Introduction of Nonacidic Side Chains on 6-Ethylcholane Scaffolds in the Identification of Potent Bile Acid Receptor Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties
Abstract
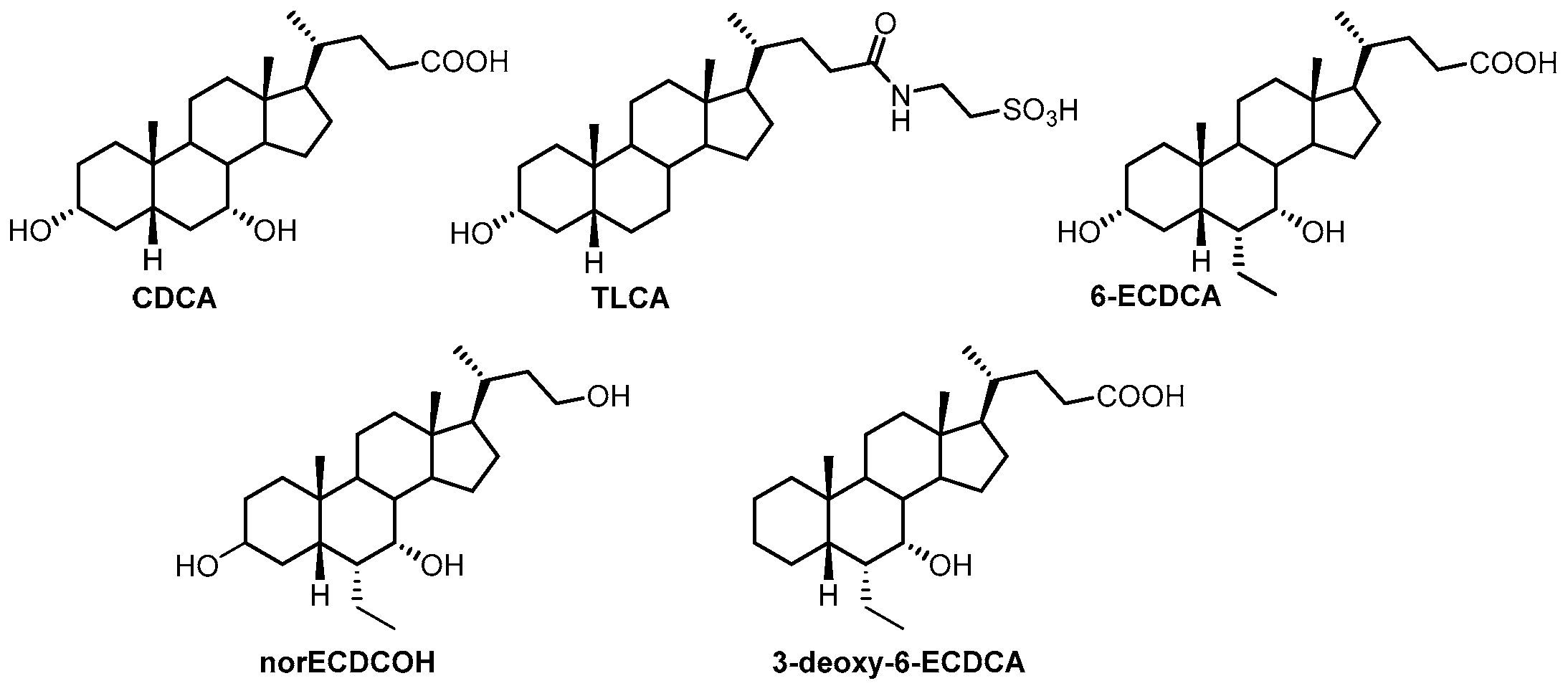
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
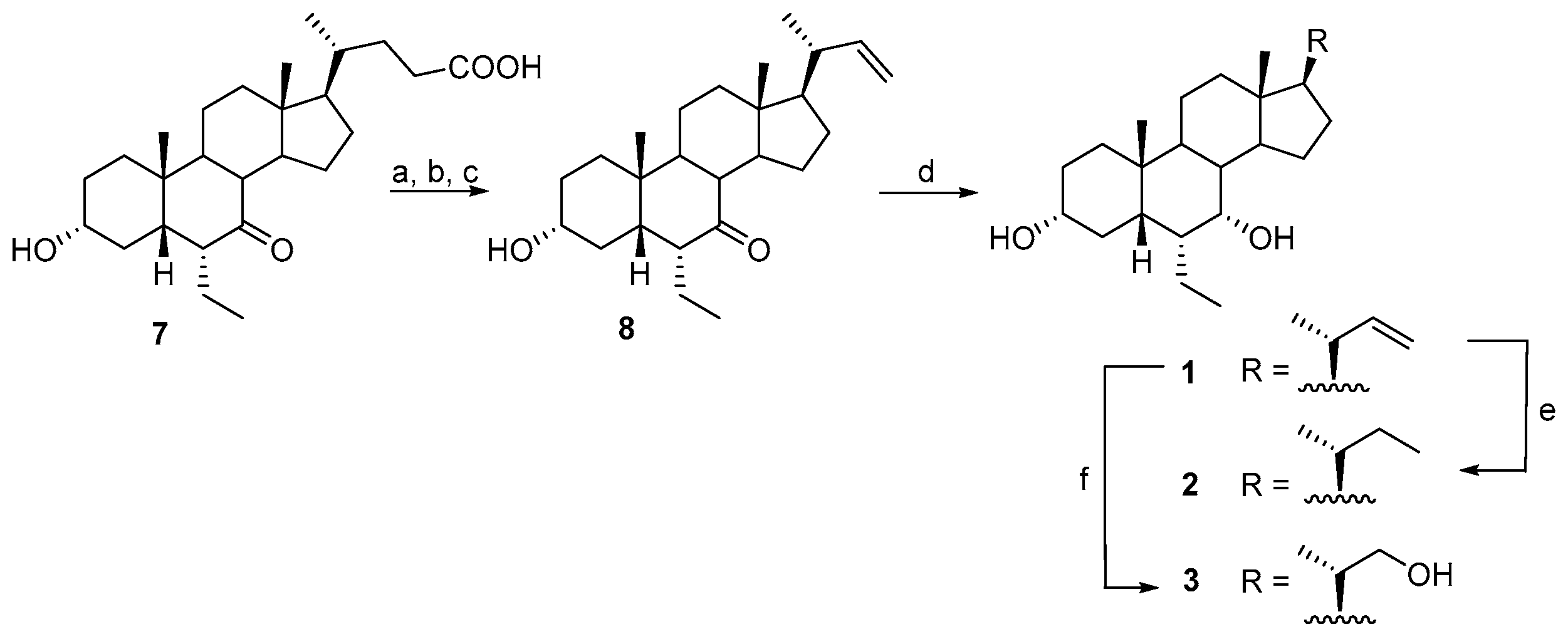
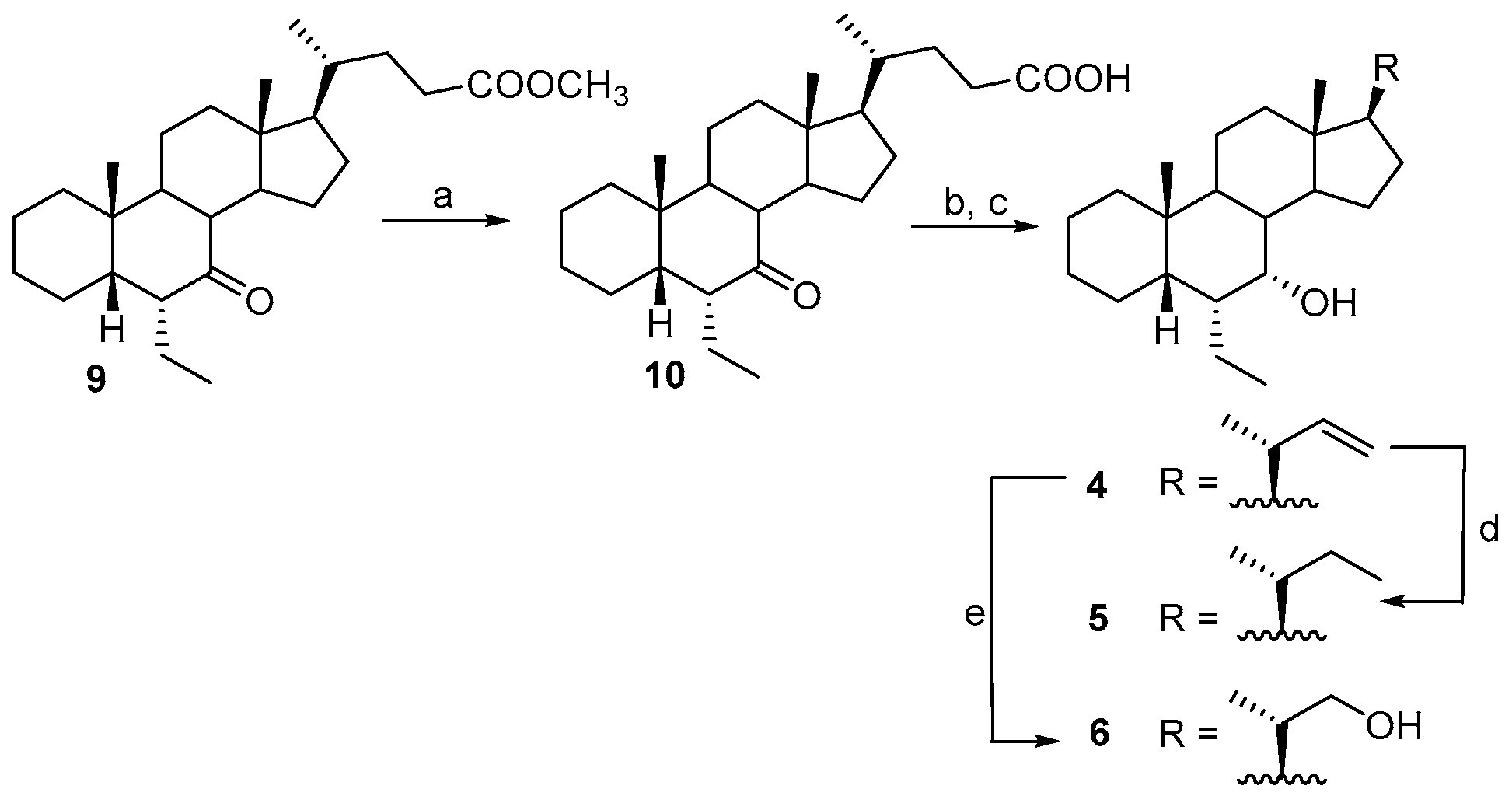
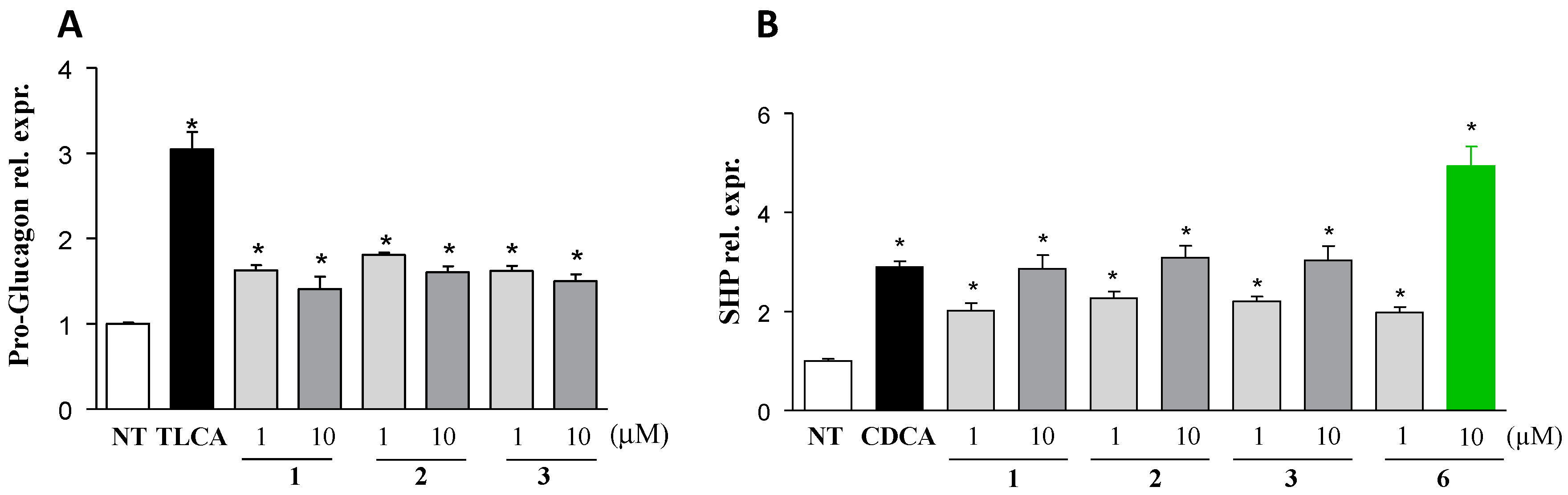
2.1. Chemical Synthesis and Evaluation of Biological Activity
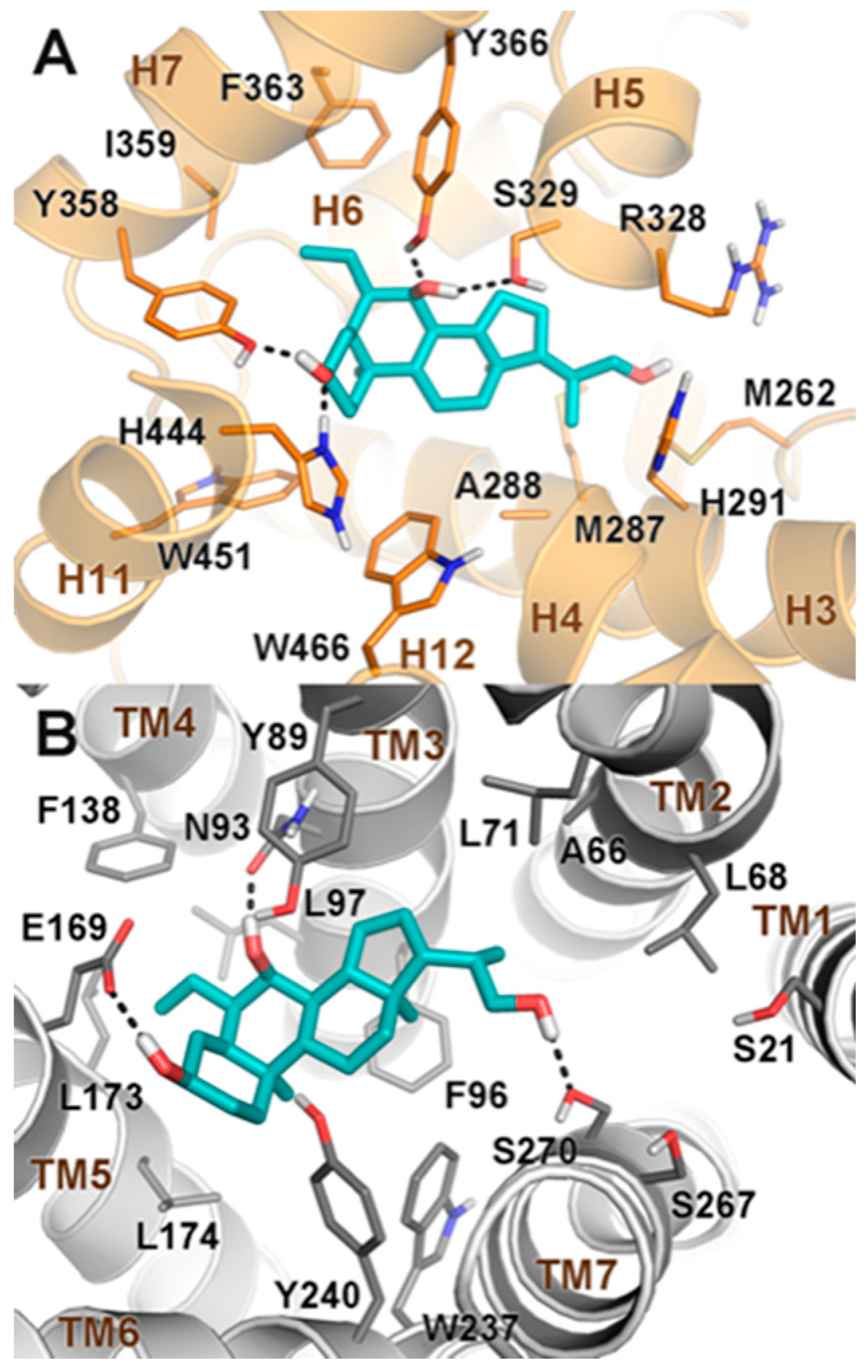
2.2. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-3α-hydroxy-7-keto-24-nor-5β-chol-23-ene (8)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-3α, 7α-dihydroxy-24-nor-5β-chol-23-ene (1)
3.2.3. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-3α, 7α -dihydroxy-24-nor-5β-cholane (2)
3.2.4. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-3α, 7α -dihydroxy-23,24-dinor-5β-cholan-22-ol (3)
3.2.5. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-7-keto-5β-cholan-24-oic acid (10)
3.2.6. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-7α-hydroxy-24-nor-5β-chol-23-ene (4)
3.2.7. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-7α-hydroxy-23,24-dinor-5β-cholane (5)
3.2.8. Synthesis of 6α-Ethyl-7α-hydroxy-23,24-dinor-5β-cholan-22-ol (6)
3.3. Biological Assays
3.3.1. Cell Culture
3.3.2. Transactivation Assay
3.3.3. Dose–Response Curve on FXR and GPBAR1
3.3.4. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
3.4. Physiochemical Properties and Pharmacokinetic Characterization
3.4.1. LC-MS/MS ADME Methods
3.4.2. Solubility Measurements
3.4.3. Microsomal Stability
3.5. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a Nuclear Receptor for Bile Acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile Acids: Natural Ligands for an Orphan Nuclear Receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Hollister, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Forman, B.M. Endogenous Bile Acids are Ligands for the Nuclear Receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, S.