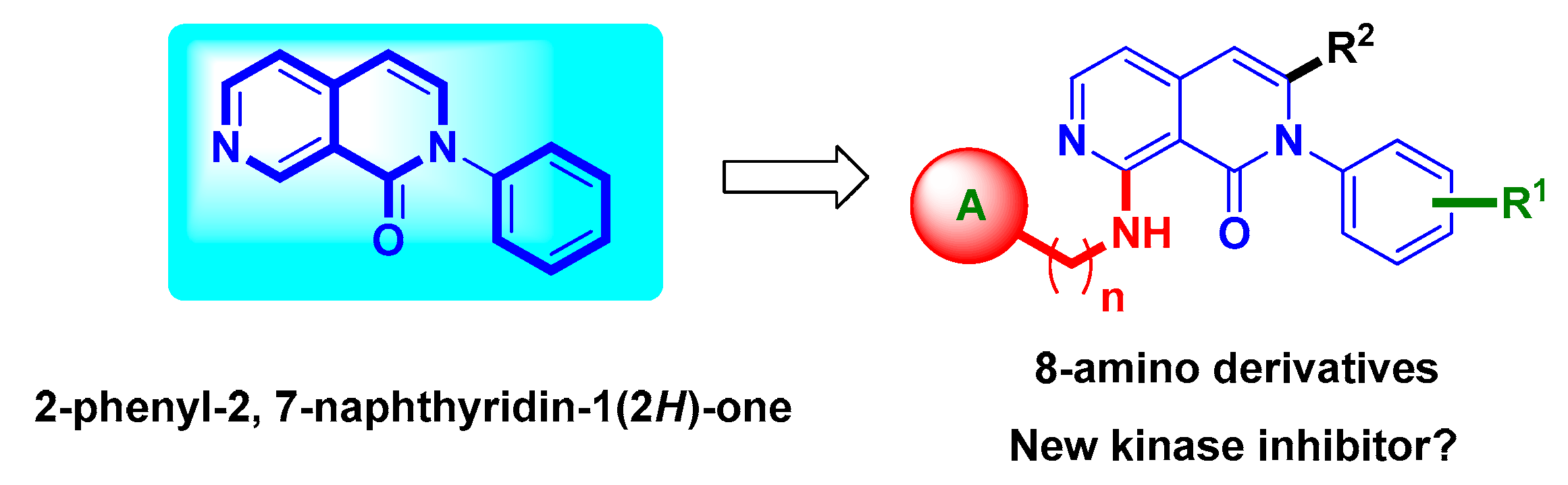
Discovery of 8-Amino-Substituted 2-Phenyl-2,7-Naphthyridinone Derivatives as New c-Kit/VEGFR-2 Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
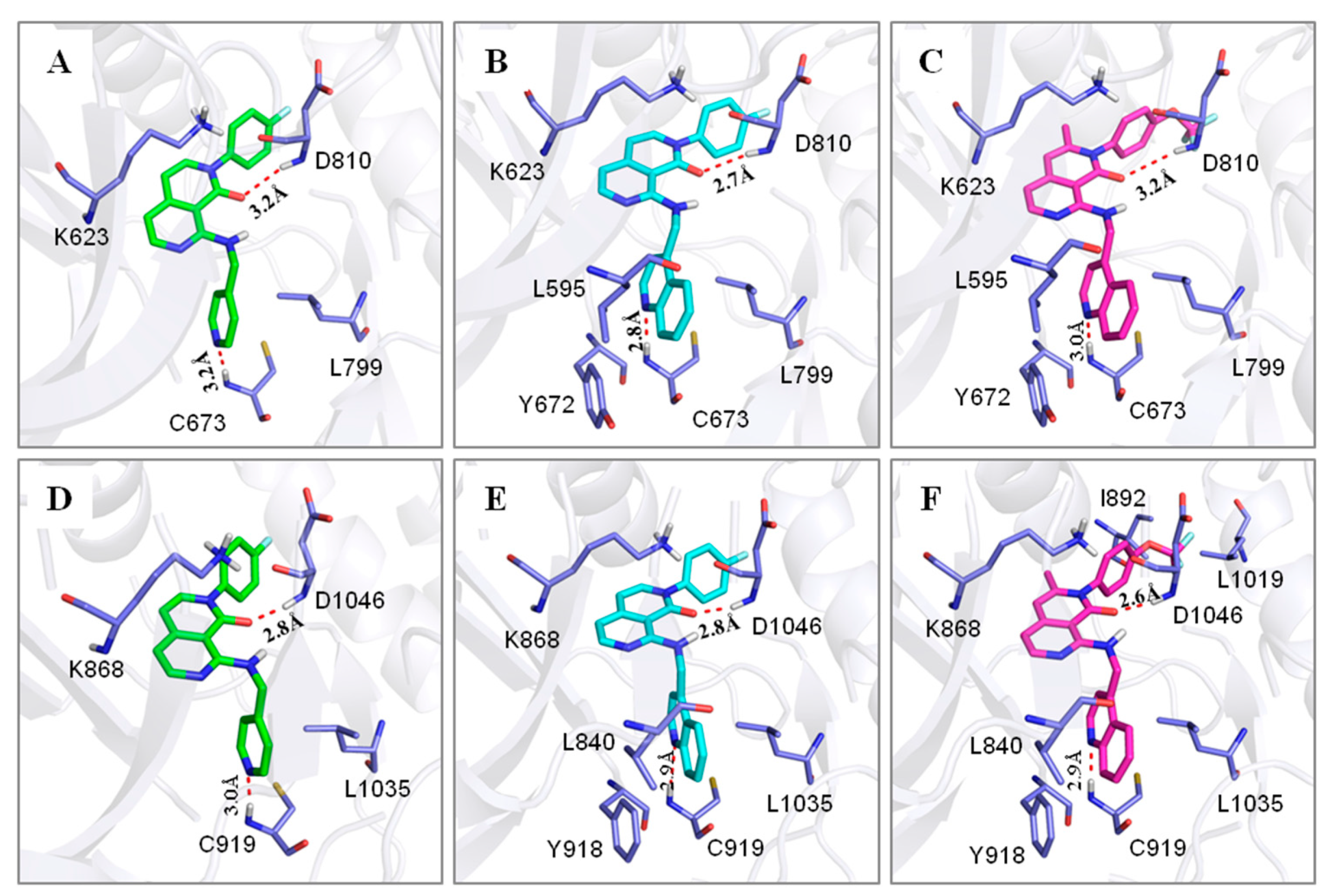
2.3. Molecular Modeling
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biochemical Kinase Assays
4.2. Molecular Modeling
4.3. Chemistry
4.3.1. General Information
4.3.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Intermediates 7a–f
4.3.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Targets 9a–k and 10a–s
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Greiner, R.; Ziegler, D.S.; Cibu, D.; Jakowetz, A.C.; Auras, F.; Bein, T.; Knochel, P. Preparation of polyfunctional naphthyridines by cobalt-catalyzed cross-couplings of halogenated naphthyridines with magnesium and zinc organometallics. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6384–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.J.; Ellman, J.A.; Taylor, E.C. The Naphthyridines; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Litvinov, V.P.; Roman, S.V.; Dyachenko, V.D. Naphthyridines. Structure, physicochemical properties and general methods of synthesis. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2000, 69, 201–220. [Google Scholar]
- Paim, C.S.; Araujo, B.V.; Volpato, N.M.; Steppe, M.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Gemifloxacin mesylate (GFM): Dissolution test based on in vivo data. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chang, Y.W.; Kuo, P.L.; Chen, Y.H. Gemifloxacin inhibits migration and invasion and induces mesenchymal–epithelial transition in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, P. Novel 1, 5-naphthyridine PI3Kδ inhibitors, an evaluation of WO2011075628. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, F.; Chua, P.C.; O’Brien, S.E.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Bourbon, P.; Haddach, M.; Michaux, J.; Nagasawa, J.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Stefan, E.; et al. Discovery and sar of 5-(3-chlorophenylamino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase ck2 for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, M.T.; Balitza, A.E.; Hoffman, J.M.; Manley, P.J.; Barnett, S.F.; Defeo, J.D.; Haskell, K.; Jones, R.E.; Leander, K.; Robinson, R.G.; et al. Allosteric inhibitors of Akt1 and Akt2: A naphthyridinone with efficacy in an A2780 tumor xenograft model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3178–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, N.; Green, N.; Li, H.Q.; Hu, Y.; Janz, K.; Gavrin, L.K.; Thomason, J.; Tam, S.; Powell, D.; Cuozzo, J.; et al. Identification of a novel class of selective Tpl2 kinase inhibitors: 4-Alkylamino-[1, 7] naphthyridine-3-carbonitriles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6425–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrin, L.K.; Green, N.; Hu, Y.; Janz, K.; Kaila, N.; Li, H.Q.; Tam, S.Y.; Thomason, J.R.; Gopalsamy, A.; Ciszewski, G.; et al. Inhibition of Tpl2 kinase and TNF-α production with 1, 7-naphthyridine-3-carbonitriles: Synthesis and structure–activity relationships. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5288–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.S.; Xu, H.C.; Wang, M.S.; Zhao, X.E.; Ming, Z.H.; Zhu, X.L.; Huang, W.; Yang, G.F. 2, 7-naphthyridinone-based MET kinase inhibitors: A promising novel scaffold for antitumor drug development. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 705–714. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Ai, J.; Peng, X.; Lin, J.P.; Ji, Y.C.; Geng, M.Y.; Long, Y.Q. Investigation on the 1, 6-naphthyridine motif: Discovery and SAR study of 1 H-imidazo [4, 5-h][1, 6] naphthyridin-2 (3 H)-one-based c-Met kinase inhibitors. Organic Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1545–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.S.; Zhuo, L.S.; Yang, F.P.; Wang, W.J.; Huang, W.; Yang, G.F. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new MET inhibitors with 1, 6-naphthyridinone scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 185, 111803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.A.; Benveniste, E.N. Protein kinase CK2: An emerging regulator of immunity. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madak, J.T.; Cuthbertson, C.R.; Miyata, Y.; Tamura, S.; Petrunak, E.M.; Stuckey, J.A.; Han, Y.Y.; He, M.; Sun, D.X.; Showalter, H.D.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 4-quinoline carboxylic acids as inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5162–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Jaggi, M.; Singh, A.T.; Madaan, A.; Sanna, V.; Singh, P.; Sharma, P.K.; Irchhaiya, R.; Burman, A.C. 1, 8-Naphthyridine-3-carboxamide derivatives with anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3356–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.J.; Xun, Z.; Hu, J.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhao, Y.W.; Huang, Z.B.; Shi, D.Q. Efficient synthesis and evaluation of antitumor activities of novel functionalized 1,8-naphthyridine derivatives. ACS Comb. Sci. 2015, 17, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, C.; Malfitano, A.M.; Parkkari, T.; Lucchesi, V.; Carpi, S.; Fogli, S.; Bertini, S.; Laezza, C.; Ligresti, A.; Saccomanni, G.; et al. New quinolone-and 1, 8-naphthyridine-3-carboxamides as selective CB2 receptor agonists with anticancer and immuno–modulatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Hills, P.; Mooberry, S.L.; Ballantine, D.L.; Murray, T.F.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Lophocladines, Bioactive Alkaloids from the Red Alga Lophocladia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumpan, K.; Nathubhai, A.; Zhang, C.; Wood, P.J.; Lloyd, M.D.; Thompson, H.T.; Lehtio, L.; Threadgill, M.D. Structure-based design, synthesis and evaluation in vitro of arylnaphthyridinones, arylpyridopyrimidinones and their tetrahydro derivatives as inhibitors of the tankyrases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3013–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theeramunkong, S.; Vajragupta, O.; Mudjupa, C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of simplified analogs of lophocladine B as potential antitumor agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Ding, C.; Cheng, C.; Yao, Q. Convenient synthesis of 2, 7-naphthyridine lophocladines A and B and their analogues. J. Comb. Chem. 2007, 9, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalsamy, A.; Shi, M.; Boschelli, D.H.; Williamson, R.; Olland, A.; Hu, Y.