Cajanolactone A from Cajanus cajan Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Stimulating Wnt/LRP5/β-Catenin Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cajanolactone A did not Stimulate the Proliferation of hBMSCs
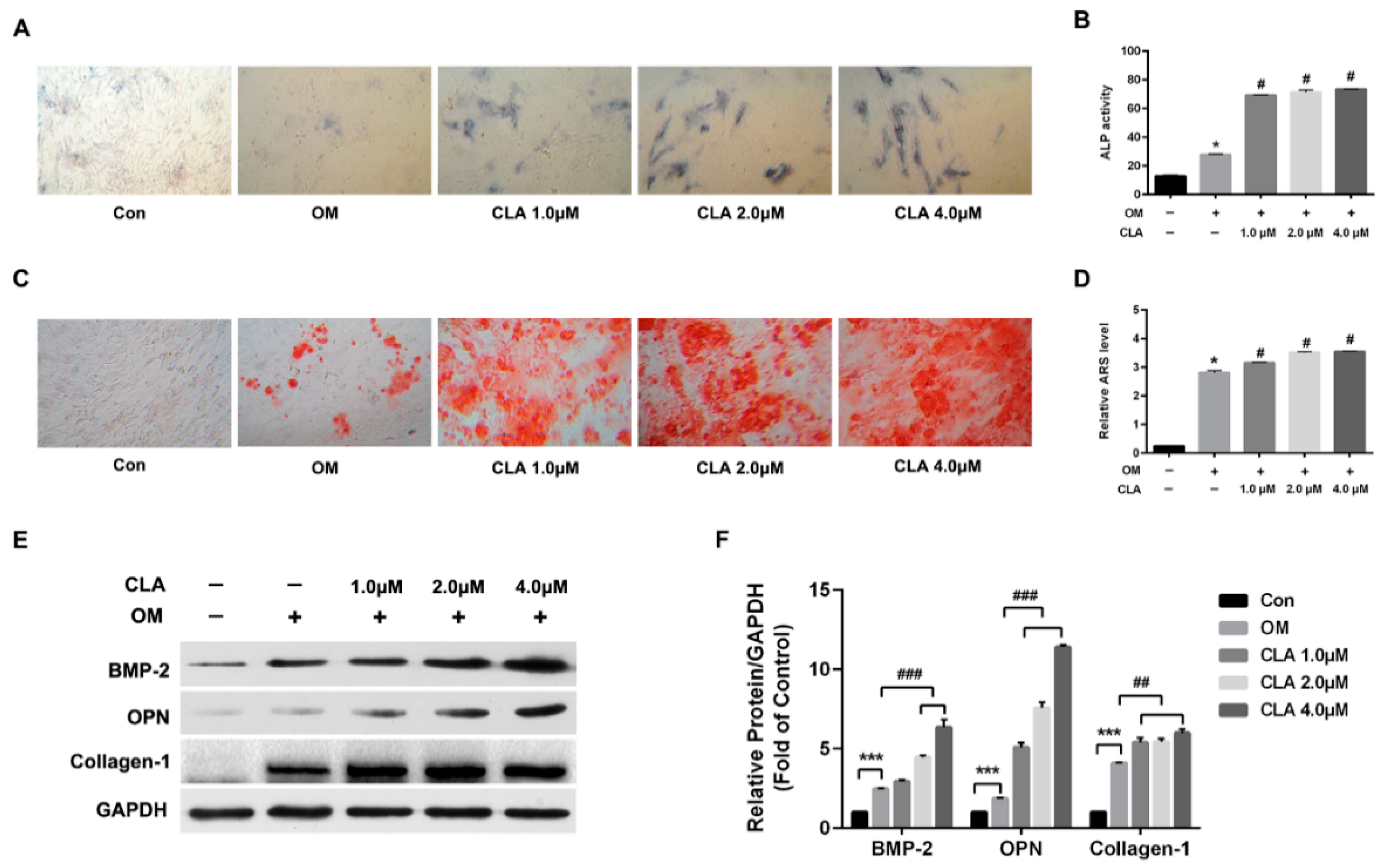
2.2. CLA Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in hBMSCs
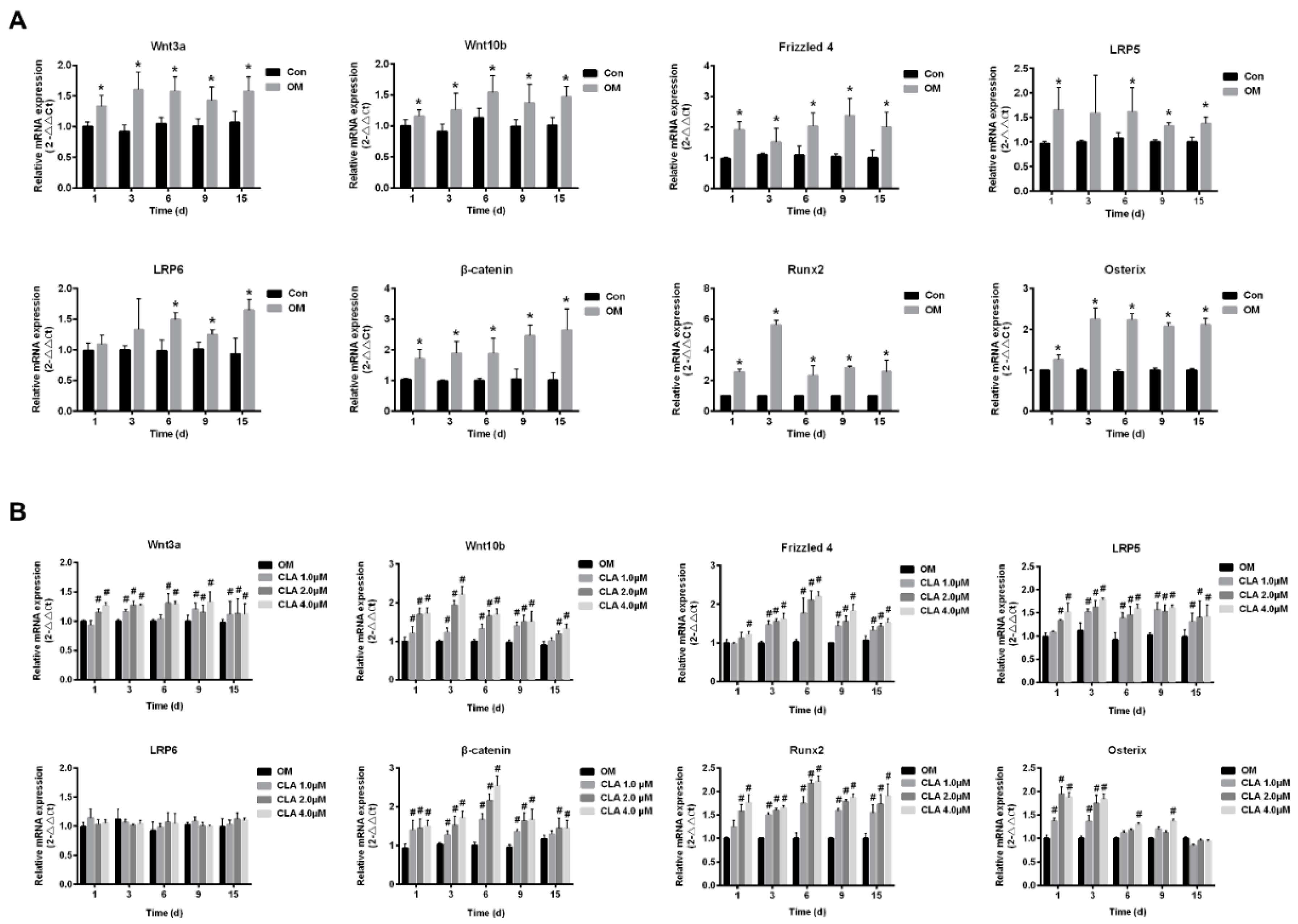
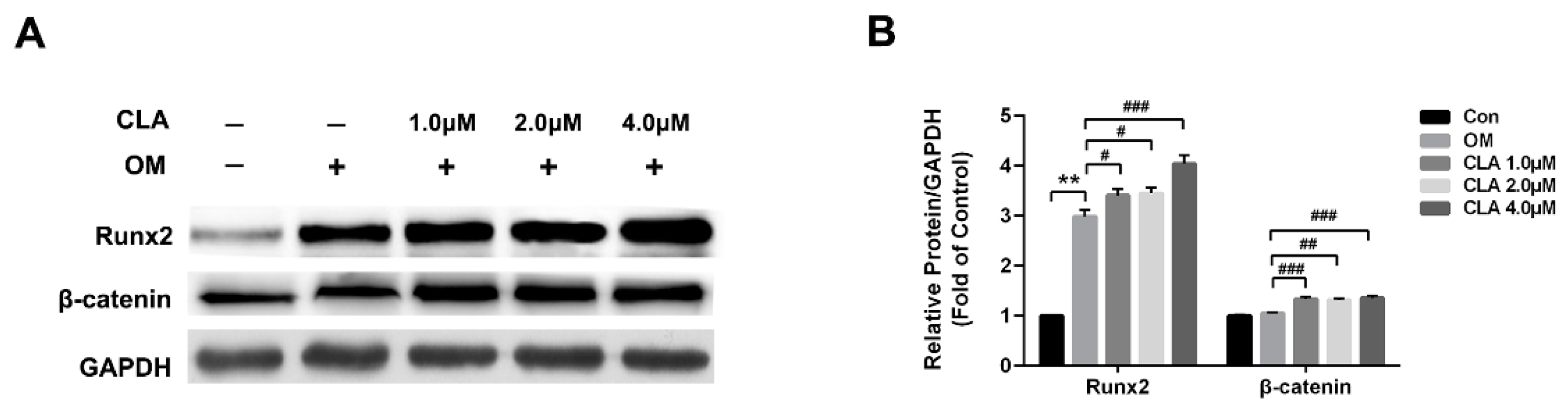
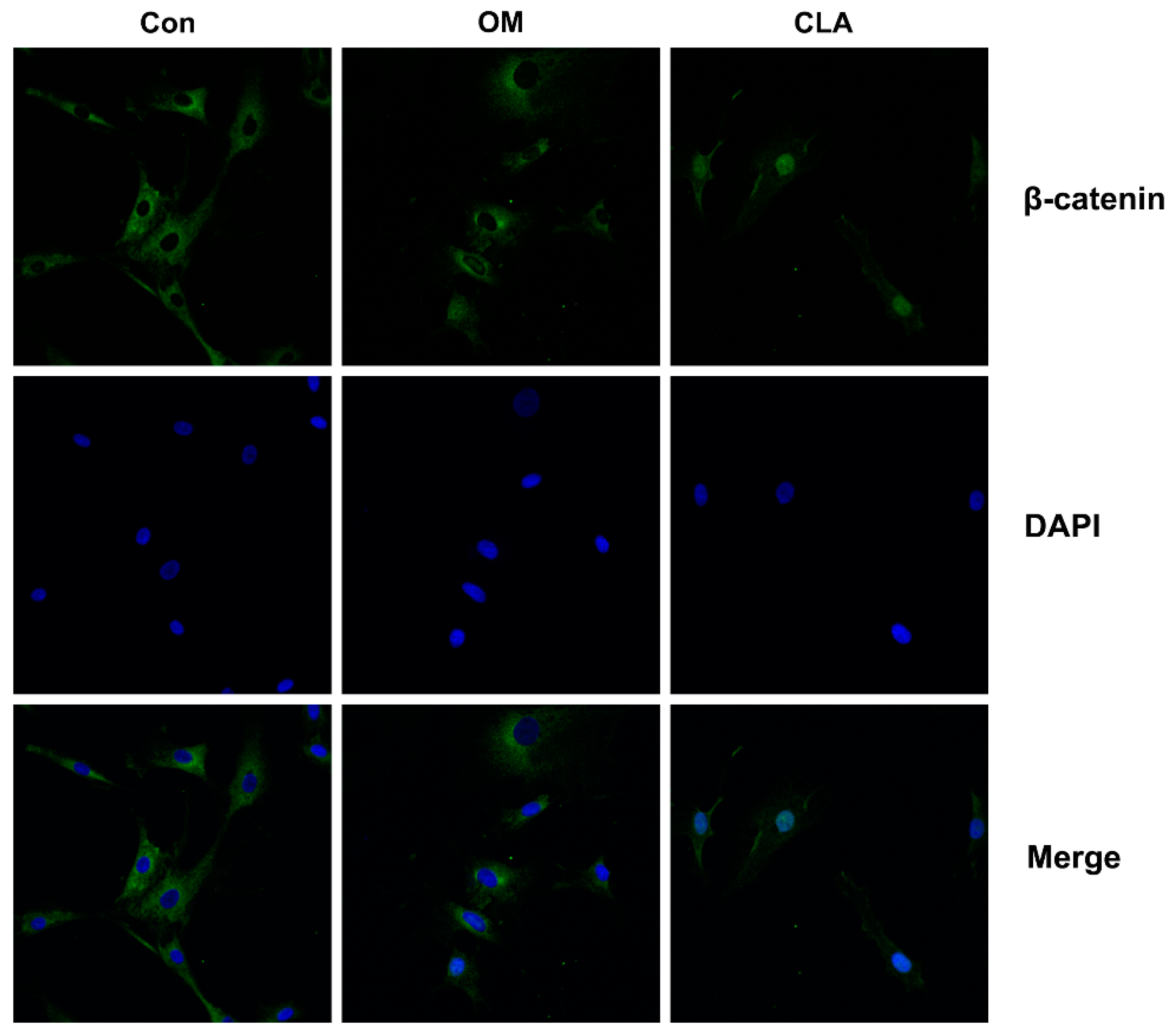
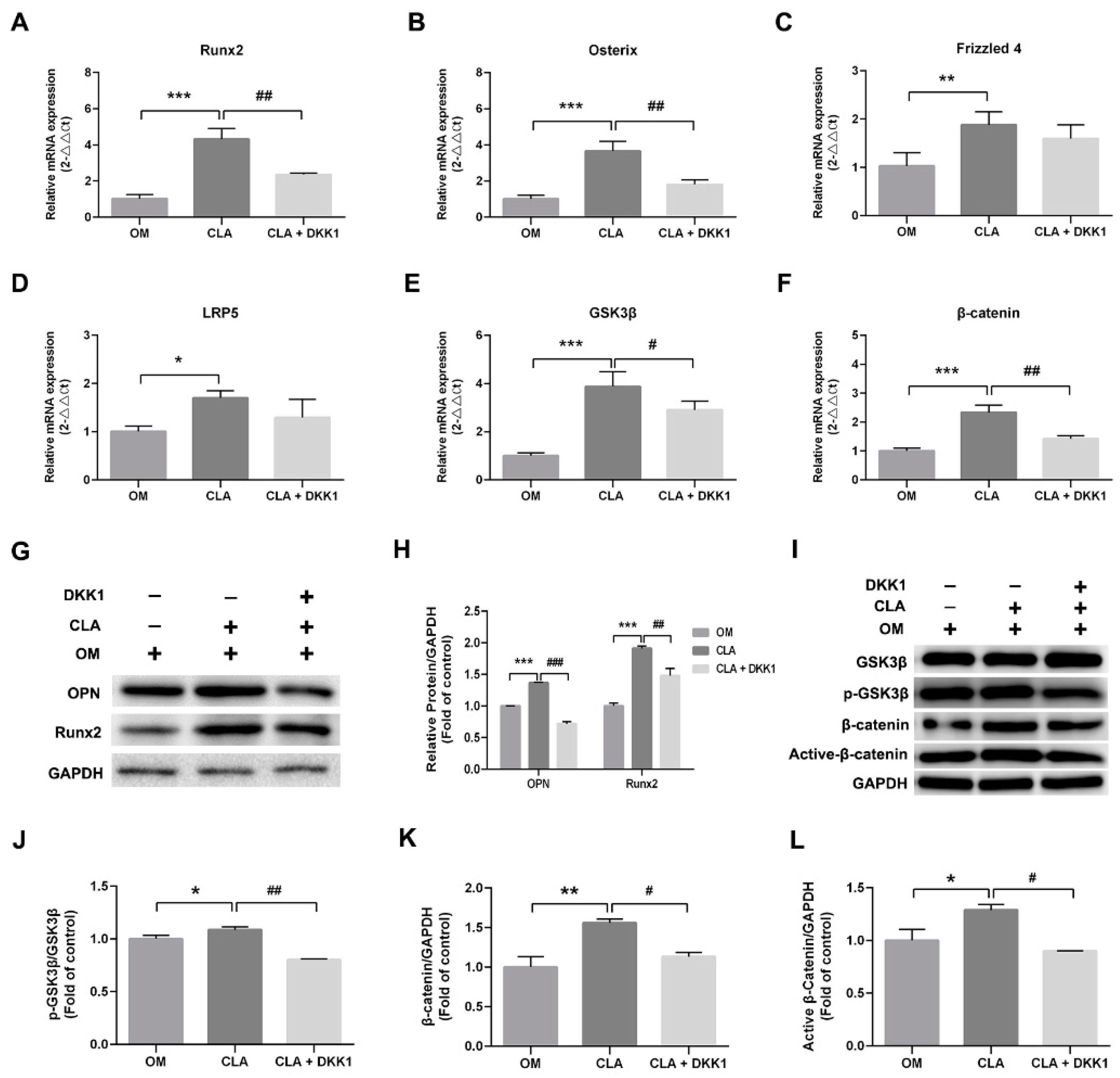
2.3. CLA Promoted the Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in hBMSCs
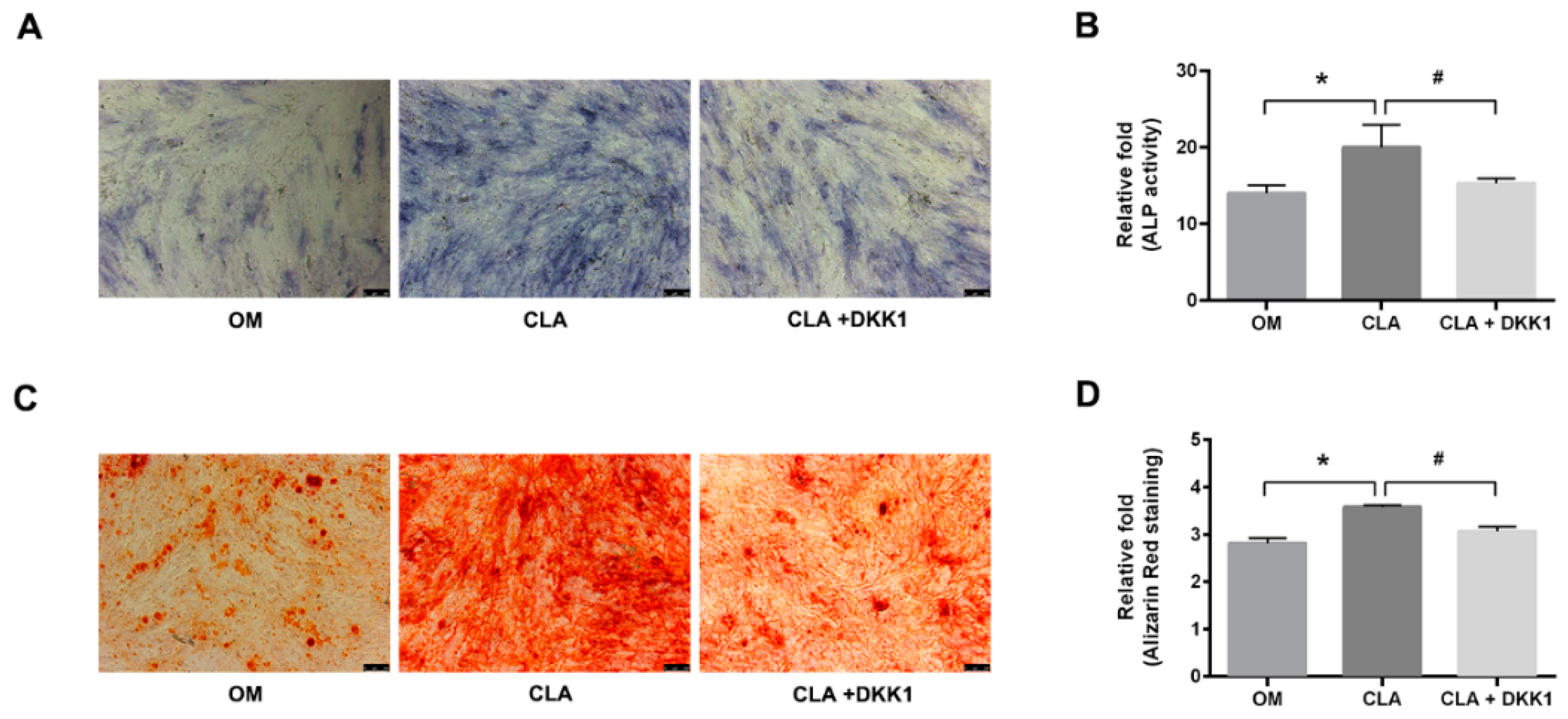
2.4. CLA did not Target the Downstream of Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway
2.5. CLA-Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation Did Not Affect the OPG/RANKL Axis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
3.2. Isolation and Structure Identification of CLA
3.3. Cell Line and Cell Culture
3.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.5. Induction for Osteoblast Differentiation
3.6. Detection of Osteoblast
3.7. Quantitative Analysis of Cellular ALP Activity
3.8. Quantitative Analysis of Extracellular Calcium Deposits
