Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of NPRG
2.2. FR-IR Spectroscopy of NPRG
2.3. Monosaccharide Composition of NPRG
2.4. The Effect of NPRG on E. coli OP50 Growth
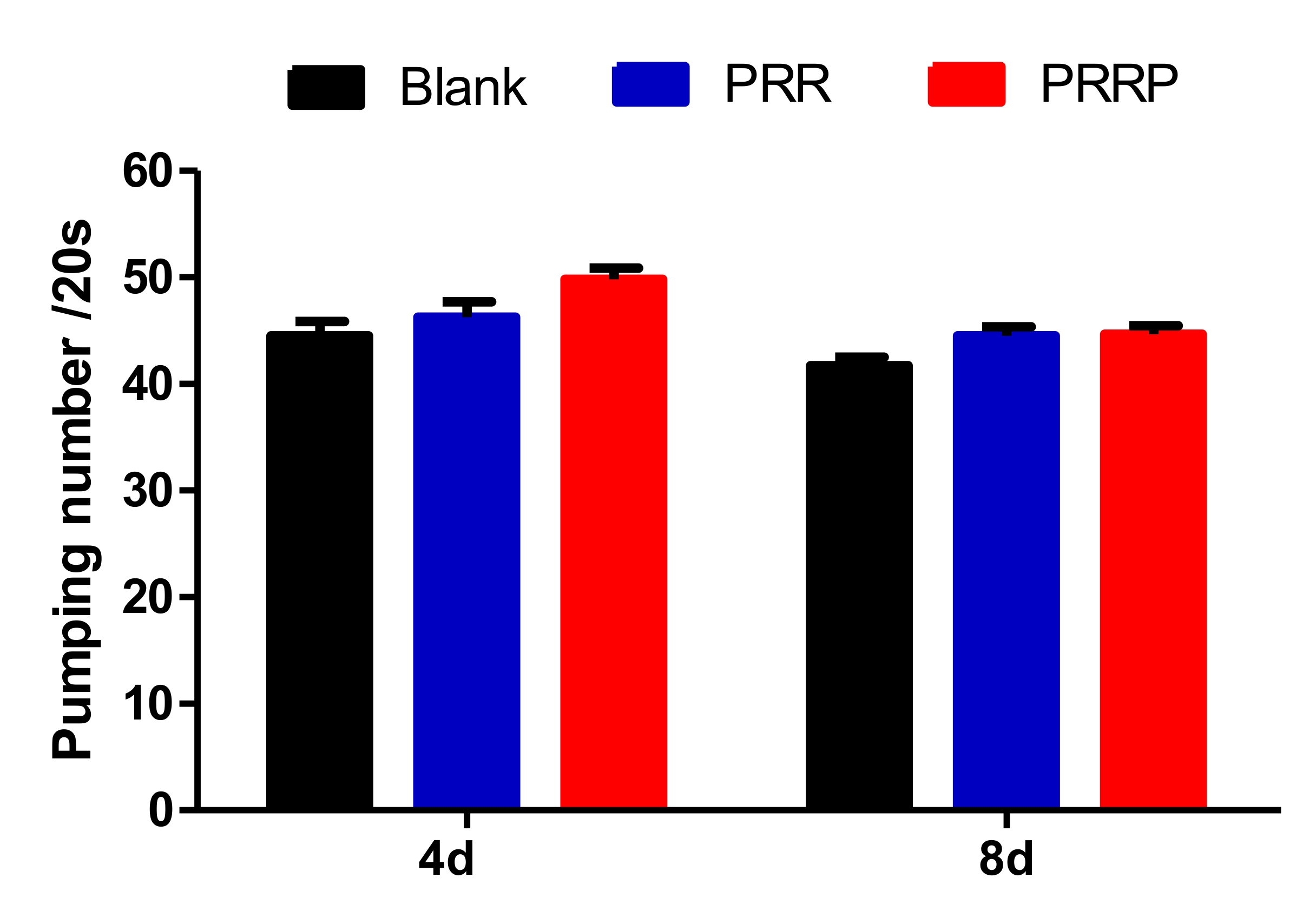
2.5. Effect of NPRG on Pharyngeal Pump Movement of Nematodes
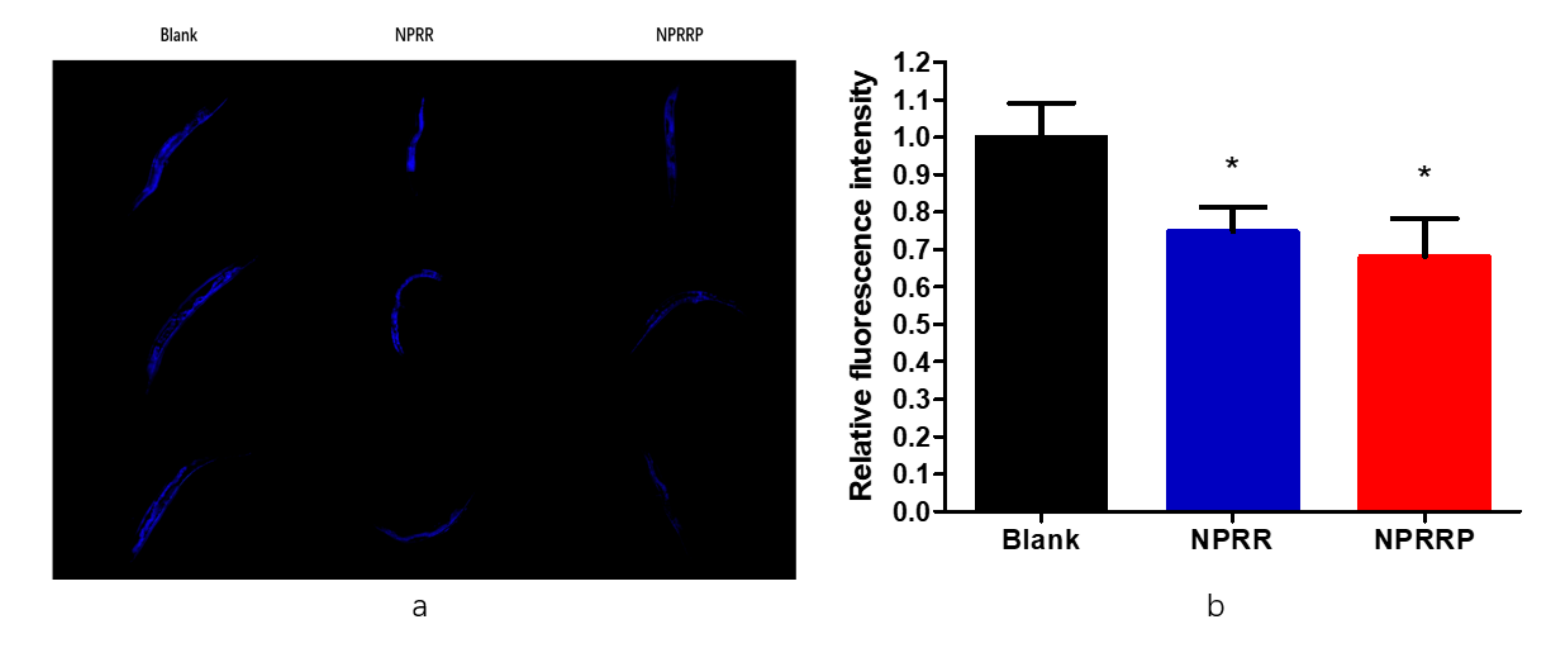
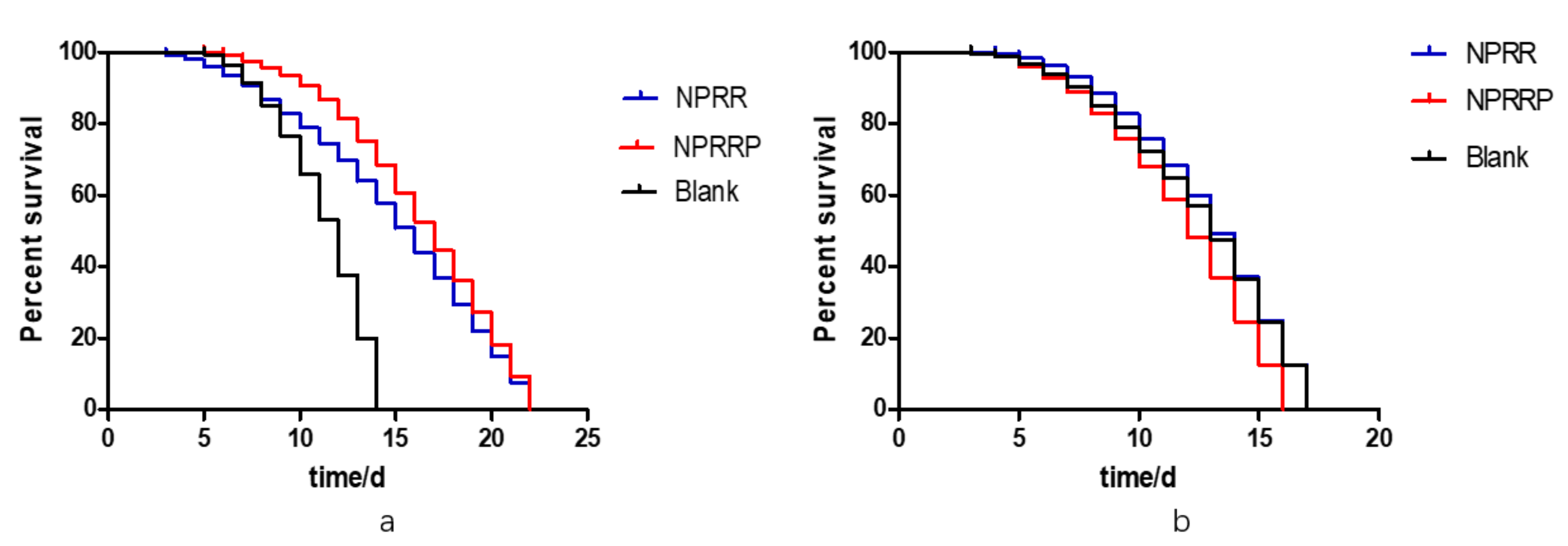
2.6. Reduction of Age Pigments Accumulation and Extension of Lifespan by NPRG in C. elegans
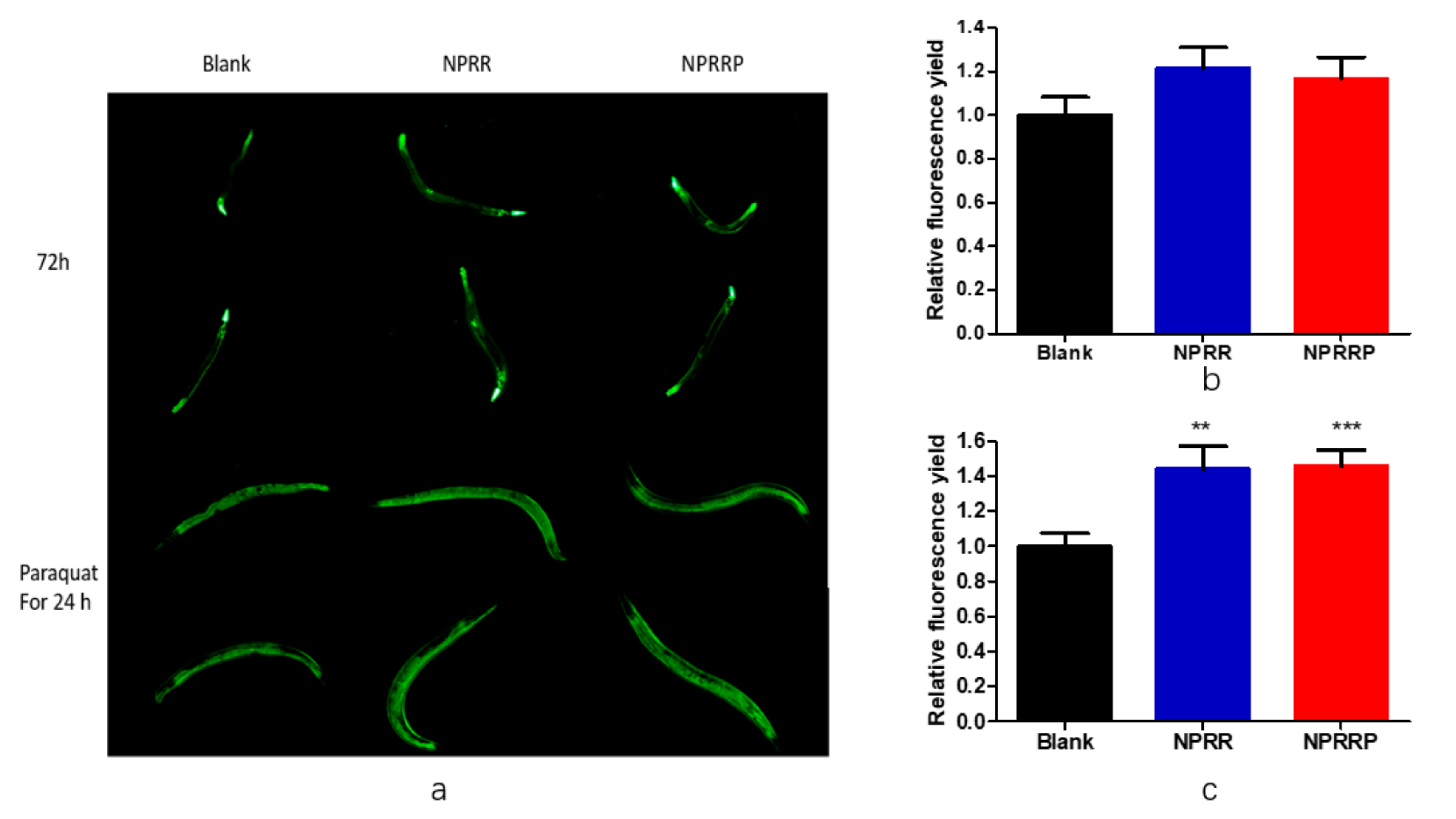
2.7. NPRG Improved the Expression and Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes in Nematode under Oxidative Stress
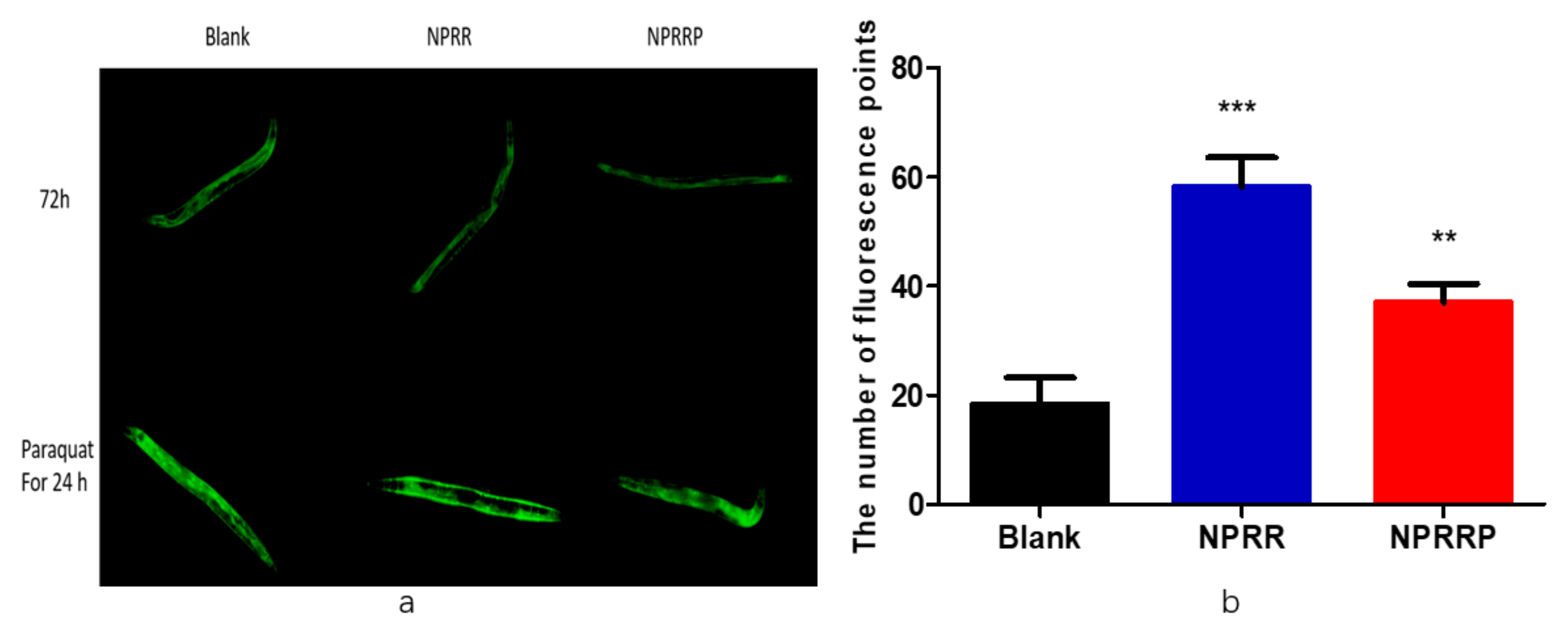
2.8. NPRG Can Induce the Nuclear Localization of DAF-16::GFP under the State of Oxidative Stress
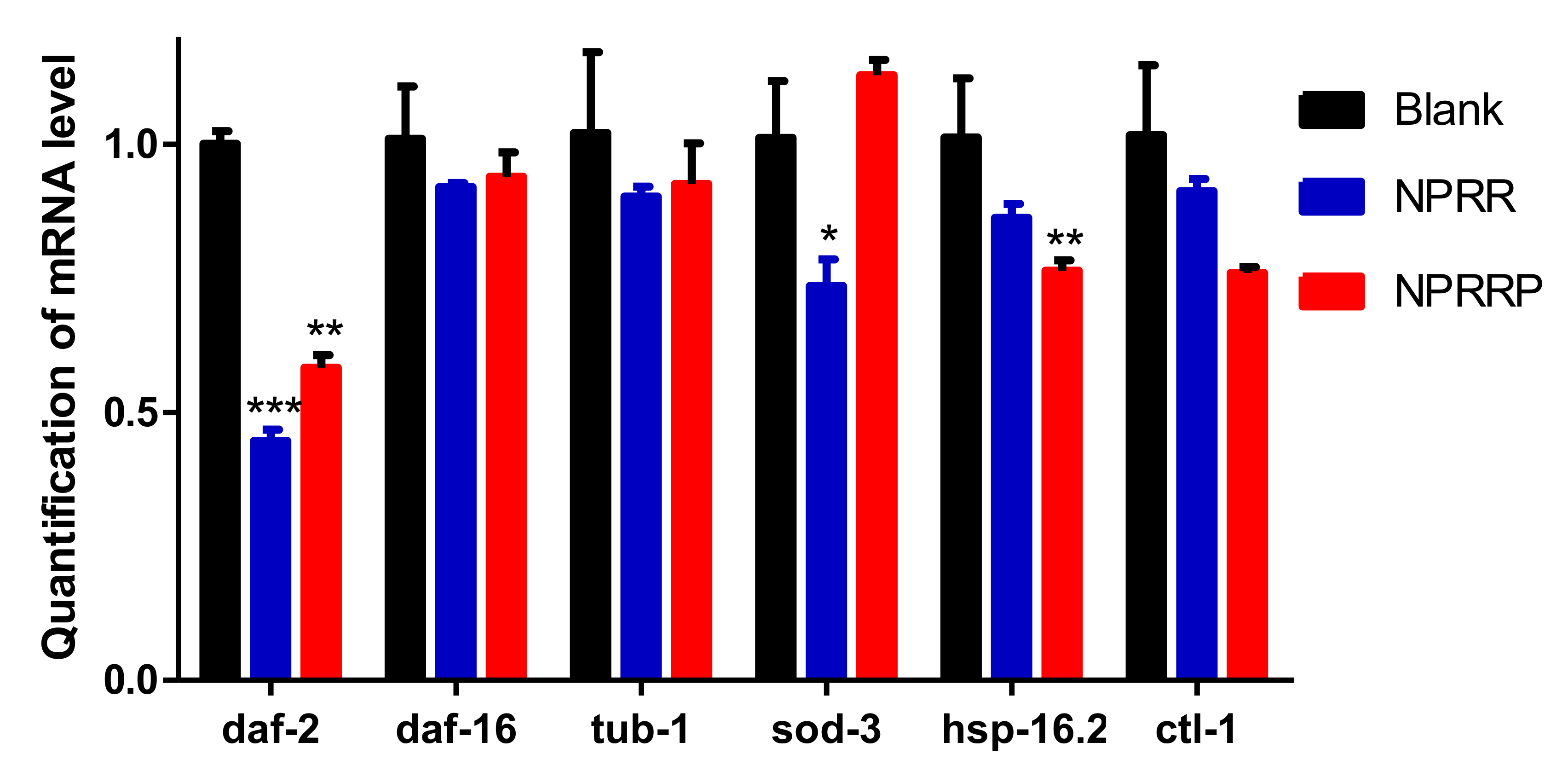
2.9. NPRG Inhibited daf-2 Gene Expression in the IIS
2.10. NPRG Can Extend the Lifespan of daf-16 Mutant DR26, but Cannot Increase Survival Rate of daf-16 Mutant CF1038
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. C. elegans Culture Conditions
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
4.3. Preparation of NPRG
4.4. Chemical Composition Analysis
4.5. FT-IR Spectroscopy
4.6. Analysis of Monosaccharide Compositions
4.7. Exposure Experiments
4.8. Bacterial Growth Assay
4.9. Pharyngeal Pump Frequency Assay
4.10. Lipofuscin Assay
4.11. Visualization of SOD-3::GFP
4.12. Measurement of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.13. Nuclear Localization of DAF-16
4.14. RT-PCR Assay
