Graphene-Based Materials as Efficient Photocatalysts for Water Splitting
Abstract
1. Introduction
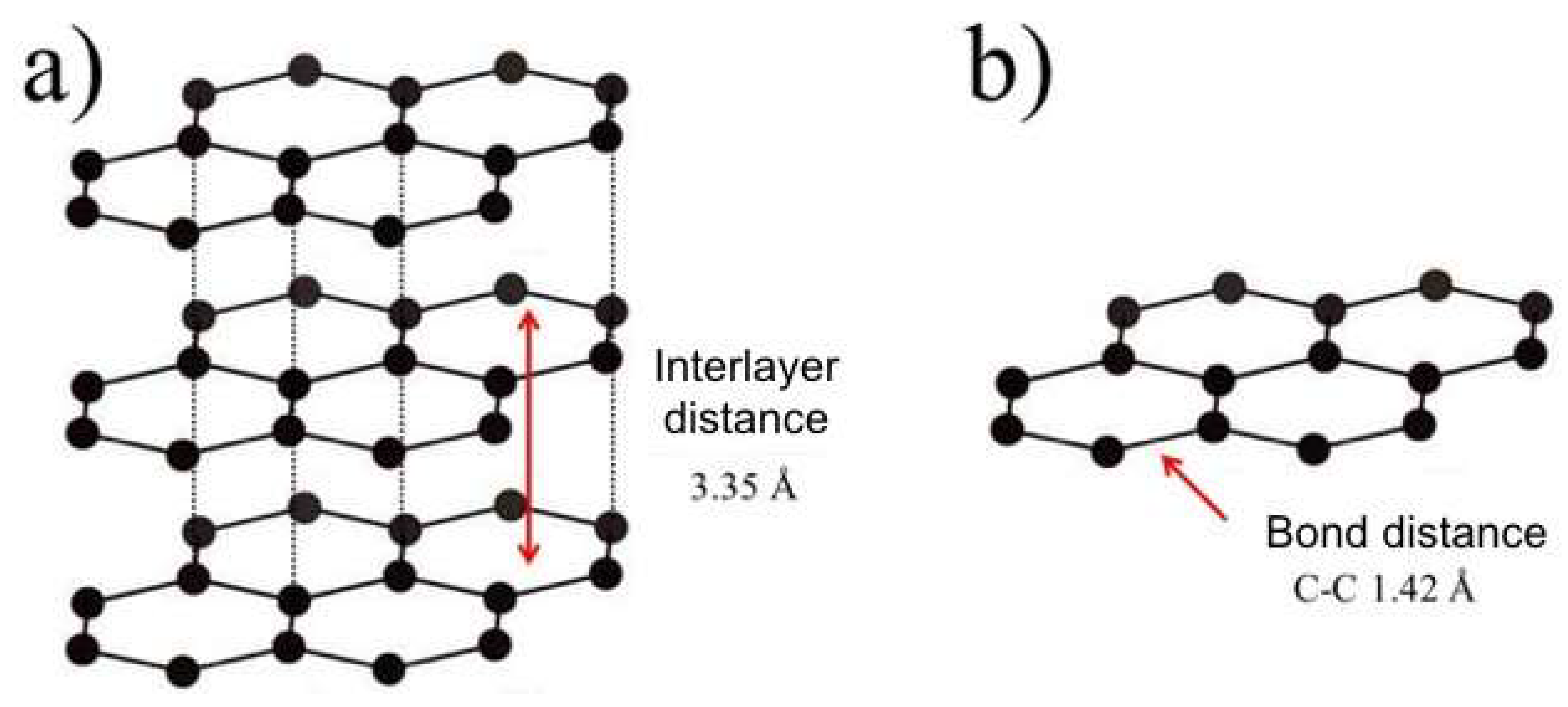
2. G-Based Materials. Properties and Preparation
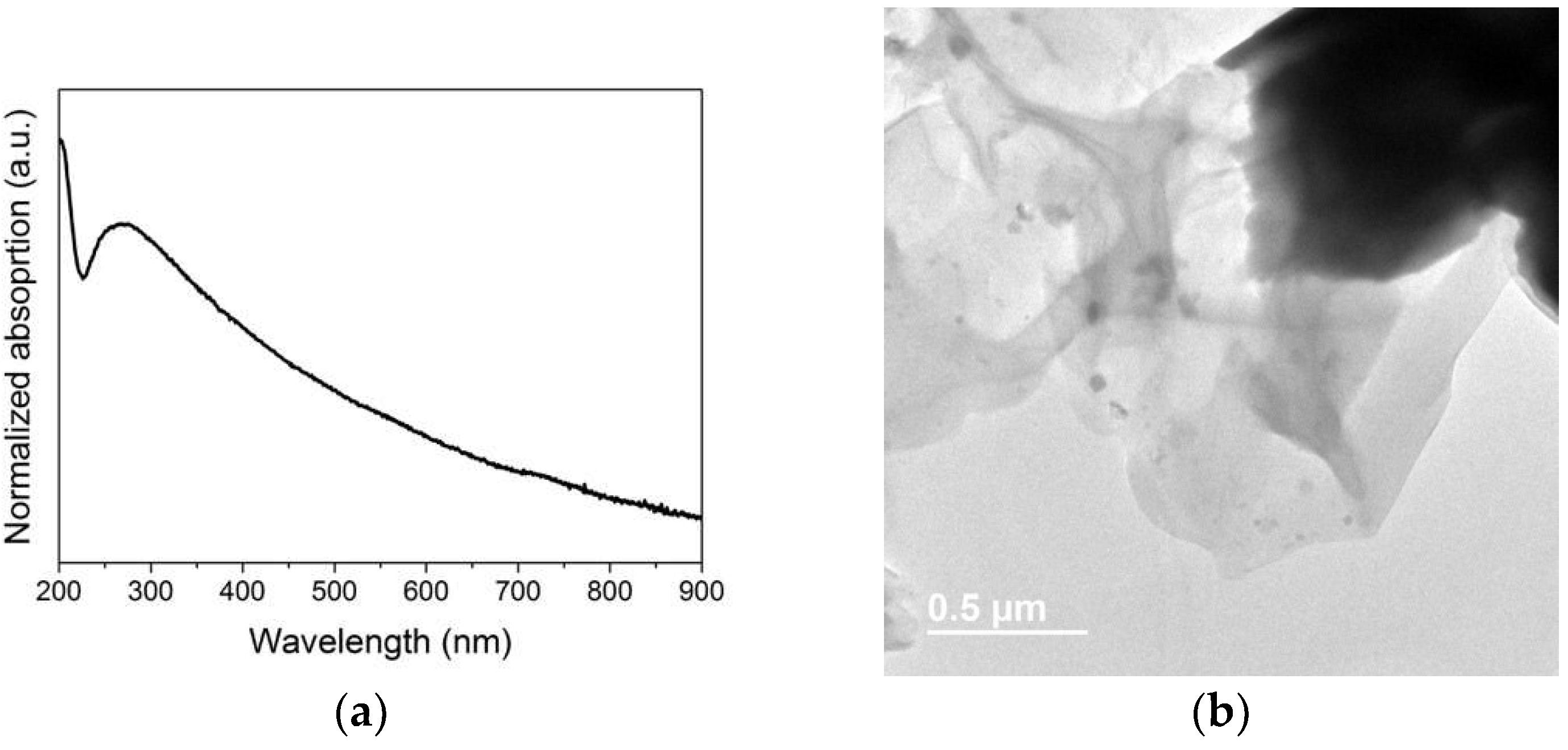
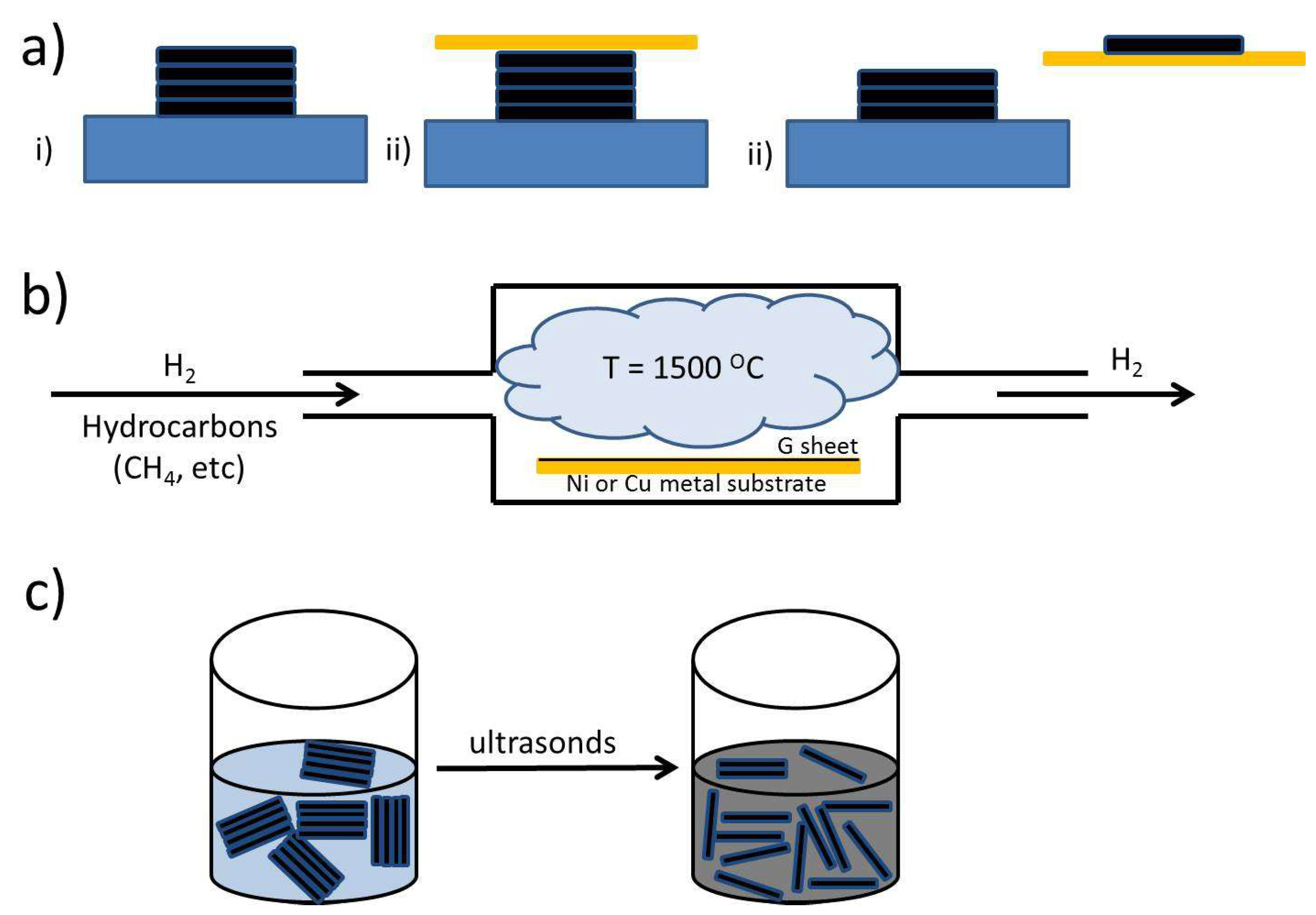
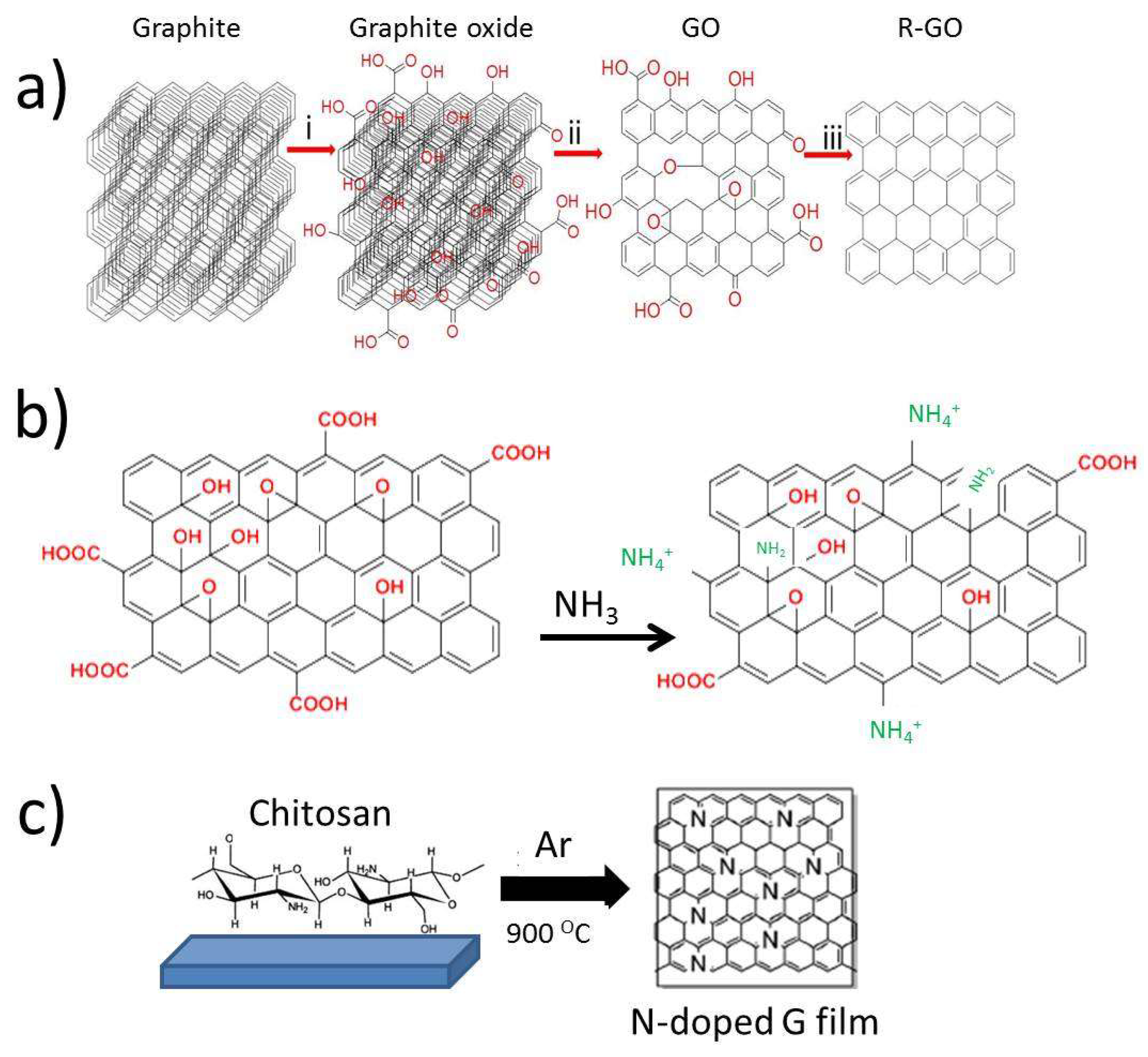
2.1. G-Based Materials Preparation Procedures
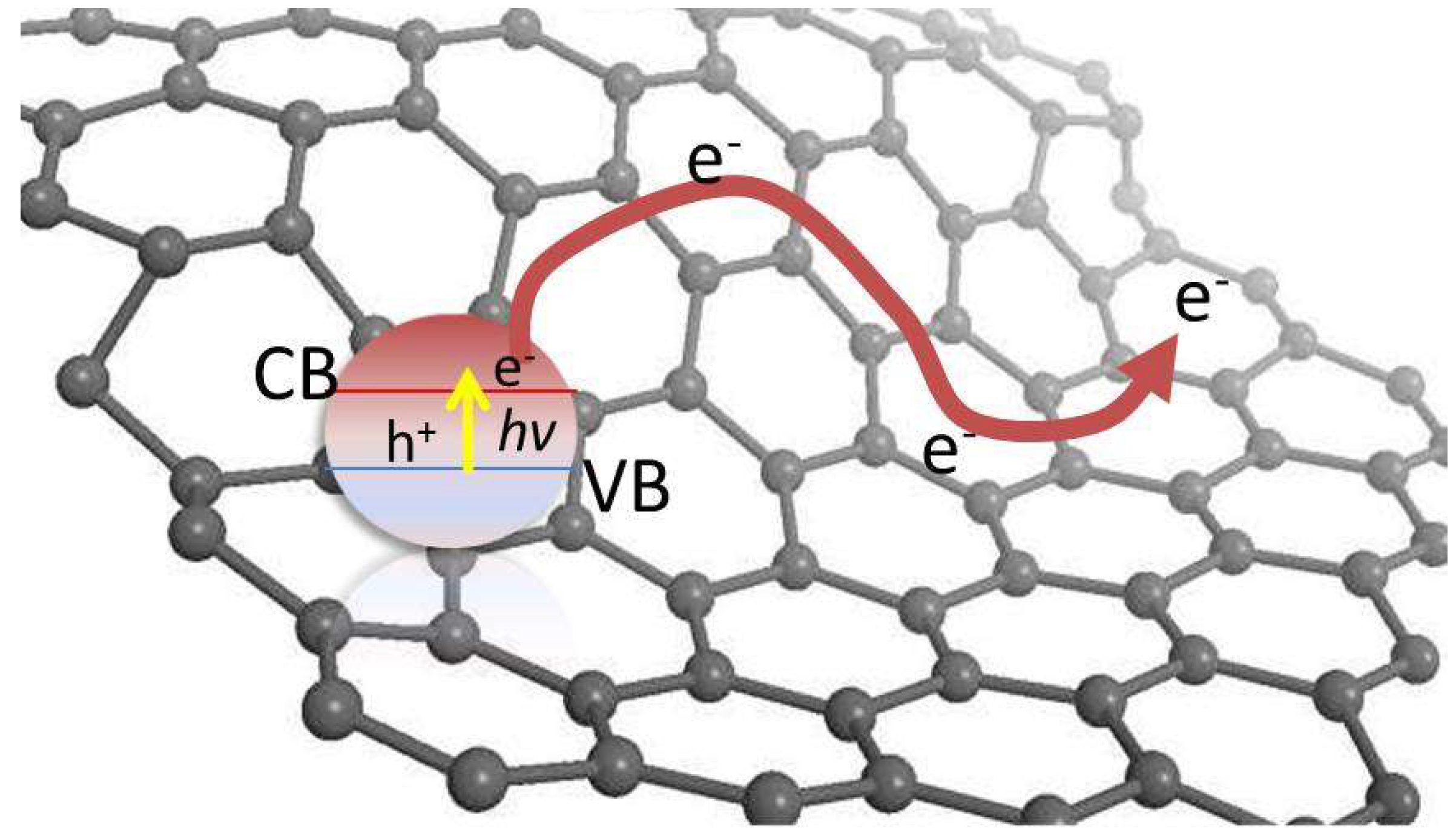
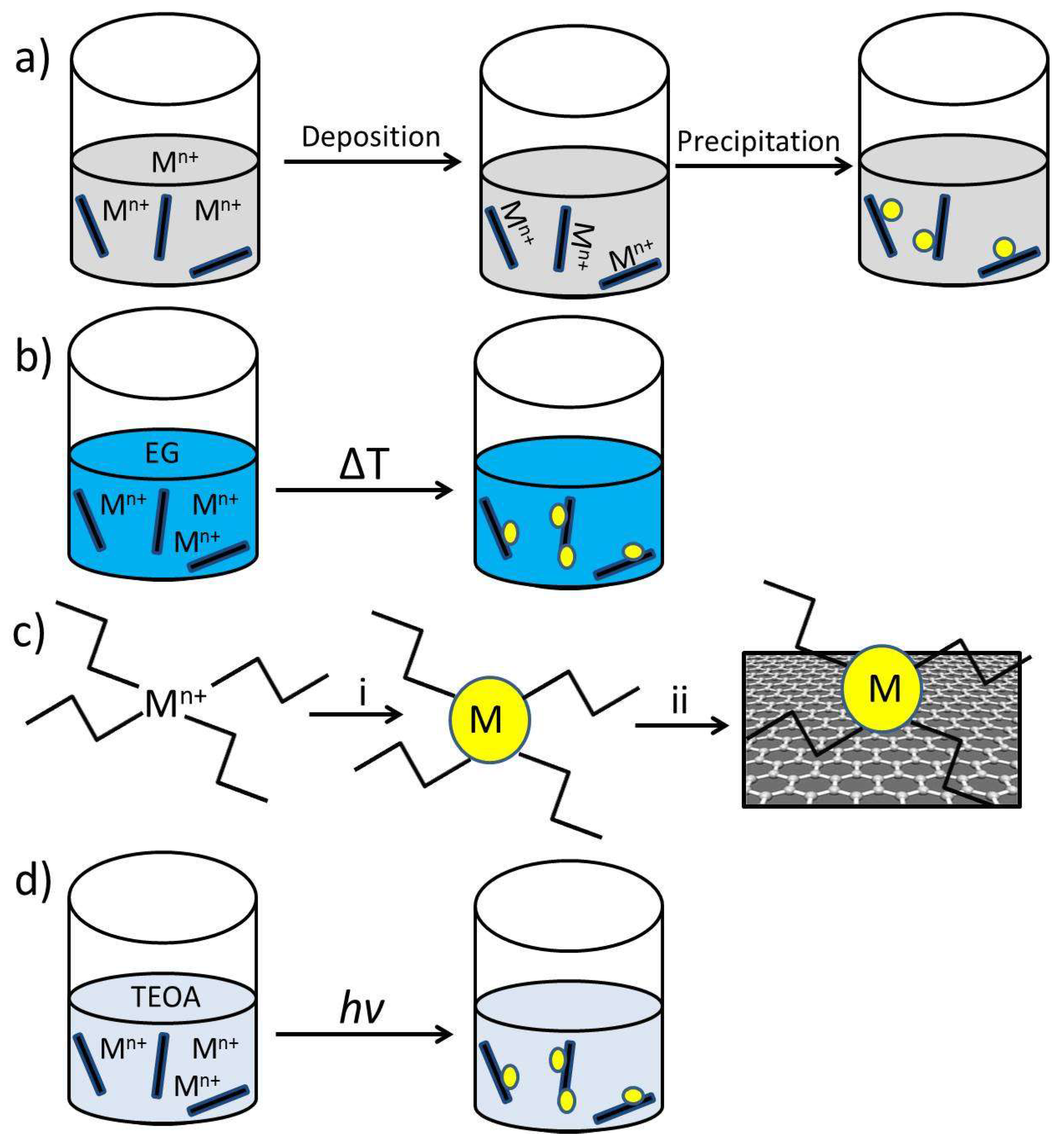
2.2. G as Support of Metal or Metal Oxide NPs
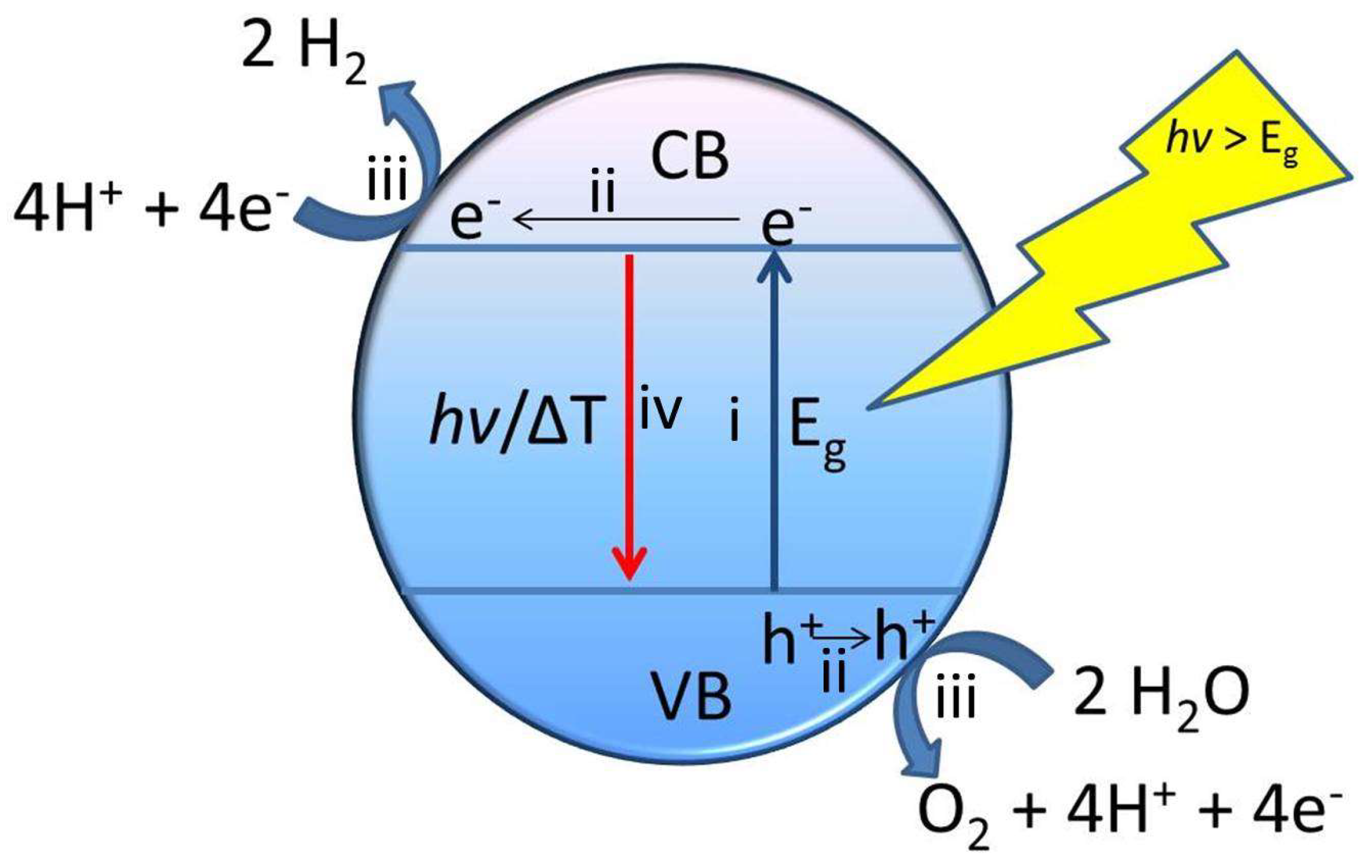
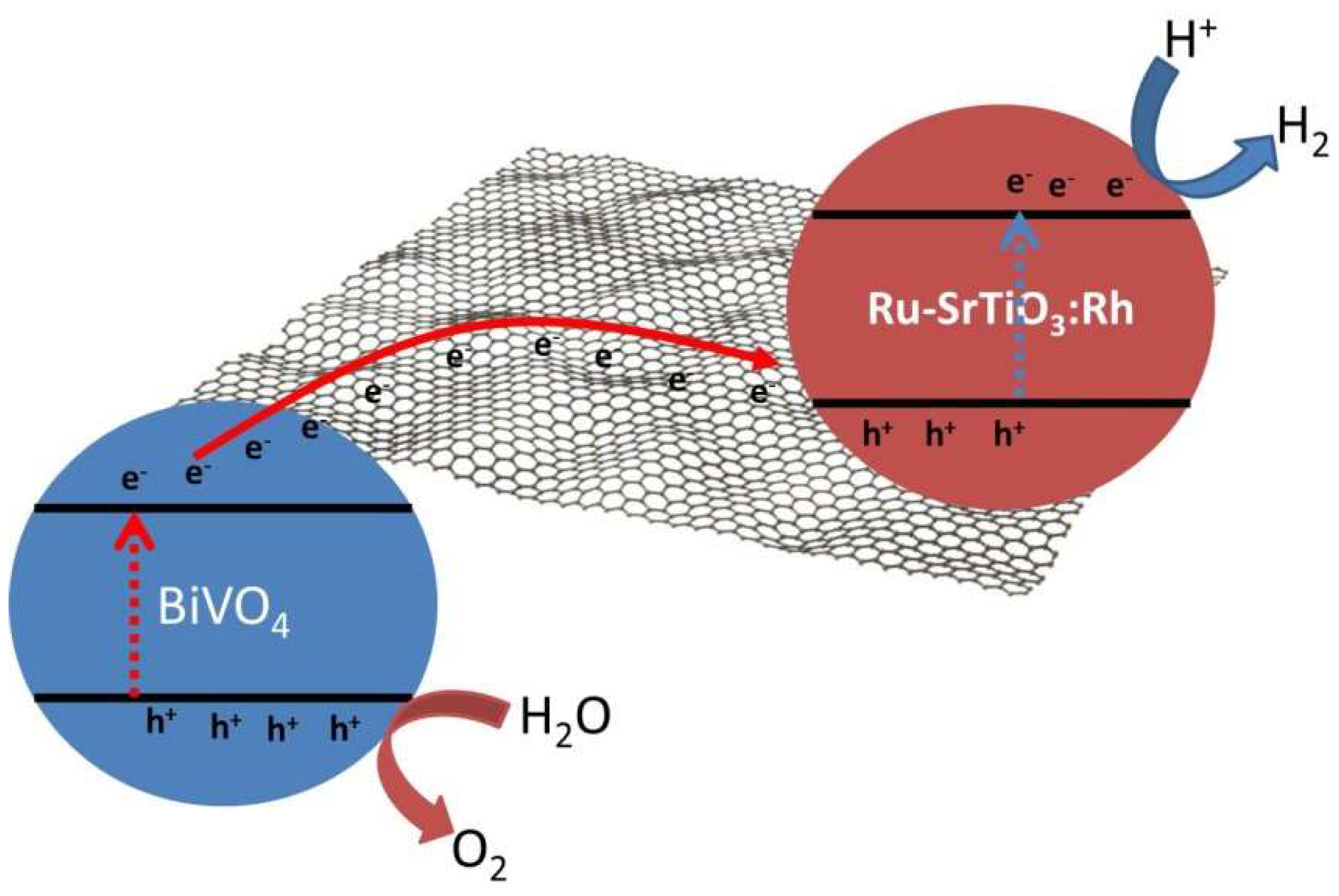
3. G-Based Materials as Photocatalysts for Water Splitting
4. Metal and Metal Oxide NPs Supported on G-Based Materials as Photocatalysts
4.1. Randomly Oriented Metal or Metal Oxide NPs
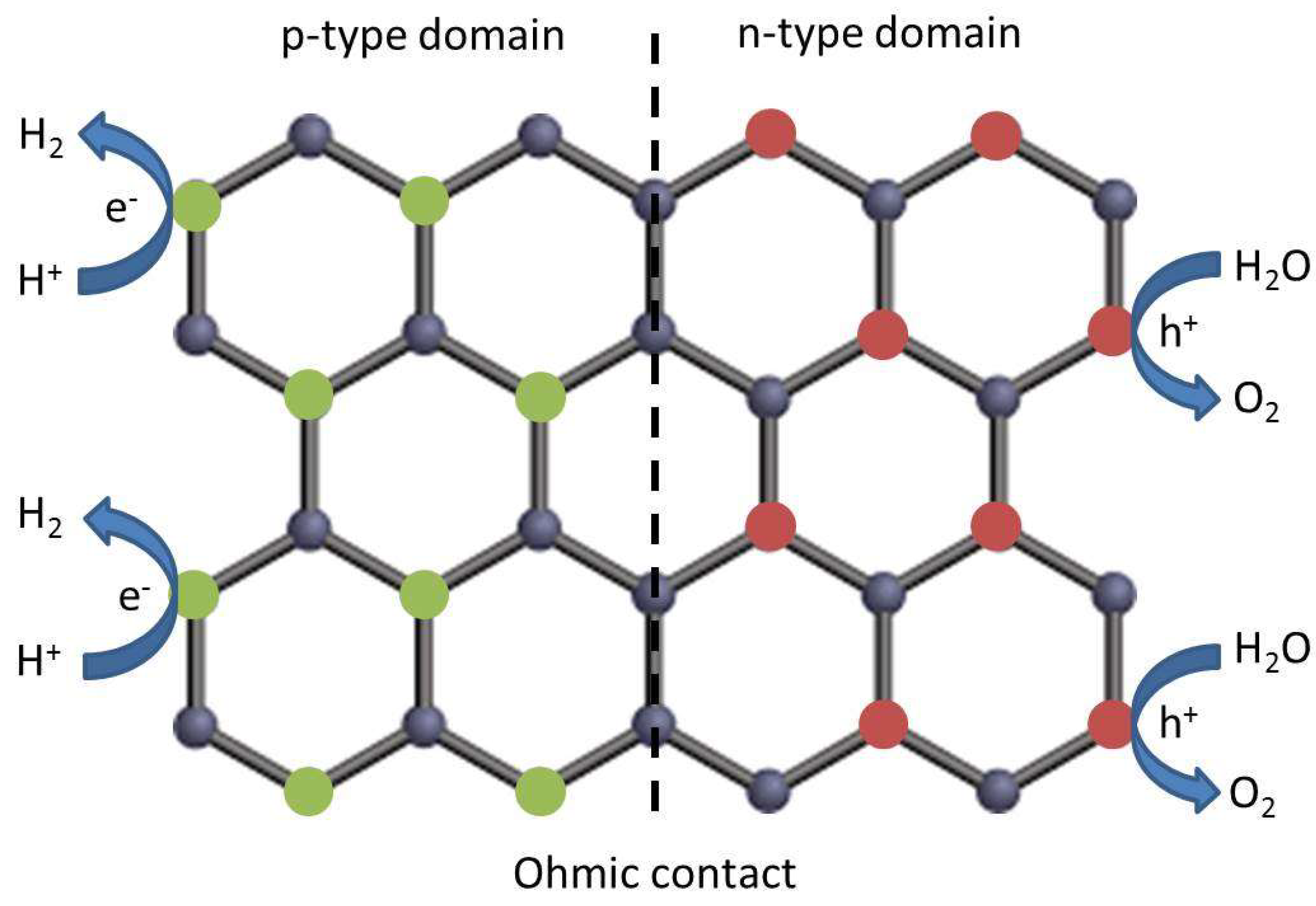
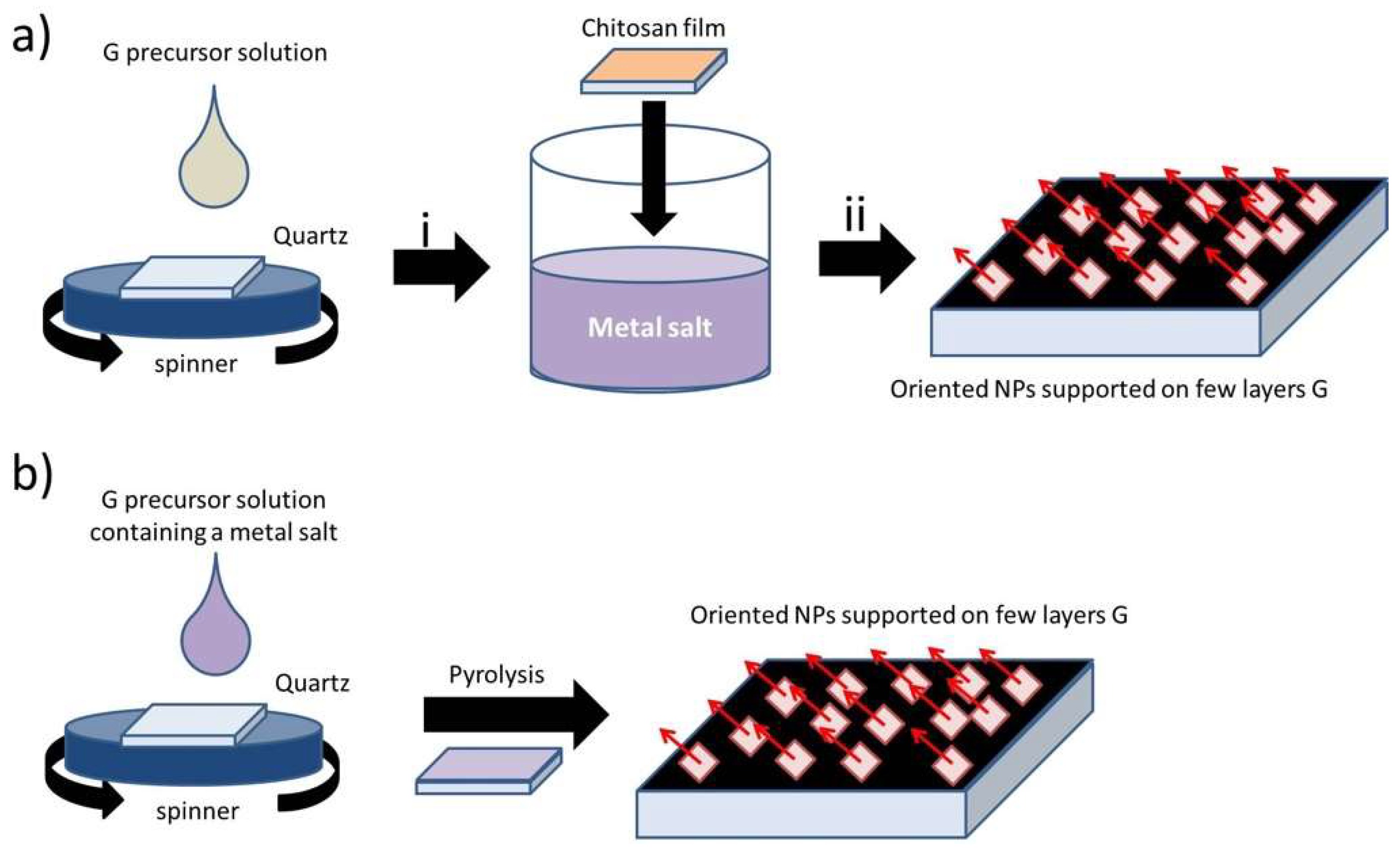
4.2. Preferential Orientation in Metal or Metal Oxide NPs
| Photocatalysts | H2 Production | Conditions | Light Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO (O: 28 wt%) | 5.67 mmol/g·h | H2O/MeOH (80:20, v:v) | 400 W Hg lamp | [35] |
| P/G (C1s /P1s: 12.73 at%) | 12 µmol/g·h | H2O/MeOH (70:30, v:v) | 300 W Xe lamp | [41] |
| N/G (N: 5.4 wt%) | 5 mmol/g·h | H2O/MeOH (70:30, v:v) | Laser pulse at 532 nm (1800 mW/cm2) | [42] |
| N/r-GO (8.25 at%) | 67 µmol/g·h | 0.1M Na2S/Na2SO3 aqueous solution | 500 W Xe lamp with visible light cut off | [43] |
| B/r-GO (3.59 at%) | 65 µmol/g·h | 0.1M Na2S/Na2SO3 aqueous solution | 500 W Xe lamp with visible light cut off | [43] |
| N/GQDs (N: 6 at%) | 0.51 µmol/g·h | Pure H2O | 300 W Xe lamp with UV light cut off | [45] |
| S/GQDs (1.9 at%) | 568 µmol/g·h | H2O/iPrOH (80:20, v:v), 95 °C, pH 8 | 500 W Xe lamp | [46] |
| Ni/GO (Ni: 3 wt%) | 70 µmol/ h | H2O/MeOH (80:20, v:v) | 400 W Hg lamp | [57] |
| Ni(OH)2/G films (Ni(OH): 1.6 wt%) | 110 µmol/g·h | Pure water | Monochromatic 254 nm | [58] |
| Ni/r-GO (Ni: 8 wt%) | 94 µmol/g·h | 2·10−4 M Eosin Y + 7.7·10−2M Trimethylamine aqueous solution | Hg lamp UV light cut off | [12] |
| MoS2/r-GO (MoS2: 52.7 wt%) | 1.2 mmol/g·h | H2O/TEOA (85:15, v:v) | Xe lamp UV light cut off (130 mW/cm2 | [60] |
| Oriented CuO2/N-G films (CuO2: 4.75 µg/cm2) | 19.5 mmol/g·h | Pure water | 300 W Xe lamp | [68] |
| Oriented Au/N-G films (Au: 1 µg/cm2) | 1.2 mol/g·h | Pure water | 300 W Xe lamp | [69] |