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Moschetta, A. Deciphering the Nuclear Bile Acid Receptor FXR Paradigm. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2010, 8, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, V.; Marchianò, S.; Finamore, C.; Baronissi, G.; Di Leva, F.S.; Carino, A.; Biagioli, M.; Fiorucci, C.; Cassiano, C.; Monti, M.C.; et al. Novel Isoxazole Derivatives with Potent FXR Agonistic Activity Prevent Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Cipriani, S.; Baldelli, F.; Mencarelli, A. Bile Acid-Activated Receptors in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia and Related Disorders. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Cipriani, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Distrutti, E.; Baldelli, F. Counter-Regulatory Role of Bile Acid Activated Receptors in Immunity and Inflammation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Rizzo, G.; Donini, A.; Distrutti, E.; Santucci, L. Targeting Farnesoid X Receptor for Liver and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, B. The Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) as a New Target in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Tamai, Y.; Oka-da, H.; Sugiyama, E.; Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Tanaka, K. Identification of Membrane-Type Receptor for Bile Acids (M-BAR). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamata, Y.; Fujii, R.; Hosoya, M.; Harada, M.; Yoshida, H.; Miwa, M.; Fukusumi, S.; Habata, Y.; Itoh, T.; Shintani, Y.; et al. A G Protein-coupled Receptor Responsive to Bile Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9435–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Mataki, C.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Kim, B.W.; Sato, H.; Messaddeq, N.; Harney, J.W.; Ezaki, O.; Kodama, T.; et al. Bile Acids Induce Energy Expenditure by Promoting Intracellular Thyroid Hormone Activation. Nature 2006, 439, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.E.; Wallis, K.; le Roux, C.W.; Wong, K.Y.