3.9. Quantitative Analysis of Secreted OPG and RANKL
3.10. RT-qPCR Analysis
3.11. Western Blot Analysis
3.12. Immunofluorescent Detection of β-Catenin
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, T.P.; Später, D.; Taketo, M.M.; Birchmeier, W.; Hartmann, C. Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Dev. Cell. 2005, 8, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, J.; von Kries, J.P.; Kühl, M.; Bruhn, L.; Wedlich, D.; Grosschedl, R.; Birchmeier, W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 1996, 382, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.; Dedhar, S. Signalling through beta-catenin and Lef/Tcf. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 1999, 56, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattner, A.; Hsieh, J.C.; Smallwood, P.M.; Gilbert, D.J.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Nathans, J. A family of secreted proteins contains homology to the cysteine-rich ligand-binding domain of frizzled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2859–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinka, A.; Wu, W.; Delius, H.; Monaghan, A.P.; Blumenstock, C.; Niehrs, C. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 1998, 391, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semënov, M.; Tamai, K.; He, X. SOST is a ligand for LRP5/LRP6 and a Wnt signaling inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26770–26775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Huang, Y.; Bajis, R.; Sahih, M.; Li, Y.P.; Dai, K.; Zhang, X. Osteoblastogenesis regulation signals in bone remodeling. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duker-Eshun, G.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Asomaning, W.A.; Oppong-Boachie, F.; Brøgger Christensen, S. Antiplasmodial constituents of Cajanus cajan. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.F.; Sun, L.; Si, J.Y.; Chen, D.H. Hypocholesterolemic effect of stilbenes containing extract-fraction from Cajanus cajan L. on diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeharsha, R.V.; Mudalkar, S.; Sengupta, D.; Unnikrishnan, D.K.; Reddy, A.R. Mitigation of drought-induced oxidative damage by enhanced carbon assimilation and an efficient antioxidative metabolism under high CO2 environment in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 188, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, X.