Optimization and Formulation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Microsphere (F-LM) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Analysis of Its Fucoxanthin Release Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
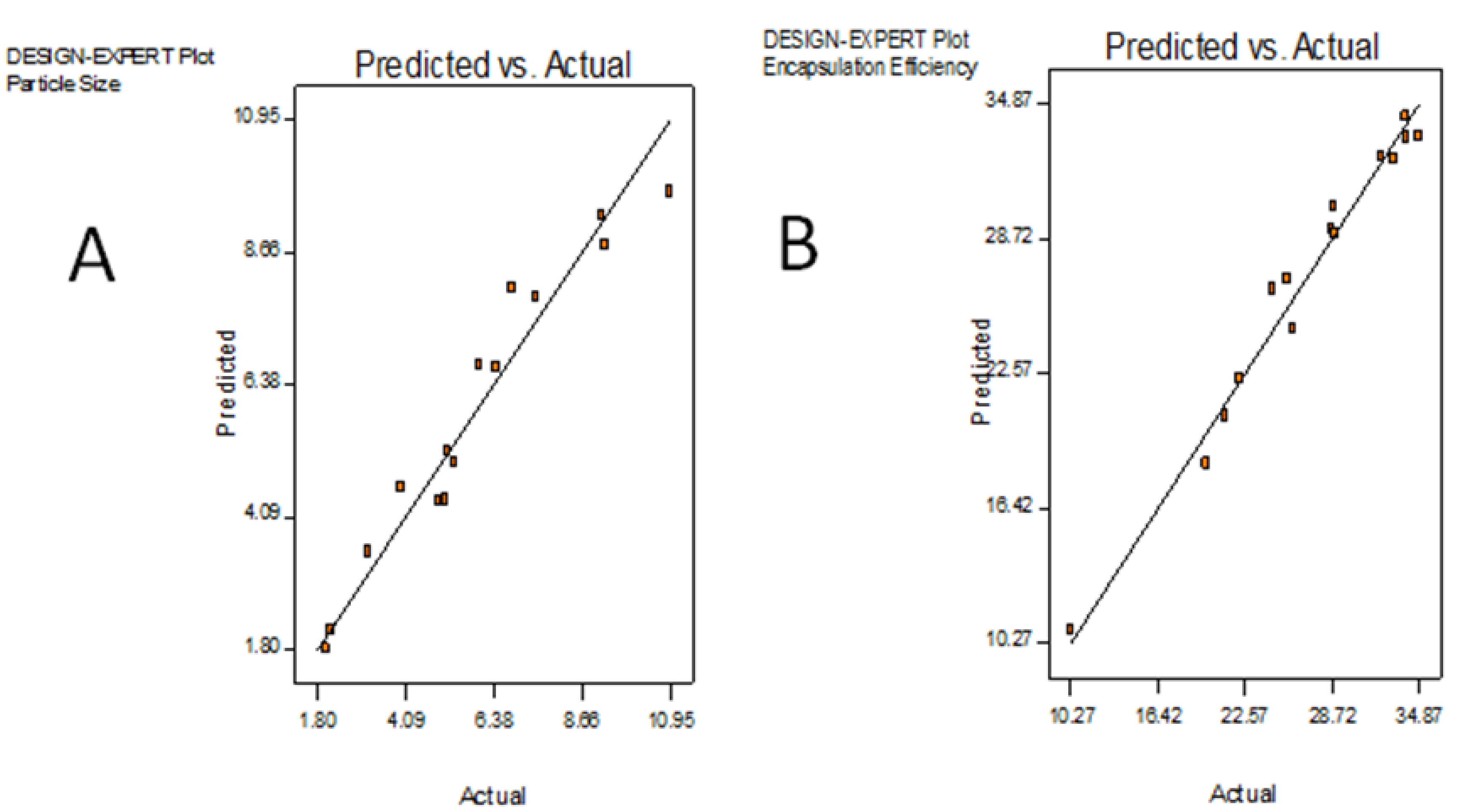
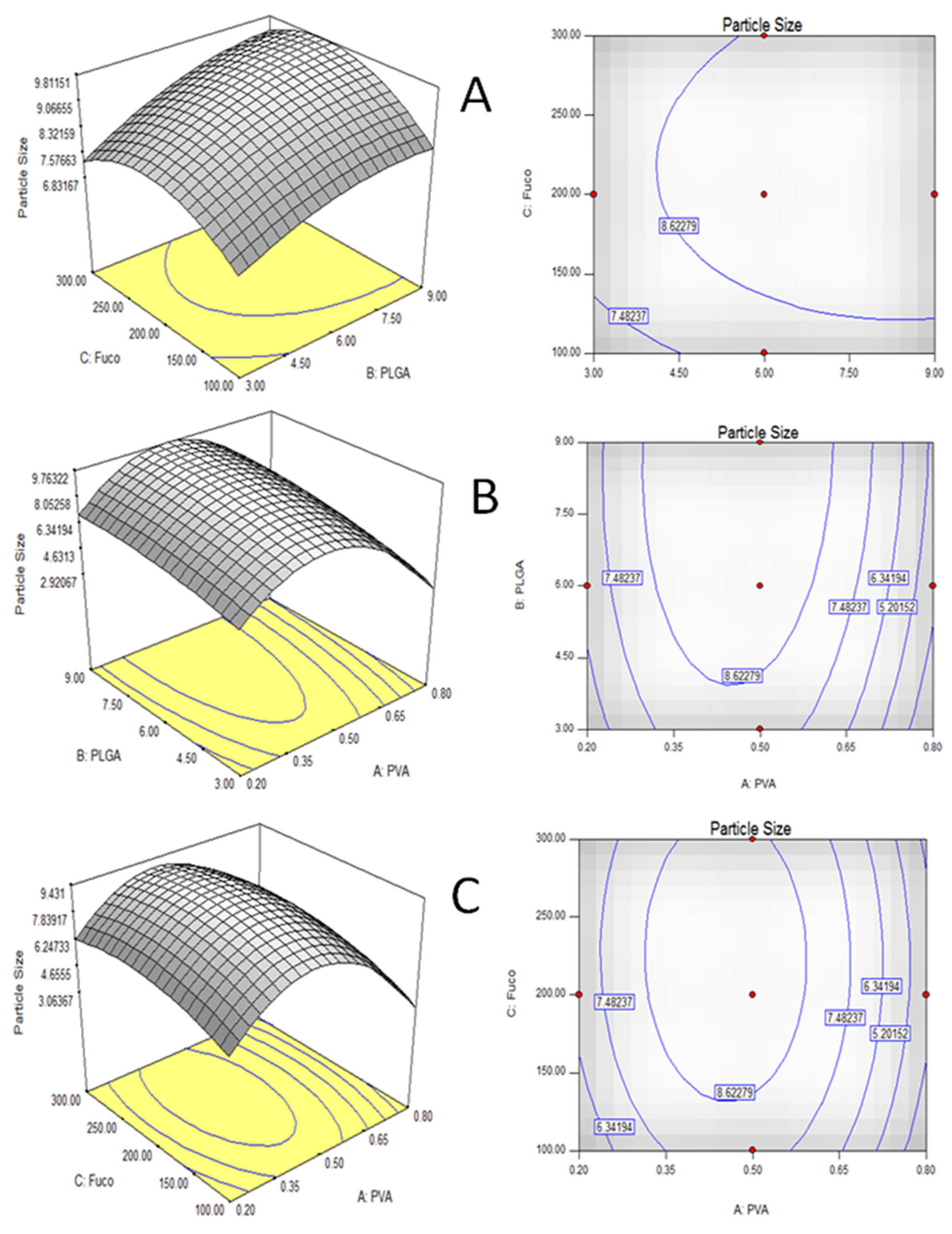
2.1. Optimization of Microencapsulation Component by RSM
2.2. Particle Size (PS), Size Distribution, and External Morphology of F-LM
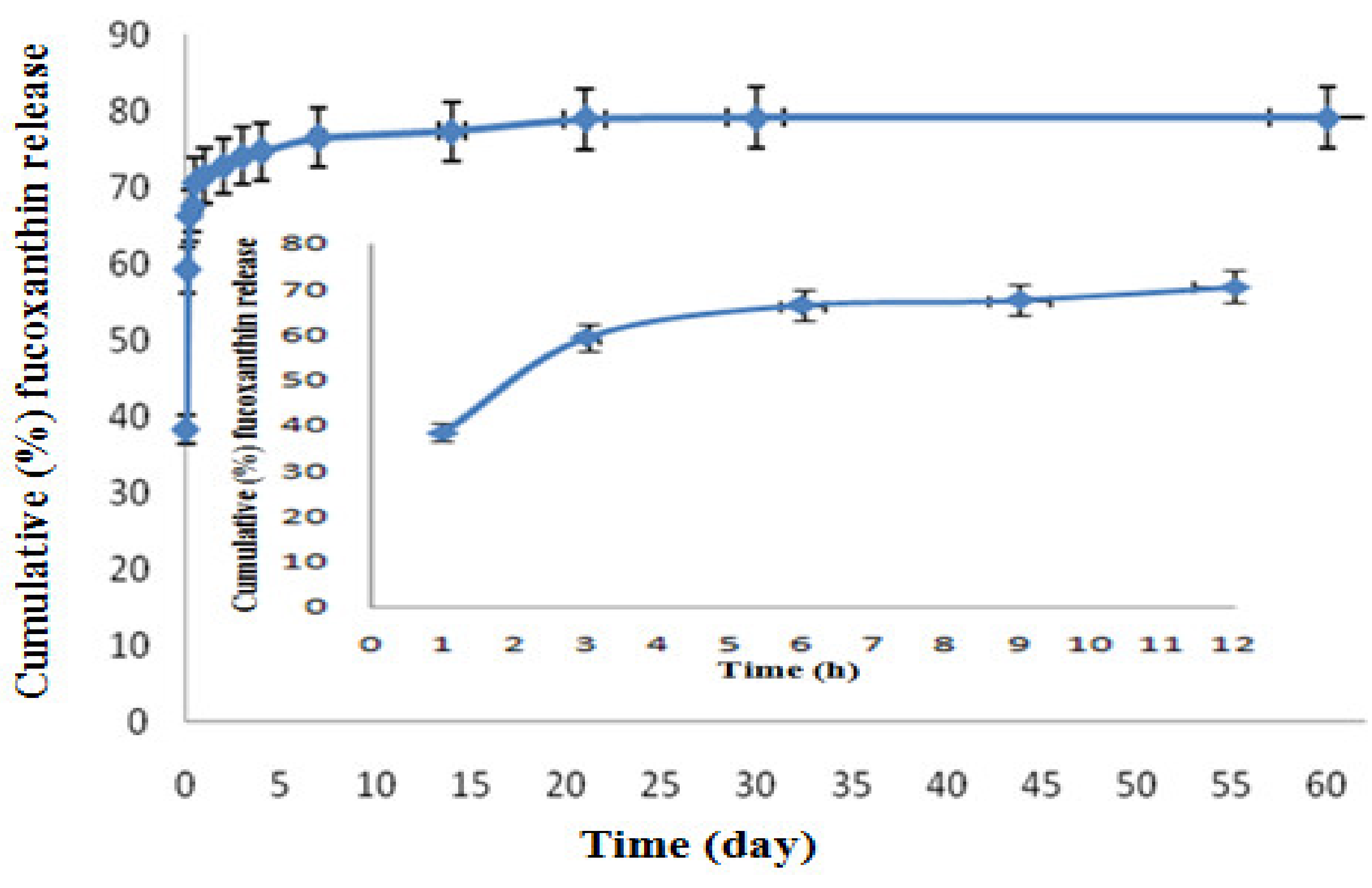
2.3. In Vitro Fucoxanthin Release Profile of F-LM
2.4. Release Kinetics of F-LM
2.5. Degradation Study of F-LM
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Optimization of Medium Component by RSM
3.3. Fabrication of F-LM
3.4. EE of F-LM
3.5. Particle Size Analysis of F-LM
3.6. External Morphology of F-LM
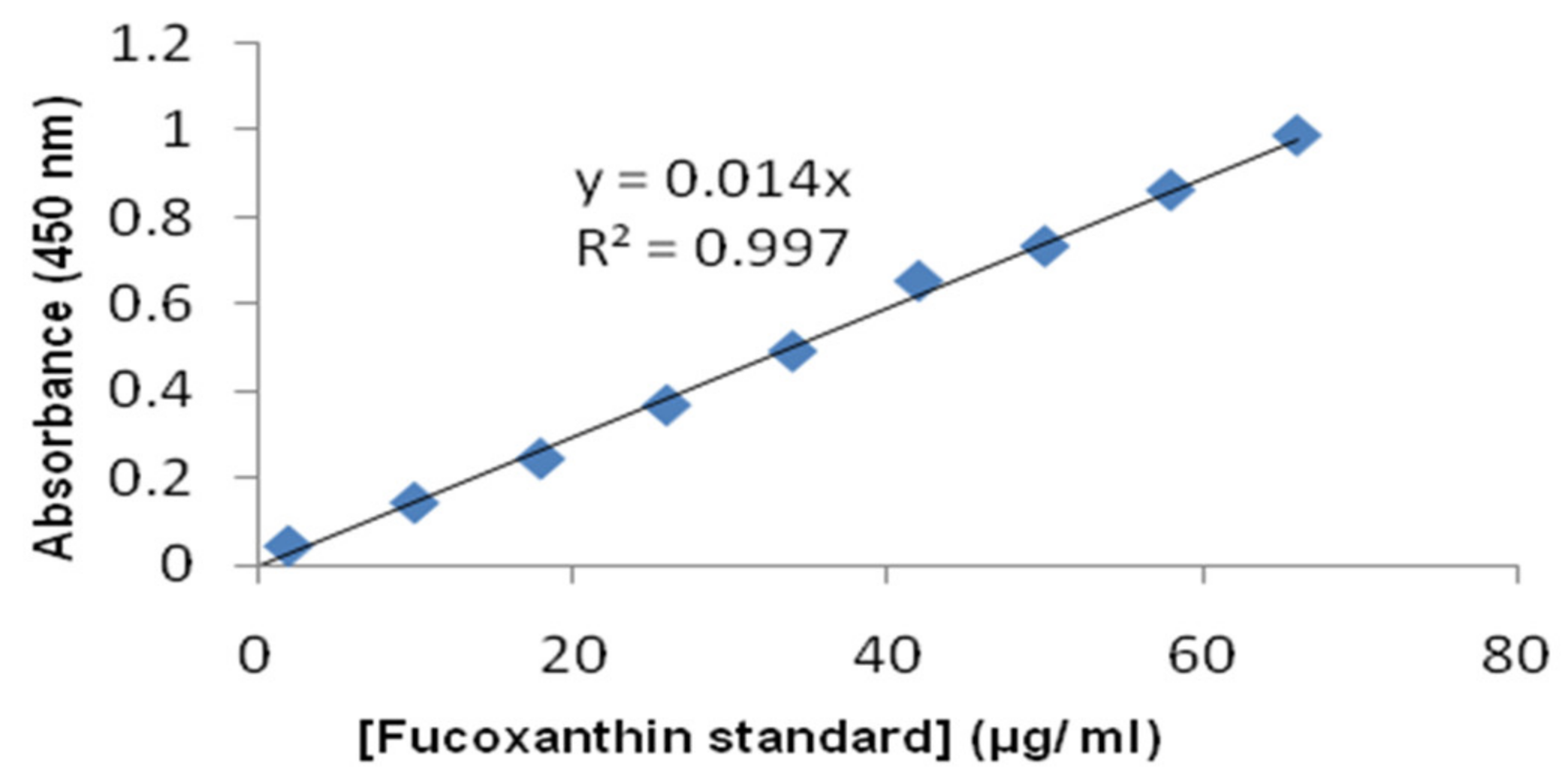
3.7. In Vitro Fucoxanthin Release Profile
3.8. Evaluation of Release Kinetics
3.9. Degradation Study of F-LM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AppaRao, B.; Shivalingam, M.R.; Reddy, Y.K.; Sunitha, N.; Jyothibasu, T.; Shyam, T. Design and evaluation of sustained release microcapsules containing diclofenac sodium. Int. J. Pharm. Biomed. Res. 2010, 1, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.R.; Hasokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid Exerting Anti-Cancer Effects by Affecting Multiple Mechanism. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satomi, Y. Antitumor and Cancer-preventative Function of Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronino, D.; Offerta, A.; Ostacolo, C.; Russo, R.; De Caro, C.; Calignano, A.; Puglia, C.; Blasi, P. Nanoparticles prolong N-palmitoylethanolamide anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects in vivo. Colloid Surf. B 2016, 141, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaylen, M.Z. Biodegradable block copolymers for delivery of proteins and water-insoluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2001, 72, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Costa, E.; Abreu, M.; Gargiulo, D.; Rocha, E.; Ramos, A.A. Anticancer effects of seaweed compounds fucoxanthin and phloroglucinol, alone and in combination with 5-fluorouracil in colon cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2017, 80, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Hwang, S.J.; Park, J.B.; Park, H.J. Preparation and characterization of drug-loaded polymethacrylate microspheres by an emulsion solvent evaporation method. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniyappan, M.; Vijayagopal, V.; Viswanathan, R.; Viruthagiri, T. Statistical optimization of substrate, carbon and nitrogen source by response surface methodology for pectinase production using Aspergillus fumigatus MTCC 870 in submerged fermentation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 6355–6363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, K.; Wang, Q. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from dried longan pulp using response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, S.W.; Tang, J.; Gu, X. Optimization of extraction process of crude polysaccharides from boat-fruited sterculia seeds by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Lugo, M.; Peppas, N.A. Transmucosal delivery systems for calcitonin: A review. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Takenaga, M.; Kitagawa, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Mizushima, Y.; Igarashi, R. Insulin-loaded biodegradable PLGA microcapsules: Initial burst release controlled by hydrophilic additives. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurus, P.B.; Kaeding, C.C. Bioabsorbable implant material review. Oper. Tech. Sports Med. 2004, 12, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhana Lekshmi, U.M.; Poovi, G.; Kishore, N.; Reddy, P.N. In vitro characterization and in vivo toxicity study of repaglinide loaded poly (methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmana Prabu, S.; Shirwaikar, A.A.; Shirwaikar, A.; Kumar, A. Formulation and evaluation of sustained release microspheres of rosin containing aceclofenac. Ars Pharm. 2009, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dhakar, R.C. From Formulation Variables To Drug Entrapment Efficiency Of Microspheres: A Technical Review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2012, 2, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, D.V.; Rajesh, N.; Moin, A.; Shivakumar, H.G. Controlled Release Behaviour of Nifedipine from the Pellets of Gelucire/Microcrystalline Cellulose Blends. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2010, 2, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha, P.; Fareed, S.; Nanda, S.; Mishra, A. Design & fabrication of tramadol HCL loaded multiparticulate colon targeted drug delivery system. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 584–595. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, G.; Feng, S.-S. Preparation and characterization of poly (lactic acid)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (lactic acid) (PLA-PEG-PLA) microspheres for controlled release of paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 5037–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Pettway, G.J.; McCauley, L.K.; Ma, P.X. The release profiles and bioactivity of parathyroid hormone from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, L.; Mou, Y.; Shan, T.; Mao, Z.; Lu, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Medium optimization for exopolysaccharide production in liquid culture of endophytic fungus Berkleasmium sp. Dzf12. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11411–11426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, C.T.; Baran, E.T.; Pinho, E.D.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Performance of biodegradable microcapsules of poly(butylene succinate), poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) and poly(butylene terephthalate-co-adipate) as drug encapsulation systems. Colloid Surf. B 2011, 84, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Gao, C.; Shi, Y.; Shen, J. Preparation of porous polylactide microspheres by emulsion-solvent evaporation based on solution induced phase separation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2005, 16, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Ng, N.P. Morphology, drug distribution, and in vitro release profiles of biodegradable polymeric microspheres containing protein fabricated by double-emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation method. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.S. Biodegradable Paclitaxel-Loaded Plga Microspheres for Regional Treatment of Peritoneal Cancers. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, P.; Hickey, A.J. Respirable PLGA microspheres containing rifampicin for the treatment of tuberculosis: Manufacture and characterization. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.F. Formulation and Evaluation of Polyester Microspheres by Solvent-Evaporation Method. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Chia, H.H.; Chung, T.S. Effect of preparation temperature on the characteristics and release profiles of PLGA microspheres containing protein fabricated by double-emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation method. J. Control. Release 2000, 69, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Zhu, K.J. An improvement of double emulsion technique for preparing bovine serum albumin-loaded PLGA microspheres. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igartua, M.; Hernández, R.M.; Esquisabel, A.; Gascón, A.R.; Calvo, M.B.; Pedraz, J.L. Enhanced immune response after subcutaneous and oral immunization with biodegradable PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 1998, 56, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.H. Controlled Release of Bioactive Agents from Lactide/Glycolide Polymers. In Biodegradable Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems; Chasin, M., Langer, R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Schaper, A.; Kissel, T. Effects of process and formulation parameters on characteristics and internal morphology of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres formed by the solvent evaporation method. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, Y.; Baek, N.; Park, K. Microencapsulation methods for delivery of protein drugs. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2001, 6, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, A.; Sonakin, O.; Kiliçarslan, M.; Baykara, T. Effects of Stirring Rate and Drug: Polymer Ratio on the Characteristics of Levobunolol HCL Loaded Poly (ε-Caprolactone) Microparticles. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 7, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderi, R.; Sturesson, C.; Carlfors, J. Effect of preparative parameters on the characteristics of poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres made by the double emulsion method. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 141, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtezazi, T.; Washington, C.; Melia, C.D. Determination of the internal morphology of poly(d,l-lactide) microspheres using stereological methods. J. Control. Release 1999, 57, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A. Development and Characterization of Double Walled Microspheres from poly(l-lactic) and poly(d-l-Lactide-co-glycolide) Blends. Ph.D. Dissertation, UMI No. 3087334. University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA, 2003; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, J.; Hamishehkar, H.; Najafabadi, A.R.; Gilani, K.; Minaiyan, M.; Mahdavi, H.; Nokhodchi, A. A novel approach to prepare insulin-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microcapsules and the protein stability study. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1712–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khang, G.; Seo, S.A.; Choi, H.S.; Rhee, J.M.; Lee, H.B. Evaluation of in vitro release profiles of fentanyl-loaded PLGA oligomer microspheres. Macromol. Res. 2002, 10, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyavathi, M.; Ramana, N.V. In vitro and In vivo studies on controlled release microspheres of Simvastatin. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, Singapore, 15 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers as Medical Devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviendri, D.; Jaswir, I.; Salleh, H.M.; Taher, M.; Miyashita, K.; Ramli, N. Fucoxanthin extraction and fatty acid analysis of Sargassum binderi and S. duplicatum. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Jaswir, I.; Noviendri, D.; Salleh, H.M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin Extractions of Brown Seaweeds and Analysis of Their Lipid Fraction in Methanol. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswir, I.; Noviendri, D.; Salleh, H.M.; Taher, M.; Miyashita, K.; Ramli, N. Analysis of fucoxanthin content and purification of all-trans-fucoxanthin from Turbinaria turbinata and Sargassum plagyophyllum by SiO2 open column chromatography and reversed phase-HPLC. J. Liquid Chrom. Rel. Tech. 2013, 36, 1340–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Averineni, R.L.; Shavi, G.V.; Gurram, A.K.; Deshpande, P.B.; Arumugam, K.; Maliyakkal, N.; Meka, S.R.; Nayanabhirama, U. PLGA 50:50 nanoparticles of paclitaxel: Development, in vitro anti-tumor activity in BT-549 cells and in vivo evaluation. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chuda, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Nagata, T. Fucoxanthin as the Major Antioxidant in Hijikia fusiformis, a Common Edible Seaweed. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntari, B.; Amid, A.; Mel, M.; Jami, M.S.; Salleh, H.M. Recombinant bromelain production in Escherichia coli: Process optimization in shake flask culture by response surface methodology. AMB Express 2012, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.N.; Alam, M.Z.; Muyibi, S.A.; Jamal, P.; Al-Mamun, A. Improvement of production of citric acid from oil palm empty fruit bunches: Optimization of media by statistical experimental designs. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3113–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salihu, A.; Alam, M.Z.; Abdulkarim, M.I.; Salleh, H.M. Optimization of lipase production by Candida cylindracea in palm oil mill effluent based medium using statistical experimental design. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 69, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; van der Walle, C.F. PLGA microcapsules with novel dimpled surfaces for pulmonary delivery of DNA. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 311, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, H.; Abdalmonemdoolaanea, A.F.; Awang, M.; Mohamed, F.; Ismail, A.F.H. High initial burst release of gentamicin formulated as PLGA microspheres implant for treating orthopaedic infection. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Arkendu, C.; Benoy, B.B.; Lait, K. Formulation, in vitro evaluation and stability of Prolong Release anti-HIV Bioadhesive Microencapsulated Vaginal Gel. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 1, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Alfatama, M.; Ahmad, K.; Mohamed, F. Microencapsulation of cassia Alata: Fabrication and characterization. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, K.; Ooi, T.; Hiraoka, M.; Oka, N.; Hamada, H.; Tamura, M.; Kusumi, T. Fucoxanthin and Its Metabolites in Edible Brown Algae Cultivated in Deep Seawater. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin and its metabolite, fucoxanthinol, suppress adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Sashima, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Comparative evaluation of growth inhibitory effect of stereoisomers of fucoxanthin in human cancer cell lines. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. pH-sensitive and Targeted PLGA-Based Drug Delivery to Colorectal Cancer. Ph.D. Thesis, Deakin University, Victoria, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siepmann, J.; Faisant, N.; Akiki, J.; Richard, J.; Benoit, J.P. Effect of the size of biodegradable microparticles on drug release: Experiment and theory. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds fucoxanthin are available from the authors. |



| Run | PVA (% w/v) | PLGA (% w/v) | Fuco (µg/mL) | PS (µm) | EE (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ex. | Pr.* | Ex. | Pr.** | ||||
| 1 | 0.80 (+1) | 6.00 (0) | 200.00 (0) | 5.12 | 4.38 | 28.91 | 28.93 |
| 2 | 0.50 (0) | 6.00 (0) | 100.00 (−1) | 7.48 | 7.90 | 22.25 | 22.35 |
| 3 | 0.20 (−1) | 9.00 (+1) | 300.00 (+1) | 6.45 | 6.67 | 33.97 | 33.33 |
| 4 | 0.20 (−1) | 3.00 (−1) | 100.00 (−1) | 4.95 | 4.34 | 19.85 | 18.43 |
| 5 | 0.20 (−1) | 9.00 (+1) | 100.00 (−1) | 5.18 | 5.22 | 25.57 | 26.85 |
| 6 | 0.80 (+1) | 9.00 (+1) | 100.00 (−1) | 3.12 | 3.48 | 21.15 | 20.64 |
| 7 | 0.50 (0) | 3.00 (−1) | 200.00 (0) | 6.85 | 8.04 | 24.56 | 26.40 |
| 8 | 0.20 (−1) | 6.00 (0) | 200.00 (0) | 6.01 | 6.69 | 33.94 | 34.30 |
| 9 | 0.20 (−1) | 3.00 (−1) | 300.00 (+1) | 5.36 | 5.02 | 28.72 | 29.13 |
| 10 | 0.80 (+1) | 9.00 (+1) | 300.00 (+1) | 3.97 | 4.59 | 28.87 | 30.19 |
| 11 | 0.50 (0) | 9.00 (+1) | 200.00 (0) | 10.95 | 9.71 | 34.87 | 33.41 |
| 12 | 0.50 (0) | 6.00 (0) | 200.00 (0) | 9.18 | 9.30 | 33.09 | 32.34 |
| 13 | 0.80 (+1) | 3.00 (−1) | 300.00 (+1) | 2.16 | 2.13 | 25.97 | 24.59 |
| 14 | 0.50 (0) | 6.00 (0) | 300.00 (+) | 9.26 | 8.79 | 32.19 | 32.47 |
| 15 | 0.80 (+1) | 3.00 (−1) | 100.00 (−1) | 2.01 | 1.80 | 10.27 | 10.82 |
| Source | Sum of Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 88.67 | 8.99 | 0.0131 |
| PVA, A | 13.39 | 12.22 | 0.0174 |
| PLGA, B | 6.96 | 6.35 | 0.0532 |
| Fuco, C | 1.99 | 1.82 | 0.2357 |
| A2 | 36.34 | 33.17 | 0.0022 |
| B2 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.5442 |
| C2 | 2.34 | 2.14 | 0.2036 |
| AB | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.6121 |
| AC | 0.058 | 0.054 | 0.8274 |
| BC | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.6208 |
| Source | Sum of Square | F-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 614.88 | 23.17 | 0.0015 |
