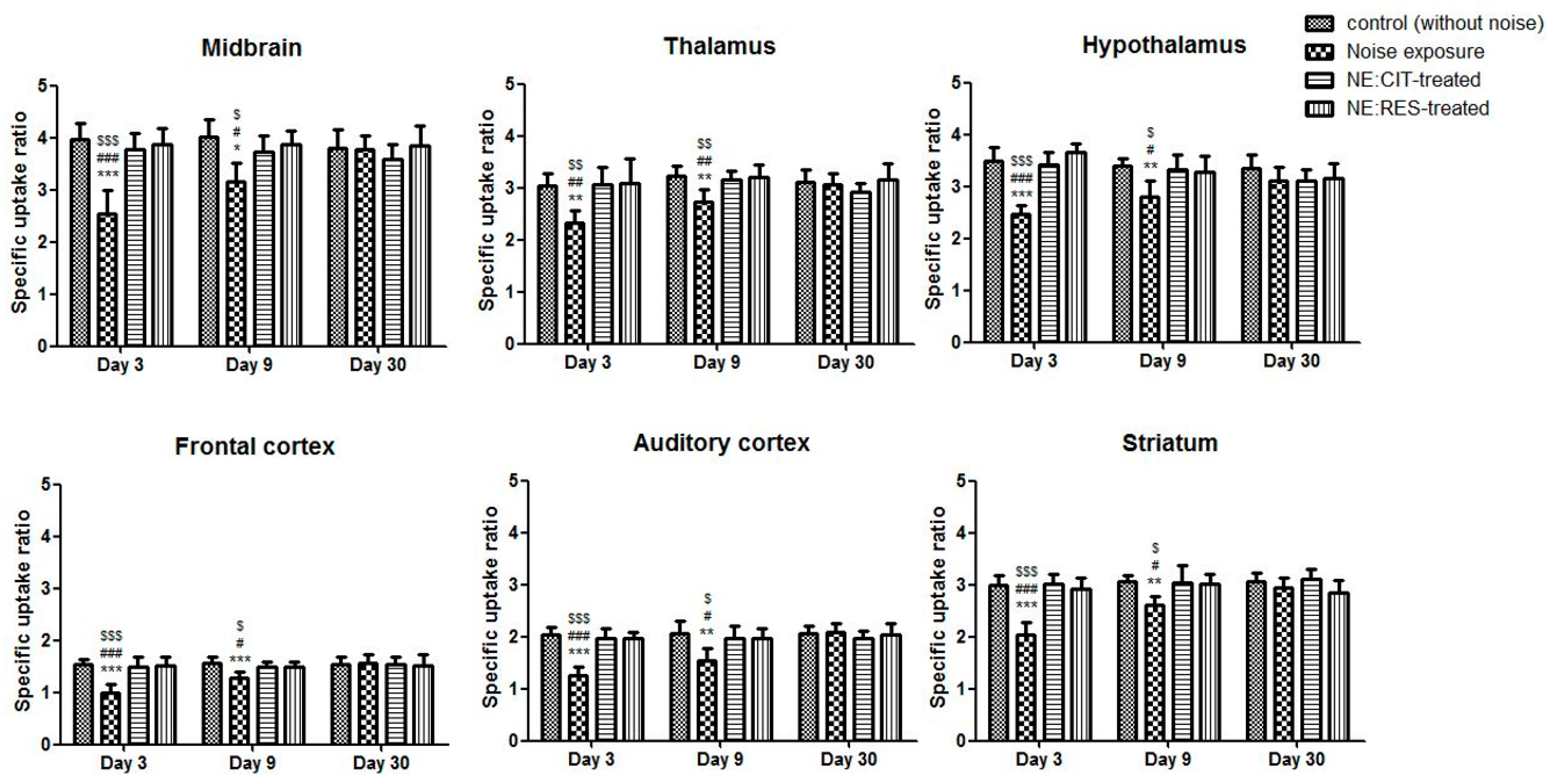
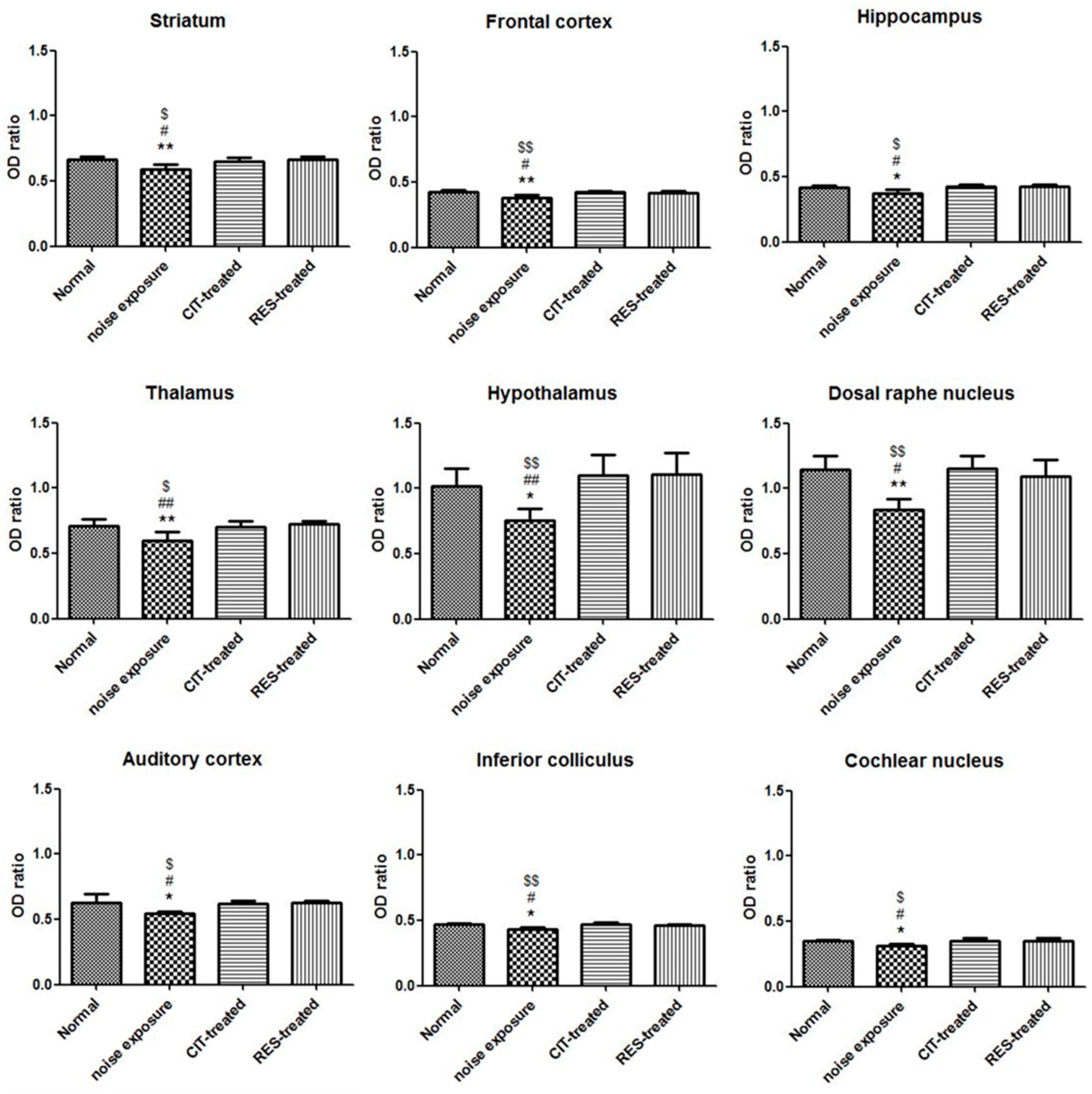
2.2. Noise Exposure Decreased SERT Levels in Multiple Brain Regions
2.3. Resveratrol Conferred Neuroprotection against Noise-Induced SERT Loss
3. Discussion
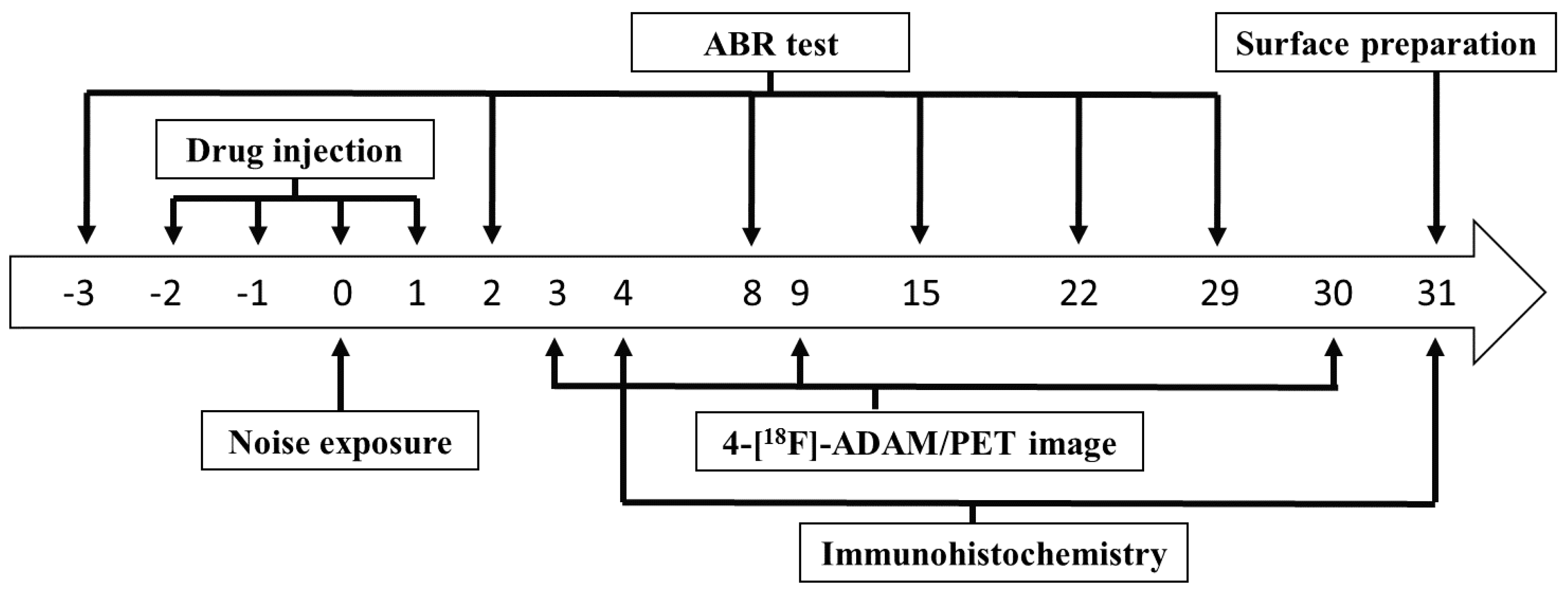
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Hearing Threshold Detection
4.3. Cochlear Surface Preparation and Actin-Staining
4.4. Small Animal-PET Imaging
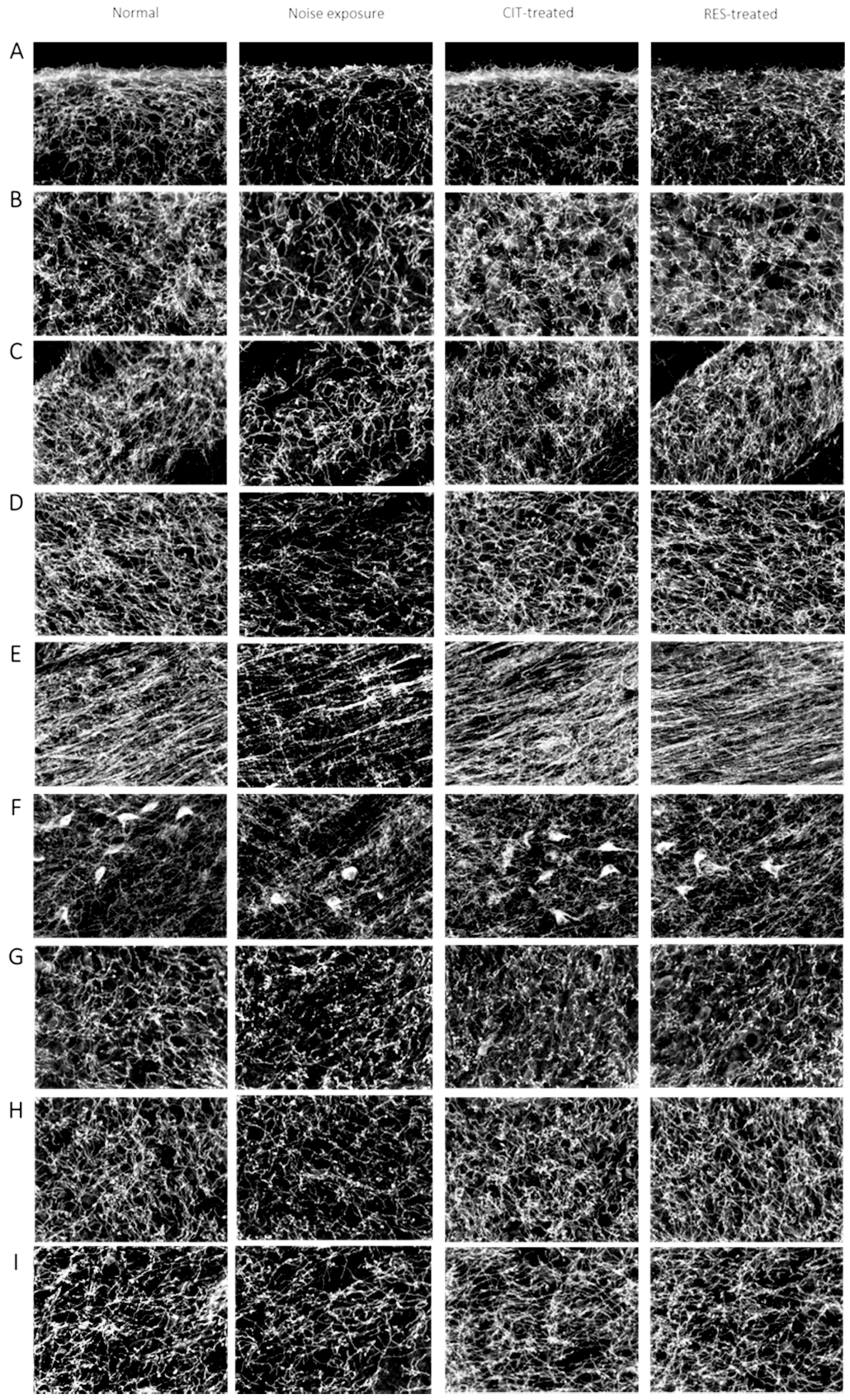
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelegrin, A.C.; Canuet, L.; Rodriguez, A.A.; Morales, M.P. Predictive factors of occupational noise-induced hearing loss in Spanish workers: A prospective study. Noise Health 2015, 17, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, J.C.; Dear, S.P.; Schneider, M.E. The anatomical consequences of acoustic injury: A review and tutorial. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 833–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottersen, O.P.; Takumi, Y.; Matsubara, A.; Landsend, A.S.; Laake, J.H.; Usami, S. Molecular organization of a type of peripheral glutamate synapse: The afferent synapses of hair cells in the inner ear. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 54, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.H. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, H.C.; Li, I.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Liu, R.S.; Huang, W.S.; Shiue, C.Y.; Ma, K.H. Investigating the effects of noise-induced hearing loss on serotonin transporters in rat brain using 4-[18F]-ADAM/small animal PET. NeuroImage 2013, 75, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Loyzaga, P.; Bartolome, V.; Vicente-Torres, A.; Carricondo, F. Serotonergic innervation of the organ of Corti. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2000, 120, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gil Loyzaga, P.E. Innervation of the auditory receptor and cochlear nuclei. An. R. Acad. Nac. Med. 1997, 114, 1063–1086, Discussion 1086–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Cransac, H.; Cottet-Emard, J.M.; Hellstrom, S.; Peyrin, L. Specific sound-induced noradrenergic and serotonergic