Degradation of Tocopherol Molecules and Its Impact on the Polymerization of Triacylglycerols during Heat Treatment of Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristic of Pressed and Refined Rapeseed Oil
2.2. Total Polar Compounds (TPC) Content
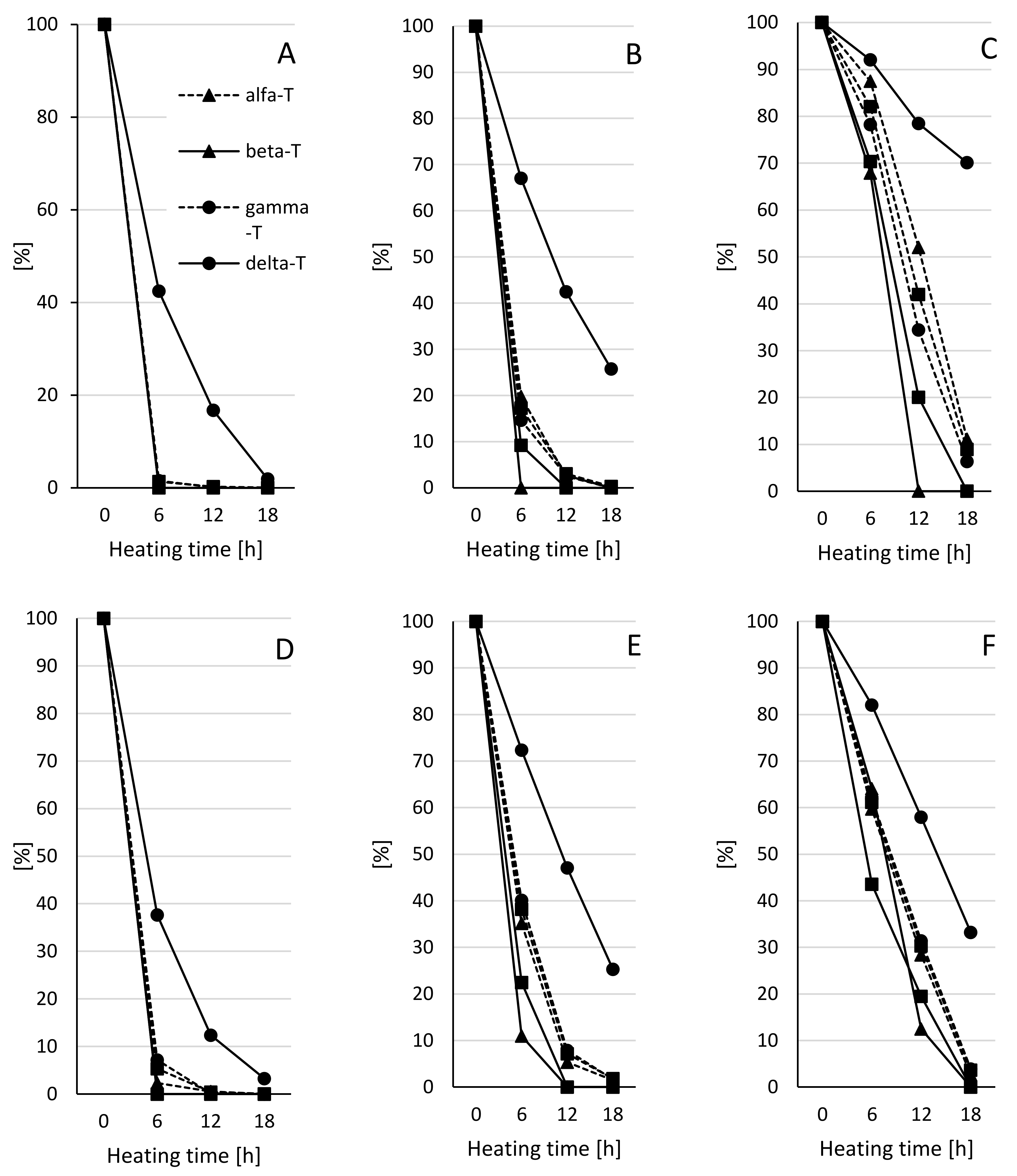
2.3. Tocopherols Content
2.4. Polymers of Triacylglycerols (TAG) Content
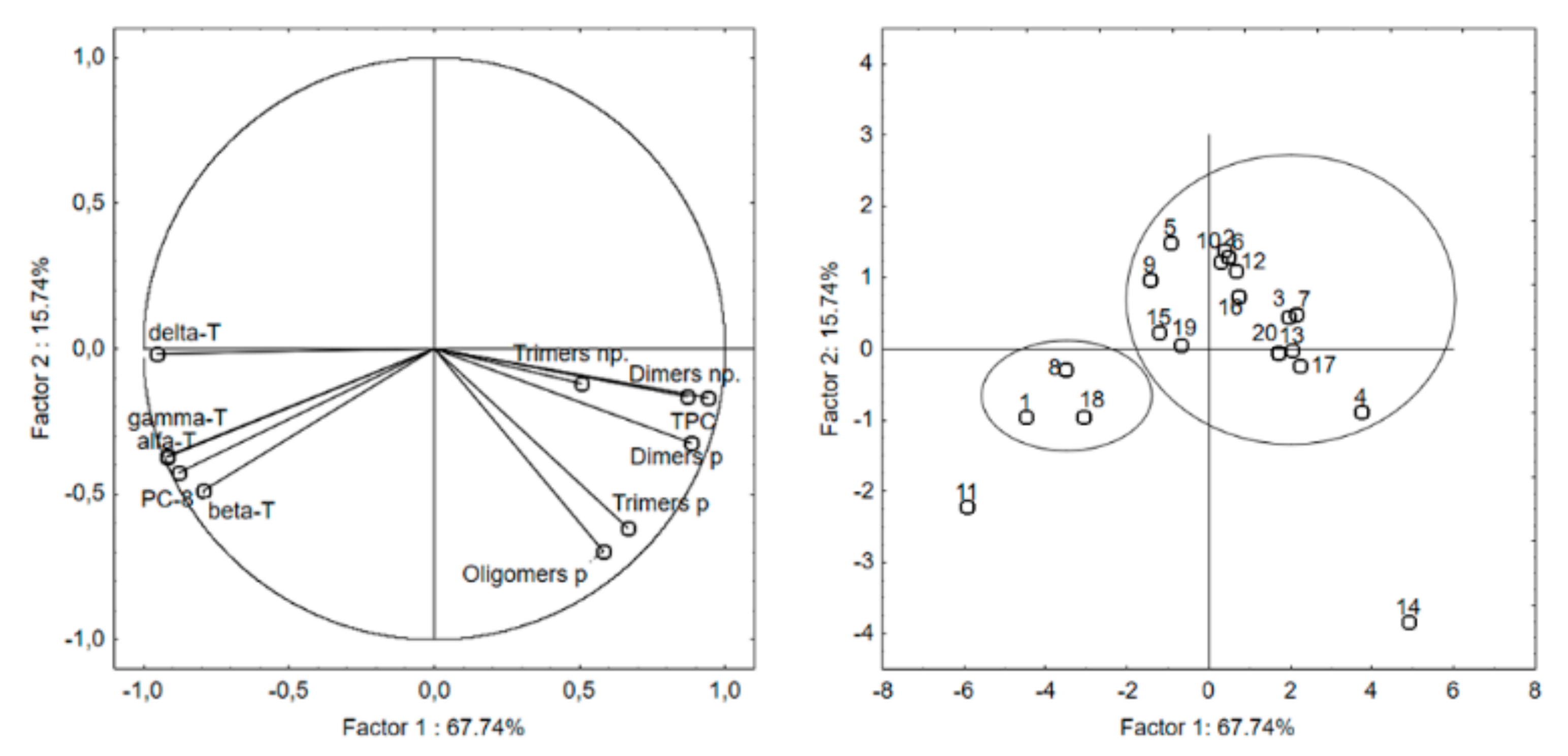
2.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Heating Process
3.3. Total Polar Compounds (TPC) Analysis
3.4. Iodine Value Calculation (CIV)
3.5. Fatty Acid Composition Analysis
3.6. Tocopherol and Plastochromanol-8 Analysis
3.7. The Fractionation Into Polar and Nonpolar Fractions
3.8. Polymer Composition Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saguy, I.S.; Dana, D. Integrated approach to deep fat frying: Engineering, nutrition, health and consumer aspects. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladedunye, F. Natural antioxidants as stabilizers of frying oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 688–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, C. Fundamentals of the frying process. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaiifar, A.M.; Achir, N.; Courtois, F.; Trezzani, I.; Trystram, G. Review of mechanisms, conditions, and factors involved in the oil uptake phenomenon during the deep-fat frying process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, C.; Klostermann, S.; Kochhar, P. Testing and comparing oxidative stability of vegetable oils and fats at frying temperature. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2000, 102, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.O.; Pereira, P.A.d.P. Influence of time, surface-to-volume ratio, and heating process (continuous or intermittent) on the emission rates of selected carbonyl compounds during thermal oxidation of palm and soybean oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliński, J.P.; Krygier, K.; Karlovits, G.; Szydłowska-Czerniak, A. Effect of specific oil surface area on the thermal stressing of rapeseed oil during heating in an electric frying pan. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steel, C.J.; Dobarganes, M.C.; Barrera-Arellano, D. Formation of polymerization compounds during thermal oxidation of cottonseed oil, partially hydrogenated cottonseed oil and their blends. Grasas Aceites 2006, 57, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzińska, M.; Hassanein, M.M.M.; Abdel-Razek, A.G.; Kmiecik, D.; Siger, A.; Ratusz, K. Influence of composition on degradation during repeated deep-fat frying of binary and ternary blends of palm, sunflower and soybean oils with health-optimised saturated-to-unsaturated fatty acid ratios. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Ruiz, G.; Ruiz-Mendez, M.V.; Velasco, J.J.; Márquez-Ruiz, G.; Ruiz-Méndez, M.V.; Velasco, J.J. Antioxidants in frying: Analysis and evaluation of efficacy. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hęś, M.; Szwengiel, A.; Dziedzic, K.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Kmiecik, D.; Górecka, D. The effect of buckwheat hull extract on lipid oxidation in frozen-stored meat products. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmiecik, D.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Korczak, J. Anti-polymerization activity of tea and fruits extracts during rapeseed oil heating. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural antioxidants: Sources, compounds, mechanisms of action, and potential applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.G.; Gordon, M.H.; Segovia, F.J.; Skowyra, M.; Almajano, M.P. Antioxidant properties of three aromatic herbs (Rosemary, Thyme and Lavender) in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, M.; Mohri, S.; Endo, Y.; Fujimoto, K. The effect of oxygen concentration on oxidative deterioration in heated high-oleic safflower oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Meshginfar, N.; Mahoonak, A.S. A review on frying: Procedure, fat, deterioration progress and health hazards. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Rastogi, N.K.; Gopala Krishna, A.G.; Lokesh, B.R. Effect of frying cycles on physical, chemical and heat transfer quality of rice bran oil during deep-fat frying of poori: An Indian traditional fried food. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvis, A.; Vélez, C.; Rada-Mendoza, M.; Villamiel, M.; Villada, H.S. Heat transfer coefficient during deep-fat frying. Food Control 2009, 20, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Okoh, A.I. Potential health implications of the consumption of thermally-oxidized cooking oils—A review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, R.J.; Kalivianakis, M.; Minich, D.M.; Bijleveld, C.M.A.; Verkade, H.J. The metabolic importance of unabsorbed dietary lipids in the colon. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Chemistry of deep-fat frying oils. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhoosh, R.; Esmaeilzadeh Kenari, R.; Poorazrang, H. Frying stability of canola oil blended with palm olein, olive, and corn oils. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y. Effects of frying oils fatty acids profile on the formation of polar lipids components and their retention in French fries over deep-frying process. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, A.; Ghazani, S.M.; Marangoni, A.G. Quality and safety of frying oils used in restaurants. FRIN 2014, 64, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosa, M.J.; Skerl, V.; Cadenazzi, M.; Olazábal, L.; Silva, R.; Suburú, G.; Torres, M. Changes produced in oils during vacuum and traditional frying of potato chips. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Chen, J.; Shen, Q. Chemical alterations taken place during deep-fat frying based on certain reaction products: A review. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2012, 165, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Nogala-Kalucka, M.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. The content and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in cold-pressed plant oils. J. Food Lipids 2008, 15, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladedunye, F.; Matthaus, B. Phenolic extracts from Sorbus aucuparia (L.) and Malus baccata (L.) berries: Antioxidant activity and performance in rapeseed oil during frying and storage. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.W.; Mier, W.; Giacosa, A.; Hull, W.E.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Phenolic compounds and squalene in olive oils: The concentration and antioxidant potential of total phenols, simple phenols, secoiridoids, lignansand squalene. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, B. Oxidation of edible oils. In Oxidation in Foods and Beverages and Antioxidant Applications—Management in Different Industry Sectors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, ISBN 978-1-84569-983-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, T.; Delcuratolo, D.; Paradiso, V.M. Pro-oxidant action of polar triglyceride oligopolymers in edible vegetable oils. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, C.J.; Dobarganes, M.C.; Barrera-Arellano, D. The influence of natural tocopherols during thermal oxidation of refined and partially hydrogenated soybean oils. Grasas Aceites 2005, 56, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscatto, M.H.; Zambiazi, R.C.; Sganzerla, M.; Pestana, V.R.; Otero, D.; Lima, R.; Paiva, F. Degradation of tocopherols in rice bran oil submitted to heating at different temperatures. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marmesat, S.; Velasco, L.; Ruiz-Méndez, M.V.; Fernández-Martínez, J.M.; Dobarganes, C. Thermostability of genetically modified sunflower oils differing in fatty acid and tocopherol compositions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.; Moser, J. Frying stability of purified mid-oleic sunflower oil triacylglycerols with added pure tocopherols and tocopherol mixtures. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.S.; Johnson, E.R.; DiLabio, G.A. Predicting the activity of phenolic antioxidants: Theoretical method, analysis of substituent effects, and application to major families of antioxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Alamprese, C.; Ratti, S. Tocopherols and tocotrienols as free radical-scavengers in refined vegetable oils and their stability during deep-fat frying. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachary, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Eskin, N.A.M.; Thiyam-Hollander, U. Crude canolol and canola distillate extracts improve the stability of refined canola oil during deep-fat frying. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampi, A.-M.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Effect of α- and γ-tocopherols on thermal polymerization of purified high-oleic sunflower triacylglycerols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogala-Kalucka, M.; Korczak, J.; Elmadfa, I.; Wagner, K.H. Effect of α- and δ-tocopherol on the oxidative stability of a mixed hydrogenated fat under frying conditions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, A.; Kaczmarek, A.; Rudzińska, M. Antioxidant activity and phytochemical content of cold-pressed rapeseed oil obtained from roasted seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, D.; Korczak, J.; Rudzińska, M.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Hęś, M. β-Sitosterol and campesterol stabilisation by natural and synthetic antioxidants during heating. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. AOCS Official Method 982.27. Polar Components in Frying Fats, 6th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. AOCS Official Method Cd 1c-85. Calculated Iodine Value, 6th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. AOCS Official Method Ce 1h-05. Determination of cis-, trans-, Saturated, Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Vegetable or Non-Ruminant Animal Oils and Fats by Capillary GLC, 6th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siger, A.; Michalak, M.; Rudzińska, M. Canolol, tocopherols, plastochromanol-8, and phytosterols content in residual oil extracted from rapeseed expeller cake obtained from roasted seed. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, D.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Kulczyński, B. Thermal decomposition of partially hydrogenated rapeseed oil during repeated frying traditional and fast French fries. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society. AOCS Official Method 993.25. Polymerized Triglycerides in Oils and Fats, 6th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| PRO | RRO | |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid composition [%] | ||