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Efferth, T. Cajanol, a novel anticancer agent from Pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] roots, induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, P. Effects of water extract of Cajanus cajan leaves on the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of mouse primary bone marrow stromal cells and the adipocytic trans-differentiation of mouse primary osteoblasts. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.F.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.Y.; Tian, R.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Shen, X.L. Effects of hydrophobic fraction of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. on bone density and blood lipid level in obese and diabetic mice. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2012, 29, 961–965. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.X.; Shen, X.L. A natural stilbenoidal medicine with hypoglycemic and anti-obese effects. Chin. Patent 2008101990126, 9 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.Z.; Tang, R.; Ye, G.F.; Qiu, S.X.; Zhang, N.L.; Hu, Y.J.; Shen, X.L. A halogen-containing stilbene derivative from the leaves of Cajanus cajan that induces osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 10839–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Qiu, S.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Shen, X.L. Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus via reversing insulin resistance and regulating lipid homeostasis in vitro and in vivo using cajanonic acid A. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2329–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, J.L.; Li, Z.; Ellis, J.M.; Zhang, Q.; Farber, C.R.; Aja, S.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Clemens, T.L.; Riddle, R.C. Wnt-Lrp5 signaling regulates fatty acid metabolism in the osteoblast. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.X.; Zheng, G.Z.; Chang, B.; Chen, R.C.; Zhang, Q.H.; Xie, P.; Xie, D.; Yu, G.Y.; Hu, Q.X.; Liu, D.Z.; et al. Connexin 43 modulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through GSK-3beta/Beta-Catenin signaling pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 247, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, C.; Piemontese, M.; Lumetti, S.; Manfredi, E.; Macaluso, G.M.; Passeri, G. GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guan, X.; Guo, F.; Zhou, J.; Chang, A.; Sun, B.; Cai, Y.; Ma, Z.; Dai, C.; Li, X.; Wang, B. miR-30e