Mercapto-Functionalized Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
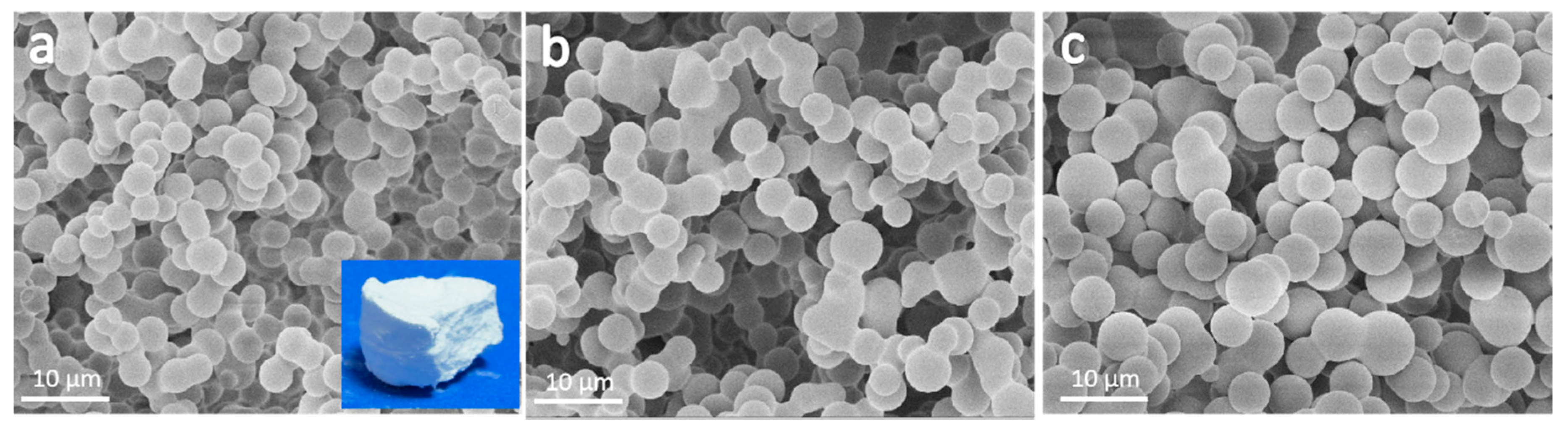
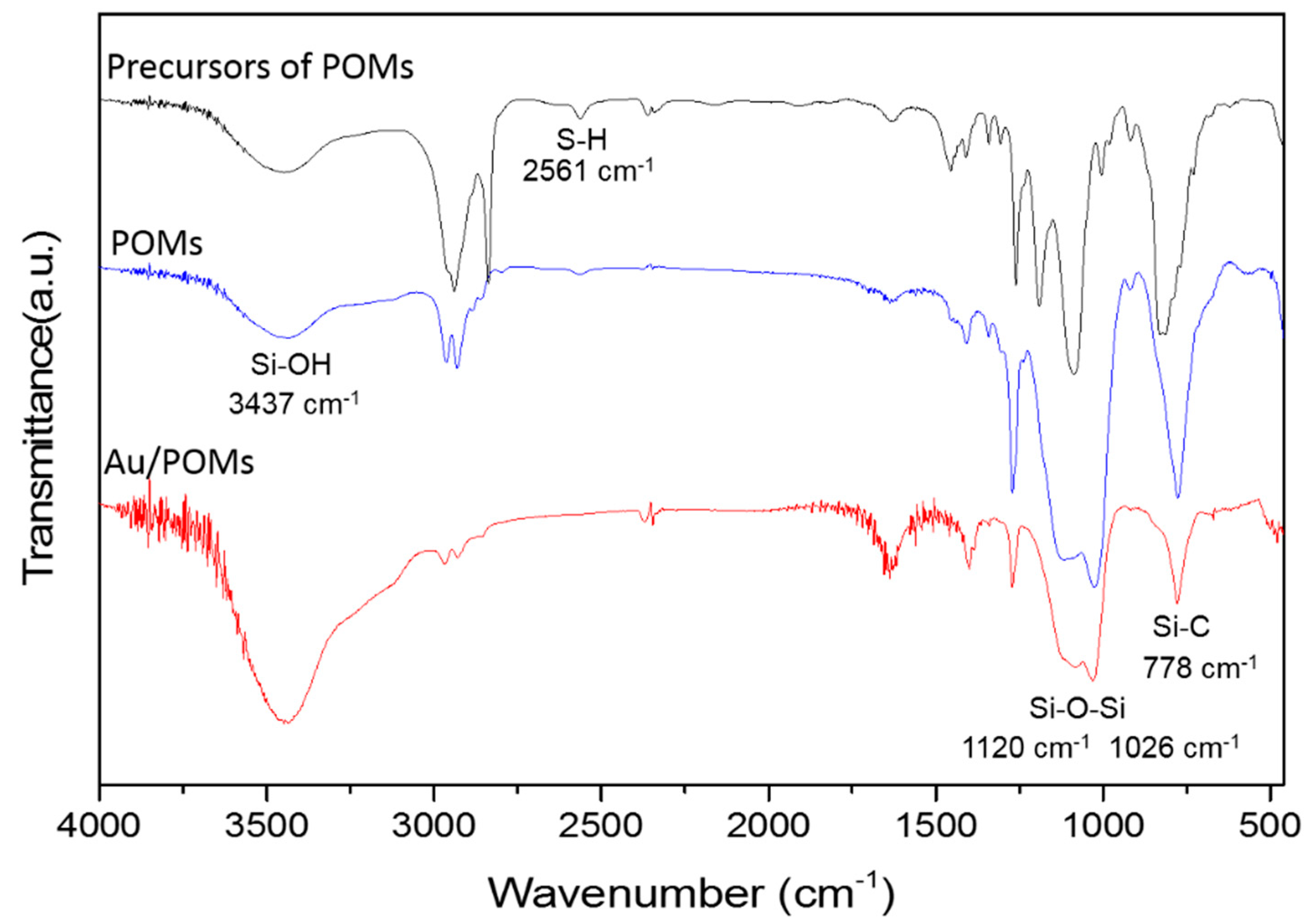
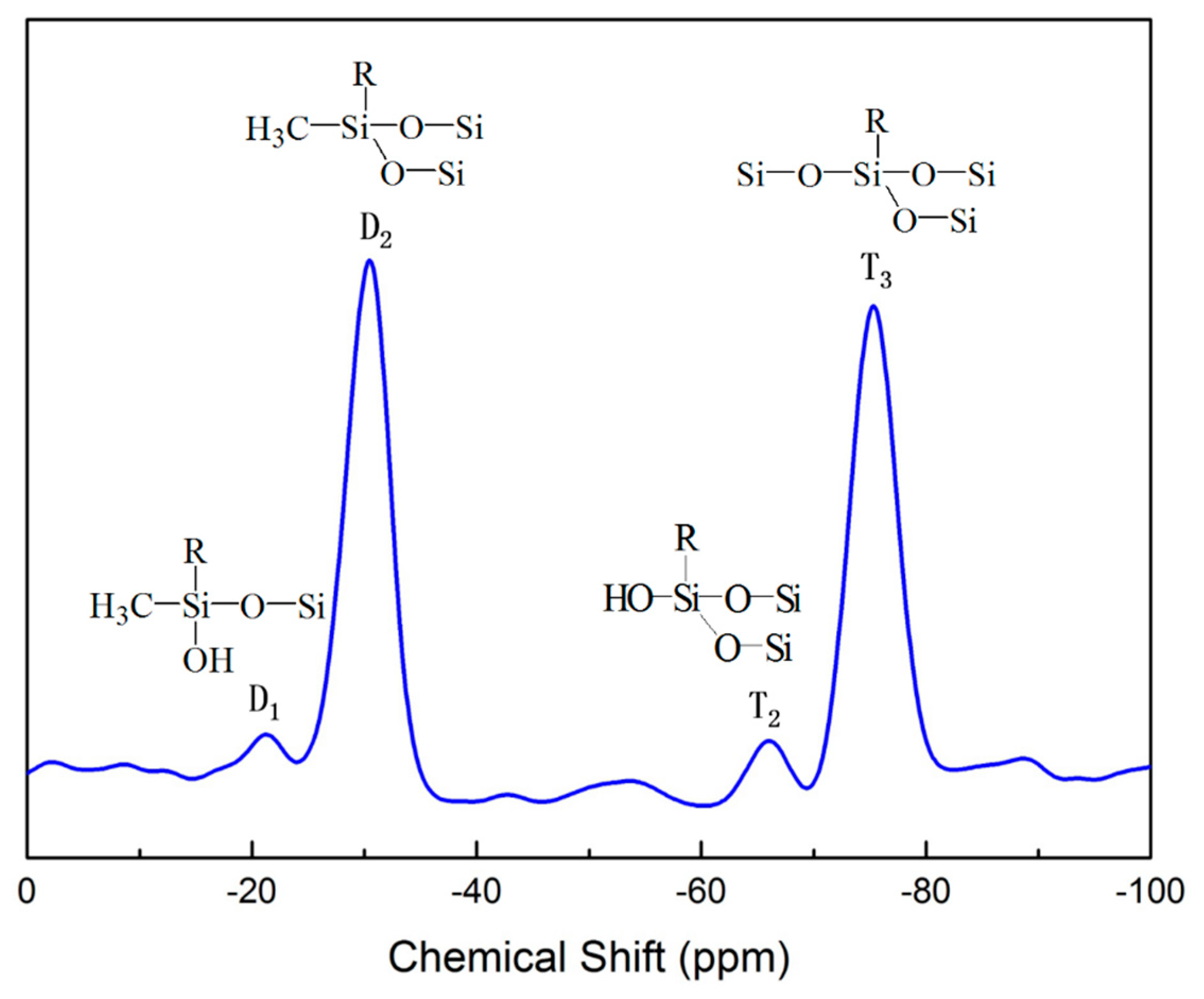
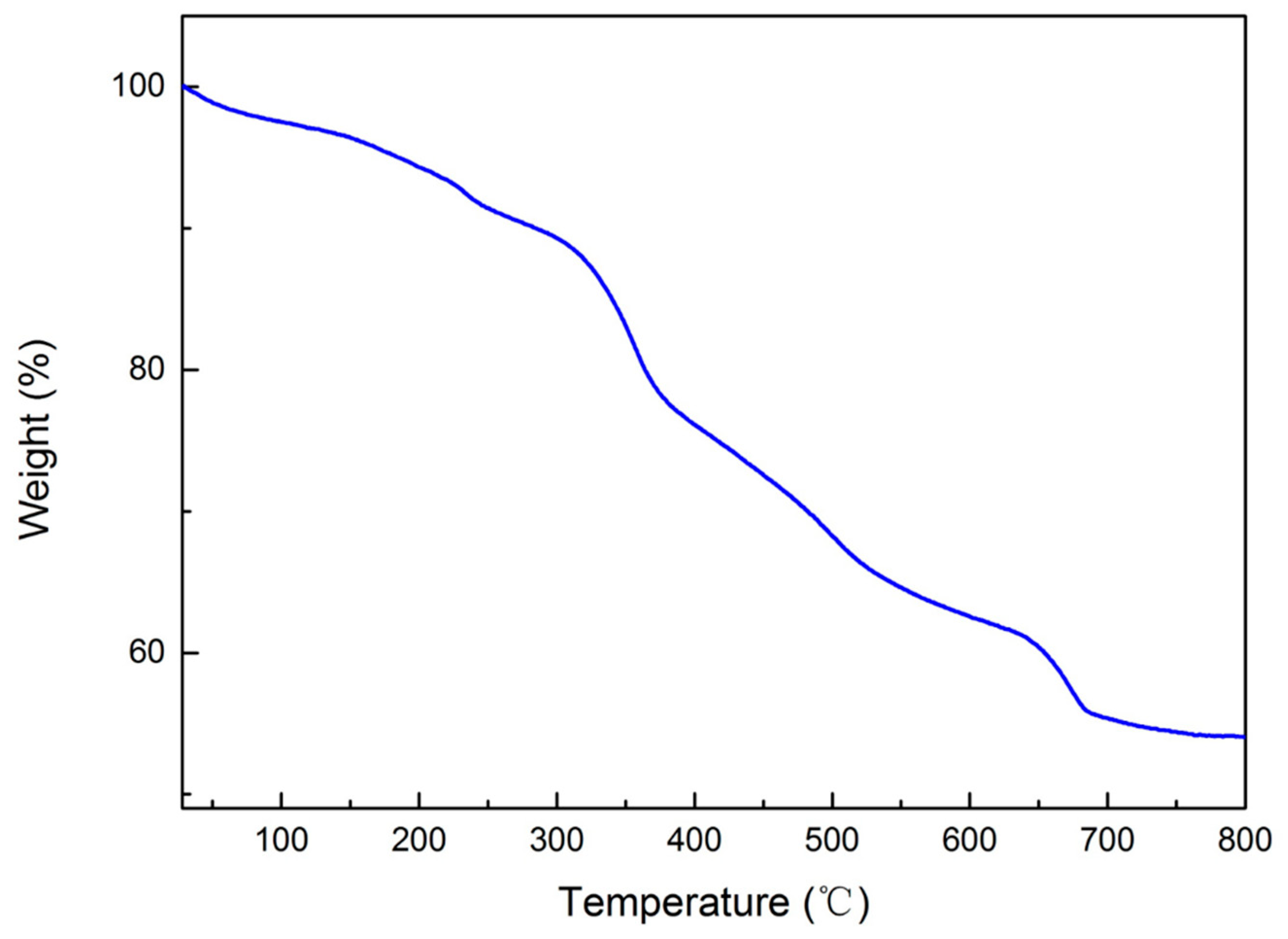
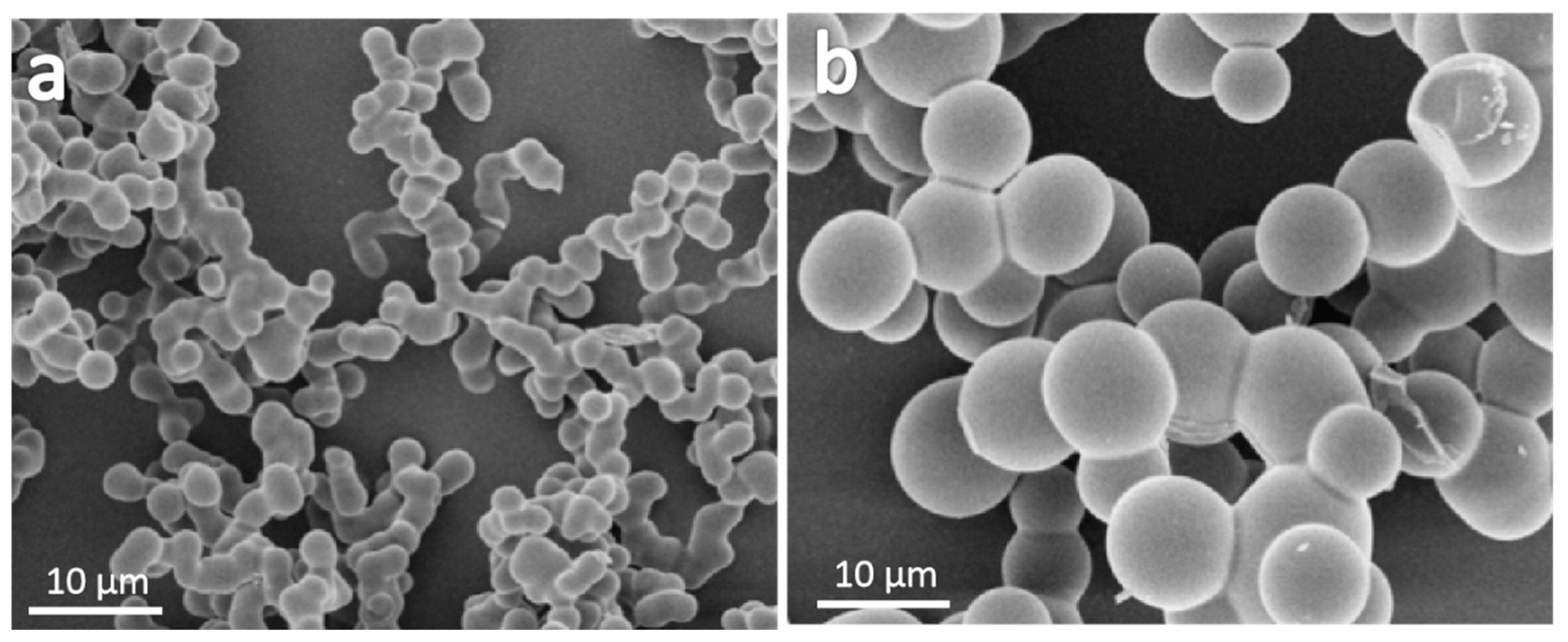
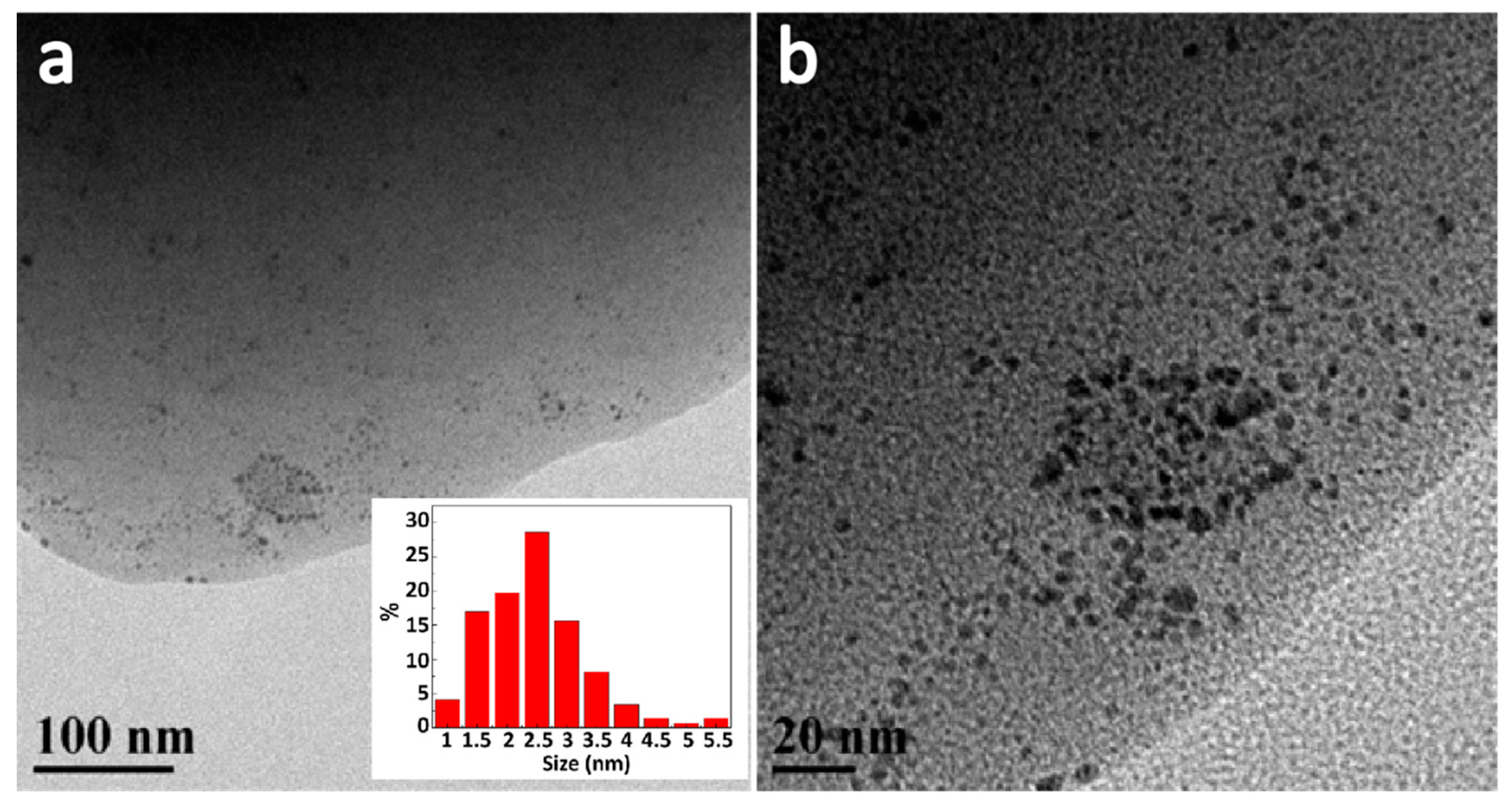
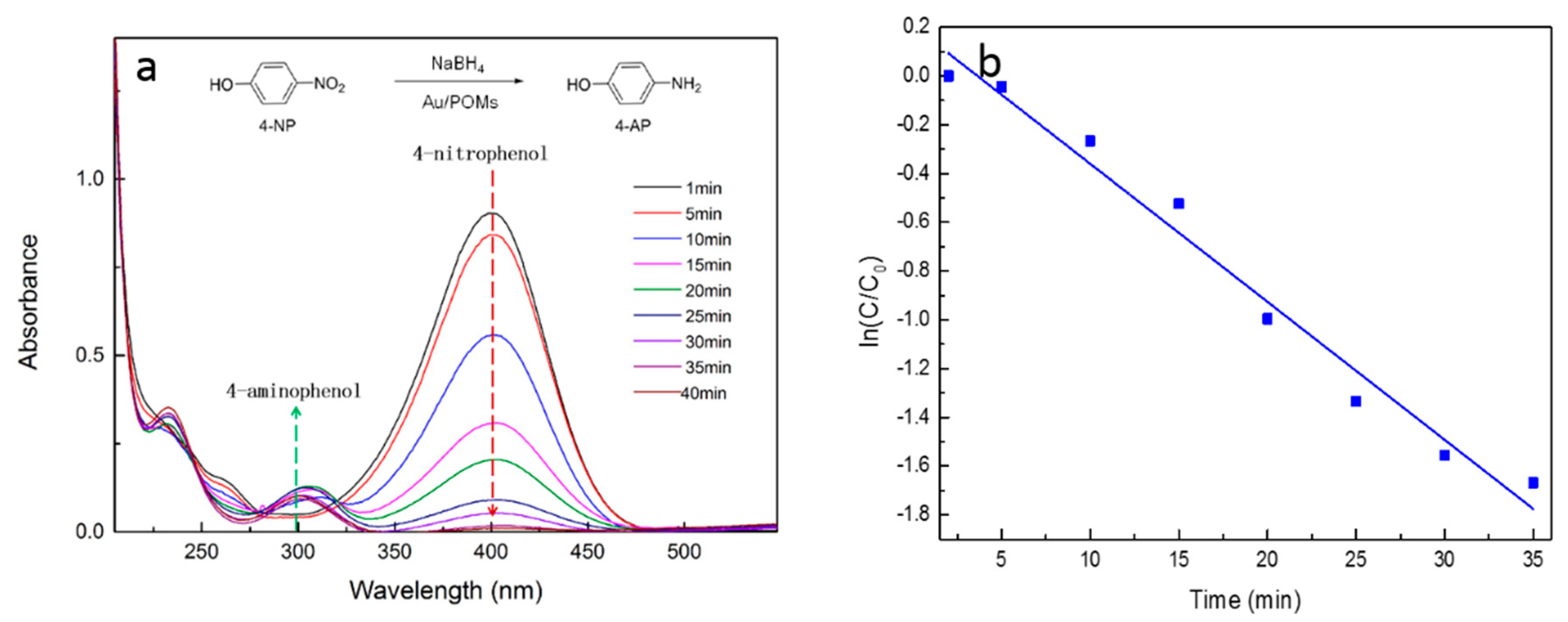
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of Porous Organosilica Monoliths (POMs)
3.3. Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles
3.4. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol with Au/POMs as the Catalyst
3.5. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleki, H.; Whitmore, L.; Husing, N. Novel multifunctional polymethylsilsesquioxane-silk fibroin aerogel hybrids for environmental and thermal insulation applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 12598–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.L.; Tan, Y.Q.; Song, Y.H.; Zheng, Q. A flyweight and superelastic graphene aerogel as a high-capacity adsorbent and highly sensitive pressure sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9074–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Y.M.; Ruan, K.P.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Y.J.; Liang, C.B.; Kong, J.; Gu, J.W. Fabrication and investigation on the pani/mwcnt/thermally annealed graphene aerogel/epoxy electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposites. Compos. Part. A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.L.; Huang, J.Y.; Li, S.H.; Meng, K.; Zhang, L.Y.