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Bile Acid-Stimulated Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, S.; Syed, B.A. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Drugs Market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2016, 15, 745–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Palladino, G.; Cipriani, S. Bile-Acid-Activated Receptors: Targeting TGR5 and Farnesoid-X-Receptor in Lipid and Glucose Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, C.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Sepe, V.; Finamore, C.; De Marino, S.; Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Monti, M.C.; Zampella, A.; et al. Exploitation of Cholane Scaffold for the Discovery of Potent and Selective Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) and G-protein Coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (GP-BAR1) Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8477–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amore, C.; Di Leva, F.S.; Sepe, V.; Renga, B.; Del Gaudio, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S.; Limongelli, V. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent Dual Agonists of Nuclear and Membrane Bile Acid Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y. Recent Progress on Bile Acid Receptor Modulators for Treatment of Metabolic Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6553–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Marchianò, S.; Biagioli, M.; Santorelli, C.; Donini, A.; Zampella, A.; Monti, M.C.; Fiorucci, S. BAR502, a Dual FXR and GPBAR1 Agonist, Promotes Browning of White Adipose Tissue and Reverses Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Distrutti, E.; Limongelli, V.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Steroidal scaffolds as FXR and GPBAR1 Ligands: From Chemistry to Therapeutical Application. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1109–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicciari, R.; Fiorucci, S.; Camaioni, E.; Clerici, C.; Costantino, G.; Maloney, P.R.; Morelli, A.; Parks, D.J.; Willson, T.M. 6-alpha-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA), a Potent and Selective FXR Agonist Endowed with Anticholestatic Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3569–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, V.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Farnesoid X Receptor Modulators 2014-Present: A Patent Review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, V.; Festa, C.; Renga, B.; Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Finamore, C.; Masullo, D.; Del Gaudio, F.; Monti, M.C.; Fiorucci, S.; et al. Insights on FXR Selective Modulation. Speculation on Bile Acid Chemical Space in the Discovery of Potent and Selective Agonists. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, J.D.; Kochi, J.K. Alkenes from Acids by Oxidative Decarboxylation. Tetrahedron 1968, 24, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, F.; Kwon, E.; Poole, D.P.; Lieu, T.; Lyo, V.; Cattaruzza, F.; Cevikbas, F.; Steinhoff, M.; Nassini, R.; Materazzi, S.; et al. The TGR5 Receptor Mediates Bile Acid-induced Itch and Analgesia. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carino, A.; Biagioli, M.; Marchianò, S.; Scarpelli, P.; Zampella, A.; Limongelli, V.; Fiorucci, S. Disruption of TFGβ-SMAD3 Pathway by the Nuclear Receptor SHP Mediates the Antifibrotic Activities of BAR704, a Novel Highly Selective FXR Ligand. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnouti, Y. Bile Acid Sulfation: A Pathway of Bile Acid Elimination and Detoxification. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasalle, M.; Hoguet, V.; Hennuyer, N.; Leroux, F.; Piveteau, C.; Belloy, L.; Lestavel, S.; Vallez, E.; Dorchies, E.; Duplan, I.; et al. Topical Intestinal Aminoimidazole Agonists of G-Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 Promote Glucagon Like Peptide-1 Secretion and Improve Glucose Tolerance. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4185–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzini, M.; Braile, C.; Valenti, S.; Cappelli, A.; Vomero, S.; Marinelli, L.; Limongelli, V.; Novellino, E.; Betti, L.; Giannaccini, G.; et al. Ethyl 8-Fluoro-6-(3-nitrophenyl)-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate as Novel, Highly Potent, and Safe Antianxiety Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4730–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglini, V.; La Regina, G.; Coluccia, A.; Pelliccia, S.; Brancale, A.; Maga, G.; Crespan, E.; Badia, R.; Riveira-Muñoz, E.; Esté, J.A.; et al. Indolylaryl-sulfones Carrying a Heterocyclic Tail as Very Potent and Broad Spectrum HIV-1 Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9945–9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuti, E.; Casalini, F.; Avramova, S.I.; Santamaria, S.; Fabbi, M.; Ferrini, S.; Marinelli, L.; La Pietra, V.; Limongelli, V.; Novellino, E.; et al. Potent Arylsulfonamide Inhibitors of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Converting Enzyme Able to Reduce Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule Shedding in Cancer Cell Models. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2622–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, L.Z.; Devarakonda, S.; Harp, J.M.; Han, Q.; Pellicciari, R.; Willson, T.M.; Khorasanizadeh, S.; Rastinejad, F. Structural Basis for Bile Acid Binding and Activation of the Nuclear Receptor FXR. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Renga, B.; Festa, C.; D’Amore, C.; Masullo, D.; Cipriani, S.; Di Leva, F.S.; Monti, M.C.; Novellino, E.; Limongelli, V.; et al. Modification on Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) Scaffold. Discovery of Bile Acid Derivatives as Selective Agonists of Cell-surface G-protein Coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (GP-BAR1). J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7687–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, F.S.; Festa, C.; Renga, B.; Sepe, V.; Novellino, E.