Direct Synthesis of Phosphonates and α-Amino-phosphonates from 1,3-Benzoxazines
Abstract
1. Introduction
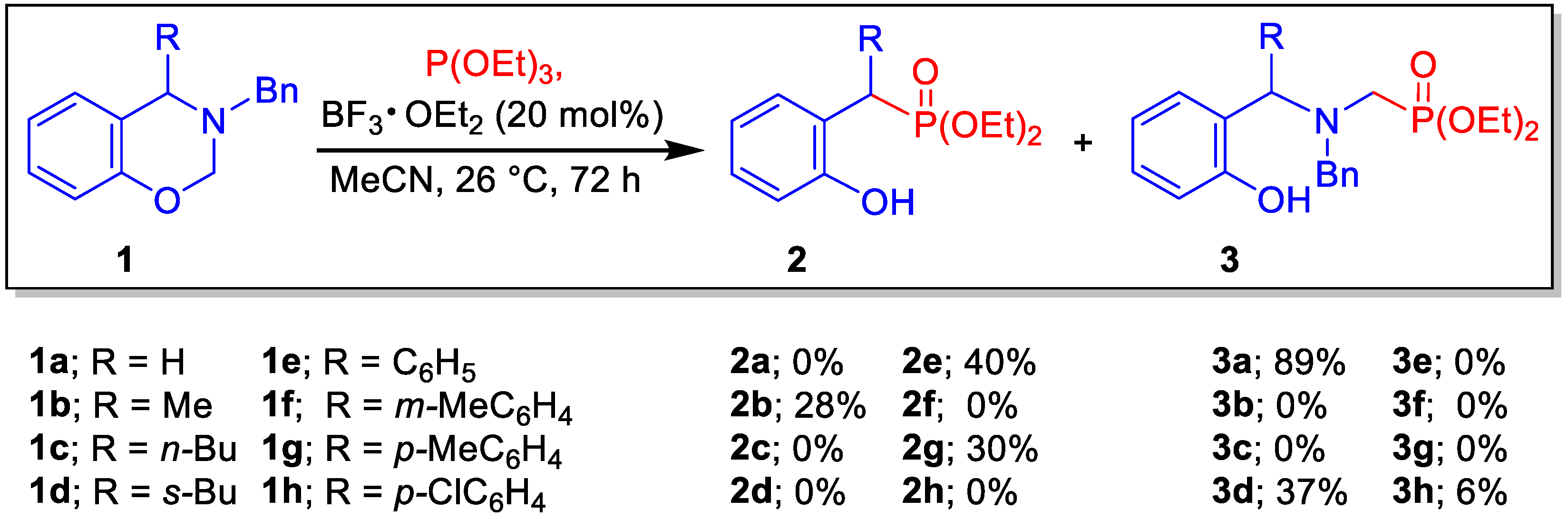
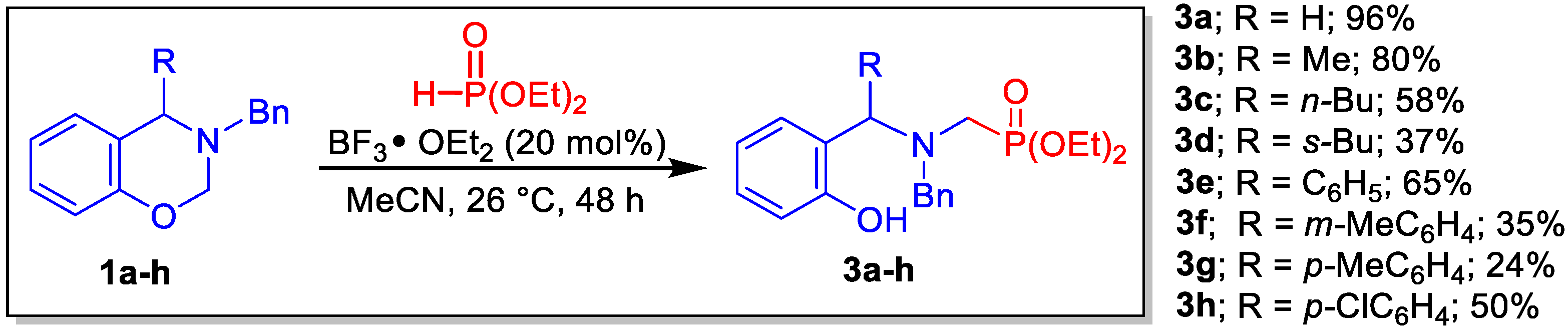
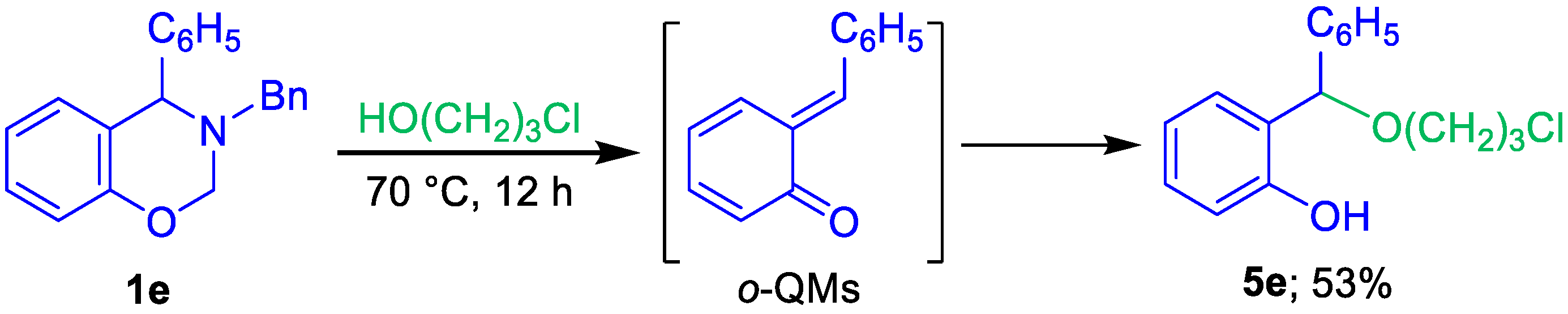
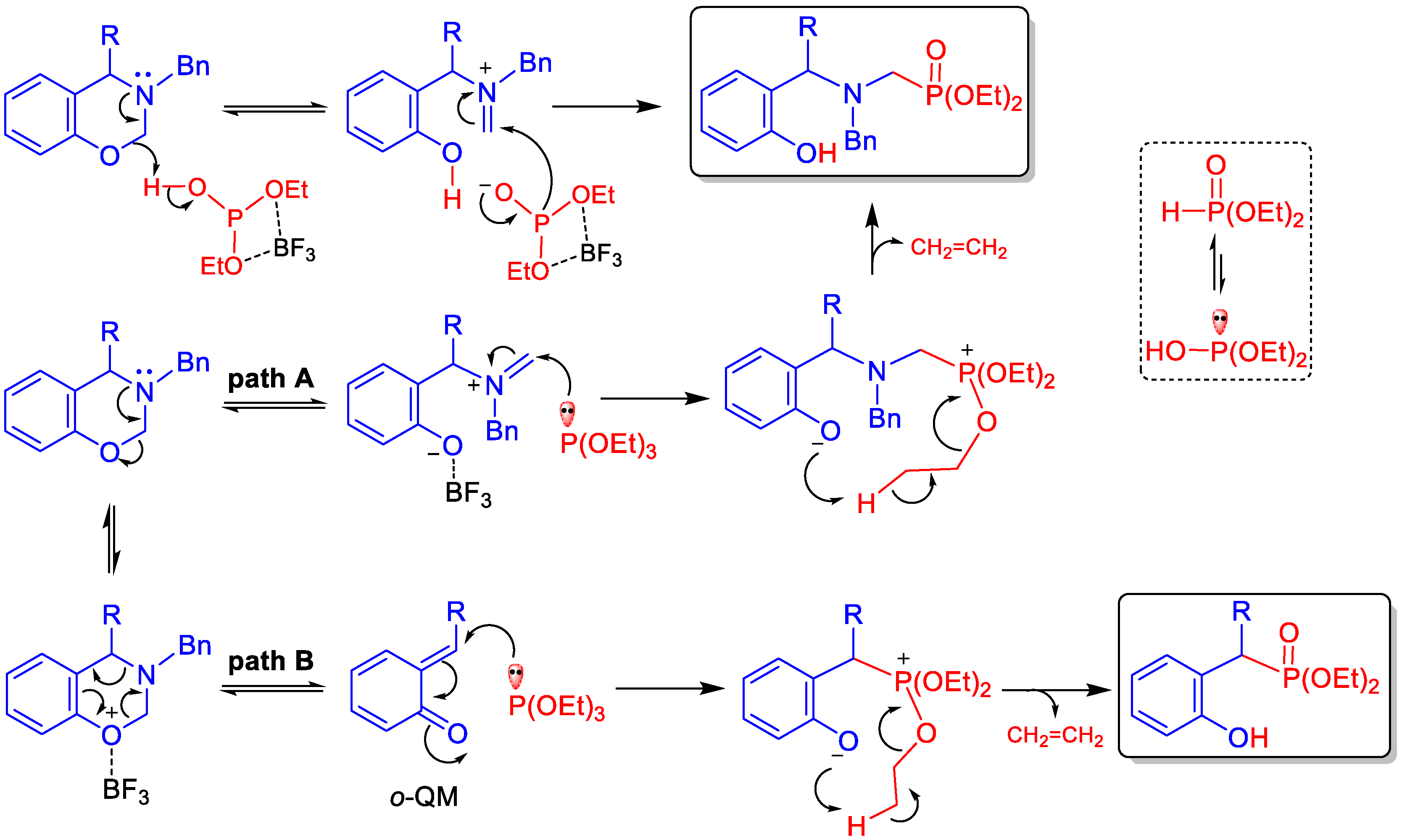
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure to Obtain the 1,3-benzoxazines 1a-h
3.2.1. 3-Benzyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1a)
3.2.2. 3-Benzyl-4-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1b)
3.2.3. 3-Benzyl-4-butyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1c)
3.2.4. 3-Benzyl-4-(s-butyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1d)
3.2.5. 3-Benzyl-4-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1e)
3.2.6. 3-Benzyl-4-(m-tolyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1f)
3.2.7. 3-Benzyl-4-(p-tolyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1g)
3.2.8. 3-Benzyl-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine (1h)
3.3. General Procedure for Preparation of 2-hydroxybenzylphosphonates 2b, 2e, 2g and α-Aminophosphonates 3a, 3d, 3h
3.3.1. Diethyl-[1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]phosphonate (2b)
3.3.2. Diethyl-[(2-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl]phosphonate (2e)
3.3.3. Diethyl-[(2-hydroxyphenyl)(p-tolyl)methyl]phosphonate (2g)
3.3.4. Diethyl{[benzyl(2-hydroxybenzyl)amino]methyl}phosphonate (3a)
3.3.5. Diethyl{benzyl[1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylbutyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3d)
3.3.6. Diethyl((benzyl((4-chlorophenyl)(2-hydroxyphenyl)methyl)amino)methyl)phosphonate (3h)
3.4. General Procedure for Preparation of α-Aminophosphonates 3a–h
3.4.1. Diethyl{[benzyl(2-hydroxybenzyl)amino]methyl}phosphonate (3a)
3.4.2. Diethyl({benzyl[1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3b)
3.4.3. Diethyl({benzyl[1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)pentyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3c)
3.4.4. Diethyl{benzyl[1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylbutyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3d)
3.4.5. Diethyl({benzyl[(2-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3e)
3.4.6. Diethyl({benzyl[(2-hydroxyphenyl)(m-tolyl)methyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3f)
3.4.7. Diethyl({benzyl[(2-hydroxyphenyl)(p-tolyl)methyl]amino}methyl)phosphonate (3g)
3.4.8. Diethyl ((benzyl((4-chlorophenyl)(2-hydroxyphenyl)methyl)amino)methyl)phosphonate (3h)
3.5. 2-[(3-Cchloropropoxy)(phenyl)methyl]phenol (5e)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moonen, K.; Laureyn, I.; Stevens, C.V. Synthetic methods azaheterocyclic phosphonates and their biological activity. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6177–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Niu, J.Q.; Ding, Y.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhong, B.H.; Feng, X.W. Antiviral effects of three novel derivatives of adefovir on the replication of hepatitis B virus. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarski, P.; Lejczak, B. Biological activity of aminophosphonic acids. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Element. 1991, 63, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M. Current status of organophosphorus insecticide and stereochemistry. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Element. 2008, 183, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, C.I.; Hill, S.B.; Hearn, M.; Manton, M.; Everall, N.; Bunn, A.; Heron, J.; Fletcher, I. Mechanism of action of phosphorus based flame retardants in acrylic polymers. Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarski, P.; Lejczak, B. Aminophosphonic acids of potential medical importance. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejczak, B.; Kafarski, P. Biological activity of aminophosphonic acids and their short peptides. Top. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009, 20, 3–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, E.D.; Todorov, P.T.; Troev, K.D. Recent synthesis of aminophosphonic acids as potential biological importance. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, F.; Sello, G.; Sisti, M. Aminophosphonic acids and derivatives. Synthesis and biological applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 264–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszner, N.; Zeuner, F.; Fisher, U.K.; Rheinberger, V. Monomers for adhesive polymers, 2. Synthesis and radical polymerisation of hydrolytically stable acrylic phosphonic acids. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabasso, I.; Smid, J.; Sahni, S.K. Radiopaque polymers based on acrylated phosphonate esters derived from polyols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1990, 41, 3025–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salasi, M.; Sharabi, T.; Roayaei, E.; Aliofkhazraei, M. The electrochemical behavior of environment-friendly inhibitors of silicate and phosphonate in corrosion control of carbon steel in soft water media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 104, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavipriya, K.; Rajendran, S.; Sathiyabama, J.; Prabha, A.S. A critical review of corrosion inhibition by phosphonic acids. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2012, 1, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, T.P. Synthetic chelating agents and compounds exhibiting complexing properties in aquatic environment. Trends Analytic. Chem. 2003, 22, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadell, J.; Hunt, B.J.; CooK, A.G.; Mantecon, A.; Cadiz, V. Flame retardance and shrinkage reduction of polystyrene modified with acrylate-containing phosphorus and crosslinkable spiro-orthoester moieties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Jain, A.K. Ignition, combustion, toxicity, and fire retardancy of