activation in central auditory structures. Hear. Res. 1998, 118, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L.M.; Thompson, A.M.; Pollak, G.D. Serotonin in the inferior colliculus. Hear. Res. 2002, 168, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, V.C.; Fujisawa, S.; Lee, F.A.; Karthikeyan, O.; Aoki, C.; Sanes, D.H. Hearing loss raises excitability in the auditory cortex. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yue, Q. Auditory gating processes and binaural inhibition in the inferior colliculus. Hear. Res. 2002, 168, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.; Basura, G.J.; Roche, J.; Daniels, S.; Mancilla, J.G.; Manis, P.B. Hearing loss alters serotonergic modulation of intrinsic excitability in auditory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wutzler, A.; Winter, C.; Kitzrow, W.; Uhl, I.; Wolf, R.J.; Heinz, A.; Juckel, G. Loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials as indicator of central serotonergic neurotransmission: Simultaneous electrophysiological recordings and in vivo microdialysis in the rat primary auditory cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Kotak, V.C.; Sanes, D.H. Conductive hearing loss disrupts synaptic and spike adaptation in developing auditory cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9417–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehrson, A.L.; Sanchez, C. Serotonergic modulation of glutamate neurotransmission as a strategy for treating depression and cognitive dysfunction. CNS Spectr. 2014, 19, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, O.L.; Kasse, C.A.; Sanchez, M.; Barbosa, F.; Barros, F.A. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors in auditory processing disorders in elderly patients: Preliminary results. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatowicz, E.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Resveratrol, a natural chemopreventive agent against degenerative diseases. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 557–569. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.D.; He, L.R. Mechanisms of cardiovascular protection by resveratrol. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleas, G.J.; Diamandis, E.P.; Goldberg, D.M. Resveratrol: A molecule whose time has come? And gone? Clin. Biochem. 1997, 30, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, U.; Sonmez, A.; Erbil, G.; Tekmen, I.; Baykara, B. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol against traumatic brain injury in immature rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 420, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez, M.; Fraiz, N.; Cano, E.; Orallo, F. Inhibitory effects of cis- and trans-resveratrol on noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and on monoamine oxidase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; You, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Barish, P.A.; Vernon, M.M.; Du, X.; Li, G.; Pan, J.; et al. Antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol: Involvement of serotonin and noradrenaline system. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Du, X.; Ruan, L.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; O’Donnell, J.M.; Pan, J.; et al. Antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol in chronic stress model: Behavioral and neurochemical evidences. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.H.; Ma, K.H.; Chen, C.F.; Cheng, C.Y.; Pao, L.H.; Weng, S.J.; Huang, Y.S.; Shiue, C.Y.; Yeh, M.K.; Li, I.H. Evaluation of brain SERT occupancy by resveratrol against MDMA-induced neurobiological and behavioral changes in rats: A 4-[(1)(8)F]-ADAM/small-animal PET study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Torres, M.A.; Davila, D.; Bartolome, M.V.; Carricondo, F.; Gil-Loyzaga, P. Biochemical evidence for the presence of serotonin transporters in the rat cochlea. Hear. Res. 2003, 182, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Loyzaga, P.; Vicente-Torres, M.A.; Garcia-Bonacho, M.; Esquifino, A. Presence of catecholamines and serotonin in the rat vestibule. Brain Res. 1997, 746, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, E.A.; Sewell, W.F. Pharmacological alterations of the activity of afferent fibers innervating hair cells. Hear. Res. 1989, 38, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L.M.; Pollak, G.D. Serotonin differentially modulates responses to tones and frequency-modulated sweeps in the inferior colliculus. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8071–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahveninen, J.; Jaaskelainen, I.P.; Pennanen, S.; Liesivuori, J.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Kahkonen, S. Auditory selective attention modulated by tryptophan depletion in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 340, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahkonen, S.; Ahveninen, J.; Pennanen, S.; Liesivuori, J.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Jaaskelainen, I.P. Serotonin modulates early cortical auditory processing in healthy subjects: Evidence from MEG with acute tryptophan depletion. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 27, 862–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.M.; Thompson, G.C. Serotonin projection patterns to the cochlear nucleus. Brain Res. 2001, 907, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, C.; Glowatzki, E.; Fuchs, P. The postsynaptic function of type II cochlear afferents. Nature 2009, 461, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, M.C.; Kujawa, S.G. Cochlear synaptopathy in acquired sensorineural hearing loss: Manifestations and mechanisms. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Vyas, P.; Glowatzki, E.; Fuchs, P.A. Opposing expression gradients of calcitonin-related polypeptide alpha (Calca/Cgrpalpha) and tyrosine hydroxylase (Th) in type II afferent neurons of the mouse cochlea. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, P.; Wu, J.S.; Zimmerman, A.; Fuchs, P.; Glowatzki, E. Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expression in Type II Cochlear Afferents in Mice. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2017, 18, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawa, S.G.; Liberman, M.C. Synaptopathy in the noise-exposed and aging cochlea: Primary neural degeneration in acquired sensorineural hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2015, 330, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, R.; Puel, J.L. Excitotoxicity, synaptic repair, and functional recovery in the mammalian cochlea: A review of recent findings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 884, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, A.