4.15. Lifespan Assay of daf-16 Mutant of Nematodes
4.16. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, C.K.; Leung, K.N.; Fung, K.P.; Choy, Y.M. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Tumour Polysaccharides from Medicinal Plants. J. Int. Med. Res. 1994, 22, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Weng, H.; Zhou, X.; Ma, C.W.; Ma, F.; Hu, M.; et al. Epimedium polysaccharide alleviates polyglutamine-induced neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans by reducing oxidative stress. Rejuvenat. Res. 2017, 20, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shi, R.; Ding, F.; Wang, H.; Han, W.; Ma, F.; Hu, M.; Ma, C.W.; Huang, Z. Astragalus Polysaccharide Suppresses 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4856761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Liu, D. Dietary antiaging phytochemicals and mechanisms associated with prolonged survival. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobet, R.A.; Pan, X.; Zhang, B.; Pak, S.C.; Asch, A.S.; Lee, M.H. Caenorhabditis elegans: A model system for anti-cancer drug discovery and therapeutic target identification. Biomol. Therap. 2014, 22, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.T.; Hu, P.J. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in C. elegans. Wormbook 2013, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne-Fran Oise, R.; Iskra, K.; Jean-Louis, B. Insulin/Insulin-like growth factor signaling controls non-Dauer developmental speed in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2011, 187, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, A. Genetics of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e129. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowski, B.; Hekimi, S. The genetics of caloric restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13091–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soultoukis, G.A.; Partridge, L. Dietary Protein, Metabolism, and Aging. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, R.M.; Barnes, R.G.; Fisher, K.; Andreou, T.; Rooney, N.; Poulin, G.B.; Whitmarsh, A.J. A nuclear role for the respiratory enzyme CLK-1 in regulating mitochondrial stress responses and longevity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Oh, S.W.; Tissenbaum, H.A. Worming pathways to and from DAF-16/FOXO. Exp. Gerontol. 2006, 41, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Kang, N.; Lu, Y.; Miao, X.; Zhang, X. The effects of polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Caenorhabditis elegans. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2019, 15, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Kan, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z. Structural features and immunological activity of a polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb roots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 61, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KačUráková, M.; Capek, P.; Sasinková, V.; Wellner, N.; Ebringerová, A. FT-IR study of plant cell wall model compounds: Pectic polysaccharides and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, N.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, G. Structural characterization of water-soluble polysaccharides from Opuntia monacantha cladodes in relation to their anti-glycated activities. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelino, S.; Chang, J.T.; Kumsta, C.; She, X.; Davis, A.; Nguyen, C.; Panowski, S.; Hansen, M. Intestinal Autophagy Improves Healthspan and Longevity in C. elegans during Dietary Restriction. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, C.T.; McCarroll, S.A.; Bargmann, C.I.; Fraser, A.; Kamath, R.S.; Ahringer, J.; Li, H.; Kenyon, C. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2003, 424, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, C.L.; Macleod, P.M. Lipofuscin and its Relation to Aging. Adv. Cell. Neurobiol. 1981, 2, 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Birkenkamp, K.U.; Coffer, P.J. Regulation of cell survival and proliferation by the FOXO (Forkhead box, class O) subfamily of Forkhead transcription factors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31(Pt. 1), 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, L.R.; Malene, H. Lessons from C. elegans: Signaling pathways for longevity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaletsky, R.; Murphy, C.T. The role of insulin/IGF-like signaling in C. elegans longevity and aging. Dis. Models Mech. 2010, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cynthia, K. The first long-lived mutants: Discovery of the insulin/IGF-1 pathway for ageing. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 2011, 366, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Libina, N.; Berman, J.R.; Kenyon, C. Tissue-Specific Activities of C. elegans DAF-16 in the Regulation of Lifespan. Cell 2003, 115, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinkove, D.; Halstead, J.R.; Gems, D.; Divecha, N. Long-term starvation and ageing induce AGE-1/PI 3-kinase-dependent translocation of DAF-16/FOXO to the cytoplasm. BMC Biol. 2006, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu-Cronin, Y.M.; Wen, J.C.; Sternberg, P.W. The L-type cyclin CYL-1 and the heat-shock-factor HSF-1 are required for heat-shock-induced protein expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2004, 168, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, S.L.; Deqing, W.; Cypser, J.R.; Vaupel, J.W.; Johnson, T.E. A stress-sensitive reporter predicts longevity in isogenic populations of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, C.; Daniel, A.; Ryan, D.; Caroline, A.; Patricia, B.; Diana, P.; Braeckman, B.P.; David, G. Increased life span from overexpression of superoxide dismutase in Caenorhabditis elegans is not caused by decreased oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Jeremy Michael, V.R.; Siegfried, H. Superoxide dismutase is dispensable for normal animal lifespan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5785–5790. [Google Scholar]
- Eun-Soo, K.; Sri Devi, N.; Kelvin, Y.; Tissenbaum, H.A. A new DAF-16 isoform regulates longevity. Nature 2010, 466, 498–502. [Google Scholar]
- Albert Tzong-Yang, C.; Chunfang, G.; Itani, O.A.; Budaitis, B.G.; Williams, T.W.; Hopkins, C.E.; Mceachin, R.C.; Manjusha, P.; Grant, A.R.; Sawako, Y. Longevity Genes Revealed by Integrative Analysis of Isoform-Specific daf-16/FoxO Mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2015, 201, 613–629. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, A.; Kwon, E.S.; Conte, D.; Liu, H.; Gilchrist, M.J.; Macneil, L.T.; Tissenbaum, H.A. Transcriptional regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans FOXO/DAF-16 modulates lifespan. Longev. Healthspan 2014, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, S.; Ruvkun, G. daf-2, daf-16 and daf-23: Genetically interacting genes controlling Dauer formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1994, 137, 107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Larsen, P.L. DAF-16-dependent and independent expression targets of DAF-2 insulin receptor-like pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans include FKBPs. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 314, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.Y.N.; Hench, J.; Ruvkun, G. Regulation of C. elegans DAF-16 and its human ortholog FKHRL1 by the daf-2 insulin-like signaling pathway. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, R.; Ashraf, J.; Kaletsky, R.; Kleemann, G.; Murphy, C.; Bussemaker, H. PQM-1 Complements DAF-16 as a Key Transcriptional Regulator of DAF-2-Mediated Development and Longevity. Cell 2013, 154, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarente, L.; Kenyon, C. Genetic pathways that regulate ageing in model organisms. Nature 2000, 408, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, S.G.; Williams, P.L. Influence of developmental stage, salts and food presence on various end points using Caenorhabditis elegans for aquatic toxicity testing. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 14, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-De-La-Riva, M.; Fontrodona, L.; Villanueva, A.; Cerón, J. Basic Caenorhabditis elegans methods: Synchronization and observation. J. Vis. Exp. Jove 2012, 64, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.G.; Joo, H.S.; Choi, J.W.; Koo, Y.M.; Chang, C.S. Purification and characterization of an extracellular polysaccharide from haloalkalophilic Bacillus sp. I-450. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 34, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaodan, W.; Wei, J.; Jiajia, L.; Ying, Y.; Bin, W. Analysis of the monosaccharide composition of water-soluble polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme by high performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, R.; Li, H.; Xiang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Hu, M.; Ma, F.; Ma, C.W.; Huang, Z. Antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of Dictyophora indusiata polysaccharide in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 192, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
