A Novel Synthetic Steroid of 2β,3α,5α-Trihydroxy-androst-6-one Alleviates the Loss of Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells Caused by Acute Intraocular Hypertension via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
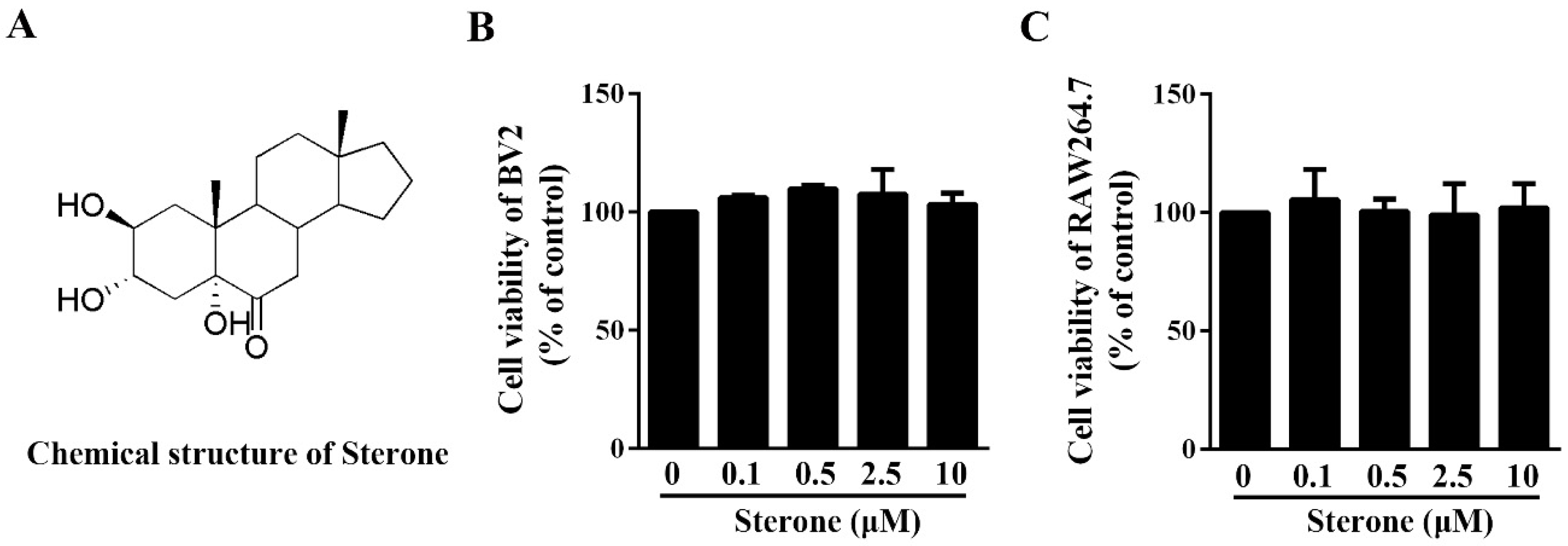
2.1. Sterone Has No Effect on the Viability of BV2 Cells and RAW264.7 Cells
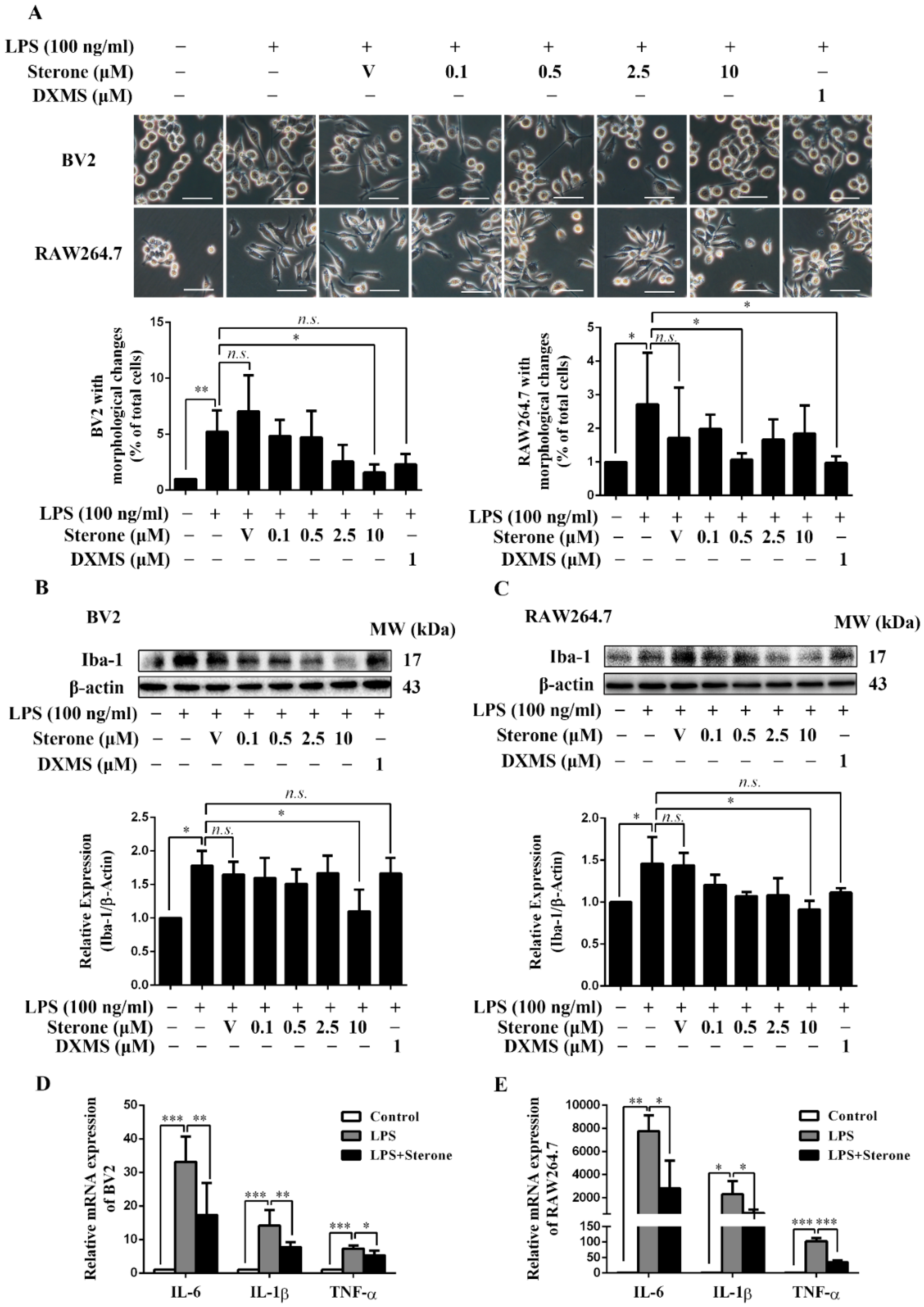
2.2. Sterone Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Activation of BV2 and RAW264.7 Cells.
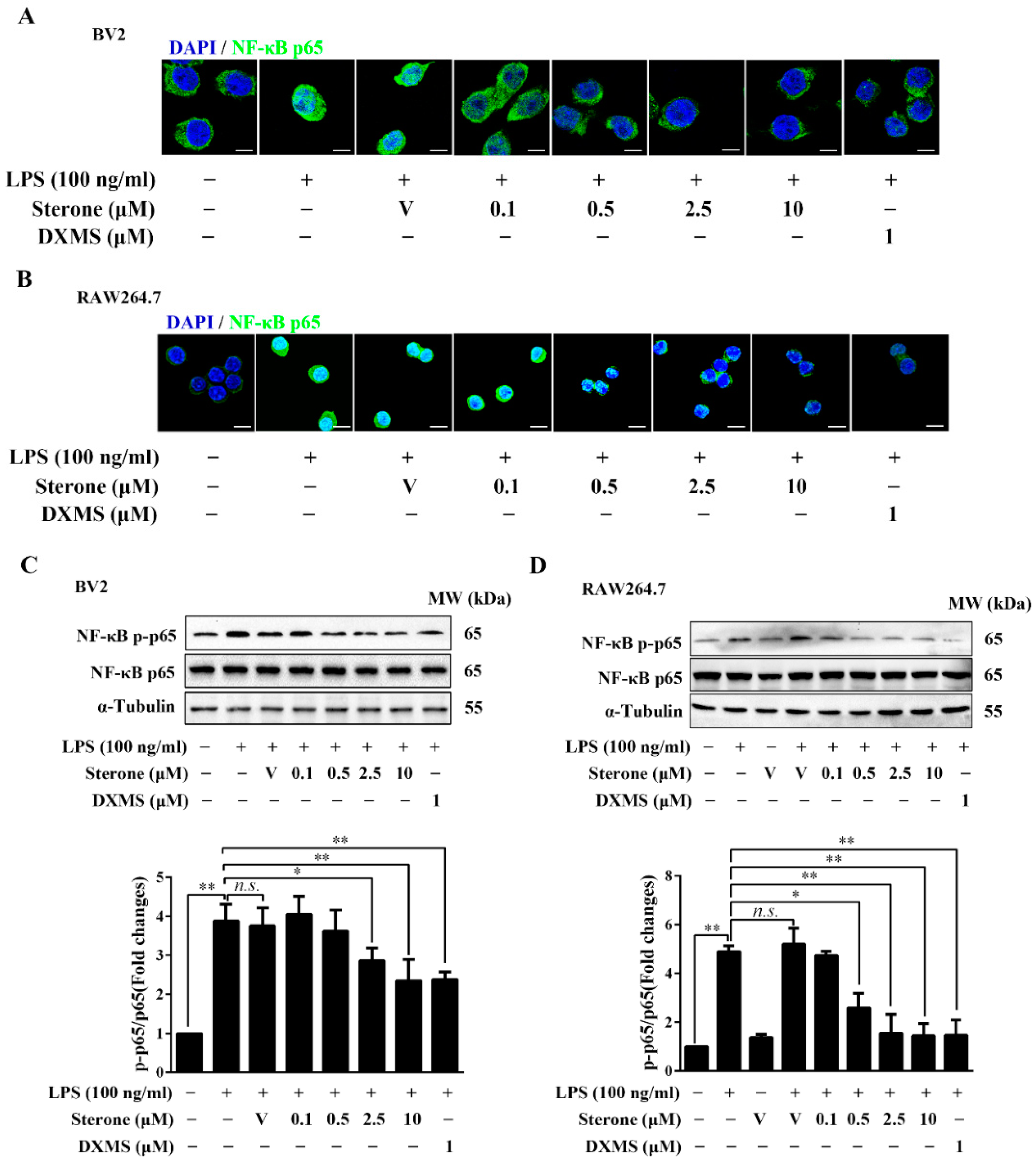
2.3. Sterone Inhibits LPS-Induced NF-κB Activation in BV2 and RAW264.7 Cells.
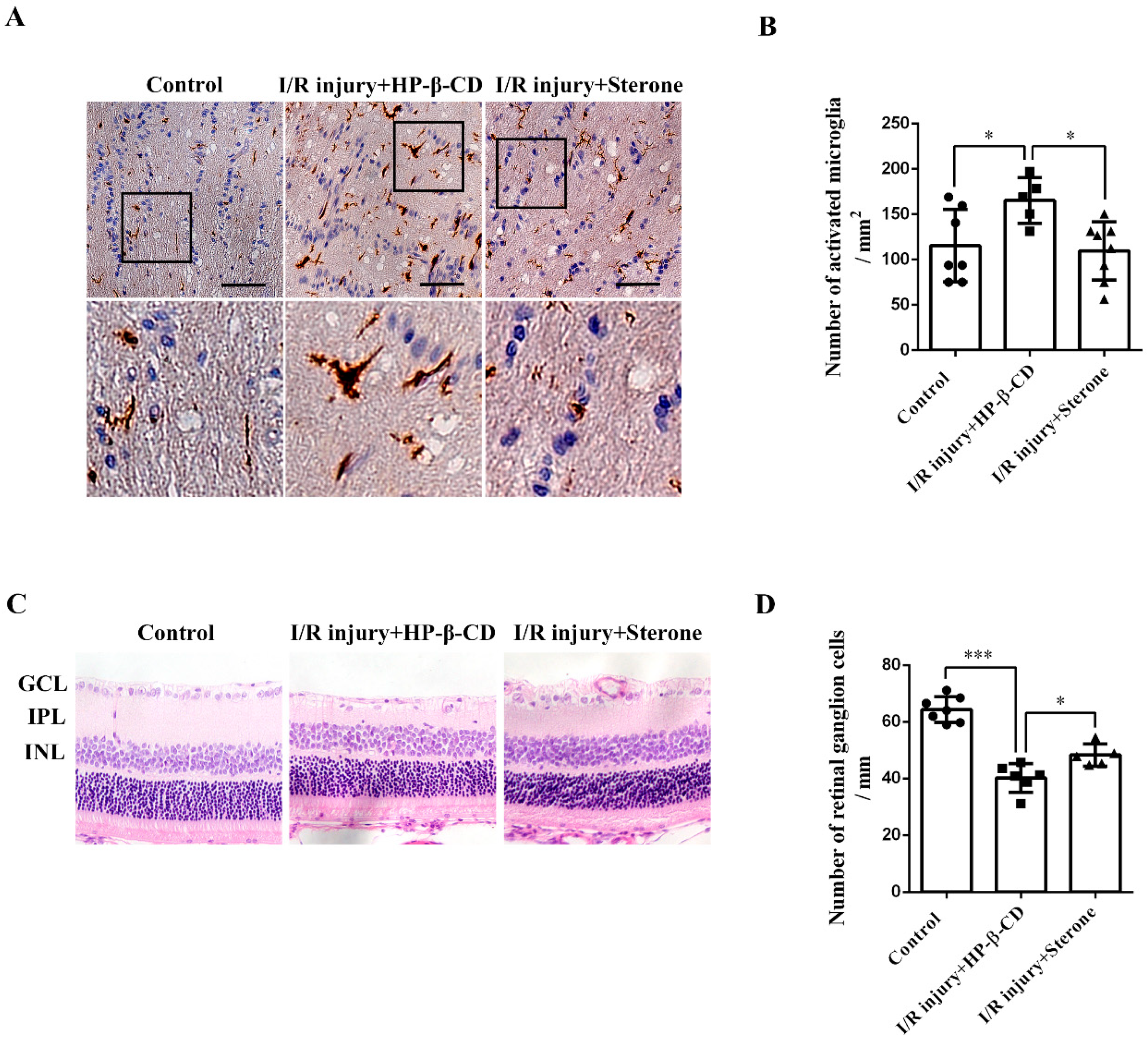
2.4. Sterone Inhibits Microglial Activation and Retinal RGCs Loss Induced via Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in a Rat AIH Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Cell Viability Analysis
4.3. Western Blotting Analysis
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.6. Retinal Ischemia/Reperfusion of AIH and Treatment
4.7. Immunohistochemistry Analysis and Hematoxylin Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almasieh, M.; Wilson, A.M.; Morquette, B.; Cueva Vargas, J.L.; Di Polo, A. The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma. Progr. Retinal Eye Res. 2012, 31, 152–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schehlein, E.M.; Novack, G.D.; Robin, A.L. New classes of glaucoma medications. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijl, A.; Leske, M.C.; Bengtsson, B.; Hyman, L.; Bengtsson, B.; Hussein, M. Reduction of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression: Results from the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leske, M.C.; Heijl, A.; Hyman, L.; Bengtsson, B.; Komaroff, E. Factors for progression and glaucoma treatment: The Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2004, 15, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, R.; Tsai, J.C.; Kolko, M. The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. Survey Ophthalmol. 2013, 58, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.A.; Marsh-Armstrong, N.; Howell, G.R. Neuroinflammation in glaucoma: A new opportunity. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 157, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Su, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhuo, Y. Trimetazidine protects retinal ganglion cells from acute glaucoma via the Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhuo, Y. Rapamycin is neuroprotective in a rat chronic hypertensive glaucoma model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, I.; Howell, G.R. The complex role of neuroinflammation in glaucoma. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.W. Functions and Mechanisms of Microglia/Macrophages in Neuroinflammation and Neurogenesis during Stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 142, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Zhu, L.; Jing, X.; Zeng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xu, A.; Liu, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, L.; Shi, Q.; et al. Rifampicin improves neuronal apoptosis in LPS-stimulated cocultured BV2 cells through inhibition of the TLR-4 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, J.; Iserovich, P. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in glaucomatous aqueous and encysted Molteno implant blebs and their relationship to pressure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2013, 54, 4851–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, J.D.; Chan, C.C.; Derevjanik, N.L.; Mahlow, J.; Chiu, C.; Peng, B.; Tobe, T.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Vinores, S.A. Blood-retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis: Comparison with vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-1beta-mediated breakdown. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 49, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Salazar, J.J.; Rojas, B.; Ajoy, D.; Lopez-Cuenca, I.; Rojas, P.; Trivino, A.; Ramirez, J.M. The Role of Microglia in Retinal Neurodegeneration: Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson, and Glaucoma. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nakazawa, C.; Matsubara, A.; Noda, K.; Hisatomi, T.; She, H.; Michaud, N.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Miller, J.W.; Benowitz, L.I. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates oligodendrocyte death and delayed retinal ganglion cell loss in a mouse model of glaucoma. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12633–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minchevatasheva, S.; Soler, R.M. NF-κB signaling pathways: Role in nervous system physiology and pathology. Neurosci. Rev. J. Bringing Neurobiol. Neurol. Psychiatry 2013, 19, 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Neurological Inflammation: A Mini Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Tang, E.; Guan, K.; Wang, C.Y. IKK beta plays an essential role in the phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 536 induced by lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5630–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Hu, W.; Wu, F.; Jiang, B.; Ling, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, W. Z-guggulsterone negatively controls microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via blocking IκB-α-NF-κB signals. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 619, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, C. Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein Attenuates Ischemic-Induced Microglia Cell Apoptosis and Activation Through NF-κB Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Liang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z. Gx-50 reduces β-amyloid-induced TNF-α, IL-1β, NO, and PGE2 expression and inhibits NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappington, R.M.; Calkins, D.J. Contribution of TRPV1 to microglia-derived IL-6 and NFkappaB translocation with elevated hydrostatic pressure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2008, 49, 3004–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, S.; Reinhard, J.; Gandej, M.; Gottschalk, I.; Stute, G.; Faissner, A. S100B immunization triggers NFkappaB and complement activation in an autoimmune glaucoma model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, R.; Singh, R. Exploring the potential of natural and synthetic neuroprotective steroids against neurodegenerative disorders: A literature review. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1126–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbioso, M.; Buomprisco, G.; Pascarella, A.; Pescosolido, N. Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on eye disorders: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaarniranta, K.; Xu, H.; Kauppinen, A. Mechanistical retinal drug targets and challenges. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2018, 126, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Luo, C.X.; Chu, W.H.; Shan, Y.A.; Qian, Z.M.; Zhu, G.; Yu, Y.B.; Feng, H. 20-Hydroxyecdysone protects against oxidative stress-induced neuronal injury by scavenging free radicals and modulating NF-κB and JNK pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, W.; Lu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J. The synthesis of polyhydroxy sterone 2β,3α,5-trihydroxy-5α-androst-6-one and its neuroprotection. Ther. Targets Neurol. Dis. 2017, 4, e1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Rangarajan, P.; Ling, E.A.; Dheen, S.T. Dexamethasone inhibits the Nox-dependent ROS production via suppression of MKP-1-dependent MAPK pathways in activated microglia. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Artelt, M.; Burnet, M.; Schluesener, H.J. Dexamethasone attenuates early expression of three molecules associated with microglia/macrophages activation following rat traumatic brain injury. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 113, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, A.; Chernushevich, O.; Qayum, A.A.; Spence, A.J.; Taruselli, M.T.; Abebayehu, D.; Barnstein, B.O.; McLeod, J.J.; Baker, B.; Bajaj, G.S.; et al. Dexamethasone rapidly suppresses IL-33-stimulated mast cell function by blocking transcription factor activity. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2016, 100, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis-Behnke, R.G.; Jonas, R.A.; Jonas, J.B. The microglial system in the eye and brain in response to stimuli in vivo. J. Glaucoma 2013, 22 (Suppl. 