In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function
Abstract
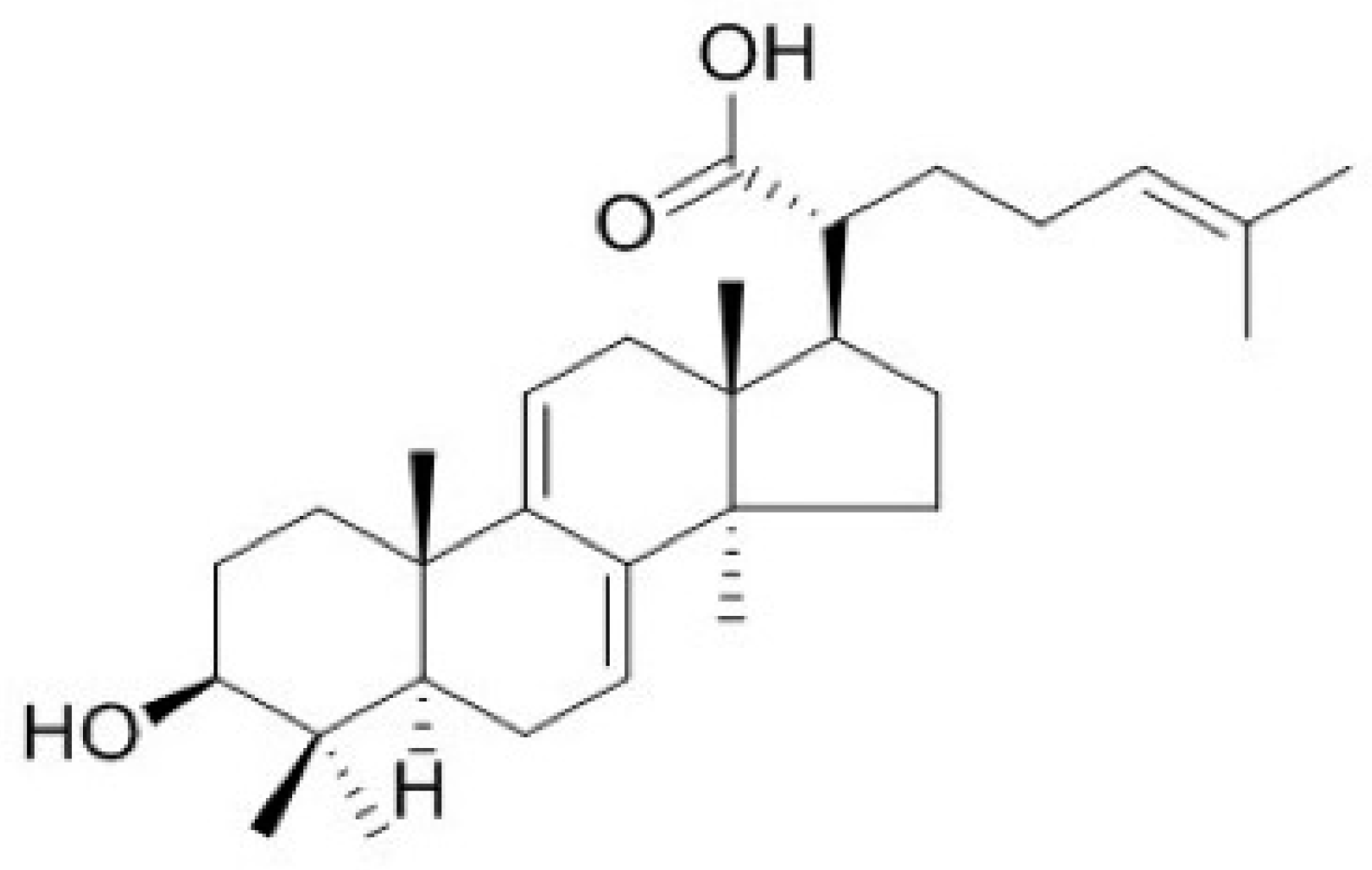
1. Introduction
2. Results
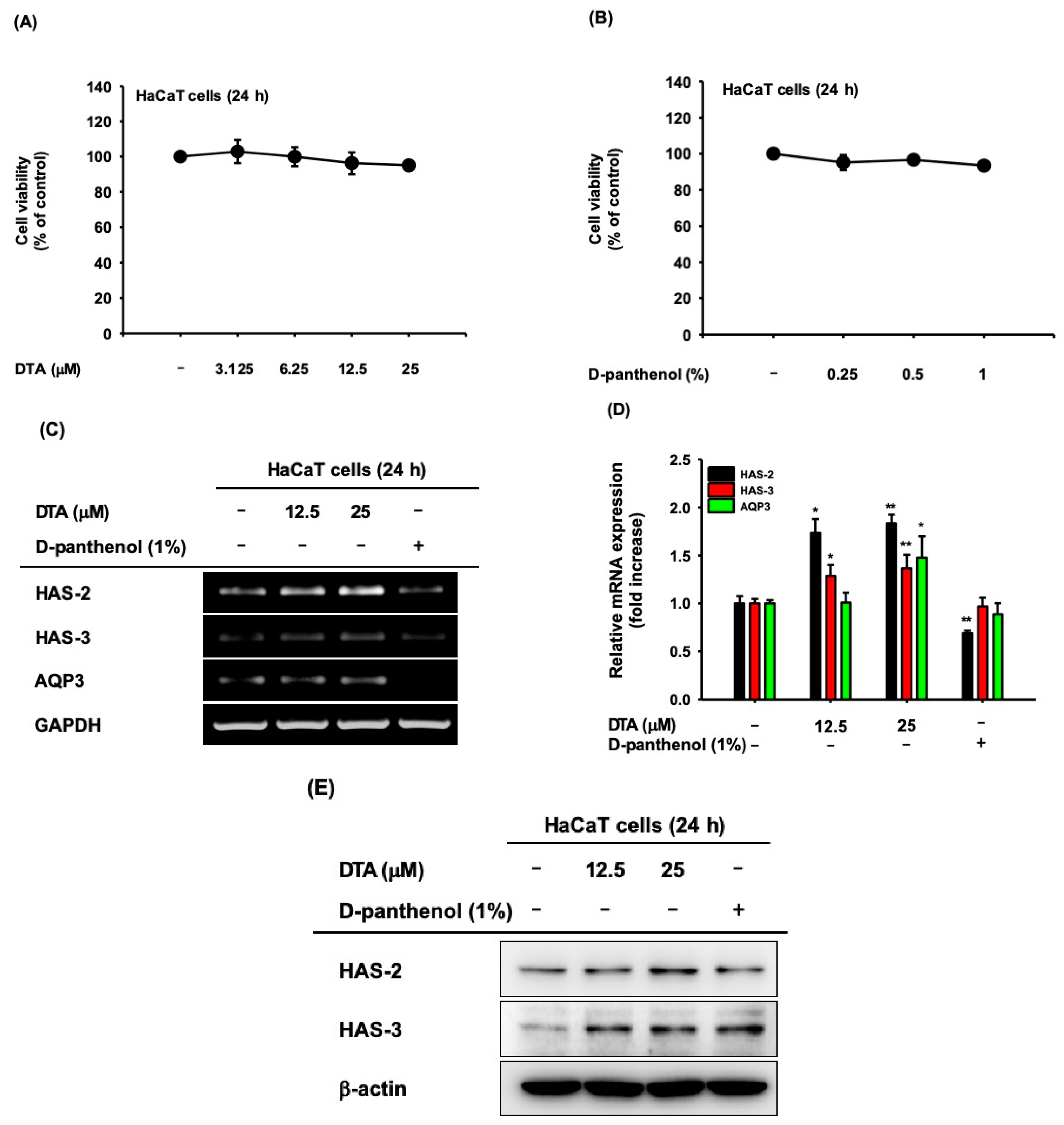
2.1. Effects of DTA on Skin Hydration
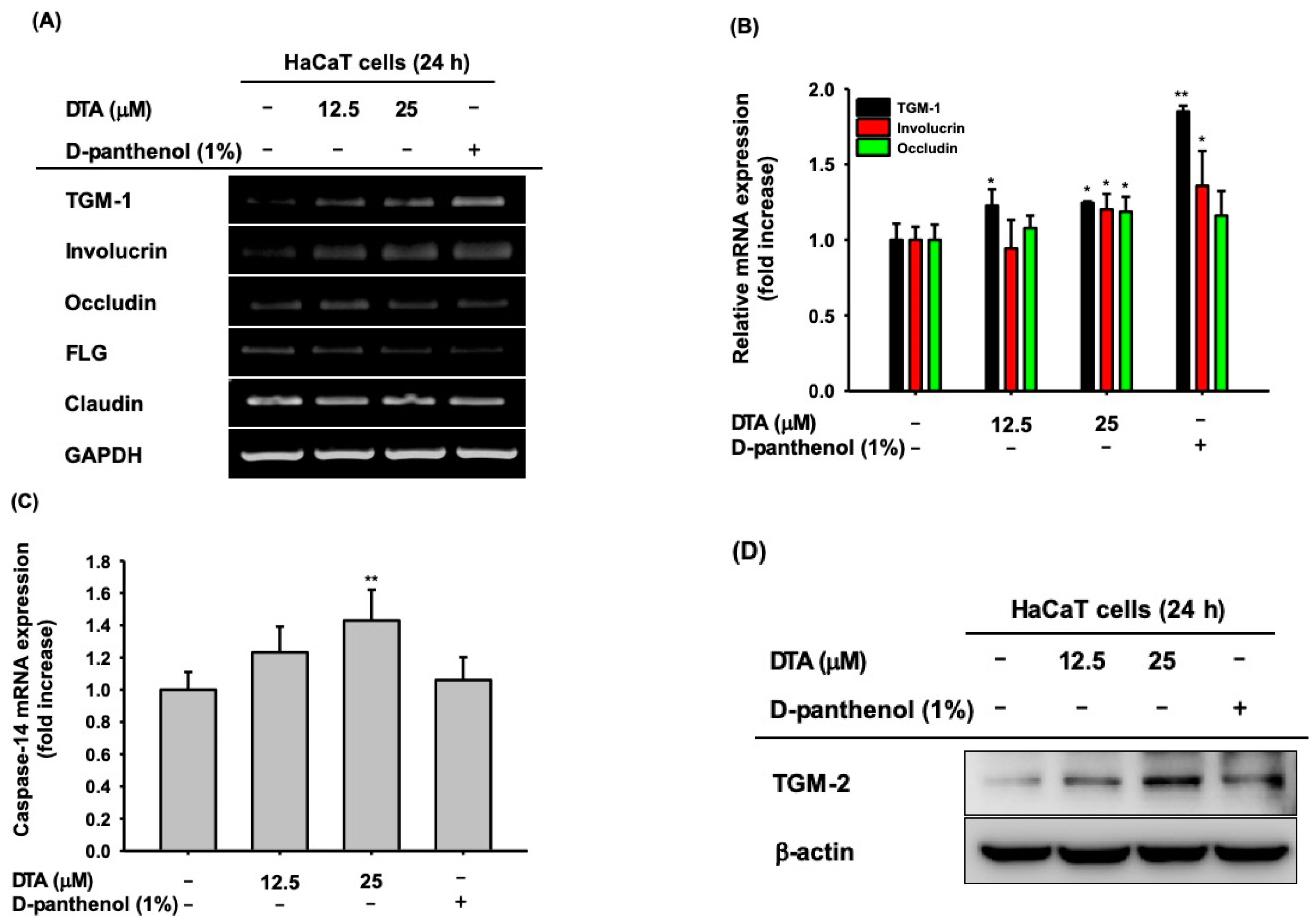
2.2. Effects of DTA in Keratinocyte Differentiation
2.3. Effects of DTA on the AP-1 Signaling Pathway
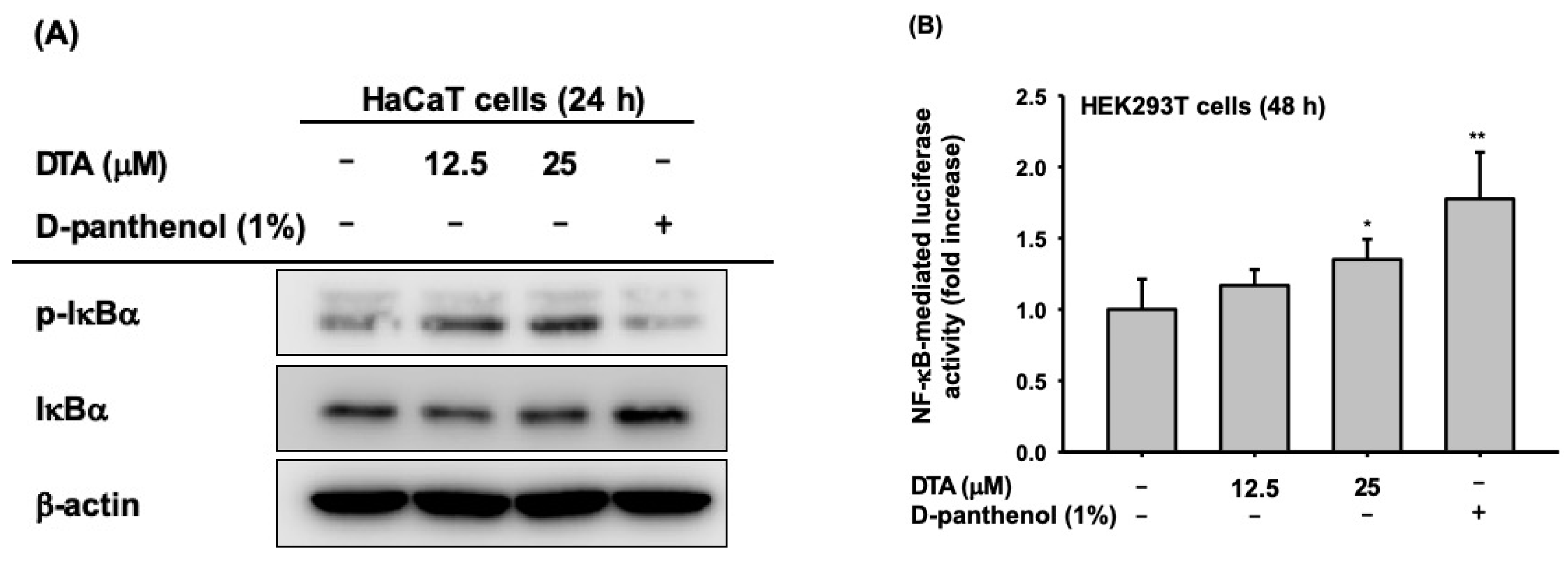
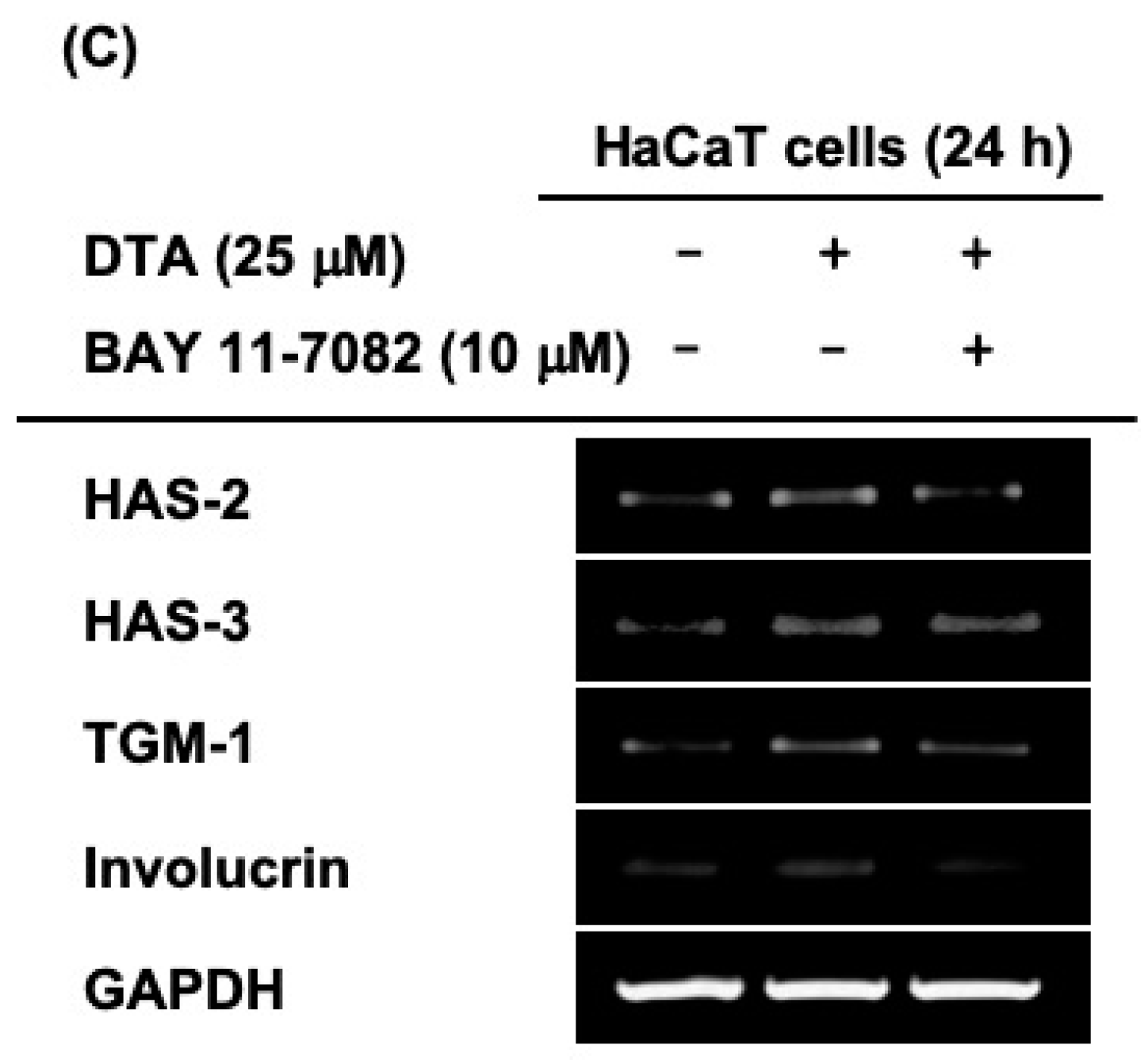
2.4. Effects of DTA on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway
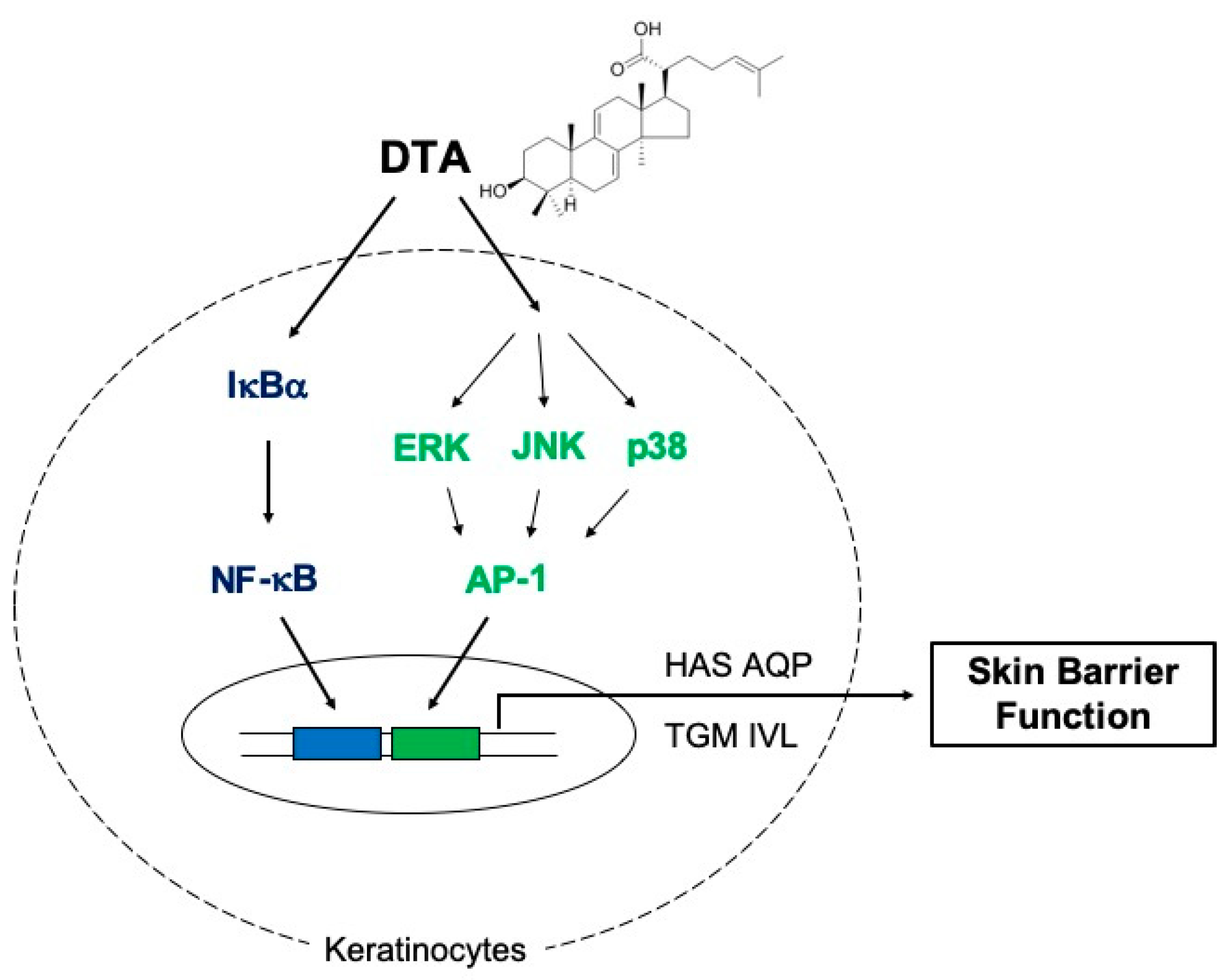
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. RT-PCR and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baroni, A.; Buommino, E.; De Gregorio, V.; Ruocco, E.; Ruocco, V.; Wolf, R. Structure and function of the epidermis related to barrier properties. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.-A.; Yi, B.-R.; Choi, K.-C. Molecular mechanisms and in vivo mouse models of skin aging associated with dermal matrix alterations. Lab. Anim. Res. 2011, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-O.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.; Seo, D.B. Antimelanogenesis and skin-protective activities of Panax ginseng calyx ethanol extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Woodfolk, J.A. Skin barrier defects in atopic dermatitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sator, P.-G.; Schmidt, J.B.; Hönigsmann, H. Comparison of epidermal hydration and skin surface lipids in healthy individuals and in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Visscher, M.; LaRuffa, A.; Wickett, R. Natural moisturizing factors (NMF) in the stratum corneum (SC). II. Regeneration of NMF over time after soaking. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2010, 61, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sayo, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Ozawa, N.; Sakai, S.; Inoue, S.; Ishikawa, O.; Tamura, M. Hyaluronan synthase 3 regulates hyaluronan synthesis in cultured human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Karvinen, S.; Törrönen, K.; Hyttinen, J.M.; Jokela, T.; Lammi, M.J.; Tammi, M.I.; Tammi, R. EGF upregulates, whereas TGF-β downregulates, the hyaluronan synthases Has2 and Has3 in organotypic keratinocyte cultures: Correlations with epidermal proliferation and differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Xue, J.F.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Shuhaidi, M.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, an efficient biomacromolecule for treatment of inflammatory skin and joint diseases: A review of recent developments and critical appraisal of preclinical and clinical investigations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienimäki, J.-P.; Rilla, K.; Fülöp, C.; Sironen, R.K.; Karvinen, S.; Pasonen, S.; Lammi, M.J.; Tammi, R.; Hascall, V.C.; Tammi, M.I. Epidermal growth factor activates hyaluronan synthase 2 in epidermal keratinocytes and increases pericellular and intracellular hyaluronan. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20428–20435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsberg, J.; Andriessen, A.; Abdulla, S.; Ahluwalia, R.; Beecker, J.; Sander, M.; Schachter, J. A review of protection against exposome factors impacting facial skin barrier function with 89% mineralizing thermal water. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Hibuse, T.; Funahashi, T. Role of aquaporin-7 and aquaporin-9 in glycerol metabolism; involvement in obesity. In Aquaporins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Takata, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; Tajika, Y. Aquaporins: Water channel proteins of the cell membrane. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 39, 1–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, M.; Verkman, A. Glycerol replacement corrects defective skin hydration, elasticity, and barrier function in aquaporin-3-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7360–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, D.B.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, S.S.; Cho, J.Y. AKT-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of Panax ginseng calyx ethanolic extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandilands, A.; Sutherland, C.; Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.I. Filaggrin in the frontline: Role in skin barrier function and disease. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinert, P.M.; Marekov, L.N. Direct evidence that involucrin is a major early isopeptide cross-linked component of the keratinocyte cornified cell envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, R.L.; Efimova, T.; Dashti, S.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Deucher, A.; Crish, J.F.; Sturniolo, M.; Bone, F. Keratinocyte survival, differentiation, and death: Many roads lead to mitogen-activated protein kinase. In Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dashti, S.R.; Efimova, T.; Eckert, R.L. MEK7-dependent activation of p38 MAP kinase in keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8059–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushina, Y.; Akihisa, T.; Ukiya, M.; Murakami, C.; Kuriyama, I.; Xu, X.; Yoshida, H.; Sakaguchi, K. A novel DNA topoisomerase inhibitor: Dehydroebriconic acid, one of the lanostane-type triterpene acids from Poria cocos. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smriga, M.; Saito, H.; Nishiyama, N. Hoelen (Poria cocos Wolf) and ginseng (Panax Ginseng CA Meyer), the ingredients of a Chinese prescription DX-9386, individually promote hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-J.; Tseng, J. Fu-Ling, a Chinese herbal drug, modulates cytokine secretion by human peripheral blood monocytes. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1996, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Nabeshima, T.; Shin, E.-J.; Chun, W.; Jhoo, J.H.; Jhoo, W.-K.; Wie, M.B.; Jang, C.-G.; Chung, H.; Sung, Y.E. PAP 9704, a Korean herbal medicine attenuates methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion via adenosine A2A receptor stimulation in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Tai, T.; Nunoura, Y.; Yajima, Y.; Kawashima, S.; Tanaka, K. Dehydrotrametenolic acid induces preadipocyte differentiation and sensitizes animal models of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus to insulin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-M.; Lee, S.-K.; Shin, D.-S.; Lee, M.