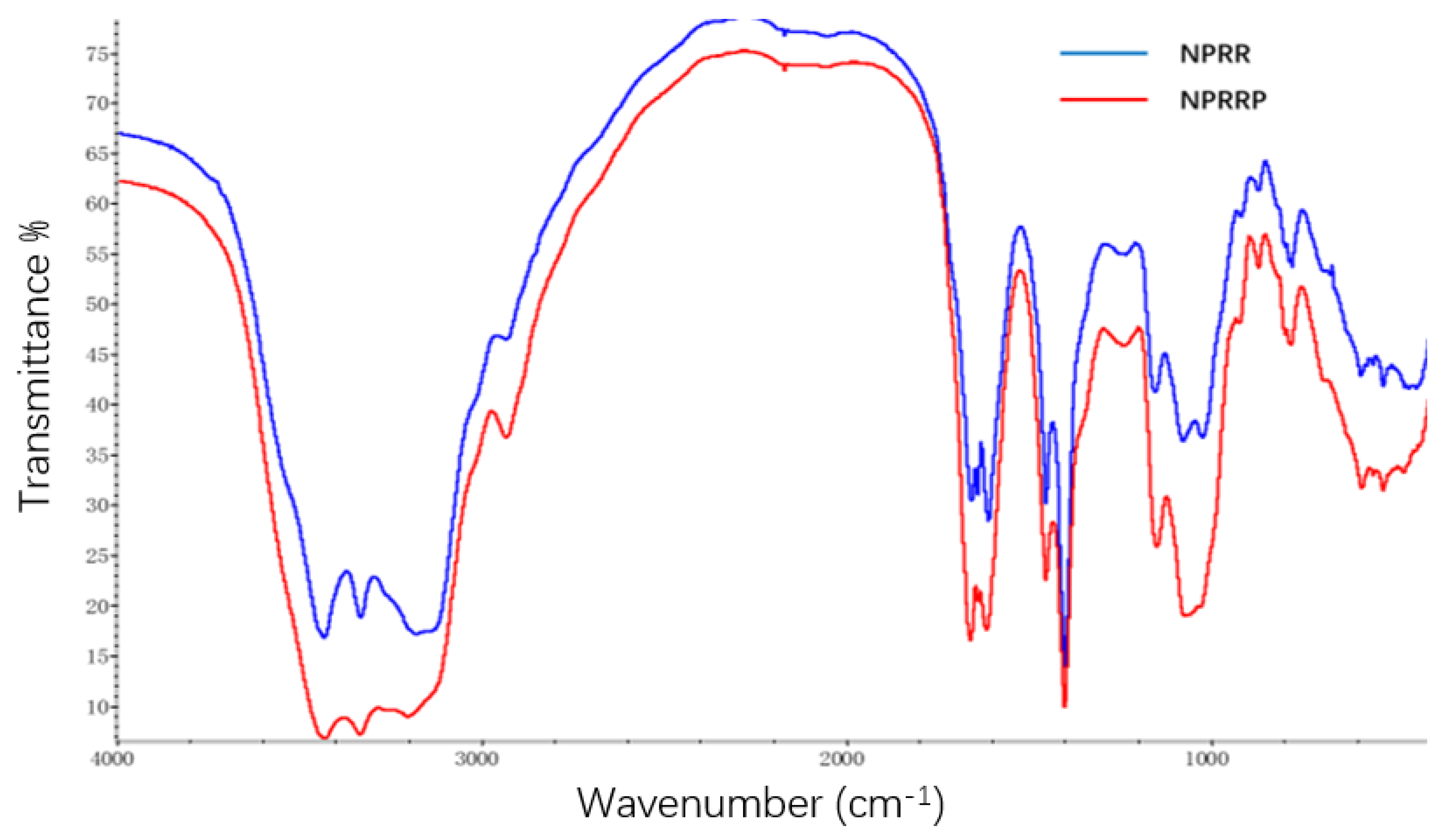
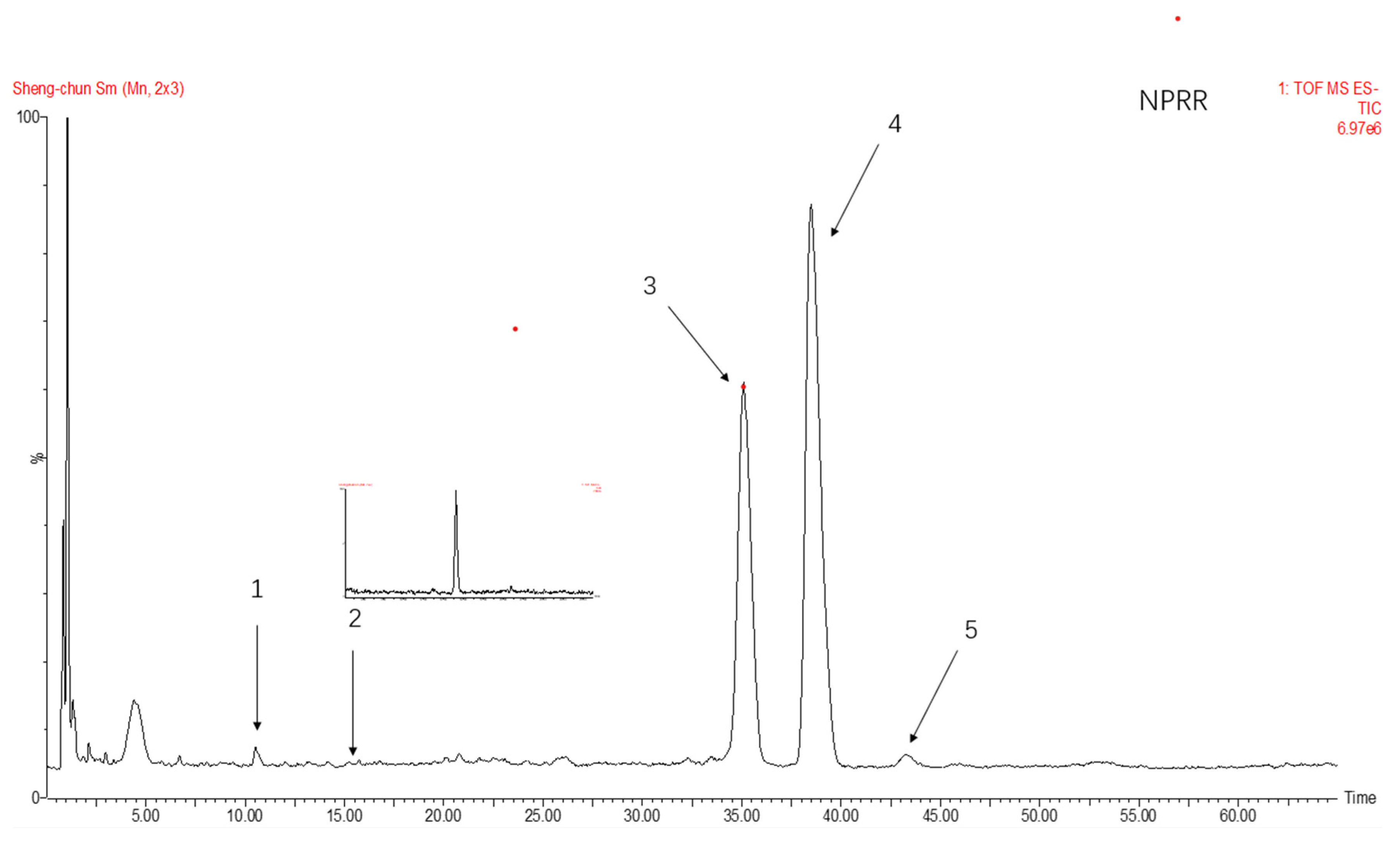
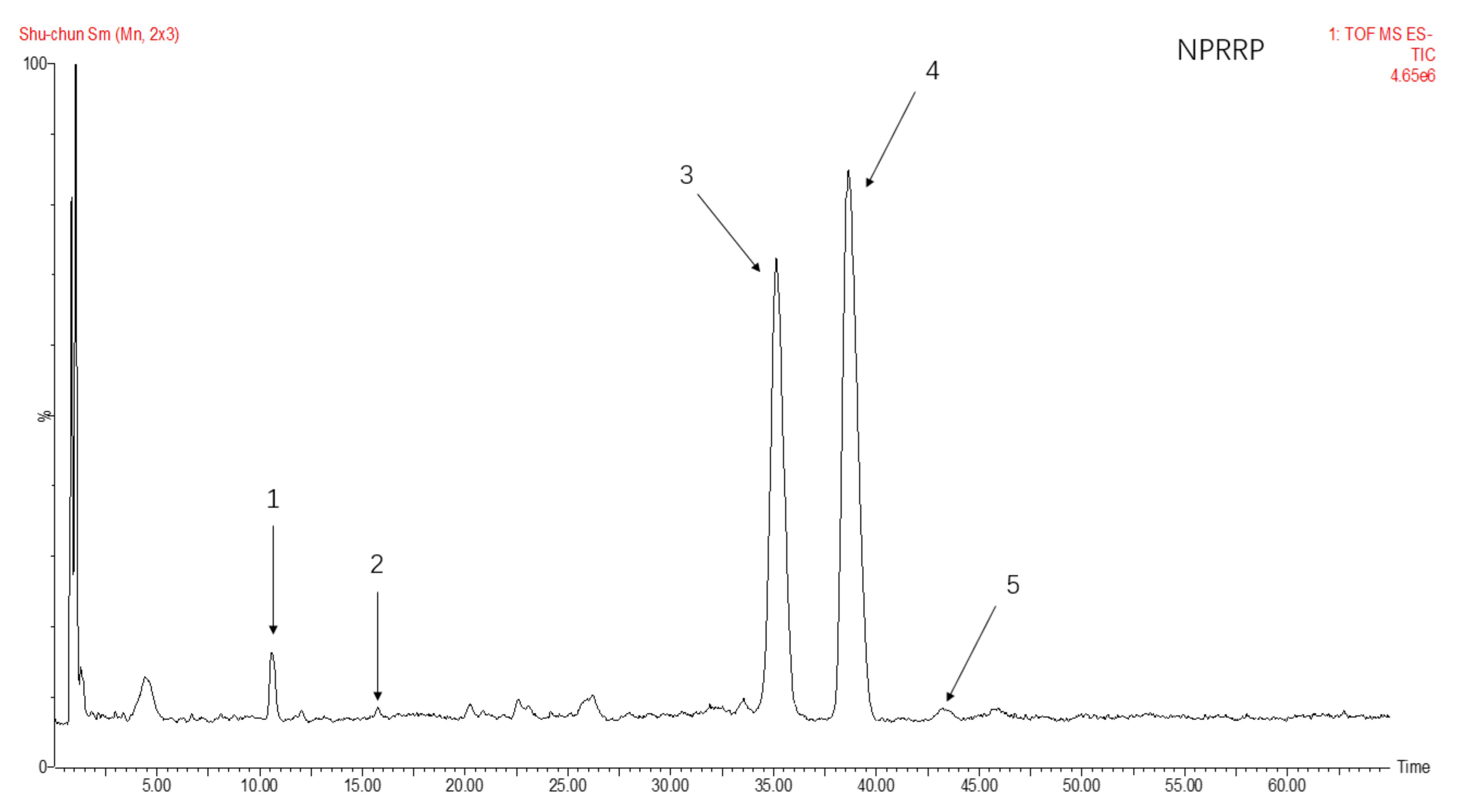

| Sample | NPRRP | NPRR |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate (%) | 81.22 | 83.55 |
| Protein (%) | 19.03 | 11.20 |
| Mannose | Rhamnose | Glucose | Galactose | Arabinose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPRR | 2.38 | 0.05 | 39.51 | 56.85 | 1.22 |
| NPRRP | 0.43 | 0.02 | 44.08 | 55.23 | 0.23 |
| Sample | SOD (U/mg) | CAT (U/mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 1.83 ± 0.035 | 5.68 ± 0.518 |
| NPRR | 3.54 ± 0.275 | 10.67 ± 1.848 |
| NPRRP | 2.66 ± 0.096 | 11.27 ± 3.037 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Kang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, P. Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2019, 24, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244592
Yuan Y, Kang N, Li Q, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Tan P. Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yanyan, Nianxin Kang, Qingxia Li, Yali Zhang, Yonggang Liu, and Peng Tan. 2019. "Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244592
APA StyleYuan, Y., Kang, N., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., & Tan, P. (2019). Study of the Effect of Neutral Polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa on Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules, 24(24), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244592