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H. Protective Effect of Edaravone on Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity in Spiral Ganglion Neurons. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 4034218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafon-Cazal, M.; Pietri, S.; Culcasi, M.; Bockaert, J. NMDA-dependent superoxide production and neurotoxicity. Nature 1993, 364, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Brask, D.; Knudsen, G.M.; Aznar, S. Immunodetection of the serotonin transporter protein is a more valid marker for serotonergic fibers than serotonin. Synapse 2006, 59, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invernizzi, R.; Bramante, M.; Samanin, R. Extracellular concentrations of serotonin in the dorsal hippocampus after acute and chronic treatment with citalopram. Brain Res. 1995, 696, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Bobermin, L.D.; Tramontina, A.C.; Wartchow, K.M.; Tagliari, B.; Souza, D.O.; Wyse, A.T.; Goncalves, C.A. Oxidative stress mediated by NMDA, AMPA/KA channels in acute hippocampal slices: Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Lastra, C.A.; Villegas, I. Resveratrol as an antioxidant and pro-oxidant agent: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure–activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschecker, J.P.; Leaver, A.M.; Muhlau, M. Tuning out the noise: Limbic-auditory interactions in tinnitus. Neuron 2010, 66, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Shippenberg, T.S.; Jayanthi, L.D. Regulation of monoamine transporters: Role of transporter phosphorylation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 129, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriage, J.; Barnes, N.M. Is central hyperacusis a symptom of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) dysfunction? J. Laryngol. Otol. 1995, 109, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papesh, M.A.; Hurley, L.M. Plasticity of serotonergic innervation