polyurethane foams: A comprehensive review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1115–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X. Synthesis, characterization, and curing properties of novel phosphorus-containing naphthyl epoxy systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Taboada, L.; Guzmann, M.; Neubecker, K.; Goethlich, A. Process and Polymer for Preventing Ba/Sr Scale with a Detectable Phosphorus Funtionality. U.S. Patent US 12/520,642, 8 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Demmer, Ch.S.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, N.; Bunch, L. Review on modern advances of chemical methods for the introduction of a phosphonic acid group. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7981–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, M.; Rojas-Cabrera, H.; Cativiela, C. An overview of stereoselective synthesis of α-aminophosphonic acids and derivates. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 17–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Su, Ch.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Han, L.B. Alcohol-based Michaelis-Arbuzov reaction: An efficient and environmentally-benign method for C-P(O) bond formation. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3408–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharova, E.V.; Artyushin, O.I.; Odinets, I.L. Synthetic routes to carbamoylmethylphosphoryl compounds-extractants for the processing of spent nuclear fuels. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Queneau, Y.; Popowycz, F. The synthesis of HMF-based α-amino phosphonates via one-pot Kabachnik—Fields reaction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31496–31501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, E.K. The Synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cytlak, T.; Skibinska, M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Kazmierczak, M.; Rapp, M.; Kubickia, M.; Koroniak, H. Functionalization of α-hydroxyphosphonates as a convenient route to N-tosyl-α-aminophosphonates. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11957–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, A.; Anna Ádám, A.; Csontos, I.; Karaghioso, K.; Czugle, M.; Ábrányi-Balogh, P.; Keglevich, G. The synthesis of α-aryl-α-aminophosphonates and α-aryl-α-aminophosphine oxides by the microwave-assisted Pudovik reaction. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, M.; Viveros-Ceballos, J.L.; Romero-Estudillo, I. Stereoselective Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonic Acids through Pudovik and Kabachnik-Fields Reaction. In Amino Acid-New Insights and Roles in Plant and Animal, 1st ed.; Asao, T., Asaduzzaman, M., Eds.; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Chapter 6; pp. 127–151. ISBN 978-953-51-3242-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.; Hu, J. Straightforward synthesis of bifunctional phosphorus phenols via phosphination of in situ generated o-quinine methides. Molecules 2018, 23, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Kang, J.Y. Organocatalytic phosphonylation of in situ formed o-quinone methides. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5988–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Prieto, J.; Galian, R.E.; Miranda, M.A.; Catalina, F.; Martín-Vargas, N.; López-Ortiz, F. Benzo[d]-1,2-oxaphospholes as precursors of stabilized C-centered radicals. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Prieto, J.; Galian, R.E.; Oña-Burgos, P.; Morant-Miñana, M.C.; Miranda, M.A.; López-Ortiz, F. Influence of substitution at the benzylic position on the behavior of stereoisomeric phosphorus compounds as precursors of stabilized carbon-centered radicals. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3869–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, R.M.N.; Lee, H.R.; Cao, J.; Yoo, J.W.; Kim, I. Phospho sulfonic acid: An efficient and reciclable solid acid catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates and their anticancer properties. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3916–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Escobar, O.; Chavelas-Hernández, L.; Domínguez-Mendoza, B.E.; Linzaga-Elizalde, I.; Ordoñez, M. Synthesis of chiral 1,4,2-oxazaphosphepines. Molecules 2015, 20, 13794–13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, G.; Cimarelli, C.; Volpini, E. Ready N-alkylation of enantiopure aminophenols: Synthesis of tertiary aminophenols. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6089–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, G. Synthesis of enantiopure o-hidroxybenzylamines by stereoselective reduction of 2-imidoylphenols: Application in the catalytic enantioselective addition of diethylzinc to aldehydes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, R.; Ronda, J.C. Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazines by Condensation of 2-Hydroxyaldehydes and Primary Amines: Application to the Synthesis of Hydroxy-Substituted and Deuterium-Labeled Compounds. Synth. Commun. 2008, 38, 2316–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliouane, N.; Helesbeux, J.-J.; Douadi, T.; Khan, M.A.; Bouet, G.; Chafaa, S.; Duval, O. Synthesis of new benzylic di-, tri-, and tetraphosphonic acids as potential chelating agents. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2011, 186, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibadullina, E.M.; Shaekhov, T.R.; Voronina, Y.K.; Pudovik, M.A.; Burilov, A.R. Reactions of [(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl]phosphonates with Phenols. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 54, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengwei, L.; Zhaobin, W.; Jianwei, S. Organocatalytic asymmetric nucleophilic addition to o-quinone methides by alcohols. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 6058–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, B.; Gandelman, K.; Sachse, R.; Wood, N.; Michel, M.C. The design and development of fesoterodine as a prodrug of 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine (5-HMT), the active metabolite of tolterodine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4481–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.A.; Yonova, I.M.; Williams, F.J.; Jarvo, E.R. Traceless directing group for stereospecific nickel-catalyzed alkyl-alkyl cross-coupling reactions. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4293–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, A.W.; Sudo, A.; Endo, T. Polymerization-depolymerization system sased on reversible addition-dissociation reaction of 1,3-benzoxazines with thiol. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metlushka, K.E.; Kashemirov, B.A.; Zheltukhin, V.F.; Sadkova, D.N.; Buchner, B.; Hess, C.; Kataeva, O.N.; McKenna, C.E.; Alfonsov, V.A. 1-(α-Aminobenzyl)-2-naphthol: A new chiral auxiliary for the synthesis of enantiopure α-aminophosphonic acids. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6718–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
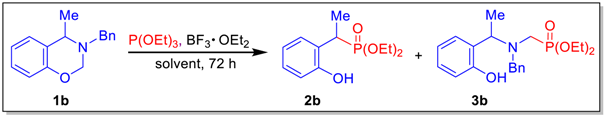
| Entry | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | P(OEt)3 (Eq) | BF3 OEt2 (mol%) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EtOH | 78 | 1.0 | - | 3b; 28 |
| 2 | DCM | 26 | 1.0 | 20 | 3b; 27 |
| 3 | DCM | 40 | 1.5 | - | 3b; 28 |
| 4 | MeCN | 26 | 1.0 | - | No product |
| 5 | MeCN | 82 | 1.0 | - | No product |
| 6 | MeCN | 26 | 2.0 | 10 | 2b; 18 |
| 7 | MeCN | 26 | 2.1 | 20 | 2b; 28 |
| 8 | MeCN | 26 | 2.2 | 50 | 2b; 28 |
| 9 | MeCN | 26 | 2.7 | 50 | 2b; 28 |
| 10 | MeCN | 82 | 3.0 | 20 | 2b; 30, 3b; 47 |
| 11 | MeCN | 82 | 3.5 | 20 | 2b; 28, 3b; 47 |
| 12 | Hexane | 26 | 3.6 | 20 | No product |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salgado-Escobar, O.; Hernández-Guadarrama, A.; Romero-Estudillo, I.; Linzaga-Elizalde, I. Direct Synthesis of Phosphonates and α-Amino-phosphonates from 1,3-Benzoxazines. Molecules 2019, 24, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020294
Salgado-Escobar O, Hernández-Guadarrama A, Romero-Estudillo I, Linzaga-Elizalde I. Direct Synthesis of Phosphonates and α-Amino-phosphonates from 1,3-Benzoxazines. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020294
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalgado-Escobar, Oscar, Alexis Hernández-Guadarrama, Ivan Romero-Estudillo, and Irma Linzaga-Elizalde. 2019. "Direct Synthesis of Phosphonates and α-Amino-phosphonates from 1,3-Benzoxazines" Molecules 24, no. 2: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020294
APA StyleSalgado-Escobar, O., Hernández-Guadarrama, A., Romero-Estudillo, I., & Linzaga-Elizalde, I. (2019). Direct Synthesis of Phosphonates and α-Amino-phosphonates from 1,3-Benzoxazines. Molecules, 24(2), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020294