| 16:0 | 4.32 ± 0.00a | 4.76 ± 0.05a |
| 18:0 | 1.54 ± 0.01a | 1.56 ± 0.02a |
| 18:1 | 63.57 ± 0.02a | 63.83 ± 0.01a |
| 18:2 | 18.74 ± 0.03a | 19.07 ± 0.05a |
| 18:3 | 10.70 ± 0.00a | 9.89 ± 0.12a |
| 20:0 | 0.54 ± 0.01a | 0.47 ± 0.20a |
| 20:1 | 0.32 ± 0.05a | 0.06 ± 0.02b |
| 22:1 | 0.18 ± 0.06a | 0.26 ± 0.03b |
| 24:0 | 0.08 ± 0.04a | 0.11 ± 0.02a |
| Total SFA | 6.48 ± 0.07a | 6.90 ± 0.07a |
| Total MUFA | 64.08 ± 0.01a | 64.14 ± 0.19a |
| Total PUFA | 29.45 ± 0.03a | 28.96 ± 0.12b |
| Total Polar Compounds [%] | 1.0 ± 0.1a | 0.9 ± 0.0a |
| Iodine value | 115.52 ± 0.06a | 114.03 ± 0.12a |
| Tocopherols [mg/100 g] | ||
| α | 25.14 ± 0.26a | 34.44 ± 0.26b |
| β | 0.07 ± 0.03a | 0.16 ± 0.01b |
| ƴ | 36.43 ± 0.25a | 41.70 ± 0.26b |
| δ | 0.66 ± 0.06a | 0.85 ± 0.03b |
| Total tocopherols | 62.29 ± 0.59a | 77.14 ± 0.04b |
| Plastochromanol-8 | 4.42 ± 0.04a | 5.00 ± 0.05a |
| Surface to Volume Ratio [cm−1] | Heating Time [h] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Heated | 6 | 12 | 18 | |
| PRO | ||||
| 0.378 | 1.0 ± 0.0aA | 15.4 ± 0.5bA | 26.4 ± 0.1cA | 40.3 ± 1.1dA |
| 0.189 | 1.0 ± 0.0aA | 6.9 ± 0.1bB | 17.9 ± 0.5cB | 31.2 ± 0.4dB |
| 0.126 | 1.0 ± 0.0aA | 4.8 ± 0.9bC | 12.3 ± 0.4cC | 20.1 ± 0.2dC |
| RRO | ||||
| 0.378 | 0.9 ± 0.0aA | 17.2 ± 0.1bA | 23.1 ± 1.8cD | 37.2 ± 0.6dD |
| 0.189 | 0.9 ± 0.0aA | 16.2 ± 0.5bA | 20.8 ± 0.1cE | 26.6 ± 0.5dE |
| 0.126 | 0.9 ± 0.0aA | 12.4 ± 1.5bD | 16.3 ± 0.1cB | 23.5 ± 1.5dF |
| Time of Heating and s/v Ratio | Polar Fraction | Nonpolar Fraction | Total Polymers | |||||
| Monomers | Dimers | Trimers | Oligomers | Monomers | Dimers | Trimers | ||
| PRO | ||||||||
| Not heated | 8.99 ± 0.06a | 0.19 ± 0.04a | nd * | nd | 962.21 ± 3.86m | nd | nd | 0.19 ± 0.04a |
| 6 h 0.378 | 109.94 ± 4.42de | 18.65 ± 2.81bcd | 1.91 ± 0.18ab | 0.82 ± 0.14b | 763.73 ± 8.43ij | 28.03 ± 1.18b | 3.37 ± 0.68b | 52.78 ± 3.90d |
| 12 h 0.378 | 150.26 ± 2.34g | 51.36 ± 2.91fg | 6.46 ± 0.90c | 1.79 ± 0.20c | 621.66 ± 3.05f | 52.28 ± 3.14c | 5.44 ± 0.78c | 117.34 ± 1.87gh |
| 18 h 0.378 | 215.99 ± 6.01i | 122.49 ± 5.63k | 14.09 ± 0.31e | 3.54 ± 0.09d | 455.59 ± 7.79b | 92.87 ± 8.32f | 5.39 ± 0.33c | 238.38 ± 11.22k |
| 6 h 0.189 | 47.39 ± 1.39b | 10.06 ± 0.65b | 0.03 ± 0.01a | nd | 838.38 ± 8.87k | 24.23 ± 2.09b | nd | 34.32 ± 1.60c |
| 12 h 0.189 | 110.58 ± 3.67de | 47.29 ± 3.54ef | 0.44 ± 0.08a | nd | 691.05 ± 15.53gh | 34.73 ± 2.03b | nd | 82.46 ± 4.94e |
| 18 h 0.189 | 177.49 ± 7.08h | 101.32 ± 2.27j | 5.10 ± 0.63c | 0.09 ± 0.03ab | 548.67 ± 7.67d | 75.14 ± 2.93e | 2.15 ± 0.26a | 183.80 ± 4.31i |