-Y.; Han, D.C.; Baek, N.-I.; Son, K.-H.; Kwon, B.-M. Dehydrotrametenolic acid selectively inhibits the growth of H-ras transformed rat2 cells and induces apoptosis through caspase-3 pathway. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Tseng, S.-W. Direct determination of d-panthenol and salt of pantothenic acid in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations by differential pulse voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 432, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, F.B., Jr.; Gaspar, L.R.; Maia Campos, P.M. Skin moisturizing effects of panthenol-based formulations. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 62, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Nam, K.-S.; Shon, Y.-H.; Jeon, B.H.; Moon, S.-K.; Kim, M.-G.; Kim, C.-H. Inhibitory effect of GBH on platelet aggregation through inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in activated human platelets. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 3063–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihisa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Uchiyama, E.; Suzuki, T.; Kimura, Y.; Uchikura, K.; Nishino, H. Triterpene acids from Poria cocos and their anti-tumor-promoting effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-Endocrinol. 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, A.; Harding, C. Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Lee, J.; Jeong, S.-G.; Hong, Y.H.; Yoo, S.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, Y.S. Artemisia asiatica ethanol extract exhibits anti-photoaging activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J. Understanding the role of natural moisturizing factor in skin hydration. Pract. Derm. 2012, 9, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A. Aquaporin-3 functions as a glycerol transporter in mammalian skin. Biol. Cell 2005, 97, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, E.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Jensen, J.-M. Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation in eczema. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 43, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Bräutigam, M.; Sepehrmanesh, M.; Pfeiffer, S.; Jensen, J.M. Role of the epidermal barrier in atopic dermatitis. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2009, 7, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, M.; Duchnik, E.; Maleszka, R.; Marchlewicz, M. Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Postepy. Dermatol. Allergol. 2016, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.; Lorz, L.R.; Choi, E.; Lim, H.Y.; Hossain, M.A.; Jang, S.; Choi, Y.I.; Park, K.J. Loliolide presents antiapoptosis and antiscratching effects in human keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Yoo, S.; Hong, Y.H.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, J. The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Hwang, K.; Lee, J.; Han, S.; Kim, E.-M.; Park, J.; Cho, J. Skin protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, S.; Mori, S.; Nakajima, H.; Yasuda, M.; Imokawa, G. The UVB-stimulated expression of transglutaminase 1 is mediated predominantly via the NF-κB signaling pathway: New evidence of its significant attenuation through the specific interruption of the p38/MSK1/NFκBp65 Ser276 axis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlier, D.; Thomasset, N. Use of MTT colorimetric assay to measure cell activation. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 94, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.G.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; et al. Nuclear factor kappa-B- and activator protein-1-mediated immunostimulatory activity of compound K in monocytes and macrophages. J. Ginseng Res 2017, 41, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Nam, G.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. BIOGF1K, a compound K-rich fraction of ginseng, plays an antiinflammatory role by targeting an activator protein-1 signaling pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage-like cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Name | Sequences (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Semi-quantitative RT-PCR | ||
| HAS-2 | F | CTGCTTGACCCTCAGAGACC |
| R | CTGCTTGACCCTCAGAGACC | |
| HAS-3 | F | GCCACTTGTCGGCGATAAGG |
| R | CACTGTCCACCCCTCAGAGC | |
| AQP3 | F | CAAAAGCTGGGAAGCCTTCT |
| R | CCATCCTTCAAAAGGCGCAG | |
| TGM-1 | F | CCGACCACCACTACAGCAAG |
| R | GGGCAGGGAACCAGCATCTT | |
| Involucrin | F | AAGGTGCAGTTTTGCCAAGG |
| R | CAACCCTCTGCACCCAGTTT | |
| Occludin | F | CACTCACGGCAAATTCAACGGCAC |
| R | GACTCCACGACATACTCAGCAC | |
| FLG | F | CACTCACGGCAAATTCAACGGCAC |
| R | GACTCCACGACATACTCAGCAC | |
| Claudin | F | CACTCACGGCAAATTCAACGGCAC |
| R | GACTCCACGACATACTCAGCAC | |
| GAPDH | F | CACTCACGGCAAATTCAACGGCAC |
| R | GACTCCACGACATACTCAGCAC | |
