Functionalized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Tunable Hydrophobic Solid Acids for Biomass Conversion
Abstract
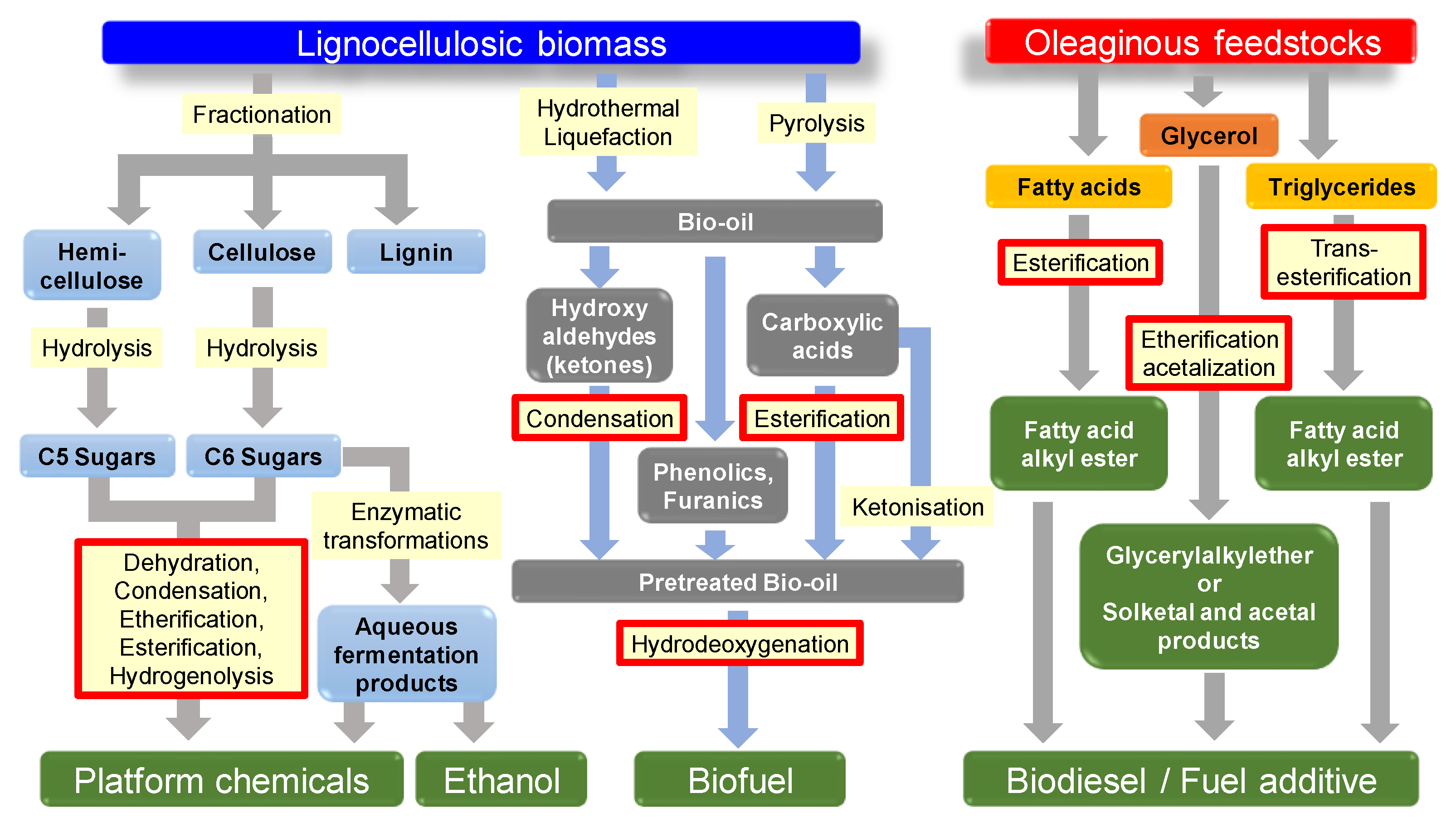
1. Introduction
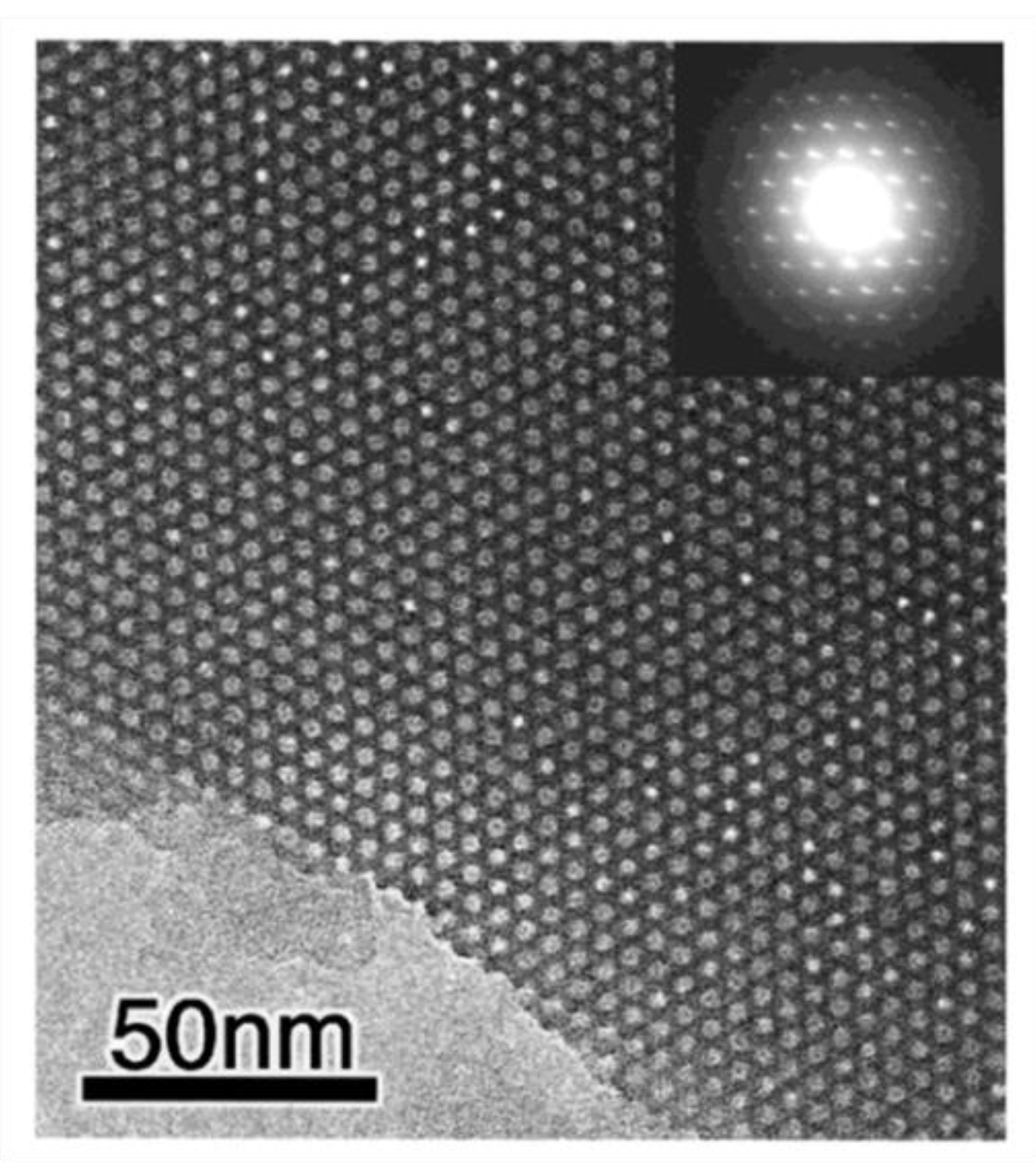
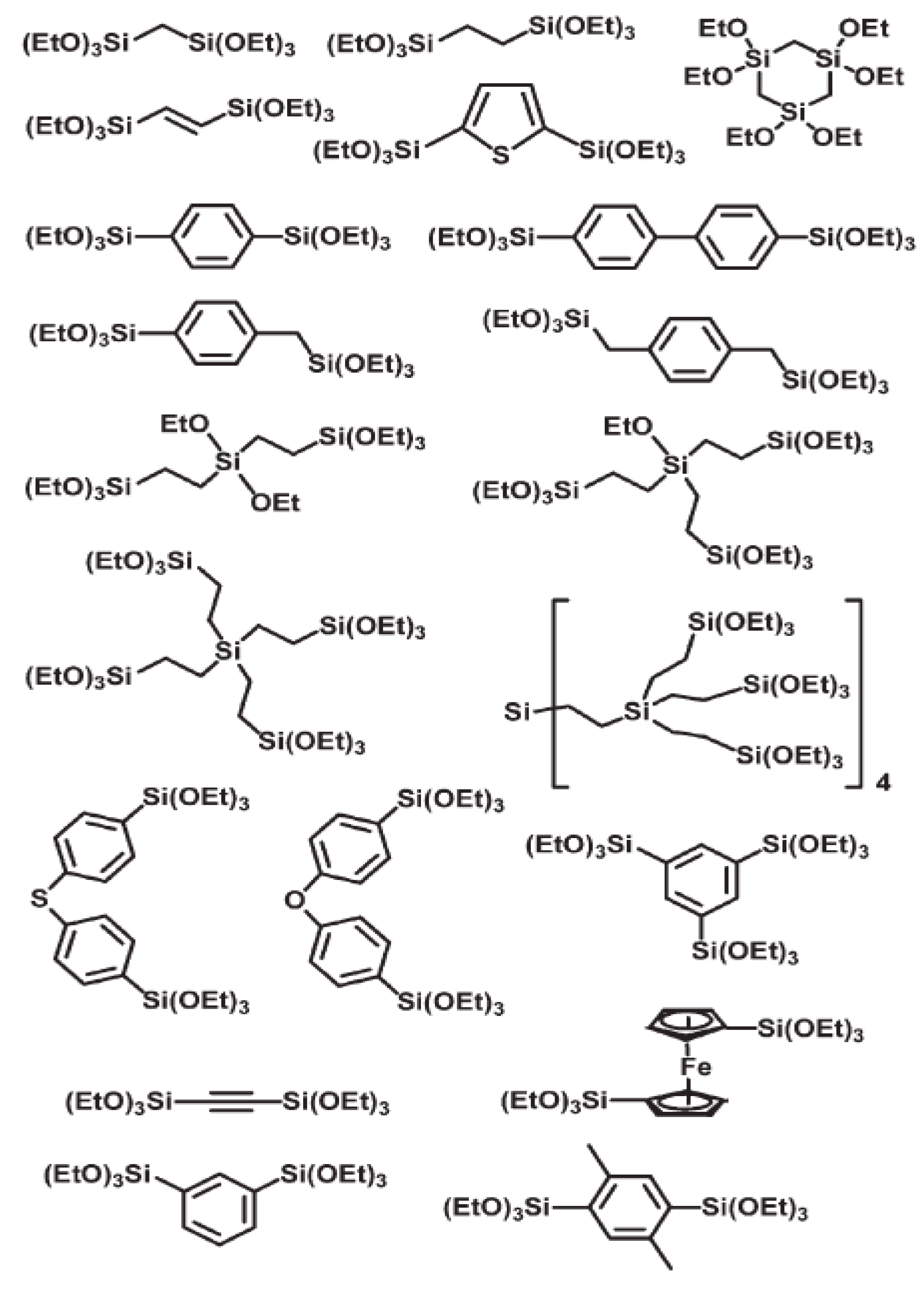
2. Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica (PMO) Materials
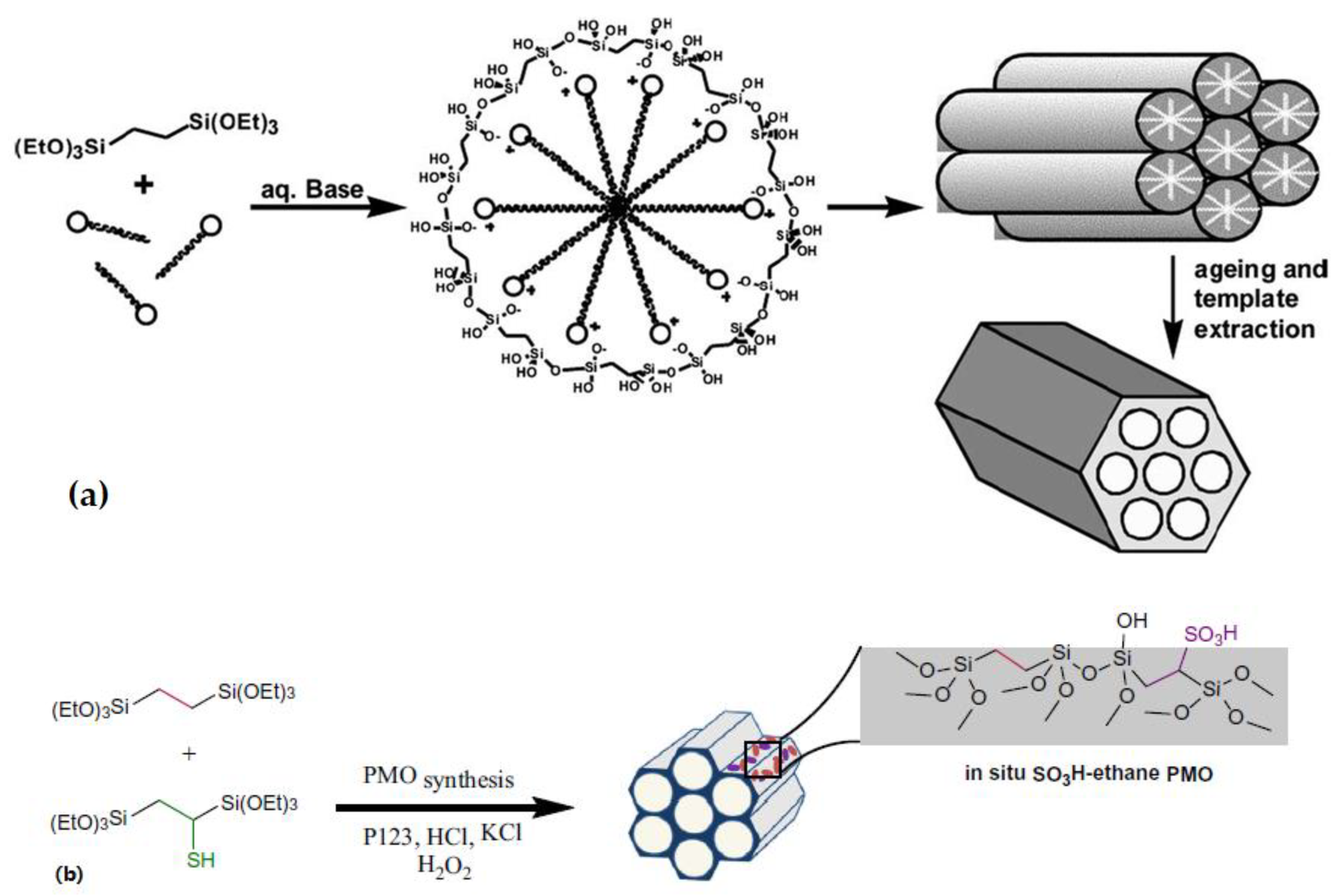
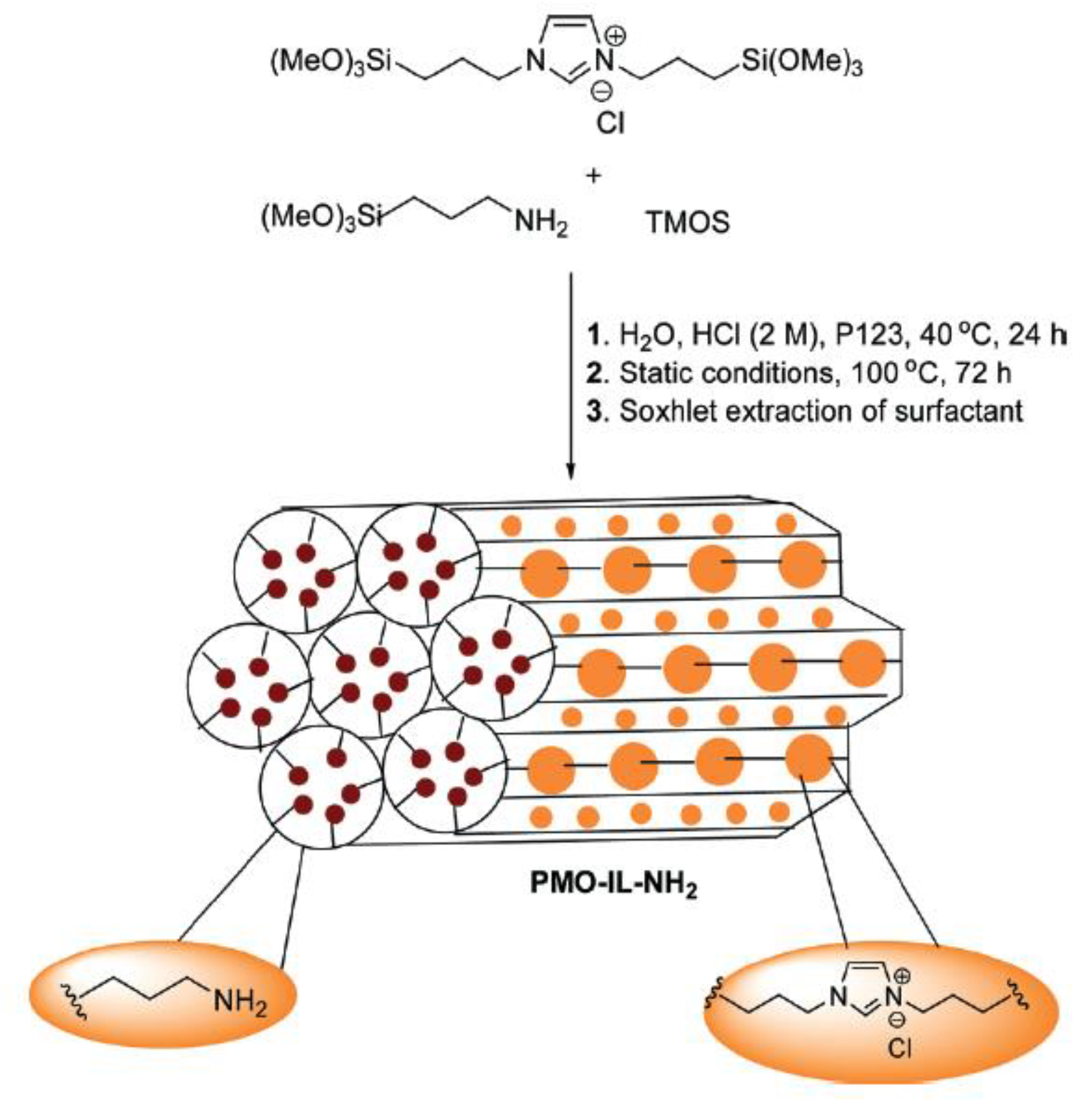
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. PMO Applications
3. Sulfonic-Acid-Functionalized PMOs
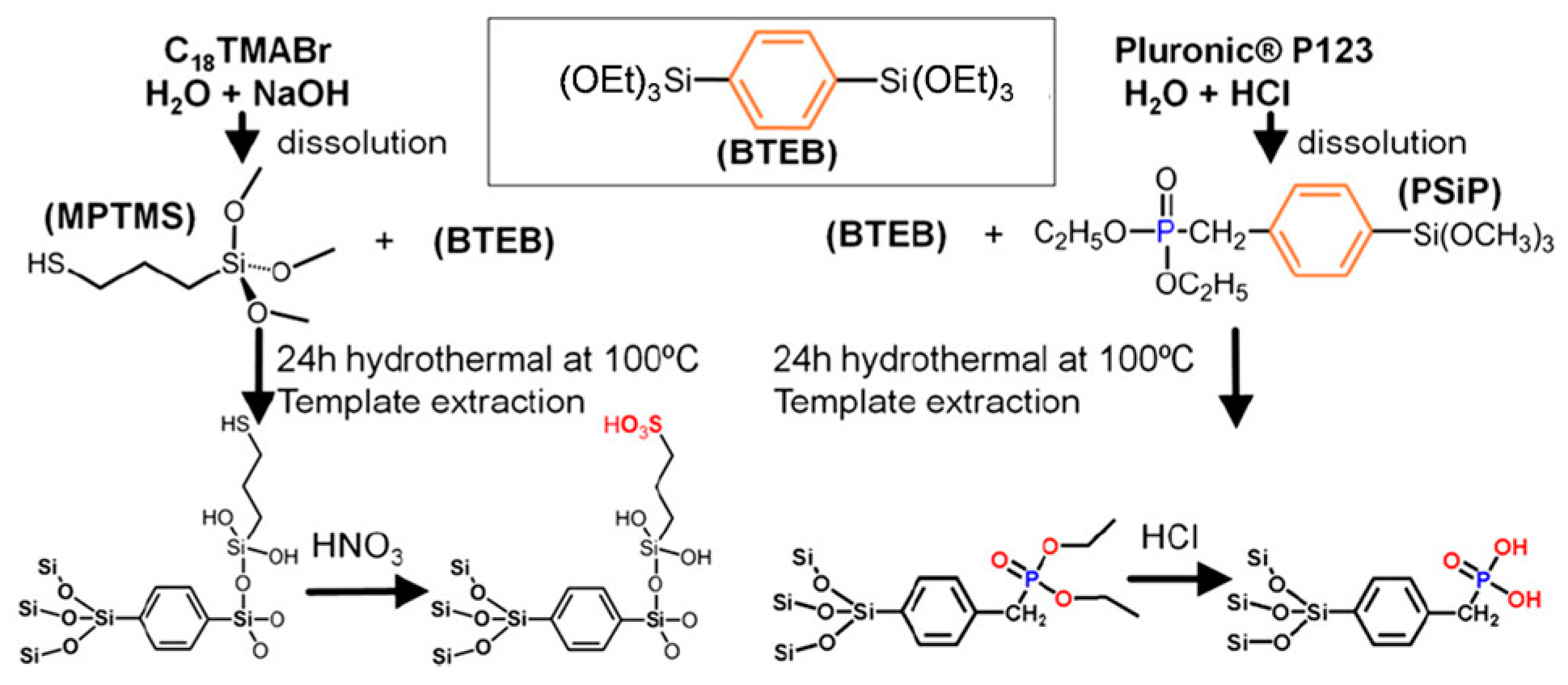
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Application in Acid-Catalyzed Reactions
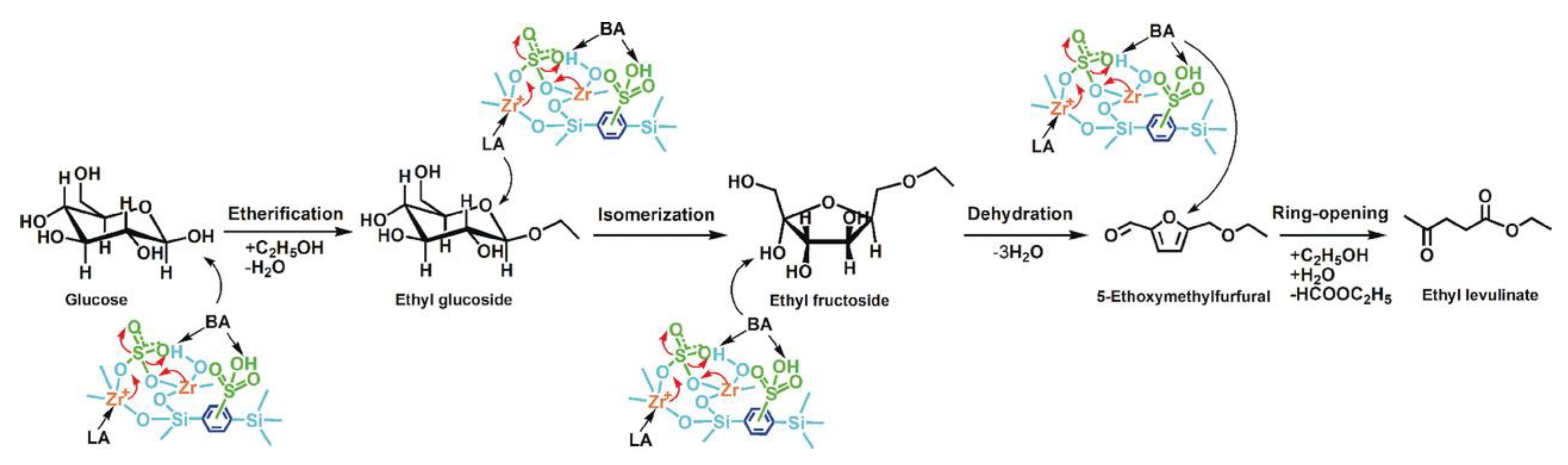
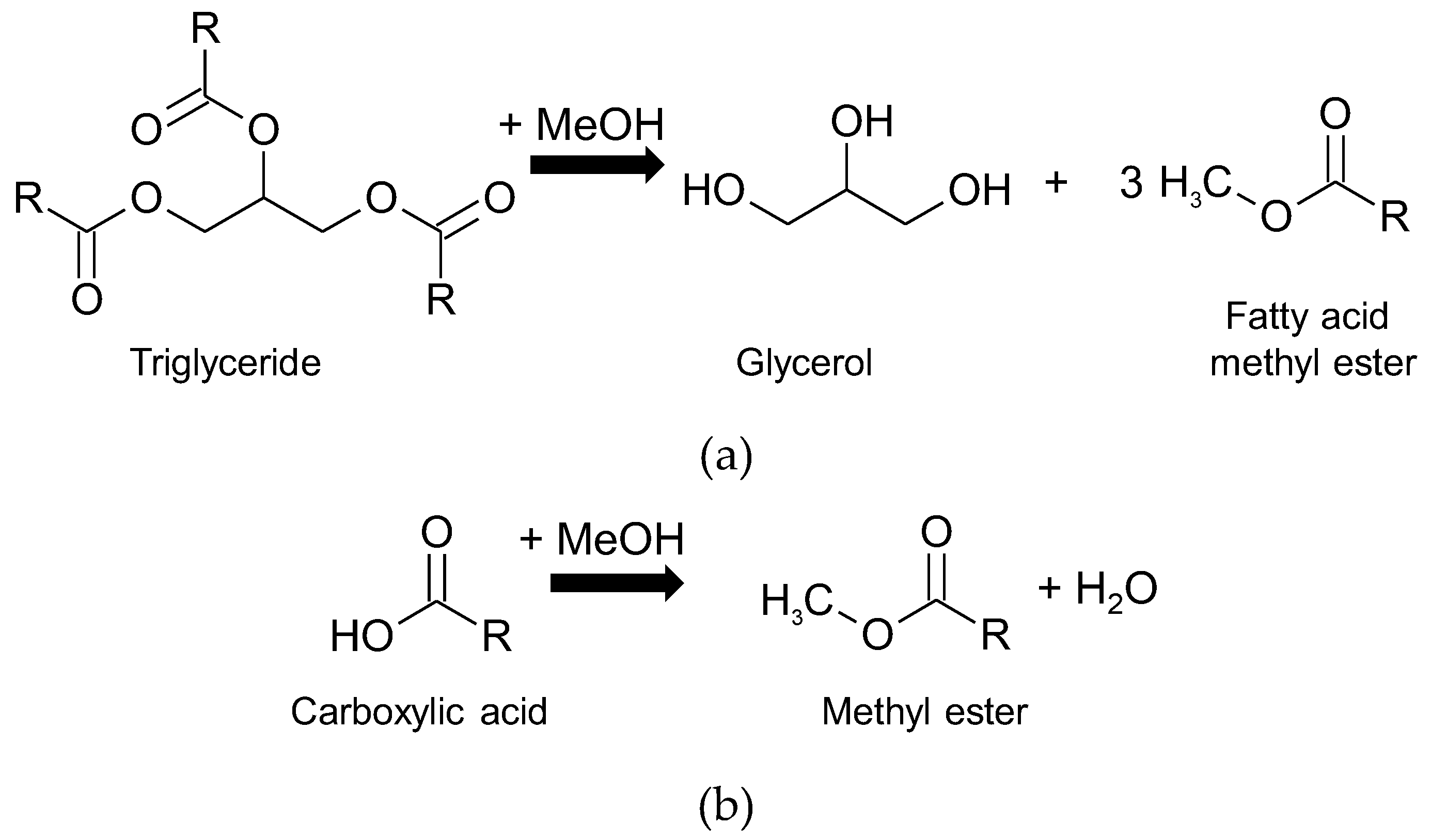
3.3. Application of Sulfonic Acid PMOs in Biofuel Synthesis
4. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armaroli, N.; Balzani, V. The future of energy supply: Challenges and opportunities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozell, J.J.; Petersen, G.R. Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates-the US Department of Energy's "Top 10" revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinsky, E.S. Chemicals from biomass: Petrochemical substitution options. Science 1981, 212, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.M. The societal significance of catalysis and the growing practical importance of single-site heterogeneous catalysts. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 468, 1884–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somorjai, G.A.; Frei, H.; Park, J.Y. Advancing the frontiers in nanocatalysis, biointerfaces, and renewable energy conversion by innovations of surface techniques. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16589–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, G.W.; Dumesic, J.A. An overview of aqueous-phase catalytic processes for production of hydrogen and alkanes in a biorefinery. Catal. Today 2006, 111, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Heterogeneously catalyzed hydrothermal processing of C5–C6 sugars. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12328–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R.; Schüth, F. Design of solid catalysts for the conversion of biomass. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Lee Adam, F. Catalyst design for biorefining. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 2016, 374, 20150081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounder, R. Hydrophobic microporous and mesoporous oxides as Brønsted and Lewis acid catalysts for biomass conversion in liquid water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, P.A.; Huang, Y.; Gonzalez-Borja, M.A.; Resasco, D.E. Silylated hydrophobic zeolites with enhanced tolerance to hot liquid water. J. Catal. 2013, 308, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delidovich, I.; Palkovits, R. Catalytic activity and stability of hydrophobic Mg–Al hydrotalcites in the continuous aqueous-phase isomerization of glucose into fructose. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 4322–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.-P.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Heterogeneous Catalysts for Converting Renewable Feedstocks to Fuels and Chemicals; Guczi, L., Erdôhelyi, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Huber, G.W. The critical role of heterogeneous catalysis in lignocellulosic biomass conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da'na, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 247, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douroumis, D.; Onyesom, I.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Mitchell, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in nanotechnology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 33, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Schüth, F. Ordered mesoporous materials in catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 77, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlett, C.M.A.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Hierarchical porous materials: Catalytic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3876–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Tavener, S.J. The application of modified mesoporous silicas in liquid phase catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, J.X. The synthesis of novel thiol/amino bifunctionalized SBA-15 and application on the Cr(VI) absorption. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 82, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.W.