5), S32–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, A.; Crish, S.D.; Steele, M.R.; Romero, C.O.; Inman, D.M.; Horner, P.J.; Calkins, D.J.; Vetter, M.L. Early reduction of microglia activation by irradiation in a model of chronic glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Yang, X.; Kain, A.D.; Powell, D.W.; Kuehn, M.H.; Tezel, G. Glaucomatous tissue stress and the regulation of immune response through glial Toll-like receptor signaling. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2010, 51, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, W.S.; Hines-Beard, J.; GoldenMerry, Y.L.; Davis, M.; Farooque, A.; Sappington, R.M.; Calkins, D.J.; Rex, T.S. Virus-mediated EpoR76E Therapy Slows Optic Nerve Axonopathy in Experimental Glaucoma. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Luo, C.; Cai, J.; Powell, D.W.; Yu, D.; Kuehn, M.H.; Tezel, G. Neurodegenerative and inflammatory pathway components linked to TNF-alpha/TNFR1 signaling in the glaucomatous human retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2011, 52, 8442–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Leng, T.; Tang, L.; Zheng, X.; Lu, B.; Li, Y.; Sheng, L.; Lin, S.; Shi, H.; Yan, G. Neuroprotectant androst-3β,5α,6β-triol suppresses TNF-α-induced endothelial adhesion molecules expression and neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells by attenuation of CYLD-NF-κB pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Leng, T.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; You, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, L.; Chen, W.; Qiu, P.; et al. The major cholesterol metabolite cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol functions as an endogenous neuroprotectant. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11426–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sa Lima, L.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Munhoz, C.D.