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamat, P.V.; Bisquert, J. Solar Fuels. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 14873–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrell, J.; Birgersson, H.; Boutonnet, M. Steam reforming of methanol over a Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst: A kinetic analysis and strategies for suppression of CO formation. J. Power Sources 2002, 106, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Takata, T.; Domen, K. Particulate photocatalysts for overall water splitting. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Fernandez-Blanco, C.; Herance, J.R.; Albero, J.; García, H. Graphenes as additives in photoelectrocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16522–16536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Sa, B.; Ahuja, R. Review of two-dimensional materials for photocatalytic water splitting from a theoretical perspective. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, K.; Guo, B.; Liu, Q.; Fang, L.; Gong, J.R. Graphene-Based Materials for Hydrogen Generation from Light-Driven Water Splitting. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3820–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albero, J.; Garcia, H. Doped graphenes in catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 408, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Metal nanoparticles supported on two-dimensional graphenes as heterogeneous catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 312, 99–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Boukherroub, R.; Shankar, K. Sunlight-driven water-splitting using two-dimensional carbon based semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 12876–12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhart, F.; Kotakoski, J.; Krasheninnikov, A.V. Structural Defects in Graphene. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Peng, S. Synergetic effect of metal nickel and graphene as a cocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution via dye sensitization. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanov, B.I.; Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G.; Österlund, L. Quantitative relation between photocatalytic activity and degree of orientation for anatase TiO2 thin films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17369–17375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Chai, S.