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Han, X.; Arndt, K.; Guo, B. Discovery of dibenzo[c,f][2,7]naphthyridines as potent and selective 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5547–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Illarionov, B.; Bacher, A.; Fischer, M.; Georg, G.I.; Ye, Q.Z.; Vander, V.D.; Fanwick, P.E.; Song, Y.; Cushman, M. A novel lumazine synthase inhibitor derived from oxidation of 1, 3, 6, 8-tetrahydroxy-2, 7-naphthyridine to a tetraazaperylenehexaone derivative. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ukita, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kubo, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Moritani, Y.; Saruta, K.; Higashijima, T.; Kotera, J.; Fujishige, K.; Takagi, M.; et al. 1, 7-and 2, 7-naphthyridine derivatives as potent and highly specific PDE5 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.O.; Ryu, J.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, N.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Joen, S.D.; Kim, J.H.; Rhee, H.I.; Cho, Y.B.; et al. Pyridine Derivatives, Methods of their Preparations, and Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing the Same. PTC Int. Appl. WO 2006112666A1, 26 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Okram, B.; Uno, T.; Ding, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Jin, Y.H.; Jin, Q.H.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.W.; Yan, S.F. Compounds and Compositions as Kinase Inhibitors. PTC Int. Appl. WO 2009097287A1, 6 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Greiner, R.; Lumpe, H.; Kqiku, L.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Knochel, P. Directed zincation or magnesiation of the 2-pyridone and 2, 7-naphthyridone scaffold using TMP bases. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5760–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Knick, V.B.; Rudolph, S.K. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlation from mouse to human with pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.J. Targeting receptor tyrosine kinase MET in cancer: Small molecule inhibitors and clinical progress. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4427–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garner, A.P.; Gozgit, J.M.; Anjum, R.; Vodala, S.; Schrock, A.; Zhou, T.; Serrano, C.; Eilers, G.; Zhu, M.; Ketzer, J.; et al. Ponatinib inhibits polyclonal drug-resistant KIT oncoproteins and shows therapeutic potential in heavily pretreated gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5745–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tasker, A.S.; Patel, V.F. PDB bank [3EFL]. to be published.