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Orellana, A.M.; Curi, R.; Rossoni, L.V.; Avellar, M.C.; Scavone, C. Ouabain activates NFκB through an NMDA signaling pathway in cultured cerebellar cells. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M.; Miao, C. Propofol attenuates BV2 microglia inflammation via NMDA receptor inhibition. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.-J.-Q.; Xue, D.-D.; Lu, B.-Z.; Li, Y.; Sheng, L.-X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.-W.; Zhang, J.-X.; Lin, G.-J.; Lin, S.-Z.; et al. A Novel Synthetic Steroid of 2β,3α,5α-Trihydroxy-androst-6-one Alleviates the Loss of Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells Caused by Acute Intraocular Hypertension via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia. Molecules 2019, 24, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020252
Sun H-J-Q, Xue D-D, Lu B-Z, Li Y, Sheng L-X, Zhu Z, Zhou Y-W, Zhang J-X, Lin G-J, Lin S-Z, et al. A Novel Synthetic Steroid of 2β,3α,5α-Trihydroxy-androst-6-one Alleviates the Loss of Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells Caused by Acute Intraocular Hypertension via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hong-Jia-Qi, Dong-Dong Xue, Bing-Zheng Lu, Yuan Li, Long-Xiang Sheng, Zhu Zhu, Yu-Wei Zhou, Jing-Xia Zhang, Gan-Jian Lin, Sui-Zhen Lin, and et al. 2019. "A Novel Synthetic Steroid of 2β,3α,5α-Trihydroxy-androst-6-one Alleviates the Loss of Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells Caused by Acute Intraocular Hypertension via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia" Molecules 24, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020252
APA StyleSun, H.-J.-Q., Xue, D.-D., Lu, B.-Z., Li, Y., Sheng, L.-X., Zhu, Z., Zhou, Y.-W., Zhang, J.-X., Lin, G.-J., Lin, S.-Z., Yan, G.-M., Chen, Y.-P., & Yin, W. (2019). A Novel Synthetic Steroid of 2β,3α,5α-Trihydroxy-androst-6-one Alleviates the Loss of Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells Caused by Acute Intraocular Hypertension via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia. Molecules, 24(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020252