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Functionalized SBA-15 materials as carriers for controlled drug delivery: Influence of surface properties on matrix−drug interactions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9568–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadjadi, S.; Heravi, M.M. Current advances in the utility of functionalized SBA mesoporous silica for developing encapsulated nanocatalysts: State of the art. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 30815–30838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolese, D.; Melero, J.A.; Christiansen, S.C.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Direct syntheses of ordered SBA-15 mesoporous silica containing sulfonic acid groups. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 2448–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brühwiler, D. Postsynthetic functionalization of mesoporous silica. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descalzo, A.B.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Hoffmann, K.; Rurack, K. The supramolecular chemistry of organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5924–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitnall, W.; Asefa, T.; Ozin, G.A. Hybrid periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; Hamoudi, S. Periodic mesoporous silica-based organic−inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3151–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, W.; Mokaya, R. Bifunctional hybrid mesoporous organoaluminosilicates with molecularly ordered ethylene groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Melde, B.J.; Schroden, R.C. Hybrid inorganic–organic mesoporous silicates—Nanoscopic reactors coming of age. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manayil, J.C.; dos Santos, V.C.; Jentoft, F.C.; Granollers Mesa, M.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Octyl co-grafted PrSO3H/SBA-15: Tunable hydrophobic solid acid catalysts for acetic acid esterification. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaraka, I.K.; Shanks, B.H. Design of multifunctionalized mesoporous silicas for esterification of fatty acid. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Santha Moorthy, M.; Ha, C.-S. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas for advanced applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, B.; Landskron, K.; Whitnall, W.; Perovic, D.; Ozin, G.A. Past, present, and future of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. The PMOs. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Voort, P.; Esquivel, D.; De Canck, E.; Goethals, F.; Van Driessche, I.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas: From simple to complex bridges; a comprehensive overview of functions, morphologies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3913–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascón, V.; Díaz, I.; Blanco, R.M.; Márquez-Álvarez, C. Hybrid periodic mesoporous organosilica designed to improve the properties of immobilized enzymes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 34356–34368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Acid catalyzed synthesis of ordered bifunctionalized mesoporous organosilicas with large pore. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 77, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfgen, B.; Malter, O.D.; Kaigarula, E.; Schüßler, A.; Ernst, S.; Thiel, W.R. A Brønsted acid functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilica and its application in catalytic condensation and THP protection/deprotection reactions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 251, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; MacLachlan, M.J.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G.A. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas with organic groups inside the channel walls. Nature 1999, 402, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Guan, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasaki, O. Novel mesoporous materials with a uniform distribution of organic groups and inorganic oxide in their frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9611–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melde, B.J.; Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Mesoporous sieves with unified hybrid inorganic/organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3302–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Kapoor, M.P.; Inagaki, S.; Li, C. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity of sulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas. J. Catal. 2004, 228, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Bispo, C.; Bion, N.; Ferreira, P.; Batonneau-Gener, I. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas as adsorbents for the organic pollutants removal in aqueous phase. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 200, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, R.; Shi, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S. One-dimensional periodic mesoporous organosilica helical nanotubes with amphiphilic properties for the removal of contaminants from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S. Sulfonated periodic-mesoporous-organosilicas column for selective separation of C2H2/CH4 mixtures. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 264, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.X.; Qiao, S.Z.; Yu, C.Z.; Ismadji, S.; Lu, G.Q. Periodic mesoporous silica and organosilica with controlled morphologies as carriers for drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhikov, A.; Daou, T.J.; Nouali, H.; Patarin, J.; Ouwehand, J.; Clerick, S.; De Canck, E.; Van Der Voort, P.; Martens, J.A. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas as porous matrix for heterogeneous lyophobic systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 260, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles: Physical chemistry, biosafety, delivery strategies, and biomedical applications. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1700831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaweera, I.; Hong, J.; D’Souza, A.; Balkus, K.J. Novel wrinkled periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for hydrophobic anticancer drug delivery. J. Porous Mater. 2015, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunks, W.J.; Ozin, G.A. Challenges and advances in the chemistry of periodic mesoporous organosilicas (PMOs). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3716–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.M.; Salvador, M.A.; Ferreira, P.; Figueiredo, F.M. Acid-functionalised periodic mesoporous benzenosilica proton conductors. Solid State Ionics 2012, 225, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. Functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas for catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirez, C.; Reche, M.T.; Lee, A.F.; Manayil, J.C.; dos-Santos, V.C.; Wilson, K. Hydrothermal saline promoted grafting of periodic mesoporous organic sulfonic acid silicas for sustainable FAME production. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vázquez, R.; Pirez, C.; Iglesias, J.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F.; Melero, J.A. Zr-containing hybrid organic–inorganic mesoporous materials: Hydrophobic acid catalysts for biodiesel production. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirez, C.; Lee, A.F.; Manayil, J.C.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Wilson, K. Hydrothermal saline promoted grafting: A route to sulfonic acid SBA-15 silica with ultra-high acid site loading for biodiesel synthesis. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4506–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.M.; Bion, N.; Figueiredo, F.M.; Ferreira, P. Tuning the acid content of propylsulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous benzene-silica by microwave-assisted synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabicka, B.E.; Jaroniec, M. Microwave-assisted synthesis of periodic mesoporous organosilicas with ethane and disulfide groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 119, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
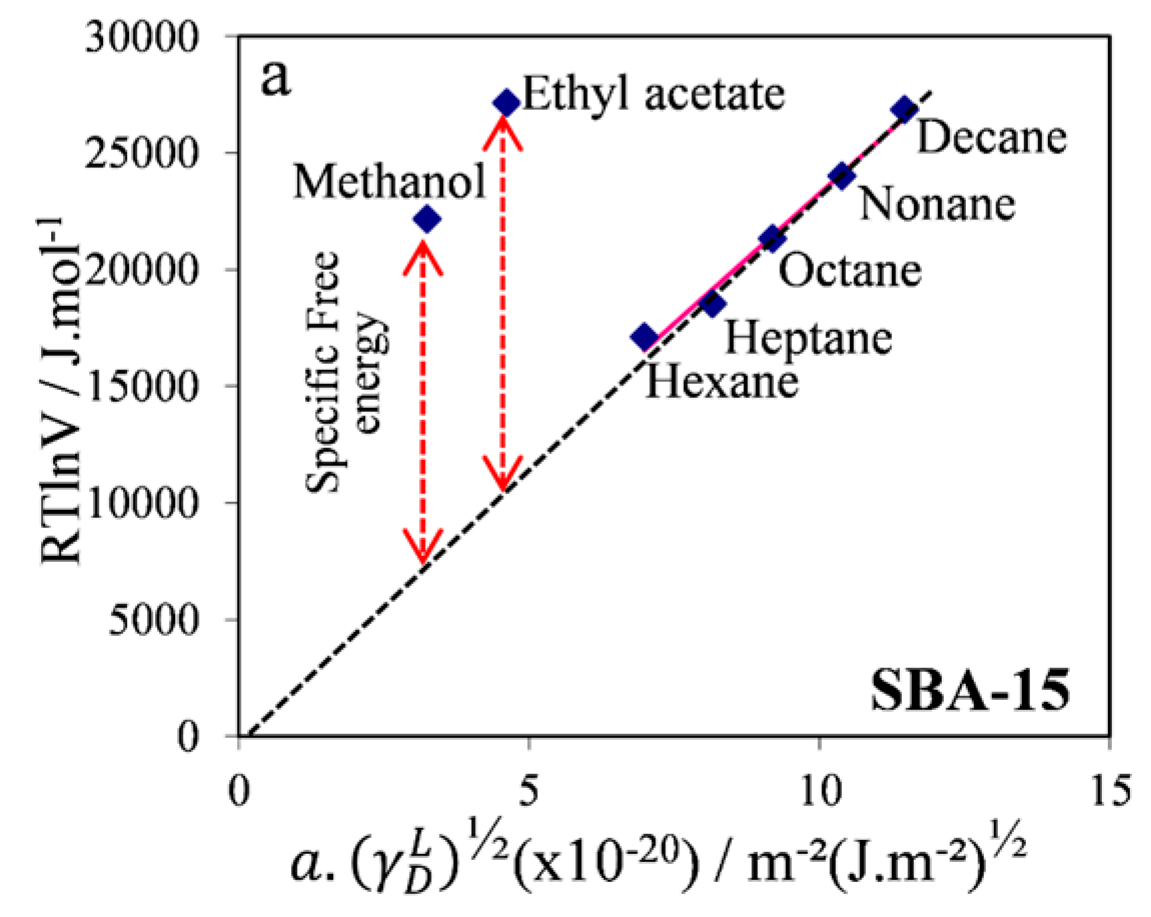
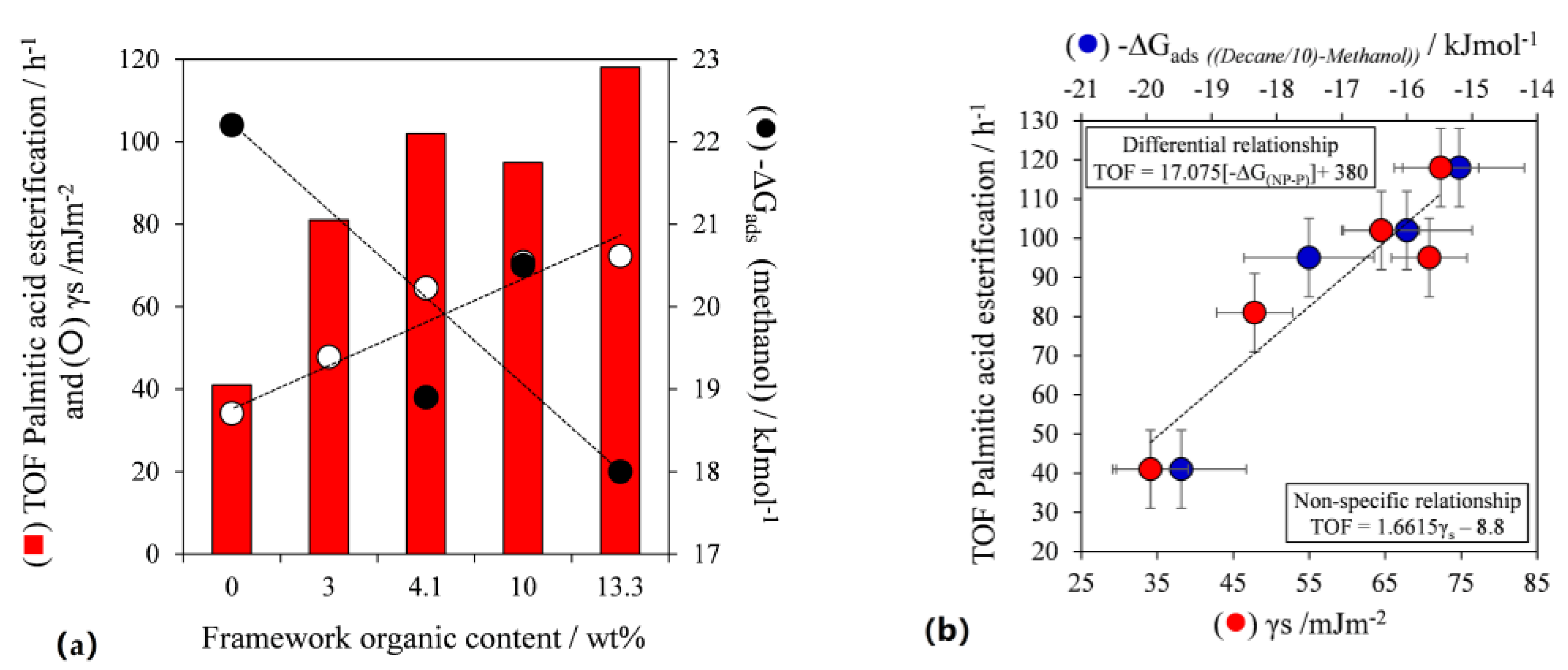
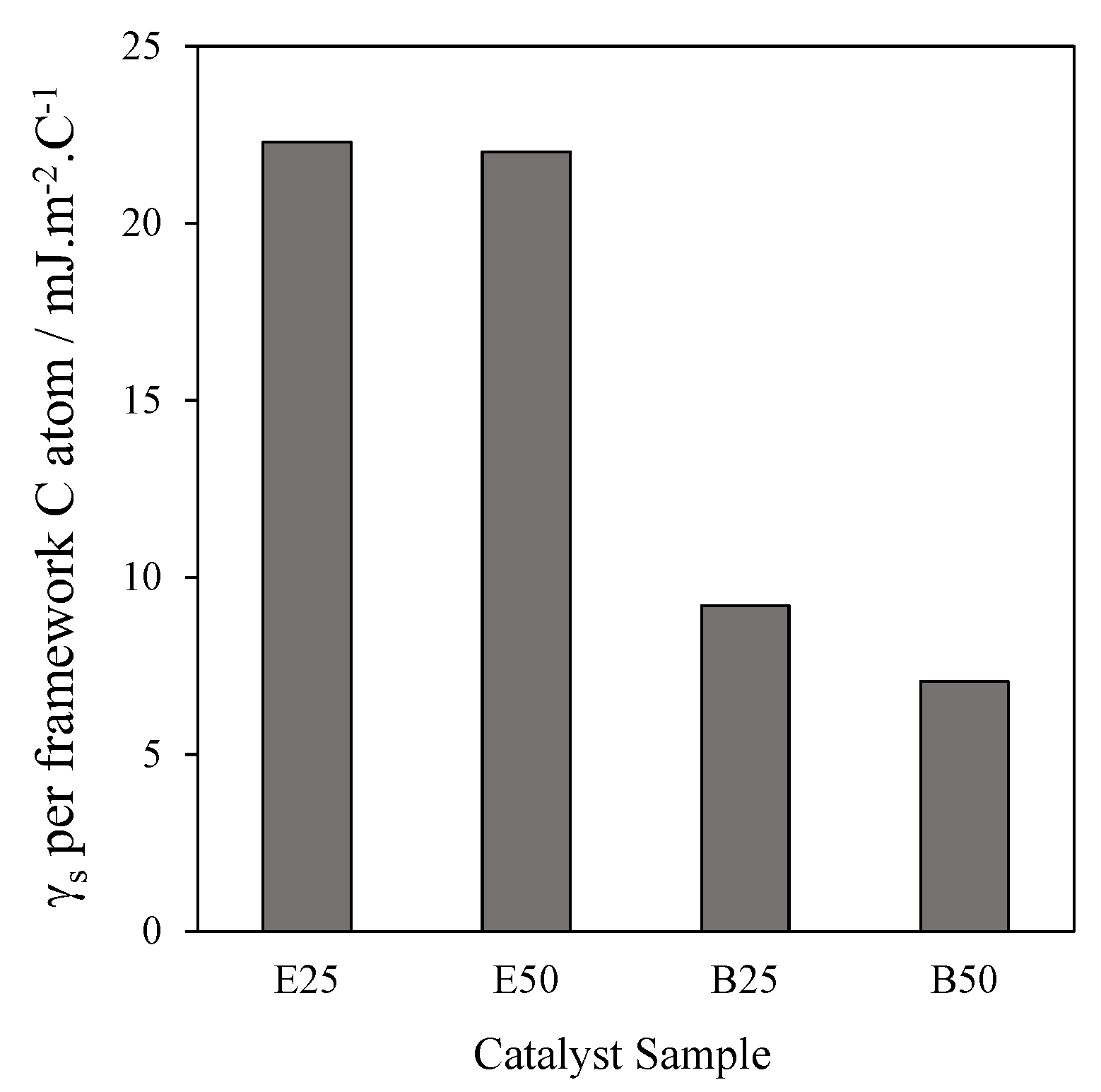
- Pirez, C.; Lee, A.F.; Jones, C.; Wilson, K. Can surface energy measurements predict the impact of catalyst hydrophobicity upon fatty acid esterification over sulfonic acid functionalised periodic mesoporous organosilicas? Catal. Today 2014, 234, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhao, D. A mild method to remove organic templates in periodic mesoporous organosilicas by the oxidation of perchlorates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dral, A.P.; Lievens, C.; ten Elshof, J.E. Influence of monomer connectivity, network flexibility, and hydrophobicity on the hydrothermal stability of organosilicas. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5527–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redzheb, M.; Van Der Voort, P.; Armini, S. Template-dependent hydrophobicity in mesoporous organosilica films. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Graaff, W.N.P.; Olvera, K.G.; Pidko, E.A.; Hensen, E.J.M. Stability and catalytic properties of porous acidic (organo)silica materials for conversion of carbohydrates. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2014, 388-389, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Elhamifar, D.; Amadeh, T.; Karimi, B. Periodic mesoporous organosilica with ionic-liquid framework supported manganese: An efficient and recyclable nanocatalyst for the unsymmetric Hantzsch reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13087–13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.A.; Grieken, R.v.; Iglesias, J.; Morales, V.; Villajos, N. Facile one-pot approach to the synthesis of chiral periodic mesoporous organosilicas SBA-15-type materials. J. Catal. 2010, 274, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, A.; George, S.C.; Jithesh, P.R.; Vinod, C.P.; Singh, A.P. Correlating the role of hydrophilic/hydrophobic nature of Rh(I) and Ru(II) supported organosilica/silica catalysts in organotransformation reactions. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 513, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jin, R.; Cheng, T.; Xu, X.; Gao, F.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilica: A highly enantioselective catalyst for the michael addition of 1,3-Dicarbonyl compounds to nitroalkenes. Chemistry 2012, 18, 15546–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.I.; Esquivel, D.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Romero-Salguero, F.J.; Van Der Voort, P. A “one-step” sulfonic acid PMO as a recyclable acid catalyst. J. Catal. 2015, 326, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Keilbach, A.; Kienle, M.; Goto, Y.; Inagaki, S.; Knochel, P.; Bein, T. Hierarchically structured biphenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17338–17344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, J.; Wolter, G.; Fröba, M. Synthesis and characterization of highly ordered thiophene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas with large pores. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhovyk, O.; Jaroniec, M. Periodic mesoporous organosilica with large heterocyclic bridging groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Klar, P.J.; Mauder, D.; Shenderovich, I.; Hoffmann, F.; Fröba, M. Synthesis and characterization of chiral benzylic ether-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Chem. 2008, 14, 5935–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Markowitz, M.A.; Spector, M.S.; Gaber, B.P. Direct synthesis of periodic mesoporous organosilicas: Functional incorporation by Co-condensation with organosilanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9935–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, S.; Kaliaguine, S. Sulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 59, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Kim, II.; Ha, C.-S. Hybrid periodic mesoporous organosilica materials prepared from 1,2-bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane and (3-cyanopropyl)triethoxysilane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 69, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-B.; Kim, D. Multifunctional periodic mesoporous organosilicas prepared with block copolymer: Composition effect on morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 113, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Inagaki, S. Self-organization of organosilica solids with molecular-scale and mesoscale periodicities. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kapoor, M.P.; Inagaki, S.; Shirokura, N.; Kondo, J.N.; Domen, K. Catalytic application of sulfonic acid functionalized mesoporous benzene–silica with crystal-like pore wall structure in esterification. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 230, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, M.; Hoffmann, F.; Fröba, M. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas with a bifunctional conjugated organic unit and crystal-like pore walls. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6674–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.Z.; Yu, C.Z.; Hu, Q.H.; Jin, Y.G.; Zhou, X.F.; Zhao, X.S.; Lu, G.Q. Control of ordered structure and morphology of large-pore periodic mesoporous organosilicas by inorganic salt. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 91, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Yang, J.; Gu, F.N.; Gao, L.; Zhu, J.H. Direct synthesis of high quality cubic Ia3d mesoporous material under organosilane assisted. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 130, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-B.; Kim, D. Direct synthesis of sulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesoporous benzene–silicas with large pores. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2008, 69, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Taylor, R.N.K.; Kullmann, S.; Bao, H.; Hartmann, M. Mesoporous organosilicas with large cage-like pores for high efficiency immobilization of enzymes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q. Periodic mesoporous hybrid monolith with hierarchical macro–mesopores. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 100, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Lehr, M.; Seidler, C.F.; Taffa, D.H.; Wark, M.; Smarsly, B.M.; Marschall, R. Proton conduction in sulfonated organic–inorganic hybrid monoliths with hierarchical pore structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25476–25488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.-G.; Zhou, H.-J.; Sun, P.-C.; Chen, T.-H. Synthesis of single-crystal-like, hierarchically nanoporous silica and periodic mesoporous organosilica, using polyelectrolyte–surfactant mesomorphous complexes as a template. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4241–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melde, B.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Dinderman, M.A.; Deschamps, J.R. Macroporous periodic mesoporous organosilicas with diethylbenzene bridging groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 130, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; Kruk, M.; Coombs, N.; Grondey, H.; MacLachlan, M.J.; Jaroniec, M.; Ozin, G.A. Novel route to periodic mesoporous aminosilicas, PMAs: Ammonolysis of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11662–11673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Kim, I.; Ha, C.-S. Bridged amine-functionalized mesoporous organosilica materials from 1,2-bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane and bis[(3-trimethoxysilyl)propyl]amine. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Markowitz, M.A.; Spector, M.S.; Gaber, B.P. Amine-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Synthesis and characterization of phosphonic acid functionalized organosilicas with bimodal nanostructure. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, D.; Rat, M.; Shen, W.; Béland, F.; Kaliaguine, S. Perfluoroalkylsulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesostructured organosilica: A strongly acidic heterogeneous catalyst. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamifar, D.; Kazempoor, S.; Karimi, B. Amine-functionalized ionic liquid-based mesoporous organosilica as a highly efficient nanocatalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4318–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Xu, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhang, H. Functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas for selective adsorption of proteins. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7126–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Webley, P.A.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of large-pore phenyl-bridged mesoporous organosilica with thick walls by evaporation-induced self-assembly for efficient benzene adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 346, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ding, M. Preparation and characterization for a new sulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous silica stationary phase. Colloids Surf. A 2007, 292, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Köhler, C.; Tölle, P.; Frauenheim, T.; Wark, M. Proton conductivity of SO3H-functionalized benzene–periodic mesoporous organosilica. Small 2011, 7, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Parambadath, S.; Ha, C.-S. Sulphonic acid functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilica with the bridged bissilylated urea groups for high selective adsorption of cobalt ion from artificial seawater. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamifar, D.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Karimi, B.; Moshkelgosha, R.; Shábani, A. Ionic liquid and sulfonic acid based bifunctional periodic mesoporous organosilica (BPMO–IL–SO3H) as a highly efficient and reusable nanocatalyst for the biginelli reaction. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Tomita, I.; Hara, M.; Hayashi, S.; Domen, K.; Kondo, J.N. A stable and highly active hybrid mesoporous solid acid catalyst. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, S.; Royer, S.; Kaliaguine, S. Propyl- and arene-sulfonic acid functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 71, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kapoor, M.P.; Inagaki, S. Sulfuric acid-functionalized mesoporous benzene−silica with a molecular-scale periodicity in the walls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9694–9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Mirzaei, H.M.; Mobaraki, A. Periodic mesoporous organosilica functionalized sulfonic acids as highly efficient and recyclable catalysts in biodiesel production. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; van Grieken, R.; Morales, G. Advances in the synthesis and catalytic applications of organosulfonic-functionalized mesostructured materials. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3790–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q. Mesoporous organosilicas containing disulfide moiety: Synthesis and generation of sulfonic acid functionality through chemical transformation in the pore wall. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 113, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.I.; Esquivel, D.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Application of sulfonic acid functionalised hybrid silicas obtained by oxidative cleavage of tetrasulfide bridges as catalysts in esterification reactions. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.-J.; Vetrivel, S.; Chiang, A.S.T.; Kao, H.-M. Synthesis and characterization of cubic periodic mesoporous organosilicas with a high loading of disulfide groups. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, R.; López, M.I.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Luna, D.; Romero-Salguero, F.J.; Bautista, F.M. Etherification of glycerol with tert-butyl alcohol over sulfonated hybrid silicas. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 526, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lofgreen, J.E.; Ozin, G.A. Why PMO? Towards functionality and utility of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Small 2010, 6, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlett, C.M.A.; Isaacs, M.A.; Beaumont, S.K.; Bingham, L.M.; Hondow, N.S.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Spatially orthogonal chemical functionalization of a hierarchical pore network for catalytic cascade reactions. Nat. Mater. 2015, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Tomita, I.; Hara, M.; Hayashi, S.; Domen, K.; Kondo, J.N. Development of highly active SO3H-modified hybrid mesoporous catalyst. Catal. Today 2006, 116, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, D.; Rat, M.; Béland, F.; Kaliaguine, S. Sulfonic acid functionalized periodic mesostructured organosilica as heterogeneous catalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, M.; Bhaumik, A. Novel and mild synthetic strategy for the sulfonic acid Functionalization in periodic mesoporous ethenylene-silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Canck, E.; Dosuna-Rodríguez, I.; Gaigneaux, M.E.; Van Der Voort, P. Periodic mesoporous organosilica functionalized with sulfonic acid groups as acid catalyst for glycerol acetylation. Materials 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.P.; Fujii, W.; Kasama, Y.; Yanagi, M.; Nanbu, H.; Juneja, L.R. An alternate approach to the preparation of versatile sulfonic acid functionalized periodic mesoporous silicas with superior catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4683–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.S.; Price, B.A.; Jones, C.W. Sulfonic acid-functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 251, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, C.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Sardo, M.; Bion, N.; Mafra, L.; Ferreira, P.; Jérôme, F. Catalytic dehydration of fructose to HMF over sulfonic acid functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas: Role of the acid density. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Guan, S.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasaki, O. An ordered mesoporous organosilica hybrid material with a crystal-like wall structure. Nature 2002, 416, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, A.; Alonso, J.C.; Gerganova, T.I.; Ferreira, P.; Bion, N.; Barrault, J.; Jérôme, F. Sulfonic acid functionalized crystal-like mesoporous benzene–silica as a remarkable water-tolerant catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Domingues, E.; De Sousa, R.; Jérôme, F.; Morais, C.M.; Bion, N.; Ferreira, P.; Mafra, L. Understanding the high catalytic activity of propylsulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesoporous benzenesilicas by high-resolution 1H solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.H.; Crisci, A.J.; Wigington, B.N.; Phadke, N.; Alamillo, R.; Zhang, J.; Scott, S.L.; Dumesic, J.A. Acid-functionalized SBA-15-type periodic mesoporous organosilicas and their use in the continuous production of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rat, M.; Zahedi-Niaki, M.H.; Kaliaguine, S.; Do, T.O. Sulfonic acid functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas as acetalization catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 112, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, C.; Ferreira, P.; Trouvé, A.; Batonneau-Gener, I.; Liu, F.; Jérôme, F.; Bion, N. Role of acidity and hydrophobicity in the remarkable catalytic activity in water of sulfonic acid-functionalized phenyl-PMO materials. Catal. Today 2013, 218-219, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, D.