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y.K. Mechanically resistant and sustainable cellulose-based composite aerogels with excellent flame retardant, sound-absorption, and superantiwetting ability for advanced engineering materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Huang, C.; Han, J.; Jiang, S. Anisotropic nanocellulose aerogels with ordered structures fabricated by directional freeze-drying for fast liquid transport. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6653–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Xu, X.; Yue, Y.; Mei, C.; Huang, C.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Q.; Han, J. Nanocellulose-mediated electroconductive self-healing hydrogels with high strength, plasticity, viscoelasticity, stretchability, and biocompatibility toward multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27987–28002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Malfait, W.J.; Demilecamps, A.; Zhang, Y.C.; Brunner, S.; Huber, L.; Tingaut, P.; Rigacci, A.; Budtova, T.; Koebel, M.M. Strong, thermally superinsulating biopolymer-silica aerogel hybrids by cogelation of silicic acid with pectin. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 14282–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Low-density open cellular sponges as functional materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2017, 56, 15520–15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Green synthesis of ant nest-inspired superelastic silicone aerogels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11222–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Brinker, C.; Hurd, A.; Rao, S. Silica aerogel films prepared at ambient pressure by using surface derivatization to induce reversible drying shrinkage. Nature 1995, 374, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, G.; Deng, L.; Li, J.; Sun, R.; Li, y.; Wong, C.-P. In situ assembly of dispersed ag nanoparticles on hierarchically porous organosilica microspheres for controllable reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotoohi, B.; Kazemzad, M.; Mercier, L. Additive-free synthesis of robust monolithic mesoporous silica support used in catalysis. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20199–20210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Lehr, M.; Seidler, C.F.; Taffa, D.H.; Wark, M.; Smarsly, B.M.; Marschall, R. Proton conduction in sulfonated organic-inorganic hybrid monoliths with hierarchical pore structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25476–25488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, A.