-P.; Yong, S.-T.; Mohamed, A.R. Facet-Dependent Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2-Based Composites for Energy Conversion and Environmental Remediation. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 690–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, J.H.; Schäffel, F.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Rümmeli, M.H. Chapter 3—Properties of Graphene. In Graphene; Warner, J.H., Schäffel, F., Bachmatiuk, A., Rümmeli, M.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 61–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, P.; Brimicombe, P.D.; Nair, R.R.; Booth, T.J.; Jiang, D.; Schedin, F.; Ponomarenko, L.A.; Morozov, S.V.; Gleeson, H.F.; Hill, E.W.; et al. Graphene-Based Liquid Crystal Device. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Navajas, P.; Asenjo, N.G.; Santamaría, R.; Menéndez, R.; Corma, A.; García, H. Surface Area Measurement of Graphene Oxide in Aqueous Solutions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13443–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Carbocatalysis by Graphene-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6179–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Wu, B.; Guo, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y. Controllable Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of Few Layer Graphene for Electronic Devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Sood, A.K.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Govindaraj, A. Graphene: The New Two-Dimensional Nanomaterial. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7752–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hernandez, Y.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. From Nanographene and Graphene Nanoribbons to Graphene Sheets: Chemical Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7640–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Ruoff, R.S.; Bielawski, C.W. From Conception to Realization: An Historial Account of Graphene and Some Perspectives for Its Future. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9336–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, A.; Atienzar, P.; Sanchez, E.; Delgado, J.M.; García, H. From biomass wastes to large-area, high-quality, N-doped graphene: Catalyst-free carbonization of chitosan coatings on arbitrary substrates. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9254–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomyakov, P.A.; Giovannetti, G.; Rusu, P.C.; Brocks, G.; van den Brink, J.; Kelly, P.J. First-principles study of the interaction and charge transfer between graphene and metals. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 195425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Moser, M.L.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.F.; Haddon, R.C. Metals on Graphene and Carbon Nanotube Surfaces: From Mobile Atoms to Atomtronics to Bulk Metals to Clusters and Catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Tsubota, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kageyama, H.; Genet, M.J.; Delmon, B. Low-Temperature Oxidation of CO over Gold Supported on TiO2, α-Fe2O3, and Co3O4. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M. Size- and support-dependency in the catalysis of gold. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Graphene−Metal Particle Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19841–19845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Bae, H.S.; Seo, E.; Jang, S.; Park, K.H.; Kim, B.-S. Hybrid gold nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide nanosheets as active catalysts for highly efficient reduction of nitroarenes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15431–15436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Ji, N.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Nanocomposites of size-controlled gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: Formation and applications in SERS and catalysis. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2733–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, S.; Abdelsayed, V.; Samy El-Shall, M. Laser synthesis of Pt, Pd, CoO and Pd–CoO nanoparticle catalysts supported on graphene. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 510, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghard, M.; Klauk, H.; Kern, K. Carbon-Based Field-Effect Transistors for Nanoelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2586–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Syu, J.-M.; Cheng, C.; Chang, T.