reciprocally regulates the differentiation of adipocytes and osteoblasts by directly targeting low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zhuang, H.T.; Xin, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.L. MiR-214 inhibits human mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into osteoblasts through targeting β-catenin. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4777–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Schoppet, M. Clinical implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases. JAMA 2004, 292, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
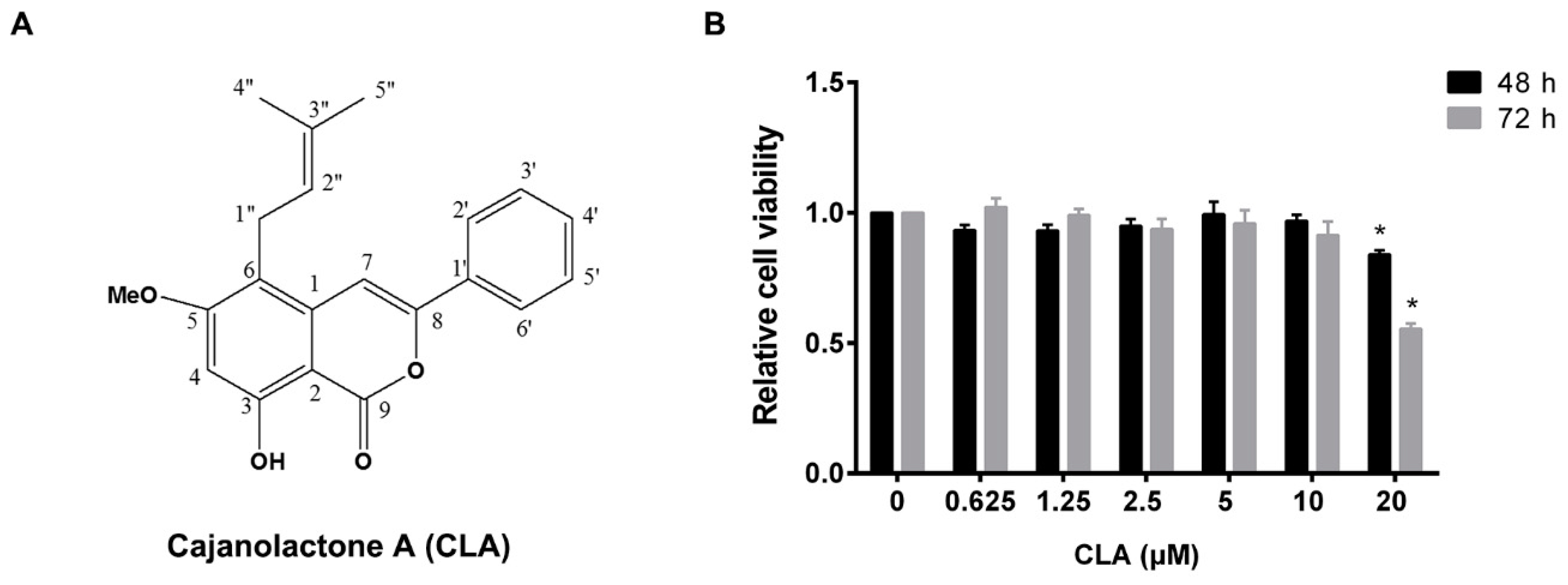


| Position | δH 1 (J in Hz) | δC 2, Type | HMBC Correlations 3 (H to C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 136.0, C | 1″ | |
| 2 | 99.6, C | 4, 7, OH | |
| 3 | 162.4, C | 4 | |
| 4 | 6.52 s | 98.2, CH | |
| 5 | 164.3, C | 4, 1″, OMe | |
| 6 | 116.0, C | 4, 7, 1″ | |
| 7 | 7.04 s | 100.0, CH | |
| 8 | 152.0, C | 7, 2′, 6′ | |
| 9 | 166.3, C | ||
| 2′, 6′ | 7.82 d (8.0) | 125.2, CH | 2′, 3′, 4′, 5′, 6′ |