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. A single au nanoparticle anchored inside the porous shell of periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres. Nano. Res. 2015, 8, 3404–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Mondal, J.; Borah, P.; Mondal, S.; Bhaumik, A.; Zhao, Y. Ruthenium bipyridyl tethered porous organosilica: A versatile, durable and reusable heterogeneous photocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10746–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Bagheri, A.R.; Jiang, S.; Golenser, J.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Exploration of macroporous polymeric sponges as drug carriers. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3215–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Strong, compressible, bendable and stretchable silicone sponges by solvent-controlled hydrolysis and polycondensation of silanes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Peng, J.; Du, G.; Peng, H.; Fang, Y. One-Step preparation of emulsion-templated amino-functionalized porous organosilica monoliths for highly efficient cr(vi) removal. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 555, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, N.; Vueva, Y.; Ivanova, Y.; Salvado, I.; Fernandes, M.; Vassileva, P.; Georgieva, R.; Detcheva, A. Synthesis and characterization of sol-gel mesoporous organosilicas functionalized with amine groups. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 378, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, K.; Min, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Min, Y. Clickable periodic mesoporous organosilica monolith for highly efficient capillary chromatographic separation. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Nagasawa, H.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Facile and scalable flow-induced deposition of organosilica on porous polymer supports for reverse osmosis desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14070–14078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaraiah, S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.W. Preparation and characterization of surface-functionalized polysilsesquioxane hard spheres in aqueous medium. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6195–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.-A.; Yoon, K.-S. Preparation of functionalized polysilsesquioxane and polysilsesquioxane-metal nanoparticle composite spheres. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Ha, C.S. Multifunctional materials based on polysilsesquioxanes. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Guo, W.; Park, S.-K.; Ha, C.-S. Controlled synthesis of novel cyanopropyl polysilsesquioxane hollow spheres loaded with highly dispersed au nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.W.; Gao, C.T.; Xie, H.B.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Luo, Z.; Sun, Q.; Dong, F.P. Controllable synthesis of hierarchical polysilsesquioxane surfaces: From spheres-on-sphere to bowls-on-sphere structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Dong, F. Uniform