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A.; Limongelli, V. Structure-based Drug Design Targeting the Cell Membrane Receptor GPBAR1: Exploiting the Bile Acid Scaffold towards Selective Agonism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; Carino, A.; Sepe, V.; Marchianò, S.; Cipriani, S.; Di Leva, F.S.; Limongelli, V.; Monti, M.C.; Capolupo, A.; et al. Targeting Bile Acid Receptors: Discovery of a Potent and Selective Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist as a New Lead in the Pharmacological Approach to Liver Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Di Leva, F.S.; Festa, C.; D’Amore, C.; De Marino, S.; Renga, B.; D’Auria, M.V.; Novellino, E.; Limongelli, V.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Binding Mechanism of the Farnesoid X Receptor Marine Antagonist Suvanine Reveals a Strategy to Forestall Drug Modulation on Nuclear Receptors. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4701–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shaw, D.E.; Shelley, M.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–6 are available from the authors. |
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXR a | GPBAR1 a | |||||||
| Compd. | R | R1 | Eff (%) b | EC50 (μM) | Eff (%) c | EC50 (µM) | ||
| vs CDCA | vs 6-ECDCA | vs TLCA | vs 6-ECDCA | |||||
| CDCA | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | |
| TLCA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.33 |
| 6-ECDCA | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | - | - | 0.9 |
| 1 | OH |  | 252 | 45.6 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 79 | 367.1 | 0.14 ± 0.032 |
| 2 | OH |  | 249 | 46.5 | 1.3 ± 0.12 | 53 | 255.2 | 1.5 ± 0.29 |