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.2r3pre, Schrödinger, LLC. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 5 December 2019).
Sample Availability: Not available. |



| No. | Block A | n | Inhibitory Activity, IC50, nM a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET | c-Kit | VEGFR-2 | |||
| 9a | A-1 | 0 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9b | A-2 | 0 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9c | A-3 | 0 | >5000 | >5000 | 691.2 |
| 9d | A-4 | 0 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9e | A-5 | 0 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9f | A-1 | 1 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9g | A-6 | 1 | >5000 | 832.0 | 601.3 |
| 9h | A-4 | 1 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9i | A-7 | 1 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9j | A-8 | 1 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 9k | A-9 | 1 | >5000 | 8.5 | 238.5 |
| 3 | 9.9 | 329.6 | 279.9 | ||

| No. | Block A | n | R1 | Inhibitory Activity, IC50, nM a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c-Met | c-Kit | VEGFR-2 | ||||
| 10a | A-4 | 0 | 4-F | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10b | A-4 | 1 | 4-F | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10c | A-6 | 1 | 4-F | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10d | A-9 | 1 | 4-F | >5000 | 1609 | 208 |
| 10e | A-4 | 0 | H | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10f | A-4 | 1 | H | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10g | A-6 | 1 | H | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10h | A-9 | 1 | H | >5000 | >5000 | 1031 |
| 10i | A-4 | 0 | 4-Cl | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10j | A-4 | 1 | 4-Cl | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10k | A-6 | 1 | 4-Cl | >5000 | >5000 | 263 |
| 10l | A-9 | 1 | 4-Cl | >5000 | 107 | 56.5 |
| 10m | A-4 | 0 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10n | A-4 | 1 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10o | A-6 | 1 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | >5000 | 538 |
| 10p | A-7 | 1 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10q | A-8 | 1 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | >5000 | >5000 |
| 10r | A-9 | 1 | 4-OCF3 | >5000 | 169 | 31.7 |
| 10s | A-9 | 1 | 2,4-F2 | >5000 | >5000 | 887 |
| 3 | 9.9 | 329.6 | 279.9 | |||
| N.O. | Compound | ΔEele | ΔEvdw | ΔGnp | ΔGpol | ΔH | -TΔS | ΔGcal | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c-Kit (4U0I) | 9g | −18.60 | −52.83 | −5.49 | 42.12 | −34.81 | 14.67 | −20.13 | 832 |
| 9k | −21.78 | −60.09 | −5.91 | 44.37 | −43.42 | 13.19 | −30.23 | 8.5 | |
| 10r | −18.78 | −59.91 | −6.52 | 45.23 | −39.98 | 15.90 | −24.08 | 169 | |
| VEGFR-2 (3EFL) | 9g | −26.32 | −53.91 | −5.36 | 40.44 | −45.15 | 15.18 | −29.97 | 601 |
| 9k | −26.56 | −60.46 | −5.86 | 42.55 | −50.34 | 15.55 | −34.79 | 238.5 | |
| 10r | −27.82 | −64.08 | −6.37 | 43.36 | −54.92 | 16.38 | −38.54 | 31.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Zhuo, L.; Dong, H.; Huang, W.; She, N. Discovery of 8-Amino-Substituted 2-Phenyl-2,7-Naphthyridinone Derivatives as New c-Kit/VEGFR-2 Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244461
Sun H, Zhuo L, Dong H, Huang W, She N. Discovery of 8-Amino-Substituted 2-Phenyl-2,7-Naphthyridinone Derivatives as New c-Kit/VEGFR-2 Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244461
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haiyan, Linsheng Zhuo, Huan Dong, Wei Huang, and Nengfang She. 2019. "Discovery of 8-Amino-Substituted 2-Phenyl-2,7-Naphthyridinone Derivatives as New c-Kit/VEGFR-2 Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244461
APA StyleSun, H., Zhuo, L., Dong, H., Huang, W., & She, N. (2019). Discovery of 8-Amino-Substituted 2-Phenyl-2,7-Naphthyridinone Derivatives as New c-Kit/VEGFR-2 Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 24(24), 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244461