and reactive hydrogen polysilsesquioxane hollow spheres immobilized with silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. Facile synthesis of marshmallow-like macroporous gels usable under harsh conditions for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, F.; Lu, L.; Li, H.; Xiong, Y.; Ha, C.-S. Raspberry-Like polysilsesquioxane particles with hollow-spheres-on-sphere structure: Rational design, controllable synthesis, and catalytic application. Polymers 2019, 11, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choi, G.M.; Bae, J.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, B.S. High-performance and simply-synthesized ladder-like structured methacrylate siloxane hybrid material for flexible hard coating. Polymers 2018, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Chen, G.X.; Li, Q.F. Synthesis and characterization of mercaptopropyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (poss). J. B. Univ. Chem. Technol (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 36, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, M.J.; Caruzi, B.B.; Gil, G.A.; Samulewski, R.B.; Bail, A.; Pereira Scacchetti, F.A.; Moises, M.P.; Bezerra, F.M. In-situ direct synthesis of hkust-1 in wool fabric for the improvement of antibacterial properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel-Hassen, R.; Boufi, S.; Salon, M.C.B.; Abdelmouleh, M.; Belgacem, M.N. Adsorption of silane onto cellulose fibers. Ii. The effect of ph on silane hydrolysis, condensation, and adsorption behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Lee, S.J.; Dong, F.; Park, S.S.; Ha, C.S. A general ph-responsive supramolecular nanovalve based on mesoporous organosilica hollow nanospheres. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8641–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, N.; Hayashi, K.; Yamaura, S.-I.; Zhang, W.; Sakamoto, W.; Yogo, T. Synthesis of inorganic-organic hybrid membranes consisting of triazole linkages formed by the azide-alkyne click reaction. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 517, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Tsuru, T. Effects of calcination condition on the network structure of triethoxysilane (tries) and how Si-H groups influence hydrophobicity under hydrothermal conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; Plans, J.; Ynduráin, F. Atomic oxygen in silicon: The formation of the Si-O-Si bond. Phys. Rev. B J. 1987, 36, 8043–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Zhang, M.C.; Zhang, W.Q. Yolk-Shell catalyst of single au nanoparticle encapsulated within hollow mesoporous silica microspheres. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leng, W.; Dong, B.; Ge, R.; Duan, H.; Gao, Y.A. Bottom-up preparation of gold nanoparticle-mesoporous silica composite nanotubes as a catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yu, G.; Le, X. Gold nanoparticle modified magnetic fibrous silica microspheres as a highly efficient and recyclable catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 8623–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds POMs-1, POMs-2, and POMs-3 are available from the authors. |

| Code | CTAB (g) | Urea (g) | HAc (mL) | MTMS (mL) | SHTMS (mL) | SHDMS (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POMs-1 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| POMs-2 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| POMs-3 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Pan, J.; Gao, C.; Ma, M.; Lu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Dong, F. Mercapto-Functionalized Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234366
Li H, Pan J, Gao C, Ma M, Lu L, Xiong Y, Dong F. Mercapto-Functionalized Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Application. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongwei, Junhui Pan, Chengtao Gao, Mengyu Ma, Liangyu Lu, Yuzhu Xiong, and Fuping Dong. 2019. "Mercapto-Functionalized Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Application" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234366
APA StyleLi, H., Pan, J., Gao, C., Ma, M., Lu, L., Xiong, Y., & Dong, F. (2019). Mercapto-Functionalized Porous Organosilica Monoliths Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Application. Molecules, 24(23), 4366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234366