| 3 | OH |  | 257 | 45 | 2.8 ± 0.45 | 55 | 243.4 | 0.43 ± 0.015 |
| 4 | H |  | 17 | 3.1 | ND | 15 | 68.8 | ND |
| 5 | H |  | 14 | 2.5 | ND | 12 | 53.4 | ND |
| 6 | H |  | 185 | 33.4 | 13.7 ± 2.05 | 19 | 87.5 | ND |
| Compd. | Solubility a (µM) | Clint b | t½ (min) | % c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-ECDCA d | 195 | 109.0 | 21.1 | 26.9 |
| 1 | 201 | 52.6 | 43.8 | 42.2 |
| 2 | 176 | 25.0 | 92.4 | 72.8 |
| 3 | 210 | 36.6 | 63.0 | 60.6 |
| 6 | 162 | 19.7 | 117.4 | 79.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Finamore, C.; Baronissi, G.; Marchianò, S.; Di Leva, F.S.; Carino, A.; Monti, M.C.; Limongelli, V.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S.; Sepe, V. Introduction of Nonacidic Side Chains on 6-Ethylcholane Scaffolds in the Identification of Potent Bile Acid Receptor Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061043
Finamore C, Baronissi G, Marchianò S, Di Leva FS, Carino A, Monti MC, Limongelli V, Zampella A, Fiorucci S, Sepe V. Introduction of Nonacidic Side Chains on 6-Ethylcholane Scaffolds in the Identification of Potent Bile Acid Receptor Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061043
Chicago/Turabian StyleFinamore, Claudia, Giuliana Baronissi, Silvia Marchianò, Francesco Saverio Di Leva, Adriana Carino, Maria Chiara Monti, Vittorio Limongelli, Angela Zampella, Stefano Fiorucci, and Valentina Sepe. 2019. "Introduction of Nonacidic Side Chains on 6-Ethylcholane Scaffolds in the Identification of Potent Bile Acid Receptor Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061043
APA StyleFinamore, C., Baronissi, G., Marchianò, S., Di Leva, F. S., Carino, A., Monti, M. C., Limongelli, V., Zampella, A., Fiorucci, S., & Sepe, V. (2019). Introduction of Nonacidic Side Chains on 6-Ethylcholane Scaffolds in the Identification of Potent Bile Acid Receptor Agonists with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties. Molecules, 24(6), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061043