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Thermal behaviour, sulfonation and catalytic activity of phenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.H.; Stein, A. Comparative studies of grafting and direct syntheses of inorganic−organic hybrid mesoporous materials. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3285–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Q. Catalytic applications of sulfonic acid functionalized mesoporous organosilicas with different fraction of organic groups in the pore wall. J. Porous Mater. 2009, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Rostamnia, S.; Han, J. Well-shaped sulfonic organosilica nanotubes with high activity for hydrolysis of cellobiose. Catalysts 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Song, D.; Lu, B.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.-H. Morphology tailoring of sulfonic acid functionalized organosilica nanohybrids for the synthesis of biomass-derived alkyl levulinates. Chem. 2015, 21, 10786–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rác, B.; Hegyes, P.; Forgo, P.; Molnár, Á. Sulfonic acid-functionalized phenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas as catalyst materials. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 299, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylesh, S.; Samuel, P.P.; Srilakshmi, C.; Parischa, R.; Singh, A.P. Sulfonic acid functionalized mesoporous silicas and organosilicas: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 274, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, A.; Dekamin, M.G.; Arefi, E.; Karimi, B. Propylsulfonic acid-anchored isocyanurate-based periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO-ICS-Pr-SO3H): A new and highly efficient recoverable nanoporous catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of bis(indolyl)methane derivatives. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Canck, E.; Nahra, F.; Bevernaege, K.; Vanden Broeck, S.; Ouwehand, J.; Maes, D.; Nolan, S.P.; Van Der Voort, P. PMO-immobilized AuI–NHC complexes: Heterogeneous catalysts for sustainable processes. ChemPhysChem 2017, 19, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Y.-H.; Hu, J.-L. Design of ordered mesoporous sulfonic acid functionalized ZrO2/organosilica bifunctional catalysts for direct catalytic conversion of glucose to ethyl levulinate. ChemCatChem 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.P.; Lee, A.F.; Pirez, C.; Wilson, K. Pore-expanded SBA-15 sulfonic acid silicas for biodiesel synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manayil, J.C.; Inocencio, C.V.M.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Mesoporous sulfonic acid silicas for pyrolysis bio-oil upgrading via acetic acid esterification. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirez, C.; Caderon, J.-M.; Dacquin, J.-P.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Tunable KIT-6 mesoporous sulfonic acid catalysts for fatty acid esterification. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manayil, J.C.; Osatiashtiani, A.; Mendoza, A.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Isaacs, M.A.; Durndell, L.J.; Michailof, C.; Heracleous, E.; Lappas, A.; Lee, A.F.; et al. Impact of macroporosity on catalytic upgrading of fast pyrolysis bio-oil by esterification over silica sulfonic acids. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3506–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Â.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F.; dos Santos, V.C.; Cons Bacilla, A.C.; Mantovani, K.M.; Nakagaki, S. Nb2O5/SBA-15 catalyzed propanoic acid esterification. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 205, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasey, J.J.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Manayil, J.C.; Isaacs, M.A.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Facile route to conformal hydrotalcite coatings over complex architectures: A hierarchically ordered nanoporous base catalyst for FAME production. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2398–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osatiashtiani, A.; Durndell, L.J.; Manayil, J.C.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Influence of alkyl chain length on sulfated zirconia catalysed batch and continuous esterification of carboxylic acids by light alcohols. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5529–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Shanks, B.H. Esterification of biomass pyrolysis model acids over sulfonic acid-functionalized mesoporous silicas. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 359, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.K.; Dash, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Adsorption of organic molecules on silica surface. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lotero, E.; Goodwin, J.G. A comparison of the esterification of acetic acid with methanol using heterogeneous versus homogeneous acid catalysis. J. Catal. 2006, 242, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.-P.; Cross, H.E.; Brown, D.R.; Düren, T.; Williams, J.J.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Interdependent lateral interactions, hydrophobicity and acid strength and their influence on the catalytic activity of nanoporous sulfonic acid silicas. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.F.; Bennett, J.A.; Manayil, J.C.; Wilson, K. Heterogeneous catalysis for sustainable biodiesel production via esterification and transesterification. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7887–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciddor, L.; Bennett, J.A.; Hunns, J.A.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Catalytic upgrading of bio-oils by esterification. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Kapoor, M.P.; Setoyama, N.; Inagaki, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Structural relation properties of hydrothermally stable functionalized mesoporous organosilicas and catalysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12250–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Mirzaei, H.M.; Mobaraki, A.; Vali, H. Sulfonic acid-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas in esterification and selective acylation reactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamifar, D.; Karimi, B.; Moradi, A.; Rastegar, J. Synthesis of sulfonic acid containing ionic-liquid-based periodic mesoporous organosilica and study of its catalytic performance in the esterification of carboxylic acids. ChemPlusChem 2014, 79, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.B.; Park, S.J.; Balard, H. Evaluation of specific interactions of solid-surfaces by inverse gas-chromatography—A new approach based on polarizability of the probes. Chromatographia 1991, 31, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Attractive forces at interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tshabalala, M.A. Influence of drying method on the surface energy of cellulose nanofibrils determined by inverse gas chromatography. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 405, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
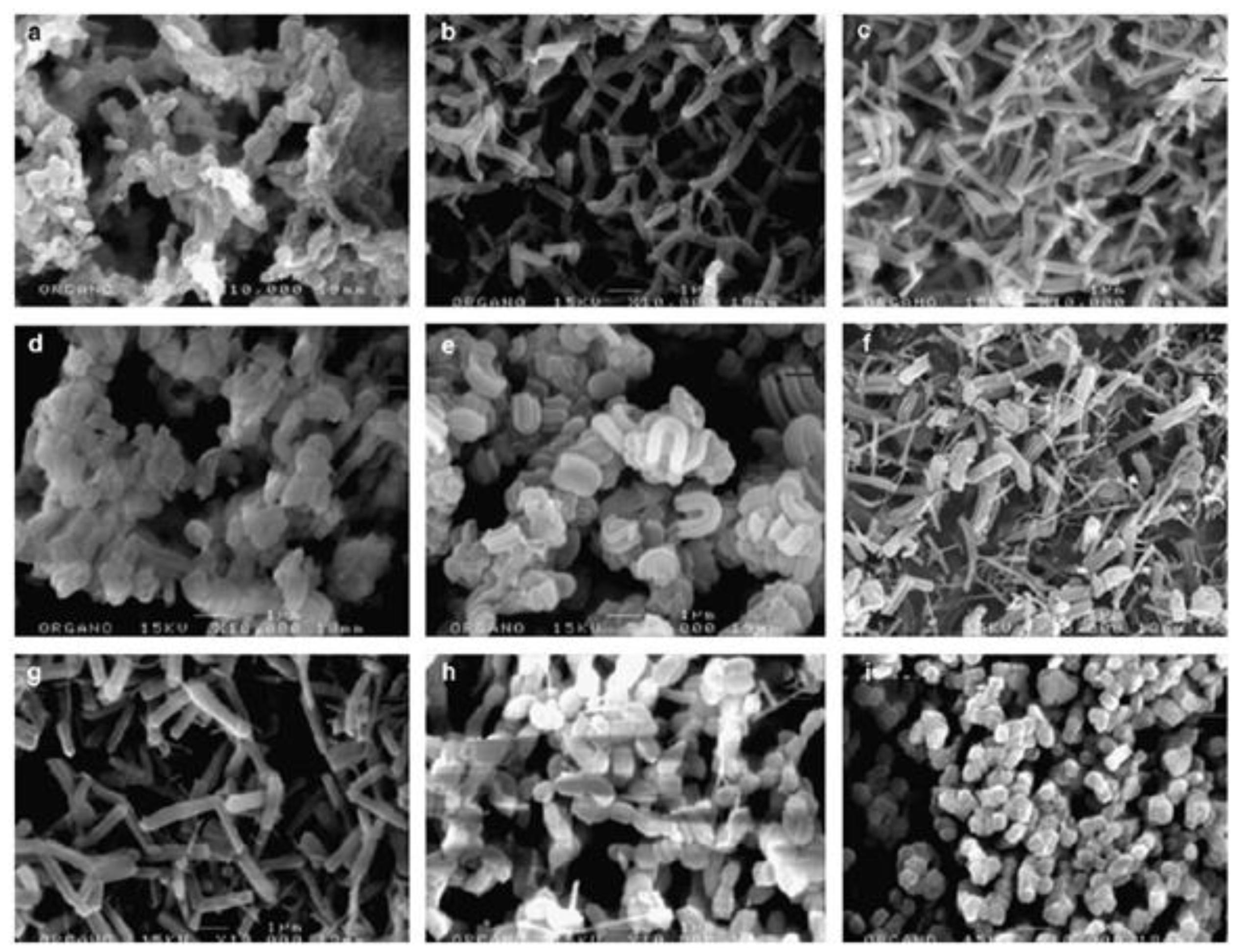
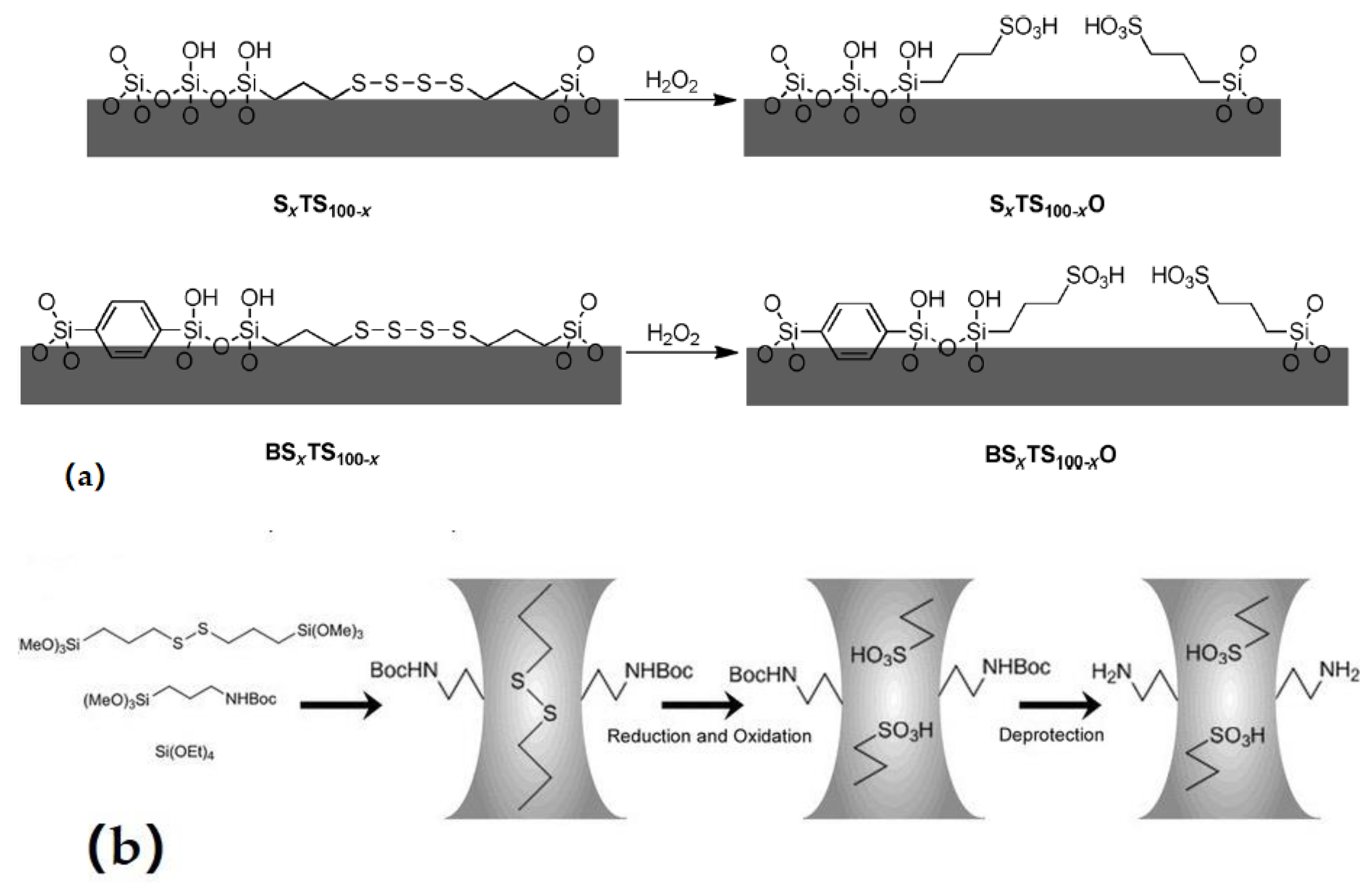
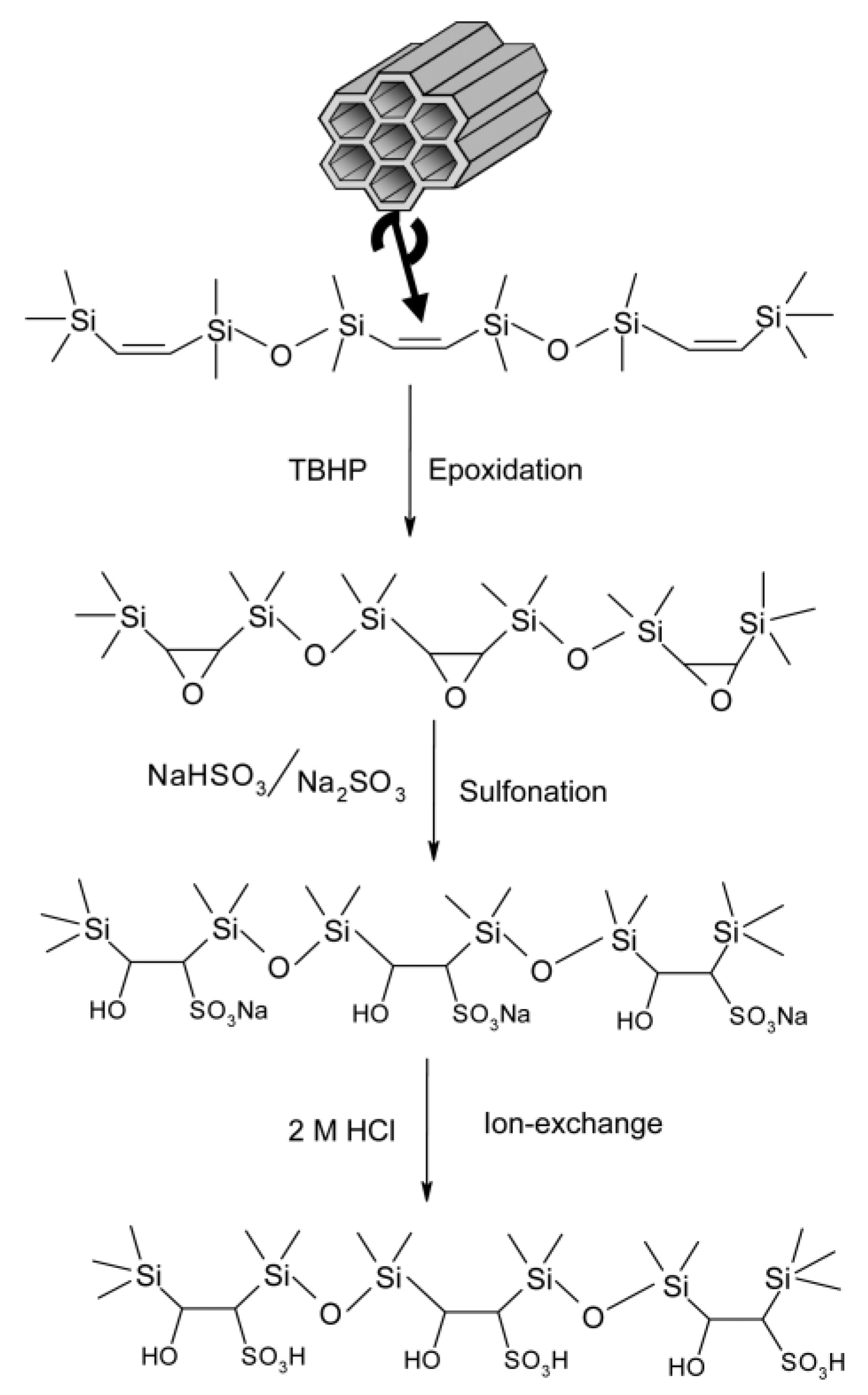
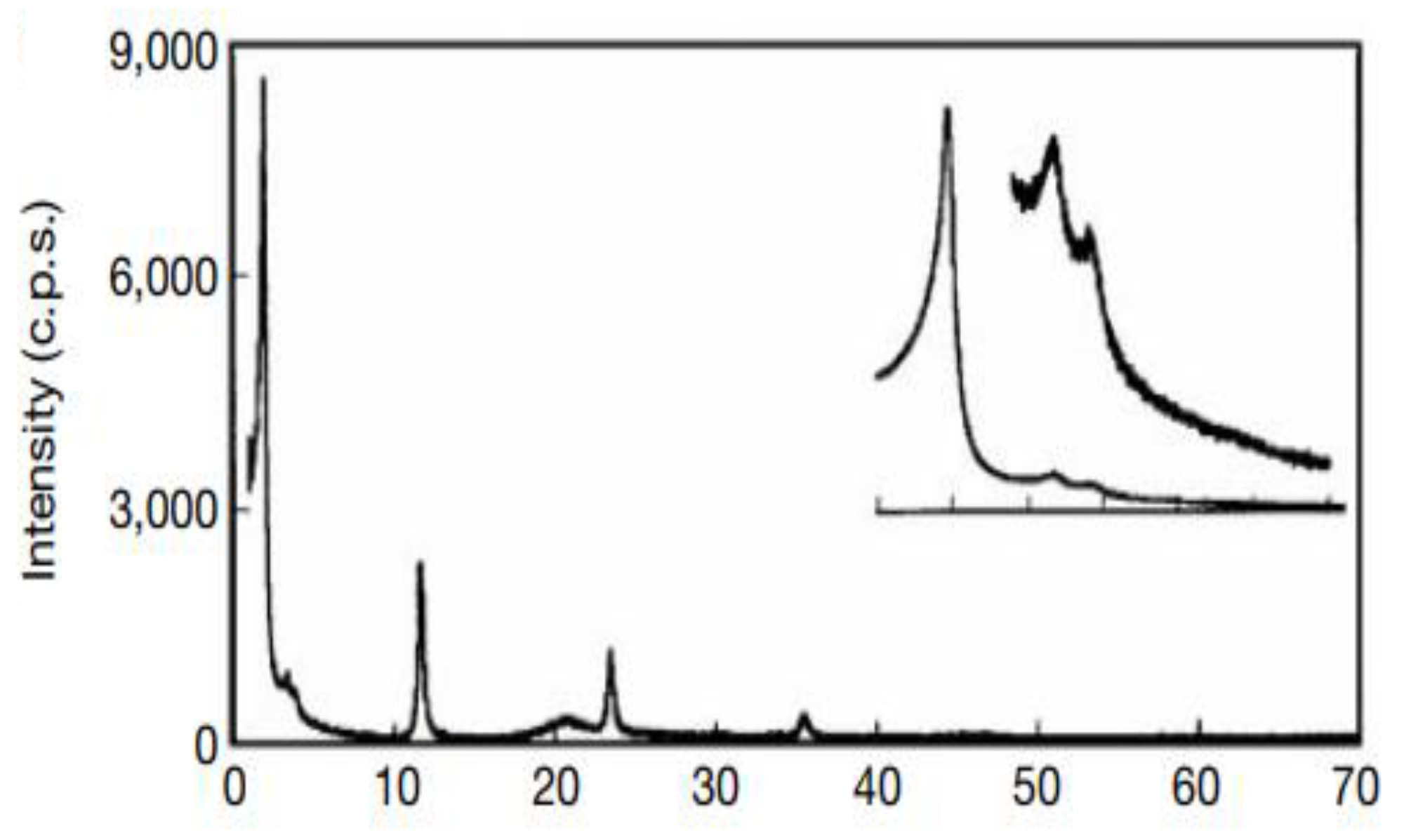
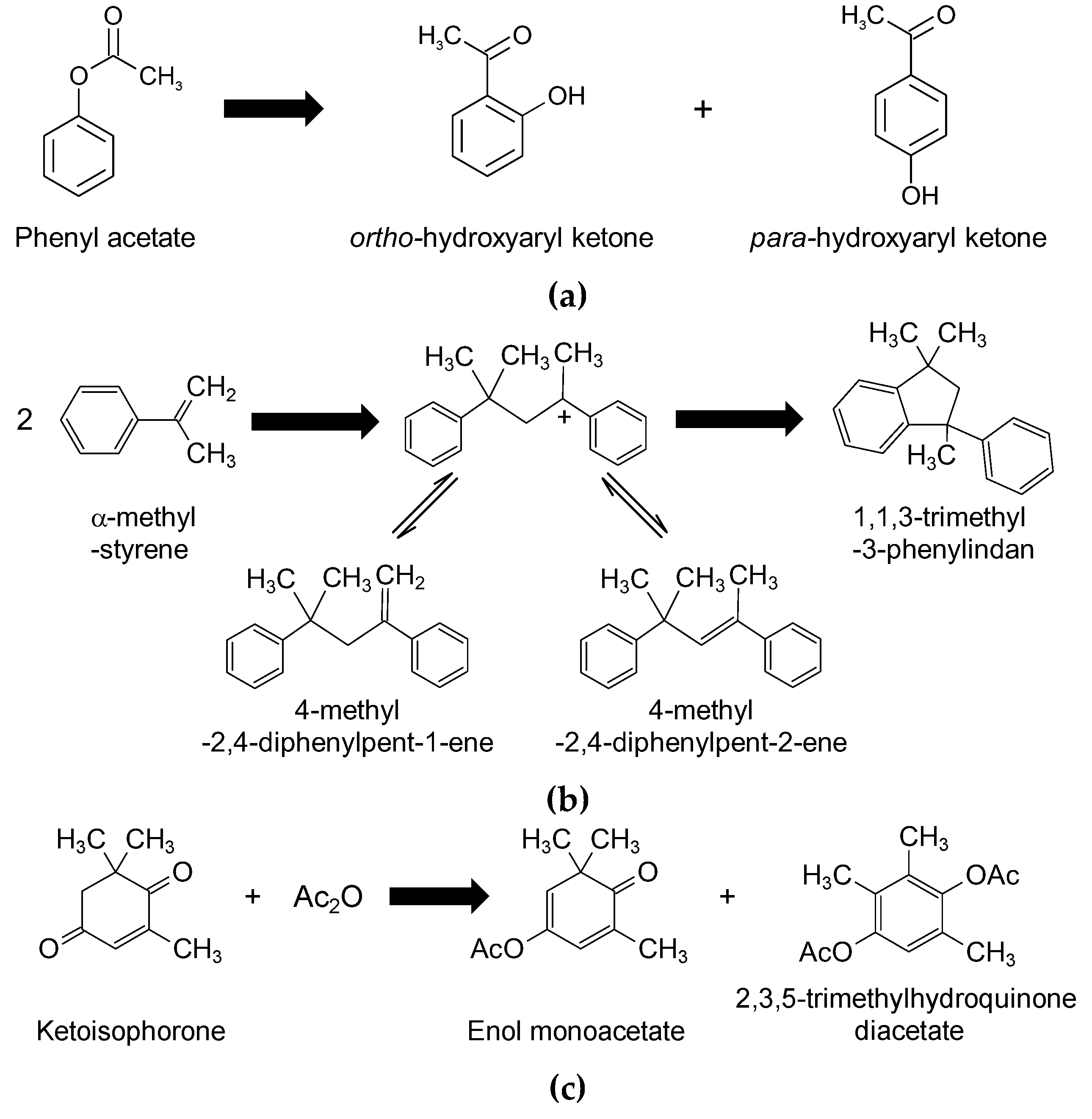
| Reaction Scheme | Performance | Refs |
|---|---|---|
Entry 1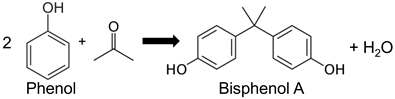 | TOF a BPA production Grafted PrSO3H–PMO b: Ethyl bridge = 17.2 h−1 Phenyl bridge = 7.6 h−1 PrSO3H–SBA = 8.8 h−1 | [43] |
Entry 2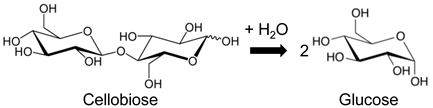 | TOF cellobiose conversion PrSO3H PMO nanotubes: Ethyl bridge = 7.5–10.4 h−1 Phenyl bridge = 7–12.1 h−1 PrSO3H/SiO2 NT c = 7.8 h−1 | [127] |
Entry 3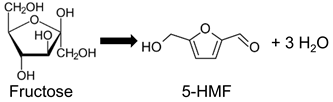 | TOF HMF production b Ethyl-bridged PMO phenyl-SO3H = 103 h−1 b SBA-phenyl-SO3H = 41 h−1 TOF fructose conversion c Ethyl-bridged PMO–PrSO3H= 520–910 h−1 c Phenyl-bridged PMO–PrSO3H = 350 h−1 | [63] d [117] e |
Entry 4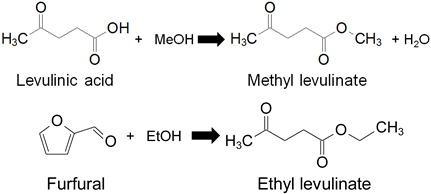 | TOF levulinic acid conversion Ethyl-bridged PMO phenyl-SO3H = 109 h−1 Amberlyst-15 = 18 h−1 TOF furfural conversion Ethyl-bridged PMO phenyl-SO3H = 10.5 h−1 Amberlyst-15 = 4 h−1 | [128] |
Entry 5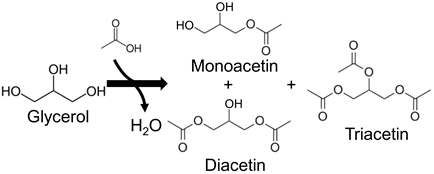 | Conversion/Selectivity Acetylation yield = 80% Monoacetin selectivity = 94% Diacetin selectivity = 6% | [114] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manayil, J.C.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Functionalized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Tunable Hydrophobic Solid Acids for Biomass Conversion. Molecules 2019, 24, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020239
Manayil JC, Lee AF, Wilson K. Functionalized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Tunable Hydrophobic Solid Acids for Biomass Conversion. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleManayil, Jinesh C., Adam F. Lee, and Karen Wilson. 2019. "Functionalized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Tunable Hydrophobic Solid Acids for Biomass Conversion" Molecules 24, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020239
APA StyleManayil, J. C., Lee, A. F., & Wilson, K. (2019). Functionalized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Tunable Hydrophobic Solid Acids for Biomass Conversion. Molecules, 24(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020239