-H.; Teng, H. Graphite Oxide as a Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Production from Water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.; Nakamura, J.; Natori, A. Semiconducting nature of the oxygen-adsorbed graphene sheet. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 113712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Chan, F.-F.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Teng, H. Graphite Oxide with Different Oxygenated Levels for Hydrogen and Oxygen Production from Water under Illumination: The Band Positions of Graphite Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 22587–22597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Domen, K. Defect Engineering of Photocatalysts by Doping of Aliovalent Metal Cations for Efficient Water Splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19386–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshi, M.; Ryoji, A.; Takeshi, O.; Koyu, A.; Yasunori, T. Band-Gap Narrowing of Titanium Dioxide by Nitrogen Doping. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, L561. [Google Scholar]
- Umebayashi, T.; Yamaki, T.; Itoh, H.; Asai, K. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide by sulfur doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre-Sánchez, M.; Primo, A.; García, H. P-Doped Graphene Obtained by Pyrolysis of Modified Alginate as a Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Water–Methanol Mixtures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11813–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavorato, C.; Primo, A.; Molinari, R.; Garcia, H. N-Doped Graphene Derived from Biomass as a Visible-Light Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Water/Methanol Mixtures. Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, L.K.; Ng, B.-J.; Ong, W.-J.; Lee, H.W.; Chang, W.S.; Chai, S.-P. Heteroatom Nitrogen- and Boron-Doping as a Facile Strategy to Improve Photocatalytic Activity of Standalone Reduced Graphene Oxide in Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4558–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, L. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Fluorine Tri-doped Graphene as a Multifunctional Catalyst for Self-Powered Electrochemical Water Splitting. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 13490–13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Teng, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Overall Water-Splitting under Visible Light Illumination. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliniak, J.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Li, C.-R.; Jokar, E.; Chang, C.-H.; Peng, C.-S.; Lin, J.-N.; Lien, W.-H.; Tsai, H.-M.; et al. Sulfur-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Generation in the Aqueous Phase. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3260–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Cihlář, J.; Chang, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.; Teng, H. Roles of graphene oxide in photocatalytic water splitting. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Seger, B.; Kamat, P.V. TiO2-Graphene Nanocomposites. UV-Assisted Photocatalytic Reduction of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, L.Y.; Garlisi, C.; Oladipo, H.; Pagliaro, M.; Sharief, S.A.; Yusuf, A.; Almheiri, S.; Palmisano, G. Inorganic semiconductors-graphene composites in photo(electro)catalysis: Synthetic strategies, interaction mechanisms and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2017, 33, 132–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozik, A.J.; Memming, R. Physical Chemistry of Semiconductor−Liquid Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 13061–13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Xiang, Q.; Cheng, B. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hierarchical macro/mesoporous TiO2–graphene composites for photodegradation of acetone in air. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 119–120, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; You, K.H.; Park, C.B. Highly Photoactive, Low Bandgap TiO2 Nanoparticles Wrapped by Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, A.; Ng, Y.H.; Ishiguro, Y.; Kudo, A.; Amal, R. Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Solid-State Electron Mediator in Z-Scheme Photocatalytic Water Splitting under Visible Light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11054–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Xie, J. Graphene in Photocatalysis: A Review. Small 2016, 12, 6640–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. 5-Graphene photocatalysts. In Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy; Lin, Z., Ye, M., Wang, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2018; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, R.