| 6 h 0.126 | 45.33 ± 3.51b | 1.52 ± 0.20a | 0.02 ± 0.01a | nd | 911.51 ± 3.27l | 4.02 ± 0.29a | nd | 5.55 ± 0.19b |
| 12 h 0.126 | 109.68 ± 2.76de | 10.04 ± 1.37b | 0.14 ± 0.03a | nd | 817.98 ± 3.15k | 21.74 ± 2.71b | nd | 31.93 ± 4.02c |
| 18 h 0.126 | 138.09 ± 5.36fg | 38.55 ± 1.89e | 0.46 ± 0.11a | nd | 705.62 ± 6.52h | 65.45 ± 4.95de | nd | 104.46 ± 3.74fg |
| RRO | ||||||||
| Not heated | 8.29 ± 0.00a | 0.08 ± 0.00a | nd | nd | 988.87 ± 0.49m | nd | nd | 0.08 ± 0.00a |
| 6 h 0.378 | 119.35 ± 5.26ef | 27.73 ± 2.07d | 4.24 ± 0.53bc | 0.12 ± 0.03ab | 671.55 ± 2.12g | 94.01 ± 4.32f | nd | 126.10 ± 4.63h |
| 12 h 0.378 | 113.55 ± 8.46de | 64.98 ± 4.59h | 13.49 ± 1.29e | 3.18 ± 0.47d | 581.51 ± 16.64e | 100.55 ± 8.99f | nd | 184.89 ± 10.13i |
| 18 h 0.378 | 155.07 ± 11.55g | 126.37 ± 3.33k | 44.20 ± 3.83h | 14.71 ± 1.11e | 425.41 ± 4.67a | 120.79 ± 4.66g | 2.18 ± 0.41a | 308.25 ± 8.03l |
| 6 h 0.189 | 94.97 ± 6.38cd | 21.25 ± 1.12cd | 5.96 ± 1.14c | nd | 747.45 ± 7.26i | 53.10 ± 6.70cd | nd | 80.31 ± 7.59e |
| 12 h 0.189 | 119.25 ± 2.30ef | 51.34 ± 2.38fg | 9.68 ± 0.29d | nd | 643.04 ± 7.55f | 67.33 ± 3.90e | nd | 128.35 ± 5.98h |
| 18 h 0.189 | 147.90 ± 4.62g | 80.02 ± 5.41i | 18.13 ± 0.75f | 2.00 ± 0.42c | 516.97 ± 13.68c | 117.05 ± 7.87g | nd | 217.21 ± 11.96j |
| 6 h 0.126 | 78.11 ± 9.65c | 11.28 ± 1.22bc | 5.75 ± 1.36c | nd | 786.35 ± 16.21j | 27.09 ± 4.95b | nd | 44.12 ± 6.52cd |
| 12 h 0.126 | 95.50 ± 4.34cd | 23.74 ± 2.03d | 13.62 ± 0.75e | nd | 696.04 ± 9.43gh | 51.26 ± 2.65c | nd | 88.62 ± 4.16ef |
| 18 h 0.126 | 118.06 ± 10.11ef | 59.96 ± 5.48gh | 25.99 ± 0.56g | nd | 579.38 ± 10.23e | 94.44 ± 7.63f | nd | 180.39 ± 3.50i |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kmiecik, D.; Fedko, M.; Siger, A.; Kulczyński, B. Degradation of Tocopherol Molecules and Its Impact on the Polymerization of Triacylglycerols during Heat Treatment of Oil. Molecules 2019, 24, 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244555
Kmiecik D, Fedko M, Siger A, Kulczyński B. Degradation of Tocopherol Molecules and Its Impact on the Polymerization of Triacylglycerols during Heat Treatment of Oil. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244555
Chicago/Turabian StyleKmiecik, Dominik, Monika Fedko, Aleksander Siger, and Bartosz Kulczyński. 2019. "Degradation of Tocopherol Molecules and Its Impact on the Polymerization of Triacylglycerols during Heat Treatment of Oil" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244555
APA StyleKmiecik, D., Fedko, M., Siger, A., & Kulczyński, B. (2019). Degradation of Tocopherol Molecules and Its Impact on the Polymerization of Triacylglycerols during Heat Treatment of Oil. Molecules, 24(24), 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244555