| PVA, A | 72.25 | 24.51 | 0.0043 |
| PLGA, B | 122.92 | 41.69 | 0.0013 |
| Fuco, C | 256.34 | 86.95 | 0.0002 |
| A2 | 1.35 | 0.46 | 0.5287 |
| B2 | 15.24 | 5.71 | 0.0721 |
| C2 | 62.48 | 21.19 | 0.0058 |
| AB | 0.99 | 0.33 | 0.5879 |
| AC | 4.73 | 1.60 | 0.2612 |
| BC | 8.93 | 3.03 | 0.1424 |
| Equation | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.719 | 0.792 | 0.841 |
| Model | Plot | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Zero order | Qt vs. t | Qt = K0t |
| First order | ln (Q0 − Qt) vs. t | ln Qt = ln Q0 − K1t |
| Higuchi | Qt vs. t1/2 | Qt = Kht1/2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaswir, I.; Noviendri, D.; Taher, M.; Mohamed, F.; Octavianti, F.; Lestari, W.; Mukti, A.G.; Nirwandar, S.; Hamad Almansori, B.B. Optimization and Formulation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Microsphere (F-LM) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Analysis of Its Fucoxanthin Release Profile. Molecules 2019, 24, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050947
Jaswir I, Noviendri D, Taher M, Mohamed F, Octavianti F, Lestari W, Mukti AG, Nirwandar S, Hamad Almansori BB. Optimization and Formulation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Microsphere (F-LM) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Analysis of Its Fucoxanthin Release Profile. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050947
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaswir, Irwandi, Dedi Noviendri, Muhammad Taher, Farahidah Mohamed, Fitri Octavianti, Widya Lestari, Ali Ghufron Mukti, Sapta Nirwandar, and Bubaker B. Hamad Almansori. 2019. "Optimization and Formulation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Microsphere (F-LM) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Analysis of Its Fucoxanthin Release Profile" Molecules 24, no. 5: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050947
APA StyleJaswir, I., Noviendri, D., Taher, M., Mohamed, F., Octavianti, F., Lestari, W., Mukti, A. G., Nirwandar, S., & Hamad Almansori, B. B. (2019). Optimization and Formulation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Microsphere (F-LM) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Analysis of Its Fucoxanthin Release Profile. Molecules, 24(5), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050947