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Xie, J. Graphene-based heterojunction photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, A.K.; Pan, C.-J.; Rick, J.; Lee, J.-F.; Su, W.-N.; Hwang, B.-J. Enhanced hydrogen generation by cocatalytic Ni and NiO nanoparticles loaded on graphene oxide sheets. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13849–13854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, J.; Gomez-solis, C.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Martinez-Luevanos, A.; Martinez, A.I.; Coutino-Gonzalez, E. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution by Flexible Graphene Composites Decorated with Ni(OH)2 Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Teng, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, H.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Architecting Nitrogen Functionalities on Graphene Oxide Photocatalysts for Boosting Hydrogen Production in Water Decomposition Process. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre-Sánchez, M.; Esteve-Adell, I.; Primo, A.; García, H. Innovative preparation of MoS2–graphene heterostructures based on alginate containing (NH4)2MoS4 and their photocatalytic activity for H2 generation. Carbon 2015, 81, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. Utilization of shape-controlled nanoparticles as catalysts with enhanced activity and selectivity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41017–41027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ciobanu, C.V.; Hu, J.; Palomares-Báez, J.-P.; Rodríguez-López, J.-L.; Richards, R. Experimental and DFT studies of gold nanoparticles supported on MgO(111) nano-sheets and their catalytic activity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Soon, A.; Han, H.; Lee, H. Shape effects of cuprous oxide particles on stability in water and photocatalytic water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendavid, L.I.; Carter, E.A. First-Principles Predictions of the Structure, Stability, and Photocatalytic Potential of Cu2O Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 15750–15760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primo, A.; Esteve-Adell, I.; Blandez, J.F.