Thiostrepton: A Novel Therapeutic Drug Candidate for Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TST Inhibits In Vitro Growth of Mab CIP 104,536 and MABSC
2.2. TST Exhibits Potent Activity against Mab Clinical Isolates and Drug-Resistant Strains
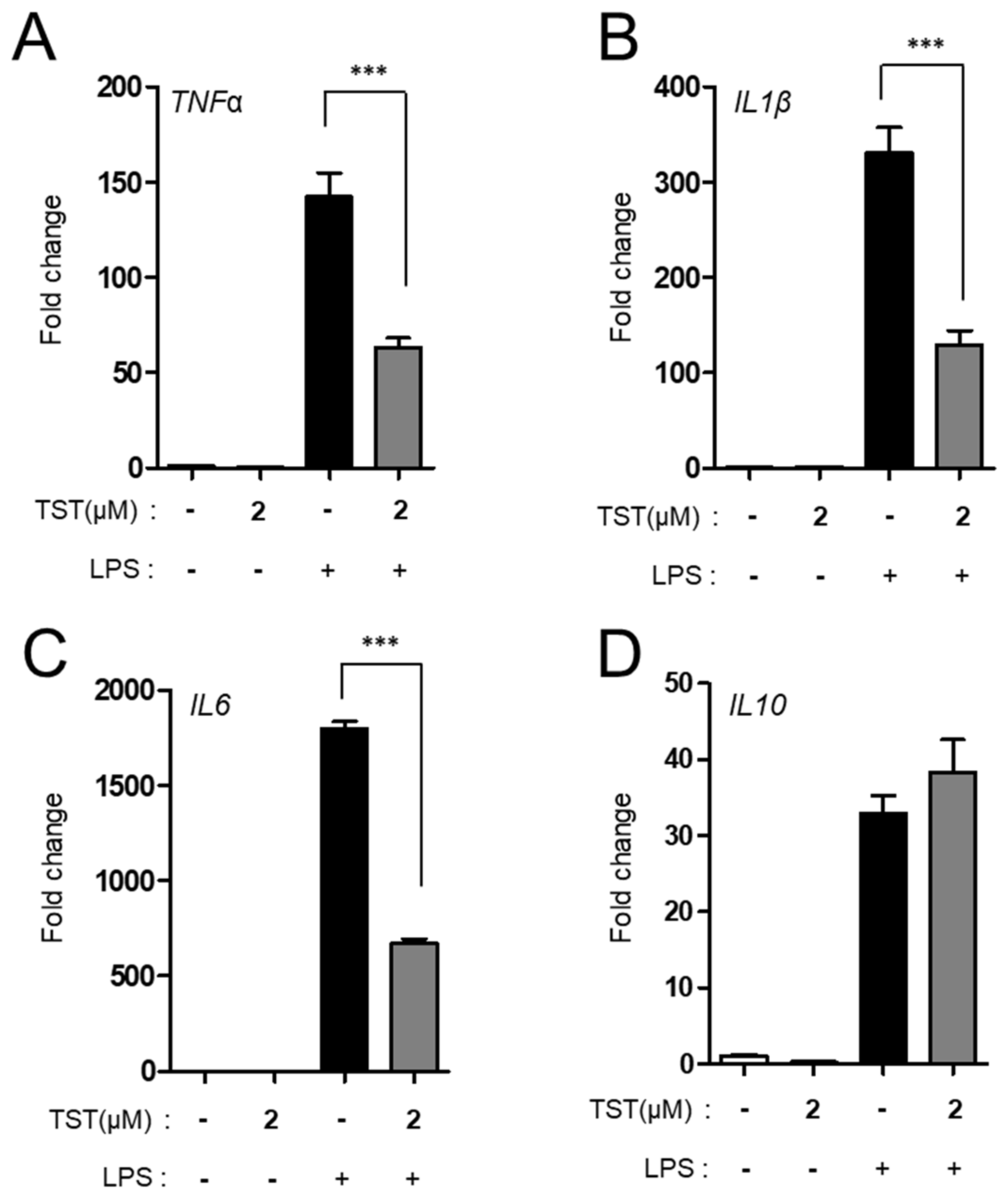
2.3. TST Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Production
2.4. Assessment of TST Activity in Mab Infected THP-1 Cells
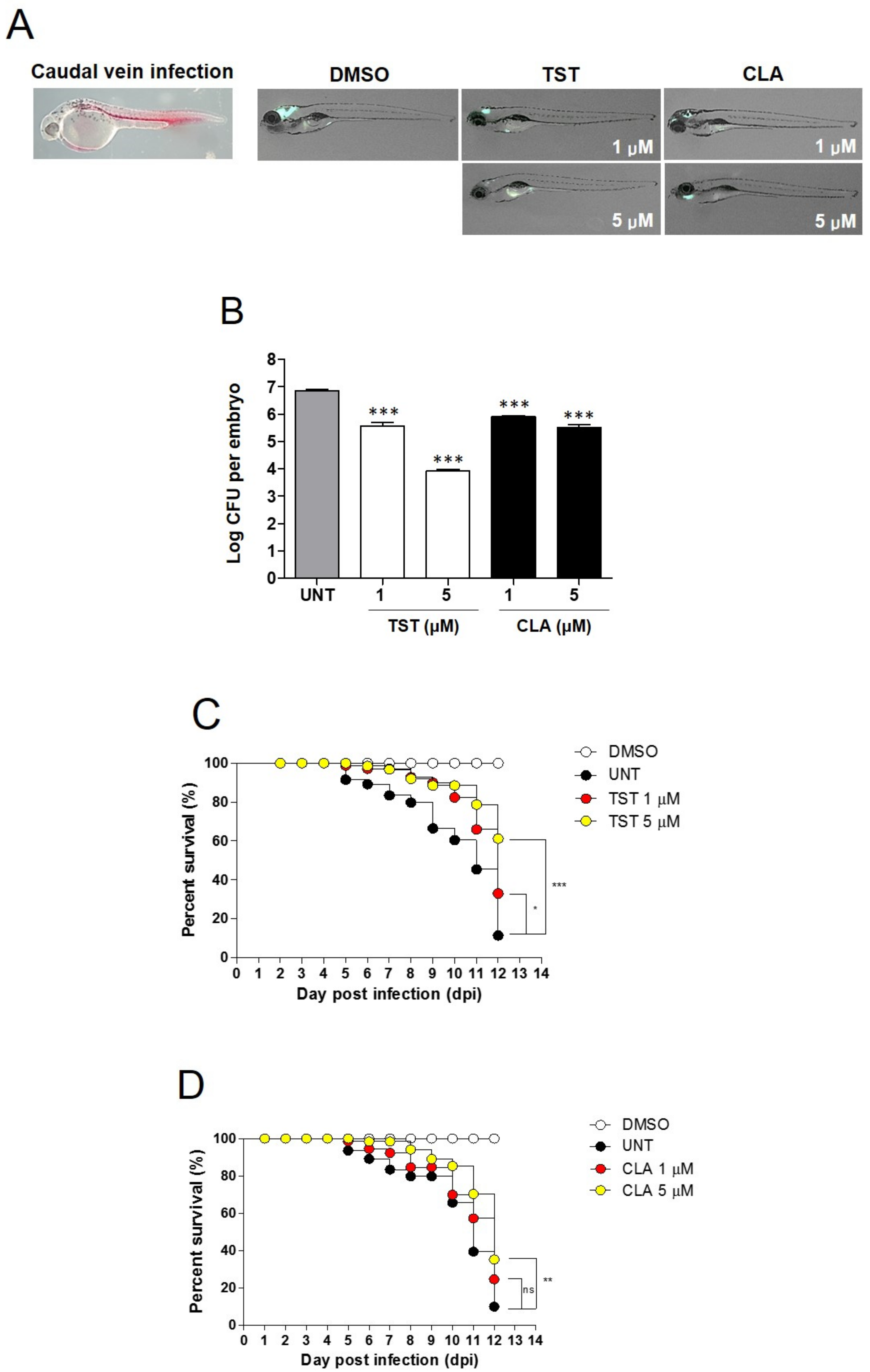
2.5. Assessment of In Vivo TST Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement
4.2. Plasmid Construction and Bacterial Culture
4.3. MIC Determination Using Resazurin Microtiter Assay (REMA)
4.4. Preparation of Human THP-1 Cell Lines for Intracellular Survival Assay
4.5. Preparation of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages, RNA Extraction, Quantitative Real-Time PCR (Qpcr), and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Microinjection of Mab into Embryos and Drug Efficacy Assessment
4.7. TST Extraction and Quantification Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.R.; Sheng, W.H.; Hung, C.C.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, L.N.; Hsueh, P.R. Mycobacterium abscessus Complex Infections in Humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.L.; Aziz, D.B.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. NTM drug discovery: Status, gaps and the way forward. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1502–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.; Byrd, T.F. Mycobacterium abscessus: Shapeshifter of the mycobacterial world. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.Y.H.; Chotirmall, S.H.; Fok, E.T.K.; Verma, A.; De, P.P.; Goh, S.K.; Puah, S.H.; Goh, D.E.L.; Abisheganaden, J.A. Profiling non-tuberculous mycobacteria in an Asian setting: Characteristics and clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients in Singapore. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Kinjo, T.; Nei, Y.; Yamashiro, S.; Fujita, J.; Kishaba, T. Causative species of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease and comparative investigation on clinical features of Mycobacterium abscessus complex disease: A retrospective analysis for two major hospitals in a subtropical region of Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, D.B.; Low, J.L.; Wu, M.L.; Gengenbacher, M.; Teo, J.W.P.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. Rifabutin Is active against mycobacterium abscessus complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00155-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novosad, S.A.; Beekmann, S.E.; Polgreen, P.M.; Mackey, K.; Winthrop, K.L. Treatment of mycobacterium abscessus infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferro, B.E.; Srivastava, S.; Deshpande, D.; Pasipanodya, J.G.; Van Soolingen, D.; Mouton, J.W.; van Ingen, J.; Gumbo, T. Failure of the amikacin, cefoxitin, and clarithromycin combination regimen for treating pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6374–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, D.E. Mycobacterium abscessus subsp abscessus lung disease: ‘trouble ahead, trouble behind…’. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougari, F.; Bouziane, F.; Crockett, F.; Nessar, R.; Chau, F.; Veziris, N.; Sapriel, G.; Raskine, L.; Cambau, E. Selection of resistance to clarithromycin in Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e00943-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nessar, R.; Cambau, E.; Reyrat, J.M.; Murray, A.; Gicquel, B. Mycobacterium abscessus: A new antibiotic nightmare. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffith, D.E. The talking mycobacterium abscessus blues. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Ingen, J.; Boeree, M.J.; Van Soolingen, D.; Mouton, J.W. Resistance mechanisms and drug susceptibility testing of nontuberculous mycobacteria. Drug Resist. Updat. 2012, 15, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rominski, A.; Roditscheff, A.; Selchow, P.; Böttger, E.C.; Sander, P. Intrinsic rifamycin resistance of Mycobacterium abscessus is mediated by ADP-ribosyltransferase MAB_0591. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurer, F.P.; Castelberg, C.; Quiblier, C.; Böttger, E.C.; Somoskövi, A. Erm(41)-dependent inducible resistance to azithromycin and clarithromycin in clinical isolates of mycobacterium abscessus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, G.E.; Shin, S.J.; Won, C.J.; Min, K.N.; Oh, T.; Hahn, M.Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Daley, C.L.; Kim, S.; et al. Macrolide treatment for Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense infection and inducible resistance. Am J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, J.J.; Winter, S.; van Gumpel, E.; Plum, G.; Rybniker, J. Extremely Low Hit Rate in a Diverse Chemical Drug Screen Targeting Mycobacterium abscessus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01008-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Lamore, S.D.; Cabello, C.M.; Lesson, J.L.; Muñoz-Rodriguez, J.L.; Wondrak, G.T. Thiostrepton is an inducer of oxidative and proteotoxic stress that impairs viability of human melanoma cells but not primary melanocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, Q.; Liu, W. Thiopeptide Antibiotics Exhibit a Dual Mode of Action against Intracellular Pathogens by Affecting Both Host and Microbe. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polikanov, Y.S.; Aleksashin, N.A.; Beckert, B.; Wilson, D.N. The Mechanisms of Action of Ribosome-Targeting Peptide Antibiotics. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, S.; Schoof, S.; Bolten, M.; Hearing, C.