of the inferior colliculus in mice following acoustic trauma. Hear. Res. 2012, 283, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, M.; Bayazit, Y.A.; Celenk, F.; Karabulut, H.; Yilmaz, A.; Gunduz, B.; Saridogan, C.; Dagli, M.; Erdal, E.; Menevse, A. Significance of serotonin transporter gene polymorphism in tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.L.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, E.Y.; Chen, C.C. Asic3(-/-) female mice with hearing deficit affects social development of pups. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viberg, A.; Canlon, B. The guide to plotting a cochleogram. Hear. Res. 2004, 197, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.H.; Huang, W.S.; Shiue, C.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, R.S.; Chyueh, S.C.; Hu, S.H.; Liao, M.H.; Shen, L.H.; Liu, J.C.; et al. Study on the neuroprotective effect of fluoxetine against MDMA-induced neurotoxicity on the serotonin transporter in rat brain using micro-PET. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.H.; Huang, W.S.; Kuo, Y.Y.; Peng, C.J.; Liou, N.H.; Liu, R.S.; Hwang, J.J.; Liu, J.C.; Chen, H.J.; Shiue, C.Y. Validation of 4-[18F]-ADAM as a SERT imaging agent using micro-PET and autoradiography. NeuroImage 2009, 45, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Glavaski-Joksimovic, A.; Virag, T.; Chang, Q.A.; West, N.C.; Mangatu, T.A.; McGrogan, M.P.; Dugich-Djordjevic, M.; Bohn, M.C. Reversal of dopaminergic degeneration in a parkinsonian rat following micrografting of human bone marrow-derived neural progenitors. Cell Transplant. 2009, 18, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Sawada, T.; Blunt, S.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal pathway on striatal serotonin innervation in adult rats. Brain Res. 1991, 562, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.C.; Chiang, Y.H.; Wang, Y. Constructing a new nigrostriatal pathway in the Parkinsonian model with bridged neural transplantation in substantia nigra. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6965–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.J.; Shiue, C.Y.; Huang, W.S.; Cheng, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Li, I.H.; Tao, C.C.; Chou, T.K.; Liao, M.H.; Chang, Y.P.; et al. PET imaging of serotonin transporters with 4-[18F]-ADAM in a Parkinsonian rat model. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noristani, H.N.; Olabarria, M.; Verkhratsky, A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Serotonin fibre sprouting and increase in serotonin transporter immunoreactivity in the CA1 area of hippocampus in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, J.N.; Woolsey, C.; Ryoo, H.; Borwege, S.; Hagner, D. Low dose pramipexole is neuroprotective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, and downregulates the dopamine transporter via the D3 receptor. BMC Biol. 2004, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, I.-H.; Shih, J.-H.; Jhao, Y.-T.; Chen, H.-C.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, C.-F.F.; Huang, Y.-S.; Shiue, C.-Y.; Ma, K.-H. Regulation of Noise-Induced Loss of Serotonin Transporters with Resveratrol in a Rat Model Using 4-[18F]-ADAM/Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography. Molecules 2019, 24, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071344
Li I-H, Shih J-H, Jhao Y-T, Chen H-C, Chiu C-H, Chen C-FF, Huang Y-S, Shiue C-Y, Ma K-H. Regulation of Noise-Induced Loss of Serotonin Transporters with Resveratrol in a Rat Model Using 4-[18F]-ADAM/Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071344
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, I-Hsun, Jui-Hu Shih, Yun-Tin Jhao, Hsin-Chien Chen, Chuang-Hsin Chiu, Chien-Fu F. Chen, Yuahn-Sieh Huang, Chyng-Yann Shiue, and Kuo-Hsing Ma. 2019. "Regulation of Noise-Induced Loss of Serotonin Transporters with Resveratrol in a Rat Model Using 4-[18F]-ADAM/Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071344
APA StyleLi, I.-H., Shih, J.-H., Jhao, Y.-T., Chen, H.-C., Chiu, C.-H., Chen, C.-F. F., Huang, Y.-S., Shiue, C.-Y., & Ma, K.-H. (2019). Regulation of Noise-Induced Loss of Serotonin Transporters with Resveratrol in a Rat Model Using 4-[18F]-ADAM/Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography. Molecules, 24(7), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071344