| 3′, 5′ | 7.44 m | 128.8, CH | 4′ |
| 4′ | 7.44 m | 129.9, CH | 2′, 3′, 5′, 6′ |
| 1″ | 3.45 br d (4.0) | 23.6, CH2 | 2″ |
| 2″ | 5.05 br s | 122.6, CH | 4″, 5″ |
| 3″ | 131.9, C | 1″, 4″, 5″ | |
| 4″ | 1.68 s | 25.7, CH3 | 2″, 5″ |
| 5″ | 1.84 s | 17.9, CH3 | 2″, 4″ |
| 5-OMe | 3.89 s | 55.9, CH3 | |
| 3-OH | 11.28 s |
| Genes | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| Wnt3a | TGGTGTCTCGGGAGTTCGC | CCGTGGCACTTGCACTTGA |
| Wnt10b | CTCCTGTTCCTGGCGTTGTG | GCAACTTCAGGCCCAGAATC |
| LRP5 | GCAGGTCTTCATGTCACTCAGCAG | TCAAAGCTGTGAATGTGGCCAAGG |
| LRP6 | GCAGCCTGTGGGACTTACTGTGTT | TGAGCACAAGGGTGCTGTCTGTAT |
| GSK3β | GGCAGCATGAAAGTTAGCAGA | GGCGACCAGTTCTCCTGAATC |
| Runx2 | GTTCAACGATCTGAGATTTG | GGGGTCTGTAATCTGACTCT |
| Osterix | ACCCAACATCAAGCAGAACCAC | TCTTCAACTTCCCAGGCTCACT |
| β-catenin | AGCTTCCAGACACGCTATCAT | CGGTACAACGAGCTGTTTCTAC |
| Frizzled 4 | AAGGATGGGACAAAGACAGACAA | ACATGCCTGAAGTGATGCCCA |
| RANKL | GGAAAGAAAGTGGGAGCAGA | ATTAGGCCCTTCAAGGTGTC |
| OPG | TCTGGTTCCCATAAAGTGAGTC | CGAAAGCAAATGTTGGCATA |