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Álvaro, M.; Candu, N.; Coman, S.M.; Parvulescu, V.I.; García, H. High catalytic activity of oriented 2.0.0 copper(I) oxide grown on graphene film. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve-Adell, I.; Bakker, N.; Primo, A.; Hensen, E.; García, H. Oriented Pt Nanoparticles Supported on Few-Layers Graphene as Highly Active Catalyst for Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Ethylene Glycol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33690–33696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- One-Step Pyrolysis Preparation of 1.1.1 Oriented Gold Nanoplatelets Supported on Graphene and Six Orders of Magnitude Enhancement of the Resulting Catalytic Activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 607–612. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, D.; Esteve-Adell, I.; Albero, J.; Primo, A.; García, H. Oriented 2.0.0 Cu2O nanoplatelets supported on few-layers graphene as efficient visible light photocatalyst for overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 201, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, D.; Esteve-Adell, I.; Albero, J.; Royo, J.F.S.; Primo, A.; Garcia, H. 111 oriented gold nanoplatelets on multilayer graphene as visible light photocatalyst for overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Lu, B.; Han, Q.; Li, Q.; Qu, L. (111) Facets-Oriented Au-Decorated Carbon Nitride Nanoplatelets for Visible-Light-Driven Overall Water Splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 38066–38072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albero, J.; Mateo, D.; García, H. Graphene-Based Materials as Efficient Photocatalysts for Water Splitting. Molecules 2019, 24, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050906
Albero J, Mateo D, García H. Graphene-Based Materials as Efficient Photocatalysts for Water Splitting. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050906
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbero, Josep, Diego Mateo, and Hermenegildo García. 2019. "Graphene-Based Materials as Efficient Photocatalysts for Water Splitting" Molecules 24, no. 5: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050906
APA StyleAlbero, J., Mateo, D., & García, H. (2019). Graphene-Based Materials as Efficient Photocatalysts for Water Splitting. Molecules, 24(5), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050906