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K.; Arndt, H.D. Molecular Determinants of Microbial Resistance to Thiopeptide Antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6973–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lougheed, K.E.; Taylor, D.L.; Osborne, S.A.; Bryans, J.S.; Buxton, R.S. New anti-tuberculosis agents amongst known drugs. Tuberculosis 2009, 89, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwok, J.M.; Myatt, S.S.; Marson, C.M.; Coombes, R.C.; Constantinidou, D.; Lam, E.W. Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.; Zhou, T.C.; Lei, X.X.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Ming, K.H.; Wang, B.C.; et al. Inhibition of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway by Thiazole Antibiotic Thiostrepton Attenuates the CD44+/CD24-stem-like population and sphere-forming capacity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.S.; Choe, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, C.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, G.; Park, D.E.; Jo, E.K.; Cho, Y.L.; et al. Activity of LCB01-0371, a novel oxazolidinone, against mycobacterium abscessus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02752-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalla, M.Y.; Ahmad, I.M.; Switzer, B.; Britigan, B.E. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 contributes to survival of Mycobacterium abscessus in human macrophages-like THP-1 cells. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaki, K.; Davis, J.M.; Winglee, K.; Ramakrishnan, L. Evaluation of the pathogenesis and treatment of Mycobacterium marinum infection in zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernut, A.; Le Moigne, V.; Lesne, T.; Lutfalla, G.; Herrmann, J.L.; Kremer, L. In Vivo assessment of drug efficacy against Mycobacterium abscessus using the embryonic zebrafish test system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4054–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, A.L.; Viljoen, A.; Bah, A.; Simeone, R.; Bernut, A.; Laencina, L.; Deramaudt, T.; Rottman, M.; Gaillard, J.L.; Majlessi, L.; et al. The distinct fate of smooth and rough Mycobacterium abscessus variants inside macrophages. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malcolm, K.C.; Caceres, S.M.; Pohl, K.; Poch, K.R.; Bernut, A.; Kremer, L.; Bratton, D.L.; Herrmann, J.L.; Nick, J.A. Neutrophil killing of Mycobacterium abscessus by intra- and extracellular mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernut, A.; Dupont, C.; Ogryzko, N.V.; Neyret, A.; Herrmann, J.L.; Floto, R.A.; Renshaw, S.A.; Kremer, L. CFTR Protects against Mycobacterium abscessus Infection by Fine-Tuning Host Oxidative Defenses. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byrd, T.F.; Lyons, C.R. Preliminary Characterization of a Mycobacterium abscessus Mutant in Human and Murine Models of Infection. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4700–4707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roux, A.L.; Ray, A.; Pawlik, A.; Medjahed, H.; Etienne, G.; Rottman, M.; Catherinot, E.; Coppée, J.Y.; Chaoui, K.; Monsarrat, B.; et al. Overexpression of proinflammatory TLR-2-signalling lipoproteins in hypervirulent mycobacterial variants. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouty, M.G.; Correa, N.E.; Barker, L.P.; Jagadeeswaran, P.; Klose, K.E. Zebrafish-Mycobacterium marinum model for mycobacterial pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 225, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordas, A.; Raterink, R.J.; Cunningham, F.; Jansen, H.J.; Wiweger, M.I.; Jong-Raadsen, S.; Bos, S.; Bates, R.H.; Barros, D.; Meijer, A.H.; et al. Testing tuberculosis drug efficacy in a zebrafish high-throughput translational medicine screen. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernut, A.; Herrmann, J.-L.; Ordway, D.; Kremer, L. The Diverse Cellular and Animal Models to Decipher the Physiopathological Traits of Mycobacterium abscessus Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ottenhoff, T.H. The knowns and unknowns of the immunopathogenesis of tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2012, 16, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.C.; Breen, R.; Miller, R.F.; Noursadeghi, M.; Lipman, M. Paradoxical reactions and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in tuberculosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 32, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Zak, M.; Rahimipour, S.; Estrada, A.A.; Lee, S.H.; O’Brate, A.; Giannakakou, P.; Ghadiri, M.R. Discovery of a biologically active thiostrepton fragment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15042–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just-Baringo, X.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. Thiopeptide antibiotics: Retrospective and recent advances. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 317–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trzasko, A.; Leeds, J.A.; Praestgaard, J.; LaMarche, M.J.; McKenney, D. Efficacy of LFF571 in a hamster model of Clostridium difficile infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4459–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fehér, C.; Soriano, A.; Mensa, J. A Review of Experimental and Off-Label Therapies for Clostridium difficile Infection. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2017, 6, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Gartel, A.L. Micelle-Encapsulated Thiostrepton as an Effective Nanomedicine for Inhibiting Tumor Growth and for Suppressing FOXM1 in Human Xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viljoen, A.; Gutiérrez, A.V.; Dupont, C.; Ghigo, E.; Kremer, L. A simple and rapid gene disruption strategy in Mycobacterium abscessus: On the design and application of glycopeptidolipid mutants. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halloum, I.; Carrère-Kremer, S.; Blaise, M.; Viljoen, A.; Bernut, A.; Le Moigne, V.; Vilchèze, C.; Guérardel, Y.; Lutfalla, G.; Herrmann, J.L.; et al. Deletion of a dehydratase important for intracellular growth and cording renders rough Mycobacterium abscessus avirulent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4228–E4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds, extract and fractions are available from the authors. |




| Agent | MIC90 in 7H9 | |
|---|---|---|
| (μM) | (μg/mL) | |
| Clarithromycin | 4.2 | 3.1 |
| Cefoxitin | 86.9 | 37.1 |
| Thiostrepton | 4.1 | 6.8 |
| Mab Subspecies | Colony Morphology | MIC90 in CAMH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (μM) | (μg/mL) | ||
| abscessus CIP104536 | R | 0.9 | 1.4 |
| bolletii CIP108541 | S | 2.2 | 3.6 |
| massiliense CIP108297 | S | 1.6 | 2.6 |
| abscessus KMRC 00136-61038 | S | 2.3 | 3.8 |
| abscessus KMRC 00136-61039 | S | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| abscessus KMRC 00136-61040 | R | 1.0 | 1.6 |
| abscessus KMRC 00136-61041 | S | 1.8 | 2.9 |
| abscessus KMRC 00200-61199 | S | 2.1 | 3.4 |
| abscessus KMRC 00200-61200 | S | 2.7 | 4.5 |
| abscessus KMRC 00200-61201 | S | 1.7 | 2.7 |
| massiliense KMRC 00200-61202 | R | 2.4 | 4.1 |
| massiliense KMRC 00200-61204 | S | 0.7 | 1.1 |
| M. abscessus (CLA-R) | S | 3.2 | 5.4 |
| M. abscessus (AMK-R) | S | 4.6 | 7.7 |
| M. abscessus (CFX-R) | S | 3.1 | 5.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.H.; Hanh, B.T.B.; Kim, G.; Lee, D.-G.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, B.S.; Ryoo, S.; Jo, E.-K.; et al. Thiostrepton: A Novel Therapeutic Drug Candidate for Mycobacterium abscessus Infection. Molecules 2019, 24, 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244511
Kim TH, Hanh BTB, Kim G, Lee D-G, Park J-W, Lee SE, Kim J-S, Kim BS, Ryoo S, Jo E-K, et al. Thiostrepton: A Novel Therapeutic Drug Candidate for Mycobacterium abscessus Infection. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244511
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Ho, Bui Thi Bich Hanh, Guehye Kim, Da-Gyum Lee, June-Woo Park, So Eui Lee, Jae-Sung Kim, Byoung Soo Kim, Sungweon Ryoo, Eun-Kyeong Jo, and et al. 2019. "Thiostrepton: A Novel Therapeutic Drug Candidate for Mycobacterium abscessus Infection" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244511
APA StyleKim, T. H., Hanh, B. T. B., Kim, G., Lee, D.-G., Park, J.-W., Lee, S. E., Kim, J.-S., Kim, B. S., Ryoo, S., Jo, E.-K., & Jang, J. (2019). Thiostrepton: A Novel Therapeutic Drug Candidate for Mycobacterium abscessus Infection. Molecules, 24(24), 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244511