| GAPDH | TCAACGACCACTTTGTCAAGC | TGTGGGCCATGAGGTCCACCA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Luo, Z.-H.; Ji, G.-M.; Guo, W.; Cai, J.-Z.; Fu, L.-C.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Y.-J.; Shen, X.-L. Cajanolactone A from Cajanus cajan Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Stimulating Wnt/LRP5/β-Catenin Signaling. Molecules 2019, 24, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020271
Liu S, Luo Z-H, Ji G-M, Guo W, Cai J-Z, Fu L-C, Zhou J, Hu Y-J, Shen X-L. Cajanolactone A from Cajanus cajan Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Stimulating Wnt/LRP5/β-Catenin Signaling. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shan, Zhuo-Hui Luo, Gui-Mei Ji, Wei Guo, Jia-Zhong Cai, Lin-Chun Fu, Juan Zhou, Ying-Jie Hu, and Xiao-Ling Shen. 2019. "Cajanolactone A from Cajanus cajan Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Stimulating Wnt/LRP5/β-Catenin Signaling" Molecules 24, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020271
APA StyleLiu, S., Luo, Z.-H., Ji, G.-M., Guo, W., Cai, J.-Z., Fu, L.-C., Zhou, J., Hu, Y.-J., & Shen, X.-L. (2019). Cajanolactone A from Cajanus cajan Promoted Osteoblast Differentiation in Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Stimulating Wnt/LRP5/β-Catenin Signaling. Molecules, 24(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020271