| Quantitative real-time PCR | ||
| HAS-2 | F | GTCCCTACCGAGTCTCTTCT |
| R | TTTTTAAGTTTCCGCTTCTG | |
| HAS-3 | F | GGTTGGACCTACAAGGAGGC |
| R | GGTTCATGCTGGTGTCCTCA | |
| AQP3 | F | TACCCCCAGGAGAAGATTCC |
| R | TTTTCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTT | |
| TGM1 | F | GAAAGCATGATCCGGGACGT |
| R | GATGGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGA | |
| Involucrin | F | CCAACGCAAAGCAATACATGA |
| R | CCTTTTTCGCTTCCCTGTTTTA | |
| Occludin | F | CCAACGCAAAGCAATACATGA |
| R | CCTTTTTCGCTTCCCTGTTTTA | |
| Caspase-14 | F | CCAACGCAAAGCAATACATGA |
| R | CCTTTTTCGCTTCCCTGTTTTA | |
| GAPDH | F | CAATGAATACGGCTACAGCAAC |
| R | AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, E.; Kang, Y.-G.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, Y.D.; Park, W.-S.; Kim, D.; Kim, E.; Cho, J.Y. In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function. Molecules 2019, 24, 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244583
Choi E, Kang Y-G, Hwang S-H, Kim JK, Hong YD, Park W-S, Kim D, Kim E, Cho JY. In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244583
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Eunju, Young-Gyu Kang, So-Hyeon Hwang, Jin Kyeong Kim, Yong Deog Hong, Won-Seok Park, Donghyun Kim, Eunji Kim, and Jae Youl Cho. 2019. "In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244583
APA StyleChoi, E., Kang, Y.-G., Hwang, S.-H., Kim, J. K., Hong, Y. D., Park, W.-S., Kim, D., Kim, E., & Cho, J. Y. (2019). In Vitro Effects of Dehydrotrametenolic Acid on Skin Barrier Function. Molecules, 24(24), 4583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244583






